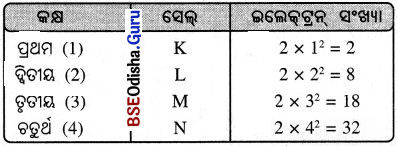
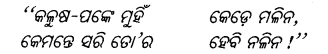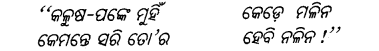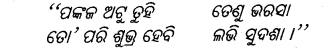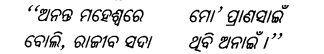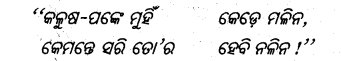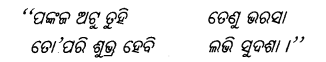Odisha State Board BSE Odisha 9th Class Odia Solutions Chapter 4 ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
BSE Odisha Class 9 Odia Solutions Chapter 4 ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ
ପାଠ୍ୟପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ଥ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନାବଳୀର ଉତ୍ତର
ସଂକ୍ଷିପ୍ତ ଉତ୍ତରମୂ ଳକ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନୋତ୍ତର
Question ୧।
ଚିନ୍ତାବା, ଝୋଲା ମାରିବା, ବୁଝିବା, ଝୁରିବା, ସ୍ମରଣ କରିବା –ଏହି ଶବ୍ଦଗୁଡ଼ିକ ମଧ୍ୟରୁ କେଉଁଟି ଶୋକ କରିବା ଅର୍ଥ ପ୍ରକାଶ କରୁଛି ?
Answer:
ଝୁରିବା ।
Question ୨।
ବନ୍ଧନୀ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଥିବା ଶବ୍ଦଗୁଡ଼ିକରୁ ଉପଯୁକ୍ତ ଶବ୍ଦ ବାଛି ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନ ପୂରଣ କର ।
(ନିବିଡ଼, ଲାଞ୍ଛିତ, ନିୟତି, ଟୀକା, ପୀଡ଼ିତ)
(କ) ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ନିଜର ଭବିଷ୍ୟତକୁ ___________________ ଉପରେ ଛାଡ଼ି ଦିଅନ୍ତି ।
(ଖ) ଗାନ୍ଧାରୀଙ୍କ ଆଶୀର୍ବାଦ ଲାଭ କରି ଦୁର୍ଯ୍ୟୋଧନ ମହାଭାରତ ଯୁଦ୍ଧରେ ବିଜୟର ________________ ହାସଲ କରିବେ ବୋଲି ଆଶାପୋଷଣ କରିଥିଲେ ।
(ଗ) ___________________ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିଙ୍କ ଉନ୍ନତି ନିମନ୍ତେ ଗାନ୍ଧିଜୀ ସର୍ବଦା ଚେଷ୍ଟିତ ଥିଲେ ।
(ଘ) ପଦ୍ମ ଓ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ________________________ ସମ୍ପର୍କ ଅଛି ।
(ଙ) ଉତ୍କଳମଣି ଗୋପବନ୍ଧୁ _________________ ଜନତାଙ୍କ ସେବା ପାଇଁ ନିଜକୁ ଉତ୍ସର୍ଗ କରିଥିଲେ ।
Answer:
(କ) ନିୟତି (ଖ) ଟୀକା (ଗ) ଲାଞ୍ଛିତ (ଘ) ନିବିଡ଼ (ଡ) ପୀଡ଼ିତ
Question ୩।
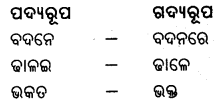
ନିମ୍ନଲିଖ ଶବ୍ଦଗୁଡ଼ିକର ଗଦ୍ୟରୂପ ଲେଖ ।
ଜନମି, ନୁହଇ, ଅରପି, କରମ, ପରାଣରେ
Answer:
ପଗଦ୍ୟରୂ – ଗଦ୍ୟରୂପ
ଜନମି – ଜନ୍ମି/ଜନ୍ମହୋଇ
ନୁହଇ – ନୁହେଁ
ଅରପି – ଅର୍ପି / ଅର୍ପଣ କରି
କରମ – କର୍ମ
ପରାଣରେ – ପ୍ର।ଣରେ
![]()
Question ୪।
ନିମ୍ନଲିଖତ ଶବ୍ଦଗୁଡ଼ିକ ମଧ୍ୟରୁ ଯେଉଁଗୁଡ଼ିକ ମାନବିକ ସୁଗୁଣର ମହତ୍ତ୍ବ ଦର୍ଶାଉଛି, ସେଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ଚିହ୍ନଟ କର ।
କ୍ରୋଧ, କ୍ଷମା, ଲୋଭ, ସହନଶୀଳତା, ହତାଶ, ସେବା, ନମ୍ରତା, ପରଶ୍ରୀକାତରତା, ଭକ୍ତି, ହିଂସା ।
Answer:
କ୍ଷମା, ସହନଶୀଳତା, ସେବା, ନମ୍ରତା, ଭକ୍ତି ।
Question ୫।
କବିତା ଅନୁସରଣରେ ନିମ୍ନରେ ଦିଆଯାଇଥିବା ଉକ୍ତିଗୁଡ଼ିକ ମଧ୍ୟରୁ ଠିକ୍ ଉକ୍ତି ବାଛି ଲେଖ ।
(କ) ଦୁଃଖ ଆମର ଭାଗ୍ୟଲିପି ।
(ଖ) ଚାଲ, ଜୀବନକୁ ମଉଜ ମଜଲିସ୍ରେ ବିତେଇ ଦେବା ।
(ଗ) ମଣିଷ ତା’ ଭିତରେ ଲୁଚି ରହିଥିବା ଶତ୍ରୁକୁ ଦମନ କଲେ ଦେବତାର ଆସନ ଲାଭ କରିପାରିବ ।
(ଘ) ଏ ପୃଥିବୀ ନିରନ୍ତର ଧ୍ୱଂସ ପଥରେ ଆଗେଇ ଚାଲିଛି ।
(ଙ) ବିଧାତାର ବରପୁତ୍ରମାନେ ଦୀନହୀନ ଭାବରେ ଜୀବନ ଯାପନ କରନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
(ଗ) ମଣିଷ ତା’ ଭିତରେ ଲୁଚି ରହିଥିବା ଶତ୍ରୁକୁ ଦମନ କଲେ ଦେବତାର ଆସନ ଲାଭ କରିପାରିବ ।
Question ୬।
ବିପରୀତାର୍ଥବୋଧକ ଶବ୍ଦ ଲେଖ ।
ଅନ୍ଧାର, ଶୃଙ୍ଖଳିତ, ଅମୃତ, ମୃତ୍ୟୁ, ବିଚାର, ସୁନ୍ଦର, ଶୁଭ ।
Answer:
ପ୍ରଶ୍ନ।ପ୍ରଦତ୍ତ ଶବ୍ଦ – ବିପରୀତାର୍ଥବୋଧକ ଶବ୍ଦ
ଅନ୍ଧାର – ଆଲୋକ / ଆଲୁଅ
ଶୃଙ୍ଖଳିତ – ମୁକ୍ତ / ବିଶୃଙ୍ଖଳିତ
ଅମୃତ – ବିଷ
ମୃତ୍ୟୁ – ଜନ୍ମ
ବିଚାର – ଅବିଚାର
ସୁନ୍ଦର – ଅସୁଦର / କଦାକାର
ଶୁଭ – ଅଶୁଭ
![]()
Question ୭ ।
‘କ’ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭର ଶବ୍ଦ ସହିତ ‘ଖ’ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭର ଉପଯୁକ୍ତ ଶବ୍ଦ ଯୋଗକରି ବାକ୍ୟ ଗଢ଼ ।

Answer:

ବାକ୍ୟ:
ନିବିଡ଼ ଅନ୍ଧାର ରାତି ମନରେ ଭୟ ସଞ୍ଚାର କରେ ।
ଏ ବିଶାଳ ଜଗତୀରେ ବହୁ ବିସ୍ମୟକର ଦୃଶ୍ୟ ପ୍ରତୀୟମାନ ହୁଏ ।
ଏ ସଂସାର ମାନବ ପାଇଁ ବିଳାସର ଲୀଳା ନିକେତନ ନୁହେଁ ।
ବିଧାତା-ବିଚାରରେ ପକ୍ଷପାତିତା ନ ଥାଏ ।
ମାନବର ଜୀବନ-ସୂତ୍ର ସର୍ବଦା ପରମେଶ୍ଵରଙ୍କ ହାତରେ ସୁରକ୍ଷିତ ରହିଛି ।
Question ୮।
ଅକ୍ଷରଗୁଡ଼ିକ ସଜାଇ ସାର୍ଥକ ଶବ୍ଦରେ ପରିଣତ କର ।
ଶୂଳିଙ୍ଖତ , ତନିକେନ, ବାଶ୍ଵସୀବି, ପନମାଅ, ରଚରାଚ ।
Answer:
ଶୂଳିଙ୍ଖତ – ଶୂଙ୍ଖଳିତ
ତନିକେନ – ନିକେତନ
ବାଶ୍ଵସୀବ – ବାଶ୍ଵବସୀ
ପନମାଅ – ଅପନମା
ରଚରାଚ – ଚରାଚର
Question ୯।
ଅଭିଧାନ ନିୟମ ଅନୁସାରେ ସଜେଇ ଲେଖ ।
ଜୀବନ, ଦେବତା, ଅରିନ୍ଦମ, ଅହମିକା, ନିକେତନ, ସନ୍ତାନ, ଜନମ ।
Answer:
ଅରିନ୍ଦମ, ଅହମିକା, ଜନମ, ଜୀବନ, ଦେବତା, ନିକେତନ, ସନ୍ତାନ ।
Question ୧୦ ।
ନିମ୍ନଲିଖତ ଶବ୍ଦଗୁଡ଼ିକର ଦୁଇଟି ଲେଖାଏଁ ପ୍ରତିଶବ୍ଦ ଲେଖ ।
ମନୁଷ୍ୟ, ବିଧାତା, ଦେବତା, ଶୋଣତ, ନିକେତନ
Answer:
ମନୁଷ୍ୟ – ମାନବ,ନର
ବିଧାତା – ଦୈବ,ବିଧ୍
ଦେବତା – ସୁର,ତ୍ରିଦଶ,ବିବୁଧ
ଶୋଣତ – ରକ୍ତ, ଲହୁ, ରୁଧ୍ର
ନିକେତନ – ଗୃହ,ଘର
![]()
Question ୧୧ ।
ଅର୍ଥଗତ ପାର୍ଥକ୍ୟ ଦର୍ଶାଇ ନିମ୍ନୋକ୍ତ ସମୋଚ୍ଚାରିତ ଶବ୍ଦଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ସାର୍ଥକ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ପରିଣତ କର ।
ଦୀନ-ଦିନ, କାଳି-କାଳୀ, ବଳି-ବଳୀ
Answer:
ଦୀନ – ଦରିଦ୍ର – ଗୋପବନ୍ଧୁ ବାସ୍ତବରେ ଥିଲେ ଦୀନଜନର ବନ୍ଧୁ ।
ଦିନ – ଦିବସ – ଦିନବେଳା ଶୋଇବା ସ୍ୱାସ୍ଥ୍ୟ ପକ୍ଷେ ଅହିତକର ।
କାଳି – ବାକି ସାଧୁ ସାହୁ କାଳିରେ ଜିନିଷ ଦିଏ ନାହିଁ ।
ସ୍ୟାହି-ଶିକ୍ଷକ ନାଲି କାଳିରେ ଖାତା ଦେଖନ୍ତି ।
କାଳୀ – ଦେବୀ ଆଦ୍ୟାଶକ୍ତି – ଦୀପାବଳି ଦିନ ମା’ କାଳୀଙ୍କର ପୂଜା ହୁଏ ।
ପ୍ରାଣୀ ହତ୍ୟା – ପୂର୍ବେ ଦେବୀ ପୀଠରେ ଛାଗ ବଳି ଦିଆଯାଉ ଥିଲା ।
ବଳି –ଦୈତ୍ୟରାଜ – ବାମନ ବଳିରାଜାଙ୍କୁ ତ୍ରିପାଦ ଭୂମି ଦାନ ମାଗିଥିଲେ ।
ବଳୀ – ବଳବାନ୍ – ଭୀମ ମହାବଳୀ ଥିଲେ ।
କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ର ଭତ୍ତରମୂଳକ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନୋତ୍ତର
Question ୧୨ ।
ମଣିଷ- ମଣିଷ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ବିଭିନ୍ନ ସମ୍ପର୍କ ଥିବା ସତ୍ତ୍ବେ ‘ଭାଇ’ ସମ୍ବୋଧନ କରାଯାଇଛି କାହିଁକି ?
