Odisha State Board CHSE Odisha Class 11 Biology Solutions Chapter 4 Classification of Animal Kingdom Textbook Questions and Answers.
CHSE Odisha 11th Class Biology Chapter 4 Question Answer Classification of Animal Kingdom
Classification of Animal Kingdom Class 11 Questions and Answers CHSE Odisha
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Multiple choice questions
Question 1.
Spicules are present in the animals of the phylum
(a) Porifera
(b) Annelida
(c) Coelenterata
(d) Platyhelminthes
Answer:
(a) Porifera
Question 2.
What is common to fishes, amphibians and reptiles?
(a) Scales
(b) Shelled egg
(c) Eggs
(d) Gills
Answer:
(d) Gills
Question 3.
Dolphin belongs to
(a) Amphibia
(b) Mammalia
(c) Pisces
(d) Reptilia
Answer:
(b) Mammalia
Question 4.
Sea horse belongs to
(a) Amphibia
(b) Aves
(c) Pisces
(d) Mammal
Answer:
(c) Pisces
Question 5.
Hair is absent in the mammalian order
(a) Cetacea
(b) Chiroptera
(c) Primates
(d) Rodentia
Answer:
(a) Cetacea
Question 6.
Asexual reproduction through gemmule formation takes place in
(a) Arthropoda
(b) Coelenterata
(c) Porifera
(d) Platyhelminthes
Answer:
(c) Porifera
Question 7.
Which one of the following is a freshwater sponge?
(a) Euplactella
(b) Hyalonema
(c) Spongilla
(d) Sycon
Answer:
(c) Spongilla
Question 8.
One of the following is not radially symmetrical.
(a) Hydra
(b) Sea cucumber
(c) Snail
(d) Starfish
Answer:
(c) Snail
Question 9.
Which one of the following is bilaterally symmetrical?
(a) Jelly fish
(b) Nematode
(c) Starfish
(d) Sea Urchin
Answer:
(b) Nematode
Question 10.
Which of the following sets belong to class-Cyclostomata?
(a) Amphioxus and Herdmania
(b) Amphioxus and Balanoglossus
(c) Petromyzon and Amphioxus
(d) Petromyzon and Myxine
Answer:
(d) Petromyzon and Myxine
Question 11.
Annelides are
(a) triploblastic
(b) radially symmetrical
(c) pseudocoelomate
(d) unsegmented
Answer:
(a) triploblastic
Question 12.
Warts are present in
(a) Amphibia
(b) Mammalia
(c) Pisces
(d) Reptilia
Answer:
(d) Reptilia
Question 13.
What type of worms are the Platyhelminth?
(a) Blind worm
(b) Flat worm
(c) Round worm
(d) Thread worm
Answer:
(b) Flat worm
Question 14.
In which of the following animals, a canal system is present?
(a) Hydra
(b) Starfish
(c) Sponge
(d) Earthworm
Answer:
(c) Sponge
Question 15.
The most highly advanced character in crocodile is
(a) four-chambered heart
(b) powerful jaws
(c) shelled eggs
(d) thecodont dentition
Answer:
(a) four-chambered heart
Question 16.
In which animal group, syrinx is present?
(a) Aves
(b) Pisces
(c) Amphibia
(d) Reptilia
Answer:
(a) Aves
Question 17.
Planaria, Taenia and Fasciola are
(a) segmented
(b) coelomates
(c) flatworms
(d) radially symmetrical
Answer:
(c) flatworms
Question 18.
Which of the following groups has largest number of species?
(a) Aves
(b) Protozoa
(c) Insecta
(d) Mammalia
Answer:
(c) Insecta
Question 19.
Find out the diploblastic animal
(a) Ohelia
(b) Earthworm
(c) Nereis
(d) Liverfluke
Answer:
(a) Ohelia
Question 20.
In which phylum nematocysts are present?
(a) Arthropoda
(b) Annelida
(c) Mollusca
(d) Coelenterata
Answer:
(d) Coelenterata
Question 21.
What type of larva is seen in Coelenterata?
(a) Planula
(b) Trochophore
(c) Tadpole
(d) Redia
Answer:
(a) Planula
Question 22.
