Odisha State Board CHSE Odisha Class 11 Biology Solutions Chapter 20 Locomotion and Movement Textbook Questions and Answers.
CHSE Odisha 11th Class Biology Chapter 20 Question Answer Locomotion and Movement
Locomotion and Movement Class 11 Questions and Answers CHSE Odisha
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Multiple choice questions
Question 1.
The total no. of bones in human body is
(a) 106
(b) 206
(c) 306
(d) 246
Answer:
(b) 206
Question 2.
The contraction of muscle of shortest duration is seen in
(a) Jaw
(b) Eye lid
(c) Heart
(d) Intestine
Answer:
(b) Eye lid
Question 3.
What is the total number of ribs in human?
(a) 12
(b) 16
(c) 20
(d) 24
Answer:
(d) 24
Question 4.
Which unstriated muscle is entirely involuntary
(a) In the diaphragm
(b) In the eyelid
(c) At the base of external ear
(d) At the pylorous
Answer:
(a) In the diaphragm
Question 5.
Total no. of muscles in human is
(a) 639
(b) 936
(c) 369
(d) 669
Answer:
(a) 639
Question 6.
Cori cycle operates within one of the following organs
(a) Liver only
(b) Liver and muscle
(c) Muscle only
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Liver and muscle
Question 7.
One of the following muscles contains myoglobin, stores oxygen and rich is in mitochondria
(a) White muscle
(b) Red muscle
(c) Both
(d) None
Answer:
(b) Red muscle
Question 8.
How many vertebrae are present in man?
(a) 33
(b) 32
(c) 31
(d) 30
Answer:
(a) 33
Question 9.
Cervical vertebrae are present in
(a) Thorax
(b) Neck
(c) Abdomen
(d) Tail
Answer:
(b) Neck
Question 10.
Study of muscle is known as
(a) Musculogy
(b) Myology
(c) Arthrology
(d) Mycology
Answer:
(b) Myology
Question 11.
Knee joint is a
(a) Ball and socket joint
(b) Pivot Joint
(c) Hinge Joint
(d) Bicondylar joint
Answer:
(d) Bicondylar joint
Question 12.
Study of joints is called
(a) Osteology
(b) Mycology
(c) Arthrology
(d) Chondrology
Answer:
(c) Arthrology
Question 13.
Joint between femur and pelvic girdle is called
(a) Ball and socket joint
(b) Saddle joint
(c) Pivot joint
(d) Hinge joint
Answer:
(a) Ball and socket joint
Question 14.
Joint between the lower jaw and skull is called
(a) Gliding
(b) Hinge
(c) Perfect
(d) Gomphoses
Answer:
(d) Gomphoses
Question 15.
Which bone is present in pectoral girdle of all mammal
(a) Scapula
(b) Ilium
(c) Coracoid
(d) Pubis
Answer:
(b) Ilium
Question 16.
If ossification occurs in a tendon, which bone is formed.
(a) Sesamoid bone
(b) Replacing bone
(c) Membrane bone
(d) Dermal bone
Answer:
(a) Sesamoid bone
Question 17.
Which of the muscles bends the fore arm upward
(a) Biceps
(b) Triceps
(c) Gastrocremius
(d) Gluteus maximus
Answer:
(b) Triceps
Question 18.
Which bone is the longest in the body
(a) Fibula
(b) Femur
(c) Tibia
(d) Ulna
Answer:
(b) Femur
Question 19.
Which bone of man is not used for protection and support in the body
(a) Stapes
(b) Atlas
(c) Ribs
(d) Scapula
Answer:
(a) Stapes
Question 20.
The joint between carpals and radius and ulna is called
(a) Condylar joint
(b) Immovable joint
(c) Gliding joint
(d) Saddle joint
Answer:
(d) Saddle joint
Question 21.
Articulation of odontoid process of axis and atlas vertebrae is an example of
(a) Gliding joint
(b) Ball & socket joint
(c) Pivot joint
(d) Hinge joint
Answer:
(c) Pivot joint
Question 22.
Articulation of metacarpal of thumb with its carpal is an example of
(a) Saddle joint
(b) Hinge joint
(c) Pivot joint
(d) Gliding joint
Answer:
(a) Saddle joint
Question 23.
Articular cavity the pectoral girdle is.
(a) Acetabulum
(b) Glenoid cavity
(c) Neural canal
(d) Foramen of Monro
Answer:
(a) Acetabulum
Question 24.
Name of the joint at acetabulum
(a) Hip joint
(b) Shoulder joint
(c) Knee joint
(d) Elbow joint
Answer:
(a) Hip joint
Question 25.
