Odisha State Board CHSE Odisha Class 11 Biology Solutions Chapter 22 Chemical Coordination and Regulation Textbook Questions and Answers.
CHSE Odisha 11th Class Biology Chapter 22 Question Answer Chemical Coordination and Regulation
Chemical Coordination and Regulation Class 11 Questions and Answers CHSE Odisha
Multiple Choices Questions
Question 1.
Banting and Best (1921) established that:
(a) Deficiency of thyroxine causes hypothyroidism
(b) Oversecretion of cortisol causes Cushing’s syndrome
(c) Deficiency of insulin causes hyperglycemia
(d) Oversecretion of growth hormone causes gigantism
Answer:
(c) Deficiency of insulin causes hyperglycemia
Question 2.
Which one of the facts about hormones is correct?
(a) Hormones are proteins
(b) Hormones are released into the blood
(c) Hormones have no specific targets
(d) Hormones are secreted by exocrine glands
Answer:
(b) Hormones are released into the blood
Question 3.
Which one of the following is not true?
(a) Steroid hormones act through second messengers
(b) Glycoprotein hormones include TSH, FSH and LH
(c) Epinephrine and norepinephrine are catecholamines
(d) Sertoli cells secrete androgen binding protein
Answer:
(a) Steroid hormones act through second messengers
Question 4.
Which of the following statements about the hypothalamic releasing and release-inhibiting hormones is true?
(a) They are secreted into capillaries in the median eminence
(b) They are transported by portal veins to the anterior pituitary
(c) They stimulate the secretion of specific hormones from the anterior pituitary
(d) All of the above are true
Answer:
(d) All of the above are true
Question 5.
The hormone primarily responsible for increasing the basal metabolic rate and promoting the maturation of the brain is:
(a) Cortisol
(b) ACTH
(c) TSH
(d) Thyroxine
Answer:
(d) Thyroxine
Question 6.
Which of the following statements about adrenal cortex is true?
(a) It is not innervated by nerve fibers
(b) It secretes some androgens
(c) The zona glomerulosa secretes aldosterone
(d) The zona fasciculata is stimulated by ACTH
(e) All of these are true
Answer:
(b) It secretes some androgens
Question 7.
Which of the following statements about insulin is true?
(a) It is secreted by alpha cells of islet of Langerhans
(b) It is secreted in response to a rise in blood glucose concentration
(c) It stimulates the synthesis of glycogen and fat
(d) Both (a) and (b) are true
(e) Both (b) and (c) are true
Answer:
(e) Both (b) and (c) are true
Question 8.
Steroid hormones are secreted by
(a) Only Adrenal cortex
(b) Only Gonads
(c) Only Thyroid
(d) Both (a) and (b)
(e) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Question 9.
The secretion of which of the following hormones will be augmented in a person with endemic goiter.
(a) TSH
(b) Thyroxine
(c) Triiodothyronine
(d) All of these
Answer:
(a) TSH
Question 10.
Which of these hormones uses cAMP as a second messenger?
(a) Testosterone
(b) Cortisol
(c) Insulin
(d) Epinephrine
Answer:
(c) Insulin
Question 11.
Which of these hormones may have a role in circadian rhythm.
(a) Estradiol
(b) Insulin
(b) ACTH
(d) Melatonin
Answer:
(d) Melatonin
Question 12.
Which one of the following about ACTH is true ?
(a) It stimulates the entire adrenal cortex
(b) It stimulates zona glomerulosa only
(c) It stimulates both zona fasciculata and reticularis
(d) It stimulates zona reticularis only
Answer:
(c) It stimulates both zona fasciculata and reticularis
Question 13.
Which one of the following statements is false?
(a) Corpus luteum secretes progesterone
(b) Progesterone maintains pregnancy
(c) FSH stimulates interstitial cells of Leydig
(d) Sertoli cells are somatic cells, secreting androgen binding protein
Answer:
(c) FSH stimulates interstitial cells of Leydig
Question 14.
Granulosa cells secrete:
(a) Cortisol
(b) Estradiol
(c) Testosterone
(d) Progesterone
Answer:
(b) Estradiol
Question 15.
Which of the following is correct?
(a) T4 changes into T3 in the target cell
(b) T3 changes into T4 in the target cell
(c) T3 and T4 act as such on target cell
(d) T3 changes into T4 and vice-versa in the target cells
Answer:
(a) T4 changes into T3 in the target cell
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Express the following statements in one word.
