Odisha State Board BSE Odisha 8th Class Geography Important Questions Chapter 2 ଭୂ-ସମ୍ବଳ, ଜଳ ସମ୍ବଳ, ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଉଭିଦ ଓ ବନ୍ୟପ୍ରାଣୀ, ଖଣିଜ ଓ ଶକ୍ତି ସମ୍ବଳ Important Questions and Answers.
BE Odisha Class 8 Geography Important Questions Chapter 2 ଭୂ-ସମ୍ବଳ, ଜଳ ସମ୍ବଳ, ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଉଭିଦ ଓ ବନ୍ୟପ୍ରାଣୀ, ଖଣିଜ ଓ ଶକ୍ତି ସମ୍ବଳ
Subjective Type Questions With Answers
ଦୀର୍ଘ ଉତ୍ତରମୂଳକ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନୋତ୍ତର
Question 1.
ଭୂସମ୍ବଳର ବିତରଣ ବିଷୟରେ ସଂକ୍ଷେପରେ ଆଲୋଚନା କର |
Answer:
- ଭୂପୃଷ୍ଠ ସୁଲଭାଗ ଓ ଜଳଭାଗକୁ ନେଇ ଗଠିତ। ସ୍ଥଳଭାଗ ଏକ ମୁଖ୍ୟ ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ସମ୍ବଳ।
- ପୃଥିବୀ ପୃଷ୍ଠର ମୋଟ୍ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରଫଳର ଶତକଡ଼ା ୨୯ ଭାଗ ସ୍ଥଳଭାଗ।
- ଏହି ସ୍ଥଳଭାଗ ସାତଗୋଟି ମହାଦେଶକୁ ନେଇ ଗଠିତ ।
- ଏସିଆ, ଇଉରୋପ, ଉତ୍ତର ଆମେରିକା, ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆମେରିକା, ଆଫ୍ରିକା, ଅଷ୍ଟ୍ରେଲିଆ, ଆଣ୍ଟାର୍କଟିକା ।
- କ୍ଷେତ୍ରଫଳ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିରୁ ଏସିଆ ବୃହତ୍ତମ ଏବଂ ଅଷ୍ଟ୍ରେଲିଆ କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ରତମ।

Question 2.
ଉଚ୍ଚତା ଭେଦରେ ଭୂସମ୍ବଳକୁ କେତେ ଭାଗରେ ଭାଗ କରାଯାଇଛି ? ସେଗୁଡ଼ିକ କ’ଣ କ’ଣ ? ଉଦାହରଣ ସହ ଲେଖ।
Answer:
- ଉଚ୍ଚତା ଭେଦରେ ସମ୍ବଳକୁ ତିନିଭାଗରେ ଭାଗ କରାଯାଇଛି; ଯଥା—(କ) ପାର୍ବତ୍ୟଭୂମି, (ଖ) ମାଳଭୂମି ଓ (ଗ) ସମତଳ ଭୂମି।
- ଅଧିକ ଉଚ୍ଚତାବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ପାହାଡ଼ ଓ ପର୍ବତଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ପାର୍ବତ୍ୟ ଭୂମି କୁହାଯାଏ। ଉଦାହରଣ – ହିମାଳୟ, ଆଲପସ୍, ରକି ଓ ଆଣ୍ଡିଜ୍ ।
- ଅଳ୍ପ ଉଚ୍ଚନୀଚ ହୋଇଥିବା ବିସ୍ତୀର୍ଷ ପଥୁରିଆ ଅଞ୍ଚଳକୁ ମାଳଭୂମି କୁହାଯାଏ । ଉଦାହରଣ – ତିବ୍ବତ, ଗୋବି, ପାଟାଗୋନିଆ, ସ୍କାଣ୍ଡିନେଭିଆ ଇତ୍ୟାଦି ।
- ସମୁଦ୍ରପତ୍ତନରୁ ଅଳ୍ପ ଉଚ୍ଚରେ ଥିବା ପ୍ରାୟ ସମାନ ଉଚ୍ଚତା ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ଅଞ୍ଚଳକୁ ସମତଳ ଭୂମି କୁହାଯାଏ। ଉଦାହରଣ – ସାଇବେରିଆ, କେନ୍ଦ୍ରୀୟ ସମତଳଭୂମି, ନଦୀ ଉପତ୍ୟକା, ତ୍ରିକୋଣଭୂମି ।
Question 3.
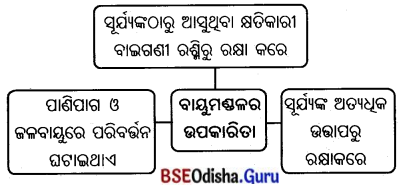
ଭୂସମ୍ବଳ ସଂରକ୍ଷଣର ଉପାୟଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଲେଖ ।
Answer:
- ପାର୍ବତ୍ୟ ଓ ପାହାଡ଼ିଆ ଅଞ୍ଚଳର ତୀଖ ଗଡ଼ାଣି ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ବୃକ୍ଷରୋପଣ କରାଗଲେ ମାଟି ଧସିବା ବନ୍ଦ ହୋଇଯିବ ଏବଂ ମୃତ୍ତିକାକ୍ଷୟ ରୋକାଯାଇପାରିବ ।
- ପର୍ବତର ଗଡ଼ାଣିଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ବୃଷ୍ଟିଜଳ ନିମ୍ନାଞ୍ଚଳକୁ ନିଷ୍କାସନ ପାଇଁ ବ୍ୟବସ୍ଥା କରିବା ପାଇଁ ନାଳ ଖନନ କରିବା ।
- ସମୁଦ୍ରକୂଳରେ ବାଲୁକାଶଯ୍ୟାରେ ଲୁଣାଜଙ୍ଗଲ ରକ୍ଷାକରିବା ସହ ଅଧିକ ଝାଉଁବଣ ସୃଷ୍ଟି କରିବା ।
- ନୂତନ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ସୃଷ୍ଟି କରିବାସହ କ୍ଷୟପ୍ରାପ୍ତ ବନଭୂମିରେ ବୃକ୍ଷରୋପଣ କରିବା ଉଚିତ ।
- ନଦୀର ଅନେକ ସ୍ଥାନରେ ବନ୍ଧବାଡ଼, ବୁରୁଜ ଆଦି ନିର୍ମାଣ ଦ୍ଵାରା ନଦୀପାର୍ଶ୍ଵରୁ ଅତଡ଼ା ଖସିବା ହ୍ରାସ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଚାରଣଭୂମିରେ ପଶୁଚାରଣ ନିୟନ୍ତ୍ରିତ କରିବାଦ୍ଵାରା ଭୂ-
ସମ୍ବଳର ସଂରକ୍ଷଣ ହୋଇଥାଏ ।

Question 4.
ମୃତ୍ତିକା ସଂରକ୍ଷଣର ବିଭିନ୍ନ ଉପାୟଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଲେଖ ।
Answer:
- ମୃତ୍ତିକାର ଆର୍ଦ୍ରତା ଅଧିକ ଦିନ ରହିଲେ ମୃଭିକାକ୍ଷୟ ବିଳମ୍ବିତ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ସମାନ ଉଚ୍ଚତାବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ସ୍ଥାନଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ପ୍ରତିବନ୍ଧକ ହୁଡ଼ା ବନ୍ଧଦ୍ଵାରା ଯୋଗକରିବା ଓ ତାହା ସାମନାରେ ଜଳ ସଂଗୃହୀତ ପାଇଁ ନାଳୀ ବ୍ୟବସ୍ଥା କରିବାଦ୍ଵାରା ମୃତ୍ତିକା ସଂରକ୍ଷଣ ହୋଇପାରିବ ।
- ଜଳ ପ୍ରବାହର ବେଗ ହ୍ରାସ କରି ମୂର୍ତ୍ତିକା କ୍ଷୟ ରୋକାଯାଇପାରିବ ।
- ସମାନ ଉଚ୍ଚତାରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ ପର୍ବତ ଓ ମାଳଭୂମିର ଗଡ଼ାଣିଆ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଭୂମିକୁ ପାହାଚ ଆକାରରେ କାଟି କ୍ଷେତ୍ର ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ କରି କୃଷିକାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କଲେ ମୃତ୍ତିକାକ୍ଷୟ କମ୍ ହେବ ଏବଂ ମୃରିକା ସଂରକ୍ଷଣ ହୋଇପାରିବ ।
- ଉପକୂଳ ଶୁଷ୍କ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ବାୟୁର ପ୍ରତିକୂଳ ଦିଗରେ ଧାଡ଼ି ଧାଡ଼ି ବୃକ୍ଷରୋପଣ କରିବା ଉଚିତ । ପଶୁଚାରଣକୁ ବନ୍ଦ କରିବାଦ୍ଵାରା ମୃରିକା କ୍ଷୟ ନିରୋଧ ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
- ମୃତ୍ତିକା ସଂରକ୍ଷଣର କୁପରିଣାମ ଓ ଏହାର ଗୁରୁତ୍ଵ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧରେ ଜନସଚେତନତା ସୃଷ୍ଟି କରିବା ଆବଶ୍ୟକ ।
Question 5.
ଖଣିଜ ସମ୍ବଳର ସଂରକ୍ଷଣ ପାଇଁ କେଉଁ ପନ୍ଥା ଅବଲମ୍ବନ କରାଯାଉଅଛି ଉଲ୍ଲେଖ କର ।
Answer:
- ତୁ ବଦଳରେ ବିକଳ୍ପ ବ୍ୟବସ୍ଥା ଅବଲମ୍ବନ କରିବା ଆବଶ୍ୟକ; ଯଥା- ଧାତୁ ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତେ ପ୍ଲାଷ୍ଟିକ୍ ବ୍ୟବହାର କଲେ ଖଣିଜ ସମ୍ବଳର ସଂରକ୍ଷଣ କି ଛି ମାତ୍ର ରେ ହୋଇପାରିବ ।
- ଖଣିଜପିଣ୍ଡ ଖଣିରୁ ଉତ୍ତୋଳନ କରିବା ସମୟରେ ଖଣିସ୍ଥଳରୁ ନିଷ୍କାସନ ସ୍ଥଳକୁ ପରିବହନବେଳେ ଖଣିଜ ନଷ୍ଟ ନ ହେବା ପାଇଁ ଅଧିକ ଧ୍ୟାନ ଦେବା ଆବଶ୍ୟକ ।
- ତମ୍ବା ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଉଥିବା ସ୍ଥାନରେ ବିଶେଷ କରି ବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ସରବରାହ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ଆଲୁମିନିୟମ୍ ତାରର ବ୍ୟବହାର ଏବଂ ମୁଦ୍ରା ପ୍ରଚଳନରେ ତମ୍ବା ବଦଳରେ ବ୍ରୋଞ୍ଜର ବ୍ୟବହାର ଦ୍ଵାରା ଧାତୁର ସଂରକ୍ଷଣ କରାଯାଇପାରିବ ।
- ପୁନଃଚକ୍ରଣ ପଦ୍ଧତିରେ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ କେତେକ ଖଣିଜଦ୍ରବ୍ୟକୁ ପୁଣି କାର୍ଯ୍ୟରେ ଲଗାଯାଇପାରିବ ।
- ନିମ୍ନମାନ ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ଖଣିଜପିଣ୍ଡର ବହୁଳ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରି ଉଚ୍ଚମାନ ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ଖଣିଜପିଣ୍ଡର କମ୍ ବ୍ୟବହାର କଲେ ଖଣିଜପିଣ୍ଡର ସଂରକ୍ଷଣ ହୋଇପାରିବ ।
Question 6.
ଭାରତରେ ଅଣପାରମ୍ପରିକ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ସର କାର୍ଯ୍ୟକାରିତା ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧରେ ଆଲୋଚନା କର ।
Answer:
- ଅଣପାରମ୍ପରିକ ଶକ୍ତି ମଧ୍ୟରେ ସୌରଶକ୍ତି, ପବନ ଶକ୍ତି, ଜୁଆରଶକ୍ତି, ବାୟୋଗ୍ୟାସ୍, ଭୂତାପଜ ଶକ୍ତି ଆଦି ନୂତନ ଶକ୍ତିଉତ୍ସର ଗୁରୁତ୍ଵ ବୃଦ୍ଧିପାଉଛି ।
- ସୌରଶକ୍ତି : ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟଙ୍କର ଉତ୍ତାପ ଓ ଆଲୋକକୁ ସୌର ସେଲ୍ରେ ଧରି ରଖାଯାଇ ବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ଉତ୍ପାଦନ କରାଯାଏ । ଭାରତ ଏକ କ୍ରାନ୍ତିମଣ୍ଡଳୀୟ ଦେଶ ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ ଏଠାରେ ପ୍ରଚୁର ସୌରଶକ୍ତି ମିଳିଥାଏ । ଏହି ସୌରଶକ୍ତିକୁ ରାସ୍ତା ଆଲୋକ, ଟ୍ରାଫିକ୍ ସିଗ୍ନାଲ, ସୌରଚୁଲ୍ଲା ଓ ସୌରକୁକର୍ରେ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଏ ।
- ପବନ ଶକ୍ତି : ସମୁଦ୍ର ଉପକୂଳମାନଙ୍କରେ ବାୟୁର ବେଗ ଅଧିକ ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ ସେଠାରେ ଏକାଧିକ ପବନକଳଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ନେଇ ପବନ ଫାର୍ମମାନ ଗଠିତ ହୋଇଅଛି । ପବନ କଳରେ ଥୁବା ପବନ ଚକ୍ରୀକୁ ଜେନେରେଟର ସହ ସଂଯୁକ୍ତ କରାଯାଇ ବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନ କରାଯାଉଛି । ଭାରତର ଉପକୂଳବର୍ତ୍ତୀ ଅଞ୍ଚଳ କର୍ଣାଟକ, ତାମିଲନାଡୁ, ଓଡ଼ିଶା, ଆଣ୍ଡାମାନ-ନିକୋବର ଦ୍ଵୀପପୁଞ୍ଜ ଓ ଲାକ୍ଷାଦ୍ଵୀପରେ ପବନଶକ୍ତିକୁ ଉପଯୋଗ କରାଯାଇ ବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନ କରାଯାଉଅଛି ।
- ଭୂତାପଜ ଶକ୍ତି : ପୃଥିବୀର ଆଭ୍ୟନ୍ତରୀଣ ତାପରୁ ଉତ୍ପନ୍ନ ଭୂତାପଜ ଶକ୍ତିକୁ ବିନିଯୋଗ କରି ବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନ କରାଯାଉଅଛି । ହିମାଚଳ ପ୍ରଦେଶର ମନିକରଣ ଏବଂ ଲଦାଖର ସୁଗା ଉପତ୍ୟକାରେ ଭୂତାପଜ କେନ୍ଦ୍ର ସ୍ଥାପିତ ହୋଇଛି ।
- ଜୁଆର ଶକ୍ତି : ସାମୁଦ୍ରିକ ଜୁଆରକୁ ଉପଯୋଗ କରି ଯେଉଁ ଶକ୍ତି ବାହାର କରାଯାଏ, ତାହାକୁ ଜୁଆର ଶକ୍ତି କୁହାଯାଏ । ଭାରତର ଗୁଜରାଟର କାୟେ ଉପକୂଳ, ପଶ୍ଚିମବଙ୍ଗର ସୁନ୍ଦରବନ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଜୁଆର ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନ କରାଯାଉଅଛି ।।
- ବାୟୋଗ୍ୟାସ୍ : ଜୈବିକ ବର୍ଜ୍ୟବସ୍ତୁରୁ ବ୍ୟାକ୍ଟେରି ଆ ସାହାଯ୍ୟରେ ବାୟୋଗ୍ୟାସ୍ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ କରାଯାଇ ରନ୍ଧନ ଓ ଆଲୋକପାଇଁ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଏ ।
Question 7.
କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଦେଖାଯାଉଥିବା ଅରଣ୍ୟ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧରେ ଏକ ବିବରଣୀ ପ୍ରଦାନ କର ।
Answer:
- କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ ଅଞ୍ଚଳର ଅରଣ୍ୟ ସାଧାରଣତଃ 5 ଉତ୍ତରରୁ 25° ଉତ୍ତର ଓ 5° ଦକ୍ଷିଣରୁ 25° ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଅକ୍ଷାଂଶ ମଧ୍ଯରେ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
- କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ମୌସୁମୀ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ତଥା ପଶ୍ଚିମୋଚୀ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ । ଋତୁକାଳୀନ ବର୍ଷା ହେଉଥିବାରୁ ଏକ ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ ଋତୁରେ ଏଗୁଡ଼ିକ ପତ୍ରଝଡ଼ା ଦେଇଥା’ନ୍ତି ।
- ଏହି ଅରଣ୍ୟରେ ଶାଳ, ପିଆଶାଳ, ଶିଶୁ, ବାଉଁଶ ଇତ୍ୟାଦି ବୃକ୍ଷ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
- ଭାରତର ପୂର୍ବାଞ୍ଚଳ, ପୂର୍ବଘାଟ ପର୍ବତମାଳାର ପୂର୍ବପାର୍ଶ୍ବ ଛୋଟନାଗପୁର ମାଳଭୂମି, ଓଡ଼ିଶା, ଛତିଶଗଡ଼ ଓ ମଧ୍ୟପ୍ରଦେଶର ପାର୍ବତ୍ୟାଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଏହି ଅରଣ୍ୟ ବହୁଳଭାବେ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଗୋଚର ହୁଏ ।
- ପୃଥିବୀର ଦକ୍ଷିଣ-ପୂର୍ବ ଏସିଆ, ଉତ୍ତର ଅଷ୍ଟ୍ରେଲିଆ, ପୂର୍ବ ଆଫ୍ରିକା, ପୂର୍ବ ବ୍ରାଜିଲ, ପଶ୍ଚିମ ଭାରତୀୟ ଦ୍ଵୀପପୁଞ୍ଜରେ -ଏହି ଅରଣ୍ୟ ରହିଛି ।

Question 8.
ଅରଣ୍ୟର ଉପକାରିତା ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧରେ ବୁଝାଇ ଲେଖ ।
Answer:
- ଅରଣ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକ ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ପରିବେଶରେ ଗଢ଼ିଉଠିଥିବା ଅମୂଲ୍ୟ ସମ୍ବଳ । ଏଥିରେ ଥିବା ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଉଦ୍ଭଦ ମନୁଷ୍ୟର ବିବିଧ ବ୍ୟବହାରରେ ଲାଗିଥାଏ ।
- ଅରଣ୍ୟ ପ୍ରାଣୀମାନଙ୍କର ଆଶ୍ରୟସ୍ଥଳ । ଅରଣ୍ୟର ବୃକ୍ଷରାଜି ଅମ୍ଳଜାନ ଯୋଗାଇଥାଏ ।
- ଭୂଗର୍ଭସ୍ଥ ଜଳ ସଞ୍ଚୟରେ ସାହାଯ୍ୟ କରେ ଏବଂ ମୃଭିକା . ଅବକ୍ଷୟ ରୋକିବାରେ ସହାୟକ ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
- ଅରଣ୍ୟରୁ ସ୍ଵାଇଘାସ, ଅରଣ୍ୟର କାଠ ଇତ୍ୟାଦିକୁ କଞ୍ଚାମାଲରୂପେ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରି କାଗଜ ଉତ୍ପାଦନ କରାଯାଏ ।
- ଅରଣ୍ୟର ଫଳମୂଳ, ମଞ୍ଜି, କ୍ଷୀର, ଅଠା ଓ ଔଷଧୀୟ ପଦାର୍ଥ| ଆଦି ମିଳିଥାଏ । ଏହିପରି ଅରଣ୍ୟର ଉପକାର ଅନେକ ।
Question 9.
ଭାରତରେ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଗୋଚର ହେଉଥିବା ବିଭିନ୍ନ ପ୍ରକାର ମୃତ୍ତିକାର ବିତରଣ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧରେ ଆଲୋଚନା କର ।
Answer:
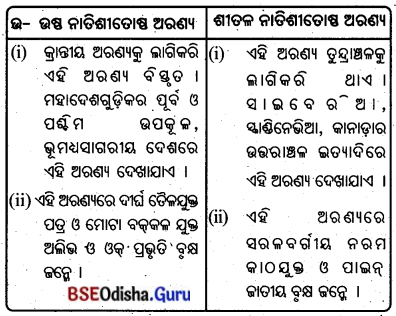
- ଭାରତରେ ମୁଖ୍ୟତଃ ପଟୁ ମୃରିକା, କୃଷ୍ଣ ଓ କୃଷ୍ଣଲୋହିତ ମୃରିକା, ଲୋହିତ ଓ ପୀତ ମୃତ୍ତିକା, ଅରଣ୍ୟ ମୃତ୍ତିକା, ମରୁସ୍ଥଳୀ ମୃତ୍ତିକା, ଲାଟେରାଇଟ୍ ମୃରିକା, ଲୁଣା ଓ କ୍ଷାରୀୟ ମୃତ୍ତିକା ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଗୋଚର ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
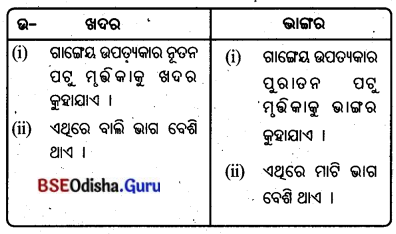
- ପଟୁ ମୃଭିକା ଭାରତର ସମସ୍ତ ନଦୀ ଉପତ୍ୟକା ଓ ତ୍ରିକୋଣଭୂମି ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଦେଖାଯାଏ । ଗାଙ୍ଗେୟ ଉପତ୍ୟକାର ନୂତନ ପଟୁ ମୃତ୍ତିକାକୁ ଖଦର ଓ ପୁରାତନ ପଟୁ ମୃତ୍ତିକାକୁ ଭାଙ୍ଗର କୁହାଯାଏ ।
- କୃଷ୍ଣ ଓ କୃଷ୍ଣଲୋହିତ ମୁଭିକା ମହାରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର, ଗୁଜରାଟ, ଆନ୍ଧ୍ରପ୍ରଦେଶ, ତାମିଲନାଡୁ ଓ ମଧ୍ୟପ୍ରଦେଶର କେତେକ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
- ଲୋହିତ ଓ ପୀତ ମୃତ୍ତିକା ମୁଖ୍ୟତଃ ଛତିଶଗଡ଼, ଝାଡ଼ଖଣ୍ଡ, ଓଡ଼ିଶା, ମହାରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର, କର୍ଣ୍ଣାଟକ ଓ ଆନ୍ଧ୍ର ପ୍ରଦେଶରେ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
- ଅରଣ୍ୟ ମୃତ୍ତିକା ହିମାଳୟ, ପୂର୍ବଘାଟ, ପଶ୍ଚିମଘାଟ ଓ ମାଳଭୂମି ଅଞ୍ଚଳମାନଙ୍କରେ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
- ମରୁସ୍ଥଳୀ ମୃରିକା ରାଜସ୍ଥାନ, ହରିୟାଣା ଓ ପଞ୍ଜାବରେ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଗୋଚର ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
- ଦକ୍ଷିଣାତ୍ୟ ମାଳଭୂମି, କର୍ଣ୍ଣାଟକ, ମହାରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର, ମଧ୍ୟପ୍ରଦେଶ, ଓଡ଼ିଶା ଓ ଝାଡ଼ଖଣ୍ଡରେ ଲାଟେରାଇଟ୍ ମୃତ୍ତିକା ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
- ଲୁଣା ଓ କ୍ଷାରୀୟ ମୃତ୍ତିକା ସମୁଦ୍ର ଉପକୂଳ, ଶୁଷ୍କ ଓ ଅଶୁଷ୍କ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଏବଂ ପିଟ୍ ଓ ଜୈବ ମୃଭିକା କେରଳ, ଓଡ଼ିଶା, ପଶ୍ଚିମବଙ୍ଗ ଓ ତାମିଲନାଡୁର ଉପକୂଳବର୍ତ୍ତୀ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
Question 10.
ଓଡ଼ିଶାରେ ଦେଖାଯାଉଥିବା ମୃରିକାର ବିତରଣ ବିଷୟରେ ଏକ ବିବରଣୀ ପ୍ରଦାନ କର ।
Answer:
- ଓଡ଼ିଶାରେ ମୁଖ୍ୟତଃ ପଟୁ ମୃରିକା, ଲୁଣା ମୃରିକା, ଲାଟେରାଇଟ୍ ା ମୃରିକା, ଲାଲ୍ ମୃତ୍ତିକା, ବାଦାମୀରଙ୍ଗର ମୃତ୍ତିକା ଦେଖିବାକୁ ମିଳେ ।
- ପଟୁ ମୃତ୍ତିକା ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ନଦୀ ଉପତ୍ୟକା ଓ ତ୍ରିକୋଣଭୂମି ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଦେଖାଯାଏ । ମହାନଦୀ, ବ୍ରାହ୍ମଣୀ, ବୈତରଣୀ, ବୁଢ଼ାବଳଙ୍ଗ, ସୁବର୍ଣ୍ଣରେଖା ଓ ଋଷିକୁଲ୍ୟା ଆଦି ନଦୀର ଅବବାହିକା ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ପଟୁ ମୃତ୍ତିକା ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
- ଲୁଣା ମୃରିକା ସମୁଦ୍ର ଉପକୂଳବର୍ତ୍ତୀ ଅଞ୍ଚଳ ଓ ତ୍ରିକୋଣଭୂମି ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
- ଲାଟେରାଇଟ୍ ମୃରିକା ପର୍ବତମାଳାର ପାଦଦେଶରେ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
- ଲାଲ୍ମାଟି ଓ ବାଦାମୀ ରଙ୍ଗର ମୃତ୍ତିକା ପାହାଡ଼ିଆ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଦେଖାଯାଏ । ଓଡ଼ିଶାର କେନ୍ଦୁଝର, ସୁକିନ୍ଦା, ସୁନ୍ଦରଗଡ଼ ଓ ମୟୂରଭଞ୍ଜ ଜିଲ୍ଲାର କେତେକ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଏହି ପ୍ରକାର ମୃତ୍ତିକା ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
- କଳାମାଟି ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଅନୁଗୁଳ, ଆଠମଲ୍ଲିକ, ବୌଦ୍ଧ ପ୍ରଭୃତି ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଦେଖିବାକୁ ମିଳେ ।

