Odisha State Board CHSE Odisha Class 11 Biology Solutions Chapter 7 Animal Tissues and Gross Anatomical Organisation of Cockroach Textbook Questions and Answers.
CHSE Odisha 11th Class Biology Chapter 7 Question Answer Animal Tissues and Gross Anatomical Organisation of Cockroach
Animal Tissues and Gross Anatomical Organisation of Cockroach Class 11 Questions and Answers CHSE Odisha
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Ligaments and tendons are formed of
(a) muscular, tissue
(b) epithelial tissue
(c) connective tissue
(d) nervous tissue
Answer:
(c) connective tissue
Question 2.
Segment of the skeletal muscle fiber between two Z-lines is called
(a) A-band
(b) H-band
(c) sarcomere
(d) sarcoplasm
Answer:
(c) sarcomere
Question 3.
Schwann cells and nodes of Ranvier are present in
(a) bone cells
(b) neurons
(c) muscle cells
(d) chondrocytes
Answer:
(b) neurons
Question 4.
Notochord originates from
(a) ectoderm
(b) mesoderm
(c) endoderm
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) ectoderm
Question 5.
Which muscle of body works non-stop till death?
(a) Unstriped
(b) Skeletal
(c) Cardiac
(d) Smooth
Answer:
(c) Cardiac
Question 6.
In an animal, the tissue is bathed in
(a) calcium chloride
(b) body fluid
(c) water
(d) sodium chloride
Answer:
(b) body fluid
Question 7.
Voluntary muscle is present in
(a) lung
(b) liver
(c) heart
(d) hindlimb
Answer:
(d) hindlimb
Question 8.
Non-cellular basement membrane is a feature of
(a) epithelial tissue
(b) vascular tissue
(c) nervous tissue
(d) connective tissue
Answer:
(a) epithelial tissue
Question 9.
A tissue is a group of cells having
(a) similar cells with dissimilar function
(b) similar cells with similar function
(c) dissimilar cells with dissimilar function
(d) dissimilar cells with similar function
Answer:
(b) similar cells with similar function
Question 10.
Intercellular matrix is minimum in
(a) bone
(b) vascular tissue
(c) muscular tissue
(d) cartilage
Answer:
(a) bone
Question 11.
Blood vessels are lined internally by
(a) ciliated epithelium
(b) squamous epithelium
(b) columnar epithelium
(d) striated epithelium
Answer:
(b) squamous epithelium
Question 12.
Transitional epithelium is found in
(a) kidney
(b) urinary bladder
(c) trachea
(d) blood vessel
Answer:
(b) urinary bladder
Question 13.
Tendon connects
(a) muscle to muscle
(b) bone to bone
(c) bone to muscle
(d) nerve to muscle
Answer:
(c) bone to muscle
Question 14.
Cardiac muscle is
(a) voluntary and striated
(b) involuntary and striated
(c) involuntary and smooth
(d) voluntary and smooth
Answer:
(b) involuntary and striated
Question 15.
Epithelium forming the peritoneal lining of the coelom is
(a) squamous epithelium
(b) cuboidal epithelium
(c) columnar epithelium
(d) glandular epithelium
Answer:
(a) squamous epithelium
Question 16.
Myelin sheath is a covering of
(a) vertebrate nerve fibre
(b) vertebrate muscle fibre
(c) insect nerve fibre
(d) ventricles of heart
Answer:
(b) vertebrate muscle fibre
Question 17.
Nature of dendrite is
(a) efferent
(b) afferent
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
Question 18.
Which type of connective tissue is a tendon?
(a) Dense
(b) Loose
(c) Fluid
(d) Skeletal
Answer:
(d) Skeletal
Question 19.
Intercalated disc is found in
(a) neuron
(b) skeletal muscle
(c) junction of muscle and nerve
(d) cardiac muscle
Answer:
(d) cardiac muscle
Question 20.
Larynx and trachea contain
(a) hyaline cartilage
(b) elastic cartilage
(c) bone
(d) fibrocartilage
Answer:
(a) hyaline cartilage
Question 21.
Myoglobin is found in
(a) white muscle fibre
(b) yellow fibre
(c) red muscle fibre
(d) All of these
Answer:
(c) red muscle fibre
Question 22.
Oil glands in mammal (rabbit) are found in
(a) epidermis of skin
(b) mucous epithelium of skin
(c) dermis of skin
(d) mucous epithelium of stomach
Answer:
(c) dermis of skin
Question 23.
