Odisha State Board BSE Odisha Class 10 English Grammar Book Solutions Chapter 7 Noun Clauses and Relative Clauses Textbook Exercise Activity Questions and Answers.
BSE Odisha Class 10 English Grammar Solutions Chapter 7 Noun Clauses and Relative Clauses
Let’s look at the following sentence :
Mohan stayed at home when everybody else in the family went to the cinema.
(ଯେତେବେଳେ ପରିବାରର ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ସଦସ୍ୟ ସିନେମାକୁ ଯାଇଥିଲେ, ମୋହନ ଘରେ ରହିଥିଲା ।)
⇒ In this sentence we have two clauses.
(ଏହି ବାକ୍ୟରେ ଦୁଇଟି ଖଣ୍ଡ ରହିଛି । ଅର୍ଥାତ ୨ଟି ଖଣ୍ଡ ବାକ୍ୟକୁ ନେଇ ଏହି ବାକ୍ୟ ତିଆରି ହୋଇଛି ।)
“Mohan stayed at home first” – Clause (Main clause or independent clause)
“when everybody else in the family went to the cinema ” – 2nd clause (subordinate clause or dependent clause)
⇒ What is a clause?
A clause is a sentence or the part of a sentence that has a subject and a predicate.
(ଏକ ଖଣ୍ଡବାକ୍ୟ ବା ବାକ୍ୟଖଣ୍ଡ ଗୋଟିଏ ବାକ୍ୟ ବା ଗୋଟିଏ ବାକ୍ୟର ଏକ ଅଂଶ ଯାହାର ଗୋଟିଏ ଉଦ୍ଦେଶ୍ୟ ଓ ଗୋଟିଏ ବିଧେୟ ଥାଏ ।)
⇒ What is a Main clause or Independent clause?
The clause that has its indepdent meaning or can stand on its own, is the Main Clause or Independent Clause.
(ଯେଉଁ ଖଣ୍ଡବାକ୍ୟର ସ୍ଵାଧୀନ ଅର୍ଥ ରହିଛି ବା ନିଜ ଅର୍ଥ ନିଜେ ପ୍ରକାଶ କରିପାରେ, ତାହାକୁ ମୁଖ୍ୟ ବା ପ୍ରଧାନ ଖଣ୍ଡବାକ୍ୟ କୁହାଯାଏ ।)
![]()
⇒ What is a Subordinate or Dependent clause?
A clause which can’t stand independently as a sentence, is called a Subordinate or Dependent Clause.
(ଯେଉଁ ଖଣ୍ଡବାକ୍ୟ ସ୍ଵାଧୀନ ଭାବରେ ଏକ ବାକ୍ୟରୂପେ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହୋଇପାରେ ନାହିଁ, ତାହାକୁ ନିର୍ଭରଶୀଳ ବା ଆଶ୍ରିତ ବାକ୍ୟଖଣ୍ଡ ବା ଉପବାକ୍ୟ କୁହାଯାଏ ।)
⇒ Let’s try to remember the three important SENTENCES through clause.
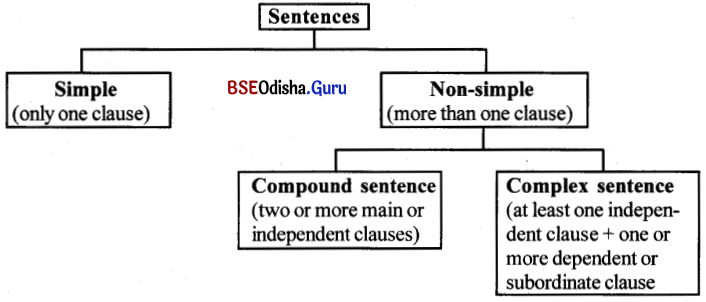
⇒ Phrase (ବାକ୍ୟାଶ) :
A phrase is a group of words, that makes sense, but not complete sense. (କେତୋଟି ଶବ୍ଦର ମିଶ୍ରଣରେ ଏକ ବାକ୍ୟାଶ ଗଠିତ, ଯାହାର ଅର୍ଥ ଥାଏ, କିନ୍ତୁ ସଂପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ ଅର୍ଥ ନୁହେଁ)
For example: Mark the underlined phrases.
⇒ Noun Phrase:
(i) To rise early in the morning is a ‘good habit’ (subject to the verb ‘is’)
(ii) He is fond of playing tennis. (Object to the preposition ‘of’)
(iii) He likes to play football. (Object to the verb ‘likes’)
⇒ A sentence or a clause must have a subject and a predicate.
But a phrase has no predicate.
Activity – 1
Mention whether the following expressions are phrases(P), clauses(C) or sentences(S).
1. Where have you been?
Answer:
Where have you been? (sentence)
2. Humpty Dumpty sat on a wall.
Answer:
Humpty Dumpty (ବାମନ) sat on a wall. (sentence)
3. Like a diamond in the sky.
Answer:
Like a diamond in the sky (phrase)
4. Who pulled her out?
Answer:
Who pulled her out? (sentence)
5. And Jill came tumbling after.
Answer:
And Jill came tumbling after (clause)
6. Under the queen’s chair
Answer:
Under the queen’s chair (phrase)
7. All the king’s horses
Answer:
All the king’s horses (phrase)
![]()
8. up the hill
Answer:
up the hill (phrase)
9. a nice fairy story
Answer:
a nice fairy story (phrase)
10. Jack fell down
Answer:
Jack fell down (sentence)
11. A stitch in time
Answer:
A stitch in time (phrase)
12. The clock struck one
Answer:
The clock struck one (sentence)
13. Pussy in the well
Answer:
Pussy in the well (phrase)
14. After sealing the letter
Answer:
After sealing the letter (phrase)
15. To fetch a pail of water
Answer:
to fetch a pail of water (phrase)
Activity – 2
Draw double lines under the main clauses and single lines under subordinate clauses in the following sentences. Ignore coordinate clauses.
(ମୁଖ୍ୟ ଖଣ୍ଡବାକ୍ୟ ତଳେ ୨ଟି ଗାର ଓ ନିର୍ଭରଶୀଳ ଖଣ୍ଡ ବାକ୍ୟ ତଳେ ଗୋଟିଏ ଗାର ଦିଅ ।)
1. I can not express how sorry I am.
Answer:
I can’t express how sorry I am.
2. Jack fell down and he broke his crown.
Answer:
Jack fell down and he broke his crown.