Which of the following animal group belongs to Acoelomata?
(a) Annelida
(b) Arthropoda
(c) Echinodermata
(d) Platyhelminthes
Answer:
(d) Platyhelminthes
Question 23.
Which one is a pseudocoelomate?
(a) Ascaris
(b) Cockroach
(c) Starfish
(d) Hydra
Answer:
(d) Hydra
Question 24.
Which one is the intermediate host of Fasciola hepatica?
(a) Cow
(b) Man
(c) Pig
(d) Snail
Answer:
(a) Cow
Question 25.
Sexual dimorphism is seen in which phylum?
(a) Coelenterata
(b) Nemathelminthes
(c) Platyhelminthes
(d) Porifera
Answer:
(b) Nemathelminthes
Question 26.
In which animal the systemic aorta is seen only on the right side?
(a) Frog
(b) Crocodile
(c) Pigeon
(d) Man
Answer:
(c) Pigeon
Question 27.
In which animal systemic aorta is present only on the left side?
(a) Frog
(b) Crocodile
(c) Pigeon
(d) Man
Answer:
(d) Man
Question 28.
Viviparity is not seen in which animal?
(a) Bat
(b) Platypus
(c) Monkey
(d) Whale
Answer:
(b) Platypus
Question 29.
In which of the following phyla, compound eyes are present?
(a) Annelida
(b) Arthropoda
(c) Echinodermata
(d) Mollusca
Answer:
(b) Arthropoda
Question 30.
Pentamerous radial symmetry is seen in which phylum?
(a) Arthopoda
(b) Annelida
(c) Mollusca
(d) Echinodermata
Answer:
(d) Echinodermata
Question 31.
Which one is not an acraniata (acrania)?
(a) Herdmnia
(b) Balanoglossus
(c) Amphioxus
(d) Petromyzon
Answer:
(a) Herdmnia
Question 32.
What type of scale is present in cartilaginous fishes?
(a) Cycloid
(b) Ctenoid
(c) Placoid
(d) Ganoid
Answer:
(c) Placoid
Question 33.
Which class of animals is not marine?
(a) Amphibia
(b) Fishes
(c) Mammalia
(d) Reptilia
Answer:
(c) Mammalia
Question 34.
Class-Aves includes animals with
(a) scales
(b) feathers
(c) hair
(d) smooth skin
Answer:
(b) feathers
Question 35.
Lizards are included in which class?
(a) Pisces
(b) Amphibia
(c) Reptilia
(d) Mammalia
Answer:
(c) Reptilia
Question 36.
Which one is a homeothermic animal?
(a) Shark
(b) Lung fish
(c) Cat fish
(d) Dolphin
Answer:
(d) Dolphin
Question 37.
Which one is a poikilothermic animal?
(a) Crocodile
(b) Seal
(c) Pigeon
(d) Whale
Answer:
(a) Crocodile
Question 38.
Whales are included in the same class as that of
(a) Alligator
(b) Dog fish
(c) Monkeys
(d) Sea horse
Answer:
(c) Monkeys
Question 39.
Body temperature is regulated at a constant rate in
(a) Cow
(b) Earthworm
(c) Frog
(d) Snake
Answer:
(a) Cow
Question 40.
A distinguishing character of chordates is
(a) feather
(b) hairy skin
(c) notochord
(d) stomochord
Answer:
(c) notochord
Question 41.
The Chief distinguishing feature of a mammal is
(a) pinnae and teeth
(b) hairy skin and oviparity
(c) hairy skin and mammary gland
(d) mammary gland and teeth
Answer:
(d) mammary gland and teeth
Question 42.
Which of the following is not an insect?
(a) Earwig
(b) Head louse
(c) Spider
(d) Silver fish
Answer:
(c) Spider
Question 43.
Prawns, shrimps and lobsters belong to which class of the Arthropoda?
(a) Arachnida
(b) Crustacea
(c) Insecta
(d) Myriapoda
Answer:
(b) Crustacea
Question 44.
The animals of which phylum are aerial, aquatic and terrestrial.