Question 11.
ସ୍ଥଳଭାଗରେ ଜଳର ବିତରଣ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧରେ ଉଲ୍ଲେଖ କର ।
Answer:
- ପୃଥିବୀର ସ୍ଥଳଭାଗରେ ଜଳରାଶି ନଦୀ, ହ୍ରଦ ଆକାରରେ ବିସ୍ତାରିତ ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
- ପୃଥିବୀପୃଷ୍ଠରେ ମୁଖ୍ୟ ନଦୀଗୁଡ଼ିକ ହେଲେ ନୀଳନଦୀ, କଙ୍ଗୋ, ’ଆମାଜନ, ମିସୋରୀ, ମିସିସିପି, ଇରାବତୀ, ହୋୟାଂହୋ, ସିକିୟାଙ୍ଗ, ଓଡ଼, ଇନ୍ସି, ଲେନା, ଟାଇଗ୍ରୀସ୍, ଇଉଫ୍ରେଟିସ୍, ଭଲ୍ଗା, ରାଇନ୍, ରୋନ୍, କଙ୍ଗୋ, ମରେ- ଡାଲିଂ ଓ ପାରାନା ପାରାଗୁଏ ଇତ୍ୟାଦି ।
- ପୃଥିବୀପୃଷ୍ଠରେ ମୁଖ୍ୟ ହ୍ରଦଗୁଡ଼ିକ ହେଲେ ଆରାଲ୍, ବୈକାଲ୍, କାସ୍ପିୟାନ୍, ଇରି, ଓଣ୍ଟାରିଓ, ସୁପିରିୟର, ମିଚିଗାନ୍, ହ୍ୟୁରନ, ଭିକ୍ଟୋରିଆ, ଆଲବର୍ଟ ଓ ଏଡଓ୍ବାର୍ଡ଼ ।
- ଭାରତର ମୁଖ୍ୟ ନଦୀଗୁଡ଼ିକ ହେଲେ ଗଙ୍ଗା, ବ୍ରହ୍ମପୁତ୍ର, ଗୋଦାବରୀ, କୃଷ୍ଣା, କାବେରୀ, ନର୍ମଦା, ତାପ୍ତି, ସତ୍ଵଲେଜ, ରାବି ଓ ବେୟାସ୍ ! ଏଠାରେ ହ୍ରଦଗୁଡ଼ିକ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଚିଲିକା, ଡାଲ ଓ ସମ୍ବର ଆଦି ପ୍ରଧାନ ।
- ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ପ୍ରଧାନ ନଦୀମାନଙ୍କ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ମହାନଦୀ, ବ୍ରାହ୍ମଣୀ, ବୈତରଣୀ, ସୁବର୍ଣ୍ଣରେଖା, ଋଷିକୁଲ୍ୟା ଇତ୍ୟାଦି ଉଲ୍ଲେଖଯୋଗ୍ୟ । ହ୍ରଦଗୁଡ଼ିକ ହେଲେ ଚିଲିକା ଓ ଅଂଶୁପା ।
Question 12.
ପୃଥିବୀର ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ ଅରଣ୍ୟର ଅବସ୍ଥିତି, ବିଶେଷତ୍ଵ ଓ ବିତରଣ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧରେ ଲେଖ ।
Answer:
- ଉଭୟ ଗୋଲାର୍ଦ୍ଧରେ 25 ଡିଗ୍ରୀରୁ 65. ଡିଗ୍ରୀ ଅକ୍ଷାଂଶ ମଧ୍ଯରେ ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ । ଏହା ଦୁଇଭାଗରେ ବିଭକ୍ତ; ଯଥା – ଉଷ୍ଣ ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଓ ଶୀତଳ ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ ଅରଣ୍ୟ । .
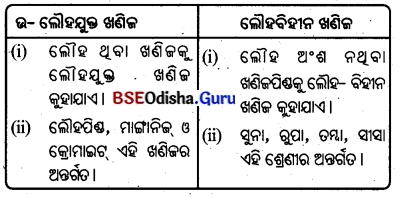
- ଉଷ୍ଣ ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ ଅରଣ୍ୟରେ ଓକ୍ ଓ ଅଲିଭ ବୃକ୍ଷ ଜନ୍ମେ । ଏଗୁଡ଼ିକ ମହାଦେଶଗୁଡ଼ିକ ପୂର୍ବ ଓ ପଶ୍ଚିମ ଉପକୂଳ ଏବଂ ଭୂମଧ୍ଯସାଗରୀୟ ଦେଶଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ଦେଖାଯାଏ’ । ଏହା କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ ଅରଣ୍ୟକୁ ଲାଗିକରି ରହିଥାଏ ।
- ଶୀତଳ ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ତୁନ୍ଦ୍ରାଞ୍ଚଳକୁ ଲାଗି ରହିଥାଏ । ଏହି ଅରଣ୍ୟର ବୃକ୍ଷଗୁଡ଼ିକ ସରଳବର୍ଗୀୟ, ନରମ କାଠଯୁକ୍ତ ଓ ପାଇନ୍ଜାତୀୟ ଅଟେ ।
- ସାଇବେରିଆ, ସ୍କାଣ୍ଟିନେଭିଆ, କାନାଡ଼ାର ଉତ୍ତରାଞ୍ଚଳ ଓ ଭାରତର ହିମାଳୟ ପର୍ବତର ଉଚ୍ଚ ଅଂଶରେ ଏହି ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
- ଏହି ଅରଣ୍ୟରେ ପାଇଜ୍, ଫିର ଆଦି ବୃକ୍ଷ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଗୋଚର ହୁଏ ।
Question 13.
ପୃଥିବୀର ବିଭିନ୍ନ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଦେଖାଯାଉଥିବା ବନ୍ୟପ୍ରାଣୀମାନଙ୍କ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧରେ ଆଲୋଚନା କର ।
Answer:
- ଆଫ୍ରିକାର ସାଭାନ୍ନା ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ବାଘ, ସିଂହ, ହରିଣ, ଜେବ୍ରା, ଜିରାଫ୍, ବଣୁଆ ଘୋଡ଼ା ଆଦି ପ୍ରାଣୀ ଦେଖାଯା’ନ୍ତି ।
- ପ୍ରେରୀ ଓ ଷ୍ଟେପୀ ତୃଣଭୂମିରେ ମେଣ୍ଢା ଓ ଘୋଡ଼ା ଅଧିକ ସଂଖ୍ୟାରେ ଦେଖାଯା’ନ୍ତି ।
- ସାହାରା ଓ ସାଉଦି ଆରବର ଗ୍ରୀଷ୍ମମଣ୍ଡଳୀୟ ମରୁଭୂମିରେ ଓଟ, କାଲାହାରୀ ମରୁଭୂମିରେ ଓଟପକ୍ଷୀ, ଅଷ୍ଟ୍ରେଲିଆ ମରୁଭୂମିରେ ଏମୁ ଓ କଙ୍ଗାରୁ ବାସକରନ୍ତି ।
- ଆଫ୍ରିକାର କଙ୍ଗୋ ଅବବାହିକା ଓ ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆମେରିକାର ଆମାଜନ ଅବବାହିକାରେ ଘଞ୍ଚ ଅରଣ୍ୟରେ ସାପ, କୁମ୍ଭୀର ବିଭିନ୍ନ ସରୀସୃପ, ମାଙ୍କଡ଼, ସିମ୍ପାଜୀ, ଓରାଙ୍ଗ ଓଟାଙ୍ଗଭଳି ବଣ୍ୟ ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ଦେଖାଯା’ନ୍ତି ।
- ଆଣ୍ଟାର୍କଟିକାର ବରଫାବୃତ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ପେଙ୍ଗୁଇନ୍ ପକ୍ଷୀ ଓ ଉତ୍ତରମେରୁ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଧଳାଭାଲୁ, ସିଲ୍, ସିଲଭର୍ ଫକ୍ସ ଆଦି ନରମ ଲୋମଯୁକ୍ତ ପ୍ରାଣୀ ବାସକରନ୍ତି ।
Question 14.
ଭାରତରେ ଥିବା ବିଭିନ୍ନ ଅଭୟାରଣ୍ୟ କେଉଁ କେଉଁ ରାଜ୍ୟରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ ଉଲ୍ଲେଖ କର ।
Answer:
- ବ୍ୟାଘ୍ର ପ୍ରକଳ୍ପଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଭାରତର ଆସାମ ରାଜ୍ୟର ମାନସ, ପଶ୍ଚିମବଙ୍ଗର ସୁନ୍ଦରବନ, ଝାଡ଼ଖଣ୍ଡର ପାଲାମୁ, ଉତ୍ତରାଖଣ୍ଡର କର୍ନେଟ ଜାତୀୟ ଉଦ୍ୟାନ, ମହାରାଷ୍ଟ୍ରର ମେଲଘାଟ, ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଶିମିଳିପାଳ ଓ କର୍ଣ୍ଣାଟକର ବାନ୍ଦୀପୁରରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ ।
- ଏକ ଶିଙ୍ଗ ଥିବା ଗଣ୍ଡା ଆସାମର କାଜିରଙ୍ଗା ଜାତୀୟ ଉଦ୍ୟାନରେ ଦେଖୁବାକୁ ମିଳନ୍ତି ।
- ସିଂହ ଗୁଜରାଟର ସୌରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ଅନ୍ତର୍ଗତ ଗୀର୍ ଜାତୀୟ ଉଦ୍ୟାନରେ ରହିଛନ୍ତି ।
- ବିଭିନ୍ନ ପ୍ରକାର ପକ୍ଷୀ ରାଜସ୍ଥାନର ଭରତପୁର ଓ ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଚିଲିକା ହ୍ରଦରେ ଦେଖାଯା’ନ୍ତି । ଏଗୁଡ଼ିକ ପକ୍ଷୀ ଅଭୟାରଣ୍ୟ ।
- ହାତୀ ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଚନ୍ଦକା ଅରଣ୍ୟରେ ଦେଖାଯା’ଛି ।
- କୁମ୍ଭୀର ସଂରକ୍ଷଣ କେନ୍ଦ୍ର ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଟିକରପଡ଼ା ଏବଂ ଭିତରକନିକାରେ ରହିଅଛି ।

Question 15.
ବିଭିନ୍ନ ଖଣିଜ ପଦାର୍ଥଗୁଡ଼ିକର ବ୍ୟବହାର ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧରେ ଉଲ୍ଲେଖ କର ।
Answer:
- ଲୁହାପଥର ମୁଖ୍ୟତଃ ଇସ୍ପାତ ଶିଳ୍ପରେ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହୁଏ ଏବଂ ଏଥୁରୁ ଲୁହା ଓ ଇସ୍ପାତ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ ହୁଏ ।
- ବକ୍ସାଇଟ୍ ସାଧାରଣତଃ ଆଲୁମିନିୟମ୍ ଶିଳ୍ପରେ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହୁଏ ।
- ମାଙ୍ଗାନିଜ ମିଶ୍ରଧାତୁ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତିରେ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହୁଏ ।
- କ୍ରୋମାଇଟ୍ ଇସ୍ପାତ ଓ ଚମଡ଼ା ଶିଳ୍ପରେ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହୁଏ ।
- ଅଭ୍ର ବୈଦ୍ୟୁତିକ ଶିଳ୍ପରେ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହୁଏ ।
Question 16.
ଭାରତର ଖଣିଜଦ୍ରବ୍ୟର ବିତରଣ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧରେ ଲେଖ ।
Answer:
- ଲୁହାପଥର ଭାରତର ଝାଡ଼ଖଣ୍ଡ, ଓଡ଼ିଶା, ଛତିଶଗଡ଼, ଆନ୍ଧ୍ର ପ୍ରଦେଶ, ମଧ୍ୟପ୍ରଦେଶ, କର୍ଣ୍ଣାଟକ ଓ ଗୋଆରେ ମିଳିଥାଏ ।
- ମାଙ୍ଗାନିଜ, ଓଡ଼ିଶା, ମଧ୍ୟପ୍ରଦେଶ, ମହାରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ଓ ଝାଡ଼ଖଣ୍ଡରେ ମିଳେ ।
- କ୍ରୋମାଇଟ୍ ଓଡ଼ିଶା, ମହାରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର, ଝାଡ଼ଖଣ୍ଡ, ଆନ୍ଧ୍ରପ୍ରଦେଶ, କର୍ଣ୍ଣାଟକ ଓ ତାମିଲନାଡୁରେ ମିଳେ ।
- ବକ୍ସାଇଟ୍ ଝାଡ଼ଖଣ୍ଡ, ଓଡ଼ିଶା, ଗୁଜରାଟ, କର୍ଣ୍ଣାଟକ ଓ ମଧ୍ୟପ୍ରଦେଶରେ ମିଳେ ।
- ଅଭ୍ର ବିହାର, ଝାଡ଼ଖଣ୍ଡ, ଆନ୍ଧ୍ରପ୍ରଦେଶ ଓ ରାଜସ୍ଥାନରେ ମିଳେ ।
- କୋଇଲା ଝାଡ଼ଖଣ୍ଡ, ପଶ୍ଚିମବଙ୍ଗ, ଓଡ଼ିଶା, ମଧ୍ୟପ୍ରଦେଶ, ଛତିଶଗଡ଼, ଆନ୍ଧ୍ରପ୍ରଦେଶ ଓ ମହାରାଷ୍ଟ୍ରରେ ମିଳେ ।
- ଖଣିଜତୈଳ ଆସାମ, ଗୁଜରାଟ ଓ ମହାରାଷ୍ଟ୍ରରେ ମିଳେ ।
Question 17.
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଖଣିଜଦ୍ରବ୍ୟର ବିତରଣ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧରେ ଆଲୋଚନା କର ।
Answer:
- ଓଡ଼ିଶାର କେନ୍ଦୁଝର, ମୟୂରଭଞ୍ଜ, ଯାଜପୁର ଓ ସୁନ୍ଦରଗଡ଼ ଜିଲ୍ଲାମାନଙ୍କରେ ପ୍ରଚୁର ଲୁହାପଥର ମିଳେ ।
- ମାଙ୍ଗାନିଜ କେନ୍ଦୁଝର, କଳାହାଣ୍ଡି, ସୁନ୍ଦରଗଡ଼, ବଲାଙ୍ଗିର ଓ କୋରାପୁଟ ଜିଲ୍ଲାମାନଙ୍କରେ ମିଳିଥାଏ । .
- କ୍ରୋମାଇଟ୍ ଯାଜପୁର, କେନ୍ଦୁଝର ଓ ଢେଙ୍କାନାଳରେ ମିଳିଥାଏ ।
- ବକ୍ସାଇଟ୍ ବରଗଡ଼, ବଲାଙ୍ଗିର, କୋରାପୁଟ ଓ କଳାହାଣ୍ଡି ଜିଲ୍ଲାମାନଙ୍କରେ ମିଳେ ।
- ଅଭ୍ର ବଲାଙ୍ଗିର ଓ କଳାହାଣ୍ଡି ଜିଲ୍ଲାରେ ରହିଅଛି ।
- କୋଇଲା ଅନୁଗୁଳ, ଝାରସୁଗୁଡ଼ା ଓ ସୁନ୍ଦରଗଡ଼ ଜିଲ୍ଲାମାନଙ୍କରେ ଅଧିକ ପରିମାଣରେ ମିଳିଥାଏ ।
ସଂକ୍ଷିପ୍ତ ଉତ୍ତରମୂଳକ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନୋତ୍ତର
ସଂକ୍ଷେପରେ ଉତ୍ତର ଲେଖ ।
Question 1.
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଭୂ-ସମ୍ବଳର ଏକ ବିବରଣୀ ପ୍ରଦାନ କର ।
Answer:
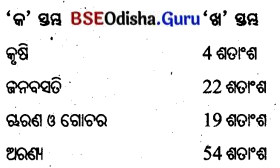
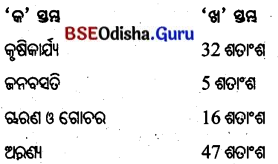
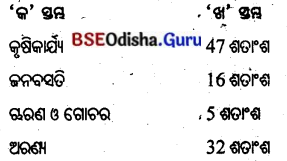
- ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଶତକଡ଼ା ୪୭ ଭାଗ ଭୂମିରେ କୃଷିକାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଓ ୧୬ ଭାଗ ଭୂମିରେ ଜନବସତି ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
- ଶତକଡ଼ା ୫ ଭାଗ ଚାରଣ ଓ ଗୋଚର ଭୂମି ଏବଂ ୩୨ ଭାଗ ଭୂମି ଅରଣ୍ୟ ରୂପେ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଏ।
Question 2.
ପରିବାହିତ ମ୍ପରିକା କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
- ଶିଳାକ୍ଷୟ ହେବାପରେ କ୍ଷୟଜାତ ପଦାର୍ଥ ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଶକ୍ତି ଦ୍ଵାରା ପରିବାହିତ ହୋଇ ଅନ୍ୟତ୍ର ସତ ହେବା ଦ୍ବାରା ଯେଉଁ ମୃତ୍ତିକା ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହୁଏ, ତାହାକୁ ପରିବାହିତ ମ୍ପରିକା କୁହାଯାଏ।
- ଏହି ମୁଭିକା ଯେଉଁ ସ୍ଥାନରେ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହୁଏ, ସେହି ସ୍ଥାନର ଅନ୍ତଭୂମି ସହିତ ତାହାର କିଛି ସାମଞ୍ଜସ୍ୟ ନଥାଏ। ଉଦାହରଣ ପଟୁମାଟି
Question 3.
ପାର୍ବତ୍ୟାଞ୍ଚଳରେ ମୃତ୍ତିକା ସଂରକ୍ଷଣ କିପରି କରାଯାଇଥାଏ ?
Answer:
- ଉଚ୍ଚ ପର୍ବତ ଓ ମାଳଭୂମିର ତୀଖ ଗଡ଼ାଣି ଅଞ୍ଚଳକୁ ପାହାଚ ଆକାରରେ କାଟି କ୍ଷେତ୍ର ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ କଲେ ତାହା କୃଷି କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ପାଇଁ ସମତଳ ସ୍ଥାନ ଯୋଗାଇବା ସହିତ ଜଳର ପ୍ରବାହର ବେଗକୁ ହ୍ରାସ କରେ
- ଏହା କରିବା ଫଳରେ ପାର୍ବତ୍ୟାଞ୍ଚଳର ମୃଭିକା କ୍ଷୟ କମ୍ ହୋଇଥାଏ।
Question 4.
ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ଜଳକୁ କିପରି ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିଥାଏ ?
Answer:
- ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ଜଳକୁ ପାନୀୟ, ରନ୍ଧନ, ପରିଷ୍କାର ପରିଚ୍ଛନ୍ନ ସହିତ କୃଷି, ଶିଳ୍ପ, ବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନ ଆଦି ବିଭିନ୍ନ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟରେ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିଥାଏ ।
- ଜଳପଥରେ ଯାତ୍ରୀ ଓ ମାଲ ପରିବହନ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ମଧ୍ୟ କରାଯାଇଥାଏ ।
Question 5.
ଜଳ ଅମଳ ପ୍ରକଳ୍ପ କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
- ଦୁଇଘଣ୍ଟା ଧରି ଲଗାଣ ବର୍ଷା ହେଲେ ସାଧାରଣ ଛାତ ଉପରେ ୬୦୦ ଲିଟର ବୃଷ୍ଟି ପଡ଼ିଥାଏ ।
- ସେହି ଜଳକୁ ଯଦି ନଳ ସାହାଯ୍ୟରେ ଏକ ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ ସ୍ଥାନରେ ଏକତ୍ର କରି ଜଳାଭାବ ସମୟରେ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଏ, ତାହାକୁ ଜଳ ଅମଳ ପ୍ରକଳ୍ପ କୁହାଯାଏ।

Question 6.
ମହୁମାଛି ଆମର କି ଉପକାର କରିଥାଏ ?
Answer:
- ମହୁମାଛିର ଫେଣାରୁ ଆମେ ମହୁ ସଂଗ୍ରହ କରିଥାଉ।
- ଏମାନେ ଫୁଲରେ ପରାଗ ସଙ୍ଗମ କରାଇଥାନ୍ତି ।
Question 7.
ଅଳ୍ପ ବୃଷ୍ଟିପାତ ହେଉଥୁବା ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଥିବା ଅରଣ୍ୟର ବିଶେଷତ୍ଵ କ’ଣ ?
Answer:
- ଅଳ୍ପ ବୃଷ୍ଟିପାତ ହେଉଥିବା ଶୁଷ୍କ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ନିକୃଷ୍ଟ ବୃକ୍ଷ ଓ କଣ୍ଟାବୁଦାମାନ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ଏବଂ ଏଗୁଡ଼ିକର ଚେର ଜଳ,, ପାଇବା ପାଇଁ ଭୂମିର ଅଧିକ ଗଭୀରତାକୁ ଯାଇଥାଏ ।
- ଅଧୂକ ଜଳୀୟବାଷ୍ପ ତ୍ୟାଗରୁ ନିଜକୁ ରକ୍ଷା କରିବାପାଇଁ ସେଗୁଡ଼ିକର ପତ୍ରପୃଷ୍ଠ ଚିକ୍କଣ ଓ ପତ୍ରଗୁଡ଼ିକ ମୋଟା ଏବଂ କଣ୍ଟାଯୁକ୍ତ ହୋଇଥାଏ।
Question 8.
ମେରୁ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ କେଉଁ ପ୍ରକାର ଉଭିଦ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ? ଏହା କେଉଁଠାରେ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
- ମେରୁ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଶିଉଳି, ହିମଗୁଳ୍ମ ମୁଖ୍ୟ ଉଦ୍ଭଦ। ଏହାକୁ ତୁନ୍ଦ୍ରା ଉଭିଦ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
- ବରଫାବୃତ ପର୍ବତ ଶିଖରଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ତୁଦ୍ରାଜାତୀୟ ଉଦ୍ଭଦ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
Question 9.
ତୃଣଭୋଜୀ ପ୍ରାଣୀ କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
- ଯେଉଁ ପ୍ରାଣୀ ନିଜର ଖାଦ୍ୟ ପାଇଁ କେବଳ ଉଭିଦ ଉପରେ ନିର୍ଭର କରନ୍ତି ତାହାକୁ ତୃଣଭୋଜୀ ପ୍ରାଣୀ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
- ହାତୀ, ସମ୍ବର, ମୃଗ, ହରିଣ, ଜେବ୍ରା, ଜିରାଫ ଏହି ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଅନ୍ତର୍ଗତ ।
Question 10.
ମାଂସାଶୀ ପ୍ରାଣୀ କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
- ଯେଉଁ ପ୍ରାଣୀ ନିଜର ଖାଦ୍ୟ ପାଇଁ କେବଳ ମାଂସ ଉପରେ ନିର୍ଭରଶୀଳ ତାହାକୁ ମାଂସାଶୀ ପ୍ରାଣୀ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
- ବାଘ, ସିଂହ ଓ ହେଟାବାଘ ଏହି ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଅନ୍ତର୍ଗତ ।

Question 11.
ଉଭୟଭୋଜୀ ପ୍ରାଣୀ କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ?
Answer:
- ଯେଉଁ ପ୍ରାଣୀ ନିଜର ଖାଦ୍ୟପାଇଁ ଉଭୟ ମାଂସ ଓ ଉଭିଦ ଉପରେ ନିର୍ଭର କରେ ତାହାକୁ ଉଭୟଭୋଜୀ ପ୍ରାଣୀ କୁହାଯାଏ।
- ବିଲୁଆ ଓ ଭାଲୁ ଉଭୟଭୋଜୀ ପ୍ରାଣୀ ଅଟନ୍ତି ।
Question 12.
ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଉଭିଦର କ୍ଷୟର ମୁଖ୍ୟ କାରଣ କ’ଣ ?
Answer:
- ମୃତ୍ତିକାକ୍ଷୟ, ସାମୁଦ୍ରିକ ବାତ୍ୟା, ଭୂସ୍ଖଳନ ଓ ବନାଗ୍ନି ଆଦି ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ କାରଣ।
- ଅରଣ୍ୟକ୍ଷୟ ଓ ଶିଳ୍ପ ନିର୍ମାଣ ଆଦି ମାନବୀୟ କାରଣଯୋଗୁଁ ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଉଭିଦ କ୍ଷୟର ମୁଖ୍ୟ କାରଣ ।
Question 13.
ବନ୍ୟପ୍ରାଣୀ ସଂରକ୍ଷଣ ପାଇଁ ସରକାର କି କି ପଦକ୍ଷେପ ଗ୍ରହଣ କରିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
- ୧୯୭୨ ମସିହାରେ ବନ୍ୟପ୍ରାଣୀ ସଂରକ୍ଷଣ ବୋର୍ଡ଼ ଗଠନ କରିଛନ୍ତି ।
- ଦେଶର ବିଭିନ୍ନ ସ୍ଥାନରେ ଅଭୟାରଣ୍ୟ, ଜାତୀୟ ଉଦ୍ୟାନ, ବ୍ୟାଘ୍ର ପ୍ରକଳ୍ପ, କୁମ୍ଭୀର ପ୍ରକଳ୍ପ ଓ ପକ୍ଷୀ ବିହାର ଆଦି ସ୍ଥାପନ କରାଯାଇଛି ।
Question 14.
ଜୀବାଶ୍ମ ଇନ୍ଧନ କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ଏବଂ କାହିଁକି କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
- କୋଇଲା, ଖଣିଜ ତୈଳ ଓ ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ବାଷ୍ପକୁ ‘ଜୀବାଶ୍ମ’ ଇନ୍ଧନ ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ ।
- ଏହା ଜୈବ ବସ୍ତୁରୁ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ ସେଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ଜୈବ ଖଣିଜ ବା ‘ଜୀବାଶ୍ମ’ ଇନ୍ଧନ ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ ।
Question 15.
କୋଇଲାର ବ୍ୟବହାର କିପରି କରାଯାଇଥାଏ ?
Answer:
- ଘରୋଇ ଜାଳେଣି, ଲୌହ-ଇସ୍ପାତ୍ ଶିଳ୍ପ, ବାଷ୍ପଚାଳିତ ଇଞ୍ଜିନ୍ ଏବଂ ବିଦ୍ୟୁତଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନରେ ଇନ୍ଧନ ରୂପେ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହୁଏ ।
- କୋଇଲାରୁ ଉତ୍ପନ୍ନ ବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ଶକ୍ତିକୁ ତାପଜ ବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ଶକ୍ତି କୁହାଯାଏ ।
Question 16.
ଅଶୋଧୀତ ତୈଳରୁ କେଉଁ ଦ୍ରବ୍ୟ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ କରାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
- ଅଶୋଧୀତ ତୈଳକୁ ବିଶୋଧନାଗାରକୁ ନିଆଯାଏ ।
- ବିଶୋଧନ ପରେ ସେଥୁରୁ ଡିଜେଲ, ପେଟ୍ରୋଲ୍, କିରୋସିନି, ୱାକ୍ସ, ପ୍ଲାଷ୍ଟିକ୍ ଏବଂ ଅନ୍ୟାନ୍ୟ ଘର୍ଷଣ ନିରୋଧକ ଦ୍ରବ୍ୟ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ କରାଯାଏ ।