3. All depends on how the work is done.
Answer:
All depends on how the work is done.
4. It is feared that he will not help us.
Answer:
It is feared that he will not help us.
5. It is clear that he is honest.
Answer:
It is clear that he is honest.
6. I asked the boy how old he was.
Answer:
I asked the boy how old he was.
7. The point is that he was absolutely honest.
Answer:
The point is that he was absolutely honest.
8. When his father will return is uncertain.
Answer:
When his father will return is uncertain.
9. His great fear is that he may not succeed.
Answer:
His great fear is that he may not succeed.
10. Humpty dumpty sat on a wall and he had a great fall.
Answer:
Humpty dumpty sat on a wall.
11. A proverb is one man’s wit but it is all men’s wisdom.
Answer:
A proverb (ପ୍ରବଚନ) is one man’s wit.
![]()
12. There is many a slip before the cup is taken to the lip.
Answer:
There is many a slip before the cup is taken to the lip.
13. Do you know when the next rain arrives?
Answer:
Do you know when the next train arrives?
14. All that glitters is not gold.
Answer:
All that glitters is not gold.
15. He says that his mother is ill.
Answer:
He says that his mother is ill.
16. He told me that he was ready.
Answer:
He told me that he was ready.
17. What he says may be true.
Answer:
What he says may be true.
18. He waved his hand and boarded the bus.
Answer:
He waved his hand.
Noun Clause
⇒ Let’s look at this sentence.
He said that oil floats on water. (Complex Sentence)
He said (Independent or Main clause)
that oil floats on water. (Dependent clause or Subordinate clause)
⇒ “that oil floats on water” (ଯେ ଜଳ ଉପରେ ତେଲ ଭାସେ) is a Dependent Clause or Subordinate Clause since (ଯେହେତୁ) it can’t stand as an independent (clause).
⇒ So “that oil floats on water ” is said to be a Noun Clause as it functions as an object to the verb “said” (what did he say ?) as a noun functions as an object.
⇒ Dependent Clause ବା Subordinate Clause “that oil floats on water ” – ଏଠାରେ ଏକ Noun Clause (ବିଶେଷ୍ୟ ଖଣ୍ଡବାକ୍ୟ) ରୂପେ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରୁଛି ଏହା verb ‘said’ ର Object (କର୍ମ) ରୂପେ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହୋଇଛି, ଯେପରି What did he say ?
Answer:
“That oil floats on water” (noun clause = object to the verb “said”)
Remember :
A noun clause is so called because it functions as a noun.
In Indirect Speech the reported statements and questions are noun clauses.
(i) Reported Statements are introduced by “that” or without “that” – Zero-introducer.
(ii) “Yes – No” questions are introduced by “if” or “whether” (ହଁ କି ନାହିଁ)
(iii) Wh-questions by the same wh-words like what, when, where, how, whom, why etc.
Examples :
(a) Statement (ଭକ୍ତି) : Mark the underlined Noun clauses :
| Direct | Indirect |
| He said, “I live in a town.” | He said (that) he lived in a town. |
| We said to him, “We are ready to help your brother.” | We told him (that) we were ready to help his brother. |
(b) Yes – No questions (Questions beginning with verbs) :
| Direct | Indirect |
| “Do you smoke ?” he inquired | He inquired (ଜାଣିବାକୁ ଚାହିଁଲା) if/whether I smoked. |
| “Have you ever been to Darjeeling ?” he asked me. | He asked me if/whether I had ever been to Darjeeling. |
| He said, “Is your dog an Alsatian ?” | He asked if/whether my dog was an Alsation. |
(c) Wh-questions: (Questions beginning with wh-words)
| Direct | Indirect |
| My friend said, “How do you like the picture ?” | My friend asked me how I liked the picture. |
| The stranger said, “Where is the ATM?” | The stranger asked where the ATM was. |
| “Who can climb that wall ?” I asked the children. | I asked the children who could climb that wall. |
![]()
⇒ Functions of Noun Clause:
(1) Noun Clause as the Subject of a sentence (ବିଶେଷ ଉପବାକ୍ୟ ଏକ କର୍ତ୍ତା ରୂପରେ)
Examples :
(i) What he says is helpful to us.(Complex Sentence)
(ସେ ଯାହା କହୁଛି, ଆମ ପାଇଁ ଦରକାରୀ ।)
[ଏଠାରେ ‘ What he says’ = Subordinating Noun Clause = Subject,
‘is helpful to us’ = Main Clause,
‘what’ = Subordinator]
(ii) That the earth moves round the Sun is truth.(Complex Sentence)
(ଯେ ପୃଥିବୀ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଚାରିପଟେ ଘୂରେ, ଏହା ସତ୍ୟ ।)
[ଏଠାରେ ‘ That the earth moves round the Sun ‘ = Subordinating Noun Clause = Subject,
‘ is truth ‘ = Main Clause,
‘that’ = Subordinator]
(2) Noun Clause as the Object to the verb (ବିଶେଷ ଉପବାକ୍ୟ କ୍ରିୟାର କର୍ମ ରୂପେ)
Examples :
(i) Gopal said (that) he was happy. (Complex Sentence)
(ଗୋପାଳ କହିଲା (ଯେ) ସେ ଖୁସି ଥିଲା ।)
[ଏଠାରେ ‘that he way happy’ = Subordinating Noun Clause
‘that’ = Subordinator,
Gopal said = Main Clause]
(ii) I asked the boy how old he was. (Complex Sentence)
(ତା’ର ବୟସ କେତେ ବୋଲି ମୁଁ ବାଳକକୁ ପଚାରିଲି ।)
(ଏଠାରେ ‘how old he was ’ = Subordinating Noun Clause,
‘how’ = Subordinator,
‘I asked the boy’ = Main Clause)
(iii) The police officer asked the driver why he was driving so speedily.(Complex Sentence)