Sutures present between various bones of the skull are
(a) Carlilaginous joint
(b) Synovial joint
(c) Hinge joint
(d) Fibrous joint
Answer:
(d) Fibrous joint
Question 26.
Number of true ribs and floating ribs are
(a) 6 and 3
(b) 0 and 2
(c) 9 and 4
(d) 20 and 4
Answer:
(d) 20 and 4
Question 27.
Which joint occurs between humerus and radius and ulna
(a) Pivot joint
(b) Hinge joint
(c) Sliding joint
(d) Ball & Socket joint
Answer:
(b) Hinge joint
Question 28.
Functions of long bones in mammal is to provide
(a) Support
(b) Support and production of RBCs
(c) Support and production of WBC
(d) Support and production of RBCs and WBCs
Answer:
(a) Support
Question 29.
Epiphyseal plate at the extremity of long bones help in
(a) Elongation of bone
(b) Bone moulding
(c) Bone formation
(d) Formation of Haversian canals
Answer:
(a) Elongation of bone
Question 30.
Muscle that bends one part over another is
(a) Extensor
(b) Flexor
(c) Adductor
(d) Abductor
Answer:
(c) Adductor
Question 31.
Malleus, incus and stapes occur in
(a) Skull
(b) Middle ear
(c) Pectoral girdle
(d) Pelvic girdle
Answer:
(b) Middle ear
Express the Following Statements in One Word or More Words, Wherever Necessary.
Question 1.
What is the name of the contractile unit of a skeletal muscle fibre.
Answer:
Myofibril
Question 2.
What is myology?
Answer:
Study of muscles
Question 3.
Where do you see pivot joint?
Answer:
Atlas-axis joint
Question 4.
Give an example of gomphosis.
Answer:
Tooth-socket articulation
Question 5.
What is the alternate name of breast bone?
Answer:
Sternum
Question 6.
In which part of the endo skeleton you come across sutures?
Answer:
Skull
Question 7.
What do you call the bones of the wrist?
Answer:
Carpals
Question 8.
How many lumber vertebrae are there in human?
Answer:
5
Question 9.
What is a vertebrate limb having five digits known as?
Answer:
Pentadoctyl limb
Question 10.
What is the alternate source of energy in a skeletal muscle?
Answer:
Thosphocreatine
Fill in the Blanks with Appropriate Words
Question 1.
……………. muscle contracts during flexon of the elbow joint.
Answer:
Biceps
Question 2.
Hip joint is an example of …………… joint.
Answer:
Multiaxial/Spheroidal
Question 3.
The centrum of mammalian vertebrae is of …………… type.
Answer:
Acoelus
Question 4.
Each T band of the muscle fiber contains a dense line at the centre, known as ………… .
Answer:
Z-line
Question 5.
…………. muscle relaxes the elbow joint.
Answer:
Triceps
Question 6.
A muscle gets fatigued by an accumulation of ………………. .
Answer:
Lactic acid
Question 7.
Myoglobin is found in ……………. .
Answer:
Red muscles
Question 8.
Knee joint is a ………… type of joint.
Answer:
Bicondylar
Question 9.
Contraction of ………… muscle helps in lifting heavy weight.
Answer:
Biceps
Question 10.
The stretch of a myofibril between two Z-lines is known as ………….. .
Answer:
sarcomere
Question 11.
The shoulder joint is classified as …………. joint.
Answer:
Ball and socket
Question 12.
Stiffening of the body after death of a person is known as ………… .
Answer:
Rigor mortis
Question 13.
There are ……….. number of vertebrae in the human vertebral column.
Answer:
26
Question 14.
Total number of bones in the human skull are …………… .
Answer:
22
Question 15.
Total number of metacarpals in the wrist of man is …………… .
Answer:
5
Question 16.
There are …………. cervical vertebrae in all mammals.
Answer:
7
Short Answer Type Questions
Answer each within 50 words.
Question 1.
What do you understand by a pentadactyl limb?
Answer:
Pentadactyl limb refers to the limb having five digits, e.g., humans.
Question 2.
Enlist the constituent parts of the appendicular skeletal system of human.
Answer:
Appendicular skeleton in human comprises of 126 bones including pectoral and pelvic girdle; limb bones-forelimb and hindlimb.
Question 3.
Enlist the constituent parts of the axial skeletal system of human.
Answer:
Axial skeleton in human consist of 80 bones including that of skull, vertebral column, ribs and sternum.
Question 4.
What is the role of troponin in muscle contraction?