Question 17.
କେଉଁ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ସୌରଶକ୍ତିର ବ୍ୟବହାର ଅଧିକ ? ସୌରଶକ୍ତିକୁ କିପରି ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
- କ୍ରାନ୍ତିମଣ୍ଡଳୀୟ ଦେଶଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ସୌରରଶ୍ମିର ପ୍ରଖରତା ଓ ସ୍ଥାୟିତ୍ଵ ଅଧିକ ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ ସେହିସବୁ ଦେଶରେ ଏହାର ବ୍ୟବହାର ସର୍ବାଧକ ।
- ଏହି ଶକ୍ତିକୁ ରାସ୍ତା ଆଲୋକ, ଟ୍ରାଫିକ୍ ସିଗ୍ନାଲ, ସୌରଚୂଲା ଓ ସୌର କୁକର୍ରେ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଇଥାଏ।
Question 18.
କେଉଁଥୁରୁ ଆଣବିକ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପନ୍ନ କରାଯାଏ ? ଭାରତର କେଉଁଠାରେ ୟୁରାନିୟମ୍ ମିଳେ ?
Answer:
- ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଅବସ୍ଥାରେ ଗଚ୍ଛିତ ଥିବା ୟୁରାନିୟମ୍, ଥୋରିୟମ୍ ଆଦି ଶକ୍ତିକୁ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରି ଆଣବିକ ରିଆକ୍ଟରରେ ଆଣବିକ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପନ୍ନ କରାଯାଏ ।
- ଭାରତର ଝାଡ଼ଖଣ୍ଡ ଓ ରାଜସ୍ଥାନରେ ବିପୁଳ ପରିମାଣରେ ୟୁରାନିୟମ୍ ମିଳେ।
Question 19.
ଭୂତାପଜ ଶକ୍ତି କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ? ଏହି ଶକ୍ତିକୁ କେଉଁ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟରେ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
- ପୃଥିବୀର ଅଭ୍ୟନ୍ତର ତାପରୁ ଉତ୍ପନ୍ନ ହେଉଥୁବା ଶକ୍ତିକୁ ଭୂତାପଜ ଶକ୍ତି କୁହାଯାଏ।
- ଏହି ଶକ୍ତିକୁ ରନ୍ଧନ, ସ୍ନାନ ଓ ଉତ୍ତପ୍ତ କରିବା କାର୍ଯ୍ୟରେ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଏ।
Question 20.
ବାୟୋଗ୍ୟାସ୍ କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ? ଏହା କେଉଁ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଅଧୁକ ଆଦୃତ ?
Answer:
- ଜୈବିକ ବର୍ଜ୍ୟବସ୍ତୁ, ଯଥା ଗୋବର, ମୃତ ଉଭିଦ, ପ୍ରାଣୀମାନଙ୍କର ଅଂଶଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ଏକ କୁଣ୍ଡରେ ପକାଇଲେ ସେଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ବ୍ୟାକ୍ଟେରିଆ ପଚାଇ ସଢ଼ାଇ ସେଥୁରୁ ମିଥେନ୍ ଓ ଅଙ୍ଗାରକାମ୍ଳ ମିଶ୍ରିତ ଗ୍ୟାସ୍ ନିର୍ଗତ ହୁଏ । ତାହାକୁ ବାୟୋଗ୍ୟାସ୍ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
- ଗ୍ରାମାଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଏହାକୁ ଲୋକମାନେ ଅଧିକ ବ୍ୟବହାର, କରିଥାନ୍ତି।
Question 21.
ପୃଥିବୀର ମୁଖ୍ୟ ସମତଳଭୂମିଗୁଡ଼ିକର ନାମ ଲେଖ ।
Answer:
- ପୃଥିବୀର ମୁଖ୍ୟ ସମତଳଭୂମିଗୁଡ଼ିକ ହେଲା – ଏସିଆର ସାଇବେରିଆ, ଉତ୍ତର ଆମେରିକାର କେନ୍ଦ୍ରୀୟ ସମତଳଭୂମି, ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆମେରିକାର ଆମାଜନ ଓ ପାରାନା ପାରାଗୁଏ ଅବବାହିକା ।
- ଆଫ୍ରିକାର ନୀଳନଦୀ ଓ କଙ୍ଗୋନଦୀ ଅବବାହିକା ଏବଂ ଭାରତର ଗାଙ୍ଗେୟ ସମତଳ ଅଞ୍ଚଳ ।
Question 22.
ପୃଥିବୀର ମୁଖ୍ୟ ମାଳଭୂମିଗୁଡ଼ିକର ଅବସ୍ଥିତି ବିଷୟରେ ଲେଖ ।
Answer:
- ତିବ୍ବତ୍ ମାଳଭୂମି ଏସିଆରେ ଓ ସ୍କାଣ୍ଡିନେଭିଆ ମାଳଭୂମି ଇଉରୋପରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ ।
- କାନାଡ଼ିଆନ ସିଲ୍ ମାଳଭୂମି ଉତ୍ତର ଆମେରି କାରେ ଥିବାବେଳେ ବ୍ରାଜିଲ ଓ ପାଟାଗୋନିଆ ମାଳଭୂମି ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆମେରିକାରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ ।

Question 23.
ଭୂ-ବ୍ୟବହାରର ‘ଚାରିଗୋଟି ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ନିୟାମକର ନାମ ଲେଖ ।
Answer:
ଭୂ–ବ୍ୟବହାରର ଚାରିଗୋଟି ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ନିୟାମକର ନାମ ହେଉଛି ଭୂ-ପ୍ରକୃତି, ମୃରିକା, ଜଳବାୟୁ ଏବଂ ଜଳର ସୁଲଭତା ।
Question 24.
ପ୍ରାଥମିକ ଶିଳା ମୃତ୍ତିକାର କେଉଁ ଗୁଣକୁ ପ୍ରଭାବିତ କରେ ?
Answer:
ପ୍ରାଥମିକ ମୃତ୍ତିକାର ରଙ୍ଗ, ବିନ୍ୟାସ, ରାସାୟନିକ ଗୁଣ ଅନ୍ତର୍ନିହିତ ଖଣିଜ ଓ ଭେଦ୍ୟତାକୁ ପ୍ରଭାବିତ କରିଥାଏ ।
Question 25.
ମୃତ୍ତିକା କିପରି ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହୁଏ ?
Answer:
- ମୃତ୍ତିକା ଶିଳା ବା ପଥରରୁ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଶିଳା କ୍ଷୟ ହେଲେ ସୂକ୍ଷ୍ମ ଶିଳାରେଣୁରେ ପରିଣତ ହୁଏ ।
- ବିଭିନ୍ନ ଶିଳାର କ୍ଷୟଜାତ ସୂକ୍ଷ୍ମରେଣୁଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଜଳ, ବାୟୁ, କ୍ଷୟିତ ଜୈବାଂଶ ଓ ଖଣିଜସହ ମିଶି ଭୂମିର ଉପରିଭାଗରେ ପତଳା ଆସ୍ତରଣ ସୃଷ୍ଟି କରେ ଏବଂ ମୃତ୍ତିକାରେ ପରିଣତ ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
Question 26.
ଭାରତରେ ହେଉଥିବା ଭୂ–ବ୍ୟବହାରର ଏକ ବିବରଣୀ ପ୍ରଦାନ କର ।
Answer:
- ଭାରତର ଭୂମି ମୁଖ୍ୟତଃ ଅରଣ୍ୟଭୂମି, ଚାରଣ ବା ଗୋଚର ଭୂମି, କୃଷିଭୂମି, ଜନବସତି, କଳକାରଖାନା ଓ ରାସ୍ତାଘାଟ ଇତ୍ୟାଦିରେ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଇଥାଏ ।
- ଭାରତରେ ସମୁଦାୟ ଭୂଭାଗର ଶତକଡ଼ା 54 ଭାଗ କୃଷିକାର୍ଯ୍ୟ, 19 ଭାଗ ଜନବସତି ଓ 4 ଭାଗ ଚାରଣ ଓ ଗୋଚରଭୂମି ଏବଂ 22 ଭାଗ ଅରଣ୍ୟଭୂମି ରୂପେ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହେଉଛି ।
Question 27.
ମୃତ୍ତିକା କ୍ଷୟର ବିଭିନ୍ନ କାରଣମାନ ଲେଖ ।
Answer:
- ମୃତ୍ତିକା କ୍ଷୟର ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ କାରଣଗୁଡ଼ିକ ହେଲା- ବୃଷ୍ଟି, ବନ୍ୟା, ଜଳପ୍ରବାହ ଓ ଭୂସ୍ଖଳନ ଇତ୍ୟାଦି ।’
- ଜଙ୍ଗଲ କ୍ଷୟ, ଅତ୍ୟଧିକ ଚାରଣ, ରାସାୟନିକ ସାର ଓ କୀଟନାଶକ ଦ୍ରବ୍ୟର ବ୍ୟବହାର, ଖଣିଜ ଉତ୍ତୋଳନ ଆଦି ମୃତ୍ତିକା କ୍ଷୟର ଅନ୍ୟାନ୍ୟ କାରଣ । ଏହି କାରଣଗୁଡ଼ିକ ମନୁଷ୍ୟକୃତ ।

Question 28.
ପୃଥିବୀରେ ଦେଖାଯାଉଥିବା ମରୁଡ଼ି ଅଞ୍ଚଳଗୁଡ଼ିକର ଅବସ୍ଥିତି ଏବଂ ସେହି ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଜଳାଭାବର କାରଣ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧରେ ଲେଖ ।
Answer:
- ଆଫ୍ରିକାର ଅଧିକାଂଶ ଅଞ୍ଚଳ, ପଶ୍ଚିମ ଏସିଆ, ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଏସିଆ, ଯୁକ୍ତରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ଆମେରିକାର ପଶ୍ଚିମସ୍ଥ କେତେକ ଅଞ୍ଚଳ, ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆମେରିକାର କେତେକ ଅଞ୍ଚଳ ଏବଂ ସମୁଦାୟ ଅଷ୍ଟ୍ରେଲିଆ ମହାଦେଶ ପୃଥିବୀର ମୁଖ୍ୟ ମରୁଡ଼ିପ୍ରବଣ ଅଞ୍ଚଳ
- ଏହି ମରୁଡ଼ି ପ୍ରବଣ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ବାର୍ଷିକ ଓ ଋତୁକାଳୀନ ବୃଷ୍ଟିପାତର ପାର୍ଥକ୍ୟ ହିଁ ସେଠାକାର ଜଳାଭାବର କାରଣ ।
Question 29.
ଓଡ଼ିଶାରେ ଦେଖାଯାଉଥିବା ବିଭିନ୍ନ ପ୍ରକାର ଅରଣ୍ୟର ନାମ ଲେଖ ।
Answer:
ଓଡ଼ିଶାରେ ଦେଖାଯାଉଥିବା ଅରଣ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକ ହେଲା-କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ ଅର୍ବଚିରହରିତ୍ ଅରଣ୍ୟ, କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ ଆର୍ଦ୍ର ପର୍ଣ୍ଣମୋଚୀ ଅରଣ୍ୟ, କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ ଶୁଷ୍କ ପର୍ଣ୍ଣମୋଚୀ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଓ ଉପକୂଳବର୍ତ୍ତୀ ଜୁଆରିଆ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ।
Question 30.
ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ ଅରଣ୍ୟର ଅବସ୍ଥିତି ଓ ବୈଶିଷ୍ଟ୍ୟ ଉଲ୍ଲେଖ କର ।
Answer:
- ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ ଅରଣ୍ୟ କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ ଅରଣ୍ୟକୁ ଲାଗି କରି ରହିଅଛି । ଏହି ଅରଣ୍ୟର ବୃକ୍ଷଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ଦୀର୍ଘ ଓ ତୈଳଯୁକ୍ତ ପତ୍ର, ମୋଟା ବକଳ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
- ମହାଦେଶଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ପୂର୍ବ ଓ ପଶ୍ଚିମ ଉପକୂଳ ଏବଂ ଭୂମଧ୍ଯସାଗର ନିକଟ ଦେଶଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ଏହି ପ୍ରକାର ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ । ଏହାକୁ ଭୂମଧ୍ଯସାଗରୀୟ ଉଦ୍ଭିଦ ମଧ୍ଯ କୁହାଯାଏ|

Question 31.
ପୃଥିବୀର ଉଭିଦକୁ କେତେ ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ବିଭକ୍ତ କରାଯାଇଅଛି, ତାହାର ଏକ ବିବରଣୀ ପ୍ରଦାନ କର ।
Answer:
- ପୃଥିବୀର ଉଭିଦକୁ ଆଲୋକ, ଉତ୍ତାପ ଓ ଆର୍ଦ୍ରତାକୁ ଭିଭି କରି ଚାରିଗୋଟି ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ବିଭକ୍ତ କରାଯାଇଅଛି ।
- ସେଗୁଡ଼ିକ ହେଲା ଅରଣ୍ୟ, ତୃଣଭୂମି, କଣ୍ଟାବନ ଓ ତୁନ୍ଦ୍ରା ।
- ଅଧିକ ବୃଷ୍ଟିପାତ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଅରଣ୍ୟ, ମଧ୍ୟମ ବୃଷ୍ଟିପାତ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ତୃଣଭୂମି, ଅଳ୍ପବୃଷ୍ଟି ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ କଣ୍ଟାବନ ଏବଂ ମେରୁ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଶିଉଳି, ହିମଗୁଳ୍ମ ଆଦି ତୁନ୍ଦ୍ରା ଉଦ୍ଭଦ
ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
Question 32.
ବନ୍ୟପ୍ରାଣୀଗୁଡ଼ିକ ବିଭିନ୍ନ ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ବିଭକ୍ତ କରି ସେଗୁଡ଼ିକ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧରେ ଆଲୋଚନା କର ।
Answer:
- ତିନିଗୋଟି ପ୍ରକାର ବନ୍ୟପ୍ରାଣୀ; ଯଥା— ତୃଣଭୋଜୀ, ମାଂସାଶୀ ଓ ଉଭୟଭୋଜୀ ପ୍ରାଣୀ ରହିଛନ୍ତି । ଏଗୁଡ଼ିକ ସେମାନଙ୍କର ଖାଦ୍ୟ ଓ ଆହାର ଉପରେ ବି ଉକ୍ତ କରାଯାଇଅଛି ।
- ଉଦ୍ଭଦ ତଥା ତୃଣ ଉପରେ ନିର୍ଭର କରିଥିବା ପ୍ରାଣୀଗୁଡ଼ିକ ହେଲେ ଗୋରୁଗାଈ, ଛେଳି, ମେଣ୍ଢା, ହାତୀ, ସମ୍ବର, ମୃଗ, ଜେବ୍ରା ଓ ଜିରାଫ୍।ଏଗୁଡ଼ିକ ତୃଣଭୋଜୀ ପ୍ରାଣୀ ଅଟନ୍ତି
- ମାଂସାଶୀ ପ୍ରାଣୀ ହେଲେ ବାଘ, ସିଂହ, ହେଟାବାଘ ଏବଂ ବିଲୁଆ, ଭାଲୁ ଇତ୍ୟାଦି । ଉଭୟଭୋଜୀ ଅର୍ଥାତ୍ ଉଭୟ ଉଦ୍ଭଦ ଓ ତୃଣଭୋଜୀ ପ୍ରାଣୀମାନଙ୍କର ମାଂସ ଉପରେ ନିର୍ଭର କରନ୍ତି ।
Question 33.
ଖଣିଜ ଉତ୍ତୋଳନର ବିଭିନ୍ନ ପ୍ରକ୍ରିୟାଗୁଡ଼ିକ ବୁଝାଇ ଲେଖ ।
Answer:
- ଖଣିଜ ଉତ୍ତୋଳନ ପ୍ରକ୍ରିୟାଗୁଡ଼ିକ ହେଲା- ସାଧାରଣ ଖନନ, ଖଣି ଖନନ ଓ ଡ୍ରିଲିଂ । ଭୂପୃଷ୍ଠରେ ଖଣିଜ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଗୋଚର ଅବସ୍ଥାରେ ଥିଲେ, ତାକୁ ସାଧାରଣ ଖନନ କୁହାଯାଏ । ଖଣି ଖନନ ପ୍ରକ୍ରିୟା ମୁକ୍ତ ଗର୍ଭ ଖଣି ଖନନ ଓ ଗଭୀର ଖନନ -ପ୍ରକ୍ରିୟା ଭାଗରେ ବିଭକ୍ତ ।
- ଭୂଗର୍ଭର ଅତ୍ୟଧିକ ଗଭୀରତାରେ ଥିବା ପେଟ୍ରୋଲ ଏବଂ ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଗ୍ୟାସ୍କୁ ବାହାରକୁ ଆଣିବାପାଇଁ କରାଯାଉଥିବା ଗଭୀର କୂପ ଖନନ ପ୍ରକ୍ରିୟାକୁ ଡ୍ରିଲିଂ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
Question 34.
ମୁଖ୍ୟ ଖଣିଜଗୁଡ଼ିକର ବ୍ୟବହାର ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧରେ ଲେଖ ।
Answer:
ଲୁହାପଥର ଷ୍ଟିଲ ଉତ୍ପାଦନ, ବକ୍ସାଇଟ୍ରୁ ଆଲୁମିନିୟମ୍, ମାଙ୍ଗାନିଜରୁ ମିଶ୍ରଧାତୁ, କ୍ରୋମାଇଟ୍ରୁ ଇସ୍ପାତ ଓ ଚମଡ଼ା ଉତ୍ପାଦନ ଏବଂ ଅଭ୍ରରୁ ବୈଦ୍ୟୁତିକ ସରଞ୍ଜାମ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ ହୋଇ ବୈଦ୍ୟୁତିକ ଶିଳ୍ପରେ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଉଅଛି ।
Question 35.
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ବିଭିନ୍ନ ଜିଲ୍ଲାରେ ମିଳୁଥିବା ଲୁହାପଥର, ବକ୍ସାଇଟ୍ ଓ ଅଗ୍ର ଆଦି ଖଣିଜ ପଦାର୍ଥ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧରେ ଆଲୋଚନା କର ।
Answer:
ଓଡ଼ିଶାରେ ଲୁହାପଥର କେନ୍ଦୁଝର ଓ ଯାଜପୁର ଜିଲ୍ଲାରେ, ବକ୍ସାଇଟ୍ କୋରାପୁଟ ଓ କଳାହାଣ୍ଡି ଜିଲ୍ଲାରେ ଏବଂ ଅଭ୍ର ବଲାଙ୍ଗୀର ଓ କଳାହାଣ୍ଡି ଜିଲ୍ଲାରେ ମିଳିଥାଏ ।
Question 36.
ଭାରତର ପ୍ରଧାନ ଖଣ୍ଟିକତୈଳ କ୍ଷେତ୍ର ଏବଂ ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ବାଷ୍ପ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରଗୁଡ଼ିକ ବିଷୟରେ ଏକ ବିବରଣୀ ପ୍ରଦାନ କର ।
Answer:
- ଭାରତରେ ଆସାମର ଦିଗ୍ବୋଇ, ମୁମ୍ବାଇର ବମ୍ବେ ହାଇ ଏବଂ ଗୋଦାବର୍ଗୀ ଓ କୃଷ୍ଣା ନଦୀର ତ୍ରିକୋଣଭୂମି ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ପେଟ୍ରୋଲିୟମ୍ ଖଣିଜତୈଳ ରହିଅଛି ।
- ଭାରତର ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ବାଷ୍ପ ରାଜସ୍ଥାନର ଜୈସାଲମୀର, କୃଷ୍ଣା, ଗୋଦାବରୀ ତ୍ରିକୋଣଭୂମି, ତ୍ରିପୁରା ଓ ମୁମ୍ବାଇ ନିକଟସ୍ଥ ସାଗର ଗର୍ଭରେ ଗଚ୍ଛିତ ରହିଛି ଏବଂ ସେଠାରୁ ଏହା ଉତ୍ତୋଳନ କରାଯାଉଅଛି

Question 37.
ଅଧାତବ ଖଣିଜ କେଉଁଠାରେ ମିଳେ ଉଲ୍ଲେଖ କର ।
Answer:
ସମତଳଭୂମି ଓ ତରୁଣ ଭଙ୍ଗିଳ ପର୍ବତଗୁଡ଼ିକର ସ୍ତରୀୟ ଶିଳାରେ ଚୂନପଥର ମିଳିଥାଏ । ଆଲଜେରିଆର ଫସ୍ଫେଟ୍, ଫ୍ରାନ୍ସର କକେସିସ୍ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଚୂନପଥର ଅଧାତବ ଖଣିଜ ପଦାର୍ଥର ଉଦାହରଣ ।
କାରଣ ଦର୍ଶାଅ ।
Question 1.
ପେଟ୍ରୋଲିୟମ୍କୁ ‘କୃଷ୍ଣ ସୁବର୍ଷ’ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
Answer:
- ପେଟ୍ରୋଲିୟମ୍ରୁ ଡିଜେଲ, ପେଟ୍ରୋଲ୍, କିରୋସିନି, ଓ୍ବାକସ୍, ପ୍ଲାଷ୍ଟିକ୍ ଏବଂ ଅନ୍ୟାନ୍ୟ ଘର୍ଷଣ ନିରୋଧକ ଦ୍ରବ୍ୟ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ କରାଯାଏ ।
- ଏହା ଅତି ମୂଲ୍ୟବାନ ଓ ଦରକାରୀ ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ ତାହାକୁ ‘କୃଷ୍ଣ ସୁବର୍ଷ’ ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ।
Question 2.
ଅବଶିଷ୍ଟ ମୃଭିକାଠାରୁ ପରିବାହିତ ମୃତ୍ତିକା ଅଧିକ ଊର୍ବର।
Answer:
- ପରିବାହିତ ସୃଷ୍ଟିକାରେ ଅତି ମାତ୍ରାରେ ସୂକ୍ଷ୍ମଶିଳାରେଣୁ ସହିତ ଜୈବାଂଶ ମିଶି କରିଥାଏ ।
- ତେଣୁ ଏହା ଅଧ୍ବକ ଉର୍ବର ଓ କୃଷିକାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ପାଇଁ ବିଶେଷ ଉପଯୋଗୀ ।
Question 3.
ଶୁଷ୍କ ମୃତ୍ତିକାକୁ ଶୁଷ୍କ ଉଭିଦଦ୍ଵାରା ଘୋଡ଼ାଇ ରଖାଯାଏ ।
Answer:
- ଶୁଷ୍କ ମୃରିକା, ଆର୍ଦ୍ର ମ୍ପରିକା ଅପେକ୍ଷା ଅଧିକ କ୍ଷୟଶୀଳ।
- ଏଣୁ ଉଭିଦ-ଉଭିଦ ମଧ୍ଯସ୍ଥ ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନକୁ ଶୁଷ୍କ ଉଦ୍ଭଦ; ଯଥା – ନଡ଼ା, କୁଟା, ଶୁଖୁଲାପତ୍ର ଦ୍ଵାରା ଘୋଡ଼ାଇ ରଖୁଲେ ମୃରିକାର ଆର୍ଦ୍ରତା ଅଧୂକ ଦିନ ରହେ ଏବଂ ଏହାଦ୍ଵାରା ମୃରିକା କ୍ଷୟ ବିଳମ୍ବିତ ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
Question 4.
ମୌସୁମୀ ଅରଣ୍ୟକୁ ପଶ୍ଚିମୋଚୀ ଅରଣ୍ୟ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
Answer:
- ନିରକ୍ଷୀୟ ଅରଣ୍ୟର ଉଭୟ ପାର୍ଶ୍ଵରେ ୫° ଉତ୍ତରରୁ ୨୫° ଉତ୍ତର ଓ ୫° ଦକ୍ଷିଣରୁ ୨୫° ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଅକ୍ଷାଂଶ ମଧ୍ଯରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଋତୁକାଳୀନ ବର୍ଷା ହେଉଥିବାରୁ ଏହାକୁ ମୌସୁମୀ ଅରଣ୍ୟ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
- ଏହି ଅରଣ୍ୟର ପତ୍ରଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଏକ ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ ଋତୁରେ ପତ୍ରଝଡ଼ା ଦେଉଥିବାରୁ ଏହାକୁ ପଶ୍ଚିମୋଚୀ ଅରଣ୍ୟ କୁହାଯାଏ । ତେଣୁ ମୌସୁମୀ ଅରଣ୍ୟକୁ ପଶ୍ଚିମୋଚୀ ଅରଣ୍ୟ କୁହାଯାଏ।

Question 5.
ବନ୍ୟଜନ୍ତୁଙ୍କ ସଂଖ୍ୟା କ୍ରମଶଃ ହ୍ରାସ ପାଇବାରେ ଲାଗିଛି ।
Answer:
- ଆଜିକାଲି ଅଣ୍ଡାର ବହୁଳ ବ୍ୟବହାର ହେତୁ ପକ୍ଷୀଙ୍କର ବଂଶ ବୃଦ୍ଧି ଘଟିପାରୁ ନାହିଁ ।
- ପକ୍ଷୀ ହତ୍ୟା ଓ ପଶୁ ହତ୍ୟା କରି ସେମାନଙ୍କର ଚମଡ଼ା, ମାଂସ, ଦାନ୍ତ ଓ ଶିଙ୍ଗର ବ୍ୟବହାର ଫଳରେ ବନ୍ୟଜନ୍ତୁଙ୍କ ସଂଖ୍ୟା କ୍ରମଶଃ ହ୍ରାସ ପାଇବାରେ ଲାଗିଛି ।
Question 6.
ଶକ୍ତି ସମ୍ବଳର ବୃଦ୍ଧି ପାଇଁ ଚେଷ୍ଟା କରାଯିବା ଉଚିତ।
Answer:
- ଆଜିକାଲି ଶକ୍ତିକୁ ବିଭିନ୍ନ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଉଛି । ତେଣୁ ଶକ୍ତିର ଚାହିଦା ବୃଦ୍ଧି ହେବାରେ ଲାଗିଛି ।
- ଅତ୍ୟଧିକ ବ୍ୟବହାର ଯୋଗୁଁ ଦିନ ଆସିବ ପୃଥିବୀ ଶକ୍ତି ସମ୍ବଳ ଶୂନ୍ୟ ହୋଇଯିବ। ତେଣୁ ଶକ୍ତି ସମ୍ବଳର ବୃଦ୍ଧି ପାଇଁ ଚେଷ୍ଟା କରାଯିବା ଉଚିତ ।
Question 7.
କ୍ରାନ୍ତିମଣ୍ଡଳୀୟ ଦେଶରେ ସୌରଶକ୍ତିର ବ୍ୟବହାର ସର୍ବାଧ୍ଵକ।
Answer:
- କ୍ରାନ୍ତିମଣ୍ଡଳରେ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟଙ୍କର ଲମ୍ବ କିରଣ ହେତୁ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟଙ୍କର ଉତ୍ତାପ ଓ ଆଲୋକକୁ ସୌରସେଲରେ ଧରାଯାଇ ସେଥୁରୁ ବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନ କରାଯାଏ ।
- ସୌର ରଶ୍ମିର ପ୍ରଖରତା ଓ ସ୍ଥାୟିତ୍ଵ ଅଧିକ ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ କ୍ରାନ୍ତିମଣ୍ଡଳୀୟ ଦେଶରେ ସୌରଶକ୍ତିର ବ୍ୟବହାର ଅଧିକ ।
Question 8.
ନେଦରଲ୍ୟାଣ୍ଡରେ ପବନ ଫାର୍ମମାନ ଗଠିତ ହୋଇଛି।
Answer:
- ସମୁଦ୍ର ଉପକୂଳ ଓ ଗିରିପଥଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ବାୟୁର ବେଗ ଅଧ୍ଵକ ହୋଇଥବାରୁ ସେଠାରେ ଏକାଧିକ ପବନକଳକୁ ନେଇ ପବନ ଫାର୍ମମାନ ଗଠିତ ହୋଇଥାଏ।
- ନେଦରଲ୍ୟାଣ୍ଡରେ ଏସବୁ ସୁବିଧା ଥିବାରୁ ଏଠାରେ ପବନ ଫାର୍ମମାନ ଗଢ଼ି ଉଠିଛି ।
Question 9.
କୋଇଲାକୁ ଜୀବାଶ୍ମ ଇନ୍ଧନ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
Answer:
- ଉଦ୍ଭଦ ଓ ପ୍ରାଣୀମାନଙ୍କ ନଷ୍ଟାବଶେଷ ନିୟୁତ ନିୟୁତ ବର୍ଷ ଧରି ଭୂଗର୍ଭରେ ତାପ ଓ ଚାପ ପ୍ରଭାବରେ ରୂପାନ୍ତରିତ ହୋଇ କୋଇଲା, ପେଟ୍ରୋଲିୟମ୍ ଆଦିରେ ପରିଣତ ହୁଏ ।
- ତେଣୁ କୋଇଲାକୁ ଜୀବାଶ୍ମ ଇନ୍ଧନ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
Question 10.
ଏବେ ସମୁଦ୍ରକୂଳରେ ଅଧିକ ଝାଉଁବଣ ସୃଷ୍ଟି କରାଯାଉଛି।
Answer:
- ସମୁଦ୍ର ଉପକୂଳରେ ବାଲୁକାଶଯ୍ୟାରେ ଝାଉଁବଣ ସୃଷ୍ଟିକଲେ ସମୁଦ୍ରର ଉଚ୍ଚ ଢ଼େଉ ଓ ବାତ୍ୟାଜନିତ କୂଳକ୍ଷୟ ହ୍ରାସପାଇବ ।
- ତେଣୁ ଏବେ ସମୁଦ୍ର ଉପକୂଳରେ ଅଧିକ ଝାଉଁବଣ ସୃଷ୍ଟି କରାଯାଉଛି ।

