Odisha State Board CHSE Odisha Class 12 Economics Solutions Chapter 7 Supply Questions and Answers.
CHSE Odisha 12th Class Economics Chapter 7 Question Answer Supply
Group – A
Short type Questions with Answers
I. Answer within Two/Three sentence.
Question 1.
Supply curve slopes upward from left to right.
Answer:
Supply curve is the geometrical representation of law of supply which shows the direct relationship between price & quantity supplied. So supply curve slopes downward from left to right.
Question 2.
Supply curve has a positive slope.
Answer:
Supply curve shows the direct relationship between price of a goods & its quantity so, It slopes upward from left to right showing a positive slope.
Question 3.
Supply of a goods differs from its stock.
Answer:
Stock refers to total quantity of goods stored by the producer; but supply of a goods refers to that part of the stock offered for sale at a given price. So, supply of a goods is a part of the stock.
Question 4.
Supply of good is different from stock of goods.
Answer:
Stock of goods refers to total quantity of goods brought & kept after production. But the supply of goods refers to quantities of a goods ofered for sale at different prices during a particular time period.
Question 5.
Supply function is a multi-variate function.
Answer:
Supply of a goods depends on price of that goods, price of related goods, cost of production, stage of technology etc. So it is a multivariate function.
![]()
Question 6.
Supply of a goods varies directly with price.
Answer:
According to law of supply, the supply of a goods increases with rise in prices & vice versa. It is due to profit motive of the producers.
Question 7.
Supply curve has a positive slope.
Answer:
As the supply of a goods is directly related to its price-level, the supply curve slopes upward from left to right. So supply curve has a positive slope.
Question 8.
Law of supply does not operate for rare goods.
Answer:
Rare goods have fixed supply. Its supply cannot be increased with rise in price-level. So law of supply does not operate in this case.
Question 9.
Stock may exceed supply but supply can never exceed stock.
Answer:
Stock refers to the goods already produced & in possession of seller. But supply of a goods refers to a part of stock brought for sale in the market at a given price.
Answer within Five/Six sentence :
(A) WRITE SHORT NOTES ON :
Question 1.
Supply Function.
Answer:
Supply refers to the quantities of goods offered for sale by the producer at given prices during a particular time period. It is associated with the production of goods. As such, supply of goods depends on the factors of production, price of goods supplied, state of technology, government policy etc. So supply function is a multi-variate function comprising of all these variables. Mathematically stated,
Sx = f (Px, Pa, Pb, Pr, T, G )
Where as Px → Price of goods, Pa, Pb → Price of inputs, Pr → price of related good, T → state of technology, G → Government policy. All these factor are classified into price-factors & non-price factors. Other things (Non-price factors) remaining constant, the quantity supplied of a goods increases with a rise in the price-level and decreases with a fall in the price-level.
Question 2.
Supply schedule.
Answer:
Supply schedule is a tabular expression on showing a list of various quantities of a goods supplied at different given prices. Supply schedule is a numerical statement of law of supply. It shows that more is supplied at higher price & less is supplied at lower price. Supply schedule is of two types i.e.Individual supply schedule & market supply schedule. Market supply schedule is considered while explaining “ Law of supply”. Market supply schedule is the aggregate of individual supply schedule that denotes quantities of goods of offered for sale to the market at different prices.
Question 3.
Law of Supply
Answer:
Law of supply is a guiding principle that shows a functional relationship between price of a good & its quantity supplied in an unchanged situation. According to this law, more of a good is supplied at higher price & less of the good is supplied at lower price. It just exhibits the direct relationship between price & quantity .of a goods supplied, it indicates that price & supply move in a same direction. For this operation, factor like price related goods, prices of inputs, technology should remain constant.
Question 4.
Supply Curve.
Answer:
Supply Curve is a geometrical representation of supply schedule. This graphical illustration of supply schedule reflects the operation of law of supply. This curve describes the direct functional relationship between price & quantity supplied. Hence, the supply curve slopes upward from left to right indicating more is supplied at higher price & less supplied at lower price. This supply curve has positive slope. ‘
Question 5.
Change in Supply.