(a) Annelida
(b) Arthropoda
(c) Echinodermata
(d) Mollusca
Answer:
(b) Arthropoda
Question 45.
The most important character of a mammal’is
(a) A four chamber heart
(b) Presence of corpus callosum
(c) Presence of metanephric kidney
(d) Presence of thecodont teeth
Answer:
(d) Presence of thecodont teeth
Question 46.
Find out the odd member in the group.
(a) Crocodile
(b) Dolphin
(c) Lizard
(d) Turtle
Answer:
(b) Dolphin
Question 47.
Echinoderms are exclusively
(a) esturiarine
(b) marine
(c) pond living
(d) riverine
Answer:
(b) marine
Question 48.
Which one is a true terrestrial animal?
(a) Frog
(b) Salamander
(c) Tortoise
(d) Toad
Answer:
(c) Tortoise
Question 49.
The genus of midwife toad to
(a) Alytes
(b) Rhacophorus
(c) Hyla
(d) Pipa
Answer:
(a) Alytes
Question 50.
A rabbit shows resemblance with a frog in
(a) nucleated RBC
(b) dorsal tubular nerve cord
(c) oval RBC
(d) renal portal system
Answer:
(a) nucleated RBC
Answer each of the following in one word or more words, wherever necessary
Question 1.
Give an example of a diploblastic animal.
Answer:
Sycon
Question 2.
What is the term used for summer sleep?
Answer:
Aestivation
Question 3.
What is the term used for winter sleep?
Answer:
Hibernation
Question 4.
What is the alternative name for cold-blooded animals?
Answer:
Poikilotherms
Question 5.
What is the alternative name for warm-blooded animals?
Answer:
Homeotherms
Question 6.
In which invertebrate phylum carapace is present?
Answer:
Arthropoda
Question 7.
In which phylum medusa is present?
Answer:
Coelentrata
Question 8.
In which non-chordate phylum flame cells are present?
Answer:
Platyhelminthes
Question 9.
In which phylum mantle is present?
Answer:
Mollusca
Question 10.
What are the excretory organs of annelids knows as?
Answer:
Nephridia
Question 11.
What is the free floating form of coelenterates known as?
Answer:
Medusa
Question 12.
What is the name of stinging cell of coelenterates?
Answer:
Nematocyst
Question 13.
What is the symmetry of Pilal
Answer:
Bilateral symmetry
Question 14.
Which animals communicate by pheromones?
Answer:
Insects
Question 15.
Name an egg-laying mammal.
Answer:
Platypus
Question 16.
Which jawless chordate suck blood from the fishes?
Answer:
Cyclostomes
Question 17.
Which phylum do sponges belong to?
Answer:
Porifera
Question 18.
Which phylum does the jelly fish belong to?
Answer:
Coelentrates
Question 19.
Which one is the largest phylum (in terms of number of species) of the animal kingdom?
Answer:
Arthropoda
Question 20.
The animals of which phylum are exclusively marine?
Answer:
Echinodermata
Question 21.
Which class does the blue whale belong to?
Answer:
Mammalia
Question 22.
Which class the sea horse belongs to?
Answer:
Pisces
Question 23.
Dinosaurs belong to which class?
Answer:
Reptilia
Question 24.
Newts and salamanders belong to which class of animals?
Answer:
Amphibia
Question 25.
Which class does the Platypus belong to?
Answer:
Mammalia
Question 26.
Bats belong to which class?
Answer:
Mammalia
Question 27.
Which phylum do the corals belong to ?
Answer:
Coelentrates
Question 28.
Name the phylum and class of pigeon.
Answer:
Phylum-Chordata ; Class -Aves
Question 29.
Crocodiles belong to which class?
Answer:
Reptilia
Question 30.
To which phylum the scorpions belong?
Answer:
Arthropoda
Question 31.
Name the phylum and class of Octopus.
Answer:
Phylum-Mollusca; Class-Cephalopoda
Question 32.
Ascaris belongs to which phylum?
Answer:
Nemathelminthes
Match the Words of Column I with those of Column II.