Answer:
The sequence of events leading to contraction is initiated by a signal in the Central Nervous System (CNS), either from the brain (voluntary activity) or from spinal cord (reflex activity) via a motor neuron. A motor neuron along with the muscle fibres connected to it, forms a motor unit and the action potential is conveyed to a motor end plate at neuromuscular junction, i.e., it is the junction between a motor neuron and sarcolemma of muscle fibre.
Question 5.
What is a synovial joint? Give two examples What is a fibrous joint? Explain with an example.
Answer:
Each articular surface is cover by a layer of hyaline cartilage.
A considerable movement is allowed at all synovial joints. It is because there is present fluid-filled synovial cavity between articulating surface of bones. These are also surrounded by tubular articular capsule.
The capsule consists of two layers, i.e., outer fibrous capsule and inner synovial membrane which ‘secretes synovial fluid’ that lubricates and is responsible for providing nourishment to articular cartilage.
Question 6.
Differentiate between rheumatoid arthrit and osteoarthritis.
Answer:
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Osteoarthritis |
| It is infammation of synovial membrane in synovial joints. | It is progressive erosion of articular cartilage at synovial joint. |
| It can occur at any age. | Usually occur in old age. |
Question 7.
What are myofilaments? How many types of myofilaments are present in a myofibril?
Answer:
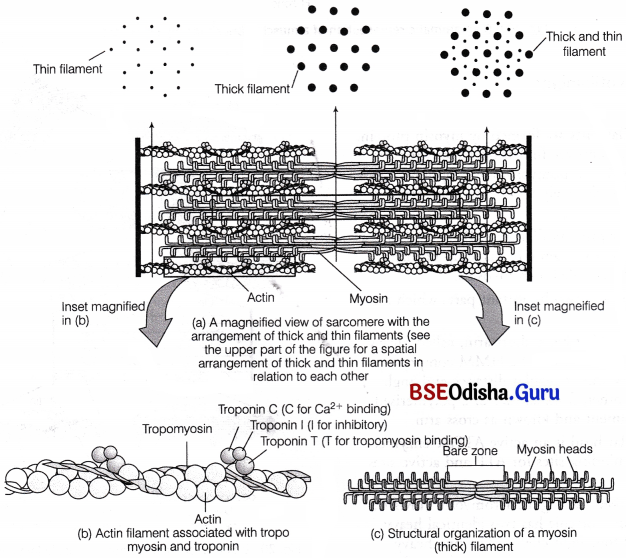
Myofilaments are large number of parallely arranged muscle fibres. These are the characteristic feature of muscle fibres. There are usually two type of myofilaments in a myofibril namely thick (myosin) and thin (actin, troponin, etc.) myofilaments.
Question 8.
Describe the role of troponin and tropomyosin in skeletal muscle contraction.
Answer:
During muscle contraction, tropomyosin moves laterally, thereby freeing the myosin head binding sites of actin.
Troponin contain Ca2+ binding sites and tropomyosin binding subunit. It binds to calcium during muscles contraction.
Question 9.
What is the role of phosphocreatine in the skeletal muscle contraction?
Answer:
Phosphocreatine acts as a reserve energy currency in mitochondria of muscle fibres and helps to form ATP. This energy rich compound transfer its phosphate group to ADP and form ATP.
Question 10.
What is sarcoplasmic reticulum? Where it is found and what is its function?
Answer:
Sarcoplasmic reticulum in myofibrils are in the form of tubules which joins to form terminal cisternae present between each anisotropic (A) and isotropic (I) bands. The sarcoplasmic reticulum in the form of tubules and terminal cisternae and transverse tubules constitutes sarco-tubular system.
Question 11.
What is muscle twitch ?
Answer:
Muscle twitch : It is the contraction of muscle fibre stimulated by nerve impulse. It is the isolated contraction of muscle, immediately after which muscle fibre relaxes.
Question 12.
What is an antagonistic muscle?
Answer:
Antagonistic muscles: These muscles acts in opposition to other muscles, e.g.; flexor/extensor, adductors/abductors, etc.
Question 13.
What is synovial fluid?
Answer:
Synovial fluid : It is secreted by the synovial membrane of synovial joint. This fluid fills the articular cavity and acts as a lubricant at articular surface and thus absorb friction.
It is dialyzed blood plasma containing hyaluronic acid secreted by synovial membrane.
Question 14.
What is the function of supinator muscle?
Answer:
Supinator muscle of the forearm and the biceps brachii of the upper arm supinate the forearm by pulling on the radius. They rotate the radius in the opposite direction of pronator muscle, moving the distal end of radius back to its position on the lateral side of the wrist.