Answer:
Supply is a multi-variate function. A number of factors like price of the goods supplied, prices of inputs, price of related goods, state of technology, government policy etc. influence the supply. Change in supply takes place due to the change in all those factors other than the price of good supplied. Price of the goods remaining constant, if these factos change, there shall happen either increase in or decrease in supply. Hence, the supply curve may shift downward to the right or upward to the left. Thus, change in supply occurs either in form of increase in supply or decrease in supply. Here, price of the goods acts as a passive factor.
Group – B
Long Type Questions With Answers
Question 1.
What is supply ? What are the factors influencing it ?
Answer:
Supply refers to the amount of goods offered for sale by the producer at a given price during a particular time period. Supply is a flow concept. It indicates flow of different quantities of goods to the market at a different prices during a given time period. Thus, supply is quoted with price & expressed for a particular time period.
Supply of any goods does not means the entire stock of it. Rather, it is a part to the stock which is offered for sale at different prices during a given period. Supply of a good can be expressed by the supply function like.
Sx = f (Px, Py, Pz, Pa, Pb, Pc, T…. )
Like demand, supply is also a multi-variate function. Supply of a goods not only depends on its price, rather it depends on price of related goods (Py,Pz) price of inputs (Pa, Pb, Pc) state of technology (f) etc. All these factors directly influence the supply of goods.
FACTORS INFLUENCING SUPPLY :
Being a multivariate function, the supply of any goods is influenced by numerous factors. The important factors influencing demand are mentioned below.
(i) Price of Goods : It is an important factor that directly influences the supply. Price & supply of goods are positively correlated. It implies that in an unchanged situation more is supplied at higher price & less is supplied at lower price. It establishes that there exists direct relationship between price of a good & its quantity supplied. It is because of the profit motive of the producer. Producer is able to earn more profit only at higher price. So he is attaracted with higher price & supply more of goods.
(ii) Prices of related Goods : The supply of a goods is greatly influenced by the price of related goods. Related goods may be a substitute goods or complementary goods. If the price of a goods substitute of other falls, the quantity supplied of it falls & the supply of the original goods increases. Similarly, a rise in price of a goods leads to a fall in the supply of other goods. On the other hand, in case of complementary goods, if price of goods rises, the quantity supplied of its complementary goods also increases. It just proves the prices of related good as an important factor.
(iii) Prices of inputs: The Prices of factors of production (inputs) are also influential in determining the quantum of supply. If the prices of factors of production rise, the supply of the concered commodity decreases. Thus, there exists inverse relationship between price of inputs & quantity supplied. For example, if the price of a raw material of a good rises, the profit margin is expected diminishing & hence the producer reduces the supply of it.
(iv) State of Technology : State of technology stands as an important determinant of supply. Technological progress or introduction of cost-saving technology reduces the cost of production & raises the supply. Because it creates higher profit expectations. Thus, new inventions or discoveries in respect of technology raises the supply of goods.
(v) Goals of Business : In a free market economy, profit-motive is an importation objective of the business. Profit maximisation is a common goal of business. As such, the producer becomes interested to supply more only at higher price. If the goal of the business is to maximise profit & the profit expectation is bright, then producer supplies more. In socialistic economy, it may not happen.
(vi) Natural Factors : Natural factors like rain fall, natural calamities etc can also influence the supply. Expected rainfall raises the agricultural productivity & hence the supply increases. On the contrary, natural calamities like flood, cyclone etc. reduces the supply.
(vii) Government Policy : Government plays a vital role in changing the pattern of supply. Imposition of higher tax increases the cost of production & thus reduces the supply of goods. For example, rise in sales Tax has adverse impact on supply of the good on which it is imposed. On the other hand, decrease in tax encourages the producer to supply more – Thus, taxation policy acts as a dominant factor in moulding the supply.
All those factors are non-priced factors. So any change in these factors cause changes in supply & the supply curve may shift either upward or downward on the basis of the nature of the change of these factors.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the “Law of supply”. What are its limitations ?
Answer:
Supply refers to the quantity of a goods which are offered for sale at different prices during a given period of time. This very expression establishes that there exist certain relationship between price of a goods & quantity supplied. Law of supply tells about this relationship.