Erythrocytes of frog are
(a) non-nucleated and biconcave
(b) nucleated biconvex
(c) nucleated biconcave
(d) non-nucleated biconvex
Answer:
(b) nucleated biconvex
Question 24.
Nerve cells develop from
(a) ectoderm
(b) mesoderm
(c) endoderm
(d) ectoderm and mesoderm
Answer:
(a) ectoderm
Question 25.
Mammary glands are
(a) apocrine
(b) holocrine
(c) merocrine
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) apocrine
Question 26.
Cardiac muscle contracts
(a) quickly and is fatigued
(b) quickly and is not fatigued
(c) slowly and is not fatigued
(d) slowly and is fatigued
Answer:
(b) quickly and is not fatigued
Question 27.
Largest erythrocytes are found in
(a) man and monkey
(b) amphiuma and proteus
(c) fish and frog
(d) lizard and snake
Answer:
(c) fish and frog
Question 28.
Which vitamin is essential for blood clotting
(a) vitamin-A
(b) vitamin-C
(c) vitamin-K
(d) vitamin-E
Answer:
(c) vitamin-K
Question 29.
Blood transports
(a) oxygen only
(b) respiratory gases and excretory product only
(c) respiratory gases nutrients and excretory products
(d) respiratory gases and nutritive substances only
Answer:
(c) respiratory gases nutrients and excretory products
Question 30.
Lymph differs from blood in the
(a) absence of RBC
(b) absence of WBC
(c) excess of water
(d) absence of protein
Answer:
(a) absence of RBC
Question 31.
Blood is composed of
(a) plasma and corpuscles
(b) plasma and RBC
(c) plasma and WBC
(d) colloid particles
Answer:
(a) plasma and corpuscles
Question 32.
If RBCs are kept in distilled water they will
(a) contract
(b) just swell up
(c) remain unaffected
(d) swell up and burst
Answer:
(d) swell up and burst
Question 33.
RBCs are kept in 8% saline solution it will
(a) burst
(b) contract
(c) remain unaffected
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) contract
Question 34.
RBC will contract if kept in
(a) isotonic solution
(b) distilled water
(c) hypertonic solution
(d) hypotonic solution
Answer:
(c) hypertonic solution
Question 35.
In 100 mL of blood of adult man amount of haemoglobin is
(a) 11 gm
(b) 12.5 gm
(c) 14 gm
(d) 20 gm
Answer:
(c) 14 gm
Question 36.
Red bone marrow occurs in
(a) ribs
(b) ribs and sternum
(c) ribs and cranium
(d) ribs, sternum and cranium
Answer:
(d) ribs, sternum and cranium
Question 37.
Secretion of sebaceous gland is
(a) holocrine
(b) apocrine
(c) epierine
(d) merocrine
Answer:
(a) holocrine
Question 38.
Which is a simple coiled tubular gland?
(a) Salivary gland
(b) Sweat gland
(c) Sebaceous gland
(d) Testes
Answer:
(b) Sweat gland
Question 39.
Haemopoietic tissue is
(a) dense connective tissue
(b) reticular tissue
(c) adipose tissue
(d) epithelial tissue
Answer:
(b) reticular tissue
Question 40.
Harmful bacteria and other foreign bodies are destroyed by
(a) plasma protein
(b) platelets
(c) phagocytosis by RBC
(d) phagocytosis by WBC
Answer:
(d) phagocytosis by WBC
Question 41.
Phagocytic cells in liver are
(a) Kupffer cell
(b) Chromaffin cell
(c) Mast cell
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Kupffer cell
Question 42.
Which is irregular in shape?
(a) RBC
(b) WBC
(c) Muscle fibre
(d) Epithelial cell
Answer:
(d) Epithelial cell
Question 43.
An erythrocyte in mammal is without nucleus because
(a) erythrocyte is not a cell
(b) nucleus is not required
(c) nucleus disappears during its formation
(d) nucleus is absent from the beginning
Answer:
(b) nucleus is not required
Question 44.
Source of energy for muscle contraction is
(a) actin
(b) myosin
(c) actomyosin
(d) ATP
Answer:
(d) ATP
Question 45.
Smooth muscles are
(a) involuntary, spindle-shaped uninucleate and tapering
(b) voluntary multinucleate and cylindrical
(c) involuntary cylindrical and multinucleate
(d) voluntary, branched and uninucleate
Answer:
(b) voluntary multinucleate and cylindrical
Question 46.
The fibrous connective tissue sheath of bones is known as
(a) pericardium
(b) perichondrium
(c) perineurium
(d) periosteum
Answer:
(d) periosteum
Question 47.