Question 1.
| I. | II. |
| Hydra | i. Round worm |
| Millipede | ii. Arthropods |
| Ascaris | iii. Crustacea |
| Sea urchin | iv. Segmented worm |
| Leech | v. Cnidaria |
| vi. Echinodermata |
Answer:
| I. | II. |
| Hydra | v. Cnidaria |
| Millipede | ii. Arthropods |
| Ascaris | i. Round worm |
| Sea urchin | vi. Echinodermata |
| Leech | iv. Segmented worm |
Question 2.
| I. | II. |
| A. Limbless reptile | i. Lamprey |
| B. Jawless vertebrate | ii. Salamander |
| C. Amphibian | iii. Snake |
| D. Cartilaginous fish | iv. Shark |
| E. Flightless bird | v. Ostrich |
Answer:
| I. | II. |
| A. Limbless reptile | iii. Snake |
| B. Jawless vertebrate | i. Lamprey |
| C. Amphibian | ii. Salamander |
| D. Cartilaginous fish | iv. Shark |
| E. Flightless bird | v. Ostrich |
Question 3.
| I | II |
| A. Coral | i. Placoid scale |
| B. Echindna | ii. Monotremata |
| C. Crab | iii. Mollusca |
| D. Octopus | iv. Coelenterata |
| E. Sexual dimorphism | v. Amphibia |
| F. Cartilaginous fish | vi. Nematoda |
| vii. Radial symmetry | |
| viii. Crustacea |
Answer:
| I | II |
| A. Coral | iv. Coelenterata |
| B. Echindna | vii. Radial symmetry |
| C. Crab | viii. Crustacea |
| D. Octopus | iii. Mollusca |
| E. Sexual dimorphism | vi. Nematoda |
| F. Cartilaginous fish | i. Placoid scale |
Short Answer Type Questions
Answer each within 50 words
Question 1.
What do you mean by cellular grade of organisation?
Answer:
In this level, the body shows some division of labour among cells. They are remarkably independent and can change their form and function. It is found in sponges. The body consists of many cells arranged as loose cell aggregates but, the cells do not form tissues rather each cell is functionally active independently, e.g. Hydra.
Question 2.
What is metamerism?
Answer:
Metamerism The body is divided into segments or metamers by ring-like grooves called anuli. The segmentation is external as well as internal.
Question 3.
What is an archaeocyte? What is its function?
Answer:
Archaecocytes are the embryonic undifferentiating cells of the mesenchyme in Porifera. These can differentiate into any of the adult cell types.
Question 4.
Why is the name of the phylum to which Hydra belongs, is Coelenterata?
Answer:
Coelentrata means hollow intestine, i.e. (Koilos: hollow; enteron: intestine). In Hydra, anus is absent and there is only one gastrovascular cavity present in the body.
Question 5.
Explain the meaning of Parazoa.
Answer:
Parazoa includes multicellular animals, but the cells do not exhibit cell-cell cooperation. Animals are diploblastic, canal system is present, digestive cavity is absent.
Question 6.
Which germ layer is the coelom derived from? How many types of coelom are there?
Answer:
Coelom is derived from mesoderm. There are two types of coelom-Pseudocoelom and Eucoelom.
Question 7.
In which phylum, neoblasts are present? What is their function?
Answer:
Neoblast cells are found in Platyhelminthes. They can differentiate into any other kind of cell.
Question 8.
Explain about sexual dimorphism in Ascaris.
Answer:
In Ascaris, sexes are separate. The females are longer than males to aid copulation.
Question 9.
Ennumerate three important characters of the phylum-Arthropoda.
Answer:
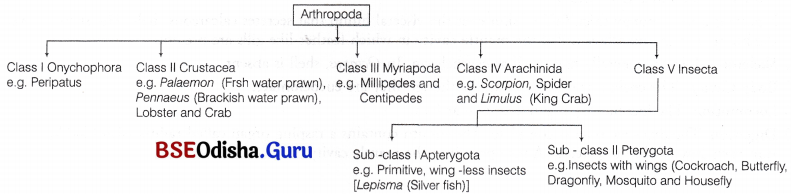
Important characters of the Phylum-Arthropoda
- Habitat and Habit They may be aquatic or terrestrial. They may occur, as free-living or parasitic forms, e.g. bed bugs, ticks, mosquitoes, etc.