Question 11.
ପୃଥିବୀର ବିଭିନ୍ନ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଭିନ୍ନ ଭିନ୍ନ ଭାବରେ ଭୂମିର ବ୍ୟବହାର ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
Answer:
- ପୃଥିବୀର ବିଭିନ୍ନ ଅଞ୍ଚଳର ଭୂବ୍ୟବହାର ଏହାର ମାନବୀୟ ଓ ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ବ୍ୟବସ୍ଥା ଉପରେ ନିର୍ଭରଶୀଳ ।
- ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଅବସ୍ଥା ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଭୂପ୍ରକୃତି, ମୃତ୍ତିକା, ଜଳବାୟୁ, ଖଣିଜ ଓ ଜଳର ସୁଲଭତା ଏବଂ ମାନବୀୟ ଅବସ୍ଥା ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଜନସଂଖ୍ୟା, ଶିକ୍ଷା, ବୈଷୟିକ ଜ୍ଞାନ ଓ ପ୍ରୟୋଗାତ୍ମକ କୌଶଳ ସବୁ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ସମାନ ନଥାଏ । ତେଣୁ ପୃଥିବୀର ବିଭିନ୍ନ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଭିନ୍ନ ଭିନ୍ନ ଭାବରେ ଭୂମିକୁ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଇଥାଏ ।
Question 12.
ମାଳଭୂମି ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ କୃଷିକାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଲାଭଜନକ ନୁହେଁ ।
Answer:
- ମାଳଭୂମି ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ମୃତ୍ତିକା ସ୍ତର ପତଳା, ପଥୁରିଆ ଓ ଜଳଧାରଣ କ୍ଷମତା କମ୍ ।
- ତେଣୁ ଏହି ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ କୃଷିକାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଲାଭଜନକ ନୁହେଁ ।
Question 13.
ଭୂମିକୁ ଏକ ଗୁରୁତ୍ଵପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ ସମ୍ବଳ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
Answer:
- ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ତା’ର ଜୀବନରେ ଗୁଜୁରାଣ ମେଣ୍ଟାଇବାକୁ ଭୂସମ୍ବଳକୁ ବିଭିନ୍ନ ଭାବରେ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିଥାଏ । ବସତି ସ୍ଥାପନ, କୃଷିକାର୍ଯ୍ୟ, ପଶୁପାଳନ୍ତ ଗମନାଗମନ ପଥ ନିର୍ମାଣ, ବନୀକରଣ, ଖଣିଜ ଉତ୍ତୋଳନ, କାରଖାନା ଓ ବାଣିଜ୍ୟ କେନ୍ଦ୍ର ନିର୍ମାଣ ଆଦିରେ ଭୂମିର ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଏ ।
- ଭୂମିବିନା ଜୀବଜଗତ ତିଷ୍ଠିବା ସମ୍ଭବ ନୁହେଁ, ତେଣୁ ଭୂମିକୁ ଗୁରୁତ୍ଵପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ ସମ୍ବଳ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
ପାର୍ଥକ୍ୟ ଦର୍ଶାଅ ।
1. ଜଳ ପ୍ରବାହ ଓ ଜଳଚକ୍ର :
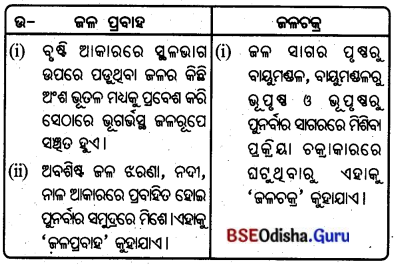
2. ତୃଣଭୋଜୀ ପ୍ରାଣୀ ଓ ମାଂସାଶୀ ପ୍ରାଣୀ :
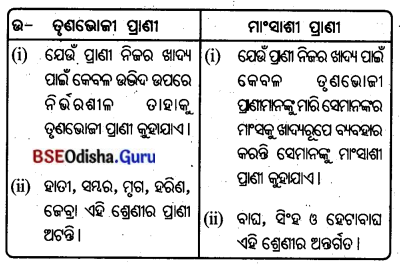
3. ଶିମିଳିପାଳ ଓ ଚନ୍ଦକା :
4. ସାଧାରଣ ଖନନ ଓ ଖଣି ଖନନ :

5. ଡ୍ରିଲିଂ ଓ ନିଷ୍କାସନ
6. ମୁକ୍ତଗର୍ଭ ଖଣି ଖନନ ଓ ଗଭୀର ଖଣି ଖନନ :
7. କୃଷ୍ଣ ହୀରକ ଓ କୃଷ୍ଣ ସୁବର୍ଷ :
8. ଜୈବମଣ୍ଡଳ ଓ ପରିସଂସ୍ଥା :
9. କାଜିରଙ୍ଗା ଓ ସୁନ୍ଦରବନ :
10. ଖଦର ଓ ଭାଙ୍ଗର :
11. ଲୌହଯୁକ୍ତ ଖଣିଜ ଓ ଲୌହବିହୀନ ଖଣିଜ :

12. ଉଷ୍ଣ ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଓ ଶୀତଳ ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ ଅରଣ୍ୟ:
13. ପଟୁମାଟି ଓ କଳାମାଟି :
14. ଆନିକଟ୍ ଓ ବ୍ୟାରେଜ୍ :
15. ଦୋରସା ମାଟି ଓ ମଟାଳ ମାଟି :
ପରୀକ୍ଷା ଉପଯୋଗୀ ସମ୍ଭାବିତ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନୋତ୍ତର
ବସ୍ତୁନିଷ୍ଠ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନୋତ୍ତର
ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନ ପୂରଣ କର ।
1. ମିଥେନ୍ ଓ ଅଙ୍ଗାରକାମ୍ଳ ମିଶ୍ରିତ ଗ୍ୟାସ୍କୁ ——— କୁହାଯାଏ ।
Answer:
ବାୟୋଗ୍ୟାସ୍
2. ପୃଥିବୀର ସର୍ବବୃହତ୍ ଭୂ-ତାପଜ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନକାରୀ ଦେଶ ହେଉଛି ———
Answer:
ଯୁକ୍ତରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ଆମେରିକା
3. ରାଣାପ୍ରତାପ ସାଗର, ——— ରାଜ୍ୟରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ ।
Answer:
ରାଜସ୍ଥାନ

4. ମୋନାଜାଇଟ୍ ବାଲୁକା, ——— ରାଜ୍ୟରେ ମିଳେ।
Answer:
କେରଳ
5. ———- ରେ ଆଣବିକ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପନ୍ନ କରାଯାଏ।
Answer:
ଆଣବିକ ରିଆକ୍ଟର
6. ——— ଦେଶଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ସୌର ଶକ୍ତିର ବ୍ୟବହାର ସର୍ବାଧକ ।
Answer:
କ୍ରାନ୍ତିମଣ୍ଡଳୀୟ
7. ଜଳଭଣ୍ଡାରର ବନ୍ଧ ତଳେ ସ୍ଥାପିତ ——— ର ପାତ ଘୂରିଲେ ଜେନେରେଟରରେ ବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ଶକ୍ତି ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହୁଏ ।
Answer:
ଟରବାଇନ୍
8. ଦିଗ୍ବୋଇ ——— ରାଜ୍ୟରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ ।
Answer:
ଆସାମ
9. ——— ଖଣିଜରୁ ସିଲିକନ୍ ଉତ୍ପାଦନ କରାଯାଏ ।
Answer:
କ୍ୱାର୍ଡ

10. ଚୂନପଥର ମିଳୁଥବା କକେସସ୍ ଅଞ୍ଚଳ ——— ଦେଶରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ ।
Answer:
ଫ୍ରାନ୍ସ
ଗୋଟିଏ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ଉତ୍ତର ଦିଅ ।
Question 1.
ପୃଥିବୀ ପୃଷ୍ଠରେ କେତେ ଭାଗ ସ୍ଥଳ ରହିଛି ?
Answer:
ପୃଥିବୀ ପୃଷ୍ଠରେ ୨୯ ଭାଗ ସ୍ଥଳ ରହିଛି।
Question 2.
ସ୍ଥଳଭାଗ କେତୋଟି ମହାଦେଶକୁ ନେଇ ଗଠିତ ?
Answer:
ସ୍ଥଳଭାଗ ସାତଗୋଟି ମହାଦେଶକୁ ନେଇ ଗଠିତ।
Question 3.
‘କେଉଁ ମହାଦେଶ ବୃହତ୍ତମ ଅଟେ ?
Answer:
ଏସିଆ ମହାଦେଶ ବୃହତ୍ତମ ଅଟେ ।
Question 4.
କେଉଁ ମହାଦେଶ କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ରତମ ଅଟେ ?
Answer:
ଅଷ୍ଟ୍ରେଲିଆ କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ରତମ ମହାଦେଶ ଅଟେ
Question 5.
କେଉଁ ମହାଦେଶ ମାନବଶୂନ୍ୟ ଅଟେ ?
Answer:
ଆଣ୍ଟାର୍କଟିକା ମହାଦେଶ ବରଫାଚ୍ଛନ୍ନ ଥିବାରୁ ତାହା ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ବାସୋପଯୋଗୀ ନୁହେଁ ।

Question 6.
ଭାରତ କେଉଁ ମହାଦେଶରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ ?
Answer:
ଭାରତ ଏସିଆ ମହାଦେଶରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ ।
Question 7.
ପାର୍ବତ୍ୟ ଭୂମି କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଅଧିକ ଉଚ୍ଚତା ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ପାହାଡ଼ ଓ ପର୍ବତଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ପାର୍ବତ୍ୟ ଭୂମି କୁହାଯାଏ ।
Question 8.
ମାଳଭୂମି କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଅଳ୍ପ ଉଚ୍ଚନୀଚ ହୋଇଥିବା ବିସ୍ତୀର୍ଣ୍ଣ ପଥୁରିଆ ଅଞ୍ଚଳକୁ ମାଳଭୂମି କୁହାଯାଏ ।
Question 9.
ସମତଳ ଭୂମି କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ସମୁଦ୍ର ପତ୍ତନରୁ ଅଳ୍ପ ଉଚ୍ଚରେ ଥିବା ପ୍ରାୟ ସମାନ ଉଚ୍ଚତା ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ଅଞ୍ଚଳକୁ ସମତଳ ଭୂମି କୁହାଯାଏ।
Question 10.
ଏସିଆ ମହାଦେଶର ମୁଖ୍ୟ ପାର୍ବତ୍ୟଭୂମିର ନାମ କ’ଣ ?
Answer:
ହିମାଳୟ ଏସିଆ ମହାଦେଶର ମୁଖ୍ୟ ପାର୍ବତ୍ୟ ଭୂମି। .
Question 11.
ଇଉରୋପର ମୁଖ୍ୟ ପାର୍ବତ୍ୟ ଭୂମିର ନାମ କ’ଣ ?
Answer:
ଆଲପ୍ସ ଇଉରୋପର ମୁଖ୍ୟ ପାର୍ବତ୍ୟ ଭୂମି।
Question 12.
ଉତ୍ତର ଆମେରିକା ଓ ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆମେରିକାର ମୁଖ୍ୟ ପାର୍ବତ୍ୟ ଭୂମିର ନାମ କ’ଣ ?
Answer:
ଉତ୍ତର ଆମେରିକାର ରକି ଓ ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆମେରିକାର ଆଣ୍ଡିଜ୍ ପର୍ବତମାଳା ମୁଖ୍ୟ ପର୍ବତମାଳା ଅଟେ।
Question 13.
ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆମେରିକାର ମୁଖ୍ୟ ମାଳଭୂମିର ନାମ କ’ଣ ?
Answer:
ବ୍ରାଜିଲ୍ ଓ ପାଟାଗୋନିଆ ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆମେରିକାର ମୁଖ୍ୟ ମାଳଭୂମି ଅଞ୍ଚଳ ଅଟେ।
Question 14.
ଭାରତର କେଉଁଠାରେ ସମତଳ ଭୂମି ଅଧିକ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଭାରତର ଗାଙ୍ଗେୟ ଓ ଉପକୂଳବର୍ତ୍ତୀ ସ୍ଥାନମାନଙ୍କରେ ସମତଳ ଭୂମି ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
Question 15.
ଭାରତର ଶତକଡ଼ା କେତେ ଭାଗ ଭୂମିରେ କୃଷି କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଭାରତର ସମୁଦାୟ ଭୂମିର ଶତକଡ଼ା ପ୍ରାୟ ୫୪ ଭାଗ ଭୂମିରେ କୃଷି କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରାଯାଏ।
Question 16.
ଭାରତର ଶତକଡ଼ା କେତେ ଭାଗ ଭୂମିରେ ଜନବସତି ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଭାରତର ଶତକଡ଼ା ୧୯ ଭାଗ ଭୂମିରେ ଜନବସତି ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।

Question 17.
ଭାରତର ଶତକଡ଼ା କେତେ ଭାଗ ଭୂମିରେ ଚାରଣ ଓ ଗୋଚର ଭୂମି ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଭାରତର ଶତକଡ଼ା ୪ ଭାଗ ଭୂମିରେ ଚାରଣ ଓ ଗୋଚର ଭୂମି ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
Question 18.
ଭାରତର ସମୁଦାୟ ଆୟତନର ଶତକଡ଼ା କେତେ ଭାଗରେ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ରହିବା ଆବଶ୍ୟକ ?
Answer:
ଭାରତର ସମୁଦାୟ ଆୟତନର ଶତକଡ଼ା ୩୩ ଭାଗରେ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ରହିବା ଆବଶ୍ୟକ।
Question 19.
ଭାରତର ସମୁଦାୟ ଆୟତନର ଶତକଡ଼ା କେତେଭାଗ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ରହିଛି ?
Answer:
ଭାରତର ସମୁଦାୟ ଆୟତନର ଶତକଡ଼ା ୨୨ ଭାଗ ଭୂମି ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଦ୍ଵାରା ଆଚ୍ଛାଦିତ ।
Question 20.
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଶତକଡ଼ା କେତେ ଭାଗ ଭୂମିରେ କୃଷି କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଶତକଡ଼ା ପ୍ରାୟ ୪୭ ଭାଗ ଭୂମିରେ କୃଷି କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରାଯାଏ।
Question 21.
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଶତକଡ଼ା କେତେ ଭାଗ ଭୂମିରେ ଜନବସତି ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଶତକଡ଼ା ୧୬ ଭାଗ ଭୂମିରେ ଜନବସତି ଦେଖାଯାଏ।
Question 22.
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଶତକଡ଼ା କେତେ ଭାଗ ଭୂମିରେ ଚାରଣ ଓ ଗୋଚର ଭୂମି ରହିଛି ?
Answer:
ଓଡ଼ିଶାରେ ଶତକଡ଼ା ୫ ଭାଗ ଭୂମିରେ ଚାରଣ ଓ ଗୋଚର ଭୂମି ରହିଛି।
Question 23.
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଶତକଡ଼ା କେତେ ଭାଗ ଭୂମି ଅରଣ୍ୟ ରୂପେ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଉଛି ?
Answer:
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଶତକଡ଼ା ପ୍ରାୟ ୩୨ ଭାଗ ଭୂମି ଅରଣ୍ୟ ରୂପେ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଉଛି ।
Question 24.
ସମୁଦ୍ର ଉପକୂଳରେ କେଉଁ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ସୃଷ୍ଟି କଲେ ସମୁଦ୍ରର ଉଚ୍ଚ ଜେଜ ଓ ବାତ୍ୟାଜନିତ’ କୂଳକ୍ଷୟ ହ୍ରାସ ପାଇବ ?
Answer:
ସମୁଦ୍ର ଉପକୂଳରେ ଝାଉଁବଣ ସୃଷ୍ଟି କଲେ ସମୁଦ୍ରର ଉଚ୍ଚ ଢେଉ ଓ ବାତ୍ୟାଜନିତ କୂଳକ୍ଷୟ ହ୍ରାସ ପାଇବ।

Question 25.
ପ୍ରାଥମିକ ଶିଳା ମୃରିକାର କେଉଁ ଗୁଣକୁ ପ୍ରଭାବିତ କରିଥାଏ ?
Answer:
ପ୍ରାଥମିକ ଶିଳା ମୃତ୍ତିକାର ରଙ୍ଗ, ବିନ୍ୟାସ, ରାସାୟନିକ ଗୁଣ, ଅନ୍ତର୍ନିହିତ ଖଣିଜ ଓ ଭେଦ୍ୟତାକୁ ପ୍ରଭାବିତ କରିଥାଏ।
Question 26.
ମୃଲିକା ସ୍ତରର ପାର୍ଶ୍ଵଚ୍ଛେଦର ନିମ୍ନଭାଗରେ କେଉଁ ସ୍ତର ରହିଛି ?
Answer:
ମୃତ୍ତିକା ସ୍ତରର ପାର୍ଶ୍ୱଚ୍ଛେଦର ନିମ୍ନଭାଗରେ ପ୍ରାଥମିକ ଶିଳାସ୍ତର ରହିଛି।
Question 27.
ମୁଭିକାର ବହଳତାକୁ କିଏ ପ୍ରଭାବିତ କରିଥାଏ ?
Answer:
ମୃତ୍ତିକାର ବହଳତାକୁ ସମୟ ପ୍ରଭାବିତ କରିଥାଏ।
Question 28.
ମୃତ୍ତିକାର ପ୍ରାଥମିକ ଶିଳା ସ୍ତରର ଉପରେ କେଉଁ ସ୍ତର ରହିଥାଏ ?
Answer:
ମୃରିକାର ପ୍ରାଥମିକ ଶିଳା ସ୍ତରର ଉପରେ ଚୂଷ୍ଣୀଭୂତ ଶିଳାଦ୍ରବ୍ୟ ରହିଥାଏ ।
Question 29.
ପଟୁମାଟି କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଯେଉଁ ମାଟିରେ ଅତିମାତ୍ରାରେ ସୂକ୍ଷ୍ମ ଶିଳାରେଣୁ ସହିତ ଜୈବାଂଶ ମିଶିକରି ଥାଏ, ତାହାକୁ ପଟୁମାଟି କୁହାଯାଏ।
Question 30.
ଦୋରସା ମାଟି କିପରି ଗଠିତ ହୁଏ ?
Answer:
ବାଲି ଓ ପଟୁ ସମପରିମାଣରେ ଥିବା ମୃରିକାକୁ ଦୋରସା ମାଟି କୁହାଯାଏ ।

Question 31.
ମଟାଳ ମାଟି କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଅତିମାତ୍ରାରେ ସୂକ୍ଷ୍ମ ଶିଳାରେଣୁ ପରିମାଣ ଅଧିକ ହୋଇ ପଟୁର ପରିମାଣ କମ୍ ହେଲେ ତାହାକୁ ମଟାଳ ମାଟି କୁହାଯାଏ ।
Question 32.
କେଉଁ ମାନବୀୟ କାରଣ ଯୋଗୁ ମୃତ୍ତିକା କ୍ଷୟ ହୋଇଥାଏ ?
Answer:
ଜଙ୍ଗଲ କ୍ଷୟ, ଅତ୍ୟଧିକ ଚାରଣ, ରାସାୟନିକ ସାର ଓ କୀଟନାଶକ ଦ୍ରବ୍ୟର ବ୍ୟବହାର, ଖଣି ଖନନ ଆଦି ମାନବୀୟ କାରଣ ଯୋଗୁ ମ୍ପରିକା କ୍ଷୟ ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
Question 33.
କେଉଁ ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ କାରଣ ଯୋଗୁ ମୃରିକା କ୍ଷୟ ହୋଇଥାଏ ?
Answer:
ବୃଷ୍ଟି, ବନ୍ୟା, ଜଳପ୍ରବାହ ଓ ଭୂସ୍ଖଳନ ଆଦି ମ୍ପରିକା କ୍ଷୟର ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ କାରଣ ଅଟେ ।
Question 34.
ପୃଥିବୀରେ ମିଳୁଥିବା ସମସ୍ତ ଜଳର ଶତକଡ଼ା କେତେଭାଗ ମଧୁର ଜଳ ?
Answer:
ପୃଥିବୀରେ ମିଳୁଥିବା ସମସ୍ତ ଜଳର ଶତକଡ଼ା ୨.୭ ଭାଗ ମଧୁର ଜଳ।
Question 35.
ଶତକଡ଼ା ୭୦ ଭାଗ ମଧୁର ଜଳ କେଉଁଠାରେ ରହିଛି ?
Answer:
ଶତକଡ଼ା ପ୍ରାୟ ୭୦ ଭାଗ ଜଳ ଗ୍ରୀନ୍ ଲାଣ୍ଡ ଓ ଉଚ୍ଚ ପର୍ବତଶିଖରମାନଙ୍କରେ ବରଫ ଚାଦର ଆକାରରେ ରହିଛି।
Question 36.
ପୃଥିବୀରେ ମିଳୁଥିବା ମଧୁର ଜଳର ଶତକଡ଼ା କେତେ ଭାଗ ମନୁଷ୍ୟର ବ୍ୟବହାରରେ ଲାଗିଥାଏ ?
Answer:
ପୃଥିବୀରେ ମିଳୁଥିବା ମଧୁର ଜଳର ଶତକଡ଼ା ମାତ୍ର ଏକ ଭାଗ ମନୁଷ୍ୟର ବ୍ୟବହାରରେ ଲାଗିଥାଏ ।
Question 37.
ଓଡ଼ିଶାରେ କେଉଁ ହ୍ରଦ ରହିଛି ?
Answer:
ଓଡ଼ିଶାରେ ଚିଲିକା ଓ ଅଂଶୁପା ହ୍ରଦ ରହିଛି।
Question 38.
ଜଳାଭାବର ମୁଖ୍ୟ କାରଣ କ’ଣ ?
Answer:
ଜଳାଭାବର ମୁଖ୍ୟ କାରଣ ହେଲା ଜନସଂଖ୍ୟା ବୃଦ୍ଧି ଓ ଶିଳ୍ପାୟନ।
Question 39.
ଜଣେ ସହରୀ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ଦୈନିକ କେତେ ଲିଟର ଜଳ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିଥାଏ ?
Answer:
ଜଣେ ସହରୀ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ଦୈନିକ ୧୫୦ ଲିଟର ଜଳ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିଥାଏ ।

Question 40.
ଡ୍ୟାମ୍ କେଉଁ ଉଦ୍ଦେଶ୍ୟ ପୂରଣ କରେ ?
Answer:
ଜଳସେଚନ, ବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନ ଓ ବନ୍ୟା ନିୟନ୍ତ୍ରଣ ଆଦି ବିଭିନ୍ନ ଉଦ୍ଦେଶ୍ୟ ପୂରଣ କରେ।
Question 41.
ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଉଭିଦ କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ମନୁଷ୍ୟର ବିନା ସାହାଯ୍ୟରେ ଆପେ ଆପେ ଜନ୍ମି ବଢୁଥିବା ବୃକ୍ଷ, ଲତା ଓ ତୃଣ ଆଦିକୁ ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଉଭିଦ, କୁହାଯାଏ।
Question 42.
“ ଡାଇକ୍ଲୋଫେନାକ୍” ଔଷଧର ବ୍ୟବହାର ଫଳରେ କେଉଁ ପକ୍ଷୀର ବଂଶଲୋପ ପାଉଛି ?
Answer:
“ ଡାଇକ୍ଲୋଫେନାକ” ଔଷଧର ବ୍ୟବହାର ଫଳରେ ଶାଗୁଣା ପକ୍ଷୀର ବଂଶଲୋପ ପାଉଛି ।
Question 43.
କେଉଁ ପକ୍ଷୀ ପରାଗ ସଙ୍ଗମରେ ସାହାଯ୍ୟ କରନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ମହୁମାଛି ପରାଗ ସଙ୍ଗମରେ ସାହାଯ୍ୟ କରନ୍ତି।
Question 44.
କେଉଁ ପକ୍ଷୀ ପରିବେଶକୁ ସଫା ରଖନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
କୁଆ ଓ ଶାଗୁଣା ପରିବେଶକୁ ସଫା ରଖନ୍ତି ।

Question 45.
କେତେ ଅକ୍ଷାଂଶ ମଧ୍ଯରେ ନିରକ୍ଷୀୟ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ବିଷୁବବୃତ୍ତର ଉଭୟ ପାର୍ଶ୍ଵରେ ୫° ଉତ୍ତର ଓ ୫° ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଅକ୍ଷାଂଶ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ନିରକ୍ଷୀୟ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ।
Question 46.
କେଉଁ ବୃକ୍ଷଗୁଡ଼ିକ ନିରକ୍ଷୀୟ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଆବୁଲ, ମେହଗାନି ଓ ରବର ନିରକ୍ଷୀୟ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଦେଖାଯାଏ।
Question 47.
ପର୍ବମୋର୍ଚ ଅରଣ୍ୟର ବିଶେଷତ୍ଵ କ’ଣ ?
Answer:
ବର୍ଷର ଏକ ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ ଋତୁରେ ଏହି ବୃକ୍ଷର ଅରଣ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକ ପତ୍ରଝଡ଼ା ଦେଇଥାଏ।
Question 48.
କେଉଁ ବୃକ୍ଷଗୁଡ଼ିକ କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ ଅରଣ୍ୟର ଅନ୍ତର୍ଗତ ?
Answer:
ଶାଳ, ପିଆଶାଳ, ଶିଶୁ ଓ ବାଉଁଶ କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ ଅରଣ୍ୟର ଅନ୍ତର୍ଗତ ।
Question 49.
ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ ଅରଣ୍ୟ କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଉଭୟ ଗୋଲାର୍ଦ୍ଧରେ ୨୫° ରୁ ୬୫° ଅକ୍ଷାଂଶ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଥିବା ଅରଣ୍ୟକୁ ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ ଅରଣ୍ୟ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
Question 50.
ଉଷ୍ଣ ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ ଅରଣ୍ୟର ପ୍ରଧାନ ବୃକ୍ଷଗୁଡ଼ିକର ନାମ କ’ଣ ?
Answer:
ଏହି ଅରଣ୍ୟରେ ଦୀର୍ଘ ତୈଳଯୁକ୍ତ ପତ୍ର ଏବଂ ମୋଟା ବକ୍କଳଯୁକ୍ତ ଅଲିଭ ଓ ଓକ୍ ପ୍ରଭୃତି ବୃକ୍ଷ ଜନ୍ମ।
Question 51.
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର କେତେଭାଗ ଭୂମିରେ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଶତକଡ଼ା ପ୍ରାୟ ୩୨ ଭାଗ ଭୂମିରେ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ।
Question 52.
କେଉଁ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଓଡ଼ିଶାରେ ଅଧିକ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ ଆର୍ଦ୍ର ପଶ୍ଚିମୋଚୀ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ସମୁଦାୟ ଅରଣ୍ୟର ଶତକଡ଼ା ପ୍ରାୟ ୮୦ ଭାଗ ଅଟେ ।
Question 53.
ବନ୍ୟପ୍ରାଣୀ କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଜଙ୍ଗଲରେ ମୁକ୍ତାଭାବରେ ବିଚରଣ କରି ବାସ କରୁଥିବା ପଶୁ, ପକ୍ଷୀ, କୀଟ, ପତଙ୍ଗ ଓ ସରୀସୃପ ଆଦିକୁ ବନ୍ୟପ୍ରାଣୀ ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ ।
Question 54.
ଉଭୟଭୋଜୀ ପ୍ରାଣୀ କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଯେଉଁ ପ୍ରାଣୀ ନିଜର ଖାଦ୍ୟପାଇଁ ଉଭୟ ଉଭିଦ ଓ ତୃଣଭୋଜୀ ପ୍ରାଣୀମାନଙ୍କର ମାଂସ ଉପରେ ନିର୍ଭର କରନ୍ତି ସେମାନଙ୍କୁ ଉଭୟଭୋଜୀ ପ୍ରାଣୀ କୁହାଯାଏ। ବିଲୁଆ ଓ ଭାଲୁ ଏହି ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଅଟନ୍ତି।