Differentiate between
Question 1.
Appendicular skeleton and Axial skeleton
Answer:
| Appendicular skeleton | Axial skeleton |
| Present along transverse axis. | Present along vertical axis. |
| Consists of 126 bones. | Consists of 80 bones |
| Comprises limb bones and girdles. | Comprises bones of skull, vertebral column, sternum and ribs. |
Question 2.
Synovial joint and Solid joint
Answer:
| Solid joint | Synovial joint |
| The bones are held together at the joint by bundles of collagen fibres. | The bones are held together at the joint by an articular capsule made up of bands of fibrous tissue and ligaments. |
| The articular surfaces of the bones are not covered by any cartilage. | The articular surface of the bones are covered by cartilage called articular cartilage. |
| A space is not present in the joint. | A space filled with synovial fluid is found in the joint. |
| The joint does not allow any movement. | The joint allows free movement. |
Question 3.
Actin and Myosin
Answer:
| Myosin filaments (Thick myofilaments) | Actin filaments (Thin myofilaments) |
| Found only in A-band of sarcomere. | Found in-both A and l-bands. |
| Thicker (0.01 mm), but longer (4.5 mm) than actin filaments. | Thinner (0.005 mm), but shorter (2-2.6 mm) than myosin filaments. |
| Cross bridges present, hence have rough surface. | Cross bridges absent, hence have smooth surface. |
| Fewer than actin filaments. | More numerous than myosin filaments, six of them surround each myosin filaments. |
| Free at both the ends. | Free at one end and are joint to Z-line by other end. |
| Consist of 2 proteins: myosin and meromysin. | Consist of 3 proteins: actin, tropomyosin and tropinin. |
| Do not slide during muscle contraction. | Slide into H-zone during muscles contraction. |
Question 4.
Rheumatoid arthritis and Osteoarthritis
Answer:
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Osteoarthritis |
| It is infammation of synovial membrane in synovial joints. | It is progressive erosion of articular cartilage at synovial joint. |
| It can occur at any age. | Usually occur in old age. |
Question 5.
Red muscle fibers and White muscle fibers
Answer:
| Red Muscle Fibres | White Muscle Fibres |
| They are dark red muscle fibres due to the presence of abundant myoglobin in them. Hence they are called slow twitch or type I fibres. | They are pale or whitish as they have less myoglobin. Hence they are called fast twitch or type II fibres. |
| Mitochondria are more in number, but they have less sarcoplasmic reticulum. | Mitochondria are few in number, but amount of sarcoplasmic reticulum is high. |
| They depend on aerobic process for energy. | They depend on anaerobic process for energy. |
| They have slow rate of contraction for long periods. | They have fast rate of contraction for short periods. |
| e.g., extensor muscle of the human back, soleus muscles of leg. | e.g., eyeball or extra-occular muscles. |
Question 6.
Biceps and Triceps
Answer:
| Biceps | Triceps |
| Made up of two muscle bundles-long head and short head. | Made up of three muscle bundles-lateral head, long head and medial head. |
| They are flexor. | They are extensor |
| It contracts and bends arm at elbow. | It contract and straighten the arm at elbow. |
Question 7.
Skeletal muscle and Cardiac muscle
Answer:
| Skeletal Muscle | Cardiac Muscles |
| It is found in limbs, tongue, pharynx and beginning of oesophagus. | It is found in the wall of the heart, pulmonary veins and superior Vena Cava, |
| Fibres are unbranched. | Fibres are branched. |
| It is multinucleated. | It is uninucleated. |
| No oblique bridges and intercalated discs. | Oblique bridges and intercalated discs are present. |
| It soon gets fatigued. | It never gets fatigued. |
| It is voluntary in action. | It is involuntary in action. |
Question 8.
Involuntary muscle and Voluntary muscle
Answer:
| Involuntary Muscles | Voluntary Muscles |
| Associated with nerves of ANS. | Associated with nerves under voluntary control. |
| Cannot be controlled conciously | Can be controlled conciously |
| Contraction is rhythmic and slow. | Contraction is rapid and forceful |
| e.g. Smooth and cardiac muscles. | e.g. skeletal muscles. |
| They are are visceral | They are attached to bones. |
Question 9.
Striated muscle and Unstriated muscle
Answer:
| Striated Muscles | Unstriated Muscles |
| Voluntary in action | Involuntary in action |
| Muscle fibres are long and cyclindrical with blunt ends. | Long, spindle shaped with pointed ends |
| Multi nucleated. | Uninucleated |
| Sarcomerepresent | Sarcomere absent. |
| e.g. biceps muscle | e.g. intestinal muscles. |
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe the sliding filament theory of skeletal muscle contraction.