Question 1.
The study of glands secreting hormones and their functions.
Answer:
Endocrinology
Question 2.
The part of the brain that secretes the releasing and release-inhibiting hormones.
Answer:
Hypothalamus
Question 3.
The stalk that attaches the pituitary with the hypothalamus.
Answer:
Infundibulum
Question 4.
The part of the hypothalamus, where the primary capillary plexus is present.
Answer:
Median eminence
Question 5.
The division of the anterior pituitary that secretes the tropic hormones.
Answer:
Adenohypophysis
Question 6.
The hormone, which acts on the renal tubule and promotes the absorption of water.
Answer:
Vasopressin
Question 7.
The hormone that regulates the height before adolescence.
Answer:
Growth hormone
Question 8.
The hormone that promotes early stages of gametogenesis.
Answer:
Testosterone
Question 9.
The hormone that promotes the development of breasts.
Answer:
Estradiol
Question 10.
The hormone that acts on the smooth muscle of uterus and facilitates the birth of a baby.
Answer:
Oxytocin
Question 11.
The blood vessel that carries the releasing, release-inhibiting hormones from the hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary.
Answer:
Hypothalamoportal vessel
Question 12.
The iodinated glycoprotein present in the colloid of the thyroid.
Answer:
Thyroglobulin
Question 13.
Hypothyroidism in children with severe mental retardation.
Answer:
Cretinism
Question 14.
Hyperthyroidism, which is caused by auto-immune attack
Answer:
Graves disease
Question 15.
The hormone that stimulates the interstitial cells of the gonads.
Answer:
Luteinizing hormone
Question 16.
A synonym for adrenal gland.
Answer:
Triple F gland
Question 17.
The cortical steroid hormone that regulates mineral metabolism.
Answer:
Aldosterone
Question 18.
The pathological condition in which inadequate glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoid fail to negatively feedback the secretion of ACTH from the anterior pituitary.
Answer:
Cushing’s syndrome
Question 19.
The hormone that fluctuates in its concentration, when one flies different time zones.
Answer:
Melatonin
Question 20.
The formation of glucose from non-carbohydrates.
Answer:
Gluconeogenesis
Question 21.
Breakdown of glycogen into glucose.
Answer:
Glycogenolysis
Question 22.
The interstitial cells that secrete androgens.
Answer:
Leydigs cell
Question 23.
The graafian follicle turns into a progesterone secreting endocrine structure following ovulation.
Answer:
Corpus luteum
Question 24.
The phenotypic characters, which identify the sex of the individual.
Answer:
Secondary sexual characters
Question 25.
A collective name for adrenal medullary hormones.
Answer:
Catecholamines
Correct the sentences without changing the works underlined.
Question 1.
Thyroid stimulating hormone is an amine hormone.
Answer:
The hormone secreted by thyroid is amine hormone.
Question 2.
Posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) originates from neural ectoderm.
Answer:
Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis) originates from neural ectoderm.
Question 3.
Pars tuberalis secretes all the tropic hormones of the anterior pituitary.
Answer:
Pars distalis secretes all the tropic hormones of the anterior pituitary.
Question 4.
Pituitary is attached to the hypothalumus.
Answer:
Pituitary is attached to the hypothalumus.
Question 5.
Growth hormone induces hyperglycemia.
Answer:
Calcitonin and epineprine induces hyperglycemia.
Question 6.
Growth hormone excess in ah adult human causes gigantism.
Answer:
Growth hormone excess in an adult human causes acromegaly.
Question 7.
Prolactin induces milk ejection.
Answer:
Prolactin induces milk formation.
Question 8.
Adrenocorticotropic hormone acts on adrenal gland.
Answer:
Adrenocorticotropic hormone acts on adrenal cortex.
Question 9.
Deficiency of antidiuretic hormone causes diabetes mellitus.
Answer:
Deficiency of antidiuretic hormone causes diabetes insipidus.
Question 10.
Releasing inhibiting hormones are secreted from the posterior pituitary.
Answer:
Releasing inhibiting hormones are secreted from the anterior pituitary.
Question 11.
Calcitonin is secreted from the parathyroid gland.
Answer:
Calcitonin is secreted from the thyroid gland.
Question 12.
Alpha cells of islet of Langerhans secrete somatostatin.