Question 55.
ଓଟ କେଉଁ ଅଞ୍ଚଳର ମୁଖ୍ୟ ପ୍ରାଣୀ ଅଟେ ?
Answer:
ସାହାରା ଓ ସାଉଦି ଆରବର ଗ୍ରୀଷ୍ମମଣ୍ଡଳୀୟ ମରୁଭୂମିଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ଓଟ ମୁଖ୍ୟ ପ୍ରାଣୀ, କାରଣ ଓଟ ଅଳ୍ପ ପାଣିପିଇ ଅଧୂକ ଦିନ ରହିପାରେ।
Question 56.
ଓଟପକ୍ଷୀ କେଉଁଠାରେ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଆଫ୍ରିକାର କାଲାହାରୀ ମରୁଭୂମିରେ ଓଟପକ୍ଷୀ ଦେଖାଯାଏ।
Question 57.
ଅଷ୍ଟ୍ରେଲିଆରେ ମୁଖ୍ୟତଃ କେଉଁ ପ୍ରାଣୀ ଦେଖାଯାଆନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ଅଷ୍ଟ୍ରେଲିଆରେ ମୁଖ୍ୟତଃ ଏମୁ ପକ୍ଷୀ ଓ କଙ୍ଗାରୁ ଦେଖାଯାନ୍ତି ।
Question 58.
ପେଙ୍ଗୁଇନ୍ କେଉଁ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଦେଖାଯାଆନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ଆଣ୍ଟାର୍କଟିକାର ବରଫାବୃତ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ପେଙ୍ଗୁଇନ୍ ଦେଖାଯାଏ।
Question 59.
ଉତ୍ତର ମେରୁ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ କେଉଁ ପ୍ରାଣୀ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଉତ୍ତର ମେରୁ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଧଳାଭାଲୁ, ସିଲ୍, ସିଲଭର ଫକ୍ସ ଆଦି ନରମ ଲୋମଯୁକ୍ତ ପ୍ରାଣୀ ବାସ କରନ୍ତି |
Question 60.
କସ୍ତୁରୀ ମୃଗ ଓ ଚମରୀ ଗାଈ କେଉଁଠାରେ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଭାରତ-ନେପାଳ ସୀମାନ୍ତରେ ହିମାଳୟ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ କସ୍ତୁରୀ ମୃଗ ଓ ଚମରୀ ଗାଈ ଦେଖାଯାଏ।
Question 61.
କାହାକୁ ଭାରତର ଜାତୀୟ ପକ୍ଷୀ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ମୟୂରକୁ ଭାରତର ଜାତୀୟ ପକ୍ଷୀ କୁହାଯାଏ।

Question 62.
କାହାକୁ ଭାରତର ଜାତୀୟ ପଶୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ବାଘକୁ ଭାରତର ଜାତୀୟ ପଶୁ କୁହାଯାଏ।
Question 63.
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର କେଉଁଠାରେ ନୀଳଗାଈ ଓ ଚଉଶିଙ୍ଗା ହରିଣ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଅନୁଗୁଳ, କୋରାପୁଟ ଓ ସମ୍ବଲପୁର ଅରଣ୍ୟମାନଙ୍କରେ ନୀଳଗାଈ ଓ ଚଉଶିଙ୍ଗା ହରିଣ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
Question 64.
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର କେଉଁଠାରେ ବଣୁଆ ମଇଁଷି ଦେଖିବାକୁ ମିଳେ ?
Answer:
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ମାଲକାନଗିରି ଓ ଖଡ଼ିଆଳ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ବଣୁଆ, ମଇଁଷି ଦେଖିବାକୁ ମିଳେ।
Question 65.
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର କେଉଁଠାରେ ଡଲଫିନ୍ ମାଛ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଚିଲିକା ହ୍ରଦରେ ଡଲଫିନ୍ ମାଛ ଦେଖାଯାଏ।
Question 66.
କେବେ ବନ୍ୟପ୍ରାଣୀ ବୋର୍ଡ଼ ଗଠନ କରାଯାଇଛି ?
Answer:
୧୯୭୨ ମସିହାରେ ବନ୍ୟପ୍ରାଣୀ ବୋର୍ଡ଼ ଗଠନ କରାଯାଇଛି ।
Question 67.
ସିଂହ ଅଭୟାରଣ୍ୟ କେଉଁଠାରେ ରହିଛି ?
Answer:
ଗୁଜୁରାଟର ସୌରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ଅନ୍ତର୍ଗତ ଗୀର ଜାତୀୟ ଉଦ୍ୟାନରେ ସିଂହ ଅଭୟାରଣ୍ୟ ରହିଛି ।

Question 68.
ରାଜସ୍ଥାନର ଭରତପୁର କାହିଁକି ପ୍ରସିଦ୍ଧ ?
Answer:
ବିଭିନ୍ନ ପ୍ରକାର ପକ୍ଷୀ ଅଭୟାରଣ୍ୟ ପାଇଁ ରାଜସ୍ଥାନର ଭରତପୁର ପ୍ରସିଦ୍ଧ ।
Question 69.
ଏକ ଶିଙ୍ଗଥିବା ଗଣ୍ଡା ଅଭୟାରଣ୍ୟ କେଉଁଠାରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ ?
Answer:
ଆସାମର ଜୋରହାଟ ଅନ୍ତର୍ଗତ କାଜିରଙ୍ଗା ଜାତୀୟ ଉଦ୍ୟାନଠାରେ ଏକ ଶିଙ୍ଗଥୁବା ଗଣ୍ଡାର ଅଭୟାରଣ୍ୟ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ। ,
Question 70.
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର କେଉଁଠାରେ ବ୍ୟାଘ୍ର ଅଭୟାରଣ୍ୟ ରହିଛି ?
Answer:
ମୟୂରଭଞ୍ଜ ଜିଲ୍ଲାର ଶିମିଳିପାଳଠାରେ ବ୍ୟାଘ୍ର ଅଭୟାରଣ୍ୟ ରହିଛି।
Question 71.
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର କେଉଁଠାରେ ହାତୀ ଅଭୟାରଣ୍ୟ ରହିଛି ?
Answer:
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଭୁବନେଶ୍ଵର ନିକଟବର୍ତୀ ଚନ୍ଦକା ଜଙ୍ଗଲରେ ହାତୀ ଅଭୟାରଣ୍ୟ ରହିଛି ।
Question 72.
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର କେଉଁଠାରେ କୁମ୍ଭୀର ସଂରକ୍ଷଣ କେନ୍ଦ୍ର ରହିଛି ?
Answer:
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଅନୁଗୁଳ ଜିଲ୍ଲା ଅନ୍ତର୍ଗତ ଟିକରପଡ଼ାର ସାତକୋଶିଆ ଏବଂ କେନ୍ଦ୍ରାପଡ଼ା ଜିଲ୍ଲାର ଭିତରକନିକାଠାରେ କୁମ୍ଭୀର ସଂରକ୍ଷଣ କେନ୍ଦ୍ର ରହିଛି।
Question 73.
ଖଣିଜ ପିଣ୍ଡ କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଯେଉଁ ଶିଳାରେ ଖଣିଜ ମିଶି ରହିଥାଏ ତାହାକୁ ଖଣିଜ ପିଣ୍ଡ କୁହାଯାଏ।
Question 74.
ଖଣିଜ କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ମନୁଷ୍ୟର ବିନା ସାହାଯ୍ୟରେ ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଅବସ୍ଥାରେ ସ୍ଥିତ ଏକ ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ ରାସାୟନିକ ମିଶ୍ରଣଯୁକ୍ତ ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ଖଣିଜ କୁହାଯାଏ ।

Question 75.
ଜୀବାଶ୍ମ ଇନ୍ଧନ କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
କୋଇଲା, ଖଣିଜ ତୈଳ, ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ବାଷ୍ପ ଜୈବ ବସ୍ତୁରୁ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ ସେଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ଜୈବ ଖଣିଜ କୁହାଯାଏ। ଜୈବ ଖଣିଜକୁ ଜୀବାଶ୍ମ ଇନ୍ଧନ କୁହାଯାଏ।
Question 76.
କେଉଁ ଦେଶ ପୃଥିବୀର ପ୍ରଥମ ଜଳ ବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ବିକାଶକାରୀ ଦେଶ ଅଟେ ?
Answer:
ନରୱେ ପୃଥିବୀର ପ୍ରଥମ ଜଳ ବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ବିକାଶକାରୀ ଦେଶ ଅଟେ ।
Question 77.
କେଉଁଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଅଣପାରମ୍ପରିକ ଶକ୍ତିର ଉତ୍ସ ଅଟେ ?
Answer:
ସୌର ଶକ୍ତି, ପବନ ଶକ୍ତି, ଜୁଆର ଶକ୍ତି, ଆଣବିକ ଶକ୍ତି ଅଣପାରମ୍ପରିକ ଶକ୍ତିର ଉତ୍ସ ଅଟେ।
Question 78.
ଭାରତର କେଉଁଠାରେ ଭୂତାପଜ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନ କେନ୍ଦ୍ର ରହିଛି ?
Answer:
ହିମାଚଳ ପ୍ରଦେଶର ମନିକରଣ ଏବଂ ଲାଦାଖର ପୁରା ଉପତ୍ୟକାରେ ଭୂତାପଜ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନ କେନ୍ଦ୍ର ରହିଛି।
Question 79.
ଭାରତର କେଉଁଠାରେ ଛୁଆର ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନ କେନ୍ଦ୍ର ରହିଛି ?
Answer:
ଭାରତର ଗୁଜୁରାଟର କାମେ ଉପକୂଳ ଓ ପଶ୍ଚି ମବଙ୍ଗର ସୁନ୍ଦରବନଠାରେ ଜୁଆର ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନ କେନ୍ଦ୍ର ରହିଛି।
Question 80.
କର୍ଣ୍ଣାଟକର କେଉଁଠାରେ ଆଣବିକ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନ କେନ୍ଦ୍ର ରହିଛି ?
Answer:
କର୍ଣାଟକର ନଇଗାଠାରେ ଆଣବିକ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନ କେନ୍ଦ୍ର ରହିଛି।
Question 81.
ମଫସଲ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ କେଉଁ ଗ୍ୟାସ୍ ଅଧିକ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ମଫସଲ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ବାୟୋଗ୍ୟାସ୍ ଅଧିକ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଏ।
Question 82.
କେଉଁ ଦେଶ ପୃଥିବୀର ସର୍ବବୃହତ୍ ଭୂ-ତାପଜଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନକାରୀ ଦେଶ ?
Answer:
ଯୁକ୍ତରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ଆମେରିକା ପୃଥିବୀର ସର୍ବବୃହତ୍ ଭୂ-ତାପଜଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନକାରୀ ଦେଶ ।
Question 83.
ତାମିଲନାଡୁର କେଉଁଠାରେ ଆଣବିକ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନ କେନ୍ଦ୍ର ରହିଛି ?
Answer:
ତାମିଲନାଡୁର କଳ୍କମଠାରେ ଆଣବିକ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନ କେନ୍ଦ୍ର ରହିଛି ।
Question 84.
ମହାରାଷ୍ଟ୍ରର କେଉଁଠାରେ ଆଣବିକ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନ କେନ୍ଦ୍ର ରହିଛି ?
Answer:
ମହାରାଷ୍ଟ୍ରର ତାରାପୁରଠାରେ ଆଣବିକ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନ କେନ୍ଦ୍ର ରହିଛି ।

Question 85.
ଉତ୍ତର ପ୍ରଦେଶର ନାରୋରା କେଉଁ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନ ପାଇଁ ପ୍ରସିଦ୍ଧ ?
Answer:
ଉତ୍ତର ପ୍ରଦେଶର ନାରୋରା ଆଣବିକ ଶକ୍ତି କେନ୍ଦ୍ର ପାଇଁ ପ୍ରସିଦ୍ଧ ।
ଗୋଟିଏ ଶବ୍ଦରେ ଉତ୍ତର ଦିଅ ।
1. ଅଧିକ ଉଚ୍ଚତା ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ପାହାଡ଼ ଓ ପର୍ବତଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ କ’ଣ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ପାର୍ବତ୍ୟଭୂମି
2. କାନାଡ଼ିଆନ୍ ସିଲଡ୍ କେଉଁ ମହାଦେଶରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ ?
Answer:
ଉତ୍ତର ଆମେରିକା
3. ପାଟଗୋନିଆ ମାଳଭୂମି କେଉଁ ମହାଦେଶରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ ?
Answer:
ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆମେରିକା
4. ପୃଥିବୀର ଯେଉଁ ଭାଗରେ ମାତ୍ର ଶତକଡ଼ା ୧୦ ଭାଗ ଲୋକ ବାସ କରନ୍ତି ସେଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ କେଉଁ ଅଞ୍ଚଳ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଜଳବିରଳ
5. କେଉଁ ନୀତି ଅନୁସାରେ ପାରିସ୍ଥିତିକ ସନ୍ତୁଳନ ପାଇଁ ଦେଶର ସମୁଦାୟ ଆୟତନର ଶତକଡ଼ା ୩୩ ଭାଗ ଭୂମି ଅରଣ୍ୟ ପାଇଁ ଆବଶ୍ୟକ ?
Answer:
ଜାତୀୟ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ନୀତି

6. ମ୍ପରିକା ସ୍ତରର ପାର୍ଶ୍ଵଚ୍ଛେଦର ନିମ୍ନଭାଗରେ କ’ଣ ଥାଏ ?
Answer:
ପ୍ରାଥମିକ ଶିଳା
7. ମନୁଷ୍ୟ, ପ୍ରାଣୀ ଓ ଉଭିଦ ସେମାନଙ୍କର ଖାଦ୍ୟ ଆବଶ୍ୟକତା ପୂରଣ ପାଇଁ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟକ୍ଷ ଓ ପରୋକ୍ଷ ଭାବରେ କାହା ଉପରେ ନିର୍ଭରଶୀଳ ?
Answer:
ମୃଭିକା
8. ଜଳ କେଉଁ ପ୍ରକ୍ରିୟାରେ ସମୁଦ୍ର ପୃଷ୍ଠରୁ ଜଳୀୟବାଷ୍ପ ଆକାରରେ ବାୟୁମଣ୍ଡଳରେ ମିଶେ ?
Answer:
ବାଷ୍ପୀଭବନ
9. ନଦୀର ଦୁଇ କୂଳକୁ ସଂଯୋଗ କରୁଥିବା କୃତ୍ରିମ ପ୍ରତିବନ୍ଧକରେ ଥିବା କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ର ଜଳ ନିଷ୍କାସନ ପଥକୁ କ’ଣ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଫୁକାର
10. ଶିଉଳି ଓ ହିମଗୁଳ୍ମ କେଉଁ ଅଞ୍ଚଳର ମୁଖ୍ୟ ଉଦ୍ଭବ ?
Answer:
ମେରୁ
ଭୌଗୋଳିକ ଶବ୍ଦଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ଗୋଟିଏ ଗୋଟିଏ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ଲେଖି ।
Question 1.
ପାର୍ବତ୍ୟଭୂମି :
Answer:
ଜୈ ଅଧ୍ବକ ଉଚ୍ଚତାବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ପାହାଡ଼ ଓ ପର୍ବତ ଥିବା ଭୂମିକୁ ପାର୍ବତ୍ୟଭୂମି କୁହାଯାଏ ।
Question 2.
ଚୂଷ୍ଣୀଭବନ :
Answer:
ବାହାରକୁ ଉନ୍ମୁକ୍ତ ଶିଳା ଉତ୍ତାପର ପର୍ଯ୍ୟାୟ କ୍ରମିକ ହ୍ରାସବୃଦ୍ଧି, କରକାର ପ୍ରଭାବ, ଉଭିଦ, ପ୍ରାଣୀ ଓ ମନୁଷ୍ୟମାନଙ୍କଦ୍ୱାରା ଖଣ୍ଡ ବିଖଣ୍ଡିତ ହୋଇ କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ର କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ର ରେଣୁରେ ପରିଣତ ହେବା ପ୍ରକ୍ରିୟାକୁ ଚୂଷ୍ଣୀଭବନ କୁହାଯାଏ ।

Question 3.
ମୃତ୍ତିକା :
Answer:
ବିଭିନ୍ନ ଶିଳାର କ୍ଷୟଜାତ ସୂକ୍ଷ୍ମ ରେଣୁଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଜଳ, ବାୟୁ, କ୍ଷୟଜାତ ଜୈବାଂଶ ଓ ଖଣିଜ ସହିତ ମିଶି ଭୂମିର ଉପରି ଭାଗରେ ଯେଉଁ ପତଳା ଆବରଣ ସୃଷ୍ଟି କରେ, ତାହାକୁ ମୃତ୍ତିକା କୁହାଯାଏ ।
Question 4.
କଳଚକ୍ର :
Answer:
ଜଳ ସାଗର ପୃଷ୍ଠରୁ ବାୟୁମଣ୍ଡଳ, ବାୟୁମଣ୍ଡଳରୁ ଭୂପୃଷ୍ଠରୁ ପୁନର୍ବାର ସାଗରରେ ମିଶିବା ପ୍ରକ୍ରିୟା ଚକ୍ରାକାରରେ ଘଟିବାରୁ ଏହାକୁ ଜଳଚକ୍ର କୁହାଯାଏ ।
Question 5.
ବ୍ୟାରେଜ୍ :
Answer:
ଜ ନିକଟଠାରୁ ଅଧିକ ଉଚ୍ଚତା ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ଲୌହଫଳକ ସଂଯୋଗରେ ନିର୍ମିତ ପ୍ରତିବନ୍ଧକ ।
Question 6.
ଜୈବ ମଣ୍ଡଳ :
Answer:
ଢ ଶ୍ମମଣ୍ଡଳ, ବାରିମଣ୍ଡଳ ଓ ବାୟୁମଣ୍ଡଳର ମିଳନ ସ୍ଥଳରେ ଥିବା ସଂକୀର୍ଣ୍ଣ ଅଞ୍ଚଳ ଯେଉଁଠାରେ ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଉଦ୍ଭିଦ ଓ ବନ୍ୟପ୍ରାଣୀମାନେ
Question 7.
ଷ୍ଟେପୀ :
Answer:
ଏସିଆର ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ ତୃଣଭୂମି ।
Question 8.
ପ୍ରେରୀ :
Answer:
ଯୁକ୍ତରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ଆମେରିକାର ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ ତୃଣଭୂମି ।
Question 9.
ଖଣିଜ :
Answer:
ମନୁଷ୍ୟର ବିନା ସାହାଯ୍ୟରେ ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଅବସ୍ଥାରେ ସ୍ଥିତ ଏକ ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ ରାସାୟନିକ ଯୁକ୍ତ ବସ୍ତୁ ।
Question 10.
ପାରମ୍ପରିକ ଶକ୍ତି :
Answer:
ଯେଉଁ ଶକ୍ତି ବହୁକାଳ ଧରି ସାଧାରଣ ଭାବରେ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହୋଇ ଆସୁଛି, ଯଥା – ଜାଳେଣି କାଠ, କୋଇଲା, ଖଣିଜ ତୈଳ ଇତ୍ୟାଦି ।

Question 11.
ଅଣପାରମ୍ପରିକ ଶକ୍ତି :
Answer:
ପାରମ୍ପରିକ ଶକ୍ତି ବଦଳରେ ସୌରଶକ୍ତି, ପବନ ଶକ୍ତି, ଜୁଆର ଶକ୍ତିର ଉତ୍ସରୁ ଉତ୍ପନ୍ନ ଶକ୍ତି ।
Question 12.
ଭୂତାପଜ ଶକ୍ତି :
Answer:
ପୃଥିବୀର କୈନ୍ଦ୍ରିକ ତାପରୁ ଉତ୍ପନ୍ନ ହେଉଥିବା ଶକ୍ତି ।
Question 13.
ଜୁଆର ଶକ୍ତି :
Answer:
ସମୁଦ୍ରର ଜୁଆରର ଶକ୍ତିକୁ ଉପଯୋଗ କରି ଉତ୍ପନ୍ନ କରାଯାଉଥିବା ଶକ୍ତି ।
ଅସଂପର୍କିତ ଶବ୍ଦଟିକୁ ବାଛ ।
1. ଏସିଆ, ଇଉରୋପ, ଭାରତ, ଅଷ୍ଟ୍ରେଲିଆ ।
Answer: ଭାରତ
2. ଉତ୍ତର ଆମେରିକା, ଯୁକ୍ତରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ଆମେରିକା, ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆମେରିକା, ଆଫ୍ରିକା।
Answer: ଯୁକ୍ତରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ଆମେରିକା
3. ଆରାବଳୀ, ହିମାଳୟ, ଆଲପ୍ସ, ରକି ।
Answer: ଆରାବଳୀ
4. ତିବ୍ବତ, ଗୋବି, ସ୍କାଣ୍ଟିନେରିଆ, ଆଣ୍ଟିଜ
Answer: ଆଣ୍ଟିଜ
5. ସାଇବେରିଆ, ଆମାଜନ ଅବବାହିକା, ଭାରତର ଦାକ୍ଷିଣାତ୍ୟ ମାଳଭୂମି, ଗାଙ୍ଗେୟ ଅବବାହିକା।
Answer: ଭାରତର ଦାକ୍ଷିଣାତ୍ୟ ମାଳଭୂମି
6. ଜନସଂଖ୍ୟା, ଭୂପ୍ରକୃତି, ମୃତ୍ତିକା, ଜଳବାୟୁ ।
Answer: ଜନସଂଖ୍ୟା (ମାନବୀୟ ଅବସ୍ଥା)
7. ଶିକ୍ଷା, ବୈଷୟିକ ଜ୍ଞାନ, ପ୍ରୟୋଗାତ୍ମକ କୌଶଳ, ଖଣିଜ ।
Answer: ଖଣିଜ (ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଅବସ୍ଥା)
8. ରଙ୍ଗ, ଉଷ୍ଣତା, ବିନ୍ୟାସ, ରାସାୟନିକ ବିଭବ।
Answer: ଉଷ୍ଣତା
9. ଉଷ୍ଣତା, ବୃଷ୍ଟିପାତ, ଅବକ୍ଷୟ, ବିନ୍ୟାସ ।
Answer: ବିନ୍ୟାସ
10. ପୀତ ମୃତ୍ତିକା, ପଟୁ ମୃଭିକା, ଖବ୍ଦର ମୃତ୍ତିକା, ଭାଙ୍ଗର ମୃଭିକା।
Answer: ପୀତ ମୃଭିକା

11. ଚିଲିକା, ଡାଲ, ଓବ୍, ସମ୍ବର।
Answer: ଓବ୍
12. ଆନିକଟ, ଜଳପ୍ରପାତ, ବ୍ୟାରେଜ, ନଦୀବନ୍ଧ ।
Answer: ଜଳପ୍ରପାତ
13. ଆବୁଲସ, ମେହଗାନି, ରବର, ବାଉଁଶ।
Answer: ବାଉଁଶ
14. ଶାଳ, ରବର, ପିଆଶାଳ, ଶିଶୁ।
Answer: ରବର
15. ପାଇନ, ଫିର, ମେହଗାନି, ଓକ୍ ।
Answer: ମେହଗାନି
16. ଧଳାଭାଲୁ, ସିଲ୍, ସିଲଭର ଫକ୍ସ, ମୟୂର ।
Answer: ମୟୂର
17. ମାଙ୍କଡ଼, ନୀଳଗାଈ, ଶିଖାଜୀ, ଓରାଂଗ୍ଓଟାଙ୍ଗ୍ ।
Answer: ନୀଳଗାଈ
18. ବାଘ, ହରିଣ, ସିଂହ, ହେଟାବାଘ।
Answer: ହରିଣ
19. ହାତୀ, ସମ୍ବର, ମୃଗ, ବାଘ ।
Answer: ବାଘ
20. ଶିମିଳିପାଳ, କାଜିରଙ୍ଗା, ଚନ୍ଦକା, ଭିତରକନିକା।
Answer: କାଜିରଙ୍ଗା (ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ନୁହେଁ)
21. ସୁନା, ଲୌହପିଣ୍ଡ, ବକ୍ସାଇଟ, ମାଙ୍ଗାନିଜ୍।
Answer: ସୁନା
22. ରୁପା, ତମ୍ବା, ବକ୍ସାଇଟ, ସୀସା ।.
Answer: ବକ୍ସାଇଟ
23. ଚୂନପଥର, ଅଭ୍ର, ଜିପ୍ସମ୍, ସୁନା।
Answer: ସୁନା
24. ସୌରଶକ୍ତି, ଜାଳେଣି କାଠ, ଜୈବାଶ୍ମ ଜାଳେଣି, କୋଇଲା ।
Answer: ସୌରଶକ୍ତି

25. ପବନ ଶକ୍ତି, ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ବାଷ୍ପ, ଆଣବିକ ଶକ୍ତି, ଭୂ-ତାପଜ ଶକ୍ତି ।
Answer: ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ବାଷ୍ପ
ଠିକ୍ ଭଲି ପାଖରେ ଠିକ୍ ଚିହ୍ନ ( ✓ ) ଓ ଭୁଲ୍ ଭରି ପାଖରେ ଭୁଲ୍ ଚିହ୍ନ ( ✗ ) ଦିଅ ।
1. ଭୂ-ପୃଷ୍ଠ ସ୍ଥଳଭାଗ ଓ ଜଳରାଗକୁ ନେଇ ଗଠିତ । ( ✗ )
2. ସମୁଦ୍ର ପତ୍ତନଠାରୁ ସ୍ଥଳଭାଗ ଆଡ଼କୁ ଭୂମିର ଉଚ୍ଚତା କ୍ରମଶଃ ହ୍ରାସ ପାଏ । ( ✓ )
3. ଅଳ୍ପ ଉଚ୍ଚନୀଚ ହୋଇଥିବା ବିସ୍ତୀର୍ଣ୍ଣ ପଥୁରିଆ ଭୂମିକୁ ମାଳଭୂମି କୁହାଯାଏ । ( ✓ )
4. ସ୍କାଣ୍ଡିନେଭିଆ ମାଳଭୂମି ଇଉରୋପ ମହାଦେଶରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ । ( ✓ )
5. ପାହାଡ଼, ପର୍ବତ ଓ ମାଳଭୂମି ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ କୃଷିକାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଲାଭଜନକ ଅଟେ । ( ✗ )
6. ଏସିଆର ସାଇବେରିଆ ଏକ ମାଳଭୂମି ଅଟେ । ( ✗ )
7. ଜାତୀୟ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ନୀତି ଅନୁସାରେ ପାରିସ୍ଥିତିକ ସନ୍ତୁଳନ ପାଇଁ ଦେଶର ସମୁଦାୟ ଆୟତନର ଶତକଡ଼ା ୩୩ ଭାଗ ଭୂମି ଅରଣ୍ୟ ହେବା ଆବଶ୍ୟକ । ( ✓ )
8. ଭାରତର ଶତକଡ଼ା ୩୩ ଭାଗ ଭୂମି ଅରଣ୍ୟ ହେବା ଆବଶ୍ୟକ। ( ✓ )
9. ଭୂ ଅବକ୍ଷୟ ପାଇଁ ମରୁକଗଣ ହେଉଛି ଏକ ମାନବୀୟ କାରଣ । ( ✗ )
10. ମୃତ୍ତିକା ଏକ ମୌଳିକ ପଦାର୍ଥ। ( ✗ )
11. ମୃଭିକାରେ ସଠିକ୍ ଅନୁପାତରେ ଖଣିଜ ଓ ଜୈବାଂଶ ମିଶି ରହିଥିଲେ ମ୍ପରିକା ଉର୍ବର ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ। ( ✓ )
12. ମଟାଳ ମାଟିରେ ପଟୁର ପରିମାଣ କମ୍ ଥାଏ। ( ✓ )
13. ମ୍ପରିକା ଏକ ନବୀକରଣ ଅଯୋଗ୍ୟ ସମ୍ବଳ ଅଟେ । ( ✗ )
14. ଶୁଷ୍କ ମ୍ପରିକା ଆର୍ଦ୍ର ମୃତ୍ତିକା ଅପେକ୍ଷା ଅଧିକ କ୍ଷୟଶୀଳ। ( ✓ )

15. ପୃଥିବୀରେ ଥିବା ମୋଟ ଜଳର ପରିମାଣ ସର୍ବଦା ସମାନ ରହିଥାଏ। ( ✓ )
16. ମରେ-ଡାଲିଂ ପୃଥିବୀର ଏକ ମୁଖ୍ୟ ନଦୀ ଅଟେ। ( ✓ )
17. ଇନ୍ସି ଏକ ହ୍ରଦର ନାମ ଅଟେ । ( ✗ )
18. ପତ୍ରଝଡ଼ା ଦୃଷ୍ଟିକୋଣରୁ ବିମ୍ମର କଲେ ଜଙ୍ଗଲ ୪ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର। ( ✗ )
19. ପଶ୍ଚିମୋଚୀ ଉଭିଦଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଶୁଷ୍କ ଋତୁରେ ପତ୍ରଝଡ଼ା ଦିଅନ୍ତି । ( ✓ )
20. ଓଡ଼ିଶାରେ ଦେଖାଯାଉଥିବା ଅରଣ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଦୁଇ ଭାଗରେ ବିଭକ୍ତ ।
21. ଆଫ୍ରିକାର ସାଭାନ୍ନା ମରୁଭୂମି ଗ୍ରୀଷ୍ମଣ୍ଡଳୀୟ ତୃଣଭୂମି ଅଟେ । ( ✓ )
22. ପୋଡ଼ୁଋଷ ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଉଭିଦ ସଂରକ୍ଷଣର ଏକ ପନ୍ଥା ଅଟେ । ( ✗ )
23. ଅଭୟାରଣ୍ୟ ଅପେକ୍ଷା ଜାତୀୟ ଉଦ୍ୟାନରେ ପଶୁପକ୍ଷୀଙ୍କର ସୁରକ୍ଷା ପ୍ରତି ଅଧୁକ ଧ୍ୟାନ ଦିଆଯାଏ । ( ✓ )
24. କାଜିରଙ୍ଗା ଜାତୀୟ ଉଦ୍ୟାନ ଆସାମର ଜୋରହାଟ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ। ( ✓ )
25. ଓଣ୍ଟାରିଓ ଓ କାନାଡ଼ା ମାଳଭୂମିରେ ଲୌହପିଣ୍ଡ ଗଚ୍ଛିତ ଅଛି । ( ✗ )
26. ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆଫ୍ରିକାର ଜୋହାନସବର୍ଗ ସୁନାଖଣି ପାଇଁ ପୃଥିବୀ ପ୍ରସିଦ୍ଧ । ( ✓ )
27. ନରୱେ ପୃଥିବୀର ପ୍ରଥମ ଜଳବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ବିକାଶକାରୀ ଦେଶ । ( ✓ )
28. ଅଳ୍ପଦୂରକୁ ଯିବାପାଇଁ ଯାନ୍ତ୍ରିକ ଗାଡ଼ି ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିବା ଉଚିତ। ( ✗ )
29. ଆଧୁନିକ ମନୁଷ୍ୟର ଶକ୍ତି ଏକ ଅପରିହାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଆବଶ୍ୟକତା । ( ✓ )
30. ମୋନାଜାଇଟ୍ ବାଲୁକାରେ ୟୁରାନିୟମ୍ ମିଳେ। ( ✗ )
Objective Type Questions With Answers
ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ମିଳନ କର ।
Question 1.