Answer:
‘ବସୁଧୈବ କୁଟୁମ୍ବକମ୍’ ନ୍ୟାୟରେ ସମଗ୍ର ମାନବଜାତି ଗୋଟିଏ ପରିବାର । ସୁତରାଂ ଜଣେ ଅନ୍ୟ ଜଣଙ୍କର ଭାଇ । ତେଣୁ କବିତାରେ ମଣିଷକୁ ‘ଭାଇ’ ବୋଲି ସମ୍ବୋଧନ କରାଯାଇଛି ।
Question ୧୩ ।
କବି ‘ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ’ ବୋଲି କେଉଁମାନଙ୍କୁ ସମ୍ବୋଧନ କରିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ସମାଜରେ ଶୋଷିତ, ଲାଞ୍ଛିତ ଓ ନିଷ୍ପେଷିତ ମଣିଷମାନଙ୍କୁ କବି ‘ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ’‘ବୋଲି ସମ୍ବୋଧନ କରିଛନ୍ତି ।
Question ୧୪ ।
ମଣିଷ କେଉଁଥିପାଇଁ ଜନ୍ମଲାଭ କରିନାହିଁ ବୋଲି କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ମଣିଷ ଝୁରି ମରିବାକୁ କିମ୍ବା ବୁଡ଼ି ମରିବାକୁ ଜନ୍ମଲାଭ କରିନାହିଁ ବୋଲି କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ।
Question ୧୫ ।
ନୈରାଶ୍ୟକୁ ଅନ୍ଧାର ରୂପେ କବି କାହିଁକି ଦେଖୁଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ମଣିଷ ଆଶାଶୂନ୍ୟ ହୋଇଗଲେ, ତାକୁ ଚାରିଆଡ଼ ଅନ୍ଧାର ଦେଖାଯାଏ, ତେଣୁ କବି ନୈରାଶ୍ୟକୁ ଅନ୍ଧାର ରୂପେ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନା କରିଛନ୍ତି ।
Question ୧୬ ।
ମଣିଷର ଭାଗ୍ୟ କାହା ମଧ୍ୟରେ ସୀମାବଦ୍ଧ ନୁହେଁ ବୋଲି କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ମଣିଷର ଭାଗ୍ୟ ଲାଞ୍ଛନା, ପ୍ରବଞ୍ଚନା ତଥା ଦୁଃଖଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣା ମଧ୍ଯରେ ସୀମାବଦ୍ଧ ନୁହେଁ ।
![]()
Question ୧୭ ।
ହତୋତ୍ସାହ ହୋଇପଡ଼ିଥିବା ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ପୃଥିବୀକୁ କେଉଁ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିରେ ଦେଖନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ହତୋତ୍ସାହ ହୋଇପଡ଼ିଥି ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ଏ ପୃଥିବୀକୁ ‘ଧ୍ଵଂସର ଯାତ୍ରୀ ତଥା ମୃତ୍ୟୁର ଧାତ୍ରୀ’ ରୂପେ ଦେଖନ୍ତି ।
Question ୧୮।
‘ଅମୃତର ସନ୍ତାନ’ ବୋଲି କେଉଁମାନଙ୍କୁ କୁହାଯାଇଛି ?
Answer:
‘ଅମୃତର ସନ୍ତାନ’ ବୋଲି ମାନବମାନଙ୍କୁ କୁହାଯାଇଛି ।
Question ୧୯ ।
ବିଶାଳ ଜଗତର ସୃଷ୍ଟି କ’ଣ ପାଇଁ ନୁହେଁ ବୋଲି କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ବିଶାଳ ଜଗତ କାହାରି ବିଳାସର ଲୀଳାକ୍ଷେତ୍ର ନିମନ୍ତେ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ନୁହେଁ ବୋଲି କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ।
Question ୨୦ ।
କେଉଁ ଧରଣର ପିପାସା ମେଣ୍ଟେ ନାହିଁ ?
Answer:
ଦୁର୍ବଳକୁ ପଦଦଳିତ କରି ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦୟଭାବରେ ତା’ପ୍ରତି ଅତ୍ୟାଚାର କରି ତା`ର ରକ୍ତକ୍ଷୟ କରିବାର ପିପାସା କେବେହେଲେ ମେଣ୍ଟେ ନାହିଁ ।
Question ୨୧ ।
ବିଶ୍ୱ କେଉଁମାନଙ୍କ ପାଇଁ ସୁନ୍ଦର ନୁହେଁ ?
Answer:
ନୈରାଶ୍ୟଦଗ୍ଧ ହୋଇ ସଂସାରକୁ ଧ୍ବଂସାଭିମୁଖୀ ତଥା ଜୀବନକୁ ମୃତ୍ୟୁପଥର ଯାତ୍ରୀ ବୋଲି ବିବେଚନା କରୁଥିବା ମାନବ ପାଇଁ ଏ ବିଶ୍ଵ ସୁନ୍ଦର ନୁହେଁ ।
Question ୨୨ ।
ବିଧାତାଙ୍କ ବିଚାରରେ କେଉଁ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଉଚିତ ନୁହେଁ ?
Answer:
ବିଶ୍ୱକୁ ବିଳାସ କ୍ଷେତ୍ର ମନେକରି ଦୁର୍ବଳକୁ ପଦଦଳିତ କରି ନିଜକୁ ନିଜେ ବିନାଶ କରିବା ବିଧାତାଙ୍କ ବିଚାର ନୁହେଁ ।
Question ୨୩ ।
କବି କିଭଳି ସଂସାରର ପରିକଳ୍ପନା କରିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
କବି ସଂସାରକୁ କର୍ମର ଶୁଭ ଭୁବନ ଭାବେ ପରିକଳ୍ପନା କରିଛନ୍ତି ।
Question ୨୪ ।
ମଣିଷ କେତେବେଳେ ବୀରତ୍ବର ଟୀକା ଲାଭ କରିପାରିବ ?
Answer:
ଲଜ୍ଜା, ଭୟ, ଅପମାନ ଓ ଅହଂକାରକୁ ତ୍ୟାଗକରି ପଶୁତ୍ଵ-ଦେବତ୍ୱ ପରୀକ୍ଷାରେ ବିଜୟୀ ହେବାପରେ ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ବୀରତ୍ବର ଟୀକା ଲାଭ କରିପାରିବ ।
![]()
Question ୨୫ ।
କବି ଏହି ପୃଥିବୀକୁ କାହାର ଭୁବନ ବୋଲି ଦର୍ଶାଇଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
କବି ଏହି ପୃଥିବୀକୁ କର୍ମର ଶୁଭଭୁବନ ବୋଲି ଦର୍ଶାଇଛନ୍ତି ।
Question ୨୬ ।
ମଣିଷର କେଉଁ ପ୍ରବୃତ୍ତିଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ତ୍ୟାଗ କରିବାପାଇଁ କବି ଆହ୍ବାନ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
କବି ମଣିଷକୁ ଲଜ୍ଜା, ଭୟ, ଅପମାନ ଓ ଅହମିକା ପ୍ରଭୃତି କୁପ୍ରବୃତ୍ତିଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ତ୍ୟାଗ କରିବାପାଇଁ ଆହ୍ୱାନ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି ।
Question ୨୭ ।
ଭଗବାନଙ୍କୁ କେତେବେଳେ ଋଣୀ କରାଯାଇପାରିବ ?
Answer:
ବିଶ୍ୱଜୀବନର କଲ୍ୟାଣ ନିମନ୍ତେ ଆୟୋତ୍ସର୍ଗ କରିପାରିଲେ ହିଁ ଭଗବାନଙ୍କୁ ଋଣୀ କରାଯାଇପାରିବ ।
Question ୨୮ ।
ମଣିଷ ଭାଇକୁ କବି ‘ଅରିନ୍ଦମ’ ବୋଲି କାହିଁକି ସମ୍ବୋଧନ କରିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ମାନବ ହିଁ କାମ, କ୍ରୋଧ, ଲୋଭ, ମୋହ, ମଦ ଓ ମାସ୍କର୍ଯ୍ୟ ପ୍ରଭୃତି ଷଡ଼ରିପୁଙ୍କୁ ଜୟ କରିପାରେ ବୋଲି କବି ତାକୁ ‘ଅରିନ୍ଦମ’ ବୋଲି କହିଛନ୍ତି ।
Question ୨୯ ।
ମଣିଷ କେତେବେଳେ ଦେବତା ରୂପେ ପୂଜିତ ହୋଇପାରିବ ?
Answer:
ମାନବ ଯେତେବେଳେ କାମ-କ୍ରୋଧାଦି ଷଡ଼ରିପୁକୁ ଜୟକରି ବିଶ୍ୱଜୀବନର କଲ୍ୟାଣ ନିମନ୍ତେ ଆୟୋତ୍ସର୍ଗ କରିବାକୁ ସମର୍ଥ ହେବ, ସେତେବେଳେ ସେ ଦେବତାରୂପେ ପୂଜିତ ହୋଇପାରିବ ।
Question ୩୦ ।
ମଣିଷ ଦୀନ-ହୀନ ଭାବରେ କେତେବେଳେ ଜୀବନ ଯାପନ କରିଥାଏ ?
Answer:
ମାନବ ଯେତେବେଳେ ମାନବିକତାକୁ ଭୁଲି ପଶୁତ୍ୱର ଅଧିକାରୀ ହୋଇଯାଏ, ସେତେବେଳେ ସେ ଯାବତୀୟ ହିଂସାତ୍ମକ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟକରି ଆପଣାକୁ କଳୁଷ କାଳିମାରେ କଳଙ୍କିତ କରିବା ସହ ସଂସାରରେ ଦୀନହୀନ ଭାବରେ କାଳଯାପନ କରେ ।
Question ୩୧ ।
କବି ‘ବରପୁତ୍ର’ ସମ୍ବୋଧନ କାହାକୁ ଏବଂ କାହିଁକି କରିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
କବି ମାନବକୁ ବିଧାତାର ବରପୁତ୍ର ବୋଲି ସମ୍ବୋଧନ କରିଛନ୍ତି, କାରଣ ମାନବ ହିଁ ଦିବ୍ୟ ମାନବୀୟ ଗୁଣାବଳୀରେ ଭୂଷିତ ହୋଇ ଦେବତ୍ୱର ଅଧିକାରୀ ହୋଇପାରେ ।
![]()
Question ୩୨ ।
ଜୀବନ କେତେବେଳେ ସୁରୁଖୁରୁରେ ଅତିବାହିତ ହୋଇପାରିବ ବୋଲି କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ମୃତ୍ୟୁ ରଜ୍ଜୁକୁ ଛିନ୍ନ କରି ଜୀବନ ସୂତ୍ରକୁ ଧରି ସ୍ବକର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟ ପଥରେ ଗତିକଲେ ଜୀବନ ସୁରୁଖୁରୁରେ ଅତିବାହିତ ହୋଇପାରିବ ବୋଲି କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ।
ସପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗ ସରଳାର୍ଥ ଲେଖ
Question ୩୩ ।
ଶୁଣ ହେ ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ !
ଅମୃତ ଦୀପ୍ତି ସନ୍ତାନ ତୁମେ ମରଣ ତୁମର କାହିଁ ?
Answer:
ଶୁଣ ହେ …………………………. ତୁମର କାହିଁ ?
ଶଂସିତ ପଦ୍ୟାଶଟି ଉତ୍କଳ ଭାରତୀ କୁନ୍ତଳା କୁମାରୀ ସାବତଙ୍କ ରଚିତ ‘ସ୍ଫୁଲିଙ୍ଗ’ କବିତା ପୁସ୍ତକରୁ ସଂଗୃହୀତ ‘ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ’ ଶୀର୍ଷକ କବିତାରୁ ଉଦ୍ଧୃତ ।
ଜାଗରଣଧର୍ମୀ ଆହ୍ବାନ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି ।
ବିଦେଶୀ ଶାସକବର୍ଗର ଅର୍ଥନୈତିକ ଶୋଷଣ, ନିପୀଡ଼ନ,ଦେଶବାସୀଙ୍କ ଉତ୍କଟ ଦାରିଦ୍ର୍ୟ, ଜମିଦାର ତଥା ବିଦେଶୀ
ଏଠାରେ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ପରାଧୀନ ଓଡ଼ିଆ ଜାତିର ନୈରାଶ୍ୟଦଗ୍ଧ ପ୍ରାଣରେ ଆଶା ଓ ଆତ୍ମବିଶ୍ଵାସ ଭରିଦେବାପାଇଁ ଜାଗରଣଧର୍ମୀ ଆହ୍ବାନ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି ।
ଶାସକଙ୍କ ପଦଲେହନକାରୀ ବିଶ୍ୱାସଘାତକଙ୍କ କୂଟ ଚକ୍ରାନ୍ତର ଶିକାର ହୋଇ ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଜନଜୀବନ ବ୍ୟତିବ୍ୟସ୍ତ ହୋଇପଡ଼ିଥିଲା । ଦୁଃଖ, ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣା ଓ ଅନୁଶୋଚନାର ତୀବ୍ର ମାନସିକ ଜ୍ଵଳନ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ମଣିଷ ଭାଗ୍ୟକୁ ଧକ୍କାର କରି ଏଥୁରୁ ନିସ୍ତାର ପାଇବାପାଇଁ ମୃତ୍ୟୁକୁ ଶ୍ରେୟସ୍କର ବୋଲି ବିଚାର କରୁଥିଲା । ଦୁର୍ଦ୍ଦଶାଗ୍ରସ୍ତ ଜନତାଙ୍କ ପାଇଁ କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ମନର କୋମଳ କାରୁଣ୍ୟ କବିତାରେ ରୂପାୟିତ ହୋଇଛି । ତେଣୁ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ମଣିଷର ଦୁଃଖରେ ବ୍ୟଥ୍ତ ହୋଇ ତା’ ମନରେ ଆଶାର ଅସରନ୍ତି ବିଶ୍ୱାସ ଭରିଦେବାକୁ ଯାଇ କହିଛନ୍ତି ଯେ ମଣିଷ ଈଶ୍ବରଙ୍କ ସୃଷ୍ଟିରେ ଅମୃତର ସନ୍ତାନ ।
ତେଣୁ ଭାଗ୍ୟକୁ ନିନ୍ଦାକରି ନିଜକୁ ମୃତ୍ୟୁପଥର ଯାତ୍ରୀ ବୋଲି ଚିନ୍ତା କରିବା ଆଦୌ ସମୀଚୀନ ନୁହେଁ । ସୁଖ-ଦୁଃଖ, ହସ-କାନ୍ଦ ମାନବ ଜୀବନର ଚିର ସହଚର । ଦୁଃଖ, ନିର୍ଯାତନା, ଦାରିଦ୍ର୍ୟ ଓ କଷଣରୁ ମୁକ୍ତି ପାଇବାପାଇଁ ମୃତ୍ୟୁକୁ ଶେଷ ପନ୍ଥା ବୋଲି ବିବେଚନା କରି କର୍ମବିମୁଖ ହେବା ଏବଂ ଏ ସଂସାରକୁ ଧ୍ବଂସପଥ ଅଭିମୁଖୀ ବୋଲି ବିବେଚନା କରିବା ଅବିବେକିତାର ପରିଚୟ । ମଙ୍ଗଳମୟ ପରମେଶ୍ୱରଙ୍କ ଦିବ୍ୟସୃଷ୍ଟିରେ ନିଜକୁ ଅମୃତର ସନ୍ତାନ ମନେକରି ସମସ୍ତ କର୍ମକୁ ଈଶ୍ବରୀୟ ବୋଲି ଗ୍ରହଣ କରିବାକୁ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ଉପଦେଶ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି ।
Question ୩୪ ।
ଏ ନୁହେଁ ବିଧାତା ବିଚାର,
ଧ୍ଵଂସର ଯାତ୍ରୀ, ମୃତ୍ୟୁର ଧାତ୍ରୀ ନୁହେଁ ଏ ସୁନ୍ଦର ସଂସାର ।
Answer:
ଏ ନୁହେଁ ………………….. ସୁନ୍ଦର ସଂସାର ।
ପ୍ରଦତ୍ତ” ପଦ୍ୟାଶଟି ପ୍ରଖ୍ୟାତ ନାରୀକବି କୁନ୍ତଳା କୁମାରୀ ସାବତଙ୍କ କବିତା ପୁସ୍ତକ ‘ସ୍କୁଲିଙ୍ଗ’ରୁ ସଂଗୃହୀତ ‘ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ’ ଶୀର୍ଷକ କବିତାରୁ ଆନୀତ ।
ଏଠାରେ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ପରମେଶ୍ଵରଙ୍କ ଅମୃତମୟ ସୃଷ୍ଟିରେ ନିୟତିର ବିଚିତ୍ର ବିଧାନ ଉପରେ ଆଲୋକପାତ କରିଛନ୍ତି । ପ୍ରାକ୍ ସ୍ବାଧୀନତା କାଳରେ ବିଦେଶୀ ଶାସକଙ୍କ ରାଜନୈତିକ ସ୍ୱେଚ୍ଛାଚାରିତା, କ୍ଷମତାଧିକାରୀଙ୍କ ଶୋଷଣ ଓ ଅତ୍ୟାଚାରରେ ଅତିଷ୍ଠ ହୋଇପଡ଼ିଥିଲା ତତ୍କାଳୀନ ଜନଜୀବନ । ବିପର୍ଯ୍ୟସ୍ତ ହୋଇପଡ଼ିଥିଲା ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ସାମାଜିକ ଜୀବନ । ଏତଦ୍ଭିନ୍ନ ବନ୍ୟା ଓ ମରୁଡ଼ିର କରାଳ ଗ୍ରାସରେ ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଜନସାଧାରଣଙ୍କ ଜୀବନ-ଜୀବିକା ବିପର୍ଯ୍ୟସ୍ତ ହୋଇପଡ଼ିଥିଲା ।
ଦୁଃଖ, ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣା ଓ ଦାରିଦ୍ର୍ୟର କଷାଘାତରେ ଅତିଷ୍ଠ ହୋଇପଡ଼ିଥିଲା ଜନଜୀବନ । ଶୋଷଣ, କଷଣ, ଅତ୍ୟାଚାର ଓ ନିର୍ଯାତନା ଅସହ୍ୟ ହୋଇପଡ଼ିଥିଲା । ମଣିଷ ଏସବୁକୁ ଭାଗ୍ୟର ବିଡ଼ମ୍ବନା ବୋଲି ଧରିନେଇ ମୃତ୍ୟୁକୁ ଶ୍ରେୟସ୍କର ମଣିଥିଲା । କବୟିତ୍ରୀ କୁନ୍ତଳା କୁମାରୀ ମଣିଷର ଏତାଦୃଶ ଦୁରବସ୍ଥା ଦର୍ଶନରେ ମ୍ରିୟମାଣ ହୋଇପଡ଼ିଛନ୍ତି । ନିଜକୁ ଅସହାୟ ବୋଧ କରୁଥିବା ଚିର ନିଷ୍ପେଷିତ, ଲାଞ୍ଚ, ବଞ୍ଚତ ମାନବ ଜାତିର ଏ ଦୁର୍ଦ୍ଦିନରେ ସମ୍ବେଦନଶୀଳ ହୋଇ ତା’ର ନୈରାଶ୍ୟଦଗ୍ଧ ପ୍ରାଣରେ ଆଶା, ଆଶ୍ୱାସନା ସଞ୍ଚାର କରିବାକୁ ଯାଇ କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ଯେ ବିଧାତାର ବିଚାର ସର୍ବଦା ନ୍ୟାୟୋଚିତ ଓ ମଙ୍ଗଳକାରକ । ଈଶ୍ୱରଙ୍କ ମହନୀୟ ସୃଷ୍ଟିରେ ମଣିଷ ହେଉଛି ଅମୃତର ସନ୍ତାନ ।
ପରମେଶ୍ବର ମଣିଷକୁ କର୍ମତତ୍ପୁର ରହି କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟ ସମ୍ପାଦନରେ ବ୍ରତୀ ହେବା ନିମନ୍ତେ ଏ ସଂସାରକୁ ପଠାଇଛନ୍ତି । ସୁଖ-ଦୁଃଖ ଓ ହସ-କାନ୍ଦର ଚିର ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନଶୀଳ ଦୁନିଆରେ ଦୁଃଖ, ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣା, ଦାରିଦ୍ର୍ୟ, ଲଜ୍ଜା ଓ ଅପମାନରେ ମଣିଷ ଯେ ଚିରକାଳ ଦଗ୍ଧଭୂତ ହେଉଥିବ– ଏହା ନିୟତିର ବିଧାନ ନୁହେଁ । ଶୋଷଣ, କଷଣ, ଅଭାବ, ଅନଟନ ଯେତେ ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣାଦାୟକ ହେଲେ ମଧ୍ୟ ତା’ର ଗତି ମୃତ୍ୟୁ ନୁହେଁ କି ଏ ସଂସାର କଦାପି ଧ୍ୱଂସାଭିମୁଖୀ ନୁହେଁ । ସମୟର ଚକ୍ର ଚିର ଘୂର୍ଣ୍ଣନଶୀଳ । ଦୁଃଖ ପରେ ସୁଖର ସମୟ ଅବଶ୍ୟ ଉପଗତ ହେବ । ଏଣୁ ମନରୁ ନୈରାଶ୍ୟ ଓ ହୀନମନ୍ୟତା ପରିହାର କରି କର୍ମରେ ନିଜକୁ ନିୟୋଜିତ କରିବାକୁ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ଆହ୍ବାନ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି ।
![]()
Question ୩୫ ।
ଶୁଣ ଶୁଣ ବିଶ୍ବବାସି !
କରମର ଶୁଭ ଭୁବନ ଏହିଟି, କରମରେ ଶ୍ରମ ନାଶି ।
Answer:
ଶୁଣ ଶୁଣ……………………….ଶ୍ରମ ନାଶି ।
ଶଂସିତ ପଦ୍ୟାଶଟି ନାରୀକବି କୁନ୍ତଳା କୁମାରୀ ସାବତଙ୍କ ରଚିତ ‘ସ୍ଫୁଲିଙ୍ଗ’ କବିତା ପୁସ୍ତକରୁ ସଂଗୃହୀତ ‘ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ’ ଶୀର୍ଷକ କବିତାରୁ ଉଦ୍ଧୃତ ।
ଏଠାରେ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ କର୍ମର ଜୟଗାନ କରି କର୍ମକୁ ଜୀବନର ମାନଦଣ୍ଡ ଭାବେ ଗ୍ରହଣ କରିବାକୁ ମନୁଷ୍ୟକୁ ଆହ୍ଵାନ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି । ପରାଧୀନ ଦେଶବାସୀ ବିଦେଶୀ ଶାସକଙ୍କ ଶୋଷଣ, କଷଣ ଓ ଅତ୍ୟଚାରରେ ଅତିଷ୍ଠ ହୋଇ ଭାଗ୍ୟକୁ ଧିକ୍କାର କରିବା ପୂର୍ବକ ମୃତ୍ୟୁକୁ ଶ୍ରେୟସ୍କର ବୋଲି ବିବେଚନା କରୁଥିଲେ । କବୟିତ୍ରୀ କୁନ୍ତଳା କୁମାରୀ ମଣିଷର ନୈରାଶ୍ୟଦଗ୍ଧ ପ୍ରାଣରେ ଆଶା ଓ ଆତ୍ମବିଶ୍ଵାସ ସୃଷ୍ଟି କରିବାପାଇଁ ତାକୁ ଭାଗ୍ୟବାଦୀ ନ ହୋଇ କର୍ମରେ ନିୟୋଜିତ ହେବାକୁ ପରାମର୍ଶ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି ।
ଈଶ୍ବର ମଣିଷକୁ କର୍ମ କରିବାପାଇଁ ଏ ଧରାଧାମରେ ଜନ୍ମ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି । ଫଳ ବାଞ୍ଛା ନ କରି ସର୍ବଦା କର୍ମରତ ରହିଲେ ମନ ମଧ୍ୟକୁ କୁଭାବନା ପ୍ରବେଶ କରିପାରେ ନାହିଁ । ନିରାଶା, ଦୁଃଖ ଓ ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣାରୁ ମୁକ୍ତି ପାଇବାର ଏକମାତ୍ର ପଥ ହେଉଛି କର୍ମତତ୍ପରତା । ଏ ସଂସାର ହେଉଛି ମାନବର କର୍ମଭୂମି । ତେଣୁ ନିଜକୁ ମଣିଷ କର୍ମରେ ଜଡ଼ିତ କରି ପରମେଶ୍ଵରଙ୍କ ଅମୃତମୟ ସୃଷ୍ଟିକୁ ମହନୀୟ କରିବାକୁ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ପରାମର୍ଶ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି । ବାସ୍ତବିକତା ଦୃଷ୍ଟିରୁ କର୍ମଠ ଜୀବନ ମାନସିକ ସନ୍ତୁଳନ ସୁରକ୍ଷା ଓ କାୟିକ ସୁସ୍ଥତା ରକ୍ଷାରେ ସହାୟକ ହୁଏ । ତେଣୁ ଜୀବନର ସବୁ ମାନ-ଅପମାନ, ଲଜ୍ଜା-ଭୟ, ଅଶ୍ରୁ-ଅଭିଳାଷ, ଦୁଃଖ-ଅବସୋସକୁ ବିଭୁ ପଦାରବିନ୍ଦରେ ସମର୍ପଣପୂର୍ବକ କର୍ମରେ ବିନିଯୁକ୍ତ ହେବାକୁ ମଣିଷ ଭାଇକୁ ନାରୀକବି ଆହ୍ୱାନ କରିଛନ୍ତି ।
Question ୩୬ ।
ବିଧାତାର ବରପୁତ୍ର
ଯୁଗାନ୍ତ-ମୃତ୍ୟୁ ରଜ୍ଜୁ ଛିଣ୍ଡାଇ ଧର ହେ ଜୀବନ ସୂତ୍ର ।
Answer:
ବିଧାତାର …………………..ଜୀବନ ସୂତ୍ର ।
ପ୍ରୋକ୍ତ ପଦ୍ୟାଶଟି ଉତ୍କଳ ଭାରତୀ କୁନ୍ତଳା କୁମାରୀ ସାବତଙ୍କ ରଚିତ ‘ସ୍ଫୁଲିଙ୍ଗ’ କବିତା ପୁସ୍ତକ ଅନ୍ତର୍ଗତ ‘ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ’ ଶୀର୍ଷକ କବିତାରୁ ଉଦ୍ଧୃତ ।
ଏଠାରେ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ଦୁଃଖ, ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣା, ଦାରିଦ୍ର୍ୟ ଓ ଅପମାନରେ ବ୍ୟଥୂତ ମୃତ୍ୟୁକାମୀ ମଣିଷ ଭାଇକୁ ତା’ର ମହାର୍ଘ ଜୀବନର ମହତ୍ତ୍ବ ରକ୍ଷାରେ ପ୍ରୟାସୀ ହେବାକୁ ଆହ୍ଵାନ କରିଛନ୍ତି । ଅନନ୍ତ ମରଣ ଯେ ମଣିଷର କପାଳ ଲିଖନ ନୁହେଁ, ଜୀବନର ଶେଷ ଗତି ନୁହେଁ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ଏହି ଭାବନା ମଣିଷ ମନରେ ଭରିଦେବାକୁ ତାଙ୍କ କବିତା ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ ଆହ୍ଵାନ କରିଛନ୍ତି । ମନର ସମସ୍ତ ନୈରାଶ୍ୟ ଓ ହତାଶବୋଧ ଦୂର କରିବାପାଇଁ କର୍ମରେ ନିମଜ୍ଜିତ ରହିବା ହିଁ ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ ବିକଳ୍ପ । କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ମତରେ ମାନବ ହେଉଛି ବିଧାତାଙ୍କ ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ ବରପୁତ୍ର ।
ଜୀବନ ଯୁଦ୍ଧରେ କ୍ଷତାକ୍ତ ହୋଇଗଲେ ମୃତ୍ୟୁକୁ ଶେଷ ଗତି ବୋଲି ଭାବି ନୀରବରେ ଅଶୁ ବିସର୍ଜନ କରିବା ବୀରତ୍ୱର ପରିଚାୟକ ନୁହେଁ । ସାମାନ୍ୟ ରକ୍ତପାତରେ ଜୀବନ କ୍ଷୀଣ ବା ଦୁର୍ବଳ ହୋଇଯାଏ ନାହିଁ କିମ୍ବା ଲଜ୍ଜା ଓ ଅପମାନର କଳଙ୍କ କାଳିମାରେ ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ଦୀନହୀନ ହୋଇଯାଏ ନାହିଁ । ବରଂ ସମସ୍ତ ବିଷାଦ-ବ୍ୟର୍ଥତା, ଦୁଃଖ-କାତରତା ଓ ହୀନମନ୍ୟତାର ବଳୟ ମଧ୍ୟରୁ ମୁକ୍ତି ପାଇବାର ପ୍ରକୃଷ୍ଟ ପନ୍ଥା ହେଉଛି କର୍ମତତ୍ପରତା । ସଂସାର ରୂପକ ଏହି ବିଶାଳ କର୍ମଭୂମିରେ ବିଭୁ ପ୍ରେରିତ କର୍ମୀ ବୋଲି ନିଜକୁ ମନେକରି କର୍ମରେ ନିୟୋଜିତ ରହିଲେ ମଣିଷ ଜୀବନ-ସୂତ୍ର ଧାରଣରେ ସମର୍ଥ ହୋଇପାରିବ । ମୃତ୍ୟୁକାମୀ ମାନବ ମନରେ ଆତ୍ମବିଶ୍ଵାସ ଭରିଦେବାରେ କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ଆଶାବାଦୀ ଆହ୍ବାନ ଓ ମାନବ ଦରଦୀ ଭାବୋଚ୍ଛାସ ପ୍ରଣିଧାନଯୋଗ୍ୟ ।
ଦୀର୍ଘ ଉତ୍ତରମୂଳକ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନୋତ୍ତର
Question ୩୭ ।
ହତୋତ୍ସାହିତ ହୋଇପଡ଼ିଥିବା ମଣିଷଙ୍କୁ କବି କି ପ୍ରକାର ପ୍ରେରଣା ଯୋଗାଇଛନ୍ତି, ପଠିତ କବିତା ଅନୁସରଣରେ ଆଲୋଚନା କର ।
କିମ୍ବା, ନୈରାଶ୍ୟବାଦୀ ମନରେ ଆଶାର ସଞ୍ଚାର କରିବା ଥିଲା ଉତ୍କଳ-ଭାରତୀ କୁନ୍ତଳା କୁମାରୀଙ୍କର ରଚନାର ବୈଶିଷ୍ଟ୍ୟ – ଏହା କେତେଦୂର ଯଥାର୍ଥ ଆଲୋଚନା କର ।
କିମ୍ବା, ଦୁଃଖ, ଦୈନ୍ୟ ଓ ଦୁର୍ଦ୍ଦଶା ପ୍ରପୀଡ଼ିତ ମାନବ ସମାଜ ପାଇଁ କବି କୁନ୍ତଳା କୁମାରୀଙ୍କର ଅକୁଣ୍ଠ ଦରଦ ସମ୍ପର୍କରେ ପଠିତ କବିତାରୁ ଏକ ସମୀକ୍ଷାମୂଳକ ତଥ୍ୟ ପ୍ରଦାନ କର।
Answer:
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ସାହିତ୍ୟର ବାଣୀ-ବିତାନରେ ଉତ୍କଳ-ଭାରତୀ କୁନ୍ତଳା କୁମାରୀଙ୍କ ସାହିତ୍ୟ ସାଧନା ଓ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ଓଡ଼ିଆ ସାହିତ୍ୟର ଇତିହାସ ପୃଷ୍ଠାରେ ଏକ ଉଲ୍ଲେଖନୀୟ ସ୍ଥାନ ଅଧିକାର କରିଛି । ଜୀବନର ସ୍ବଳ୍ପକାଳ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ପ୍ରତିଭାର ସୁବିନିଯୋଗ କରି ଓଡ଼ିଆ ସାହିତ୍ୟ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ନିଜର ଅମଳିନ ପରିଚୟ ରଖୁ ଯାଇଛନ୍ତି ନାରୀକବି । କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ କାବ୍ୟ ପରିକ୍ରମାରେ ପରିଣତ ପର୍ଯ୍ୟାୟରେ ତାଙ୍କୁ ବାସ୍ତବବାଦୀ ହୋଇପଡ଼ିଥିବା ଦେଖିବାକୁ ମିଳେ । ଭାଷା ଓ ଭାବର ପ୍ରାଞ୍ଜଳତାରେ, ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତ କଥା- ବସ୍ତୁର ବାସ୍ତବବାଦୀ କାରୁଣ୍ୟରେ ତଥା ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନାଭଙ୍ଗୀର ନିରାଭରଣ ସାବଲୀଳତାରେ କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ କବିତାମାନ ଅଧିକ ପ୍ରାଣବନ୍ତ ହୋଇଛି ।
ଅବିନଶ୍ବର ପ୍ରତିଭାଦୀପ୍ତ ଏହି ପ୍ରଜ୍ଞାପରିମିତାଙ୍କ ସୃଷ୍ଟିନିଚୟ ବାସ୍ତବବାଦ ସହ ଆଶାବାଦର ମଧୁର ସମନ୍ବୟରେ ଯେଭଳି ଅନୁରଣିତ ହୋଇଛି ତା’ର ପଟାନ୍ତର ନାହିଁ । କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ଲେଖନୀ ନିଃସୃତ ‘ଅଞ୍ଜଳି’, ‘ଉଲ୍ଲାସ’, ‘ଅର୍ଜନା’, ‘ସ୍ଫୁଲିଙ୍ଗ’ ଓ ‘ଆହ୍ବାନ’ ଆଦି କବିତା ପୁସ୍ତକ; ‘ଭ୍ରାନ୍ତି’, ‘ନ’ତୁଣ୍ଡୀ, ‘ପରଶମଣି, ‘ରଘୁ ଅରକ୍ଷିତ’, ‘କାଳୀବୋହୂ’ଆଦି ଉପନ୍ୟାସ ତାଙ୍କ ଅମଳିନ ବହୁମୁଖୀ ପ୍ରତିଭାର ବଳିଷ୍ଠ ନିଦର୍ଶନ । ଡାକ୍ତରୀ ବିଦ୍ୟା ତାଙ୍କର ବୃତ୍ତି ଥିଲେ ମଧ୍ୟ ସାହିତ୍ୟ ସାଧନକୁ ନିଜର ବ୍ରତ ଭାବେ ଗ୍ରହଣ କରି ନେଇଥିଲେ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ । ବିଶ୍ବଜନୀନତା, ସେବାପରାୟଣତା, ଭଗବତ୍ ବିଶ୍ଵାସ ଓ କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟପରାୟଣତାକୁ ଆଧାର କରି କାବ୍ୟକବିତା ରଚନା କରିବାରେ କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ଲେଖନୀ ଶତମୁଖ ହୋଇଥିଲା ।
‘ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ ଶୀର୍ଷକ କବିତା କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ‘ସ୍ଫୁଲିଙ୍ଗ’କବିତା ପୁସ୍ତକରୁ ସଂଗୃହୀତ । ଏହି ପୁସ୍ତକର ରଚନାକାଳ ପ୍ରାକ୍- ସ୍ଵାଧୀନତାକାଳୀନ, ଯେତେବେଳେ ବିଦେଶୀ ଶାସକର ସ୍ବେଚ୍ଛାଚାରିତା, ଶୋଷଣ ଓ ଅତ୍ୟାଚାର, ଜମିଦାର ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି- ବିଶେଷଙ୍କ ଜୁଲମ ଓ ନାଲିଆଖୁ ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ସାଧାରଣ ଜନଜୀବନକୁ ଦୁର୍ବିସହ କରିଦେଇଥିଲା । ନିଷ୍ପେଷିତ, ଲାଞ୍ଛିତ ମଣିଷ ନିନ୍ଦା, ଅପମାନ, ଲଜ୍ଜା ଓ ଭୟରେ କାକୁସ୍ଥ ହୋଇ ଦୁଃଖ ଓ ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣାରେ ଅତିଷ୍ଠ ହୋଇଉଠିଥିଲା ।
ଏତଦ୍ଭିନ୍ନ ବନ୍ୟା ଓ ମରୁଡ଼ି ପରି ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ବିପର୍ଯ୍ୟୟ ରାଜ୍ୟବାସୀଙ୍କୁ ଦାରିଦ୍ର୍ୟ ମଧ୍ୟକୁ ଠେଲିଦେଇ ଏକ ହାହାକାରମୟ ପରିସ୍ଥିତି ସୃଷ୍ଟି କରିଥିଲା । ରାଜ- ପ୍ରପୀଡ଼ନର ଦୁଃଖ, ଦୁର୍ଦ୍ଦଶା ସହ ଦାରିଦ୍ର୍ୟର କଷାଘାତରେ ଜର୍ଜରିତ ମଣିଷର ଦୁର୍ବିପାକ ସନ୍ଦର୍ଶନରେ କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ମାନବ- ଦରଦୀ ମନ ଚହଲି ଯାଇଛି । ସାମାଜିକ ଜୀବନର ବିପର୍ଯ୍ୟସ୍ତ ପରିସ୍ଥିତି ଓ ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ ହୃଦୟରେ ବସା ବାନ୍ଧିଥିବା ନୈରାଶ୍ୟ ଅବଲୋକନରେ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ମ୍ରିୟମାଣ ହୋଇପଡ଼ିଛନ୍ତି । ଉତ୍କଟ ବାସ୍ତବବାଦୀ କବିତାଟିରେ କୁନ୍ତଳା କୁମାରୀଙ୍କ ଓଡ଼ିଆ ଜାତିପ୍ରୀତି, ଦୁର୍ଦ୍ଦଶାଗ୍ରସ୍ତ ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ ପ୍ରତି ସମ୍ବେଦନଶୀଳତା ତଥା ଆଶାବାଦର ସୁମଧୁର ସମନ୍ୱୟ କବିତାକୁ ଅଧିକ ପ୍ରାଣବନ୍ତ ଓ ମନୋଜ୍ଞ କରିଛି ।
![]()
ରାଜନୈତିକ ତଥା ସାମାଜିକ ଜୀବନର ସମସ୍ତ ପ୍ରତିକୂଳତାର ସମ୍ମୁଖୀନ ହୋଇ ମଣିଷ ଭାଗ୍ୟବାଦୀ ହେବାକୁ ବାଧ୍ୟ ହୋଇଛି । ଦୁଃଖ, ଲାଞ୍ଛନା, ଅପମାନ ଓ ଅପବାଦକୁ ଭାଗ୍ୟଲିପି ବୋଲି ଧରିନେଇ ସଂସାରକୁ ଧ୍ବଂସପଥର ଯାତ୍ରୀ ଓ ମୃତ୍ୟୁ ପଥର ଧାତ୍ରୀ ବୋଲି ଚିନ୍ତା କରିଛି । ମୃତ୍ୟୁରେ ହିଁ ଦୁଃଖପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ ଜୀବନର ପରିସମାପ୍ତି ବୋଲି ତା’ର ମନରେ ଦୃଢ଼ ଧାରଣା ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହୋଇଛି । ସେମାନଙ୍କ ନୈରାଶ୍ୟଦଗ୍ଧ ପ୍ରାଣରେ ଆଶା ଓ ଆତ୍ମବିଶ୍ଵାସ ଭରିଦେବା ପାଇଁ କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ଲେଖନୀରୁ ଝରିପଡ଼ିଛି କବିତା ‘ ମଣିଷ ଭାଇଁ । ସେମାନଙ୍କ ଦୁଃଖରେ ସମଦୁଃଖୀ ହୋଇ କବି ଗାଇ ଉଠିଛନ୍ତି –
‘‘ ଶୁଣ ହେ ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ ! ଝୁରି ମରିବାକୁ ବୁଡ଼ି ମରିବାକୁ
ମଣିଷ ଜନମି ନାହିଁ ।”
ହତୋତ୍ସାହିତ ମଣିଷ ଭାଇକୁ ବଞ୍ଚିବାର ରାହା ଦେଖାଇବାକୁ ଯାଇ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ କେତୋଟି ମୂଲ୍ୟବାନ୍ ପରାମର୍ଶ ଦେବା ସଙ୍ଗେ ସଙ୍ଗେ ଆଶାବାଦୀ ଅନୁପ୍ରେରଣାରେ ସେମାନଙ୍କ ମନରେ ଆତ୍ମବିଶ୍ଵାସ ଜାଗ୍ରତ କରିବାକୁ ପ୍ରୟାସ କରିଛନ୍ତି । ପ୍ରଥମେ ଦୁଃଖ ଦୁର୍ଦ୍ଦଶାକୁ ବିଧ ଅଭିପ୍ରେତ ବୋଲି ବିବେଚନା କରି ଭାଗ୍ୟକୁ ଧ୍କାର ନ କରିବାକୁ କି ଶତ ହତଶ୍ବାସରେ ଜୀବନକୁ ଅଧିକ ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣା ଜର୍ଜରିତ ନ କରିବାକୁ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ସମ୍ବେଦନଭରା ଆଶ୍ବାସନା ବାଣୀ ଶୁଣାଇଛନ୍ତି ।
କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ମତରେ ମାନବ ନିୟତିର ଅଧୀନ ହେଲେ ମଧ୍ୟ ଜଣେ ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣାଦଗ୍ଧ ଅନ୍ଧକାର କାରାଗୃହରେ ଚିର ଶୃଙ୍ଖଳିତ, ଲାଞ୍ଛିତ ଓ ବଞ୍ଚିତ ଜୀବନ ଅତିବାହିତ କରୁଥୁବ; ଏହା ବିଧ୍ୱନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ ନୁହେଁ । ମାନବ ଜାତି କଦାପି ଧ୍ୱଂସପଥର ଯାତ୍ରୀ ନୁହେଁ କି ଏ ସଂସାର ମୃତ୍ୟୁର ମରଣଯନ୍ତା ନୁହେଁ । ଈଶ୍ଵର ସୃଷ୍ଟ ଏ ନିଷ୍ଫଳ ବିଶ୍ବ ହେଉଛି ମାନବର କର୍ମଭୂମି । ଅମୃତର ସନ୍ତାନ ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ପରମେଶ୍ଵରଙ୍କ ମହନୀୟ ସୃଷ୍ଟି । ହସ- କାନ୍ଦ, ସୁଖ-ଦୁଃଖ, ଭଲ-ମନ୍ଦର ସଦା ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତିତ ସମୟକୁ ନେଇ ଏ ସଂସାରରେ ସବୁକିଛି ଆତଯାତ ହେଉଛି । ତେଣୁ ସୁଖ- ସ୍ଵପ୍ନଭରା ଅତୀତକୁ ଝୁରି ତଥା ସାମ୍ପ୍ରତିକ ଦୁଃଖ – ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣାର କାରୁଣ୍ୟରେ ହୃଦୟକୁ ଭାରାକ୍ରାନ୍ତ କରି ପଳାୟନପନ୍ଥୀ ପରି ନୈରାଶ୍ୟଦଗ୍ଧ ଜୀବନ ଅତିବାହିତ କରିବା ବିବେକୀର ଲକ୍ଷଣ ନୁହେଁ ।
ନାରୀକବିଙ୍କ ମତରେ ଏ ସଂସାର ହେଉଛି ମାନବ ପାଇଁ କର୍ମଭୂମି । ସଦା କର୍ମତତ୍ପର ରହି କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟ ସମ୍ପାଦନ କରିଯିବାକୁ ପରମେଶ୍ୱର ଏହି ସୁନ୍ଦର ସଂସାରକୁ ଆମକୁ ପଠାଇଛନ୍ତି । ଫଳ ବାଞ୍ଛା ନ କରି କର୍ମ ସମ୍ପାଦନ କରି ଚାଲିଲେ ଲାଞ୍ଛନା, ଅପମାନ, ଅପବାଦକୁ ବିସ୍ତୃତ ହେବା ସଙ୍ଗେ ସଙ୍ଗେ ମନରୁ କୁଭାବନା ଦୂରେଇ ରହିବ । ମନରେ ଅହମିକା ପୋଷଣ କରି କ୍ରୋଧଯୁକ୍ତ ହେଲେ କିମ୍ବା ପ୍ରତିଶୋଧପରାୟଣ ମନୋବୃତ୍ତି ପୋଷଣ କଲେ ତା’ର ବିଷକ୍ରିୟାରେ ମନକୁ ପାଶବିକତା ଗ୍ରାସ କରିବ । ଜୀବନର ସବୁ ମାନ – ଅପମାନ, ଦୁଃଖ-ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣାକୁ ବିଭୁ ପଦାରବିନ୍ଦରେ ସମର୍ପଣ ପୂର୍ବକ ନିଜକୁ କର୍ମତତ୍ପର ରଖୁରିଲେ ହିଁ ଈଶ୍ୱରଙ୍କ ଆଶୀର୍ବାଦ ପ୍ରାପ୍ତ ହେବ ।
ପଶୁତ୍ଵ-ଦେବତ୍ୱର ପରୀକ୍ଷାରେ ଉତ୍ତୀର୍ଣ୍ଣ ହେବାପାଇଁ ଅନ୍ତଃରିପୁ ଦମନ ପ୍ରତି ଯତ୍ନଶୀଳ ହେବାକୁ ମଧ୍ୟ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ପରାମର୍ଶ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି । ତାଙ୍କ ମତରେ କାମ, କ୍ରୋଧ, ଲୋଭ, ମୋହ, ମଦ, ମାସର୍ଯ୍ୟାଦି ଷଡ଼ରିପୁ ତଥା ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟ ସୁଖ ଲାଳସା ମାନବାତ୍ମାକୁ କଳୁଷିତ କରି ପାପାତ୍ମାରେ ପରିଣତ କରିଥାଏ । ତେଣୁ ସେହି ଷଡ଼ରିପୁ ଦମନରେ ପ୍ରୟାସୀ ହେଲେ ମଣିଷ ଦିବ୍ୟଜୀବନ ଲାଭ କରିବାରେ ସମର୍ଥ ହୋଇ ଦେବତ୍ୱର ଅଧିକାରୀ ହୋଇପାରିବ । ପରମେଶ୍ବରଙ୍କୁ ଋଣୀ କରିବାପାଇଁ ମାନବୀୟ ଧର୍ମର ଯଥାଯଥ ପାଳନ ଅନିବାର୍ଯ୍ୟ । ତେଣୁ ଈଶ୍ବରଙ୍କ ଏହି ମହନୀୟ ସୃଷ୍ଟିର ସୌନ୍ଦର୍ଯ୍ୟ ବୃଦ୍ଧିରେ ନିଜକୁ ଉତ୍ସର୍ଗ କରି ଜୀବନକୁ ସତ୍ଵକର୍ମରେ ବିନିଯୁକ୍ତ କରିବାକୁ ନାରୀକବି ଆହ୍ୱାନ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି । ତାଙ୍କ ଭାଷାରେ –
‘‘ଋଣୀ କର ଭବରାଣେ
ତା’ଙ୍କ ରଚା ଚରାଚର ପରାଣରେ ବଳି ଦିଅ ନିଜ ପ୍ରାଣେ ।’’
ମଙ୍ଗଳମୟ ପରମେଶ୍ବର ତାଙ୍କ ଅମୃତମୟ ସୃଷ୍ଟିର ଅଭିନବ ବିକାଶ ଦର୍ଶନରେ ଚିର ଆଗ୍ରହୀ । ସେ ହିଁ ମଣିଷର ସବୁ ବିଷାଦ -ବ୍ୟର୍ଥତା, ଦୁଃଖ – କାତରତା ତଥା ଯାବତୀୟ ହୀନମନ୍ୟତା ରୂପକ କଳଙ୍କ କାଳିମାକୁ ତାଙ୍କ ଦିବ୍ୟସ୍ପର୍ଶରେ ଧୋଇଦେଇ ତାକୁ ଅମୃତ ପିପାସୀ କରାଇବେ । ତେଣୁ ମୃତ୍ୟୁକାମୀ ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ ମନରୁ ସମସ୍ତ ନୈରାଶ୍ୟ ଓ ଅସହାୟବୋଧ ଭାବନାକୁ ପରିହାର କରି ଜୀବନ ସୂତ୍ର ଧାରଣ କରିବାକୁ ନାରୀକବି ଆହ୍ୱାନ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି । ନାରୀକବିଙ୍କ ମାନବପ୍ରେମୀ ଆଭିମୁଖ୍ୟ ଆଶାବାଦିତାର ଉଜ୍ଜ୍ବଳ ମୟୂଖରେ ଯେ ଚିର ଦୀପ୍ତିମାନ, ଆଲୋଚ୍ୟ କବିତାରୁ ତାହା ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ପରିଦୃଷ୍ଟ ହୁଏ ।
Question ୩୮ ।
କବି ଜଣେ ମାନବବାଦୀ – ଏ ଭକ୍ତିର ଯଥାର୍ଥତା ‘ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ’ କବିତା ଅବଲମ୍ବନରେ ପ୍ରତିପାଦନ କର ।
କିମ୍ବା, ନାରୀକବି କୁନ୍ତଳାକୁମାରୀଙ୍କ ଲେଖନୀ ମୁନରେ ମାନବବାଦର ଯେଉଁ ଜ୍ଵଳନ୍ତ ସ୍ଫୁରଣ ଘଟିଛି, ତାହା ଆଲୋଚନା କର ।
କିମ୍ବା, କୁନ୍ତଳାକୁମାରୀଙ୍କର ‘ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ’ କବିତା ଆମୂଳଚୂଳ ମାନବବାଦର ଆଦର୍ଶରେ ଭରପୂର– ଏହାର ଯଥାର୍ଥତା ପ୍ରତିପାଦନ କର ।
Answer:
ଆଧୁନିକ ଓଡ଼ିଆ ସାହିତ୍ୟର ପ୍ରବହମାନ କାଳ ବକ୍ଷରେ ସବୁଜ ଯୁଗ ଓ ପ୍ରଗତିବାଦର ସନ୍ଧିକ୍ଷଣରେ ବାସ୍ତବବାଦ, ଆତ୍ମଭୌତିକ ଚେତନା ଓ ରହସ୍ୟବାଦକୁ ଆଧାର କରି ସ୍ଵକୀୟ ଲେଖନୀ ଚାଳନା କରିଥିଲେ ମାନବବାଦୀ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ଉତ୍କଳ ଭାରତୀ କୁନ୍ତଳା କୁମାରୀ ସାବତ । ବିଶେଷତଃ ପ୍ରାକ୍-ସ୍ବାଧୀନତା କାଳରେ ଜଣେ ଏକକ ନାରୀକଣ୍ଠର ସ୍ବର – ସମ୍ଭାର ତତ୍କାଳୀନ ଓଡ଼ିଶାବାସୀଙ୍କୁ କେବଳ ଯେ ଚମତ୍କୃତ କରିଥିଲା ତାହା ନୁହେଁ, ବରଂ ପ୍ରତିଷ୍ଠିତ ସାହିତ୍ୟିକମାନଙ୍କୁ ତାଙ୍କ ସାରସ୍ବତ ସୃଷ୍ଟିନିଚୟ ବିସ୍ମିତ କରିଥିଲା ।
ବୃତ୍ତିରେ ଚିକିତ୍ସକ ଓ ପ୍ରବୃତ୍ତିରେ ସାହିତ୍ୟ ସାଧନା; କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ବହୁମୁଖୀ ପ୍ରତିଭାର ଉଜ୍ଜ୍ଵଳ ନିଦର୍ଶନ । ମାତ୍ର ୩୮ ବର୍ଷର ସ୍ୱଳ୍ପ ଜୀବନକାଳ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ପ୍ରତିଭାର ସୁବିନିଯୋଗ କରି ସେ ଓଡ଼ିଆ ସାହିତ୍ୟ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ନିଜର ଅମଳିନ ପରିଚୟ ରଖିଯାଇଛନ୍ତି । କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ସାରସ୍ବତ ସୃଷ୍ଟିସମ୍ଭାର ମଧ୍ୟରେ ‘ଅଞ୍ଜଳି, ‘ଉଲ୍ଲାସ, ‘ଅର୍ଜନା’, ‘ସ୍କୁଲିଙ୍ଗ ଓ ‘ ଆହ୍ୱାନ ପରି କବିତା ପୁସ୍ତକ; ‘ ଭ୍ରାନ୍ତି’, ‘ନ’ତୁଣ୍ଡୀ, ‘ ପରଶମଣି, ‘ରଘୁ ଅରକ୍ଷିତ ଓ ‘ କାଳୀବୋହୂ’ ଆଦି ଉପନ୍ୟାସ ନାରୀକବିଙ୍କ ସାରସ୍ବତ ପ୍ରତିଭାର ବଳିଷ୍ଠ ନିଦର୍ଶନ । ବିଶ୍ୱଜନୀନତା, ସେବାପରାୟଣତା, କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟପରାୟଣତା, ଭଗବତ୍ ବିଶ୍ୱାସ ଓ ସର୍ବୋପରି ମାନବିକ ମୂଲ୍ୟବୋଧ କବିଙ୍କ କାବ୍ୟକବିତାର ବୈଶିଷ୍ଟ୍ୟ ।
ଆଲୋଚ୍ୟ ‘ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ କବିତାଟି କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ କବିତାଗୁଚ୍ଛ ‘ସ୍ଫୁଲିଙ୍ଗ’ରୁ ସଂଗୃହୀତ । କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ପ୍ରାକ୍- ସ୍ଵାଧୀନତାକାଳୀନ ଏହି କବିତାରେ ତତ୍କାଳୀନ ସମାଜ ଓ ଜନଜୀବନର ନିଚ୍ଛକ ଚିତ୍ର ପ୍ରକାଶ ପାଇଛି । ପରାଧୀନ ଓଡ଼ିଶାରେ ବିକଟ ଦାରିଦ୍ର୍ୟ ଓ ନିପୀଡ଼ିତ ଜୀବନ ନେଇ ଓଡ଼ିଆ ଜାତି ନୈରାଶ୍ୟର ଘନ ଅନ୍ଧକାର ମଧ୍ଯରେ ସଢ଼ୁଥିଲାବେଳେ ସେମାନଙ୍କ ବ୍ୟର୍ଥିତ ପ୍ରାଣରେ ଆଶାର ସଞ୍ଜୀବନୀ ବାରି ବର୍ଷଣ କରିବାକୁ କୁନ୍ତଳା କୁମାରୀଙ୍କ କାଳଜୟୀ ଲେଖନୀ ଆଗେଇ ଆସିଛି। ସମ୍ବେଦନଶୀଳ କବି ହୃଦୟରୁ ମାନବ ପ୍ରୀତି ଝରିପଡ଼ିଛି କବିତା ‘ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ’ରେ ।
ଶୋଷିତ, ଲାଞ୍ଛିତ ଜନଜୀବନର ଦାରିଦ୍ର୍ୟ, କଷଣ, ରୋଗବ୍ୟାଧ୍ ଓ ଅଭାବ ଅନଟନଜନିତ ଅସହାୟବୋଧ, ନାରୀକବିଙ୍କ ଦରଦୀ ପ୍ରାଣରେ ବ୍ୟଥା ଓ ବିଷାଦ ଭରିଦେଇଛି । ତାଙ୍କ ଆୟୋପଲବ୍ଧି ଓ ମାନବୀୟ ମହତ୍ତ୍ଵ ଯେ ଗଭୀର ଆଶାବାଦିତାର ଉଜ୍ଜ୍ବଳ ମୟୂଖରେ ଦୀପ୍ତିମାନ ହୋଇଉଠିଛି ତାହା କବିତାର ପଂକ୍ତିଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ରୂପାୟିତ । ମଣିଷ ଭାଇକୁ ହତାଶାବୋଧର ଘୂର୍ତ୍ତି ମଧ୍ୟରୁ ରକ୍ଷା କରିବାପାଇଁ କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ପ୍ରେରଣାପୂର୍ଣ ଆହ୍ବାନ ତଥା ଉପଯୁକ୍ତ ଦିଗ୍ଦର୍ଶନ ପ୍ରଦାନ, ତାଙ୍କ ଦୃଢ଼ ମାନସିକତା, ମାନବିକ ମୂଲ୍ୟବୋଧ ତଥା ପ୍ରଗାଢ଼ ଆଶାବାଦିତାର ପରିଚୟ ଦେଇଥାଏ ।
କବିତା ‘ ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ’ରେ ନୈରାଶ୍ୟଦଗ୍ଧ ମଣିଷକୁ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ଯେଉଁ ପରାମର୍ଶଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି, ସେଥୁରୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଭାବେ ପ୍ରତୀତ ହୁଏ ଯେ, ସେ ଥିଲେ ଜଣେ ସଫଳ ମନୋବିଜ୍ଞାନୀ । କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ଅନୁଭବ କରିଥିଲେ ଯେ ତତ୍କାଳୀନ ସାମାଜିକ ପରିସ୍ଥିତି ମଣିଷକୁ ମାନସିକ ଭାବେ ଦୁର୍ବଳ କରିଦେଇଛି । ତେଣୁ ତା’ ମନରେ ପ୍ରଥମେ ସାହସ ଓ ଧୈର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଭରିଦେବାକୁ ବାଣୀ ପ୍ରୟୋଗ କରିଛନ୍ତି । କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ଭାଷାରେ –
![]()
‘‘ଶୁଣ ହେ ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ ! ଝୁରି ମରିବାକୁ ବୁଡ଼ି ମରିବାକୁ
ମଣିଷ ଜନମି ନାହିଁ । ”
ଅମୃତ ଦୀପ୍ତି ସନ୍ତାନ ତୁମେ ମରଣ ତୁମର କାହିଁ ?”’
ତତ୍ପରେ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ଅନୁଭବ କରିଛନ୍ତି ଯେ ଅସହାୟ ମଣିଷ ମନରେ କର୍ମମୁଖର ଜୀବନର ଜୟଗୀତି ଶୁଣାଇବାକୁ ହେବ । କର୍ମରେ ନିୟୋଜିତ ରହିଲେ ମଣିଷ ଯେ ଦୁଃଖ, ଅବସାଦ, ଅପମାନ, ଲଜ୍ଜା ଓ ଭୟ ଆଦି ମାନସିକ ଦୌର୍ବଲ୍ୟଜନିତ ବସ୍ତୁତ ହେବ, କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ଏହା ଆତ୍ମପଲବ୍ଧିରୁ ଅବଗତ ଥିଲେ । ତେଣୁ କର୍ମର ଜୟଗାନ କରି ସେ ଗାଇଛଠିଛନ୍ତି –
‘‘ ଶୁଣ ଶୁଣ ବିଶ୍ୱବାସୀ ! କରମର ଶୁଭ ଭୁବନ ଏହିଟି,
କରମରେ ଶ୍ରମ ନାଶି । ’’
କବିୟତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ମତରେ ଏ ସଂସାର ହେଉଛି ମାନବର କର୍ମଭୂମି । ଫଳବାଞ୍ଛାବିହୀନ କର୍ମରେ ନିଯୁକ୍ତ ରହିବାକୁ ପରମେଶ୍ୱର ଆମକୁ ଏ ବିଶାଳ ସଂସାରକୁ ପ୍ରେରଣ କରିଛନ୍ତି । ମଣିଷ କର୍ମତତ୍ପର ରହି ସ୍ଵକର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟ ସମ୍ପାଦନ କରିଚାଲିଲେ ଈଶ୍ବର ସୃଷ୍ଟିର ସାର୍ଥକତାରେ ପରମ ପ୍ରୀତ ହେବେ । ଅନନ୍ତ ମରଣକୁ କପାଳଲିଖନ ବୋଲି ବିବେଚନା ନ କରି କର୍ମକୁ ଜୀବନର ମାନଦଣ୍ଡ ଭାବେ ଗ୍ରହଣ କରିବାକୁ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ପରାମର୍ଶ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି । ସମସ୍ତ ମାନସିକ ସ୍କାନିକୁ ଦୂର କରିବାପାଇଁ ଜଣେ ସଫଳ କର୍ମଯୋଗୀ ଭାବେ ଜୀବନ ଯାପନ କରିବାକୁ କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ଦିବ୍ୟ ପରାମର୍ଶ ହିଁ ବାସ୍ତବିକ ଉଲ୍ଲେଖଯୋଗ୍ୟ । ଦୁଃଖ, ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣାକୁ କର୍ମହୀନ ଜୀବନ ବହୁଗୁଣିତ କରିଥାଏ ।
ଆଳସ୍ୟପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ ଜୀବନ ମାନବକୁ ଅନ୍ତଃରିପୁମାନଙ୍କ ଦୌରାତ୍ମ୍ୟ ମଧ୍ୟକୁ ଠେଲି ଦେଇଥାଏ । କାମ, କ୍ରୋଧ, ଲୋଭ, ମୋହ, ମଦ ଓ ମାସର୍ଯ୍ୟାଦିର ଅଧୀନ ହୋଇଗଲେ ତା’ ମନରେ ପାଶବିକ ପ୍ରବୃତ୍ତିର ଅଭ୍ୟୁଦୟ ଘଟେ, ପରବର୍ତ୍ତୀ ସମୟରେ କ୍ରୋଧ ଓ ପ୍ରତିଶୋଧପରାୟଣ ମନୋବୃତ୍ତି ତା’ ପୁଣ୍ୟ ମାନବାତ୍ମାରେ କଳୁଷ କାଳିମାର କଳଙ୍କ ଲଗାଇ ପାପାତ୍ମାରେ ପରିଣତ କରେ । ସଂସାରକୁ ଧ୍ବଂସପଥର ଯାତ୍ରୀ ବୋଲି ଚିନ୍ତା କରୁଥିବା ଅସହାୟ ମଣିଷକୁ ଅମୃତର ସନ୍ତାନ ଭାବେ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନା କରି ସକଳ କର୍ମ ମଧ୍ଯରେ ‘ଆଧାତ୍ମିକତାର ପୀୟୂଷ ପାନ କରିବାକୁ କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ମହାପରାମର୍ଶ ଲାଜ, ଭୟ, ଅପମାନ ଓ ଲାଞ୍ଛନା ପରି ମାନସିକ ଅସନ୍ତୁଳନତାର ମହାନ୍ ଦାନ କହିଲେ ଅତ୍ୟୁକ୍ତି ହେବ ନାହିଁ । ନାରୀକବିଙ୍କ ଭାଷାରେ –
‘‘ ଉଠ ଦେବ ତେଜେ ତେଜି ଲାଜ ଭୟ ଅପମାନ ଅହମିକା,
ପଶୁତ୍ବ ଦେବତ୍ୱ ପରୀକ୍ଷାରେ ଜୟୀ ଲଭ ବୀରତ୍ଵର ଟୀକା
ଋଣୀ କର ଭବରାଣେ
ତା’ଙ୍କ ରଚା ଚରାଚର ପରାଣରେ ବଳିଦିଅ ନିଜ ପ୍ରାଣେ ।’’
ଭାଗ୍ୟବାଦୀ ମଣିଷକୁ ନିୟତି ବିଚାରର ନିରପେକ୍ଷତା ତଥା ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନଶୀଳ ଦୁନିଆର ବହମାନ ସ୍ରୋତରେ ସୁଖ- ଦୁଃଖ, ହସ-କାନ୍ଦ ଓ ସମ୍ପଦ– ଦାରିଦ୍ର୍ୟର ପଟ୍ଟ ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନ ରୂପ ସ୍ମରଣ କରାଇଛନ୍ତି । ତେଣୁ ନିଜକୁ ହୀନମନ୍ୟ ଚିନ୍ତାଚେତନାରୁ ମୁକ୍ତ କରି ଜୀବନକୁ ଅମୃତଅନ୍ଵେଷୀ କରିବା ଯେ ମାନବୋଚିତ ଧର୍ମ ଏହି ପରାମର୍ଶ ଦେଇ ନିରାଶାନ୍ଧକାରରେ ପଥଚ୍ୟୁତ ମଣିଷକୁ ନାରୀକବି ଆହ୍ୱାନ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି । ମୃତ୍ୟୁ ଯେ ଜୀବନର ଶେଷ ଗତି ନୁହେଁ ଏହି ଦିବ୍ୟ ଭାବନାକୁ ହୃଦୟରେ ଧାରଣ କରି କର୍ମପ୍ରବଣ ଜୀବନ ଯାପନରେ ପ୍ରୟାସୀ ହେଲେ ଜୀବନ ଅଧ୍ବକ ଉପଭୋଗ୍ୟ ହୋଇଉଠିବ ବୋଲି ନାରୀକବିଙ୍କ ମହାନ୍ ଉପଦେଶ ତାଙ୍କ ମାନବବାଦୀ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଭଙ୍ଗୀର ବଳିଷ୍ଠ ପ୍ରମାଣ ପ୍ରଦାନ କରେ ।
Question ୩୯ ।
ଅମୃତର ସନ୍ତାନ ମଣିଷ କିପରି ତା’ର ଜୀବନକୁ ସରସ ସୁନ୍ଦର କରିପାରିବ ବୋଲି କବି ପ୍ରେରଣା ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି ?
କିମ୍ବା, ମଣିଷ, ଅମୃତର ସନ୍ତାନ– ଏହି ଆଶାବାଦମୂଳକ ଆୟୋପଲବ୍ଧିକୁ କବି ମଣିଷ ମନରେ ସଞ୍ଚାର କରିବାକୁ କି ଦିଗ୍ଦର୍ଶନ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି, ପଠିତ କବିତା ଅବଲମ୍ବନରେ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନା କର ।
Answer:
ଉତ୍କଳ ସାରସ୍ଵତ ଗଗନର ଅନ୍ୟତମ ଜ୍ୟୋତିର୍ମୟ ଜ୍ୟୋତିଷ୍କ, ଆଧ୍ୟାତ୍ମିକ ଚେତନାର ବାର୍ତ୍ତାବହ ତଥା ମାନବବାଦର ଯଥାର୍ଥ ରୂପକାର ନାରୀକବି ଉତ୍କଳ ଭାରତୀ କୁନ୍ତଳା କୁମାରୀ ସାବତ ପ୍ରାକ୍-ସ୍ଵାଧୀନତା କାଳର ଏକ ସୁଦୂରପ୍ରସାରୀ ନାମ । ବିପ୍ଳବର ଅନିର୍ବାଣ ଅଗ୍ନିଶିଖା ତଥା ମାନବତାର ପରିପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ ଉତ୍ସ କୁନ୍ତଳା କୁମାରୀ ଉଭୟ ଗୁଣ ଓ ପରିଣାମରେ ପ୍ଲାବନ କଲାଭଳି ଏପରି ଏକ ସାହିତ୍ୟିକ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିତ୍ବ, ଯାହା ଏ ପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ ଓଡ଼ିଆ ନାରୀ ଜଗତରେ ଦେଖା ଦେଇନାହିଁ ।
କବିତା, ପ୍ରବନ୍ଧ ଓ ଉପନ୍ୟାସ ଆଦି ସାହିତ୍ୟର ବିଭିନ୍ନ ଦିଗକୁ ତାଙ୍କ ଲେଖନୀ ସ୍ପର୍ଶ କରିଛି । ପୂର୍ବଗୌରବାନୁଚିନ୍ତା, ଦେଶାତ୍ମବୋଧ, ପ୍ରେମ, ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରାଣତା, ବିଭୁଚେତନା ପ୍ରଭୃତି କାବ୍ୟକବିତାର ବିଭିନ୍ନ ବିଭାଗ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ତାଙ୍କ ଲେଖନୀର ଜୟଯାତ୍ରା ପରିଲକ୍ଷିତ ହୁଏ । କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ସାରସ୍ବତ ସୃଷ୍ଟିନିଚୟ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ‘ଅଞ୍ଜଳି’, ‘ଉଲ୍ଲାସ’, ‘ଅର୍ଜନା’, ‘ସ୍କୁଲିଙ୍ଗ’, ‘ଆହ୍ବାନ’ ଆଦି କବିତା ପୁସ୍ତକ; ‘ଭ୍ରାନ୍ତି’, ‘ନ’ତୁଣ୍ଡୀ’, ‘ପରଶମଶି’, ‘ରଘୁ ଅରକ୍ଷିତ’, ‘କାଳୀବୋହୂ’ ଆଦି ଉପନ୍ୟାସ ତାଙ୍କ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ନୈପୁଣ୍ୟର ପରିଚାୟକ ।
କବିତା ‘ ମଣିଷ ଭାଇଁ ନାରୀକବିଙ୍କ କବିତା ପୁସ୍ତକା ‘ସ୍ଫୁଲିଙ୍ଗ’ ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକ୍ତ ଏକ ଆହ୍ୱାନଧର୍ମୀ ସମ୍ବୋଧୀ କବିତା । ସ୍ଵାଧୀନତା ପ୍ରାପ୍ତି ପୂର୍ବରୁ ଦେଶବାସୀ ବିଦେଶୀ ଶାସକର ଶୋଷଣ, ଅତ୍ୟାଚାରରେ ଅତିଷ୍ଠ ହୋଇ ଦୟନୀୟ ଜୀବନ ଯାପନ କରୁଥିଲେ । ଭୂମିକା, ରୋଗବ୍ୟାଧ, ବନ୍ୟା ଓ ମରୁଡ଼ିଜନିତ ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ବିପର୍ଯୟ ଆଦି ନାନାବିଧ ପ୍ରତିକୂଳ ପରିସ୍ଥିତି ମଧ୍ୟଦେଇ ଘୋର ନୈରାଶ୍ୟପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ ଜୀବନ ଅତିବାହିତ କରୁଥିଲେ । ଅସହାୟ ମଣିଷ ନିଜ ଦୁରବସ୍ଥା ପାଇଁ ଭାଗ୍ୟକୁ ଦାୟୀ କରି ଓ ମୃତ୍ୟୁରେ ହିଁ ଜୀବନଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣାର ମଣିଷକୁ ମଣିଷପରି ବଞ୍ଚିବାପାଇଁ କବିତାଟିରେ ରହିଛି ନାରୀକବିଙ୍କର ଆଶାନ୍ବିତ ଆହ୍ୱାନ।
ଅମୃତର ସନ୍ତାନ ମଣିଷ ପାଇଁ ନାରୀ କବିଙ୍କର ଆତ୍ମବିଶ୍ବାସଭରା ଆଶା ଆଶ୍ବାସନାର ଦିବ୍ୟବାଣୀ ରହିଛି କବିତାଟିରେ । ଦୁଃଖ ଦୁର୍ଦ୍ଦଶାକୁ କପାଳ ଲିଖନ ବୋଲି ବିବେଚନା କପାଳ ଲିଖନ ବୋଲି ବିବେଚନା କରି ଶତ ହତଶ୍ଵାସରେ ଭାଗ୍ୟକୁ ଧିକ୍କାର କରି ଓ ଜୀବନକୁ ମୃତ୍ୟୁପଥର ଯାତ୍ରୀ ବୋଲି ଧରିନେଇ ଘୋର ନୈରାଶ୍ୟ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଛଟପଟ ହେଉଥିବା ମଣିଷ ପ୍ରତି ନାରୀକବି ସମ୍ବେଦନଶୀଳ ହୋଇଛନ୍ତି । ତାଙ୍କ ମତରେ ମାନବ ଜୀବନ ନିୟତି ଅଧୀନ ହେଲେ ମଧ୍ୟ ଚିର ଶୃଙ୍ଖଳିତ ଜୀବନ ନେଇ ମାନବ ଯେ ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣାର କାରାଗାରରେ ଚିର ବନ୍ଦୀ ହୋଇ ପଡ଼ିଥିବ ଏହା କଦାପି ଭାଗ୍ୟଲିପି ନୁହେଁ ମାନବ ଜାତି କଦାପି ହଂସପଥର ଯାତ୍ରୀ ନୁହେଁ କି ଏ ସଂସାର ମୃତ୍ୟୁଯନ୍ତା ନୁହେଁ ।
![]()
ଦୁଃଖ, ଯାତନା ଓ ଅନୁଶୋଚନାର ତୀବ୍ର ଜ୍ଵଳନକୁ ନତଶିର ହୋଇ ଚିରଦିନ ସହ୍ୟ କରିବା ମାନବର ନିୟତି ନୁହେଁ । ସେହିପରି ଧନୀ, ପୁଞ୍ଜିପତି ଓ କ୍ଷମତାଧ୍ୟାକାରୀ ଅତ୍ୟାଚାରୀ ଶାସକ ଦୁର୍ବଳ ନିରୀହ ଜନତା ଉପରେ ଚିର ଆଧୂପତ୍ୟ ବିସ୍ତାର କରି ଶୋଷଣ, କଷଣରେ ଜୀବନକୁ ଦୁର୍ବିଷହ କରିଚାଲିଥବ, ଏହା କଦାପି ବିଧାତା ବିଧାନ ନୁହେଁ । ନାରୀକବିଙ୍କ ଭାଷାରେ –
କୁର ଅତ୍ୟାଚାରେ ଦଳିବ ଦୁର୍ବଳେ ରକ୍ତ ପିପାସା ଶମିବ
ନତଶିରେ ସୁଖେ ଶ୍ରୀପାଦେ ଅରପି ଆପଣାକୁ ଆପେ ବଧୂବ
ଏ ନୁହେଁ ବିଧାତା ବିଚାର,
ଧ୍ଵଂସର ଯାତ୍ରୀ, ମୃତ୍ୟୁର ଧାତ୍ରୀ ନୁହେଁ ଏ ସୁନ୍ଦର ସଂସାର ।’’
ନାରୀକବିଙ୍କ ମତରେ ପରମେଶ୍ବରଙ୍କ ସୃଷ୍ଟ ଏ ସଂସାର ଚିର ଆନନ୍ଦମୟ ଓ ମଙ୍ଗଳମୟ । ସଂସାରବାସୀ ହେଉଛନ୍ତି ଅମୃତର ସନ୍ତାନ । ମଣିଷ ଚାହିଁଲେ ତା’ ଜୀବନକୁ ମଧୁମୟ, ସରସ ଓ ସୁନ୍ଦର କରିପାରିବ । ତେଣୁ ମୃତ୍ୟୁପଥର ଯାତ୍ରୀ ବୋଲି ଭାବି ମଣିଷ ସ୍ଵକର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟ ସମ୍ପାଦନରୁ ନିବୃତ୍ତ ରହିବା ଅବିବେକତାର ପରିଚୟ । ନାରୀକବି ବିଶ୍ବବାସୀଙ୍କୁ ସଦା କର୍ମତତ୍ପର ରହି କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟ କରିଯିବାକୁ ଉପଦେଶ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି । କର୍ମରେ ନିମଜ୍ଜିତ ରହିଲେ ମନ ଭିତରୁ ନୈରାଶ୍ୟ ଓ ହତାଶାବୋଧ ଦୂରକରିବା ସମ୍ଭବ ।
ମନ ମଧ୍ଯରୁ ଲଜ୍ଜା, ଭୟ, ଅପମାନ ଓ ଅପବାଦକୁ ବିସ୍ମୃତ ହେବାପାଇଁ କର୍ମଯୋଗ ହିଁ ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ ଉପଚାର । ମନରେ ଅହମିକା ପୋଷଣ କରି କ୍ରୋଧଯୁକ୍ତ ହେଲେ ବା ପ୍ରତିଶୋଧପରାୟଣ ଭାବନା ମନରେ ଧାରଣ କଲେ ଆତ୍ମା କଳୁଷିତ ହୁଏ । କାମ, କ୍ରୋଧ, ଲୋଭ, ମୋହ, ମଦ, ମାସର୍ଯ୍ୟାଦି ଅନ୍ତଃରିପୁମାନଙ୍କୁ ଦୃଢ଼ ଭାବେ ଦମନ କରି ମାନବୀୟ ଗୁଣାବଳୀରେ ଭୂଷିତ ହେଲେ ପରମେଶ୍ୱରଙ୍କ ଆଶୀର୍ବାଦ ପ୍ରାପ୍ତ ହୁଏ । ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟଲାଳସା ପରିହାର କରି ମନରେ ଦିବ୍ୟଚେତନା ଜାଗ୍ରତ କଲେ ମାନବ ଦେବତ୍ୱର ଅଧିକାରୀ ହେବ । ନୈତିକତାପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ ଜୀବନ ଶୈଳୀକୁ ପାଥେୟ କରି ଓ ମନରେ ଫଳପ୍ରାପ୍ତି ବାଞ୍ଛା ନ କରି କର୍ମରେ ନିୟୋଜିତ ରହିଲେ ସବୁ ସମସ୍ୟା ସହଜରେ ସମାହିତ ହୋଇପାରିବ ବୋଲି କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ଦୃଢୋକ୍ତି ପ୍ରକାଶ କରିଛନ୍ତି ।
କର୍ମମୟ ସଂସାରରେ କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟ ସମ୍ପାଦନରେ ବ୍ରତୀ ହେବା ହିଁ ମାନବିକତାର ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ ପରିଚୟ । କର୍ମତତ୍ପରତାଦ୍ବାରା ଈଶ୍ଵରଙ୍କ ଇଚ୍ଛା ପୂର୍ଣ କରାଯାଇପାରିବ ଓ ପଶୁତ୍ଵ- ଦେବତ୍ୱର ଭୀଷଣ ପରୀକ୍ଷାରେ ସଫଳତାର ସହିତ ଉତ୍ତୀର୍ଣ୍ଣ ହୋଇ ମଣିଷ ମାନବିକ ମୂଲ୍ୟବୋଧର ବିଜୟ ବୈଜୟନ୍ତୀ ଉଡ଼ାଇପାରିବ । ଫଳତଃ ପରମେଶ୍ଵର ତାଙ୍କ ସୃଷ୍ଟିର ସାର୍ଥକତା ଅବଲୋକନ କରି ଚିର ସନ୍ତୁଷ୍ଟ ହେବେ ଓ ମାନବ ନିକଟରେ ଚିର ଋଣୀ ରହିବେ । ତାଙ୍କ ଅମୃତମୟ ସୃଷ୍ଟିକୁ ସୁନ୍ଦରତର କରିବାରେ ମଣିଷ ନିଜକୁ ଉତ୍ସର୍ଗ କରିବାକୁ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ଆହ୍ବାନ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି । ତାଙ୍କ ଭାଷାରେ –
‘‘ଉଠ ଦେବ ତେଜେ ତେଜି ଲାଜ ଭୟ ଅପମାନ ଅହମିକା,
ପଶୁତ୍ଵ ଦେବତ୍ୱ ପରୀକ୍ଷାରେ ଜୟୀ ଲଭ ବୀରତ୍ଵର ଟୀକା
ଋଣୀ କର ଭବରାଣେ
ତା’ଙ୍କ ରଚା ଚରାଚର ପରାଣରେ ବଳି ଦିଅ ନିଜ ପ୍ରାଣେ ।’’
କବିଙ୍କ ମତରେ ମାନବ ହେଉଛି ବିଧାତାର ବରପୁତ୍ର । ଜୀବନ ଯୁଦ୍ଧରେ ସାମାନ୍ୟ କ୍ଷତାକ୍ତ ହୋଇଗଲେ ସେ ନିଜକୁ କ୍ଷୀଣ ବା ଦୁର୍ବଳ ମନେକରିବା ଅନୁଚିତ । ଦୁଃଖ, ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣା, ଲଜ୍ଜା, ଅପମାନ, ଅପବାଦରେ ନିଜକୁ ଦୀନ-ହୀନ ମନେକରିବା ମଧ୍ୟ ଅନୁଚିତ । ଧୈର୍ଯ୍ୟ, ସାହସ ଓ ବିକ୍ରମ ସହ ଜୀବନ ସଂଗ୍ରାମର ସମ୍ମୁଖୀନ ହେବା ବୀରୋଚିତ ଲକ୍ଷଣ । କାରଣ ପରମେଶ୍ଵର ତାଙ୍କ ଅମୃତମୟ ସୃଷ୍ଟିର ଅଭିନବ ବିକାଶ ଦର୍ଶନରେ ଚିର ଆଗ୍ରହୀ, ଅମୃତ ସନ୍ତାନ ମାନବର ଆଧ୍ୟାତ୍ମିକ ବିକାଶ ଦର୍ଶନରେ ସେ ସଦା ସନ୍ତୁଷ୍ଟ ।
ତେଣୁ ମଣିଷର ସବୁ ବିଷାଦ – ବ୍ୟର୍ଥତା, ଦୁଃଖ – କାତରତା, ତଥା ଯାବତୀୟ ହୀନମନ୍ୟତା ରୂପକ କଳଙ୍କ କାଳିମାକୁ ଧୋଇଦେଇ କ୍ଷତାକ୍ତ ମାନବାତ୍ମାକୁ ସେ ତାଙ୍କ ସୁଧାସ୍ପର୍ଶରେ ନବରୂପ ପ୍ରଦାନ ପୂର୍ବକ ତାକୁ ପୀୟୂଷ ପିପାସୀ କରାଇବେ । ଫଳରେ ଜୀବନ ହୋଇଉଠିବ ସରସ, ସୁନ୍ଦର, ଆନନ୍ଦମୟ ଓ ଅମୃତମୟ । ମଣିଷ ମନରେ ଆତ୍ମଚୈତନ୍ୟ, ପ୍ରାଣପ୍ରାଚୁର୍ଯ୍ୟ ତଥା କର୍ମମୟ ଜୀବନରେ ଉନ୍ମାଦନା ଭରିଦେବାରେ ‘ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ’ କବିତା ଯେ ନାରୀକବିଙ୍କର ଏକ ସାର୍ଥକ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ଏଥରେ ଦ୍ବିରୁକ୍ତି ନାହିଁ ।