(ଡ୍ରାଇଭର କାହିଁକି ଏତେ ଜୋର୍ରେ ଗାଡ଼ି ଚଳାଉଥିଲା ବୋଲି ପୋଲିସ୍ ଅଫିସର ଡ୍ରାଇଭରକୁ ପଚାରିଲେ ।)
[ଏଠାରେ ‘Why he was driving speedily’ = Subordinating Noun Clause,
‘why’= Subondinator,
“The police officer asked the driver’ = Main Clause]
(3) Noun Clause as object to the Preposition
(ବିଶେଷ୍ୟ ଉପବାକ୍ୟ Preposition ବା ବିଭକ୍ତ; ଯଥା at / on / in / for with from ଇତ୍ୟାଦିର କର୍ମ ରୂପେ)
Examples:
(i) Pay careful attention to what I am going to say. (Complex Sentence)
(ମୁଁ କ’ଣ କରିବି ଧ୍ୟାନ ଦିଅ ।)
[ଏଠାରେ ‘ What I am going to say’ = Subordinating Noun Clause = Object to the preposition ‘to’,
‘what’ = Subordinator,
‘to’ = Preposition,
‘Pay careful attention to’ = Main Clause]
(ii) There is no meaning in what Gopal says. (Complex Sentence)
(ଗୋପାଳ କ’ଣ କହୁଛି ସେଥିରେ କିଛି|ଅର୍ଥ ନାହିଁ ।)
[ଏଠାରେ ‘what Gopal says’ = Subordinating Noun Clause = Object to the preposition ‘in’,
‘what’ = Subordinator,
‘in’ = Preposition,
There is no meaning in = Main Clause]
![]()
(iii) Mother is anxious about when her son will return from school.(Complex Sentence)
(ତାଙ୍କ ପୁଅ କେତେବେଳେ ସ୍କୁଲରୁ ଫେରିବେ, ସେ ନେଇ ମା’ ଉଦ୍ବିଗ୍ନ ।)
[ଏଠାରେ ‘when her son will return from school’ = Subordinating Noun Clause = Object to the preposition ‘about’,
‘when’ = Subordinator,
‘from ’ = Preposition,
‘Mother is anxious’ = Main Clause]
(4) Noun Clause as ‘Complement to the ‘Verb’
(ବିଶେଷ୍ୟ ଉପବାକ୍ୟ verb ବା କ୍ରିୟାର ପୂରକ ରୂପେ)
Examples:
(i) The difficulty was how we would arrange the fund.(Complex Sentence) (gl§9dl $[QI 21169016® 9191 §09 601919 9Q§ l)
[ଏଠାରେ ‘how we would arrange the fund’ = Subordinating Noun Clause = Complement to the verb ‘was’,
‘how’ = Subordinator,
‘was’ = ‘be’ verb,
‘The difficulty was’ = Main Clause]
(ii) It appears (that) price won’t come down in the near future. (Complex Sentence)
(ଜଣାପଡୁଛି ମୂଲ୍ଯବୃଦ୍ଧି ନିକଟ ଭବିଷ୍ୟତରେ କମିବ ନାହିଁ ।)
[ଏଠାରେ (that) price won’t come down in the near future = Subordinating Noun Clause = Complement to the verb ‘appears’,
‘that’ = Subordinator,
‘appears’ = Verb,
‘It appears’ = Main Clause]
(5) Noun Clause as Apposition to the Nouns or Pronouns
(ବିଶେଷ୍ୟ ଉପବାକ୍ୟ ବିଶେଷ୍ୟ ପଦ ବା ସର୍ବନାମର apposition ବା ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟାନ ପଦ ରୂପେ)
Examples:
(i) The news that his father has come, is true. (Complex Sentence)
(ଯେ ତା’ ବାପା ଆସିଛନ୍ତି ସତ କଥା ।)
[ଏଠାରେ ‘that his father has come’ = Subordinating Noun Clause = Apposition to the noun ‘news’,
‘that’ = Subordinator,
“The news is true” = Main Clause]
(ii) The statement that she found the money in the street, is not believable. (Complex Sentence)
(ଯେ ସେ ରାସ୍ତାରୁ ଟଙ୍କା ପାଇଲା, ବିଶ୍ବାସ ହେଉ ନାହିଁ ।)
[ଏଠାରେ ‘that she found the money in the street’ = Subordinating Noun Clause = Apposition to the noun ‘statement’,
‘that’ = subordinator,
The statement is not believable = Main Clause]
⇒ Joining Two Sentences Making One into a Noun Clause :
(ଦୁଇଟି ବାକ୍ୟ ମଧ୍ୟରୁ ଗୋଟିଏକୁ ବିଶେଷ୍ୟ ଖଣ୍ଡବାକ୍ୟ ରୂପେ ଯୋଗ କରିବା ପଦ୍ଧତି) :
(1) Using Subordinator ‘That’ (Omitting so, it, this) if both the sentences are in declarative pattern.
[ଯଦି ଉଭୟ ବାକ୍ୟ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନରେ ଦିଆଯାଇଥିବ। Declarative Sentence Pattern ରେ ଥାଏ ତା’ହେଲେ so, it, this କୁ ଉଠାଇ ସେଠାରେ ‘That’ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହୁଏ । ]
Examples:
(i) Her mother is ill. Nirmal says so.
Answer:
Nirmal says that her mother is ill. (Omitting ‘so’)
(ii) The man was absolutely (ସଂପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣରୂପେ) dishonest. (ଅସାଧୁ)
This is the point.
Answer:
The point is that the man was absolutely dishonest.
(2) Retaining What / How, etc. [What / How ଇତ୍ୟାଦିକୁ ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନ ନ କରି ]
(Who words + Subject + Verb)
Examples:
(i) Who wrote the Ramayan? Can you tell me?
Answer:
Can you tell me who wrote the Ramayan?
![]()
(ii) When did the last train arrive?
A stranger asked the man at the counter.
Answer:
A stranger asked the man at the counter when the last train arrived.
(iii) What is your name?
The gentleman asked the girl.
Answer:
The gentleman asked the girl what her name was.
(3) Using If/ Whether (ହଁ କି ନୁହେଁ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରି)
If one sentence in the question begins with helping verb
(ଯଦି ପ୍ରଶ୍ନରେ କୌଣସି ବାକ୍ୟ ସାହାଯ୍ୟ କ୍ରିୟାରୁ ଆରମ୍ଭ ହୋଇ ଥାଏ )
Examples:
(i) Will you do this work for me ? (will=helping verb)
Tell me.
Answer:
Tell me if/whether you will do this work for me.
(ii) Are you living here?
I can’t say.
Answer:
I can’t say if you are living here.
Activity – 1
Underline the noun clause in the following sentences. Mention whether they work as subject, object, complement, object of preposition or in apposition to another noun or pronoun.
(i) It is not clear who has done it.
Answer:
It is not clear who has done it. (Complement to the adjective ‘ clear ’)
(ii) You know how hard she works.