Answer:


Question 2.

Answer:

Question 3.

Answer:

Question 4.

Answer:

Question 5.

Answer:


Question 6.
Answer:

Question 7.
Answer:
Question 8.

Answer:


Question 9.

Answer:

Question 10.
Answer:

Question 11.

Answer:

Question 12.

Answer:

Question 13.

Answer:


Question 14.

Answer:

Question 15.

Answer:

Question 16.

Answer:

Question 17.

Answer:

Question 18.
Answer:


Question 19.
Answer:

Question 20.

Answer:

Question 21.

Answer:

Question 22.

Answer:


Question 23.

Answer:

ବନ୍ଧନୀ ମଧ୍ଯରୁ ଉପଯୁକ୍ତ ଶବ୍ଦ ବାଛି ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନ ପୂରଣ କର ।
ଭୂ-ସମ୍ବଳ
1. ପୃଥିବୀ ପୃଷ୍ଠର ମୋଟ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରଫଳର ଶତକଡ଼ା ସ୍ଥଳଭାଗ।
(୨୬%, ୨୭%, ୨୮%, ୨୯%)
Answer: ୨୯%
2. ପୃଥିବୀ ପୃଷ୍ଠର ମୋଟ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରଫଳର ଶତକଡ଼ା ……….. ଭାଗ ଜଳଭାଗ ।
(୭୦%, ୭୧%, ୭୨%, ୭୩%)
Answer: ୭୧%
3. ଅଷ୍ଟ୍ରେଲିଆରେ ଶତକଡ଼ା ……….. ଭାଗ ଭୂମିରେ କୃଷି କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରାଯାଏ।
(୬%, ୭%, ୮%, ୯%)
Answer: ୬%
4. ଭାରତର ଶତକଡ଼ା …………. ଭାଗ ଭୂମିରେ କୃଷିକାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରାଯାଏ।
(୫୧, ୫୨, ୫୩, ୫୪)
Answer: ୫୪

5. ଭାରତର ଶତକଡ଼ା …………. ଭାଗ ଭୂମିରେ ଜନବସତି ରହିଛି।
(୧୯, ୨୦, ୨୧, ୨୨)
Answer: ୧୯
6. ଭାରତରେ ଶତକଡ଼ା ——– ରହିଛି। ଭାଗ ସ୍ତରଣ ଓ ଗୋଚର ଭୂମି
(ଏକ, ଦୁଇ, ତିନି, ଊରି)
Answer: ଊରି
7. ଭାରତର ଶତକଡ଼ା ———– ଭାଗ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଭୂମିଦ୍ଵାରା ଆଚ୍ଛାଦିତ ।
(୨୧, ୨୨, ୨୩, ୨୪)
Answer: ୨୨
8. ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଶତକଡ଼ା ପ୍ରାୟ ———– ଭାଗ ଭୂମିରେ କୃଷି କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରାଯାଏ।
(୪୫, ୪୬, ୪୭, ୪୮)
Answer: ୪୭
9. ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଶତକଡ଼ା ପ୍ରାୟ ———– ଭାଗ ଭୂମିରେ ଜନବସତି ରହିଛି।
(୧୫, ୧୬, ୧୭, ୧୮)
Answer: ୧୬
10. ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଶତକଡ଼ା, ———- ଭାଗ ଭୂମି ଅରଣ୍ୟ ରୂପେ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହେଉଛି ।
(୩୦, ୩୧, ୩୨, ୩୩)
Answer:
11. ଗୋବି ଏକ ——|
(ମାଳଭୂମି, ମରୁଭୂମି, ପର୍ବତଶ୍ରେଣୀ, ସମତଳ)
Answer: ୩୨
12. ବ୍ରାଜିଲ ମାଳଭୂମି —— ମହାଦେଶରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ ।
(ଏସିଆ, ଆଫ୍ରିକା, ଉତ୍ତର ଆମେରିକା, ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆମେରିକା)
Answer: ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆମେରିକା

13. ଆଲପ୍ସ ପର୍ବତମାଳା ———- ମହାଦେଶରେ ରହିଛି । ।
(ଏସିଆ, ଆଫ୍ରିକା, ଇଉରୋପ, ଉତ୍ତର ଆମେରିକା)
Answer: ଇଉରୋପ
ମୃତ୍ତିକା ସମ୍ବଳ
1. ଗାଙ୍ଗେୟ ସମତଳର ନୂତନ ପଟୁ ମୃଭିକାକୁ ———- କୁହାଯାଏ ।
(ଖଦର, ଭାଙ୍ଗର, କଙ୍କର, ଭାବର)
Answer: ଖଦର
2. ଗାଙ୍ଗେୟ ସମତଳର ପୁରାତନ ପଟୁ ମୃଭିକାକୁ ———- କୁହାଯାଏ ।
(ଖଦର, ତରାଇ, ରେ, ଭାଙ୍ଗର)
Answer: ଭାଙ୍ଗର
3. ସମୁଦ୍ର ଉପକୂଳ ଶୁଷ୍କ ଓ ଅଶୁଷ୍କ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ———- ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
( ପଟୁ, ଲୋହିତ, ଲୁଣା ଓ କ୍ଷାରୀୟ, ପିଟ୍ ଓ ଜୈବ)
Answer: ଲୁଣା ଓ କ୍ଷାରୀୟ
4. ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ତ୍ରିକୋଣ ଭୂମି ଓ ସମୁଦ୍ର ଉପକୂଳବର୍ତ୍ତୀ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ———- ମୃଭିକା ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
(ଲୁଣା, ଲୋହିତ, ପିଟ୍, ଅରଣ୍ୟ)
Answer: ଲୁଣା
5. ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ପର୍ବତମାଳାର ପାଦଦେଶରେ ———- ମ୍ପରିକା ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
(ପଟୁ, କୃଷ୍ଣ, ଲାଟେରାଇଟ୍, ଲାଲମାଟି)
Answer: ଲାଟେରାଇଟ୍

6. ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଅନୁଗୁଳ, ଆଠମଲ୍ଲିକ, ବୌଦ୍ଧ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ———- ମ୍ପଭିକା ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
(କଳାମାଟି, ଲାଲମାଟି, ବାଦାମୀ ମାଟି, ପଟୁମାଟି)
Answer: କଳାମାଟି
7. ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ପାହାଡ଼ିଆ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ———- ମ୍ପରିକା ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
(ଲାଲମାଟି, କଳାମାଟି, ପଟୁମାଟି, ବାଦାମୀମାଟି)
Answer: ଲାଲମାଟି
ଜଳ ସମ୍ବଳ
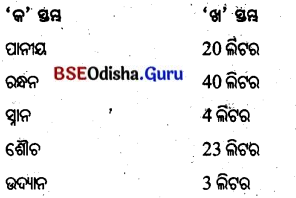
1. _______ କୁ ଜଳୀୟ ଗ୍ରହ ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ।
(ବୁଧ, ମଙ୍ଗଳ, ପୃଥବୀ, ଶୁକ୍ର)
Answer: . ପୃଥିବୀ
2. ପୃଥିବୀରେ ମିଳୁଥିବା ସମସ୍ତ ଜଳର ଶତକଡ଼ା _______ ମଧୁର ଜଳ ଅଟେ।
(୨.୬, ୨.୭, ୨.୮, ୨.୯)
Answer: ୨.୭
3. ପୃଥିବୀରେ ମିଳୁଥିବା ମଧୁର ଜଳର ଶତକଡ଼ା” _______ ଭାଗ ମନୁଷ୍ୟର ବ୍ୟବହାରରେ ଲାଗିଥାଏ।
(ଏକ, ଦୁଇ, ତିନି, ଊରି)
Answer: ଏକ
4. ଜଣେ ସହରୀ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ଦୈନିକ _______ ଲିଟର ଜଳ ପାନୀୟ ଭାବେ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିଥାଏ।
(ଏକ, ଦୁଇ, ତିନି, ଋରି)
Answer: ତିନି
5. ଜଣେ ସହରୀ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ଦୈନିକ _______ ଲିଟର ଜଳ ରନ୍ଧନରେ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିଥାଏ।
(ଏକ, ଦୁଇ, ତିନି, ଋରି)
Answer: ପ୍ସରି
6. ଜଣେ ସହରୀ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ଦୈନିକ _______ ଲିଟର ଜଳ ସ୍ନାନ ପାଇଁ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିଥାଏ।
(୧୦, ୨୦, ୩୦, ୪୦)
Answer: ୨୦

7 ଜଣେ ସହରୀ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ଶୌଚରେ ଦୈନିକ _______ ଲିଟର ଜଳ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିଥାଏ।
(୧୦, ୨୦, ୩୦, ୪୦)
Answer: ୪୦
8. ଜଣେ ସହରୀ _______ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ପୋଷାକ ସଫେଇରେ ଲିଟର ଜଳ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିଥାଏ।
(୨୦, ୪୦, ୩୦, ୮୦)
Answer: ୪୦
9. ବାସନ ସଫେଇରେ ଜଣେ ସହରୀ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି _______ ଲିଟର ଜଳ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିଥାଏ ।
(୧୦, ୧୫, ୨୦, ୨୫)
Answer: ୨୦
10. ଜଣେ ସହରୀ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ଉଦ୍ୟାନ ପାଇଁ _______ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିଥାଏ।
(୨୧, ୨୨, ୨୩, ୨୪)
Answer: ୨୩
11. ଜଣେ ସହରୀ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ଦୈନିକ _______ ଲିଟର ଜଳ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିଥାଏ ।
(୧୦୦, ୧୫୦, ୨୦୦, ୨୫୦)
Answer: ୧୫୦
12. ନଦୀର ଉଭୟ କୂଳକୁ ସଂଯୋଗ କରୁଥିବା କଂକ୍ରିଟ ଓ ମାଟିର ବନ୍ଧକୁ _______ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
(ଆନିକଟ, ବ୍ୟାରେଜ, ବୁରୁଜ, ଡ୍ୟାମ୍)
Answer: ଡ୍ୟାମ୍
13. ଦୁଇଘଣ୍ଟା ଲଗାଣ ବର୍ଷାରେ ଛାତ ଉପରେ ସାଧାରଣଭାବେ, ଲିଟର ଜଳ ବ୍ୟବହାର _______ ମି.ମି. ବୃଷ୍ଟି ପଡ଼େ।
(୫୦୦, ୭୦୦, ୮୦୦, ୧୦୦୦)
Answer: 800
ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଉଭିଦ ଓ ବନ୍ୟପ୍ରାଣୀ
1. ବିଷୁବରେଖାର ଉଭୟ ପାର୍ଶ୍ଵରେ ୫°ଉତ୍ତର ଓ ୫°, ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଅକ୍ଷାଂଶରେ ——– ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
(ନିରକ୍ଷୀୟ, କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ, ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ, ତୁଦ୍ରା)
Answer: ନିରକ୍ଷୀୟ
2. ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆମେରିକାର ଆମାଜନ ଅବବାହିକା, ଆଫ୍ରିକାର କଙ୍ଗୋନଦୀ ଓ ଭାରତର ପଶ୍ଚିମଘାଟ ପର୍ବତମାଳାର ପଶ୍ଚିମାଂଶରେ——– ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ।
(ନିରକ୍ଷୀୟ, ତୁଦ୍ରା, କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ, ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ)
Answer: ନିରକ୍ଷୀୟ
3. ନିରକ୍ଷୀୟ ଅରଣ୍ୟର ଉଭୟ ପାର୍ଶ୍ଵରେ ୫° ରୁ ୨୫° ଉତ୍ତର ଓ ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଅକ୍ଷାଂଶ ମଧ୍ଯରେ ——– ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
(ନିରକ୍ଷୀୟ, କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ, ତୃଦ୍ରା, ମରୁ)
Answer: କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ
4. ଉଭୟ ଗୋଲାର୍ଦ୍ଧର ୨୫°ରୁ ୬୫° ଅକ୍ଷାଂଶ ମଧ୍ଯରେ ——– ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
(କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ, ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ, ନିରକ୍ଷୀୟ, କଣ୍ଟାବନ)
Answer: ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ
5. ପୃଥିବୀର ——– ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଶୀତଳ ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ନାହିଁ ।
(ସାଇବେରିଆ, ସ୍କାଣ୍ଡିନେଭିଆ, କାନାଡାର ଉତ୍ତରାଞ୍ଚଳ, ଜାପାନର ପୂର୍ବ ଭାଗ)
Answer: ଜାପାନର ପୂର୍ବ ଭାଗ
6. ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ——– ଭାଗ ଭୂମିରେ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
(୩୧, ୩୨%, ୩୩୫, ୩୪%)
Answer: ୩୨%
7. ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଅରଣ୍ୟକୁ ——– ଭାଗରେ ଭାଗ କରାଯାଇଛି ।
(ଏକ, ଦୁଇ, ତିନି, ଊରି)
Answer: ଊରି
8. ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ——– ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଶତକଡ଼ା ପ୍ରାୟ ୮୦ ଭାଗ ଅଟେ ।
(କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ ଆର୍ଦ୍ର ପଶ୍ଚିମୋଚୀ, କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ ଅର୍ଶ ଚିରହରିତ୍, କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ ଶୁଷ୍କ ପଶ୍ଚିମୋଚୀ, ଜୁଆରିଆ)
Answer: କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ ଶୁଷ୍କ ପଶ୍ଚିମୋଚୀ
9. ଆଣ୍ଟାର୍କଟିକାର ବରଫାବୃତ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ——– ପକ୍ଷୀ ବାସ କରନ୍ତି।
( ପେଙ୍ଗୁଇନ୍, ଏମ୍, ଓଟପକ୍ଷୀ, ମୟୂର)
Answer: ପେଙ୍ଗୁଇନ୍
10. ——– କୁ ଭାରତରେ ଜାତୀୟ ପକ୍ଷୀ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
( ଶୁଆ, ସାରୀ, ମୟୂର, ହଂସ)
Answer: ମୟୂର
11. ——– କୁ ଭାରତର ଜାତୀୟ ପଶୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
(ବାଘ, ସିଂହ, ହରିଣ, ହାତୀ)
Answer: ବାଘ
12. ——– ମସିହାରେ “ ବନ୍ୟପ୍ରାଣୀ ବୋର୍ଡ” ଗଠନ କରାଯାଇଥିଲା।
(୧୯୬୨, ୧୯୭୨, ୧୯୮୨, ୧୯୯୨)
Answer: ୧୯୭୨
13. ରାଜସ୍ଥାନର ଭରତପୁର ——– ଅଭୟାରଣ୍ୟ ପାଇଁ ପ୍ରସିଦ୍ଧ ।
(ହାତୀ, ବାଘ, ସିଂହ, ପକ୍ଷୀ)
Answer: ପକ୍ଷୀ
14. ଆସାମର କାଜିରଙ୍ଗା ଜାତୀୟ ଉଦ୍ୟାନ ——– ଅଭୟାରଣ୍ଯ ପାଇଁ ପ୍ରସିଦ୍ଧ ।
(ଏକଶିଙ୍ଗ ଗଣ୍ଡା, ହାତୀ, ବାଘ, ସିଂହ)
Answer: ଏକଶିଙ୍ଗ ଗଣ୍ଡା

15. ଗୁଜରାଟର ସୌରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ଅନ୍ତର୍ଗତ ଗୀର ଜାତୀୟ ଉଦ୍ୟାନ ——– ପାଇଁ ପ୍ରସିଦ୍ଧ ।
(ଗଣ୍ଡା, ହାତୀ, ସିଂହ, କୁମ୍ଭୀର)
Answer: ସିଂହ
16. ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ——– ଠାରେ ବାଘ ଅଭୟାରଣ୍ୟ ରହିଛି ।
(ଶିମିଳିପାଳ, ଚନ୍ଦକା, ଟିକରପଡ଼ା, ଭିତରକନିକା)
Answer: ଶିମିଳିପାଳ
17. ଶିମିଳିପାଳ ଅଭୟାରଣ୍ୟ ———- ଜିଲ୍ଲାରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ ।
(କଟକ, ମୟୂରଭଞ୍ଜ, କେନ୍ଦ୍ରାପଡ଼ା, କୋରାପୁଟ)
Answer: ମୟୂରଭଞ୍ଜ
18. ଭିତରକନିକା ଅଭୟାରଣ୍ୟ ——– ଜିଲ୍ଲାରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ।
(କଟକ, କେନ୍ଦ୍ରାପଡ଼ା, କଳାହାଣ୍ଡି, କୋରାପୁଟ)
Answer: କେନ୍ଦ୍ରାପଡ଼ା
19. ମାନସ ବ୍ୟାଘ୍ରପ୍ରକଳ୍ପ ——– ରାଜ୍ୟରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ ।
(ଝାଡ଼ଖଣ୍ଡ, ଆସାମ, କର୍ଣ୍ଣାଟକ, ପଶ୍ଚିମବଙ୍ଗ)
Answer: ଆସାମ
ଖଣିଜ ସମ୍ବଳ
1. ଖଣିଜପଦାର୍ଥକୁ ———- ଭାଗରେ ଭାଗ କରାଯାଇଛି ।
(ଏକ, ଦୁଇ, ତିନି, ଊରି)
Answer: ଦୁଇ
2. ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆଫ୍ରିକାର ଜୋହାନ୍ସବର୍ଗ ———- ଖଣି ପାଇଁ ପୃଥିବୀ ପ୍ରସିଦ୍ଧ ।
(ସୁନା, ରୁପା, ତମ୍ବା, ଅଭୂ)
Answer: ସୁନା

3. ଫ୍ରାନ୍ସର କକେସସ୍ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ———- ଖଣିଜ ଗଚ୍ଛିତ ଅଛି ।
(ସୁନା, ଅଭ୍ର, ଚୂନପଥର, ଜିପସମ୍)
Answer: ଚୂନପଥର
4. ମିଶ୍ରଧାତୁ ପାଇଁ ———- ଖଣିଜ ଦ୍ରବ୍ୟ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଇଥାଏ।
(ଲୁହାପଥର, ମାଙ୍ଗାନିଜ, କ୍ରୋମାଇଟ, ବକ୍ସାଇଟ୍)
Answer: ମାଙ୍ଗାନିଜ
5. ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ———- ଜିଲ୍ଲାରେ ମାଙ୍ଗାନିଜ ଖଣି ନାହିଁ ।
(କେନ୍ଦୁଝର, କେନ୍ଦ୍ରାପଡ଼ା, କଳାହାଣ୍ଡି, ସୁନ୍ଦରଗଡ଼)
Answer: କେନ୍ଦ୍ରାପଡ଼ା
6. ଇସ୍ପାତ ଓ ଚମଡ଼ା ଶିଳ୍ପରେ ———- ଖଣିଜ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଏ।
(କ୍ରୋମାଇଟ, ମାଙ୍ଗାନିଜ, ଲୁହାପଥର, ବକ୍ସାଇଟ୍)
Answer: କ୍ରୋମାଇଟ୍
7. ଆଲୁମିନିୟମ୍ ———- ଖଣିଜରୁ ବାହାର କରାଯାଇଥାଏ।
(ମାଙ୍ଗାନିଜ, କ୍ରୋମାଇଟ, କୋଇଲା, ବକ୍ସାଇଟ୍)
Answer: ବକ୍ସାଇଟ୍
8. ଅଭୁ ———- ଶିଳ୍ପରେ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଏ।
(ଚମଡ଼ାଶିଳ୍ପ, ବୈଦ୍ୟୁତିକ, ଲୌହ ଓ ଇସ୍ପାତ, ତାପଜ ବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ଶିଳ୍ପ)
Answer: ବୈଦ୍ୟୁତିକ
9. ———- ରାଜ୍ୟରେ ଅଭ୍ର ଖଣି ନାହିଁ ।
(ଝାଡ଼ଖଣ୍ଡ, ରାଜସ୍ଥାନ, ବିହାର, ଗୋଆ)
Answer: ଗୋଆ

10. ———- ଖଣିଜପିଣ୍ଡରୁ ଆଲୁମିନିୟମ୍ ମିଳେ।
(କ୍ରୋମାଇଟ୍, ବକ୍ସାଇଟ୍, ମାଙ୍ଗାନିଜ୍, ଅଭ୍ର)
Answer: ବକ୍ସାଇଟ୍
11. ପୃଥିବୀରେ ———- ପ୍ରକାର ଖଣିଜ ଚିହ୍ନିତ ହୋଇଛି ।
(100, 500, 1800, 2800)
Answer: 2800
ଶକ୍ତି ସମ୍ବଳ
1. ———– ବ୍ୟବହାର ଗ୍ରାମାଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଅଧିକ।
(ଜାଳେଣି କାଠ, କୋଇଲା, ଖଣିଜ ତୈଳ, ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଗ୍ୟାସ)
Answer:
2. ———– କୁ ପୋତା ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟାଲୋକ କୁହାଯାଏ।
(ଜାଳେଣି କାଠ, କୋଇଲା, ପେଟ୍ରୋଲିୟମ୍, ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଗ୍ୟାସ୍)
Answer:
3. ———– କୁ ‘କୃଷ୍ଣହୀରକ’ ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ।
(ଲୁହାପଥର, ମାଙ୍ଗାନିଜ, ଖଣିଜତୈଳ, କୋଇଲା)
Answer:
4. ———– କୁ ଘର୍ଷଣ ନିରୋଧକ ତେଲ ରୂପେ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଏ।
(ନଡ଼ିଆତେଲ, କିରୋସିନ, ପେଟ୍ରୋଲିୟମ୍, ତାର୍ପିନ)
Answer:
5. ———– କୁ ‘କୃଷ୍ଣ ସୁବର୍ଷ’ ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ ।
(କୋଇଲା, ପେଟ୍ରୋଲିୟମ୍, ଜାଳେଣିକାଠ, ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ବାଷ୍ପ)
Answer:
6. ପୃଥିବୀର ପ୍ରଥମ ଜଳବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ———– ବିକାଶକାରୀ ଦେଶ।
( ଇରାକ, ଇରାନ, ନର େ, ସାଉଦି ଆରବ)
Answer:
7. ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ———-ନଦୀବନ୍ଧ ଯୋଜନା ରହିଛି।
(ହୀରାକୁଦ, ଭାକ୍ରାନଙ୍ଗଲ, ଗାନ୍ଧିସାଗର, ନାଗାର୍ଜୁନସାଗର)
Answer:
8. ଭାରତର ———– ରାଜ୍ୟରେ ମିଳୁଥିବା ମୋନାଜାଇଟ୍ ବାଲୁକାରେ ବହୁତ ପରିମାଣରେ ଥୋରିୟମ୍ ମିଳେ।
(ଆନ୍ଧ୍ରପ୍ରଦେଶ, ତାମିଲନାଡୁ, କର୍ଣ୍ଣାଟକ, କେରଳ) ରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ।
Answer:
9. ———– ଦେଶ ପୃଥିବୀରେ ଜୁଆର ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନରେ ଅଗ୍ରଣୀ
( ରୁଷିଆ ଓ ଗ୍ରୀସ୍, ଚୀନ ଓ ନେପାଳ, ଜାପାନ ଓ ଜର୍ମାନୀ, ଇଂଲଣ୍ଡ ଓ ହଲାଣ୍ଡ)
Answer: ରୁଷିଆ ଓ ଗ୍ରୀସ୍

10. ଗ୍ରାମାଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଲୋକମାନେ ———– କୁ ଅଧିକ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରନ୍ତି ।
( ପବନ, ବାୟୋଗ୍ୟାସ୍, ସୌର, ଜୁଆର ଶକ୍ତି)
Answer: ବାୟୋଗ୍ୟାସ
11. ପୁଗା ଉପତ୍ୟକା ———– ଠାରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ।
( ହିମାଚଳ ପ୍ରଦେଶ, ଲାଦାଖ, ଅରୁଣାଚଳ ପ୍ରଦେଶ, ମଧ୍ୟପ୍ରଦେଶ)
Answer: ଲାଦାଖ
12. ମନିକରଣ ଭୂତାପଜ କେନ୍ଦ୍ର ———–ରାଜ୍ୟରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ ।
(ଆସାମ, ହିମାଚଳ ପ୍ରଦେଶ, ଉତ୍ତରାଖଣ୍ଡ, ଜାମ୍ମୁ-କାଶ୍ମୀର )
Answer: ହିମାଚଳ ପ୍ରଦେଶ
ସମ୍ଭାବ୍ୟ ଉତ୍ତର ବାଛି ଲେଖ।
ଭୂ-ସମ୍ବଳ
Question 1.
ପୃଥିବୀ ପୃଷ୍ଠର ମୋଟ ସ୍ଥଳଭାଗକୁ କେତୋଟି ମହାଦେଶରେ ଭାଗ କରାଯାଇଛି ?
(A) ୫
(B) ୬
(C) ୭
(D) ୮
Answer:
(C) ୭
Question 2.
କେଉଁଟି କ୍ଷେତ୍ରଫଳ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିରୁ ବୃହତ୍ତମ ମହାଦେଶ ?
(A) ଏସିଆ
(B) ଆଫ୍ରିକା
(C) ଅଷ୍ଟ୍ରେଲିଆ
(D) ଉତ୍ତର ଆମେରିକା
Answer:
(A) ଏସିଆ