Sarcolemma is a membrane present on the outer side of
(a) nerve fibre
(b) bone
(c) muscle fibre
(d) RBC
Answer:
(c) muscle fibre
Question 48.
Tissue covering of the body surface is
(a) epithelial
(b) connective
(c) muscle
(d) adipose
Answer:
(a) epithelial
Question 49.
White matter of the spinal cord is made up of
(a) nerve cells
(b) non-myelinated nerve fibers
(c) myelinated nerve fibers
(d) connective tissue cells
Answer:
(c) myelinated nerve fibers
Question 50.
Haemopoiesis in adult human occurs in
(a) liver and spleen
(b) liver
(c) spleen
(d) red bone marrow
Answer:
(d) red bone marrow
Question 51.
In human, haemoglobin is present
(a) in the liver
(b) dissolved in the blood plasma
(c) in erythrocytes
(d) in spleen
Answer:
(c) in erythrocytes
Question 52.
Maximum number of cell bodies (cytons) are present in
(a) spinal cord
(b) retina
(c) brain
(d) ganglia
Answer:
(c) brain
Question 53.
If bone is kept in 5% KOH solution for some days.
(a) Be unaffected
(b) Dissolve
(c) Becomes soft and elastic
(d) Break
Answer:
(a) Be unaffected
Question 54.
Which salt is found in maximum quantity in bones?
(a) Calcium carbonate
(b) Calcium phosphate
(c) Sodium chloride
(d) Magnesium chloride
Answer:
(b) Calcium phosphate
Question 55.
If a bone is suspended in dilute hydrochloric acid, for a few days, it
(a) becomes harder
(b) becomes softer and malleable
(c) remains unaffected
(d) dissolves
Answer:
(b) becomes softer and malleable
Question 56.
Mast cells occur in
(a) nervous tissue
(b) connective tissue
(c) epithelial tissue
(d) skeletal tissue
Answer:
(b) connective tissue
Question 57.
Afferent nerve fibre carries nerve impulse
(a) from central nervous system to a receptor
(b) from receptor to the central nervous system
(c) from central nervous system to the effector organ
(d) from effector organs to the central nervous system
Answer:
(b) from receptor to the central nervous system
Question 58.
Increase in the number of erythrocytes is called
(a) polycythemia
(b) glycosuria
(c) hyperglycemia
(d) hypoglycemia
Answer:
(a) polycythemia
Question 59.
Epithelial tissue performs the following functions
(a) protection, secretion, absorption and respiration
(b) protection, secretion, sensation and absorption
(c) absorption, respiration, secretion and sensation
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 60.
The cells responsible for dissolving the bone matrix are called
(a) osteoblasts
(b) osteoclasts
(c) osteocytes
(d) chondrocytes
Answer:
(b) osteoclasts
Question 61.
Colourless plasma without corpuscles and fibrinogen is also known as
(a) chyle
(b) lymph
(c) serum
(d) thrombus
Answer:
(c) serum
Question 62.
Mammary glands are modified
(a) holocrine glands
(b) endocrine glands
(c) sebaceous glands
(d) sweat glands
Answer:
(d) sweat glands
Question 63.
Horns of a rhinoceros are composed of
(a) bone
(b) cartilage
(c) chitin
(d) keratin
Answer:
(d) keratin
Question 64.
A nerve is nothing, but a bundle of
(a) axons
(b) dendrites
(c) ganglia
(d) cell bodies
Answer:
(a) axons
Question 65.
Possible function of Nissl’s body is
(a) protein synthesis
(b) RNA synthesis
(c) RNA storage
(d) impulse conduction
Answer:
(a) protein synthesis
Question 66.
The male cockroach is identified by the presence of
(a) anal cerci
(b) long antennae
(c) anal styles
(d) wingless body
Answer:
(c) anal styles
Question 67.
In cockroach or insects the excretory organs are
(a) Malpighian tubules
(b) Nephridia
(c) Malpighian corpuscles
(d) Flame cells
Answer:
(a) Malpighian tubules
Question 68.
Cockroach is
(a) omnivorous
(b) sanguivorous
(c) insectivorous
(d) carnivorous
Answer:
(a) omnivorous
Question 69.
The juvenile stage of cockroach is known as
(a) larva
(b) pupa
(c) maggot
(d) nymph
Answer:
(c) maggot
Question 70.
In cockroach, the number of spiracles is
(a) 8 pairs
(b) 10 pairs
(c) 12 pairs
(d) 14 pairs
Answer:
(b) 10 pairs
Question 71.