Answer:
You know how hard she works. (Object to the verb ‘know’)
(iii) That he is honest is known to all.
Answer:
That he is honest is known to all. (Subject to the verb ‘is’)
(iv) The film depends on how it ends.
Answer:
The film depends on how it ends. [Object to the preposition ‘on’)
(v) “I’m glad to hear it”, Mrs Bethy said.
Answer:
“I’m glad to hear it”. Mrs Bethy said. (Subject to the verb ‘said’)
(vi) My decision is that he must help you.
Answer:
My decision is that he must help you. (Complement to the verb ‘is’)
(vii) What is in our fate can’t be avoided.
Answer:
What is in our fate can’t be avoided. (Subject to the verbs ‘ can’t be avoided’)
(viii) The matter is that they have cheated us.
Answer:
The matter is that they have cheated us. (Complement to the verb ‘is’)
(ix) Shanti didn’t know that her uncle had come.
Answer:
Shanti didn’t know that her uncle had come. (Object to the verbs ‘didn’t know’)
(x) Can you tell me who wrote ‘the Ramayan’?
Answer:
Can you tell me “who wrote the Ramavan”? (Object to the verbs ‘can tell”)
![]()
(xi) No one can say how the war will come to an end.
Answer:
No one can say how the war will come to an end. (Object to the verbs ‘can say’)
(xii) Mr. Gupta promised that he would put some flowers on her brother’s grave.
Answer:
Mr Gupta promised that he would put some flowers on her brother’s grave. (Object to the verb ‘promised’)
Activity – 2
Complete the following sentences using noun clauses.
Can you tell me ________?
Answer:
Can you tell me who will take our science class?
His looks prove ________.
Answer:
His looks (ଚାହାଁଣୀ) prove that he is disappointed.
We all thought that ________.
Answer:
We all thought that we would win the match.
His plan is that ________.
Answer:
His plan is that he will succeed.
________ is known to all.
Answer:
That the earth moves round the sun is known to all.
He admitted that ________.
Answer:
He admitted that he had stolen my mobile.
He wanted to know ________.
Answer:
He wanted to know if I would come with him.
I have no objection to ________.
Answer:
I have no objection to what you do.
Copernicus proved that ________.
Answer:
Copernicus proved that the earth moves round the sun.
The rumour ________ is true.
Answer:
The rumour that Rahul Gandhi will get married is true.
Relative Clause
⇒ Study the following sentence :
I have already read the book which you gave me.
The underlined clause “which you gave me”, a dependent clause or (subordinate clause) is a relative clause or adjective clause as it modifies the meaning of the norm “book”.
![]()
A : Which book have I already seen?
B : Which you gave me. (Relative clause or Adjective clause)
Another example:
A : Which boy are you talking about?
B : I’m talking about the boy who came to our house yesterday.
Her the second speaker (B) is identifying ‘the boy’ he (the speaker) is talking about by using the relative clause “who came to our house yesterday”
Note :
The Primary function of a Relative clause is to identify a noun.
⇒ How to form Relative Clause Rules :
(1) First find out the identical norm phrase in the two sentence to be combined or joined.
(2) Replace one of the identical noun phrases with an appropriate relative pronoun.
(3) Then move the relative pronoun to the beginning of the relative clause.
(4) Finally, place the relative clause immediately after its antecedent or noun phrase.
⇒ Let’s understand:
I have read the book ________ Naba sir wrote the book.
I have read the hook ________ Naba sir wrote which.
I have read the book which Naba Sir wrote.
[The hook-identical noun phrase, which-relative pronoun]
⇒ Step-to-step method of making Relative clause :
The girl was very friendly. I talked to the girl.
Step 1/2 : The girl was very friendly. ________. I talked to whom.
Step 3 : The girl was very friendly. who/whom I talked to.
Step 4 : The girl who / whom I talked to was very friendly.
Example 2:
The people were kind. Father stayed with them.
Step 1/2 : The people were kind. ________ father stayed with
Step 3 : The people were kind. Who father stayed with.
Step 4 : The people who father stayed with were kind.
Or,
Step 1/2 : The people were,kind. ________ father stayed With whom
Step 3 : The people were kind. With whom father stayed.
Step 4 : The people with whom father stayed were kind.
Example 3 :
Did you see the letter ? It came this morning.
Step 1/2 : Did you see letter ? That came this morning.
Step 3 : Did you see the letter that came this morning ?
the letter – identical noun phrase
that – relative pronoun
⇒ Defining Relative Clause / Identifying Relative clause :
The teacher who has worked here for thirty years is retiring next week. (Complex sentence)
Here the relative clause “who has worked for thirty years” is a defining relative clause since we speaks of the particular teacher who has worked here for thirty years.
⇒ Non-defining relative clause / Non-identifying Relative Clause :
“Mr. Mohanty, who has worked here for thirty years, is retiring next week. ”
Here “who has worked here for thirty years” gives more information about Mr Mohanty.
So we drop this clause, the sentence will have no harm. So this is the example of a Nondefining relative clause.
![]()
Remember :
A non-defining relative clause must have comma (,), before and after the relative clause.
“That not ‘which’ is used after all, everything, anything, little, much, only, none, no, nothing. same, superlatives (superlative degree of adjectives), first, last, next, and after two antecedents, one personal and the other non-personal.
Examples:
(i) All / Everything / Anything that (not ‘which’) you see here is unclean.
(ii) There is little / nothing that I can do for you. (not ‘which’)
(iii) There is not much that I can do for you. (not ‘which’)
(iv) This is perhaps the last that we can expect. (not ‘which’)
(v) The next car that arrives here will find the gates closed. (not ‘which’)
(vi) Man is the only animal that can talk. (not ‘which’)
(vii) This is the same bicycle that my brother has lost. (not ‘which’)
(viii) The boy (personal) and his dog (non-personal) that had entered the club were turned (not ‘which’)
⇒ Relative adverbs introducing relative clauses.
Mark the underlined relative clauses.
(i) Do you remember the year when (in which) Sarojini Naidu died?
(ii) The day when (on which) the prince (ରାଜପୁତ୍ର) was born was celebrated (ପାଳନ କରାଯାଇଥିଲା) with rejoicings (ଆନନ୍ଦ ଉଲ୍ଲାସର ସହିତ).
(iii) The reason why he came wasn’t disclosed.
(iv) The house where (in which) we lived had a mud floor and a thatched house.
In these sentences when, where, why are relative adverbs introducing relative clauses.