- Body Parts Body is segmented externally. It has distinct head, thorax and abdomen. Head bears many fused segments and sense organs.
- Symmetry and Body Organisation Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical. They are triploblastic with organ system level of organisation.
Question 10.
Explain about enterocoelic coelom.
Answer:
Enterocoelic coelom originates as pouches from the endoderm. The animals possessing it are called deuterostomes. In these animals blastopore forms the anus, e.g. echinodermata, chordata.
Question 11.
Despite being radially symmetrical, echinoderms are included in the division-Bilatria. Give reasons.
Answer:
Echinoderms possess pentamerous radial symmetry. This symmetry is considered as secondary symmetry. The primary symmetry is bilateral which occur in their larval form. Hence, they are included in the grade bilatria.
Question 12.
Describe about amphibious breathing habit in Pila?
Answer:
Pila possess both lungs and gills (ctenidia). They can carry out respiration both in water (through gills) and land (through pulmonary sac). Hence, they possess amphibious breathing habit.
Question 13.
Ennumerate three important chordate characters.
Answer:
Retrogressive Metamorphosis The larva possess advanced characters which are lost during the development. Adult is either sedentary or degenerated with primitive characters.
For characteristics of chordates.
Question 14.
What is retrogressive metamorphosis?
Answer:
Animals belonging to phylum-Chordata are fundamentally characterised by the presence of a notochord, a dorsal hollow nerve cord and paired pharyngeal gill slits. These are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, coelomate animals with organ system level of organisation. They possess a post-anal tail and a closed circulatory system.
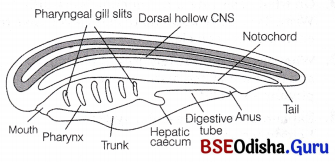
Question 15.
Name two structures in the pharynx of Amphioxus, which fulfil the filter feeding mechanism.
Answer:
Endostyle and dorsal lamina in the pharynx of Amphioxus facilitate ciliary or filter feeding.
Question 16.
Distinguish Agnatha from Gnathostomata in two important features.
Answer:
| Agnatha | Gnathostomata |
| (a) Jaws are absent | Jaws are present |
| (b) Paired fins are absent | Paired fins are present |
| e.g. Cyclostomata | e.g. Pisces. |
Question 17.
Explain the meaning of Cyclostomata.
Answer:
Cylostomata means circular mouth. Mouth is not guarded by jaws and hence remain open all the time, e.g. Myxine.
Question 18.
What is a paired fin? How many paired fins are present in a fish? Name them.
Answer:
Paired fins are the pectoral and pelvic fins, corresponding to the fore and hindlimbs of higher animals. In fishes two pairs of paired fins are present namely pectoral and pelvic.
Question 19.
What is a living fossil? Name one living fossil among fishes.
Answer:
Living fossil is an organism that has remained unchanged from earlier geologic times and whose close relatives are usually extinct. Among fishes Latimeria chalumnae is a living fossil.
Question 20.
Rat fish connects cartilaginous fishes and bony fishes. Explain.
Answer:
Ratfish (a chondrichthyes) have an operculum, a hard bony layer of tissue covering the gills which is found in many bony fishes, but absent in all other chondrichthyes. Hence, it connects cartilaginous fishes with bony fishes.
Question 21.
What is the function of lateral line system?
Answer:
Laternal line system functions as a rheoreceptor, i.e. it detects the direction of water current by perceining vibrations.
Question 22.
What is the basis of division of Tetrapoda into Anamniota and Amniota?
Answer:
Tetrapoda is divided into Anamniota and Amniota based on the absence or presence of extra-embryonic membranes (amnion, chorion, yolk sac and allantois).
Question 23.
Explain the meaning of Tetrapoda.
Answer:
Tetrapoda means the presence of four foot including a pair a forelimbs and a pair of hindlimbs.
Question 24.
Frogs and toads belong to the class-Amphibia. Give one reason.
Answer:
Frogs and toads can breath both in water and in land. Hence, they belong to the class-Amphibia.
