Odisha State Board BSE Odisha Class 9 English Grammar Book Solutions Chapter 12 The Predicate Phrase Textbook Exercise Activity Questions and Answers.
BSE Odisha Class 9 English Grammar Solutions Chapter 12 The Predicate Phrase
What is Predicate ? (ବିଧେୟ କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ?)
The word or words which say something about the person or the thing denoted by the subject are called Predicate. (କର୍ରାଦ୍ଵାରା ସୂଚିତ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ବା ବସ୍ତୁ ସଂପର୍କରେ ଯେଉଁ ଶବ୍ଦସମୂହ କିଛି କହେ ତାହାକୁ ବିଧେୟ ବା ବାକ୍ୟାଶ କୁହାଯାଏ ।)
| Subject | Predicate |
| (i) Fire | bums. |
| (ii) A fierce fire (ଭୟଙ୍କର ଅଗ୍ନିକାଣ୍ଡ) | burnt down the building. |
| (iii) A fierce fire that broke out yesterday evening | burnt the building and many others in the same street. |
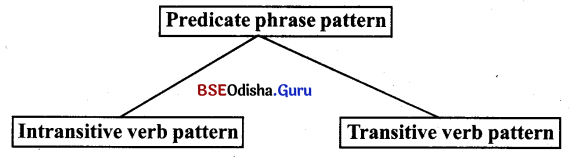
Predicate phrase pattern (ବିଧେୟ ବାକ୍ୟାଶ କ୍ରମ ଗଠନ)
A predicate phrase pattern consists of two – verb pattern since verb is the indispensable part of a predicate phrase.
(ଦୁଇ ପ୍ରକାର କ୍ରିୟାପଦ ଗଠନ ପ୍ରଣାଳୀକୁ ନେଇ ଗୋଟିଏ predicate phrase pattern ଗଠିତ ହୋଇଥାଏ, ଯେହେତୁ କ୍ରିୟାପଦ ହେଉଛି ଗୋଟିଏ ବିଧେୟର ଅବିଚ୍ଛେଦ୍ୟ ଅଂଶ ।)
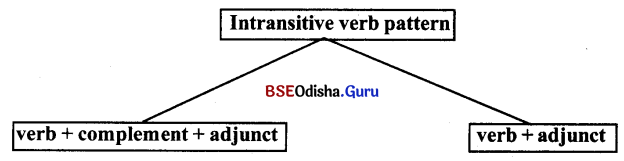
A. InTransitive verb pattern
In the intransitive verb pattern, the usual orders are (ଅକର୍ମକ କ୍ରିୟାର କ୍ରମ ଗଠନ ପ୍ରଣାଳୀରେ)
(i) verb କ୍ରିୟା + complement (ପୂରକ ) + adjunct (ବିବର୍ଷକ)
(b) verb କ୍ରିୟା + adjunct (ବିବଦ୍ଧକ)
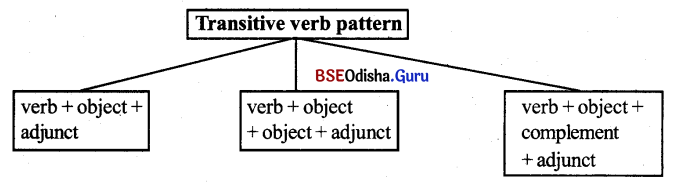
B. Transitive verb pattern (ସକର୍ମକ କ୍ରିୟାର ଗଠନ ପ୍ରଣାଳୀ)
In the transitive verb pattern, the usual orders are:
(i) Transitive verb (କ୍ରିୟା) + object (କର୍ମ) + adjunct ((ବିବର୍ଷକ))
(ii) verb (କ୍ରିୟା) + object (କର୍ମ) + object (କର୍ମ) + adjunct ((ବିବର୍ଷକ))
(iii) verb (କ୍ରିୟା) + object (କର୍ମ) + complement (ପୂରକ) + adjunct ((ବିବର୍ଷକ))
![]()
Let’s know about verbs (Transitive or Intransitive), object, complement and adjunct in the predicate phrase. (Predicate phrase patterns ବ୍ୟବହୃତ କ୍ରିୟାପଦ, କର୍ମ, ପୂରକ ଓ ବିବର୍ଷକ ବିଷୟରେ ଜାଣିବା ।)
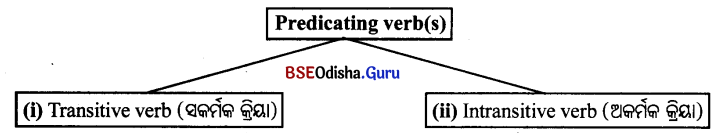
(i) Transitive verb is the verb that is used with an object or objects in a sentence. (ବାକ୍ୟରେ ଯେଉଁ କ୍ରିୟା ସହିତ କର୍ମ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହୁଏ, ସେଭଳି କ୍ରିୟାକୁ ସକର୍ମକ କ୍ରିୟା କୁହାଯାଏ ।)