Answer:
Biochemical Events during Muscle Contraction:
The sequence of events leading to contraction is initiated by a signal in the Central Nervous System (CNS), either from the brain (voluntary activity) or from spinal cord (reflex activity) via a motor neuron. A motor neuron along with the muscle fibres connected to it, forms a motor unit and the action potential is conveyed to a motor end plate at neuromuscular junction, i.e., it is the junction between a motor neuron and sarcolemma of muscle fibre.
A neurotransmitter (acetylcholine) is released at the junction by the neural signal which generates an action potential in the sarcolemma. This spreads and causes the release of calcium ions into sarcoplasm. Calcium plays a key regulatory role in muscle contraction. Increase in calcium ions level leads to binding of Ca+ ions to the troponin subunit on actin filament. This removes the masking of active sites for myosin.
Formation of Cross-Bridge:
An ATP molecule joins the active site on myosin head of myosin myofilament. These heads contain an enzyme, myosin ATPase that along with Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions catalyses the breakdown of ATP.
![]()
The energy is transferred to myosin head, which energises and straightens to join an active site on actin myofilament, forming a cross bridge.
The energised cross-bridges produce a power stroke and move, causing the attached actin filaments to move towards the centre of A-band. The Z-line is also pulled inwards causing shortening of sarcomere, i.e., contraction. It is clear from the above explanation that during contraction, A-bands retain the length, while I-bands get reduced.
After the power stroke, the myosin head releases ADP and Pi, relaxes to its low energy state. The head detaches from actin myofilaments when new ATP joins it (cross-bridge broken).
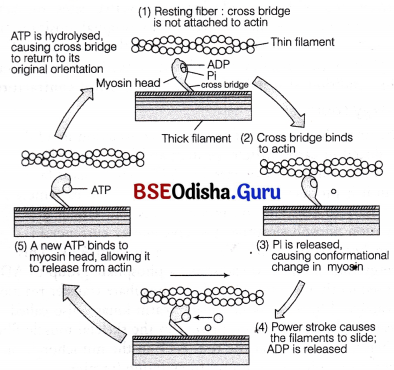
The cross bridge cycle that causes sliding of myofilaments and hence muscle contraction
In repeating cycle, the free head cleaves the new ATP.
The cycles of cross-bridge formation and breakage is repeated causing further sliding. As ATP is required to dislodge ADP, in the absence of it, ADP remain bounded to myosin head. The myosin head further remain permanently bound to action and hence, the muscle is never relaxed. This condition is called rigor mortis. If occurs after death when there is complete depletion of ATP and phosphocreatine.
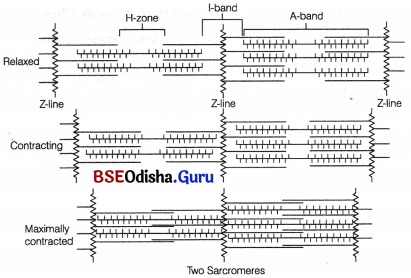
Sliding filament theory of muscle contraction (movement of the thin filaments and the relative size of the I-band and H-zones
Muscle Relaxation:
After contraction, the calcium ions are pumped back to the sarcoplasmic cisternae, blocking the active sites on actin myofilaments. The Z-line returns to original position, i.e. relaxation of muscle fibre takes place. If the movement of Ca2+ into the reticulum is inhibited, relaxation doesn’t occur. The condition of sustained contraction is called contracture.
Energy sources:
The immediate source of energy for contraction is ATP, produced in carbohydrate, protein and lipid catabolism. However, during heavy exercise, ATP may be used faster than it is produced. A rapid renewal of ATP is extremely necessary to keep the contration process on. Under this situation phosphocreatine, a reserve energy currency in mitochondria of muscle fibers, serves to form ATP. This energy-rich compound transfers its phosphate group to ADP, consequently forming ATP.
This phosphate transfer reaction is catalyzed by an enzyme called creatin kinase, also called creatine phosephokinases, present in the skeletal muscle fiber. When the muscle is at the rest. ATP in the mitochondrion transfers its phosphate group to creratine forming phosphocreatine. Thus, there is a build up of phosphocreatine to serve during exigencey. its concentration is more than three times the concentration of ATP in a muscle cell.
Question 2.
Draw a neat labeled diagram of a sarcomere of skeletal muscle fiber (No description is necessary).
Answer: