Odisha State Board CHSE Odisha Class 11 Biology Solutions Chapter 1 Biodiversity Textbook Questions and Answers.
CHSE Odisha 11th Class Biology Chapter 1 Question Answer Biodiversity
Biodiversity Class 11 Questions and Answers CHSE Odisha
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Choose the correct option
Question 1.
How many years ago did life originate on Earth?
(a) 3 billion
(b) 3.5 billion
(c) 4 billion
(d) 4.5 billion
Answer:
(b) 3.5 billion
Question 2.
Which one of the following is a characteristic feature of living?
(a) Reproduction
(b) Response to stimuli
(c) Metabolism
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 3.
Which of these statements is wrong?
(a) Breakdown of glucose molecules in respiration is catabolism
(b) Many metabolic processes are similar in microbes, plants and animals
(c) In some non-living objects metabolic processes also occur
(d) Immune system is a characteristic of living beings
Answer:
(c) In some non-living objects metabolic processes also occur
Question 4.
Find out the wrong one.
(a) A single-celled organism grows only in mass
(b) A multicellular organism grows not only in mass, but also in number of cells
(c) Fungi produce large number of spores during reproduction
(d) Gametes fuse to produce offsprings in asexual reproduction
Answer:
(d) Gametes fuse to produce offsprings in asexual reproduction
Question 5.
Identify the incorrect statements.
(a) Plants are influenced by external stimuli such as light, temperature and water
(b) All organisms do not possess consciousness
(c) Combined interactions of molecules make life to continue
(d) Organisms have the ability to regulate the chemical substances entering into their bodies
Answer:
(b) All organisms do not possess consciousness
Question 6.
Richness of the living species on earth is termed as
(a) ecosystem
(b) community
(c) biodiversity
(d) population
Answer:
(c) biodiversity
Question 7.
Who is referred to as the Father of Taxonomy?
(a) WG Rosen
(b) EO Wilson
(c) John Ray
(d) Carolus Linnaeous
Answer:
(d) Carolus Linnaeous
Question 8.
Full form of ICBN
(a) International Code for Botanical Nomenclature
(b) International Code for Biological Nomenclature
(c) International Code for Bacterial Nomenclature
(d) International Code for Bryophyte Nomenclature
Answer:
(a) International Code for Botanical Nomenclature
Question 9.
Who proposed the three domain system of biological classification?
(a) Carl Woese
(b) RH Whittaker
(c) Charles Darwin
(d) Robert Hooke
Answer:
(a) Carl Woese
Question 10.
In the scientific name of man, sapiens represents name of the
(a) genus
(b) species
(c) scientist
(d) place
Answer:
(b) species
Question 11.
The scientific names are derived from which language?
(a) English
(b) French
(c) Latin
(d) Greek
Answer:
(c) Latin
Question 12.
Under which domain does the kingdom-protista come?
(a) Archaea
(b) Bacteria
(c) Eukarya
(d) Plantae
Answer:
(c) Eukarya
Question 13.
Which is not true about the organisms of the domain Bacteria?
(a) Have diacyl glycerol diester lipids in their cell membranes
(b) Have no nuclear membrane
(c) Contain a genome composed of bacterial rRNA
(d) Thermophiles and halophiles come under the domain
Answer:
(d) Thermophiles and halophiles come under the domain
Question 14.
Which of the following about organisms is not dealt by Taxonomy?
(a) Nomenclature
(b) Identification
(c) Classification
(d) Evolutionary history
Answer:
(d) Evolutionary history
Question 15.
Which chemical solution is used for the preservation of organisms?
(a) Nitric acid
(b) Formalin
(c) Chloroform
(d) Sodium hydroxide
Answer:
(b) Formalin
Question 16.
Name the botanical garden present in Bengaluru.
(a) Lai Bagh
(b) Empress Garden
(c) Indian Botanic Garden
(d) Malampuzha Garden
Answer:
(a) Lai Bagh
Question 17.
Binomial System of Nomenclature was proposed by
(a) Carolus Linnaeus
(b) RH Whittaker
(c) Carl Woese
(d) JB Lamarck
Answer:
(a) Carolus Linnaeus
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name the author of the book ‘Systerna Naturae’.
