Odisha State Board CHSE Odisha Class 12 Math Notes Chapter 4 Matrices will enable students to study smartly.
CHSE Odisha 12th Class Math Notes Chapter 4 Matrices
It is a system of mn numbers arranged in a rectangular system of m rows and n columns.
Example : \(\left(\begin{array}{lll}
a_{11} & a_{12} & a_{1 n} \\
a_{21} & a_{22} & a_{2 n} \\
a_{m_1} & a_{m_2} & a_{m_n}
\end{array}\right)\) is a m × n matrix.
Note : We write the above matrix in short as [aij]m×n or [aij]m×n or ||aij||m×n.
Important types matrices:
(a) Square matrix:
It is a matrix where the number of rows are equal to the number of columns.
(b) Null (zero) matrix:
If all the entries of a matrix are zero, then the matrix is a zero matrix denoted by 0m×n.
(c) Diagonal matrix:
It is a square matrix in which all the elements except those in main (or leading) diagonal are zero.
(d) Unit matrix:
It is a diagonal matrix where all the elements in the leading (main) diagonal are one.
(e) Scalar matrix:
It is a diagonal matrix with all the elements in the leading (main) diagonal are α (α ≠ 0 or 1).
(f) Singular matix:
A square matrix ‘A’ is singular iff |A| = 0, otherwise it is a non singular matrix.
(g) Symmetric matrix:
A square matrix is symmetric if A = A’ and skew-symmetric if A = -A’.
![]()
Matrix algebra:
(a) Addition and subtraction:
If A = [aij]m×n and B = [bij]m×n then A ± B = [aij ± bij]m×n
(b) Scalar multiplication:
If A = [aij]m×n then for any scalar ‘k’
kA = [kaij]m×n
(c) Matrix multiplication:
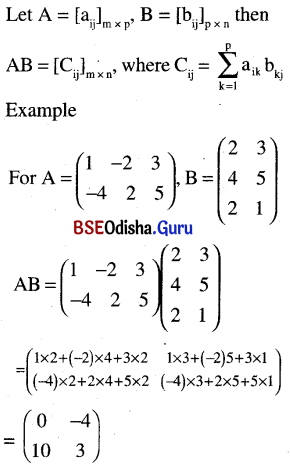
Properties:
1. Matrix addition is commutative as well as associative.
2. 0m×n is the additive identity.
3. A is the zero additive inverse of A.
4. We can add or subtract matrices if they are of same order.
5. We can multiply two matrices if the number of columns of 1st is equal to the number of rows of 2nd.
6. Matrix multiplication is non commutative but associative.
7. Matrix multiplication is distributive over addition.
8. AB = 0 ≠ A = 0 or B = 0 for two matrices A and B. Also AB = AC ≠ B = C.
9. If A is a square matrix of order n then
In = 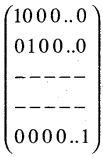 is the multiplicative identity.
is the multiplicative identity.
Transpose and adjoint of a matrix:
(a) The transpose of a matrix A = [aij]m×n is AT or A’ = [aji]n×m.
Properties:
(i) (A’)’ = A
(ii) (A ± B)’ = A’ ± B’
(iii) (AB)’ = B’A’
(iv) (KA)’ = KA’
(v) Any matrix A can be expressed as sum of a symmetric and a skew-symmetric matrix as
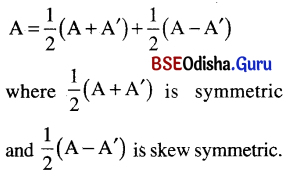
(b) Adjoint of a matrix:
If A is a square matrix then Adj A = The transpose of the matrix of co-factors
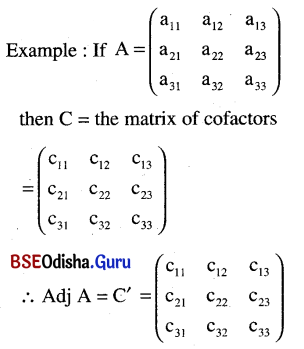
Properties:
1. (Adj A) A = A (Adj A) = |A|In
∴ A-1 = \(\frac{{Adj} A}{|~A|}\)
2. |Adj A| = An-1
3. Adj (AdjA) = |A|n-2A
4. (AdjA)’ = Adj (A’)
5. (AB)-1 = B-1A-1
![]()
Solution of system of linear equations (matrix method):
Let the system of linear equations is
a1x + b1y + c1z = d1
a2x + b2y + c2z = d2
a3x + b3y + c3z = d3
Let
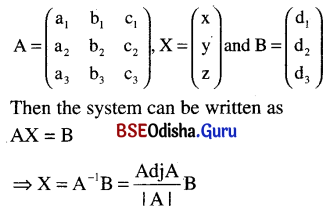
Note: If the system is homogeneous i.e. d1 = d2 = d3 = 0, then the system has a trivial solution x = 0, y = 0, z = 0 for |A| ≠ 0. In case |A| = 0 then the system has infinitely many solutions.