(ii) The intransitive verb is the verb that is used with no object in a sentence. (ବାକ୍ୟରେ କ୍ରିୟା ସହିତ କର୍ମ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହୋଇନଥାଏ, ତାହାକୁ ଅକର୍ମକ କ୍ରିୟା କୁହାଯାଏ ।)
Object (କର୍ମ)
An object in a sentence receives the action performed by the subject. (କର୍ତ୍ତାର କାର୍ଯ୍ୟକୁ ଗ୍ରହଣ କରୁଥିବା ଶବ୍ଦକୁ କର୍ମ କୁହାଯାଏ ।)
Like the two types of predicating verb (s), the object in a sentence or predicate phrase is of two types. (ବାକ୍ୟରେ ଦୁଇ ପ୍ରକାର predicating verb ଭଳି, object ବା କର୍ମ ମଧ୍ଯ ଦୁଇ ପ୍ରକାରର ।)
(i) Direct Object (D.O.) is one which answers the question ‘what’ to the verb and denotes thing. (କ୍ରିୟାପଦରେ ‘କ’ଣ’ ଲଗାଇ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନ ପଚାରିଲେ ଓ ବସ୍ତୁ ବା ପଦାର୍ଥର ଉତ୍ତର ମିଳିଲେ, direct object ହୁଏ ।)
(ii) Indirect Object (I.O) is one which answers the question ‘whom’ to the verb and denotes person or animal. (କ୍ରିୟାପଦରେ କାହାକୁ ବା କାହାପାଇଁ ଲଗାଇ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନକଲେ ଓ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ବା ପ୍ରାଣୀର ଉତ୍ତର ମିଳିଲେ ତାହା Indirect Object ହୁଏ ।)
If there is only one object in a sentence, it is always treated as the direct object. (ବାକ୍ୟରେ ଗୋଟିଏ ମାତ୍ର object ଥିଲେ ତାହାକୁ direct object ର ମାନ୍ୟତା ଦିଆଯାଏ।)
Complement (ପୁରକ) :
The aditional word or words by which the predicate is made complete is called the complement (ଯେଉଁ ଅତିରିକ୍ତ ଶବ୍ଦ ବା ଶବ୍ଦ ସମୂହ ଦ୍ଵାରା Predicate ବା ବିଧେୟକୁ ପୂରଣ କରାଯାଏ, ତାହାକୁ complement କୁହାଯାଏ ।)
(i) Subject intransitive complement is called so as the verb (s) is intransitive. (କ୍ରିୟାପଦ ଅକର୍ମକ ଥିବାରୁ ଓ subject ର complete କରୁଥିବାରୁ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ଶବ୍ଦ ବା ଶବ୍ଦ ସମୂହ subject intransitive କୁହାଯାଏ ।)
(ii) Object (transitive) complement is called so as the verb (s) is transitive.
(କ୍ରିୟାପଦ ସକର୍ମକ ଥିବାରୁ ଓ object ବା କର୍ମର ଅର୍ଥକୁ ଶବ୍ଦ ବା ଶବ୍ଦ ବିଶେଷ complete କରୁଥିବାରୁ ତାହାକୁ object (transitive) complement କୁହାଯାଏ ।)
Subject complement (intransitive)
Examples:
(i) Honey tastes sweet. – tastes – intransitive verb, sweet – compliment
(ii) This pillow feels soft. – feels – intransitive verb, soft – complement
(iii) The old man became weak. – became – intransitive verb, weak – complement
(iv) I am a teacher. – am – intransitive verb, a teacher – compliment.