“Law of supply” speaks about the inter-relationship between the price of a goods & the quantity supplied of it. It describes the response or reaction of the sellers or producers with regard to supply of a goods to the prevailing price at a particular time-period. The price at which the goods are offered for sale (supplied) is called “Supply Price”. The supply price denotes the quantity or quantities of good supplied at different prices.
According to this law, “Other things remaing constant, the amount supplied of a good increases with the rise in its price & decreases with the fall in the price.”
So it clearly indicates a positive correlationship between price of a goods & its quantity supplied. This relationship holds goods in an unchanged situation i.e. some factors like price of related goods, Price of inputs, state of technology, Government Policy etc. should remain constant. In this situation, price of a goods & quantity supplied move in the same direction.
Illustration of law : The law of supply can be illustrated with the help of market supply schedule. Market supply schedule is a tabular expression showing a lilst of various quantities of a goods supplied at a different prices. This is purely a numerical exposition of law of supply.
MARKET SUPPLY SCHEDULE
| Numerical Analysis Price of good (inRs.) | Amount of good Supplied (in units) |
| 1 | 10 |
| 2 | 20 |
| 3 | 30 |
| 4 | 40 |
| 5 | 50 |
This numerical analysis revals that the quantity supplied of a goods increases with the rise in its price. It clearly shows a positive relation between price of a good & quantity supplied of it. When price of good X rises from Rs. 1 to Rs. 5 the quantity supplied of it increases from 10 units to 50 units. This is the theoretical aspect of “Law os supply.
Graphical Analysis.
The same theory can also be explain with the help of a graph.
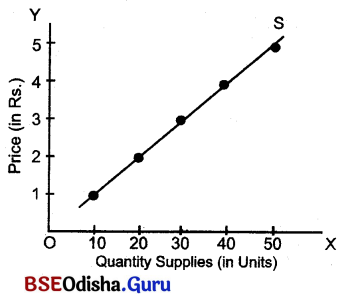
The above figure shows that with the rise in price (measured on OY-axis) the quantity supplied (Measured on OX – axis) increases. When price is Rs. 1.00 the quantity supplied is 100 units. When the price rises to Rs 2.00,3.00,4.00 & 5.00, the quantity supplied increases to 20 unit, 30 units, 40 units, 40 units respectively. It just shows the direct positive relationship between the quantity supplied & price of a goods. By joining all these points, the supply curve can be obtained. Supply curve is, thus a graphical representation of supply schedule. It slopes upwards from left to right showing a positive slope. SS is the supply curve.
LIMITATIONS
Law of supply suffers from certain limitations which are presented below.
(a) Fixed supply : In case of some goods, the supply is found to be a fixed. The supply of such goods can not be increased irrespective of any change in its price. For example, the supply of rare collections, ancient coins, ancient manuscripts can not be increased with the change in price. Thus the law of supply does not operate in these cases.
(b) Change in other things : The law of supply does not hold goods if the non-price factors do change. In case of change in technology, prices of inputs, price of related goods, Government policy etc. the direct relationship between price of a good & its supply can not be proved.
(c) Prestigious Goods : The law is also not applicable to prestigious goods bearing a symbol of social status. Because, the supply of such goods are limited. So in spite of rise in price of these goods, the supply remains unchanged.
(d) Supply of labour : Through the law of supply speaks about the direct relationship between price of a good & quantity supplied of it, yet this does not hold good in case of supply of labour. Wage is the price of labour. A rise in wage creates more income to labour for- less horns work. So the labourer at higher wage rate prefers leisure to work. As such, the supply of labour gets reduced at higher wage rate.
(e) Future Expectation of Price-Change : If future change, in price is expected, the supply is also influenced. If the there is apprehension of fall in price in future, there shall be more supply at a currect price & vice-versa. As such, the law of supply loses its theoretical validity.
(f) Clearance Sale : In case of auction or clearance sale, the law of supply does not operate. In this case, more is supplied at lower price.
(g) Change in Taste & Preference : If any change in taste & preference of the consumer is observed the supply of goods decreases without any change in price.
In spite of all these limitations, the law of supply is treated as a universal law for its practical implications & tremendous significance. No doubt, the law of supply has practical validity for which it is appreciated.
Question 3.
What is change in supply ? What are the factors responsible for this ?