⇒ Preposition introducing relative clause :
(i) The chair on which I sit on is a shaking, cracking thing.
(The chair when I sit on is a shaking, cracking thing) (Preposition ‘on’) (ଯାହା ଉପରେ)
(ii) Mr Tripathy with whom father works in this office, is a kind person.
(Mr. Tripathy father works with in this office, is a kind person) (Preposition – with) (ଯାହାଙ୍କ ସହିତ)
⇒ Changing Complex Sentence into Simple Sentences :
(1) Noun Clause
Complex : I do not know where Mr Roy lives.
Simple : I do not know Mr Roy’s address.
Complex : Can you teel me when your father will arrive.
Simple : Can you tell me the time of your father’s arrival?
Complex : I do not believe what he says.
Simple : I do not believe his words.
Complex : The teacher remarked how intelligent the boy was.
Simple : The teacher remarked about the great intelligence of the boy.
Complex : I told the teacher why I was absent.
Simple : I told the teacher the reason of my absence.
Complex : This proves that you are guilty.
Simple : This proves your guilt.
Complex : I know who has done this wrongful act.
Simple : I know the doer (ଯାହାଙ୍କ ସହିତ) of this wrongful act.
Complex : Nobody knows where Ram is.
Simple : Nobody knows Ram’s whereabouts.
(2) Relative Clause:
Complex : I have no money that I can spare.
Simple : I have no money to spare.
Complex : Students who work hard will succeed.
Simple : Hard-working students will succeed.
Complex : He likes to die in the village where he was born.
Simple : He likes to die in his native village.
Complex : The book which he lost has been found.
Simple : His lost book has been found.
Complex : The exact time when he died was not known.
Simple : The exact time of his death was not known.
Complex : I do not know the place where he will go.
Simple : I don not know his destination.
Complex : The young man who was the glory of the family is dead.
Simple .: The young man, the glory of the family, is dead.
![]()
Activity – 1
Combine the following pairs of sentences using one of them as a relative clause :
| The birds are chirping. | + | The birds live in the neighbourhood. |
| I write with the pen. | + | My father bought the pen for me. |
| The sick were delighted. | + | Florence Nightingale nursed the sick. |
| I like the man. | + | The man has a smiling face. |
| The thief escaped in the dark. | + | The thief had robbed me. |
| The boy is our monitor. | + | I have borrowed his book. |
| The chair has a cracked leg. | + | He is sitting in the chair. |
Answers:
(i) The birds which live in the neighbourhood are chirping.
(ii) I write with the pen which my father bought for me.
(iii) The sick whom Florence Nightingale nursed were delighted.
(iv) I like the man who /that has a smiling face.
(v) The thief who had robbed me escaped in the dark.
(vi) The boy whose book I have borrowed is our monitor.
(vii) The chair whiah/that he is sitting in has a cracked leg.
Activity – 2
In some of the following sentences the relative pronoun can be dropped. Rewrite those sentences without the relative pronouns. [You are not allowed to perform any other change.]
The children who are playing cricket live in this locality.
I have read the story book that my father bought yesterday.
The shopkeeper who I was working for is a good person.
It is the best possible explanation that we can give about Socrates.
The only question that drew everybody’s attention is worth discussing.
Our school, which works for the young people of our area, is highly popular.
Pramod, who is my classmate, is very sincere.
The travellers who knew about the floods took another road.
The travellers, who knew about the floods, took another road.
The man that Mohan was talking to is his uncle.
The music which we were listening to was a 16th century devotional song.
I write with the pen which my father bought.
Answers:
l have read the story book my father bought yesterday.
The shopkeeper I was working for is a good person.
It is the best possible explanation we can give about Socrates.
The man Mohan was talking to is his uncle.
The music we were listening to was a 16th century devotional song (ଭକ୍ତି ସଙ୍ଗୀତ).
I write with the pen my father bought.
Remember :
From all relative clause, relative pronouns can’t be dropped. The means all relative clauses can’t be zero – relatives.)
![]()
Activity – 3
Define the terms given in the example.
Example: A greengrocer
Answer:
is a person who sells fruits and vegetables.
A driver is a person who…
Answer:
A driver is a person who drives motors.
An actor is a person who…
Answer:
An actor (କଳାକାର) is a person who acts.
A journalist is a person who…
Answer:
A journalist (ସାମ୍ବାଦିକ) is a person who writes for newspaper.
A farmer is a person who…
Answer:
A farmer is a person who works on a farm.
A patient is a person who…
Answer:
A patient is a person who suffers from disease (s).
A newspaper is a document in which …
Answer:
A newspaper is a document in which there are different news.
A conductor is a person who…
Answer:
A conductor is a person who collects fares on buses.
A teacher is a person who…
Answer:
A teacher is a person who teaches.
A plumber is a person who…
Answer:
A plumber (ଜଳ ପାଇପ ମରାମତିକାରୀ) is a person who mends (ମରାମତି କରେ) water-pipes.
A doctor is a person who…
Answer:
A doctor is a person who treats patients.
A hospital is a place where…
Answer:
A hospital is a place where the patients are treated.
A transitive verb is a verb which…
Answer:
A transitive (ସକର୍ମକ) verb is a verb which has object (s).
![]()
Activity – 4
In the following four columns some proverbs or quotations have been given. Expressions in column A and column D belong to the same proverb. Put a suitable relative pronoun in column B and choose the correct expression from column C. In this way write the proverbs. As soon as you complete, raise your hand and draw the teacher’s attention.
| A | B | C | D |
| All | ________ | pays the piper | is not gold. |
| People | ________ | laughs last | should not throw stones. |
| All’s well | ________ | prays together | well. |
| He | ________ | glitters | calls the tune. |
| He | ________ | blows nobody | laughs best. |
| It’s along lane | ________ | do not want | |
| It’s an ill wind | ________ | ends | any good. |
| There are no one | ________ | ||
| so deaf as those | ________ | live in glass houses | to hear. |
| The family | ________ | has no turning | stays together. |
Answer:
| A | B | C | D |
| All | that | glitters | is not gold. |
| People | who | live in glass houses | shouldn’t throw stones. |
| All’s well | that | ends | well. |
| He | who | pays the piper | calls the tune. |
| He | who | laughs last | laughs best. |
| It’s a long lane | that | has no turning. | |
| It’s an ill wind | that | blows nobody | |
| There are no one | |||
| so deaf as those | that | don’t want | to hear |
| The family | that | prays together | stays together |
Activity – 5
Underline the relative clauses in the following sentences. Write D for defining and N for non-defining relative clauses.