Object complement (transitive)
Examples:
(i) Mother has made the curry spicy. – (has made – transitive verb, the curry – object, spicy – object complement)
![]()
2. Subject + Verb + Complement Pattern (S+V+C)
Remember: The complement may come in different forms- a noun or noun phrase, an adjective or adjective phrase, prepositional phrase, adverb phrase and a clause. (ବାକ୍ୟରେ complement ବା ପୂରକ ବିଭିନ୍ନ ରୂପରେ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହୋଇପାରେ; ଯଥା ଏକ ବିଶେଷ୍ୟ (ବାକ୍ୟାଶ), ବିଶେଷଣ (ବାକ୍ୟାଶ), ବିଭକ୍ତି ସୂଚକ ଅବ୍ୟୟ ବାକ୍ୟାଶ, କ୍ରିୟା ବିଶେଷଣ (ବାକ୍ୟାଶ) ବା ଏକ ଖଣ୍ଡବାକ୍ୟରେ)
3. Subject + Verb + Complement (S+V+C)
| SUBJECT (S) | VERB (V) | COMPLEMENT (C) (Intransitive) |
| Dasaratha | was | a king (noun phrase). |
| Honey | tastes | sweet (adjective). |
| Uncle | is | on the way (Prepositional phrase). |
| The car | stopped | there (adverb). |
| I | am | what my father has made (clause). |
4. Subject + Verb + Adjunct Pattern (S+V+A)
| SUBJECT (S) | VERB (V) (Intransitive) | ADJUNCT (A) |
| The man | is walking | slowly (adverb of manner). |
| Father | has left | just now (adverb of time). |
| I | get up | early in the morning (adverb of time). |
Predicate Phrase Pattern (Transitive Verb Pattern)
1. Subject + Verb + Object Pattern (S+V+O)
| SUBJECT (S) | VERB (V) (Intransitive) | OBJECT (O) Direct object |
| The baby Meera The officer Kamini |
broke worked out will suspend is knitting (ବୁଣୁଛି) |
the toy all the sums, the clerk, a sweater. |
2. Subject + Verb + Object + Object Pattern (S+V+O+O)
| SUBJECT (S) |
VERB (Transitive) |
OBJECT (Indirect(କାହାକୁ) |
Object (Direct) (କ’ଣ) |
| Tapaswini Ipsita Mother The government |
gave will send has made has offered |
her friend me me the players |
a book, some money, some tasty cakes, a lot of land. |
We can interchange the objects (ଆମ୍ଭେମାନେ କର୍ମଗୁଡ଼ିକର ସ୍ଥାନ ବଦଳାଇ ପାରିବା) :
Examples:
(i) Tapaswini gave a book to her friend.
(a book = direct object, to her friend = indirect object)
(ii) Mother has made some tasty cakes for me.
(some tasty cakes = direct object, for me = indirect object)
![]()
3. Subject + Verb + Object + Complement Pattern (S+V+O+C)
| SUBJECT (S) |
VERB (V) (Transitive) |
OBJECT (O) (Direct) |
COMPLEMENT |
| Uncle The headmaster The subjects The judge The government I We |
painted has put made set ordered found have made |
the door the school him the prisoner the man the child the girl |
blue. (adjective) into good order, (prepositional object) king, (noun) free, (adjective) to be arrested, (infinitive) asleep, (adverb) what she is today, (clause) |
4. Subject + Verb + Object + Adjunct Pattern (S+V+O+A)
| SUBJECT (S) |
VERB (Transitive) |
OBJECT (Indirect)(କାହାକୁ) |
ADJUNCT (Direct) (କ’ଣ) |
| We | saw | a tiger | in the jungle, (placed adverb) |
| The teacher | has beaten | my brother | mercilessly, (adverb of manner) |
| They | found | the blind man | on the village road, (adverb of place) |
Remember After the verbs like put, keep, and place (ରଖିବା), we use complements after the objects. (put, keep, pleace ପରେ ଆମ୍ଭେମାନେ object ପରେ complement ବ୍ୟବହାର କରୁ ।)
Examples:
(i) I put the book on the table.
(the book = direct object, put = transitive verb,
on the table = complement (adverb of place / prepositional phrase)
(ii) Father keeps his money in the post office.
(keeps = transitive verb, his money = direct object (adverb),
in the post office = (place) complement)
Textual Activities With Answers
Activity – 1
Underline the Main Verb (M.V.) and say whether it is Transitive (V) or Intransitive (Vin) (ମୁଖ୍ୟ କ୍ରିୟାପଦକୁ ରେଖାଙ୍କିତ କରି ସକର୍ମକ ବା ଅକର୍ମକ ଲେଖ ।)
1. John is playing outside.
Answer:
is playing = intransitive verb (no object), outside = adverb of place
2. Children like sweets very much.
Answer:
like = transitive verb. sweets = direct object, very much = adverb of degree
3. He has changed a lot.
Answer:
has changed = intransitive verb, a lot = adverb of degree.