The blood-filled cavity of cockroach is known as
(a) coelom
(b) haemocoel
(c) enteron
(d) pseudocoel
Answer:
(b) haemocoel
Question 72.
Cockroach respires by
(a) cuticle
(b) lungs
(c) trachea
(d) book lung
Answer:
(c) trachea
Question 73.
In cockroach, the main excretory product is
(a) ammonia
(b) urea
(c) uric acid
(d) hippuric acid
Answer:
(c) uric acid
Question 74.
Mouth parts of cockroach are of
(a) sponging type
(b) piercing type
(c) sucking type
(d) biting and chewing type
Answer:
(d) biting and chewing type
Question 75.
Muscles associated with heart of cockroach are
(a) pericardial muscles
(b) striped muscles
(c) tergo-sternal muscles
(d) alary muscles
Answer:
(d) alary muscles
Question 76.
The tubular heart of cockroach is composed of
(a) 6-chambers
(b) 9-chambers
(c) 10-chambers
(d) 13-chambers
Answer:
(d) 13-chambers
Question 77.
In cockroach nerve cord is
(a) single, ventral, solid
(b) double, ventral solid
(c) single, ventral, hollow
(d) double, ventral, hollow
Answer:
(b) double, ventral solid
Question 78.
Characters common in cockroach spider and prawn is
(a) book lungs
(b) jointed legs
(c) green glands
(d) compound eye
Answer:
(b) jointed legs
Question 79.
In cockroach the food is crushed and strained in
(a) crop
(b) gizzard
(c) mesenteron
(d) hepatic caecae
Answer:
(b) gizzard
Question 80.
Blood does not transport oxygen in
(a) bird
(b) earthworm
(c) rabbit
(d) cockroach
Answer:
(d) cockroach
Question 81.
How many chitinous teeth does the gizzard of cockroach have?
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 6
(d) 8
Answer:
(c) 6
Question 82.
In female cockroach the 7th sternum forms a boat-shaped structure called
(a) hypogynium
(b) gonapophyses
(c) phallomere
(d) podial plate
Answer:
(b) gonapophyses
Question 83.
Each ovary of cockroach is composed of
(a) 4 ovarioles
(b) 6 ovarioles
(c) 8 ovarioles
(d) 16 ovarioles
Answer:
(c) 8 ovarioles
Question 84.
Which of the following serves as the tongue of cockroach?
(a) Labium
(b) Maxillae
(c) Mandible
(d) Hypopharynx
Answer:
(d) Hypopharynx
Question 85.
Hepatic caeca in cockroach from
(a) junction of midgut and hindgut
(b) gizzard
(c) midgut
(d) junction of gizzard and midgut
Answer:
(c) midgut
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words
Question 1.
Lifespan of erythrocytes is ……………. days.
Answer:
120
Question 2.
Junction of two neurons is called ……………. .
Answer:
Synapse
Question 3
………… is the structural and functional unit of a muscle fiber.
Answer:
Sarcomere
Question 4
……………. are the longitudinal canals found in bone.
Answer:
Haversian canals
Question 5.
Nissl’s granules are found in …………….. .
Answer:
Cyton
Question 6.
Outer most layer of a cartilage is known as ……………. .
Answer:
Perichondrium
Question 7.
Bone forming cells are called ……………. .
Answer:
Osteoblasts
Question 8.
Cell bodies of most neurons in peripherial nervous system are grouped together as ……………. .
Answer:
Ganglion
Question 9.
Cartilage is formed by cells, called ……………. .
Answer:
Chondroblasts
Question 10.
……………… are periodic constrictions in the axon of a myelinated nerve fiber.
Answer:
Nodes of Ranvier
Question 11.
Branch of the science dealing with the study of tissues is known as ……………. .
Answer:
Anatomy
Question 12.
Brush border cuboidal epithelial cell possess ……………. at their free ends.
Answer:
Cilia
Question 13.
Plasma without fibrinogen is known as ……………. .
Answer:
Serum
Question 14.
A neuron receives the nerve impulse through ……………. and transmit it through ……………. .
Answer:
Dendrites, axon
Question 15.
Heart contains ……………. muscle.
Answer:
Cardiac
Question 16.
Transportation of ……………. is the main function of blood which is carried by a conjugate protein called ……………. .
Answer:
Oxygen, Haemoglobin
Question 17.
Epithelial tissue lining the blood vessel is known as ……………. .
Answer:
Endothelium
Question 18.
…………….. is the group of cells specialised to perform a specific function.
Answer:
Tissue
Question 19.
Haversian canal is found in ……………. .
Answer:
Bones
Answer each of the following in single word
Question 1.