(i) A greengrocer is a person who sells fruits and vegetables.
Answer:
(D)
(ii) Bhola, who is a greengrocer, goes to the fields every morning.
Answer:
(N)
(iii) What is the name of your friend who often comes to our house?
Answer:
(D)
![]()
(iv) Where does Amit, who often comes to our house, live?
Answer:
(N)
(v) My uncle who is a judge is coming here tomorrow.
Answer:
(D)
(vi) My uncle, who is a judge, is coming here tomorrow.
Answer:
(N)
(vii) My father, who is a teacher, loves ot take.
Answer:
(N)
(viii) Uneasy lies the head that wears a crown.
Answer:
(D)
(ix) We love the man who thinks of our welfare.
Answer:
(D)
(x) We call uncle Bhola, who thinks of our welfare as the Gandhi of our village.
Answer:
(N)
Activity – 6
Put commas in the following sentences, if they are necessary.
(i) The man whom the police arrested is not known to us.
(ii) The strike at the factory which lasted ten days is over now.
(iii) My father who is working at Koraput is a doctor.
(iv) I have found the book which I was looking for.
(v) Mira’s grandmother who is sick is in hospital now.
(vi) Eintstein who discovered the theory of relativity once failed in an examination.
(vii) Engineer Choudhury who got this bridge built is on a visit to our village.
(viii) Mother Teresa who faithfully served the poor is called a saint now.
(ix) The chairman of the committee who is impartial solves all the problems cleverly.
Answers:
(iii) My father, who is working at Koraput, is a doctor.
(iv) Mira’s grandmother, who is sick, is in hospital now.
(v) Eintstein, who discovered the theory of relativity, once failed in an examination.
(vii) Engineer Choudhury, who got this bridge built, is on a visit to our village.
(viii) Mother Teresa, who faithfully served the poor, is called a saint now.
(ix) The chairman of the committee, who is impartial, solves all the problems cleverly.
Activity – 7
Fill in the blanks with relative pronouns such as who, which, where, whose, that etc.
The house in ________ I lived as a child has been pulled down now.
Answer:
The house in which I lived as a child has been pulled down now.
My grandmother, ________ was an extraordinary woman, lived to the age of one hundred.
Answer:
My grandmother, who was an extraordinary woman, lived to the age of one hundred.
![]()
Stop him ! He’s the man ________ stole my purse.
Answer:
Stop him ! He’s the man who stole my purse.
They have invented a television set ________ is as small as a watch.
Answer:
They have invented a television set that is as small as a watch.
There are many people ________ lives have been spoilt by this factory.
Answer:
There are many people whose lives have been spoilt by this factory.
Is that the button ________ you pressed?
Answer:
Is that the button that you pressed?
Could everybody ________ answer sheets are with me raise their hands?
Answer:
Could everybody whose answer sheets are with me raise their hands?
That scientist has invented a kind of ink ________ is visible in darkness.
Answer:
That scientist has invented a kind of ink that is visible in darkness.
Activity – 8
Work in pairs. Think of puzzle whose answer you now. The clue you give must have a relative clause.
For example:
A black and white bird which can swim but can’t fly.
Answer:
Penguin (seven letters)
Now, the other partner (friend) must think of a puzzle whose answer must contain one of the letters of Penguine. For example, A snow house that an Eskimo builds.
Answer:
(Igloo) (Five letters).
In this process make a cross-word puzzle, always an existing letter, e.g.
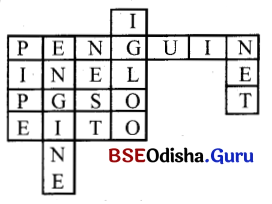
A wind that is strong and hot – (Loo), The tool that we write with – (Pen), A thing that is hung at the post for game – (Net), A tool that is used for carrying under ground water – Pipe, The tool is fitted in vehicles to make it run – Engine, The place where birds lie – Nest
At A Glance
⇒ The Noun Clause :
A Noun functions as subject, object, complement or apposition to some other noun.
(ଏକ ବିଶେଷ୍ୟ ପଦ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ଏକ କର୍ତ୍ତା, କର୍ମ, ପୂରକ ବା ଅନ୍ୟ ଏକ ବିଶେଷ୍ୟ ପଦର apposition ରୂପେ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରେ।)
Similarly a Noun clause functions as subject, object, complement etc.
(ସେଇଭଳି ଏକ ବିଶେଷ୍ୟ ଖଣ୍ଡବାକ୍ୟ ଏକ କର୍ତ୍ତା, କର୍ମ ବା ପୂରକ ଆଦି ରୂପେ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରେ।)
A Noun clause being a subordinate clause begins with subordinators like that or whether / if or Wh-words.
(ଏକ ବିଶେଷ୍ୟ ଖଣ୍ଡବାକ୍ୟ ଏକ ଆଶ୍ରିତ ବା ନିର୍ଭରଶୀଳ ଖଣ୍ଡବାକ୍ୟ ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ ଏହା subordinator; ଯଥା – that ବା whether / if ବା Wh – ରୁ ଆରମ୍ଭ ହୋଇଥାଏ।)
⇒ In Apposition to Nouns :
(a) The fact that he betrayed his friends is well-known. (ଯେ ସେ ତାହାର ବନ୍ଧୁପ୍ରତି ବିଶ୍ୱାସଘାତକତା କଲା ।)
(b) Who gave you the idea that I can sing (ଯେ ମୁଁ ଗାଇପାରେ) ? ( = apposition to the noun ‘idea)
(c) My question, who is responsible for our sad plight, (କିଏ ଆମର ଦୁଃଖଦ ଅବସ୍ଥା ପାଇଁ ଦାୟୀ), has not yet been answered (= apposition to the noun ‘question’)
![]()
Relative Clauses:
⇒ Defining Relative Clause :
I. I met a friend (who was at school with me ten years ago).
[The clause inside the brackets “who was at school with me ten years ago (ଯିଏ ମୋ ସହିତ ଦଶବର୍ଷ ପୂର୍ବରୁ ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟରେ ପଢ଼ୁଥିଲା ।) is a Defining Relative Clause answering the question ‘Which friends ?’]
II. The shot (ଗୁଳି) (that hit him on the head) killed him.
Similarly, the clause inside the brackets that hit him on the head (ଯେଉଁଟି ତାହାର ମୁଣ୍ଡରେ ଆଘାତ ଦେଲା) is also a Defining Relative Clause answering the question ‘Which shot ?’
