Odisha State Board CHSE Odisha Class 12 Biology Important Questions Chapter 13 Applications of Biotechnology Important Questions and Answers.
CHSE Odisha 12th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 13 Applications of Biotechnology
Applications of Biotechnology Class 12 Important Questions CHSE Odisha
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Choose the correct option
Question 1.
A biotech company that released first ever genetically manipulated flower into the market is
(a) Cryobank
(b) Eli Lilly
(c) Florigene
(d) Genentech
Ans.
(c) Florigene
Question 2.
When an abnormal gene is replaced by normal gene, what do you call it? (2023)
(a) Gene mutation
(b) Gene donning
(c) Gene therapy
(d) Gene ligation
Ans.
(c) Gene therapy
Question 3.
Cry II Ab and Cry I Ab produce toxins that control
(a) cotton bollworms and corn borer, respectively
(b) corn borer and cotton bollworms, respectively
(c) tobacco budworms and nematodes, respectively
(d) nematodes and tobacco budworms, respectively
Ans.
(a) cotton bollworms and corn borer, respectively
Question 4.
First genetically modified plant commercially released in India is
(a) golden rice
(b) slow ripening tomatoes
(c) Bt-bringal
(d) Bt-cotton
Ans.
(d) Bt-cotton
Question 5.
Crystals of Bt toxin produced by some bacteria do not kill the bacteria themselves because
(a) bacteria are resistant to the toxin
(b) toxin is immature
(c) toxin is inactive
(d) bacteria enclose toxin in a special sac
Answer:
(c) toxin is inactive
Question 6.
Basic principle of developing transgenic animals is to introduce the gene of interest into the nucleus of
(a) somatic cell
(b) vegetative cell
(c) germ cell
(d) body cell
Answer:
(c) germ cell
Question 7.
Which among the following pharmaceutical products is harvested by using transgenic animals as bioreactors?
(a) Urokinase
(b) Insulin
(c) Lactoferrin
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 8.
The superbug can be used in
(a) oil spills
(b) water pollution
(c) eutrophication
(d) air pollution
Answer:
(a) oil spills
Question 9.
Biopatents are usually awarded for the discovery of
(a) new cell lines
(b) new DNA sequences
(c) GM strains
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 10.
Exploitation of patent biological resources of a country by another country is known as?
(a) biopatent
(b) biopiracy
(c) biowar
(d) All of these
Answer:
(b) biopiracy
Question 11.
Patents are given for
(a) discoveries
(b) inventions
(c) biopiracy
(d) gene therapy
Answer:
(b) inventions
Questions 12.
Which one of the following known as ‘Superbug’?
(a) Pseudomonas putida
(b) E. coli
(c) Aspergillus niger
(d) Acetobacter aceti
Answer:
(a) Pseudomonas putida
Questions 13.
US Patent on turmeric was challanged by
(a) CSIR
(b) EPO
(c) FSSAI
(d) FDI
Answer:
(a) CSIR
Questions 14.
Biopiracy is
(a) the use of biological patent
(b) thefts of plants and animals
(c) the use of bioresources of a country without proper authorisation
(d) stealing of biological resources
Answer:
(c) the use of bioresources of a country without proper authorisation
Correct the statements, if required, by changing the underlined words
Question 1.
An amorphous mass of parenchyma cells developed by tissue culture is called embryo.
Answer:
Callus
Question 2.
Petunia is ice minus strain which when sprayed on crops prevents frost formation.
Answer:
Pseudomonas
Question 3.
The natural source of vitamin-E is α-tocopherol.
Answer:
γ-tocopherol
Question 4.
The first GMO was created by Watson.
Answer:
Herbert Boyer and Stanley Cohen.
Question 5.
Soil bacterium Nitrosomonas syringae promotes ice nucleation in plants.
Answer:
Pseudomonas
Question 6.
The C-peptide is added during the maturation of pro-insulin to insulin.
Answer:
deleted
Question 7.
ADA treatment uses monocytes.
Answer:
lymphocytes
Question 8.
Antitrypsin is an agent that dissolves blood clot.
Answer:
Tissue Plasminogen Activator (TPA).
Question 9.
The first transgenic cow was Lilly.
Answer:
Rosie
Question 10.
A Pacific transgenic whale was generated by a growth hormone transgene.
Answer:
salmon
Question 11.
Transgenic mouse is smaller than the normal mouse.
Answer:
larger
Question 12.
Human protein α-2-trypin is used to treat emphysema.
Answer:
α-1-antitrypsin
Express in one or two word(s)
Question 1.
Define callus.
Answer:
It is undifferentiated mass of totipotent cells in the culture media.
Question 2.
Name one plant used to create novel transgenic plants.
Answer:
Petunia
Question 3.
Name the drugs isolated from Catharanthus roseus for cancer treatment.
Answer:
Vincristine and vinblastine.
Question 4.
Which microorganism is used as cloning host cell to produce humulin?
Answer:
E. coli
Question 5.
State the number of polypeptides found in mature human insulin.
Answer:
Two
Question 6.
What do you mean by the term transgene?
Answer:
oreign gene that is incorporated in an orgainsm to bring about desirable changes.
Question 7.
Where the LDL receptors are present?
Answer:
On the surface of hepatocytes
Question 8.
What is the name of the scientist who coined a sheep named Dolly?
Answer:
Keith Campbel and Ian Wilmut.
Question 9.
Name the institute that came up with a cloned sheep, named Dolly.
Answer:
Ian Wilmut of Roslin Institute in Scottland.
Question 10.
Which department of the Goverment of India is the nodal centre for Indian biosafety network?
Answer:
Department of biotechnology.
Question 11.
Which bacterium species is involved in Diamond vs Chakraborty case?
Answer:
Pseudomonas
Question 12.
What are transgenic animals?
Answer:
Genetically modified organism
Question 13.
Name the first transgenic cow that produced human protein enriched milk.
Answer:
Rosie
Question 14.
Name a transgenic animal being used in testing the safety of polio vaccine.
Answer:
Mouse
Question 15.
Mention the name of two common diseases that can be treated by medicines that contain biological products of transgenic animals.
Answer:
Cystic fibrosis and rheumatoid arthritis
Question 16.
What is patent?
Answer:
It is an open latter, a set of legal right, privilege and authority granted by a sovereign state to a person or institution for an invention for a limited period of time.
Fill in the blanks
Question 1.
…………… is a mammalian protein that have been successfully expressed in plants.
Answer:
Enkephalin.
Question 2.
Genetically engineered rice rich in vitamin-A is known as ……………… .
Answer:
golden rice
Question 3.
The recombinant human insulin is known as …………. .
Answer:
humulin
Question 4.
The full form of ELISA is ………… .
Answer:
Enzyme Linked Immunosorbant Assay.
Question 5.
Primarily, insulin is synthesised as ……………. .
Answer:
single polypeptide.
Question 6.
SCID is caused due to failure of synthesis of enzyme ………….. .
Answer:
adenosine deaminase.
Question 7.
…………. is the precursor of vitamin-A.
Answer:
ß-carotene
Question 8.
………… infects the roots of tobacco plants.
Answer:
Agrobacterium
Question 9.
The transgenic mouse is called as …………….. .
Answer:
Super mouse
Question 10.
…………. is a transgenic sheep.
Answer
Dolly
Question 11.
…………. is an infant nutrition formula that have been harvested using transgenic animals as bioreactors.
Answer:
Lactoferrin.
Question 12.
In 1990 ……….. the transgenic ewe was born in Scottland.
Answer:
Tracy
Question 13.
Full from of TPA is ……………. .
Answer:
Tissue Plasminogen Activator.
Question 14.
Neem patent case was first awarded in favour of ……………. .
Answer:
USA.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Find out from the internet what is golden rice.
Answer:
Golden rice is a genetically modified rice with high levels of ß-carotene and other carotenoids. This rice is modified in order to enhance the quantity of vitamin-A in it. It is called golden due to the gold-like colour it gets from ß-carotene.
Question 2.
Can a disease be detected before its symptoms appear? Explain the principle involved.
Answer:
When the symptoms of the disease are not visible and the pathogen concentration is very low, then detection by conventional diagnostic tests is very difficult. However, detection at the above stated stage is made possible by molecular diagnostic techniques like the amplification of their nucleic acid by Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). The principle involved here is that a single DNA molecule can be copied endlessly in a test tube, using primers, DNA polymerase enzyme and free nucleotides and appropriate conditions.
Question 3.
How is DNA recombinant technology helpful in detecting the presence of mutated genes in the cancer patients?
Answer:
Molecular diagnosis in DNA recombinant technology uses a single-stranded DNA or RNA tagged with a radioactive molecules. It is allowed to hybridise to its complementary DNA in a clone of cells followed by detection using autoradiography. The clone having the mutated gene will not appear on the photographic film, because the probe used will not be complementary to the mutated gene. In this way, presence of mutated genes can be detected.
Question 4.
Why is the functional insulin produced, considered better than the ones used earlier by diabetic patients?
Answer:
Insulin prepared by rDNA technology does not produce sensitive allergic reactions and complications to the foreign protein which occurred in the case of earlier extracted insulin from the pancreas of slaughtered cattle or pigs. Thus, it is considered better than the earlier used insulin.
Question 5.
How is a mature, functional insulin hormone different from its pro-hormone form?
Answer:
Mature functional insulin is obtained by the processing of pro-hormone which contains extra peptide called C-peptide. This C-peptide is removed during the maturation of pro-insulin to insulin.
Question 6.
Refer to the diagram given below and answer the questions that follows
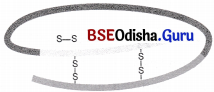
(i) The diagram shown above is insulin or proinsulin? Justify.
(ii) How is mature insulin synthesised?
Answer:
(i) The diagram is proinsulin as it contains C-peptide.
(ii) Mature insulin is synthesised by the removal of extra stretch called C-peptide.
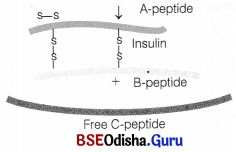
Question 7.
How did an American Company, Eli Lilly use the knowledge of rDNA technology to produce human insulin?
Or
How did Eli Lilly synthesise the human insulin? Mention one difference between this insulin and the one produced by the human pancreas.
Or
What is humulin?
Answer:
The production cost was high due to its complex extraction and purification processes. Additionally, the purified insulin was contaminated by many pathogenic viruses. These problems have been overcome by the use of recombinant DNA technology. Insulin that is produced by recombinant DNA technology is known as recombinant human insulin.
Question 8.
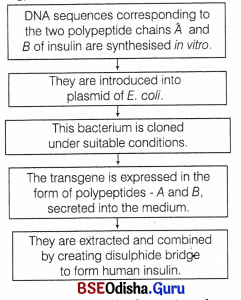
Recombinant DNA technology is of great
importance in the field of medicine. With the help of a flow chart, show how this technology has been used in preparing genetically engineered human insulins.
Answer:
Insulin production by using recombinant DNA technology is shown in flow chart below
Question 9.
What is gene therapy? Name the first clinical case in which it was used.
Or
What is gene therapy? Illustrate using the example of Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) deficiency.
Answer:
It is a method of treatment which allows correction of a biochemical (like phenylketonuria) or a genetic defect*that has been diagnosed in a child or embryo. The defective mutant alleles of the gene are replaced by the normal gene insertion to take over the function of and compensate for the non-functional gene. Gene therapy is widely used to treat
- Biochemical disorder, e.g. alkaptonuria, phenylketonuria, albinism, etc.
- Chromosomal and gene disorders, e.g. Down’s syndrome, Turner’s, syndrome, Klinefelter’s syndrome, fragile X-syndrome, cri-du chat, Huntington’s disease, Tay-Sach’s syndrome, etc.
Question 10.
Write a note on genetically modified organism.
Answer:
The plants, bacteria, fungi and animals whose genes have been altered by manipulation are called Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO).
These are also called transgenic organisms, as they contain and express one or more foreign genes called transgenes. Herbert Boyer and Stanley Cohen developed the first GMO in 1973.
They transferred the Kanamycin antibiotic resistance gene of a bacterium into the another Kanamycin sensitive bacterium.
The genes which are being transferred are called transgenes.
The recepient bacterium later acquired Kanamycin resistance. Following many such discoveries, GMOs were developed. Novel plants and animals were created by genetic manipulation for human welfare.
Question 11.
Write a short note on transgenic plants.
Answer:
Herbicide resistant plants Herbicide resistant transgenic plants are generated by transferring bacterial herbicide resistant genes into plant cells grown in culture. Glyphosate is the most widely used broad-spectrum herbicide world over.
A glyphosate resistant gene from Petunia plant is transferred into isolated plant cell§ in culture and glyphosate resistant plants are generated.
Question 12.
Write a short note with 2-3 important points on Bacillus thuringiensis.
Or
Why do the toxic insecticide proteins secreted by Bacillus thuringiensis kill insects?
Answer:
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) It is a soil-borne, Gram-positive bacterium. It is used to create transgenic plants having resistance to different pests. The genes having insecticidal properties in the bacterium are isolated and incorporated into plants by using advanced biotechnological methods to create Bt plants. During sporulation, many Bt strains produce crystal proteins (proteinaceous inclusions) called S-endotoxins, that have insecticidal action.
When consumed by insect, these toxins bind to the surface of midgut epithelial cells and create pores that cause cell swelling and lysis, leading to the death of an insect, e.g. 5r-cotton, fir-tomato, soybean, coffee, etc.
Question 13.
Why does Bt toxin cannot kill the bacterium that produces it, but kills the insect that ingests it?
Answer:
Bt toxin is produced by a soil bacterium called Bacillus thuringiensis. This toxin does not kill the bacterium which produces it, because in them, it is present in an inactive and crystalline form. It becomes active and toxic only when it is consumed by insects such as lepidopterans, etc. due to the alkaline pH of the gut.
Question 14.
Bt cotton is resistant to pests, such as lepidopterans, dipterans and coleopterans. Is Bt cotton resistant to other pests as well?
Answer:
Bt cotton is made resistant only to certain specific taxa of pests. It is quite likely that in future some other pests may infest this Bt cotton. It is similar to immunisation against smallpox which does not provide immunity against other pathogens like those that cause cholera, typhoid, etc.
Question 15.
Why certain cotton plants are called Bt cotton?
Answer:
Cotton plants are called Bt cotton because they bear specific Bt toxin genes which were isolated from Bacillus thuringiensis and incorporated into certain cotton plants. This helps the host plants in developing resistance against and various pests like bollworms, etc.
Question 16.
Differentiate the terms ‘Cry’ and ‘cry’.
Answer:
‘Cry’ refers to protein symbol and its first letter is always capital. It is written in Roman letters, ‘cry’ refers to the gene which is usually written in small letters and is invariably in italics.
Question 17.
What are Cry proteins? Name an organism that produces it. How has man exploited this protein to his benefit?
Or
Name the source and type of cry genes used for incorporation into crops by biotechnologists. Explain, how have these genes brought beneficial changes in the genetically modified crops.
Answer:
The proteins encoded by the gene named cry are called Cry proteins. Organism that produces Cry proteins is Bacillus thuringiensis.
The cry genes are incorporated in several crop plants, which then develop resistance to a specific targeted pest, e.g. cry IAc and cry IIAb control the cotton bollworms and cry LAb controls corn borer.
Question 18.
Expand GMO. How is it different from a hybrid?
Answer:
GMO stands for Genetically Modified Organism.
It differs from a hybrid because in a hybrid, cross is done between total genomes of two species or strains, whereas in a GMO, foreign genes from entirely dilferent species are introduced in the organism and are usually maintained as extrachromosomal entity or are integrated into the genome of the organism.
Question 19.
Describe any three potential applications of genetically modified plants.
Answer:
Potential applications of genetically modified plants are
- Nutritional enhancement, e.g vitamin-A enriched rice.
- Stress tolerance crops are more tolerant to abiotic stresses such as cold, drought, etc.
- Creation of tailor made plants by using GM plants to supply alternative resources to industries in the form of starches, biofuels, etc.
Question 20.
What is meant by transgenic animals?
Answer:
Animals that have had their DNA manipulated to possess and express an extra (foreign) gene are known as transgenic animals, e.g. transgenic rats, rabbits, pigs, sheep, cows and fish. Over 95% of all the existing transgenic animals are mice. The gene that is being transferred is called transgene.
Question 21.
Comment on how transgenic animals have proved to be beneficial in
(i) Production of biological products?
(ii) Chemical safety testing?
Answer:
(i) The transgenic animals have been proved to be beneficial in the production of biological products like human protein α-1 antitrypsin (by coding genes from that protein only), in the treatment of emphysema and production of human protein (α-lactalbumin) enriched milk by transgenic cow, i.e. Rosie. This milk was more nutritionally balanced for human beings than natural cow’s milk.
(ii) Transgenic animals are studied for testing toxicity of drugs and other chemicals as they carry genes that make them more sensitive to toxic substances.
Question 22.
What is the utility of transgenic animals?
Or
With respect to understanding diseases, discuss the importance of transgenic animal models.
Answer:
Transgenic animals are important in the following fields
(i) They are being used in basic science research to elucidate the role of genes in the development of diseases like cancer, cystic fibrosis, rheumatoid arthritis and Alzheimer’s disease.
(ii) They are valuable tools in the drug development process itself.
(iii) Milk producing transgenics can produce medicines or human proteins (insulin, growth hormone, etc.) in large quantities.
(iv) Transgenics can be a source of transplant organs as well.
Question 23.
(i) Which animals are being used for testing the safety of vaccines? Name the vaccine for which trials are going on.
(ii) Name the first transgenic cow. Why is it important?
Answer:
(i) Transgenic mice are used for testing the safety of vaccines.
The trials are going on for polio vaccine.
(ii) Rosie was the first transgenic cow. It is important because it produces human protein enriched milk, even better than a natural cow’s milk.
Question 24.