Answer:
Supply is a multi-valued function comprising of certain price & non-price elements. The direct relationship between price of a good & its quantity supplied can be proved only when these non-price factors remain unchanged. The change in these non-price factors shifts the supply curve either upwards or down-wards on the basis of the nature of change. This is truly called “ change in supply”.
Change in supply denotes increase or decrease in the supply as a result of the change in the factors other then the price of goods. Rise in price of inputs, rise in price of related goods, change in technology change in Government policy leads to, change in supply. In case of such change, the supply curve shifts either upwards or downward. Thus, it needs to analyse increase or decrease in supply & to discuss about the factors causing this increase or decrease.
Increase in Supply
Increase in supply takes place when more is supplied at same price & same is supplied at lower price. This figure presented below clarifies this concept.
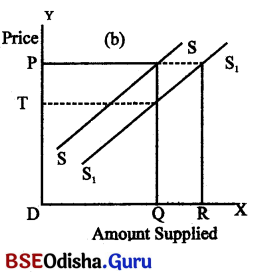
SS is the intial supply curve at OP price (on OY – axis) the quantity supplied (on OX – axis) is OQ.
In case of increase in supply, the supply curve shifts to the right (S1S1) Price remaining same it is clear that more of goods OR can be supplied at OP price due to increase in supply. On the other hand, same quantity (OQ) can also be supplied at the lower price OP because of increase in supply.
Decrease in Supply : Decrease in supply takes place when less is supplied at same price & same is supplied at higher price. The figure presented shows the concept of decrease in supply.
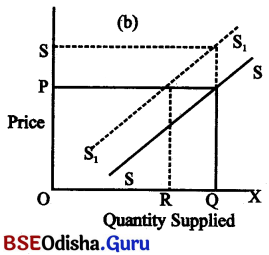
The figure shows the shift of supply curve to the left & becomes S1S1 Intially, at OP price OQ quantity is supplied. But as a result of change in supply, less (OR) is supplied at same price (OP) & same (OQ) is supplied at higher price(OS).
Causes of Increase or decrease in Supply.
(a) Change in Price of inputs : If the price of the factors of production decreases, the cost falls & there results higher profit expectation. So the supply increases even price remains constant. On the contrary, if the price of inputs rises, the supply gets reduced at the same price.
(b) Price of Related goods : The price of substitute goods & complementary goods also causes change in supply. If the price of substitutes falls, it reduces the supply of this goods & it raises the supply of the original goods in question. Its reverse case leads to decrease in supply.
(c) Change W Technology : In case of technological progress the cost of production gets reduced & its supply increases. In case of traditional technology, the supply gets decreased.
(d) Tax Policy : Imposition of tax on good leads to increase in the cost of production which reduces the supply of goods. On the other hand, if the tax rate on goods gets reduced, the supply of goods increases because of lower cost.
(e) Future Price Expectation : If the price of the goods is expected to rise in fixture, its quantity supplied at present gets reduced & in its reverse case i.e. expectation of fall in price in future, the supply at present price increases.
All these factors cause a change in supply of the goods. In all the case, the price of the goods remains unchanged, only the non-price factors leads to increase in or decrease in supply.
Group – C
Objective type Questions with Answers
I. Multiple Choice Questions with Answers :
Question 1.
In economics, supply of a goods refers to
(i) stock of the goods
(ii) total production of the goods
(iii) quantity offered for sale
(iv) All of the above
Answer:
(iii) quantity offered for sale
Question 2.
According to law of supply, supply of a goods & its price are
(i) inversely related
(ii) directly related
(iii) proportionately related
(iv) disproportionately related
Answer:
(ii) directly related
![]()
Question 3.
Supply made by the producer mainly depends on
(i) cost of production
(ii) price of the goods
(iii) willingness of the producer
(iv) ability to sell
Answer:
(ii) price of the goods
Question 4.
If the cost of production increases, the supply of goods
(i) increases
(ii) decreases
(iii) remains same
(iv) all of the above
Answer:
(ii) decreases
Question 5.
Supply is always quoted with
(i) cost of production & time period
(ii) price of goods & time period
(iii) technological development
(iv) transport cost
Answer:
(ii) price of goods & time period
Question 6.