Non-Defining Relative Clause :
III. I met Robin (who was at school with me ten years ago).
The clause inside the brackets who was at school with me ten years ago is a Non-Defining Relative Clause called so because it already answers the question ‘which friend ?’
Answer:
Who was a school with me ten years ago.
In the Main Clause (I met Robin) the use of proper noun ‘Robin’ only makes the friend definite, (ପ୍ରଥମ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ମୁଖ୍ୟ ଖଣ୍ଡବାକ୍ୟରେ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ନାମବାଚକ ବିଶେଷ୍ୟ Robin କେବଳ Noun phrase ‘a friend’ କୁ ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ କରୁଛି ।) (‘Robin’ only gives some information about the Noun phrase)
| Defining Relative Clause (without comma) (Noun phrase as antecedent indefinite) | Non-Defining Relative clause (with comma) or antecedent. Noun phrase is made definite with proper noun or determiners this, that, these, those, one two, second, tenth, my, his, her, their, etc.) |
| (Mark the underlined determiners or proper nouns in Non-Defining Relative Clauses and commas.) | |
| I. Don’t ride in a bus which has poor brakes, (norm phrase – ‘a bus’) | Don’t ride in this bus, which has poor brakes. (noun phrase – ‘this bus’) |
| II. The shot that hit him on the head killed him. (noun phrase – ‘the shot’) | The second shot, which hit his on the head, killed him. (noun phrase – ‘the second shot’) |
| III. The dog which is black wears a collar. (noun phrase – ‘the dog’) | My dog, which is black, wears a collar, (noun phrase – ‘my dog’) |
Noun Clauses And Relative Clauses Additional Questions With Answers
Noun Clauses
⇒ Identify the subordinate clauses
1. It is clear that he is innocent.
Answer:
that he is honest
2. All that glitters is not gold.
Answer:
that glitters
3 . When his father will return is uncertain.
Answer:
when his father will return
4. What he says doesn’t affect me.
Answer:
what he says.
5. The house he lives in has been damaged.
Answer:
he lives in
6. All depends on how the work is done.
Answer:
how the work is done.
7. This is what you say.
Answer:
what you say
![]()
8. After sealing the letter, he posted it.
Answer:
After sealing the letter
9. I will help him if he comes.
Answer:
If he comes
10. Since he is liar, nobody likes him.
Answer:
since he is a liar
11. He says that his mother is ill.
Answer:
that his mother is ill
12. He wanted to know whether I needed any help.
Answer:
whether I needed any help
13. He arrived here after everybody had left.
Answer:
after everybody had left
14. I cannot express how I am sorry.
Answer:
how I am sorry
15. The news that he has come is true.
Answer:
that he has come
⇒ Say the functions of the noun clauses.
1. That he is honest is known to all.
Answer:
Subject of a verb,
2. My decision is that he must help you.
Answer:
Complement of verb,
3. You know how hard she works.
Answer:
Object of verb,
4. It is true that his father has come.
Answer:
In apposition to noun,
5. You should pay attention to what I say.
Answer:
Object of a preposition,
6. I asked her how she felt.
Answer:
Object of verb,
7. The problem is that we do not have any money.
Answer:
Complement of verb,
![]()
8. Can you tell me who wrote Meghadoot?
Answer:
Object of verb,
9. What is in our fate cannot be avoided.
Answer:
Subject of verb,
10. Whether he will stay here depends on him.
Answer:
Subject of verb,
11. I expected that he would pass in the examination.
Answer:
Object of verb,
12. It appears that he won’t help me.
Answer:
Complement of verb,
13. The fact that he is dead is true.
Answer:
In apposition to noun,
14. It is not clear who has done it.
Answer:
In apposition to pronoun,
15. I don’t believe in what you say.
Answer:
Object of preposition,
16. Life is how we spend it.
Answer:
Complement of verb,
17. Tell me where you are going.
Answer:
Object of verb,
18. He didn’t agree to what I said.
Answer:
Object of preposition,
⇒ Complete the sentences using noun clauses.
1. The teacher told ________.
Answer:
that the earth moves round the sun.
2. His plan is ________.
Answer:
that he will study science.
3. Do you object to ________.
Answer:
what he says?
4. I suggested that ________.
Answer:
we should go home.
![]()
5. I don’t believe in ________.
Answer:
what you say.
6. Give it to ________.
Answer:
whoever comes first.
7. I told you ________.
Answer:
what I thought.
8. ________ is a mystery.
Answer:
where he lives.
9. ________ is true.
Answer:
what he said.
10. No one can say ________.
Answer:
when the earth was created.
11. ________ cannot can be taken hack.
Answer:
what is said.
12. It seems that ________.
Answer:
no one knew it.
13. ________ is doubtful.
Answer:
whether he will come.
14. I knew ________.
Answer:
what his name is.
15. Copernicus proved that ________.
Answer:
the sun is stationary.
⇒ Combine the sentences making one of the clauses as Noun Clause.
1. She will be a doctor. This is Shruti’s plan.
Answer:
Shruti’s plan is that she will be a doctor.
2. When will the train come ? The station master cannot say it.
Answer:
The station master cannot say when the train will come.
3. Did I need any help ? He wanted to know it.
Answer:
He wanted to know if I needed any help.
4. Who has done it ? It is not clear.
Answer:
It is not clear who has done it.
5. Her uncle has come. Bubli doesn’t know it.
Answer:
Bubli doesn’t know that her uncle has come.
![]()
6. Deepak has misbehaved. He admits so.
Answer:
Deepak admits that he has misbehaved.
7. What have I said? I can prove it.
Answer:
I can prove what I have said.
8. The earth is flat. People in the old times believed it.
Answer:
People in the old times believed that the earth is flat.
9. Oil floats on water. Everybody knows this.
Answer:
Everybody knows that oil floats on water.
10. How will the war come to an end? Nobody can say this.
Answer:
Nobody can say how the war will come to an end.
11. What is our fate? It cannot be avoided.
Answer:
What is in our fate cannot be avoided.
12. We don’t have any money. This is the problem.
Answer:
The problem is that we don’t have any money.
13. Man is mortal. The teacher said it.
Answer:
The teacher said that man is mortal.
14. What does she say? Do you object to it?
Answer:
Do you object to what she says?
15. His father has come. The news is true.
Answer:
The news that his father has come is true.