Answer:
Delta cells of islet of Langerhans secrete somatostatin.
Question 13.
Adrenocorticotropic hormone acts on zona glomerulosa and promotes the secretion of aldosterone.
Answer:
Adrenocorticotropic hormone acts on zona fasciculata and zona reticularis of the adrenal cortex to secrete cortisol.
Question 14.
Cortisol and epinephrine are hyperglycemic by promoting gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis, respectively.
Answer:
Cortisol and epinephrine are hyperglycemic by promoting gluconeogenesis and hepatic glycogenolysis, respectively.
Question 15.
Cells of the adrenal cortex are called chromaffin cells.
Answer:
Cell of the adrenal medulla are called chromaffin cells.
Question 16.
Day light induces the pineal gland to secrete less melatonin.
Answer:
Day light stimulus decreases the sympathetic stimulation of Pineal gland.
Question 17.
Sertoli cells secrete androgens.
Answer:
Interstitial cells secrete androgens.
Question 18.
Granulosa cells of the ovary secrete estrogens.
Answer:
Granulosa cells of the ovary secrete estrogens and inhibin.
Question 19.
Steroid hormones use the second messenger mechanism in their action on target cells.
Answer:
Protein hormones use the second messenger mechanism in their action on target cells.
Question 20.
Dwarfism is a consequence of prolactin deficiency before adolescence.
Answer:
Dwarfism is a consequence of growth hormone deficiency before adolescence.
Question 21.
Deficiency of dietary iodine causes thyrotoxicosis.
Answer:
Deficiency of dietary iodine causes endemic goiter.
Fill in the blanks
Question 1.
The active substance from the small intestine that stimulated the release of pancreatic juice was discovered by ……………. and ……………. in 1902.
Answer:
William M Bayliss, Earnest H starling
Question 2.
The word hormone was used by ……………. in 1905 for the active substance, secretin.
Answer:
Starling
Question 3.
Glycoprotein hormones include ……………. FSH and LH.
Answer:
TSH
Question 4.
Epinephrine and norepinephrine together constitute a group of hormones, known as ……………… .
Answer:
Catecholamines
Question 5.
All steroid hormones are derived from the parent compound, ……………. .
Answer:
Cholesterol
Question 6.
The role of 3,5 cAMP as a second messenger in the mechanism of hormone action was suggested by ……………. .
Answer:
Sutherland
Question 7.
Some hormones act through cell membrane receptors that stimulate adenylate cyclase activity and formation of ……………. .
Answer:
cAMP
Question 8.
The pituitary gland is attached to the floor of a part of fore brain, known as ……………. .
Answer:
hypothalamus
Question 9.
The pituitary is constituted by adenohypophysis and ……………. .
Answer:
neurohypophysis
Question 10.
The anterior pituitary is regulated by ……………. a part of the diencephalon.
Answer:
Hypothalamus
Question 11.
Adrenal medulla is constituted by cells that stain with chromates and hence are known as ……………. cells.
Answer:
Chromaffin cells
Question 12.
Posterior pituitary secretes two hormones, namely ……………. and ……………. .
Answer:
oxytocin, vasopressin
Question 13.
The group of hormones that binds to nuclear receptors is derived from the parent compound, ……………. .
Answer:
cholesterol
Question 14.
Tropic hormones are secreted from ……………. of the anterior pituitary.
Answer:
Pars distalis
Question 15.
The hormone, ……………. promotes breast development in female.
Answer:
estrogen
Question 16.
Oversecretion of growth hormone in adults causes an abnormality, known as ……………. .
Answer:
Acromegaly
Question 17.
ACTH is formed from a larger polypeptide, known as ……………. .
Answer:
Proopiomelanocortin
Question 18.
FSH stimulates the Sertoli cells to synthesise androgen binding protein and two hormones, namely inhibin and ……………. .
Answer:
activins
Question 19.
During development, the regression of mullerian ducts occur in the male by a hormone called antimullerian hormone. This hormone is secreted from the ……………. cells of the testis.
Answer:
Sertoli cells
Question 20.
The hormone ……………. is responsible for the ejection of milk from the breast of the lactating mother.
Answer:
Oxytocin
Question 21.
The growth promoting effects of growth hormone are mediated by ……………. polypeptides synthesised by the liver cells under its influence.
Answer:
IFG-I like
Question 22.
Delta cells of the pancreas synthesise ……………. which acts as growth hormone inhibiting hormone.