Question 3.
କେଉଁଟି ପୃଥିବୀର କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ରତମ ମହାଦେଶ ?
(A) ଏସିଆ
(B) ଆଫ୍ରିକା
(C) ଅଷ୍ଟ୍ରେଲିଆ
(D) ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆମେରିକା
Answer:
(C) ଅଷ୍ଟ୍ରେଲିଆ
Question 4.
କେଉଁଟି ମହାଦେଶ ହେଲେ ମଧ୍ୟ ଏହା ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ବାସୋପଯୋଗୀ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ଆଫ୍ରିକା
(B) ଆଣ୍ଟାର୍କଟିକା
(C) ଅଷ୍ଟ୍ରେଲିଆ
(D) ଇଉରୋପ
Answer:
(B) ଆଣ୍ଟାର୍କଟିକା
Question 5.
କେଉଁଟି ଭିନ୍ନ ଅଟେ ?
(A) ଏସିଆ – ହିମାଳୟ
(B) ଇଉରୋପ – ଆଲପସ
(C) ଉତ୍ତର ଆମେରିକା – ରକି
(D) ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆମେରିକା – ପାଟାଗୋନିଆ
Answer:
(D) ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆମେରିକା – ପାଟାଗୋନିଆ
Question 6.
କେଉଁଟି ମାଳଭୂମି ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ତିବ୍ବତ୍
(B) ଗୋବି
(C) ଆଣ୍ଡିଜ୍
(D) ସ୍କାଣ୍ଟିନେଭିଆ
Answer:
(C) ଆଣ୍ଡିଜ୍
Question 7.
କେଉଁଟି ଭାରତର ପାର୍ବତ୍ୟ ଭୂମି ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ହିମାଳୟ
(B) ଆରାବଳୀ
(C) ବିଦ୍ଯ
(D) ଆଲପସ୍
Answer:
(D) ଆଲପସ୍

Question 8.
କେଉଁଟି ଅନ୍ୟଠାରୁ ଭିନ୍ନ ଅଟେ ?
(A) ଏସିଆ – ସାଇବେରିଆ
(B) ଇଉରୋପ – ସ୍କାଣ୍ଡିନେରିଆ
(C) ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆମେରିକା – ଆମାଜନ ନଦୀ ଅବବାହିକା – କଙ୍ଗୋନଦୀ ଅବବାହିକା
(D) ଆଫ୍ରିକା
Answer:
(B) ଇଉରୋପ – ସ୍କାଣ୍ଡିନେରିଆ
Question 9.
କେଉଁ ଦେଶରେ ଗରଣ ଭୂମି ଅଧିକ ରହିଛି ?
(A) ଚୀନ
(B) କାନାଡ଼ା
(C) ବ୍ରାଜିଲ
(D) ଅଷ୍ଟ୍ରେଲିଆ
Answer:
(D) ଅଷ୍ଟ୍ରେଲିଆ
Question 10.
ନିମ୍ନୋକ୍ତ କେଉଁ ଦେଶରେ ସର୍ବାଧିକ ଶତାଂଶ କୃଷିଭୂମି ରହିଛି ?
(A) ଫ୍ରାନସ୍
(B) ଭାରତ
(C) ଜାପାନ
(D) ରୁଷିଆ
Answer:
(B) ଭାରତ
Question 11.
ନିମ୍ନୋକ୍ତ କେଉଁ ଦେଶରେ ସର୍ବାଧିକ ଶତାଂଶ କୃଷିଭୂମି ରହିଛି ?
(A) ରୁଷିଆ
(B) ଯୁକ୍ତରାଜ୍ୟ
(C) ଯୁକ୍ତରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ଆମେରିକା
(D) ଜାପାନ
Answer:
(B) ଯୁକ୍ତରାଜ୍ୟ

Question 12.
ନିମ୍ନୋକ୍ତ କେଉଁ ଦେଶରେ ସର୍ବାଧିକ ଶତାଂଶ ସ୍ମରଣ ଭୂମି ରହିଛି ?
(A) ଯୁକ୍ତରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ଆମେରିକା
(B) ରୁଷିଆ
(C) ଯୁକ୍ତରାଜ୍ଯ
(D) ଭାରତ
Answer:
(C) ଯୁକ୍ତରାଜ୍ଯ
Question 13.
କେଉଁଟି ଭୂବ୍ୟବହାରର ମାନବୀୟ ନିୟାମକ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ଶ୍ରମଶକ୍ତି
(B) ଖଣିଜ
(C) ପ୍ରୟୋଗାତ୍ମକ କୌଶଳ
(D) ଜନସଂଖ୍ୟା
Answer:
(B) ଖଣିଜ
Question 14.
ପୃଥିବୀର ମୋଟ ସ୍ଥଳଭାଗର ଶତକଡ଼ା ୩୦ ଭାଗ ଭୂମିରେ ପୃଥିବୀର ମୋଟ ଜନସଂଖ୍ୟାର କେତେଭାଗ ଲୋକ ବାସକରନ୍ତି ?
(A) ୭୦
(B) ୮୦
(C) ୯୦
(D) ୧୦୦
Answer:
(C) ୯୦
Question 15.
କେଉଁ ପାର୍ବତ୍ୟଭୂମି ଉତ୍ତର ଆମେରିକାରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ ?
(A) ଆଣ୍ଡିକ
(B) ଆଲପ୍ସ
(C) ରକି
(D) ହିମାଳୟ
Answer:
(C) ରକି

Question 16.
କେଉଁ ଯୋଡ଼ିଟି ଠିକ୍ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ଆମାଜନ–ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆମେରିକା
(B) ପାରାନା ପାରାଗୁଏ-ଉତ୍ତର ଆମେରିକା
(C) କଙ୍ଗୋ ଅବବାହିକା-ଆଫ୍ରିକା
(D) ସାଇବେରିଆ-ଏସିଆ
Answer:
(B) ପାରାନା ପାରାଗୁଏ-ଉତ୍ତର ଆମେରିକା
ମୃତ୍ତିକା ସମ୍ବଳ
Question 1.
କେଉଁଟି ମୃତ୍ତିକା ସୃଷ୍ଟିର ପ୍ରାଥମିକ ଶିଳାର ଅନ୍ତର୍ଗତ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ରଙ୍ଗ
(B) ବିନ୍ୟାସ
(C) ଖଣିଜ
(D) ଉଷ୍ଣତା
Answer:
(D) ଉଷ୍ଣତା
Question 2.
ମୃତ୍ତିକାର ବହଳତା କାହା ଉପରେ ନିର୍ଭର କରେ ?
(A) ରଙ୍ଗ
(B) ସମୟ
(C) ଉଚ୍ଚତା
(D) ବୃଷ୍ଟିପାତ
Answer:
(B) ସମୟ

Question 3.
କେଉଁଟି ପରିବାହିତ ମୃତ୍ତିକାର ଅନ୍ତର୍ଗତ ?
(A) ପଟୁ
(B) ଲୋହିତ
(C) ଅରଣ୍ୟ
(D) ଲାଟେରାଇଟ୍
Answer:
(A) ପଟୁ
Question 4.
କେଉଁଟି ଅବଶିଷ୍ଟ ମୃତ୍ତିକାର ଅନ୍ତର୍ଗତ ?
(A) ପଟୁ
(B) ଭାଙ୍ଗର
(C) କଳାମାଟି
(D) ମଟାଳମାଟି
Answer:
(C) କଳାମାଟି
Question 5.
କେଉଁଟି ମୃରିକା ଗଠନର ମୁଖ୍ୟ ନିୟାମକ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ଭୂପ୍ରକୃତି
(B) ଜଳବାୟୁ
(C) ପ୍ରାଥମିକ ଶିଳା
(D) ରଙ୍ଗ
Answer:
(D) ରଙ୍ଗ
Question 6.
କେଉଁ ସ୍ଥାନରେ କୃଷ୍ଣ ଓ କୃଷ୍ଣଲୋହିତ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ନାହିଁ ?
(A) ମହାରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର
(B) ଓଡ଼ିଶା
(C) ଗୁଜରାଟ
(D) ତାମିଲନାଡୁ
Answer:
(B) ଓଡ଼ିଶା
Question 7.
ଲୋହିତ ଓ ପୀତ ମୂରିକା କେଉଁ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ନାହିଁ ?
(A) ମଧ୍ୟପ୍ରଦେଶ
(B) ଛତିଶଗଡ
(C) ଝାଡ଼ଖଣ୍ଡ
(D) ଓଡ଼ିଶା
Answer:
(A) ମଧ୍ୟପ୍ରଦେଶ
Question 8.
କେଉଁଠାରେ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ମୃଦ୍ଧିକା ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
(A) କର୍ଣ୍ଣାଟକ
(C) ରାଜସ୍ଥାନ ।
(B) ହିମାଳୟ
(D) ଆନ୍ଧ୍ରପ୍ରଦେଶ
Answer:
(D) ଆନ୍ଧ୍ରପ୍ରଦେଶ

Question 9.
କେଉଁ ସ୍ଥାନରେ ମରୁସ୍ଥଳୀ ମୃତ୍ତିକା ଦେଖାଯାଏ ନାହିଁ ?
(A) ରାଜସ୍ଥାନ
(B) ପଞ୍ଜାବ
(C) ହରିୟାଣା
(D) ଓଡ଼ିଶା
Answer:
(D) ଓଡ଼ିଶା
Question 10.
କେଉଁଟି ମୃତ୍ତିକା କ୍ଷୟର ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ କାରଣ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ବନ୍ଯା
(B) ବାତ୍ଯା
(C) ଅତ୍ୟଧିକ ଗରଣ
(D) ଜଳପ୍ରବାହ
Answer:
(C) ଅତ୍ୟଧିକ ଗରଣ
Question 11.
କେଉଁଟି ମୃତ୍ତିକାକ୍ଷୟର ମାନବୀୟ କାରଣ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ଜଙ୍ଗଲକ୍ଷୟ
(B) ଅତ୍ୟଧିକ ଗରଣ
(C) ରାସାୟନିକ ସାର ବ୍ୟବହାର
(D) ଭୂସ୍ଖଳନ
Answer:
(D) ଭୂସ୍ଖଳନ
Question 12.
ମୃର୍ତ୍ତିକା ସ୍ତରର ବହଳତା କେଉଁ ନିୟାମକଦ୍ଵାରା ପ୍ରଭାବିତ ହୋଇଥାଏ ?
(A) ପ୍ରାଥମିକ ଶିଳା
(B) ଜଳବାୟୁ
(C) ଗଠନ ସମୟର ଅବଧୂ
(D) ଉଦ୍ଭଦ ଓ ପ୍ରାଣୀ
Answer:
(C) ଗଠନ ସମୟର ଅବଧୂ

Question 13.
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର କେଉଁଠାରେ କଳାମାଟି ଦେଖିବାକୁ ମିଳେ ?
(A) ବାଲିଗୁଡ଼ା
(B) ଆଠମଲ୍ଲିକ
(C) ବଲାଙ୍ଗୀର
(D) କଳାହାଣ୍ଡି
Answer:
(B) ଆଠମଲ୍ଲିକ
ଜଳ ସମ୍ବଳ
Question 1.
ଶତକଡ଼ା କେତେ ଭାଗ ମଧୁର ଜଳ ଆଣ୍ଟାର୍କଟିକା, ଗ୍ରୀନ୍ଲ୍ୟାଣ୍ଡ ଓ ଉଚ୍ଚ ପର୍ବତ ଶିଖରମାନଙ୍କରେ ବରଫ ଊଦର ଆକାରରେ ରହିଅଛି ?
(A) ୫୦%
(B) ୬୦%
(C) ୭୦%
(D) ୮୦%
Answer:
(C) ୭୦%
Question 2.
କେଉଁଟି ନଦୀ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ଇରାବତୀ
(B) ହୋୟାଂହୋ
(C) ସିକ୍ରିୟାଂଗ
(D) ଆରାଲ
Answer:
(D) ଆରାଲ
Question 3.
କେଉଁ ନଦୀ ଆଫ୍ରିକା ମହାଦେଶର ଅଟେ ?
(A) ଓବ୍
(B) ଇଗା
(C) ନୀଳନଦୀ
(D) ରୋନ୍
Answer:
(C) ନୀଳନଦୀ

Question 4.
କେଉଁଟି ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ନଦୀ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ନର୍ମଦା
(B) ମହାନଦୀ
(C) ବ୍ରାହ୍ମଣୀ
(D) ବୈତରଣୀ
Answer:
(A) ନର୍ମଦା
Question 5.
କେଉଁଟି ଭାରତର ନଦୀ ଅଟେ ?
(A) ଆମାଜନ୍
(B) ପାରାନା ପାରାଗୁଏ
(C) ବିତସ୍ତା
(D) କଙ୍ଗୋ
Answer:
(C) ବିତସ୍ତା
Question 6.
କେଉଁଟି ପୃଥିବୀର ମୁଖ୍ୟ ହ୍ରଦ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ଅଂଶୁପା
(B) ଆରାଲ
(C) ବୈକାଲ
(D) ମିଚିଗାନ
Answer:
(A) ଅଂଶୁପା
Question 7.
କେଉଁଟି ଭାରତର ହ୍ରଦ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ଚିଲିକା
(B) ଡାଲ
(C) ହ୍ୟୁରନ
(D) ସମ୍ବର
Answer:
(C) ହ୍ୟୁରନ
Question 8.
କେଉଁଟି ଜଳାଭାବର କାରଣ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ଜନସଂଖ୍ୟା ବୃଦ୍ଧି
(B) ଶିଳ୍ପାୟନ
(C) ଜଳବାୟୁ
(D) ସହରୀକରଣ
Answer:
(C) ଜଳବାୟୁ

Question 9.
କେଉଁଟି ଏକ ହ୍ରଦ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ଏଡ଼ୱାର୍ଡ
(B) ଆଲବର୍ଟ
(C) ଭଲଗା
(D) ଭିକ୍ଟୋରିଆ
Answer:
(C) ଭଲଗା
ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଉଭିଦ ଓ ବନ୍ୟପ୍ରାଣୀ
Question 1.
ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଉଭିଦ ଓ ବନ୍ୟପ୍ରାଣୀ ମନୁଷ୍ୟର ବିନା ସାହାଯ୍ୟରେ ଆପେ ଆପେ ଜନ୍ମି, ବଢ଼ୁଥିବା ବୃକ୍ଷ, ଲତା ଓ ତୃଣ ଆଦିକୁ କ’ଣ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
(A) ଅଶ୍ମମଣ୍ଡଳ
(B) ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଉଭିଦ
(C) ପ୍ରାଣୀ
(D) ଜୈବମଣ୍ଡଳ
Answer:
(B) ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଉଭିଦ
Question 2.
କେଉଁଟି ଅରଣ୍ୟଜାତ ଦ୍ରବ୍ୟ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ଫଳ
(B) ମଞ୍ଜି
(C) ଅଠା
(D) ଖଣିଜ
Answer:
(D) ଖଣିଜ

Question 3.
ନିମ୍ନୋକ୍ତ କେଉଁ ପକ୍ଷୀ ପରିବେଶ ସଫାକରିବାରେ ସାହାଯ୍ୟ କରିଥାନ୍ତି ?
(A) ପାରା ଓ ଶୁଆ
(B) କୁଆ ଓ ଶାଗୁଣା
(C) ଶାରୀ ଓ ବଣି
(D) କୋଇଲି ଓ କୁମ୍ଭାଟୁଆ
Answer:
(B) କୁଆ ଓ ଶାଗୁଣା
Question 4.
ଉଭିଦର ବୃଦ୍ଧି କାହା ଉପରେ ମୁଖ୍ୟତଃ ନିର୍ଭର କରି ନ ଥାଏ ?
(A) ଆଲୋକ
(B) ଉତ୍ତାପ
(C) ଜନସଂଖ୍ୟା
(D) ଆର୍ଦ୍ରତା
Answer:
(C) ଜନସଂଖ୍ୟା
Question 5.
ପୃଥିବୀର ଉଭିଦକୁ କେତେ ଭାଗରେ ଭାଗ କରାଯାଇଛି ?
(A) ଏକ
(B) ଦୁଇ
(C) ତିନି
(D) ପ୍ସରି
Answer:
(D) ପ୍ସରି
Question 6.
ମେରୁ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ କେଉଁ ପ୍ରକାର ଉଭିଦ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
(A) ଅରଣ୍ୟ
(B) ତୃଣଭୂମି
(C) କଣ୍ଟାବନ
(D) ତୁନ୍ଦ୍ରା
Answer:
(D) ତୁନ୍ଦ୍ରା
Question 7.
କେଉଁଟି ତୁନ୍ଦ୍ରା ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଉଭିଦ ଅଟେ ?
(A) ଶିଉଳି
(B) ଶାଳ
(C) ସାଗୁଆନ
(D) ଖଇର
Answer:
(A) ଶିଉଳି
Question 8.
କେଉଁ ଅରଣ୍ୟର କାଠ ଶକ୍ତ ଓ ଚିରହରିତ୍ ଅରଣ୍ୟର ଅନ୍ତର୍ଗତ ?
(A) ତୁଦ୍ରା
(B) ଶୀତଳ ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ
(C) କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ
(D) ନିରକ୍ଷୀୟ
Answer:
(D) ନିରକ୍ଷୀୟ

Question 9.
କେଉଁଟି ନିରକ୍ଷୀୟ ଅରଣ୍ୟର ବିଶେଷତ୍ଵ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ଶକ୍ତ କାଠ
(B) ଘନ ଅରଣ୍ୟ
(C) ପତ୍ରଗୁଡ଼ିକ ପତ୍ରଝଡା ଦିଅନ୍ତି
(D) ଚିର ସବୁଜ
Answer:
(C) ପତ୍ରଗୁଡ଼ିକ ପତ୍ରଝଡା ଦିଅନ୍ତି
Question 10.
କେଉଁଟି ନିରକ୍ଷୀୟ ଅରଣ୍ୟର ବୃକ୍ଷ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ଆବୁଲସ
(B) ମେହଗାନି
(C) ବାଉଁଶ
(D) ରବର
Answer:
(C) ବାଉଁଶ
Question 11.
କେଉଁ ଅରଣ୍ୟକୁ ମୌସୁମୀ ଅରଣ୍ୟ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
(A) କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ
(B) ଚିରହରିତ୍
(C) ନିରକ୍ଷୀୟ
(D) ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ
Answer:
(A) କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ
Question 12.
କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ ଅରଣ୍ୟକୁ କେଉଁ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ ?
(A) ଚିରହରିତ୍
(B) ପଶ୍ଚିମୋଟୀ
(C) ଶୁଷ୍କ ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ
(D) କଣ୍ଟାବନ
Answer:
(A) କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ
Question 13.
କେଉଁ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ନାହିଁ ?
(A) ଦକ୍ଷିଣ-ପୂର୍ବ ଏସିଆ
(B) ଉତ୍ତର ଅଷ୍ଟ୍ରେଲିଆ
(C) କଙ୍ଗୋ ଅବବାହିକା
(D) ପୂର୍ବ ଆଫ୍ରିକା
Answer:
(C) କଙ୍ଗୋ ଅବବାହିକା
Question 14.
ଭାରତର କେଉଁ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ନାହିଁ ?
(A) ପୂର୍ବାଞ୍ଚଳ
(B) ପଶ୍ଚିମାଞ୍ଚଳ
(C) ଛୋଟନାଗପୁର ମାଳଭୂମି
(D) ମଧ୍ୟପ୍ରଦେଶର ମାଳଭୂମି
Answer:
Question 15.
କେଉଁଟି କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ ଅରଣ୍ୟର ବୃକ୍ଷ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ଶାଳ
(C) ରବର
(B) ପିଆଶାଳ
(D) ଶିଶୁ
Answer:
Question 16.
କେଉଁଟି କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ ଅରଣ୍ୟର ବୃକ୍ଷ ଅଟେ ?
(A) ରବର
(C) ମେହଗାନି
(B) ଆବୁଲସ
(D) ବାଉଁଶ
Answer:
(D) ବାଉଁଶ

Question 17.
କେଉଁ ଅରଣ୍ୟରେ ଦୀର୍ଘ ତୈଳଯୁକ୍ତ ପତ୍ର ଓ ମୋଟା ବକ୍କଳଯୁକ୍ତ ବୃକ୍ଷ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
(A) ଉଷ୍ଣ ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ
(B) ନିରକ୍ଷୀୟ ଅରଣ୍ୟ
(C) କ୍ଳାନ୍ତୀୟ ଅରଣ୍ୟ
(D) ତୁନ୍ଦ୍ରା ଅରଣ୍ୟ
Answer:
(A) ଉଷ୍ଣ ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ
Question 18.
କେଉଁଟି ଉଷ୍ଣନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ ଅରଣ୍ୟର ବୃକ୍ଷ ଅଟେ ?
(A) ଶିଉଳି ଓ ହିମଗୁଳ୍ମ
(B) ଅଲିଭ୍ ଓ ଓକ୍
(C) ଶାଳ ଓ ପିଆଶାଳ
(D) ରବର ଓ ବାଉଁଶ
Answer:
(B) ଅଲିଭ୍ ଓ ଓକ୍
Question 19.
ମହାଦେଶଗୁଡ଼ିକର ପୂର୍ବ ଓ ପଶ୍ଚିମ ଉପକୂଳ ଏବଂ ଭୂମଧ୍ଯ ସାଗରୀୟ ଦେଶଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ କେଉଁ ପ୍ରକାର ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
(A) ନିରକ୍ଷୀୟ
(B) କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ
(C) ଉଷ୍ଣ ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ
(D) ଶୀତଳ ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ
Answer:
(C) ଉଷ୍ଣ ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ
Question 20.
କେଉଁ ଅରଣ୍ୟର ବୃକ୍ଷଗୁଡ଼ିକ ସରଳବର୍ଗୀୟ ନରମ କାଠଯୁକ୍ତ ଓ ପାଇନ୍ ଜାତୀୟ ଅଟେ ?
(A) ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ
(B) ଉଷ୍ଣନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ
(C) କ୍ରାନ୍ତୀୟ
(D) ଶୀତଳ ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ
Answer:
(D) ଶୀତଳ ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ
Question 21.
କେଉଁଟି ଶୀତଳ ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ ଅରଣ୍ୟର ବୃକ୍ଷ ଅଟେ ?
(A) ପାଇନ ଓ ଫିର
(C) ଶାଳ ଓ ପିଆଶାଳ
(B) ଅଲିଭ୍ ଓ ଓକ୍
(D) ଚନ୍ଦନ ଓ ଶିଶୁ
Answer:
(A) ପାଇନ ଓ ଫିର
Question 22.
ଭାରତର କେଉଁ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଶୀତଳ ନାତିଶୀତୋଷ୍ଣ ଅରଣ୍ୟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
(A) ବିନ୍ଧ୍ୟ ପର୍ବତର ଉଚ୍ଚ ଅଂଶ
(B) ପୂର୍ବଘାଟ
(C) ହିମାଳୟ ପର୍ବତର ଉଚ୍ଚ ଅଂଶ
(D) ପଶ୍ଚିମଘାଟ ପର୍ବତର ଉଚ୍ଚ ଅଂଶ
Answer:
(C) ହିମାଳୟ ପର୍ବତର ଉଚ୍ଚ ଅଂଶ

Question 23.
କେଉଁ ପ୍ରାଣୀ ଅନ୍ୟ ତିନୋଟିଠାରୁ ଭିନ୍ନ ଅଟେ ?
(A) ହାତୀ
(B) ବାଘ
(C) ସମ୍ବର
(D) ମୃଗ
Answer:
(B) ବାଘ
Question 24.
କେଉଁଟି ମାଂସାଶୀ ପ୍ରାଣୀ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ବାଘ
(B) ସିଂହ
(C) ହେଟାବାଘ
(D) ହରିଣ
Answer:
(D) ହରିଣ
Question 25.
କେଉଁଟି ଉଭୟଭୋଜୀ ପ୍ରାଣୀ ?
(A) ମୃଗ ଓ ହରିଣ
(B) ବିଲୁଆ ଓ ଭାଲୁ
(C) ସିଂହ ଓ ବାଘ
(D) ହାତୀ ଓ ସମ୍ବର
Answer:
(B) ବିଲୁଆ ଓ ଭାଲୁ
Question 26.
ଆଫ୍ରିକାର କଙ୍ଗୋ ଅବବାହିକା ଓ ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆମେରିକାର ଆମାଜନ ଅବବାହିକାରେ କେଉଁ ପ୍ରକାର ପ୍ରାଣୀ ଦେଖାଯାଆନ୍ତି ?’
(A) ମାଙ୍କଡ, ଶିମ୍ପାଜୀ, ଓରାଂଗ ଓଟାଙ୍ଗ୍
(B) ହରିଣ, ଜେବ୍ରା, ଜିରାଫ
(C) ବାଘ, ସିଂହ, ହାତୀ
(D) ଓଟ, ବାଘ, ହରିଣ
Answer:
(A) ମାଙ୍କଡ, ଶିମ୍ପାଜୀ, ଓରାଂଗ ଓଟାଙ୍ଗ୍
Question 27.
କେଉଁ ତୃଣଭୂମିରେ ମାଂସାଶୀ ଓ ତୃଣଭୋଜୀ ପ୍ରାଣୀ ଦେଖାଯାଆନ୍ତି ?
(A) ଷ୍ଟେପି
(B) ପ୍ରେରୀ
(C) ସାଇନା
(D) ଲିଆନସ
Answer:
(C) ସାଇନା
Question 28.
ସାହାରା ଓ ସାଉଦି ଆରବର ଗ୍ରୀଷ୍ମମଣ୍ଡଳୀୟ ମରୁଭୂମି ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ କେଉଁ ପ୍ରାଣୀ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
(A) ବାଘ
(B) ଓଟ
(C) ହରିଣ
(D) ହାତୀ
Answer:
(D) ହାତୀ

Question 29.
ଆଫ୍ରିକାର କାଲାହାରୀ ମରୁଭୂମିରେ କେଉଁ ପ୍ରକାର ପକ୍ଷୀ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
(A) ଓଟପକ୍ଷୀ
(B) ପେଙ୍ଗୁଇନ୍
(C) ଓରାଙ୍ଗ ଓଟାନ
(D) ଏମୁ
Answer:
(A) ଓଟପକ୍ଷୀ
Question 30.
କେଉଁ ଦେଶରେ ଏମ୍ ଓ କଙ୍ଗାରୁ ପ୍ରଧାନ ପ୍ରାଣୀ ?
(A) ବ୍ରାଜିଲ
(B) କାନାଡା
(C) ଅଷ୍ଟ୍ରେଲିଆ
(D) ଚୀନ
Answer:
(C) ଅଷ୍ଟ୍ରେଲିଆ
Question 31.
କେଉଁଟି ଉତ୍ତର ମେରୁ ଅଞ୍ଚଳର ପ୍ରାଣୀ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ଧଳାଭାଲୁ
(B) ସିଲ
(C) ସିଲଭର ଫକ୍
(D) କଙ୍ଗାରୁ
Answer:
(D) କଙ୍ଗାରୁ
Question 32.
ନେପାଳ ଓ ଭାରତ ସୀମାନ୍ତରେ ହିମାଳୟ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ କେଉଁ ବନ୍ୟପ୍ରାଣୀ ଦେଖାଯାଆନ୍ତି ?
(A) କସ୍ତୁରୀ ମୃଗ ଓ ଚମରୀଗାଈ
(B) ତମ୍ପ ଓ ନାଗ
(C) ଗୋଧ୍ ଓ କୁମ୍ଭୀର
(D) ମୟୂର ଓ ଶୁଆ
Answer:
(A) କସ୍ତୁରୀ ମୃଗ ଓ ଚମରୀଗାଈ
Question 33.
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର କେଉଁଠାରେ ନୀଳଗାଈ ଓ ଚଉଶିଳ୍ପୀ ହରିଣ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
(A) କୋରାପୁଟ, ମାଲକାନଗିରି, ରାୟଗଡ଼ା
(B) ଅନୁଗୁଳ, ସମ୍ବଲପୁର, କୋରାପୁଟ
(C) ସମ୍ବଲପୁର, ସୁନ୍ଦରଗଡ଼, ବଲାଙ୍ଗିର
(D) ଗଞ୍ଜାମ, ମୟୂରଭଞ୍ଜ, କେନ୍ଦ୍ରାପଡ଼ା
Answer:
(B) ଅନୁଗୁଳ, ସମ୍ବଲପୁର, କୋରାପୁଟ
Question 34.
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ମାଲକାଗିରି ଓ ଖଡ଼ିଆଳ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ କେଉଁ ବନ୍ୟପ୍ରାଣୀ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
(A) ନୀଳଗାଈ
(B) ଚଉଶିଙ୍ଗା ହରିଣ
(C) ବଣୁଆ ମଇଁଷି
(D) ଝିଙ୍କ
Answer:
(C) ବଣୁଆ ମଇଁଷି