The supply curve slopes
(i) upward from left to right
(ii) downward from left to right
(iii) like a vertical straight line
(iv) like a horizontal straight line
Answer:
(i) upward from left to right
Question 7.
When the seller has the fear of fall in price of a goods in future, its supply will
(i) increase
(ii) decrease
(iii) remains unaffected
(iv) cannot say
Answer:
(i) increase
Question 8.
Supply of commodity and stock of it are:
(i) Different concepts
(ii) All of the above
(iii) Same concepts
(iv) None of the above
Answer:
(i) Different concepts
Question 9.
With the rise in price of the substitutes supply of a goods will:
(i) Increase
(ii) Decrease
(iii) Remain the same
(iv) None of the above
Answer:
(ii) Decrease
Question 10.
With the rise in cost of production, supply tends to :
(i) Decrease
(ii) Increase
(iii) Remain the same
(iv) None of he above
Answer:
(i) Decrease
Question 11.
If the rise in price is expected in future, the supply of a commodity will:
(i) Increase
(ii) Decrease
(iii) Remain the same
(iv) None of the above
Answer:
(ii) Decrease
Question 12.
If a fall in price in future is apprehended, the supply will:
(i) Increase
(ii) Decrease
(iii) Remain the same
(iv) None of the above
Answer:
(i) Increase
Question 13.
Supply curve has a :
(i) Positive slope
(ii) Negative slope.
(iii) All of the above
(iv) None of the above.
Answer:
(i) Positive slope
Question 14.
According to Law of Supply, there exists :
(i) Indirect relationship between price and quantity supplied.
(ii) Direct relationship between price and quantity supplied
(iii) All of the above
(iv) None of the above
Answer:
(ii) Direct relationship between price and quantity supplied
Question 15.
If the price of a rare painting increases, its supply will:
(i) Increase
(ii) Decrease
(iii) Remain the same
(iv) None of the above
Answer:
(iii) Remain the same
Question 16.
Increase in supply refers to :
(i) Same supply at same price
(ii) Same supply at more price
(iii) More supply at same price
(iv) None of the above
Answer:
(iii) More supply at same price
II. Fill in the blanks :
Question 1.
Supply varies _____ with price.
Answer:
directly.
Question 2.
Price & _____ of a goods moves in same direction.
Answer:
supply
Question 3.
Supply curve & _____ schedule provides same information.
Answer:
supply
Question 4.
Supply curve has a _____ slope.
Answer:
positive
Question 5.
Supply of a goods depends on its _____
Answer:
price.
Question 6.
A fall in price of substitute goods leads to _____ in its supply.
Answer:
decrease
Question 7.
Supply of a goods _____ with the rise in price of its Substitutes.
Answer:
decreases
![]()
Question 8.
Supply tends to _____ with the rise in cost of production.
Answer:
fall
Question 9.
Supply of a commodity _____ if the rise in price is expected.
Answer:
decreases
Question 10.
Supply of a commodity _____ if a fall in prices in future is apprehended.
Answer:
increases
Question 11.
Supply curve has a _____ slope.
Answer:
positive
Question 12.
Supply remains _____ to any price change of rare paintings.
Answer:
Unchanged
Question 13.
_____ in supply refers to more supply at same price or same supply at less price.
Answer:
Increase
Question 14.
Decrease in supply refers to _____ supply at same price.
Answer:
less
III. Correct the Sentences :
Question 1.
Supply refers to the total quantities of goods produced during a particular time period.
Answer:
Incorrect:
Correct: Supply refers to the quantities of goods offered for sale at different prices during a particular time period.
Question 2.
Stock is a part of the supply.
Answer:
Incorrect :
Correct: Supply is a part of the stock.
Question 3.
Supply Schedule is a numerical statement of law of supply.
Answer:
Correct:
Question 4.
Supply varies indirectly with price.
Answer:
Incorrect:
Correct: Supply varies directly with price.
Question 5.
Price & supply of a good moves in opposite direction.
Answer:
Incorrect:
Correct: Price & supply of a goods moves,in same direction.
Question 6.
Supply curve & supply schedule provides same information.
Answer:
Correct:
Question 7.
Supply curve has a negative slope.