Name a mammal having nucleated RBC.
Answer:
Camel
Question 2.
What type of cartilage is found in the intervertebral disc?
Answer:
Hyaline cartilage
Question 3.
Name the longest cell in the body?
Answer:
Neuron
Question 4.
Which animal possesses pneumatic bone?
Answer:
Birds
Question 5.
Who coined the term epithelium ?
Answer:
Raysch
Question 6.
Which muscle doesn’t get fatigued throughout life?
Answer:
Cardiac muscle
Question 7.
In which cell, Nissl granules are present?
Answer:
Neuron (cyton)
Question 8.
Volkman’s canal is present in which tissue?
Answer:
Bone
Question 9.
Who is known as father of histology?
Answer:
Xavier Bichat
Question 10.
Name the structural and functional unit of nervous tissue.
Answer:
Neuron
Question 11.
Name the tissue connecting muscle to a bone.
Answer:
Tendon
Question 12.
What is the expanded from of RBC?
Answer:
Red blood cell
Question 13.
Name the protein which constitutes the collagen fibre.
Answer:
Collagen
Question 14.
What type of cartilage is found in ear pinnae?
Answer:
Elastic cartilage
Question 15.
What type of tissue does blood come under?
Answer:
Connective tissue
Question 16.
Where are Schwann cells found?
Answer:
Axon
Question 17.
Which muscle is self excitatory?
Answer:
Cardiac muscle
Short Answer Type Questions
Answer each of the following within 50 words
Question 1.
What is a ligament?
Answer:
Ligament is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones and is also known as articular ligament. They usually serves to hold structures together and keep them stable.
Question 2.
How would you obtain pavement epithelium?
Answer:
Simple sqamous epithelium is formed by a single layer of flat or spindle-shaped cells. The cells are closely fitted like the tiles on a floor with serrated edges. Therefore this epithelium is often known as pavement epithelium. Each cell contains a centrally placed spherical nucleus.
Question 3.
Why blood does not clot in blood vessel?
Answer:
Blood does not clot inside the body due to the presence of naturally occurring anticoagulant heparin, secreted by basophils and mast cells.
Question 4.
What is the advantage of having transitional epithelium in the wall of the urinary bladder?
Answer:
The number of cells in transitional epithelium changes with time. For example, the wall of the distended urinary bladder has 2-3 layers of cells. However when the bladder contracts, this number increases To 5-6. This is advantageous in having transitional epithelium in the wall of the urinary bladder.
Question 5.
What do you understand by pseudostratified epithelium?
Answer:
Pseudostratified Epithelium
The epithelium is one-cell thick, but appears 2-layered because all the cells do not reach the , . free surface. The cells are attached to the * basement membrane, hence they are called pseudostratified.
The mucus secreting goblet cells also occur in this epithelium.
Question 6.
What is the fundamental difference between spongy bone and compact bone?
Answer:
(a) Spongy (Cancellace) Bone it contains a ncrwork of thin and irrcgularly longitudinal and ransvcrsc bony bars called trabeculae covered by the cndosteum. it is found at che ends of long bones (epiphyses).
(b) Compact (Dense) Bone It is hard and compact and found in the shaft of long bones. It contains ydilow bone marrow and has Haversian systems.
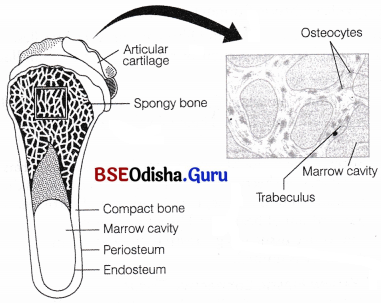
Structure of cancellous (spongy) bone
(a) Spongy bone at the end of a long bone and
(b) microscopic structure of spongy bone
Question 7.
Name different types of leucocytes and enumerate their functions.
Answer:
The different types of leucocytes are
- Neutrophils They are attracted by chemotactic factors secreted by bacteria at the site of infection and acts as phagocytes and engulf and digest them.
- Eosinophils They are phagocytic cells with an affinity for antigen-antibody complexes formed at the site of inflammation and allergic reaction.
- Basophils These store histamine and heparin.
- Lymphocytes They play a key role in the immune response of the body.
- Monocyte They are phagdcytic in nature.
Question 8.
Why have tendons and ligaments more tensile strength?
Answer:
Tendon and ligaments are composed of dense connective tissue. These have densely packed collagen fibers. These cells are few and the ground substance is less. This gives them more tensile strength.
Question 9.
What do you mean by involuntary muscle?
Answer:
Involuntary muscles are muscles that contracts without conscious control and found in walls of internal organs such as stomach, intestine, bladder and blood vessels.
Question 10.
What is the difference between G-actin and F-actin?
Answer:
Actin forms microfilaments, it is globular and multifunctional protein. It is thus known as globular actin or G-actin. A G-actin molecule has an ATPase activity and a myosin head binding site. Several G-actins joins linearly forming a fibrous actin or f-actin. Two f-actins helically coil forming an actin filament.
Question 11.
Describe the role of troponin and tropomyosin in skeletal muscle contraction.
Answer:
Tropomyosin blocks myosin binding sites on actin molecules, preventing cross bridge formation, which prevents contraction in a muscle without nervous input. The protein complex troponin binds to tropomyosin, helping to position it on the actin molecule.
Question 12.
How does cardiac muscle differ from skeletal muscle?
Answer:
Difference between Skeletal muscle and Cardiac muscle
| Skeletal muscle | Cardiac muscle |
| Attached to bones and cartilages. | Present in the wall of heart and the wall of large blood vessels in the vicinity of their entering or leaving the heart. |
| Voluntary and undergo fatigue. | Involuntary and never undergo fatigue. |
| Muscle fibers are long and cylindrical and never branch. | The fibers are branched. The branches anastomoise with each other. |
| The fibers are muitinucleated (syncytial). | The fibers are uninucleate, occasionally binucleated. |
| Intercalated dis.cs are absent. | Intercalated discs are present at the anastomosing points. |
Question 13.
Name the cells, which from myelin sheaths in axons of central nervous system and peripheral nervous systems.
Answer:
Schwann cells forms myelin sheaths in axons of central nervous system and peripheral nervous system.
Question 14.
Name the macrophage associated with the nervous tissue. What is its function?
Answer:
Microglia are the smallest neuroglial cells. Their function is like that of macrophages of the connective tissue. When nervous tissue is damaged or injured, the microglial cells migrate to the site, proliferate and remove the debris by phagocytoses.
Write short notes on the following
Question 1.
Cartilage
Answer:
Cartilage
It is a tough, semitransparent, elastic and flexible tissue. The cartilage cells (chondrocytes) lie in groups of 2-3 in , fluid-filled spaces called lacunae. The cartilage is bounded externally by a stiff sheath called perichondrium containing white fibrous tissue. Cartilage is present in the tip of nose, outer ear joint, between adjacent bones of the vertebral column, limbs and hand in adults.
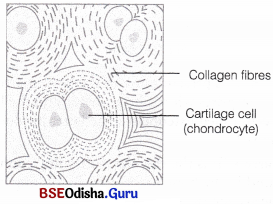
Question 2.
Bone of mammal
Answer:
Bone:
It is a hard and rigid connective tissue. These are non-pliable ground substance rich in calcium salts and collagen fibres providing strength to the bone. The cells of bone are found in a calcified matrix made up of ossein. The bone cells known as osteocytes are lodged in the spaces called lacunae.
They also interact with skeletal muscles attached to them to bring about movements.
A characteristic feature of mammalian bones are present in the matrix. Each Haversian canal contains an artery, a vein, a lymph vessel, a nerve and some bone cells.
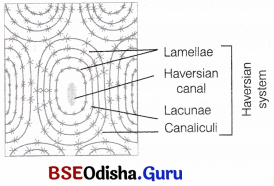
Question 3.
Neuron
Answer:
Neurons are the functional unit of neural system. These are excitable cells. A neuron consists of a cell body (cyton) or soma and fine protoplasmic processes called neurites arising from the cell body.
Question 4.
Cardiac muscle
Answer:
Cardiac Muscles
The cardiac muscles are contractile tissues present only in the heart and in the wall of large veins which enter the heart. The cardiac muscle fibres show the characters of both unstriped and striped muscle fibres. Each fibre is a v long and cylindrical structure which has a definite – sarcolemma. The fibres are uninucleate and the nuclei lie near the centre.
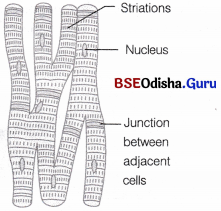
Question 5.
Myofibril
Answer:
Myofibril It is also known as a muscle fibril. It is a basic rod-like unit of a muscle cell. Muscles are composed of tubular cells called myocytes, known as muscle fibres in striated and these cells in turn contain many chain of myofibrils.
Question 6.
Adipose tissue
Answer:
Adipose Tissue It is a modified type of areolar tissue. Its matrix contains large number of adipose cells along with fibrocytes and macrophages. White and yellow fibres are present in the matrix. The cells of this tissue are specialised to store fats.
The excess of nutrients which are not used immediately are converted into fats and are stored in this tissue. The adipose tissues are found in the subcutaneous region, around the heart, kidneys, eyeballs, etc. It is also found in the blubber of whales and elephants, hump of camel, fat bodies of frog and yellow bone marrow.
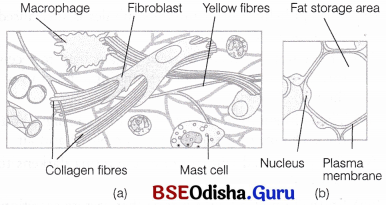
Loose connective tissue
(a) Areolar (b) A cell of adipose tissue
Question 7.
Stratified epithelium
Answer:
Stratified Compound Epithelia The stratified epithelia consist of many layers of cells. On the basis of the shape of the cells present in the superficial layers, the stratified epithelium are of four types
Stratified Squamous Epithelium The cells in the basal (deepest) layer are columnar or cuboidal with oval nuclei. It is called germinal layer. The cells in this region keep dividing by mitosis to form new cells.
The stratified squamous epithelium is further subdivided as two main types, i.e. keratinised and non-keratinised.
Question 8.
Neuroglia
Answer:
The neuroglia or glia cells are supporting cells which form a packing around the neurons in the brain, spinal cord and ganglia. Neuroglia make up more than one half the volume of neural tissue in our body. These cells have different shapes and many processes.
The neuroglia cells have various roles like myelin formation, transport of materials to neurons, maintenance of ionic balance and phagocytosis.
Question 9.
Haversian system
Answer:
Haversian System The osteon or Haversian system is the fundamental functional unit of much compact bone. Osteons are roughly cylindrical structures that are typically several millimeters long around 0.2 mm in diameter.
Question 10.
Leucocytes
Answer:
Leucocytes or White Blood Corpuscles (WBCs) lack haemoglobin and are colourless. They are nucleated with rounded or irregular shape. They can change their shape and are capable of amoeboid movement.
Question 11.
Sarcomere
Answer:
Sarcomere It is the basic unit of striated muscle tissue. It is the repeating unit between the two Z-lines. Skeletal muscles are composed of tubular muscle cells (myocytes called muscle fibres or myofibers), which are formed in a process known as myogenesis.
Differentiate between the following
Question 1.
Axon and Dendron
Answer:
Differences between dendrites and axons are
| Dendrite | Axon |
| These are short fibres which branch repeatedly and project out of the cell body and also contain Nissl’s granules. | The axon is a long branched fibre, which terminates as a bulb-like structure called synaptic knob. It possesses synaptic vesicles containing chemicals called neurotransmitters. |
| These fibres transmit impulses towards the cell body. | The axons transmit nerve impulses away from the cell body to a synapse. |
| Its branches terminate into bulb like synaptic knobs. | Their branches do not have synaptic knobs. |
Question 2.
Epithelial tissue and Connective tissue
Answer:
Difference between epithelial tissue and connective tissue are
| Epithelial tissue | Connective tissue |
| The cells of a sub type are homogenous, e.g. squamous, columnar. | The cells of a sub type may be different, e.g. histiocytes, mast cells, adipose cells, etc. |
| Intercellular space is absent. | Large intercellular spaces are present. |
| It lies on basement membrane. | Basement membrane is absent. |
| The main functions of epithelial tissue are protection, secretion and perception of stimuli of different kinds. | To support organs and to provide connection between organs. |
Question 3.
Cartilage and Bone
Answer:
Differences between bone and cartilage are
| Bone | Cartilage |
| It is hard and inflexible. | It is comparatively soft and flexible. |
| The matrix contains ossein. | The matrix composes of chondrin. |
| Bone is highly vascular. Blood vessels occur in periosteum, endosteum marrow cavity, Haversian cannals and Volkmann’s canals. | Cartilage is largely a vascular. Vascular supply is limited to outer sheath or perichodrium. |
| It can be solid hollow or spongy. | It is always solid. |
| Osteocytes occur singly. | Chondrocytes may occur singly or in groups of 2-4. |
| Marrow is often present in the centre. | Marrow is absent. |
Question 4.