4. Barsha offered me a nice gift.
Answer:
offered = transitive verb, me = indirect object, a nice gift = direct object
5. Little men desire high posts.
Answer:
desire = transitive verb, high posts = direct object
Activity – 2
Interchange the objects using ‘to’ or ‘for. (‘to’ ଏବଂ ‘for’ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରି କର୍ମର ସ୍ଥାନ ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନ କର ।)
(i) The chief guest offered me a prize.
Answer:
The chief guest offered a prize to me.
(ii) Fetch me a glass of water.
Answer:
Fetch (ଯାଇ ଆଣ) a glass of water for me.
(iii) Chumki sent Sunita and Tapan her best wishes.
Answer:
Chumki sent her best wishes (ଶୁଭେଚ୍ଛା) to Sunita and Tapan.
(iv) Trees give us plenty of valuable things.
Answer:
Trees give plenty of valuable things to us.
![]()
(v) Please bring me the book of the latest edition.
Answer:
Please bring the book of the latest edition (ନୂତନ ସଂସ୍କରଣ) for me.
Activity – 3
Find out the objects and complements in the following sentences. (ନିମ୍ନଲିଖତ ବାକ୍ୟମାନଙ୍କରୁ “କର୍ମ” ଓ “ପୂରକ’ ବାହାର କର ।)
1. Sita looks fine.
Answer:
fine – complement (looks – link verb)
2. Ramababu is a nice gentleman.
Answer:
a nice gentleman – Complement (‘be’ verb is)
3. Padminee plays chess.
Answer:
chess – direct object (What does play)
4. Trees grow well in spring.
Answer:
well – complement (manner adverb), in spring (time adverb)
5. They are making a plan.
Answer:
a plan – direct object (What are they making?)
6. Rabi is looking at the sky.
Answer:
the sky – object (What is Rabi looking at ?)
7. He is sitting on a string charpoy.
Answer:
on a string charpoy – adjunct (no complement)
8. The court rejected her appeal.
Answer:
her appeal (ଆବେଦନ) – direct object (What rejected ?)
9. Her questions often puzzle me.
Answer:
me-direct object (Whom puzzle)
10. I like green vegetables.
Answer:
green vegetables – direct object (What do you like ?)
Activity – 4
Identify the adjuncts and complements in the following sentences.
(ନିମ୍ନୋକ୍ତ ବାକ୍ୟମାନଙ୍କରେ ବିବର୍ଷକ ଓ ପୂରକ ଚିହ୍ନାଅ ।)
1. This pen costs twenty rupees.
Answer:
twenty rupees – complement
![]()
2. My brother usually writes poems.
Answer:
usually-adjunct, poems – direct object
3. Gopabandhu is an eloquent speaker.
Answer:
an eloquent speaker (ବାଗ୍ମୀ ବକ୍ତା) – complement
4. My friend got first division in the exam.
Answer:
in the examination – adjunct (noun phrase), first division – direct object
5. He became weak in a few days.
Answer:
weak – complement (adjunct), in a few days – adjunct (adverb of time)
6. Meera appears foolish.
Answer:
foolish-complement (adjunct)
7. The man has ten acres of land in our village.
Answer:
ten acres of land – complement (noun phrase), in our village – adjunct (adverb of place)
8. He has still in a state of shock.
Answer:
still-adjunct (adverb of time), in a state of shock-complement (noun phrase)
9. The dog is at the front gate.
Answer:
at the front gate – complement (adverb of place)
10. He rejected my proposals outright.
Answer:
my proposals – direct object, outright (ରୋକ୍ଠୋକ) – adjunct (adverb of manner)
Activity – 5
Which Noun Phrases in the following sentences work as objects and which are the complements? (ନିମ୍ନ ପ୍ରଦତ୍ତ ବାକ୍ୟମାନଙ୍କରେ object ଓ complement ରୂପେ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରୁଥିବା କୁ ଚିହ୍ନାଅ ।)
1. Economics is my favorite subject.
Answer:
my favorite subject = noun phrase (compliment)
2. My friend never tells a lie.
Answer:
a lie – object = noun phrase (direct)
3. An honorable man never betrays his friends.
Answer:
his friends – object = noun phrase (direct object)
4. We call Gandhiji the Father of the Nation.
Answer:
Gandhiji – direct object = noun phrase, The Father of Nation = complement = noun phrase
![]()
5. Everyone called him Sunny.
Answer:
him- direct object = noun phrase, Sunny-complement = noun phrase
6. She gives her children expensive presents.
Answer:
her children – indirect object = noun phrase, expensive (ମୂଲ୍ୟବାନ୍) presents – direct object = noun phrase
7. The students selected Bakul their monitor.
Answer:
Bakul – direct object = noun phrase, their monitor – complement = noun phrase
8. My father tasted the curry.
Answer:
the curry – direct object = noun phrase
9. None but the brave deserves the fair.
Answer:
the fair (praise) (ପ୍ରଶଂସା) – direct object = noun phrase
10. I have a house at Cuttack.
Answer:
a house complement = noun phrase, at Cuttack – adjunct
The Predicate Phrase Additional Questions With Answers
Read the following sentences and say whether the verb used in the sentence is Transitive or Intransitive.
1. We heard a noise.
Answer:
heard – Transitive
2. The thief stole the money.
Answer:
stole – Transitive
3. The policeman saw the thief.
Answer:
saw Transitive
4. The young man became an officer.
Answer:
became – Intransitive
5. The flower smells nice.
Answer:
smells – Intransitive
6. The child feels cold.
Answer:
feels Intransitive
7. The enemy attacked the town.
Answer:
attacked – Transitive
8. Children like sweets very much.
Answer:
like – Transitive
9. My mother passed me the salt.
Answer:
passed – Transitive
10. The old man died last week.
Answer:
died Intransitive
11. He left just now.
Answer:
left Intransitive
12. Padminee plays chess.
Answer:
plays Transitive
13. I gave him a book.
Answer:
gave Transitive
![]()
14. I bought a frock.
Answer:
bought Transitive
15. The child fell down.
Answer:
fell down – Intransitive
Find out the objects and complements in the following sentences.
1. The court rejected his appeal.
Answer:
his appeal – Object
2. Trees give us plenty of valuable things.
Answer:
us – Indirect Object, plenty of valuable things – Direct object
3. My teacher taught the grammar.
Answer:
the grammar – Object
4. The cat killed the rat.
Answer:
the rat – Object
5. The boy looks tired.
Answer:
tired Complement
6. The sky got dark.
Answer:
dark – Complement
7. My mother is a teacher.
Answer:
a teacher – Complement
8. Honey tastes sweet.
Answer:
sweet – Complement
9. Minakshi writes poems.
Answer:
poems – Object
10. Abdul broke the window.
Answer:
the window – Object
11. The man seems restless.
Answer:
restless – Complement
12. My brother became a doctor.
Answer:
a doctor – Complement
13. I feel very cold.
Answer:
very cold – Complement
![]()
14. He gave me a present.
Answer:
me – Indirect Object,
a present – Direct Object
15. We found him dead.
Answer:
him – Object, dead – Complement
Write the pattern of the following sentences.
1. She is on the way.
Answer:
SVC
2. We returned yesterday.
Answer:
SVA
3. The girl drew a picture.
Answer:
SVO
4. The old lady passed away.
Answer:
SV
5. I gave him a book.
Answer:
SVOO
6. The man is walking slowly.
Answer:
SVA
7. The baby cried loudly.
Answer:
SVA
8. They looks tired
Answer:
SVC
9. The book made him famous.
Answer:
SVOC
10. Neha offered me a nice gift.
Answer:
SVOO
11. Little men desire high posts.
Answer:
SVO
12. The girl is hemming her kerchief.
Answer:
SVO
13. My house is nearby.
Answer:
SVC
14. They elected me chairman.
Answer:
SVOC
15. The driver kept the car in the garage.
Answer:
SVOC (Adjunct)
Identify the adjuncts and complements in the following sentences.
1. This pen costs twenty rupees.
Answer:
twenty rupees – complement
![]()
2. The girl appears foolish.
Answer:
foolish – compliment
3. The dog is at the front gate.
Answer:
at the front gate – complement
4. He left just now.
Answer:
just now – adjunct
5. I get up early in the morning.
Answer:
early in the morning – adjunct
6. Mr. Mishra is a doctor.
Answer:
a doctor – complement
7. The wind blew slowly.
Answer:
slowly – adjunct
8. Fire burns quickly.
Answer:
quickly – adjunct
9. It seems strange.
Answer:
strange – compliment
10. The old man feels cold.
Answer:
cold- complement
11. I made it last year.
Answer:
last year – adjunct
12. The children returned happily.
Answer:
happily – adjunct
13. He met me today.
Answer:
today – adjunct
14. The baby is always crying.
Answer:
always – adjunct
15. It smells nice.
Answer:
nice compliment