Question 25.
Explain neoteny and paedogenesis.
Answer:
Neoteny – Prolongation of larval life.
Paedogenesis – Attainment of sexual maturity during larval life.
Question 26.
What is a pentadactyl limb?
Answer:
Pentadactyl limbs means presence of five digits or fingers.
Question 27.
What is the basis of division of the class-Reptilia into four subclasses?
Answer:
Class-Reptilia is divided into four subclasses based on the absence or presence of temporal fossae and if present, the number of temporal fossae.
Question 28.
Give the scientific names of three crocodiles found in Orissa.
Answer:
Three crocodiles found in Orissa are
- Gavialis gangeticus (Gharial)
- Crocodilus palustris (Mugger)
- Crocodilus porosus (Marsh Crocodile)
Question 29.
Ennumerate three identifying features of common cobra.
Answer:
Identifying features of common cobra
- Length around 5.5 feet.
- Broad hood, a spectacle most behind the hood.
- Cuneate scale is present, occipital scales absent.
- Lay eggs in holes and crevices.
Question 30.
Give the scientific names of two types of Kraits.
Answer:
- Common Krait – Bungarus coeruleus.
- Banded Krait – Bungarus fasciatus.
Question 31.
What is Archaeopteryx? Enlist four of its important characters.Answer:
Answer:
Archaeopteryx is a fossil and a connecting link between reptiles and aves. Its characteristics involves
- Teeth present in the beak.
- Wings with clawed digits.
- Bipedal locomotion.
- Forelimbs modified into wings.
Question 32.
Give the common names of two fightless birds
Answer:
Flightless birds are ostrich and peacock.
Question 33.
Name two egg laying mammals.
Answer:
Platypus and spiny ant eaters are egg laying mammals.
Question 34.
Kangaroo is known as a marsupial mammal. Why?
Answer:
Kangaroo possess a marsupium for the nourishment of the young ones. Hence, it is called marsupial mammal.
Question 35.
Name two mammals possessing nucleated erythrocytes.
Answer:
Camel and rabbit possess nucleated RBCs.
Question 36.
What do you understand by oviparous and viviparous?
Answer:
| Oviparous | Viviparous |
| Egg laying animals. | Give birth to young ones. |
| e.g. fishes, reptiles. | e.g. Humans. |
Question 37.
What is the type of body plan in Hydra?
Answer:
Body plan in Hydra
- Tissue grade of organisation.
- Diploblastic animals with outer ectoderm.
- Radially symmetrical.
Question 38.
What is the type of body plan in sponges?
Answer:
Body plan in sponges
- Cellular grade of organisation,
- Diloblastic with outer pinacoderm and inner choanoderm.
- Radially symmetrical.
Question 39.
What is the type of body plan in flat worms?
Answer:
Body plan in flatworms
- Incipiently triploblastic.
- Bilaterally symmetrical.
- Organ system grade of organisation.
Question 40.
What is the type of body plan in nematodes?
Answer:
Body plan in nematodes
- Organ system grade of organisation.
- Triploblastic with pseudocoelom and syncytial ectoderm.
- Bilaterally symmetrical.
Question 41.
What is the type of body plan in earthworm?
Answer:
Body plan in earthworm
- Truly triploblastic with schizocoelom.
- Body is metamerically segmented.
- Bilaterally symmetrical.
Differentiate between two words in the following pairs of words
Question 1.
Homoiothermic and Poikilothermic
Answer:
Differences between homeothermic and poikilothermic are
| Homeothermic | Poikilothermic |
| Body temperature remains constant. | Body temperature varies with environment. |
| Warm-blooded. | Cold-blooded. |
| Possess a thermoregulatory centre in body, e.g. birds, mammals. | Do not possess thermoregulatory centre in body, e.g. pisces, reptiles. |
Question 2.
Urochordata and Cephalochordata
Answer:
Differences between Urochordata and Cephalochordata are
| Urochordates | Cephalochordates |
| Notochord is present only in the tail of the larva. | Notochord extend the entire length of the body. |
| Notochord disappear in the adults. | Notochord persists throughout the life. |
| Coelom is absent. | A true enterocoelus coelom is present. |
| e.g. Salpa, Doliolum. | e.g. Branchiostoma. |
Question 3.