Striated muscle and Non-striated muscle
Answer:
Difference between striated muscle and non-striated muscle
| Striated muscle | Non-striated muscle |
| Striations present. | Striations absent. |
| it is voluntary in action. | It is involuntary in action. |
| The muscle fibres are long and cylindrical with blunt ends. | The muscle fibres are long spindle shaped with pointed ends. |
| The fibres are multinucleate. | The fibres are uninucleated. |
| Sarcoplasmic reticulum is well-developed. | Sarcoplasmic reticulum is poorly developed. |
| Sarcomeres present. | Sarcomeres absent. |
| Numerous mitochondria and glycogen are present. | Less mitochondria and glycogen granules are present. |
| Striated muscle is seen attached to skeleton. | Non-striated muscle is seen in internal organs. |
Question 5.
Tendon and Ligament
Answer:
Differences between tendons and ligaments are
| Tendons | Ligaments |
| The tendons are dense regular connective tissues, which attach the muscles to bones. | The ligaments are dense regular connective tissues, which attach the bones at the joints. |
| It is formed of white fibrous connective tissue. | It is formed of yellow elastic connective tissue. |
Question 6.
Muscle cell and Nerve cell
Answer:
Difference between nerve cell and muscle cell are
| Nerve cell | Muscle cell |
| It is the structural and functional unit of nervous tissue. | It is structural unit of muscle unit of nervous tissue. |
| It is specialised for transmission of impulses. | In addition to transmission of impulses, it involves in contraction and relaxation muscles. |
| Its plasma membrane is called neurolemma. | Its plasma membrane is called sarcolemma. |
| Its cytoplasm is called neuroplasm. | Its cytoplasm is called sarcoplasm. |
Question 7.
Blood and Lymph
Answer:
Differences between blood and lymph are
| Blood | Lymph |
| It contains plasma, erythrocytes, leucocytes and platelets. | It contains plasma and leucocytes. |
| The presence of haemoglobin imparts red colour to it. | It is colourless as haemoglobin is absent. |
| Its plasma contains more protein, and phosphorus as compared to lymph. | Its plasma has fewer protein and calcium less calcium and phosphorus than blood. |
| Contains moderate amount of CO2 and other metabolic wastes. | Contains excessive amount of CO2 and other metabolic wastes. |
Question 8.
Cardiac muscle and Skeletal muscle
Answer:
Difference between Skeletal muscle and Cardiac muscle
| Cardiac muscle | Skeletal muscle |
| Present in the wall of heart and the wall of large blood vessels in the vicinity of their entering or leaving the heart. | Attached to bones and cartilages. |
| Involuntary and never undergo fatigue. | Voluntary and undergo fatigue. |
| The fibers are branched. The branches anastomoise with each other. | Muscle fibers are long and cylindrical and never branch. |
| The fibers are uninucleate, occasionally binucleated. | The fibers are muitinucleated (syncytial). |
| Intercalated discs are present at the anastomosing points. | Intercalated dis.cs are absent. |
Question 9.
Myelinated and Non-myelinated nerve fibre
Answer:
Differences between myelinated and non-myelinated nerve fibres are
| Myelinated nerve fibre | Non-myelinated nerve fiber |
| The myelinated nerve fibres are enveloped with Schwann cells, which form a myelin sheath around the axon. | Non-myelinated nerve fibres are enclosed by a Schwann cell that does not from a myelin sheath around the axon. |
| Myelinated nerve fibres are found in spinal and cranial nerves. | These are commonly found in autonomous and the somatic nervous systems. |
Question 10.
RBC and WBC
Answer:
Difference between RBC and WBC are
| RBC (Erythrocytes) | WBC (Leucocytes) |
| RBCs are small, circular, biconcave and non-nucleate cells. | Larger than RBC, amoeboid and nucleated cells. |
| Red due to the presance of haemoglobin. | Colourless due to the absence of haemoglobin. |
| More numerous than WBCs i.e. vary from 4.5 to 5.5 millions/ mm³. | Less numerous than . RBC- i.e. vary from 8000 to 10000 mm³. |
| Lifespan is approximately 120 days. | Lifespan is only a few days. |
| Carry molecules oxygen from the lungs to the tissues. | Mostly defend the body from external aggression. |
Question 11.
Areolar tissue and Adipose tissue
Answer:
Difference between areolar tissue and adipose tissue are
| Areolar tissue | Adipose tissue |
| Areolar tissue is mainly connective. | It is a mainly concerned with the storage of fat. |
| It usually fixes skin with the muscles. | The cells are spherical or oval and are packed in a matrix. |
| It forms packaging of the material in all organs between the muscles. | The matrix of the tissue consists of fibroblasts, macrophages and collagen fibres. |
| It has two types of fibres white and yellow. | It is found around the kidneys, blood vessels and also heart. |