Answer:
Carolus Linnaeus
Question 2.
Under which domain comes the kingdom- Animalia?
Answer:
Domain Eukarya
Question 3.
Arrange the following taxa from highest to lowest : Genus, Class, Phylum, Order.
Answer:
Phylum → Class → Order → Genus
Question 4.
Which botanical garden is named after Sir Jagdish Chandra Bose?
Answer:
Acharya Jagadish Chandra Bose Indian Botanical Garden, Kolkata
Question 5.
Which district Nanadankanan Biological Park is situated?
Answer:
Bhubaneswar
Short Answer Type Questions
Answer the following in three sentences each
Question 1.
What is taxonomical hierarchy?
Answer:
Taxonomic Hierarchy
The taxonomic hierarchy is the system of arranging taxonomic categories in a descending order. It was first introduced by Linnaeus (1751) and hence, it is also known as Linnaean hierarchy.
Groups represent category and category further denotes rank. Each rank or taxon represents a unit of classification. These taxonomic groups/categories are distinct biological entities and not merely morphological aggregates.
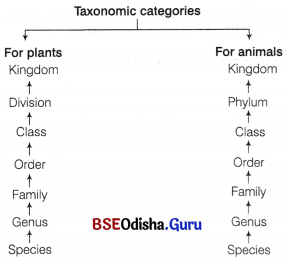
Taxonomic categories showing hierarchical arrangement in ascending order
Question 2.
Explain the concept of species.
Answer:
Taxonomic studies consider a group of individual organisms with fundamental similarities as a species. Species is considered as the lowest or basic taxonomic category, which consists of one or more individuals of a population that resemble one another more closely than individuals of other species.
The members of species interbreed freely and are reproductively isolated from other species, e.g. Mangifera indica (mango), Solarium tuberosum (potato) and Panthera leo (lion). All the three names indica, tuberosum and leo represent the specific epithets while, the first words Mangifera, Solanum and Panthera are genera and represent another higher level of taxon or category.
Each genus may have one or more than one specific epithets representing different organisms, but having morphological similarities, e.g. Panthera has another specific epithet called tigris and Solanum includes species like nigrum and melongena.
Question 3.
State the usefulness of taxonomic tools.
Answer:
Taxonomic tools include museums, zoos, herbaria, botanical gardens, etc. They are required because taxonomic study of plants, animals and other organisms is very much essential. The biologists need the help of some taxonomical tools to gather knowledge on various bioresources, their diversity and measures required for their conservation.
Question 4.
Write down the names of the phylum, class order and family and the scientific name in respect of man, housefly, mango and wheat.
Answer:
(some organisms with their taxonomic categories)
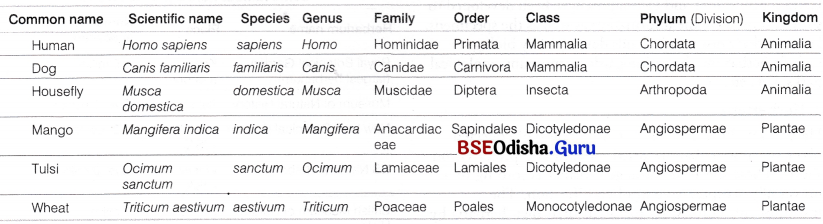
Question 5.
What are the objectives of zoological parks?
Answer:
These are the places where wild animals are kept in protected environments under human care and which enable us to learn about their food habits and behaviour. Zoological parks provide natural habitat to the animals.
In India there are about 200 zoological parks. These zoos are managed by the Central Zoo Authority of India. The World Zoo Conservation Strategy (WZCS) refers to all these zoological institutions as zoos.
Role of Zoological Parks
- Zoos are the centres for conservation of threatened and rare animal species.
- These provide sites for ex situ conservation through captive breeding of endangered animals.
- The zoological parks increase the public interest in an understanding of wildlife.
- These are the centres for recreation and education.