Amphibia and Reptilia
Answer:
Differences between amphibia and reptilia are
| Amphibia | Reptilia |
| Body is divisible into head and trunk. | Body is divisible into head, neck, trunk and tail. |
| Skin is smooth, moist highy glandular. | Skin is dry, rough and non-glandular. |
| Skull is dioondylic. | Skull is monocondylic. |
| 12 pairs of cranial nerves present. | 10 pairs of cranial nerves present. |
| e.g. Salamandra Bufo, etc. | e.g. Draco, Naja, etc. |
Question 4.
Agnatha and Gnathostomata
Answer:
Differences between agnatha and gnathostomata are
| Agnatha | Gnathostomata |
| Jawless vertebrates. | Jawed vertebrates. |
| Paired appendages are absent. | Paired appendages are present. |
| Single external nostril present. | A pair of external nostrils present. |
| Internal ear with two semicircular canals. | Internal ear with three semicircular canals. |
| e.g. Animals belonging to class-Cyclostomata. | e.g. Animals belonging to class-Pises to Mammalia. |
Question 5.
Plathyelminthes and Nemathelminthes
Answer:
Differences between plathyelminthes and nemathelminthes are
| Platyhelminthes | Nemathelminthes |
| Commonly called flat | Commonly called round worms. |
| Acoelomates. | Pseudocoelomates. |
| Hermaphrodite. | Sexes are separate. |
| Excretion by flame cells. | Excretion by H-shaped excretory canal. |
Question 6.
Chondrichthyes and Osteichthyes
Answer:
Differences between Chondrichthyes and Osteichthyes are
| Chondrichthyes (Cartilaginous fishes) | Osteichthyes (Bony fishes) |
| They are always marine. | They may be marine or fresh water. |
| Skin is covered by small placoid scales. | Skin is covered with large cycloid or gonoid or ctenoid scales. |
| Endoskeieton is cartilaginous. | Endoskeieton is partly or wholly bony. |
| Gill slits are not covered by gill covers. | Gill slits are covered by gill covers. |
| Mouth is ventral and intestine has scroll valve. | Mouth is anterior and intestine lacks scroll valve. |
| Swim bladder is absent. | Swim bladder is present. |
| Tail fin is asymmetrical (heterocercal). | Tail fin is symmetrical (homocercal). |
| Excretory matter is urea. | Excretory matter is ammonia. |
| They exhibit sexual dimorphism. | Sexual dimorphism is usually absent. |
| Mostly viviparous, e.g, sharks, rays, skates. | Usually oviparous, e.g. Labeo, Catla, sea horse. |
Question 7.
Acraniata and Craniata
Answer:
Differences between acraniata and craniata are
| Acraniata | Craniata |
| They are protochordates. | They are vertebrates. |
| Cranium and jaws are absent. | Cranium and jaws are present. |
| Include subphyla Hemichordata, Urochordata and Cephalochordata. | Include two divisions-agnatha and gnathostomata. |
| e.g. Herdmania, Amphioxus. | e.g. Petromyzon fish. |
Question 8.
Chordata and Non-chordata
Answer:
Differences between chordates and non-chordates are
| Chordates | Non-chordates |
| Notochord is present. | Notochord is not present. |
| Central nervous system is dorsal, hollow and single. | Central nervous system is ventral, solid and double. |
| Pharynx perforated by gill slits. | Gill slits are absent. |
| Heart is ventral. | Heart is dorsal (if present). |
| Post-anal part (tail) is present. | Post-anal tail is absent. |
Question 9.
Annelida and Arthropoda
Answer:
Differences between annelida and arthropoda are
| Annelida | Arthropoda |
| Body is metamerically segmented. | Body is segmented with joined appendages. |
| First body segment is peristomium. | First body segment is head. |
| Coelom is schizocoelom. | Coelom is Haemocoel. |
| Cutaneous respiration occurs. | Respiration occur by gills, trachea, book lungs. |
| Excretion by nephridia. | Excretion by malpighian tubules. |
Question 10.