Question 35.
ଚିଲିକାର କେଉଁ ମାଛ ଦେଖିବାକୁ ପର୍ଯ୍ୟଟକମାନେ ଆସିଥାନ୍ତି ?
(A) ଡଲଫିନ୍
(B) ଶାଙ୍କୁଚ
(C) ମଗର
(D) ତିମି
Answer:
(A) ଡଲଫିନ୍
Question 36.
କେଉଁଟି ଅରଣ୍ୟ କ୍ଷୟ ରୋକିବାର ଉପାୟ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ମନଇଚ୍ଛା ଜଙ୍ଗଲ କାଟିବା ବନ୍ଦ
(B) ସ୍ଥାନାନ୍ତରିତ କୃଷି ପଦ୍ଧତି ବନ୍ଦ
(C) ପଶୁସ୍କରଣ ବନ୍ଦ
(D) ନିର୍ମାଣ ଶିକ
Answer:
(D) ନିର୍ମାଣ ଶିକ
Question 37.
କେଉଁ ବ୍ୟାଘ୍ର ପ୍ରକଳ୍ପଟି ଭିନ୍ନ ଅଟେ ?
(A) ଆସ୍କାମ୍ — ମାନସ
(B) ପଶ୍ଚିମବଙ୍ଗ – ସୁନ୍ଦରବନ
(C) ଝାଡ଼ଖଣ୍ଡ – ପାଲାମୁ
(D) ଗୁଜରାଟ – ଗୀର
Answer:
(D) ଗୁଜରାଟ – ଗୀର
Question 38.
କେଉଁ ବ୍ୟାଘ୍ର ପ୍ରକଳ୍ପଟି ଭିନ୍ନ ଅଟେ ?
(A) ଉତ୍ତରାଖଣ୍ଡକର୍ନେଟ ଜାତୀୟ ଉଦ୍ୟାନ
(B) ମହାରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର-ମେଲଘାଟ
(C) ଆସାମ-ପାଲାମୁ
(D) କର୍ଣାଟକ-ବାନ୍ଦୀପୁର
Answer:
(C) ଆସାମ-ପାଲାମୁ
Question 39.
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଚନ୍ଦକା ଅରଣ୍ୟ କେଉଁ ଅଭୟାରଣ୍ୟ ପାଇଁ ପ୍ରସିଦ୍ଧ ?
(A) ବାଘ
(B) ହାତୀ
(C) କୁମ୍ଭୀର
(D) ସିଂହ
Answer:
(B) ହାତୀ
Question 40.
ଚନ୍ଦକା ଅଭୟାରଣ୍ୟ କେଉଁଠାରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ ?
(A) କଟକ
(B) ରାଉରକେଲା
(C) ବ୍ରହ୍ମପୁର
(D) ଭୁବନେଶ୍ଵର
Answer:
(D) ଭୁବନେଶ୍ଵର
Question 41.
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର କେଉଁଠାରେ କୁମ୍ଭୀର ସଂରକ୍ଷଣ କେନ୍ଦ୍ର ରହିଛି ?
(A) ଚନ୍ଦକା ଓ ଶିମିଳିପାଳ
(B) ଟିକରପଡ଼ା ଓ ଭିତରକନିକା
(C) ବ୍ରହ୍ମପୁର ଓ ରାୟଗଡ଼ା
(D) ଛତ୍ରପୁର ଓ ବାରିପଦା
Answer:
(B) ଟିକରପଡ଼ା ଓ ଭିତରକନିକା
Question 42.
ଚିଲିକା ହ୍ରଦ କେଉଁ ଅଭୟାରଣ୍ୟ ପାଇଁ ପ୍ରସିଦ୍ଧ ?
(A) ହାତୀ
(B) ବାଘ
(C) ପକ୍ଷୀ
(D) କୁମ୍ଭୀର
Answer:
(C) ପକ୍ଷୀ
Question 43.
କେଉଁ ବନ୍ୟପ୍ରାଣୀ ପାଇଁ ଓଡ଼ିଶାରେ ସଂରକ୍ଷଣ କରାଯାଇ ନାହିଁ ?
(A) ବାଘ
(B) ହାତୀ
(C) କୁମ୍ଭୀର
(D) ସିଂହ
Answer:
(D) ସିଂହ
Question 44.
ଟିକରପଡ଼ା ସାତକୋଶିଆ କୁମ୍ଭୀର ସଂରକ୍ଷଣ କେନ୍ଦ୍ର କେଉଁ ଜିଲ୍ଲାରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ ?
(A) ଅନୁଗୁଳ
(B) କେନ୍ଦ୍ରାପଡ଼ା
(C) ମୟୂରଭଞ୍ଜ
(D) କୋରାପୁଟ
Answer:
(A) ଅନୁଗୁଳ
Question 45.
ଫୁଲରେ ପରାଗ ସଂଗମ ପାଇଁ କିଏ ମୁଖ୍ୟତଃ ଦାୟୀ ?
(A) ପଶୁ
(B) ପକ୍ଷୀ
(C) ମହୁମାଛି
(D) ଝିଣ୍ଟିକା
Answer:
(C) ମହୁମାଛି

Question 46.
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର କେଉଁଠାରେ ଏକ କୁମ୍ଭୀର ସଂରକ୍ଷଣ କେନ୍ଦ୍ର ରହିଛି ?
(A) ଶିମିଳିପାଳ
(B) ଚିଲିକା
(C) ଭିତରକନିକା
(D) ଅଂଶୁପା
Answer:
(C) ଭିତରକନିକା
Question 47.
କେଉଁ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଏମୁ ଦେଖାଯା’ନ୍ତି ?
(A) କାଲାହାରୀ ମରୁଭୂମି
(B) ଗୋବି ମାଳଭୂମି
(C) ସାଭାନ୍ନା ତୃଣଭୂମି
(D) ଅଷ୍ଟ୍ରେଲିଆ ମରୁଭୂମି
Answer:
(D) ଅଷ୍ଟ୍ରେଲିଆ ମରୁଭୂମି
ଖଣିଜ ସମ୍ବଳ
Question 1.
କେଉଁ କ୍ରମଟି ଅଜୈବ ଖଣିଜର ଅନ୍ତର୍ଗତ ?
(A) ଲୁହା, ସୁନା, ତମ୍ବା
(B) କୋଇଲା, ଲୁହା, ତମ୍ବା
(C) ଖଣିଜତୈଳ, ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଗ୍ୟାସ୍, ତମ୍ବା
(D) ଲୁହା, କୋଇଲା, ଖଣିଜତୈଳ
Answer:
(A) ଲୁହା, ସୁନା, ତମ୍ବା
Question 2.
କେଉଁ କ୍ରମଟି ଜୈବ ଖଣିଜର ଅନ୍ତର୍ଗତ ?
(A) ସୁନା, ଲୁହା, ତମ୍ବା
(B) ତମ୍ବା, କୋଇଲା, ସୁନା
(C) କୋଇଲା, ଖଣିଜତୈଳ, ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଗ୍ୟାସ୍
(D) ତମ୍ବା, ସୀସା, ଖଣିଜତୈଳ
Answer:
(C) କୋଇଲା, ଖଣିଜତୈଳ, ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଗ୍ୟାସ୍
Question 3.
କେଉଁ ଖଣିଜକୁ ଜୀବାଶ୍ମ ଇନ୍ଧନ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
(A) ସୁନା
(B) କୋଇଲା
(C) ତମ୍ବା
(D) ଲୁହା
Answer:
(B) କୋଇଲା

Question 4.
କେଉଁଟି ଧାତବ ଖଣିଜ ପଦାର୍ଥ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ଲୌହପିଣ୍ଡ
(B) ବକ୍ସାଇଟ
(C) ମାଙ୍ଗାନିଜ୍
(D) ଚୂନପଥର
Answer:
(D) ଚୂନପଥର
Question 5.
କେଉଁଟି ଅଧାତବ ଖଣିଜ ପଦାର୍ଥ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ଚୂନପଥର
(B) ଅଲ୍ପ
(C) ବକ୍ସାଇଟ
(D) ଜିପ୍ସମ୍
Answer:
(C) ବକ୍ସାଇଟ
Question 6.
କେଉଁଟି ଲୌହଯୁକ୍ତ ଖଣିଜ ପଦାର୍ଥ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ଲୌହପିଣ୍ଡ
(B) ମାଙ୍ଗାନିକ
(C) କ୍ରୋମାଇଟ୍
(D) ସୁନା
Answer:
(D) ସୁନା
Question 7.
କେଉଁଟି ଲୌହବିହୀନ ଖଣିଜର ଅନ୍ତର୍ଗତ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ସୁନା
(B) ରୁପା
(C) ମାଙ୍ଗାନିଜ
(D) ତମ୍ବା
Answer:
(C) ମାଙ୍ଗାନିଜ
Question 8.
କେଉଁଟି ଖଣିଜ ଉତ୍ତୋଳନ ପ୍ରକ୍ରିୟା ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ସାଧାରଣ ଖନନ
(B) ଖଣିଖନନ
(C) ଡ୍ରିଲିଂ
(D) ନିଷ୍କାସନ
Answer:
(D) ନିଷ୍କାସନ

Question 9.
ଭୂଗର୍ଭର ଅତ୍ୟଧ୍ଵକ ଗଭୀରତାରେ ଥିବା ପେଟ୍ରୋଲ ଏବଂ ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଗ୍ୟାସ୍କୁ ବାହାରକୁ ଆଣିବା ପାଇଁ କରାଯାଉଥିବା ଗଭୀର କୂପ ଖନନ ପ୍ରକ୍ରିୟାକୁ କ’ଣ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
(A) ଖଣି ଖନନ
(B) ଡ୍ରିଲିଂ
(C) ସାଧାରଣ ଖନନ
(D) ମୁକ୍ତଗର୍ଭ ଖନନ
Answer:
(B) ଡ୍ରିଲିଂ
Question 10.
କେଉଁ ଖଣିଜ ଆଗ୍ନେୟ ଓ ରୂପାନ୍ତରିତ ଶିଳାରେ ଗଠିତ ହୋଇଥିବା ମାଳଭୂମିରେ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
(A) ଧାତବ
(C) ଲୌହମୁକ୍ତ
(B) ଅଧାତବ
(D) ଲୌହବିହୀନ
Answer:
(A) ଧାତବ
Question 11.
ଇଉଡ୍ରେନ୍ ଓ ଆଲଜେରିଆରେ କେଉଁ ଖଣିଜ ଗଳିତ ଅଛି ?
(A) ଜିପ୍ସମ୍ ଓ ଫସ୍ଫେଟ୍
(B) ଚୂନପଥର ଓ ଅମ୍ଳ
(C) ସୁନା ଓ ରୁପା
(D) କୋଇଲା ଓ ମାଙ୍ଗାନିଜ
Answer:
(A) ଜିପ୍ସମ୍ ଓ ଫସ୍ଫେଟ୍
Question 12.
କେଉଁ ଖଣିଳ ସ୍ତରୀଭୂତ ଶିଳାରେ ଗଚ୍ଛିତ ଥାଏ ?
(A) ଲୌହ ଓ ନିକେଲ
(B) କ୍ରୋମାଇଟ୍ ଓ ପ୍ଲାଟିନମ୍
(C) କୋଇଲା ଓ ପେଟ୍ରୋଲିୟମ୍
(D) ସୁନା ଓ ରୁପା
Answer:
(C) କୋଇଲା ଓ ପେଟ୍ରୋଲିୟମ୍
Question 13.
ନିମ୍ନୋକ୍ତ କେଉଁ ଦେଶରେ ଲୁହାପଥର ଉତ୍ପାଦନ ଅଧିକ ହୋଇଥାଏ ?
(A) ବାଂଲାଦେଶ
(B) ଚୀନ
(C) ଯୁକ୍ତରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ଆମେରିକା
(D) ବ୍ରାଜିଲ
Answer:
(C) ଯୁକ୍ତରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ଆମେରିକା
Question 14.
ନିମ୍ନୋକ୍ତ କେଉଁ କ୍ରମଟି ଲୁହାପଥର ଉତ୍ପାଦନ ରାଜ୍ୟ ଅଟେ ?
(A) ଓଡ଼ିଶା, ମହାରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର, ଛତିଶଗଡ଼
(B) ଉତ୍ତର ପ୍ରଦେଶ, ବିହାର, ଆସାମ,
(C) ଉତ୍ତରାଖଣ୍ଡ, ଛତିଶଗଡ଼, ତାମିଲନାଡୁ
(D) କେରଳ, ମହାରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର, ଗୁଜରାଟ
Answer:
(A) ଓଡ଼ିଶା, ମହାରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର, ଛତିଶଗଡ଼
Question 15.
ନିମ୍ନୋକ୍ତ କେଉଁ କ୍ରମଟି ମାଙ୍ଗାନିଜ ଉତ୍ପାଦନରେ ପୃଥିବୀରେ ଅଗ୍ରଣୀ ଦେଶ ?
(A) ଭାରତ, ଶ୍ରୀଲଙ୍କା, ପାକିସ୍ତାନ
(B) ନେପାଳ, ଚୀନ, ଜର୍ମାନୀ
(C) ଜାପାନ, ଇରାକ, ଇରାନ
(D) ରୁଷିଆ, ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆଫ୍ରିକା, ବ୍ରାଜିଲ
Answer:
(D) ରୁଷିଆ, ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆଫ୍ରିକା, ବ୍ରାଜିଲ
Question 16.
କେଉଁ କ୍ରମଟି ମାଙ୍ଗାନିଜ ଉତ୍ପାଦନରେ ଭାରତରେ ଅଗ୍ରଣୀ ରାଜ୍ୟ ?
(A) ବିହାର, ଝାଡଖଣ୍ଡ, ଉତ୍ତରାଞ୍ଚଳ
(B) ଓଡ଼ିଶା, ମଧ୍ୟପ୍ରଦେଶ, ମହାରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର
(C) ହିମାଚଳ ପ୍ରଦେଶ, ପଞ୍ଜାବ, ହରିୟାଣା
(D) ମଧ୍ୟପ୍ରଦେଶ, ରାଜସ୍ଥାନ, ଗୁଜରାଟ
Answer:
(B) ଓଡ଼ିଶା, ମଧ୍ୟପ୍ରଦେଶ, ମହାରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର

Question 17.
କେଉଁ କ୍ରମଟି କୋଇଲା ଉତ୍ପାଦନରେ ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଅଗ୍ରଣୀ ଜିଲ୍ଲା ?
(A) କଟକ, କଳାହାଣ୍ଡି, କନ୍ଧମାଳ
(B) କୋରାପୁଟ, ସମ୍ବଲପୁର, ବୌଦ୍ଧ
(C) ଅନୁଗୁଳ, ଝାରସୁଗୁଡ଼ା, ସୁନ୍ଦରଗଡ଼
(D) ବରଗଡ଼, ବଲାଙ୍ଗିର, ମୟୂରଭଞ୍ଜ
Answer:
(C) ଅନୁଗୁଳ, ଝାରସୁଗୁଡ଼ା, ସୁନ୍ଦରଗଡ଼
Question 18.
ଭାରତ କେଉଁ ରାଜ୍ୟ ଖଣିଜ ତୈଳ ସହ ସଂପୃକ୍ତ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ଆସାମ
(B) ଗୁଜରାଟ
(C) ଆନ୍ଧ୍ର ପ୍ରଦେଶ
(D) ମହାରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର
Answer:
(C) ଆନ୍ଧ୍ର ପ୍ରଦେଶ
Question 19.
କେଉଁଟି ଆଲୁମିନିୟମ୍ ଶିଳ୍ପରେ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହୁଏ ?
(A) କ୍ରୋମାଇଟ୍
(B) ବକ୍ସାଇଟ୍
(C) ମାଙ୍ଗାନିଜ୍
(D) ଅଭ୍ର
Answer:
(B) ବକ୍ସାଇଟ୍
Question 20.
କେଉଁଟି ଲୌହବିହୀନ ଖଣିଜ ?
(A) ସୀସା
(B) ମାଙ୍ଗାନିଜ୍
(C) କ୍ରୋମାଇଟ୍
(D) ଲୌହପିଣ୍ଡ
Answer:
(A) ସୀସା
ଶକ୍ତି ସମ୍ବଳ
Question 1.
କେଉଁଟି ପାରମ୍ପାରିକ ଶକ୍ତି ସମ୍ବଳର ଅନ୍ତର୍ଗତ ?
(A) ଜୁଆର ଶକ୍ତି
(B) ପବନ ଶକ୍ତି
(C) ଜଳବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ଶକ୍ତି
(D) ଆଣବିକ ଶକ୍ତି
Answer:
(C) ଜଳବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ଶକ୍ତି

Question 2.
କେଉଁଟି ପାରମ୍ପରିକ ଶକ୍ତି ସମ୍ବଳର ଅନ୍ତର୍ଗତ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ଜାଳେଣିକାଠ
(B) କୋଇଲା
(C) ଖଣିଜତୈଳ
(D) ଭୂ-ତାପଜଶକ୍ତି
Answer:
(D) ଭୂ-ତାପଜଶକ୍ତି
Question 3.
କେଉଁଟି ଜୀବାଶ୍ମ ଜାଳେଣିର ଅନ୍ତର୍ଗତ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) କୋଇଲା
(B) ପେଟ୍ରୋଲିୟମ୍
(C) ଜାଳେଣି କାଠ
(D) ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଗ୍ୟାସ୍
Answer:
(C) ଜାଳେଣି କାଠ
Question 4.
ନିମ୍ନୋକ୍ତ କେଉଁ ଦେଶ ପୃଥିବୀର ମୁଖ୍ୟ କୋଇଲା ଉତ୍ପାଦନକାରୀ ରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ?
(A) ଚୀନ, ଯୁକ୍ତରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ଆମେରିକା, ରୁଷିଆ
(B) ଜାପାନ, ଜର୍ମାନୀ, ଇଂଲଣ୍ଡ
(C) ବ୍ରାଜିଲ, ଚିଲି, ପେରୁ
(D) କାନାଡ଼ା, ପୋଲାଣ୍ଡ, ସୁଇଜରଲ୍ୟାଣ୍ଡ
Answer:
(A) ଚୀନ, ଯୁକ୍ତରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ଆମେରିକା, ରୁଷିଆ
Question 5.
କେଉଁଟି ପୃଥିବୀର ମୁଖ୍ୟ ପେଟ୍ରୋଲିୟମ୍ ଉତ୍ପାଦନକାରୀ ରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ସମୂହ ଅଟନ୍ତି ?
(A) ଭାରତ, ଜାପାନ, ଇଂଲଣ୍ଡ
(B) ସିରିଆ, ବୁଲଗେରିଆ, ଜୋର୍ଡାନ,
(C) ଶ୍ରୀଲଙ୍କା, ଜାଭା, ମାଲୟେସିଆ
(D) ଇରାକ, ଇରାନ, ସାଉଦି ଆରବ
Answer:
(D) ଇରାକ, ଇରାନ, ସାଉଦି ଆରବ

Question 6.
ଘରୋଇ ଇନ୍ଧନ ଓ କାରଖାନାଗୁଡ଼ିକର ଜାଳେଣି ଇନ୍ଧନ ରୂପେ କାହାକୁ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଇଥାଏ ?
(A) କୋଇଲା
(B) ପେଟ୍ରୋଲିୟମ୍
(C) ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଗ୍ୟାସ୍
(D) ଜାଳେଣି କାଠ
Answer:
(C) ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଗ୍ୟାସ୍
Question 7.
ପୃଥିବୀର କେଉଁ ଦେଶଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଗ୍ୟାସ୍ ଉତ୍ପାଦନ ହୋଇଥାଏ ?
(A) କାନାଡ଼ା, ବ୍ରାଜିଲ, ନରସ୍ଵେ
(B) ରୁଷିଆ, ନର େ, ଯୁକ୍ତରାଜ୍ୟ
(C) ଜାପାନ, ଚୀନ, ଭାରତ
(D) ସ୍କଟଲ୍ୟାଣ୍ଡ, ପୋଲାଣ୍ଡ, ଇଂଲଣ୍ଡ
Answer:
(B) ରୁଷିଆ, ନର େ, ଯୁକ୍ତରାଜ୍ୟ
Question 8.
ପୃଥିବୀର ଉତ୍ପନ୍ନ ହେଉଥିବା ମୋଟ ବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ଶକ୍ତିର କେତେ ଭାଗ ଜଳବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ଶକ୍ତି ?
(A) ଏକ
(B) ଦୁଇ
(C) ଚିନି
(D) ସ୍ପରି
Answer:
(D) ସ୍ପରି
Question 9.
କେଉଁଟି ଅଣପାରମ୍ପାରିକ ଶକ୍ତିର ଉତ୍ସ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ସୌରଶକ୍ତି
(B) ପବନଶକ୍ତି
(C) ଜୁଆରଶକ୍ତି
(D) ତାପଜଶକ୍ତି
Answer:
(D) ତାପଜଶକ୍ତି
Question 10.
ସୌର ଓ ପବନଶକ୍ତି ବ୍ୟବହାର କରୁଥିବା ପୃଥିବୀର ପ୍ରଥମ ବସ୍ ଆଶ୍ରୟସ୍ଥଳୀ କେଉଁ ଦେଶରେ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ ?
(A) ପୋଲାଣ୍ଡ
(B) ଇଂଲଣ୍ଡ
(C) ସ୍କଟଲ୍ୟାଣ୍ଡ
(D) ନେଦରଲ୍ୟାଣ୍ଡ
Answer:
(C) ସ୍କଟଲ୍ୟାଣ୍ଡ

Question 11.
କେଉଁ ଦେଶଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ପବନ ଫାର୍ମମାନ ଗଠିତ ହୋଇଛି ?
(A) ନେଦରଲ୍ୟାଣ୍ଡ, ଜର୍ମାନୀ, ଡେନମାର୍କ
(B) ରୁଷିଆ, ନେପାଳ, ‘ମିଆଁମାର
(C) ଶ୍ରୀଲଙ୍କା, ଆର୍ଜେଣ୍ଟିନା, କାନାଡ଼ା
(D) ବ୍ରାଜିଲ, ଦକ୍ଷିଣ ଆଫ୍ରିକା, ସୁଇଡେନ
Answer:
(A) ନେଦରଲ୍ୟାଣ୍ଡ, ଜର୍ମାନୀ, ଡେନମାର୍କ
Question 12.
ୟୁରାନିୟମ୍ ଓ ଥୋରିୟମ୍କୁ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରି କେଉଁ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନ କରାଯାଏ ?
(A) ସୌରଶକ୍ତି
(B) ବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ଶକ୍ତି
(C) ତାପଜ ଶକ୍ତି
(D) ଆଣବିକ ଶକ୍ତି
Answer:
(D) ଆଣବିକ ଶକ୍ତି
Question 13.
କେଉଁଟି ପୃଥିବୀର ବୃହତ୍ ଆଣବିକ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନକାରୀ ରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ଅଟେ ?
(A) ନେପାଳ
(B) ପାକିସ୍ଥାନ
(C) ଯୁକ୍ତରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ଆମେରିକା
(D) ଉତ୍ତର କୋରିଆ
Answer:
(C) ଯୁକ୍ତରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ଆମେରିକା
Question 14.
ଭାରତର କେଉଁ ରାଜ୍ୟରେ ବିପୁଳ ପରିମାଣରେ ୟୁରାନିୟମ୍ ମିଳେ ?
(A) ଓଡ଼ିଶା ଓ ଆନ୍ଧ୍ରପ୍ରଦେଶ
(B) ଝାଡ଼ଖଣ୍ଡ ଓ ରାଜସ୍ଥାନ
(C) ବିହାର ଓ ଆସାମ
(D) ଗୋଆ ଓ ପୁଡୁଚେରୀ
Answer:
(B) ଝାଡ଼ଖଣ୍ଡ ଓ ରାଜସ୍ଥାନ
Question 15.
ଭାରତର କେଉଁ ଆଣବିକ ଶକ୍ତି କେନ୍ଦ୍ରଟି ଭିନ୍ନ ଅଟେ ?
(A) ତାମିଲନାଡୁ – କଳ୍ପକମ୍
(B) ମହାରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର – ପୁନେ
(C) ରାଜସ୍ଥାନ – ରାଣାପ୍ରତାପ ସାଗର
(D) କର୍ଣାଟକ ନଇଗା
Answer:
(B) ଝାଡ଼ଖଣ୍ଡ ଓ ରାଜସ୍ଥାନ
Question 16.
କେଉଁ ଯୋଡ଼ିଟି ବିଷମ ଅଟେ ?
(A) ମହାରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର – ତାରାପୁର
(B) ଉତ୍ତର ପ୍ରଦେଶ – ନାରୋରା
(C) କର୍ଣାଟକ – ନାଇଗା
(D) ରାଜସ୍ଥାନ – କଳ୍ପକମ୍
Answer:
(B) ଝାଡ଼ଖଣ୍ଡ ଓ ରାଜସ୍ଥାନ
Question 17.
କେଉଁ ଦେଶଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଭୂତାପଜ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନରେ ଅଗ୍ରଣୀ ଭାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ଅଟନ୍ତି ?
(A) ଅଷ୍ଟ୍ରେଲିଆ, ଶ୍ରୀଲଙ୍କା, ଭାରତ
(B) ନିଉଜିଲ୍ୟାଣ୍ଡ, ଆଇସଲ୍ୟାଣ୍ଡ, ଫିଲିପାଇନସ୍
(C) ଜାପାନ, ଜର୍ମାନୀ, ଇଂଲଣ୍ଡ
(D) ବ୍ରାଜିଲ, କାନାଡ଼ା, ପେରୁ
Answer:
(B) ନିଉଜିଲ୍ୟାଣ୍ଡ, ଆଇସଲ୍ୟାଣ୍ଡ, ଫିଲିପାଇନସ୍

Question 18.
ଭାରତର ହିମାଚଳ ପ୍ରଦେଶର ମନିକରଣ ଓ ଲଦାଖର ସୁଗା ଉପତ୍ୟକାରେ କେଉଁ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନ କରାଯାଏ ?
(A) ତାପଜ ଶକ୍ତି
(C) ଜୁଆର ଶକ୍ତି
(B) ସୌର ଶକ୍ତି
(D) ଭୂ-ତାପଜ ଶକ୍ତି
Answer:
(D) ଭୂ-ତାପଜ ଶକ୍ତି
Question 19.
ଭାରତର ଗୁଜୁରାଟର କାମେ ଉପକୂଳ ଓ ପଶ୍ଚିମ ବଙ୍ଗର ସୁନ୍ଦରବନ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ କେଉଁ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନ କରାଯାଉଛି ?
(A) ଭୂତାପଜ
(B) ପବନ
(C) ଜୁଆର
(D) ସୌରଦ
Answer:
(C) ଜୁଆର
Question 20.
କେଉଁଟି ସର୍ବବୃହତ୍ ଭୂତାପଜ ଶକ୍ତି ଉତ୍ପାଦନକାରୀ ଦେଶ ?
(A) ଯୁକ୍ତରାଜ୍ଯ
(B) ଯୁକ୍ତରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ଆମେରିକା
(C) ସୁଇଡ଼େନ
(D) ନିଉଜିଲାଣ୍ଡ
Answer:
(C) ଜୁଆର
![]()

![]()
![]()



![]()




![]()



![]()