Answer:
Incorrect:
Correct: Supply curve has a positive slope.
Question 8.
Price of a goods depends on its supply.
Answer:
Incorrect:
Correct: Supply of a goods depends on its price.
Question 9.
Supply of a goods is more when its price is higher.
Answer:
Correct:
Question 10.
A fall in price of a substitute goods leads to increase in its supply.
Answer:
Incorrect:
Correct: A fall in price of substitute goods leads to decrease in its supply.
Question 11.
Change in supply can be explained on same supply curve.
Answwer:
Incorrect:
Correct: Change in supply can be explained on different supply curve.
Question 12.
Supply curve shifts upward in case of increase in supply.
Answer:
Incorrect:
Correct: Supply curve shifts downward in case of increase in supply.
Question 13.
Supply of a commodity and stock of it are same concepts.
Answer:
Incorrect.
Correct: Supply of a commodity and stock of it are different concepts.
Question 14.
Supply of a goods increases with the rise in price of its substitutes.
Answer:
Incorrect.
Correct: Supply of a goods decreases with the rise in price of its substitutes.
Question 15.
Supply tends to increase with the rise in cost of production.
Answer:
Incorrect.
Correct: Supply tends to fall with the rise in cost of production.
![]()
Question 16.
Supply of a commodity increases if the rise in price is expected in future.
Answer:
Incorrect.
Correct: Supply of a commodity decreases if the rise in price is expected.
Question 17.
Supply of a commodity decreases if a fall in price in future is apprehended.
Answer:
Incorrect.
Correct: Supply of a commodity increases if a fall in prices in future is apprehended.
Question 18.
Supply curve has a negative slope.
Answer:
Incorrect.
Correct: Supply curve has a positive slope.
Question 19.
According to Law of supply there exists direct relationship between price and quantity supplied.
Answer:
Correct.
Question 20.
If the price of a rare painting increases, its supply increases.
Answer:
Incorrect.
Correct: Supply remains unaffected to any price change of rare paintings.
Question 21.
Increase in supply refers to same supply at same price or same supply at more price.
Answer:
Incorrect.
Correct: Increase in supply refers to more supply at same price or same supply at less price.
Question 22.
Decrease in supply refers to less supply at same price.
Answer:
Correct.
IV. Answer the following questions in one word :
Question 1.
What is supply ?
Answer:
Supply refers to quantity of commodity offered for sale at different given prices during a prticular time period.
Question 2.
What is supply function ?
Answer:
The supply function shows the functional relationship between the supply of a goods & its price-level, while other things remaining constant.
Question 3.
What sort relationship exists between price of a goods & its quantity supplied ?
Answer:
There exists direct relationship between price of a goods & its quantity supplied.
Question 4.
What happens to supply of a goods if the price of its substitute rises ?
Answer:
The supply of goods decrease if the price of its substitutes rises.
Question 5.
What happens to supply of a goods if its price of inputs rises ?
Answer:
The supply of goods decreases if its price inputs rises.
Question 6.
What happens to supply of goods if higher price is expected in future.
Answer:
The supply of goods decreases if higher price is expected in future.
Question 7.
What is a supply schedule ?
Answer:
Supply schedule is a tabular expression showing various quantities of goods offered for sale at each prices during time period.
Question 8.
What is law of supply ?
Answer:
Law of supply states that more is supplied at higher price & less is supplied at lower price in an unchanged situation.
Question 9.
What similarity exists between supply schedule & supply curve ?
Answer:
Both supply schedule & supply curve explains law of supply.
Question 10.
What supply curve ?
Answer:
Supply curve is a n upwards sloping curve showing more quantities supplied at higher price & vice-versa.
Question 11.
What is the slope if supply curve ?
Answer:
Supply curve has positive slope.
Question 12.
In which case law of supply does not operate ?
Answer:
In case of Auction sale, the law of supply does not operate.
Question 13.
What is the shape of the supply curve ?
Answer:
Supply curve slopes upward from left to right.
Question 14.
State a reason for which supply curve slopes upward ?
Answer:
Profit motive of the producer causes upward sloping of supply curve.
Question 15.
What is change in supply ?
Answer:
Change in supply refers to increase or decrease in supply that happens due to the factors other than the price of goods.