Some famous zoos of India
| Zoos | Place |
| National Zoological Park | Delhi |
| Nandankanan Zoo | Odisha (Bhubaneshwar) |
| Nehru Zoological Park | Hyderabad |
| Sanjay Gandhi Jaivik Udyan | Bihar (Patna) |
| Rajiv Gandhi Zoological Park | Maharashtra (Pune) |
| Alipore Zoological Garden | Kolkata |
| Guwahati Zoo | Assam |
| Madras Crocodile Bank Trust | Tamil Nadu (Chennai) |
| Mysore Zoo | Karnataka |
| Allen Forest Zoo | Uttar Pradesh (Kanpur) |
Differentiate between following (For Complete Chapter)
Question 1.
Anabolism and Catabolism
Answer:
The important differences between anabolism and catabolism are
| Anabolism | Catabolism |
| It is the sum total of constructive processes. | It is the sum total of destructive processes. |
| Complex substances are formed from simpler ones. | Simpler substances are formed from complex ones. |
| Energy is stored. | Energy is released. |
| Anabolism is required for growth and maintenance. | Catabolism is required for performance of activities. |
Question 2.
Archaea and Bacteria
Answer:
The differences between archaea and bacteria are
| Archaea | Bacteria |
| Their ceil wall lacks peptidoglycan. | Their cell wall is made up of peptidoglycan. |
| Have several kind of RNA polymerase. | Have one kind of RNA polymerase. |
| The archae constitute a domain or kingdom of single-celled microorganisms. These microbes are prokaryotes, meaning that they have no cell nucleus or any other membrane bound organelles in their cells. | Bacteria constitute large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometers in length, bacteria have a number of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals. |
Question 3.
Taxonomy and Systematics
Answer:
The differences between taxonomy and systematics are
| Taxonomy | Systematics |
| It is related to identification, nomenclature and classification. | It is the science of identification nomenclature, description and classification. |
| Taxonomic studies are based on rules and principles of classification. | Systematics is related to unique properties at every level of classification. |
Question 4.
Genus and Species
Answer:
The differences between genus and species are
| Genus | Species |
| Genus rank higher than the species in the taxonomic hierarchy. | Species is the most specific and comes at the lowest in taxonomic hierarchy. |
| Two fertile animals from one genus may or may not produce a fertile progeny. | Two fertile animals from one species can produce a fertile progeny. |
| Genus is the first name in binomial nomenclature. | Species is the second name in binomial nomenclature. |
Question 5.
Museum and Herbarium
Answer:
The differences between museum and herbarium are
| Museum | Herbarium |
| Museum contains many preserved specimens of animals and plants. | Herbarium is a collection of plant specimens only and data relating to them for future taxonomic studies and research. |
| Preservation in museum is done in jars, containers, stuffed specimens, etc. | The specimens preserved may be whole plants or plant parts that are dried, pressed and mounted on sheets of paper. |
Question 6.
Botanical Gardens and Herbarium
Answer:
The differences between botanical gardens and herbarium are
| Botanical Gardens | Herbarium |
| Places where living plant collections of different varities are maintained. | Places where a collection of dried, presed and well preserved plants species are kept. |
| These include medicinal, economic important, industrial, cultivated ornamental, etc., plants. | Here plant materials are arranged according to a system of classification. |
| Here the living plants are only grown. | It also possesses wood materials, microslides, photographs, drawings, etc. |
| Modem botanical gardens are quite big and possess greenhouses, a herbarium, a library and research laboratories. | Herbarium is comparatively a small institution present inside a botanical garden or in an university. |
Question 7.
Taxon and Species
Answer:
The difference between taxon and species are
| Taxon | Species |
| Taxon is the representation of any level of taxonomic category. | Species includes all the . organisms that are similar to breed and produce fertile offspring. |
| It is constructed by individual biological objects. | Species is one taxonomic category and is an abstract term. |
| Taxon can be of monophyletic or polyphyletic generation. | Species is always |
Question 8.
Classification and Taxonomy
Answer:
The differences between classification and taxonomy
| Classification | Taxonomy |
| It is systematic arrangement In groups or categories according to established criteria. | It is orderly classification of plants and animals according to their presumed natural relationship. |
| The term is broad one that encompasses any type of grouping according to criteria. | It is the process of giving names to things or groups of things according to their positions in a hierarchy. |