Gemmule and Spicule
Answer:
Differences between annelida and arthropoda are
| Gemmule | Spicule |
| It is asexual reproductive body in sponges. | Form the supporting skeleton in sponges. |
| Formed of central archeocytes covered by thick layer. | Either calcareous or silicious in nature. |
Question 11.
Lizard and Snake
Answer:
Differences between lizard and snake are
| Lizards | Snakes |
| Two pairs of limbs are present. | Limbs are absent. |
| Scales are of uniform size. | Scales are differentiated-into plates and shields. |
| Eyelids are movable. | Eyelids are immovable. |
| Nictitating membrane is present. | Absent. |
| Tongue is not bifid. | It is protrusible and bifid. |
| Urinary bladder is present. | It is absent. |
| Jaw bones are fixed. | These are movable. |
Question 12.
Protostomia and Deuterostomia
Answer:
Differences between lizard and snake are
| Protostomia | Deuterostomia |
| During embryonic development, blastopore forms the mouth. | During embryonic development, blastopore forms the anus. |
| Nerve cord is ventral. | Nerve cord is dorsal. |
| Cleavage is spiral. | Cleavage is determinate. |
| e.g. flat worms, annelids. | e.g. echinoderms, chordates. |
Question 13.
Eucoelomata and Pseudocoelomata
Answer:
Differences between Eucoelomata and Pseudocoelomata are
| Eucoelomata | Pseudocoelomata |
| True coelom present. | False coelom present. |
| Coelom lined by mesoderm. | Coelom is not lined by mesoderm. |
| Arises as a cavity in the embryonic mesoderm. | Derived from blastocoel of embryo. |
| Internal organs are suspended in it. | Internal organs are not suspended in it. |
| e.g. Annelida. | e.g. Nemathelminthes. |
Question 14.
Enterocoelic and Shcizocoelic coelom.
Answer:
Differences between enterocoelic and shcizocoelic coelom. are
| Schizocoelic Coelom | Enterocoelic Coelom |
| The coelom is formed by the splitting of mesoderm bands. | The coelom is derived from the dorsolateral mesodermal pouches from the wall of the archenteron. |
| The mesoderm is derived from a source other than the archenteron. | The mesoderm is derived from the archenteric roof. |
| The mesodermal cells separate off from the endoderm early during development. | The mesodermal cells remain associated with the endoderm and separate off late during the embryonic development. |
| e.g,, Animals belonging to the phyla, Annelida, Arthropoda and Mollusca | e.g., Animals belonging to the phyla, Echinodermata, Hemichordata and Chordata |
Question 15.
Cartilagineous fish and Bony fish
Answer:
Differences between cartilagineous fish and bony fish are
| Chondrichthyes (Cartilagineous fishes) | Osteichthyes (Bony fishes) |
| They are always marine. | They may be marine or fresh water. |
| Skin is covered by small placoid scales. | Skin is covered with large cycloid or gonoid or ctenoid scales. |
| Endoskeieton is cartilaginous. | Endoskeieton is partly or wholly bony. |
| Gill slits are not covered by gill covers. | Gill slits are covered by gill covers. |
| Mouth is ventral and intestine has scroll valve. | Mouth is anterior and intestine lacks scroll valve. |
| Swim bladder is absent. | Swim bladder is present. |
| Tail fin is asymmetrical (heterocercal). | Tail fin is symmetrical (homocercal). |
| Excretory matter is urea. | Excretory matter is ammonia. |
| They exhibit sexual dimorphism. | Sexual dimorphism is usually absent. |
| Mostly viviparous, e.g, sharks, rays, skates. | Usually oviparous, e.g. Labeo, Catla, sea horse. |
Question 16.
Marsupiale and Placentale
Answer:
Differences between marsupiale and placentale are
| Marsupiale | Placentale |
| No internal placenta is present. | Internal placenta is present. |
| Females possess marsupial pouch. | No marsupial pouch is present. |
| They replace certain teeth only. | Possess two sets of teeth. |
| Low body temperature and basal metabotic rate. | High body temperature and basai metabotic rate. |