Answer:
Somatostatin
Question 23.
Parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland secrete a hormone, known as ……………. .
Answer:
Calcitonin
Question 24.
The iodinated glycoprotein present in the thyroid follicle is known as ……………. .
Answer:
Thyroglobulin
Question 25.
Interstitial cells of the testis are the targets of action of ……………. .
Answer:
FSH
Question 26.
Blood calcium level is monitored by hormones ……………. and ……………. .
Answer:
Calcitonin, parathyroid hormone
Question 27.
The releasing and inhibiting hormones of the hypothalamus act on the anterior pituitary via a blood vessel, known as ……………. .
Answer:
Hypophyseal portal vein
Question 28.
Alpha cells of .the pancreatic islets secrete a hormone, known as ……………. .
Answer:
glucagon
Question 29.
Over secretion of thyroid hormones causes an abnormality of the thyroid, known as ……………. .
Answer:
Hyper thyroidism
Question 30.
The enzyme ……………. catalyses the conversion of ATP into 3,5 cyclic AMP.
Answer:
adenylate cyclase
Question 31.
Estrogens are secreted by ……………. cells of the ovary.
Answer:
granulosa cells
Question 32.
Corpus luteum is an important source of a steroid hormone, ……………. .
Answer:
progesterone
Question 33.
Day night cycle is regulated by a hormone ……………. secreted from ……………. .
Answer:
melatonin, pineal gland
Question 34.
……………. has been designated as emergency hormone.
Answer:
Adrenaline
Question 35.
Inadequate secretion of both glucocorticoids and mineral ocorticoids from the adrenal cortex causes-a disease, known as ……………. .
Answer:
Addison’s disease
Question 36.
During stress, the immune system is suppressed by the hormone ……………. .
Answer:
Glucocorticoids
Question 37.
There is an insulin insufficiency in ……………. diabetes mellitus.
Answer:
Type I
Question 38.
Severe retardation of the nervous system in children due to a lack of thyroid hormones has been identified as ……………. .
Answer:
Cretinism
Question 39.
Excess release of ……………. can lead to water retention and consequently high blood pressure.
Answer:
ADH
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the relationship between hypothalamus and anterior pituitary?
Answer:
Hypothalamus and pituitary are related through blood supply. Hypothalamus regulates the synthesis and secretion of pituitary hormones.
Question 2.
Pituitary is not a master gland. Is it correct?
Answer:
No, it is not correct.
It is the smallest endocrine gland, but serves very important role in the human endocrine system. It directly or indirectly controls almost all other endocrine glands of the body. It is also known as master gland.
Question 3.
How are insulin and glucagon related?
Answer:
Insulin and glucagon are secreted by the gland pancreas. Insulin is hypoglycemic while glucagon is antagonistic to insulin and thus is hyper glycemic.
Question 4.
Name the hormone secreted by the delta cells of the pancreatic islet. What is its function?
Answer:
The hormone secreted by the delta cells of pancreas is somatostatin. Function of somatostatin is to inhibit the secretion of insulin and glucagon.
Question 5.
Pancreas is a mixocrine gland. Explain
Answer:
It is a composite gland that acts as both exocrine and endocrine gland. Such glands are also called heterocrine gland.
Origin: It originates from the endoderm of the embryonic germ layers.
Location: It lies below the stomach, in the loop of duodenum.
Question 6.
Why are catecholamines termed as emergency hormones?
Answer:
Both hormones belong to the category of compounds known as catecholamines and are secreted in response to any kind of stress, danger and during emergency situations like increased respiratory rate, heartbeat, etc.
The CNS at the time of stress or danger stimulates the adrenal medulla to release both these hormones. These are also known as emergency hormones or hormones of fight or flight.
Question 7.
How does cortisol handle stress?
Answer:
Cortisol
These are the hormones, which regulate the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Cortisol is the main glucocorticoid found in our body.
1. Cortisol is involved in the maintenance of cardiovascular system and in proper functioning of kidney.
2. Cortisol produces anti-inflammatory reactions and also during stress conditions functions by suppression of immune response.
Question 8.
Explain diabetes insipidus.
Answer:
Diabetes insipidus is a condition caused by the deficiency of hormones vasopressin. In this disease, there is a loss of water by frequent urination of dilute urine.
Question 9.
What is the main cause of type 1 diabetes mellitus?