Relative Clauses
⇒ Fill in the blanks with suitable relative pronouns.
1. Man is the only animal ________ can talk.
Answer:
that
2. All ________ glitters is not gold.
Answer:
that
3. He is the tallest man ________ I have ever seen.
Answer:
that
4. The bus ________ I waited for came late.
Answer:
which
5. The house in ________ he lives is new.
Answer:
which
6. This is the lady ________ age you can never guess.
Answer:
whose
7. God helps those ________ help themselves.
Answer:
who
![]()
8. Papu, with ________ I competed yesterday, was a better player.
Answer:
whom
9. The book, ________ I wanted, was published last month.
Answer:
which
10. There are many people ________ lives have been spoilt by this factory.
Answer:
whose
11. He is the man ________stole my purse.
Answer:
who
12. They have invented a television set ________ is as small as a watch.
Answer:
which
13. The scientist has invented a kind of ink ________ is visible in darkness.
Answer:
which
14. He ________ God loves, dies young.
Answer:
whom
15. This is the film ________ story is very interesting.
Answer:
whose
16. I have, no one ________ can help me.
Answer:
that
17. She is the best girl ________ I have ever seen.
Answer:
that
18. A conductor is a person ________ collects fares on a bus.
Answer:
who
19. The camel ________ lives in desert, is called the ship of the desert.
Answer:
which
20. All ________ is mine is yours.
Answer:
that
21. This is the age ________ children become naughty.
Answer:
when
22. Tree ________ oxygen, sustains life.
Answer:
which
23. Mr. Panda ________ son is staying in Calcutta, is a close friend of father’s.
Answer:
whose
24. He ________ laughs last laughs best.
Answer:
who
![]()
25. I have a plan ________ will succeed.
Answer:
that
26. The girl ________ everyone admires is my daughter.
Answer:
whom
27. There was nothing ________ you could do.
Answer:
that
28. Here is a notice ________ warns us not to go head.
Answer:
which
29. The man ________ was injured was taken to hospital.
Answer:
who
30. She was wearing a dress ________colour is red.
Answer:
whose.
⇒ Identify the relative clause and say whether it is defining or non-defining relative clause.
1. Uneasy lies the head that wears a crown.
Answer:
that wears a crown – defining relative clause.
2. A conductor is a person who collects fare in a bus.
Answer:
who collects fare in a bus – defining relative clause.
3. My father, who is working at Puri, is a doctor.
Answer:
who is working at Puri – non-defining relative clause.
4. Dibankar, who is my classmate, is very sincere.
Answer:
who is my classmate – non-delining relative clause.
5. Our school, which works for the young people of our area, is highly popular.
Answer:
which works for the young people of our area – non-defining relative clause.
6. Rakesh, who always gives me books, is my friend.
Answer:
who always gives me books – non-defining relative clause.
7. I have read the book that my father bought yesterday.
Answer:
that my father bought yesterday – defining relative clause.
8. We love the man who thinks of our welfare.
Answer:
who thinks of our welfare – defining relative clause
9. Pragyan’s grandmother, who is sick, is in hospital now.
Answer:
who is sick- non-defining relative clause.
![]()
10. Mother Teresa, who faithfully served the poor, is called a saint now.
Answer:
who faithfully served the poor – non-defining relative clause.
11. This is the cheapest thing that I know.
Answer:
that I know – defining relative clause.
12. My uncle, who is a judge, is coming here tomorrow.
Answer:
who is a judge – non-defining relative clause.
13. We call Bhola uncle, who thinks of our welfare, as the Gandhi of our village.
Answer:
who thinks of our welfare – non-defining relative clause.
14. Einstein, who discovered the theory of relativity, once failed in an examination.
Answer:
who discovered the theory of relativity – non-defining relative clause.
15. Do you remember the year in which he was born?
Answer:
in which he was born – defining relative clause.
⇒ Combine the sentences making one of them as relative clause.
1. All is well. It ends well.
Answer:
All is well that ends well.
2. All is not gold. It glitters.
Answer:
All that glitters is not gold.
3. Sumitra is my classmate. She is very sincere.
Answer:
Sumitra, who is very sincere, is my classmate.
4. Krushna is my best friend. Everybody loves him.
Answer:
Krushna, whom everybody loves, is my best friend.
5. The man is his father. Mahesh is talking to him.
Answer:
The man that Mahesh is talking to is his father.
6. Is this the book? You asked me for it.
Answer:
Is this the book which you asked me for.
7. The boy is our monitor. I have borrowed his book.
Answer:
The boy whose book I have borrowed is our monitor.
8. The thief escaped in the dark. He robbed me.
Answer:
The thief who robbed me escaped in the dark.
9. I like the man. He has a bald head.
Answer:
I like the man who has a bald head.
![]()
10. The chair has a broken leg. He is sitting on the chair.
Answer:
The chair which he is sitting on has a broken leg.
11. The girl is Lata’s sister. She is wearing a red frock.
Answer:
The girl who is wearing a red frock is Lata’s sister.
12. The shopkeeper is a good person. I was working for him.
Answer:
The shopkeeper for whom I was working is a good person.
13. A driver is a person. He drives a motor car.
Answer:
A driver is a person who drives a motor car.
14. She is lady. You can never guess her age.
Answer:
She is a lady whose age you can never guess.
15. Tell me the name of the person. You gave him the money.
Answer:
Tell me the name of the person whom you gave the money.
16. We admire the pictures. You drew them yourself.
Answer:
We admire the pictures which you drew yourself.
17. They are searching for the tiger. It has been wounded in the leg.
Answer:
They are searching for the tiger which has been wounded in the leg.
18. I like the man. The man has a smiling face.
Answer:
I like the man who has a smiling face.
19. The sick were delighted. Florence Nightingale nursed them.
Answer:
The sick whom Florence Nightingale nursed were delighted.
20. The birds are chirping. They live in the neighbourhood.
Answer:
The birds which live in the neighbourhood are chirping.
21. The children live in this locality. They are playing cricket.
Answer:
The children who are playing cricket live in this locality.
22. I have read the book. My father bought it yesterday.
Answer:
I have read the book which my father bought yesterday.
23. The man is not known to us. The police arrested him.
Answer:
The man whom the police arrested is not known to us.
![]()
24. Uneasy lies the head. It wears a crown.
Answer:
Uneasy lies the head that wears a crown.
25. The number is busy. You are calling it.
Answer:
The number that you are calling is busy.