(i) Explain alpha lactalbumin. Where is it produced in human body?
(ii) In what manner biotechnology has helped in production of more nutritionally balanced milk?
Answer:
(i) Alpha lactalbumin is a human milk protein which helps to increase the production of lactose in the body. It is produced in human milk.
(ii) Biotechnology has lead to production of transgenic cow, Rosie that produced around 2.4 g/L human protein enriched milk. This milk contained the human alpha lactalbumin and was nutritionally more balanced than a natural cow’s milk.
Question 25.
While creating genetically modified organisms, genetic barriers are not respected. How can this be dangerous in the long run?
Answer:
Genetic modification of organisms can have unpredictable results when such organisms are introduced into the ecosystem. Because the real effects of gene manipulation are visible only when such organisms interact with other components and organisms of the ecosystem.
Question 26.
Biopiracy should be prevented. State why and how?
Answer:
Biopiracy should he prevented because
(i) The countries and people concerned are not given adequate compensatory payment.
(ii) The countries/people also lose their right to grow and use breeding experiments to improve the other varieties of the same species.
It may be prevented by implementing specific laws that takes into consideration all the biopatents and biopiracy related issues.
Question 27.
State the initiative taken by the Indian Parliament against biopiracy.
Answer:
The Indian Parliament has recently passed the second amendment to the Indian Patents Bill that takes action against biopiracy. In India, the Patent Act was enacted in 1970 to protect their resources and traditional knowledge from being exploited by other countries.
This act has undergone many amendments in 1999, 2002, 2005 and 2006. The Indian biosafety network is headed by the Department of Biotechnology.
Question 28.
Write a self-explanatory note on biopatent.
Or What is patent?
Answer:
When an individual develops a new product or process innovation using his intellect, the innovation becomes his own. Various rules at national and international lands protects the misuse of this innovation, and also safeguards the rights of the innovater.
The new inventions can be safe protected by patents, design trademark, trade secrets and copy rights, etc.
It is a set of exclusive legal rights granted by a government to the inventors or their assignee for a limited period of time to prevent others from commercial use of their invention. When patent is granted for biological entities and for products derived from them, they are called biopatents. Primarily USA, Japan and members of European Union are awarding biopatents.
Question 29.
Name a set of principles that may be used to regulate human activities in relation to the biological world. Why are they important?
Answer:
A set of principles that may be used to regulate human activities in relation to the biological world are called bioethics.
These are important because the genetic modification of an organism can have unpredictable results when such organisms are introduced into the ecosystem.
Question 30.
What is meant by biopiracy?
Answer:
It refers to the use of bioresources by multinational companies and other organisations without proper authorisation from the countries and people concerned without compensatory payment. The majority of industrialised nations are financially rich but poor in biodiversity and traditional knowledge, in comparison to developing and underdeveloped countries.
Another cause of biopiracy is bioprospecting which means a thorough survey of a source material to expand the knowledge and applications in biotechnology. During the course of bioprospecting, scientists may transfer any biological resource which they may consider as novel.
Differentiate between the following (for complete chapter)
Question 1.
Herbicide resistant plants and Frost resistant plants.
Answer:
Differences between herbicide resistant plants and frost resistant plants are as follows
| Herbicide resistant plants | Frost resistant plants |
| Generated by transferring bacterial herbicide resistant gene into plant cells. | Generated by deleting a gene that promotes ice nucleation. |
| e.g. Petunia contains glyphosate resistant gene which is being isolated to generate glyphosate resistant plants. | e.g. Pseudomonas syringae contains gene promoting ice nucleation. It is deleted by genetic engineering to produce ice minus strain. |
Question 2.
Humulin and Wosulin.
Answer:
Differences between humulin and wosulin are as follows
| Humulin | Wosulin |
| Manufactured by Eli Lilly corporation, USA. | Manufactured by wokhardt limited India. |
| First recombinant drug approved by FDA for human use. | General drug to treat diabetes. |
Question 3.
Ex vivo gene therapy and In vivo gene therapy.
Answer:
Differences between Ex vivo gene therapy and In vivo gene therapy are as follows.
| Ex vivo gene therapy | In vivo gene therapy |
| The cells are removed from the patient and genetic material is inserted in them in vitro, prior to transplantation of modified cells. | The genetic material is transferred directly into cells within a patient. |
| This approach is applicable to tissues that can be removed from the body and returned later and survive for longer period of time, e.g. hematopoietic cells. | It is only possible in tissues where the individual cells cannot be cultured in vitro in sufficient numbers or where cultured cells cannot be efficiently reimplanted, e.g. brain cells. |