Answer:
Type 1. diabetes is known as juvenile onset diabetes and it appears in people below the age of 20. It is caused, when beta cells are progressively destroyed by autoimmune attack by killer T lymphocyte. The consequence is that there is insulin deficiency.
Long Answer Type Question
Question 1.
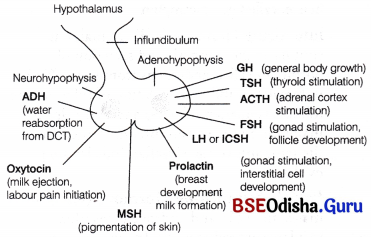
Give an account of the structure of human pituitary gland and describe the functions of hormones secreted from it.
Answer:
Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis):
It is the smallest endocrine gland, but serves very important role in the human endocrine system. It directly or indirectly controls almost all other endocrine glands of the body. It is also known as master gland.
Origin: It originates from the ectoderm of the embryonic germ layers.
Location and Structure:
It is reddish grey in colour and is roughly oval in shape. It is about a size of a pea seed. The pituitary gland is located in a small bony cavity of the brain called sella tursica.
Anatomy:
The pituitary gland has three major lobes, i.e., anterior, intermediate and posterior lobe.
It is anatomically divided into two major portions
(i) Adenohypophysis It is the glandular anterior portion of the pituitary gland. It further consists of two parts, i.e., pars distalis and pars intermedia. These two parts represent the anterior and intermediate lobes of pituitary.
(a) Pars Distalis It also called anterior pituitary. It produces different hormones.
These hormones are given below with their functions
• Growth Hormone (GH), stimulates the somatotroph cells of anterior lobe of pituitary gland to release its growth hormone or somatotrophin. It stimulates body growth, protein, fat and carbohydrate metabolism. It also promotes skeletal growth by acting on epiphysical cartilages of long bones of children and adolescents.
• Prolactin (PRL) The prolactin releasing hormone stimulates lactotroph cells of the anterior lobe of pituitary gland to secrete its prolactin. PRL regulates the growth of mammary glands and formation of milk in them.
• Thyroid Stimulating
Hormone (TSH) Thyroid releasing hormone stimulates thyrotroph cells of the anterior lobe of pituitary to secrete its thyroid Stimulating Hormone, i.e., TSH or thyrotrophin. This TSH stimulates the synthesis and secretion of thyroid hormones from the thyroid gland.
• Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone
(ACTH) This is secreted when Adrenocorticotrophin Releasing Hormone (ACRH) stimulates the corticotroph cells of anterior lobe of pituitary. This stimulates the synthesis and secretion of steroid hormones called glucocorticoids from the adrenal cortex.
• Gonadotrophin Hormone It is the gonadotroph cells of anterior lobe of the pituitary gland, which secrete, luteinising Hormone (LH) and Follicle Stimulating hormone (FSH). Both of these hormones stimulate the gonadal activity hence, called gonadotrophin.
• luteinising Hormone (LH) In males, it stimulates the synthesis and secretion of hormones called androgens from testis. ‘While, in females, it induces ovulation of fully mature follicles (Graafian follicles) and also helps in maintaining the corpus luteum formed from the remnants of the Graafian follicles after ovulation.
• Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) In males, the FSH and androgens together regulate spermatogenesis. In females, this hormone stimulates the growth and development of ovarian follicles.
(b) Pars Intermedia or Intermediate Lobe This portion of adenohypophysis secretes only one hormone,
• Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone
(MSH) The melanocyte releasing hormone stimulates the intermediate lobe of pituitary gland to secrete its Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone. MSH acts on melanocytes (melanin containing cells) and regulates the pigmentation of the skin.
(ii) Neurohypophysis It is a collection of axonaf projections from the hypothalamus, which terminate behind the anterior pituitary gland. It is pars nervosa of the neurohypophysis that forms the posterior lobe of pituitary gland.
The posterior pituitary stores and releases two hormones given below
(a) Oxytocin It is a short peptide of nine amino acids, also known as pitocin. It acts on the smooth muscles of our body and stimulates a vigorous contraction of uterus at the time of child birth. It also plays role in ejection of milk from the mammary glands in females.
(b) Vasopressin It is a small peptide hormone, also known as Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) or pitressin. This hormone acts mainly at the kidney, stimulating the reabsorption of water and electrolysis by the distal tubules.
Thereby reducing the loss of water through urine (diuresis).