Question ୪୦ ।
ବିଷାଦଗ୍ରସ୍ତ ହୋଇପଡ଼ିଥିବା ତୁମର ଜଣେ ବନ୍ଧୁଙ୍କୁ କବିତା ଅନୁସରଣରେ ଆଶ୍ୱାସନାର ବାଣୀ ଦେଇ ପତ୍ରଟିଏ ଲେଖ ।
Answer:
କଟକ
ତା ୨୫.୩.୨୦୧୮
ପ୍ରିୟ ସାଥୀ ସ୍ବାତୀ,
ଶୁଭେଚ୍ଛା ନେବୁ । ମଉସା, ମାଉସୀଙ୍କୁ ମୋର ପ୍ରଣାମ ଜଣାଇବୁ ଓ ତୋ’ ଗେହ୍ଲା ଭାଇ ସୁମନକୁ ମୋର ସ୍ନେହ । କାଲି ତୋ’ ଚିଠି ପାଇଲି । ତୋ’ ଜେଜେଙ୍କ ମୃତ୍ୟୁରେ ତୁ’ ଯେ ଗଭୀର ଭାବେ ମର୍ମାହତ ତାହା ମୁଁ ଅନୁଭବ କଲି । ତୋ’ ଦୁଃଖରେ ସମବେଦନା ଜଣାଇବାକୁ ଦୁଇଧାଡ଼ି ଲେଖୁଛି । ତତେ ଉପଦେଶ ଦେଉଛି ବୋଲି ଭାବିବୁନି । ଏହା ଅବଶ୍ୟ ସତ ଯେ ମଣିଷ ଯାହାଠାରୁ ବେଶୀ ସ୍ନେହ ଆଦର ପାଇଥାଏ ତା’ ବିୟୋଗରେ ମନ ଭିତରେ ଯେଉଁ ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହୁଏ ତାହା ଅପୂରଣୀୟ। ତାଙ୍କର ସେହି ସ୍ନେହବୋଳା ଡାକ, ମମତାଭରା କଥାପଦେ ତୁ ଆଉ ଶୁଣିବୁନି ।
କିନ୍ତୁ ଏକଥା ମଧ୍ୟ ସତ ଯେ ‘ଜାତସ୍ୟ ହି ଧ୍ରୁବମୃତ୍ୟୁ ।’’ ମଣିଷ ଦିନେ ନା ଦିନେ ଧରାଧାମରୁ ବିଦାୟ ନେବ ଏବଂ ଏହା ବିଧ୍ଵନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ । ସାର୍ କହୁଥିଲେ, ଆତ୍ମାର ମୃତ୍ୟୁ ନାହିଁ । ଜରାଜୀର୍ଣ୍ଣ ପୋଷାକ ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନ କରି ଏକ ନୂତନ ପୋଷାକ ପରିଧାନ କରିବା ପରି ଆତ୍ମା କେବଳ ଘଟ ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନ କରେ । ସ୍ୱର୍ଗରେ ଥାଇ ତାଙ୍କ ଆତ୍ମା ତୋ’ ଉପରେ ନିଶ୍ଚୟ ଆଶିଷ ବର୍ଷା କରିବେ ଏଥିରେ ସନ୍ଦେହ ନାହିଁ । ତା’ ଛଡ଼ା ତାଙ୍କ ପାଇଁ ମନକୁ ବିଷାଦିତ କରି ବସିରହିବା ମଧ୍ୟ ବିବେକୀର ଲକ୍ଷଣ ନୁହେଁ ।
ମନ ଭାରାକ୍ରାନ୍ତ ରହିଲେ କୌଣସି କାମରେ ଉତ୍ସାହ ଆସେନାହିଁ ସତ୍ୟ; ମାତ୍ର କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟରେ ଅବହେଳା କଲେ ତା’ର ପରିଣାମ ଆମକୁ ହିଁ ଭୋଗିବାକୁ ପଡ଼ିବ । ଯିଏ ଯେତେଦିନ ପାଇଁ ଆସିଛନ୍ତି ସେଥୁରୁ ମୁହୂର୍ଭେ ଅଧିକ ସମୟ ରଖୁବା କଦାପି ସମ୍ଭବ ନୁହେଁ । ଜନ୍ମ ଓ ମୃତ୍ୟୁ ପରି ଜୀବନର ଦୁଇ ମହାସତ୍ୟକୁ ଆମକୁ ମାନିବାକୁ ହେବ । ଠିକ୍ ଅନୁରୂପଭାବେ ଆମ କର୍ମମୟ ଜୀବନକୁ କିପରି କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟ ସମ୍ପାଦନ ପୂର୍ବକ ଅଧ୍ଵ ସାର୍ଥକ କରିହେବ ତାହା ଚିନ୍ତା କରିବାକୁ ହେବ । କର୍ମ ହିଁ ଜୀବନ । କର୍ମତତ୍ପର ରହିବାଦ୍ୱାରା ଆମେ ଆମ ମନର ସବୁ ଦୁଃଖ ଭୁଲିଯାଇ ପାରିବା ।
ତା’ ଛଡ଼ା ମନର ସୁସ୍ଥତା ରହିଲେ କର୍ମରେ ଉତ୍ସାହ ଆସେ । ତୁ’ ତ ଜାଣୁ, ଯେ ଆମେ ଯେତେବେଳେ କୌଣସି ଏକ କାମରେ ନିୟୋଜିତ ରହୁ, ସେତେବେଳେ ଅନ୍ୟକୌଣସି ଭାବନା ମନକୁ ଆସେନାହିଁ । ତୁମର ମଧ୍ଯ କୁନ୍ତଳା କୁମାରୀଙ୍କ ‘ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ’ କବିତା ପଢ଼ା ସରିଥିବ । ନାରୀକବି କର୍ମର ଜୟଗାନ କରି ଯେଉଁ ପରାମର୍ଶଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି ସେଗୁଡ଼ିକ ବହୁତ ମନଛୁଆଁ ନା ! ଈଶ୍ବରଙ୍କ ଏହି ଚିରଶୋଭାମୟ ସଂସାର ହେଉଛି ମାନବର କର୍ମଭୂମି । ତାଙ୍କ ପଦାରବିନ୍ଦରେ ସବୁ ଦୁଃଖ, ଦୁର୍ଭାବନାକୁ ସମର୍ପଣ କରି କର୍ମରେ ନିୟୋଜିତ ରହିଲେ, ସେ ସବୁ ସମସ୍ୟାର ସମାଧାନ କରିଦେବେ ।
ସ୍ୱାତୀ, ତୋ’ ପଢ଼ାପଢ଼ି ବିଷୟରେ ଲେଖୁ ଜଣାଇବୁ । ମାସିକ ପରୀକ୍ଷାଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ କେମିତିସବୁ ନମ୍ବର ଆସୁଛି ଜଣାଇବୁ । ଗଲା ପରୀକ୍ଷାରେ ଗଣିତରେ ମୋର ଭଲ ହେଲା; କିନ୍ତୁ ବିଜ୍ଞାନରେ ଭଲ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତି ନ ଥିବାରୁ ବହୁତ ଖରାପ ନମ୍ବର ଆସିଲା । ଭଲ ମନ୍ଦ ଜଣାଇ ମଝିରେ ମଝିରେ ଚିଠି ଖଣ୍ଡେ ଖଣ୍ଡେ ଦେଉଥୁବୁ । ରହୁଛି ।
ତୋର ସାଙ୍ଗ
![]()
| ଠିକଣା | |
| ପ୍ରେରକ : |
ପ୍ରାପ୍ତେଷୁ : [ଉ।କଟିକଟ] |
| ପୂଜା ପ୍ରିୟଦଶିନୀ ମାଫିତ୍ – ସଂଗ୍ରାମ ପଟ୍ଟନାୟକ ସେକ୍ଟର – ୬ ସି.ଡି.ଏ. ମର୍କତ ନଗର, କଟକ – ୭୫୩୦୧୪ |
ସ୍ୱ।ତୀ ସ୍ୱ।ଗତିକା ମାଫିତ – ପ୍ରବୀର ମହାପାତ୍ର କ୍ବାଟର ନମ୍ବର – ସି ୯୫ ଛେଣ୍ଡ କଲୋନୀ ରାଉରକେଲା – ୭୫୯୦୦୨ |
ତୁମପାଇଁ କାମ
୪୧ । କୁନ୍ତଳା କୁମାରୀଙ୍କ ରଚନାଗୁଡ଼ିକ ସଂଗ୍ରହ କରି ପଢ଼ ।
୪୨ । କୁନ୍ତଳା କୁମାରୀଙ୍କ ସମସାମୟିକ କବିମାନଙ୍କର ଏକ ତାଲିକା ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ କର ।
୪୩ । ମାନବିକ ମୂଲ୍ୟବୋଧ ପ୍ରକାଶ କରୁଥିବା ପଦଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ବାଛି ଟିପାଖାତାରେ ଟିପି ରଖ ।
ପରୀଷା ଉପଯୋଗୀ ଅତିରିକ୍ତ ପ୍ରଶୋତ୍ତର
ଅତିସଂକ୍ଷିପ୍ତ ଓ ବସ୍ତୁନିଷ୍ଠ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନୋତ୍ତର
A ଗୋଟିଏ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ଉତ୍ତର ଲେଖ ।
1. କବି ‘ବରପୁତ୍ର’ ବୋଲି ସମ୍ବୋଧନ କାହାକୁ କରିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
କବି ମାନବକୁ ବିଧାତାର ବରପୁତ୍ର ବୋଲି ସମ୍ବୋଧନ କରିଛନ୍ତି ।
2. କବି ମାନବକୁ ‘ବରପୁତ୍ର’ ବୋଲି କାହିଁକି କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ମାନବ ଦିବ୍ୟ ମାନବୀୟ ଗୁଣାବଳୀରେ ଭୂଷିତ ହୋଇ ଦେବତ୍ୱର ଅଧିକାରୀ ହୋଇପାରେ । କବି ମାନବକୁ ବରପୁତ୍ର ବୋଲି କହିଛନ୍ତି ।
3. ହୋଇପାରିବ ବୋଲି କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ମୃତ୍ୟୁରଜୁକୁ ଛିନ୍ନ କରି ଜୀବନ ସୂତ୍ରକୁ ଧରି ସ୍ଵକର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟ ପଥରେ ଅଗ୍ରସର ହେଲେ ଜୀବନ ସୁରୁଖୁରୁରେ ଅତିବାହିତ ହୋଇପାରିବ ବୋଲି କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ।
4. କବି ‘ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ’ ବୋଲି କେଉଁମାନଙ୍କୁ ସମ୍ବୋଧନ କରିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ସମାଜରେ ଶୋଷିତ, ଲାଞ୍ଛିତ ଓ ନିଷ୍ପେଷିତ ମଣିଷମାନଙ୍କୁ କବି ‘ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ’ ବୋଲି ସମ୍ବୋଧନ କରିଛନ୍ତି ।
5. ମଣିଷ କେଉଁପାଇଁ ଜନ୍ମଲାଭ କରିନାହିଁ ବୋଲି କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ମଣିଷ ଝୁରି ମରିବାକୁ କିମ୍ବା ବୁଡ଼ି ମରିବାକୁ ଜନ୍ମଲାଭ କରିନାହିଁ ବୋଲି କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ।
6. ନୈରାଶ୍ୟକୁ ଅନ୍ଧାର ରୂପେ କବି କାହିଁକି ଦେଖୁଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ମଣିଷ ଆଶାଶୂନ୍ୟ ହୋଇଗଲେ, ତାକୁ ଚାରିଆଡ଼ ଅନ୍ଧାର ଦେଖାଯାଏ, ତେଣୁ କବି ନୈରାଶ୍ୟକୁ ଅନ୍ଧାର ରୂପେ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନା କରିଛନ୍ତି ।
7. ମଣିଷର ଭାଗ୍ୟ କାହା ମଧ୍ୟରେ ସୀମାବଦ୍ଧ ବୋଲି କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ମଣିଷର ଭାଗ୍ୟ ଲାଞ୍ଛନା, ପ୍ରବଞ୍ଚନା ତଥା ଦୁଃଖଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣା ମଧ୍ୟରେ ସୀମାବଦ୍ଧ ନୁହେଁ ।
8. ହତୋତ୍ସାହ ହୋଇପଡ଼ିଥି ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ପୃଥିବୀକୁ କେଉଁ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିରେ ଦେଖେ ?
Answer:
ହତୋତ୍ସାହ ହୋଇପଡ଼ିଥି ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ଏ ପୃଥିବୀକୁ ‘ଧ୍ୱଂସର ଯାତ୍ରୀ ତଥା ମୃତ୍ୟୁର ଧାତ୍ରୀ’ ରୂପେ ଦେଖେ ।
୨. ‘ ଅମୃତର ସନ୍ତାନ’ ବୋଲି କେଉଁମାନଙ୍କୁ କୁହାଯାଇଛି ?
Answer:
‘ଅମୃତର ସନ୍ତାନ’ ବୋଲି ମାନବମାନଙ୍କୁ କୁହାଯାଇଛି ।
10. ବିଶାଳ ଜଗତର ସୃଷ୍ଟି କ’ଣ ପାଇଁ ନୁହେଁ ବୋଲି କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ବିଶାଳ ଜଗତ କାହାରି ବିଳାସର ଲୀଳାକ୍ଷେତ୍ର ନିମନ୍ତେ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ନୁହେଁ ବୋଲି କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ।
11. କେଉଁ ଧରଣର ପିପାସା ମେଣ୍ଟେ ନାହିଁ ?
Answer:
ଦୁର୍ବଳକୁ ପଦଦଳିତ କରି ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦୟଭାବରେ ତା’ପ୍ରତି ଅତ୍ୟାଚାର କରି ତା’ର ରକ୍ତକ୍ଷୟ କରିବାର ପିପାସା କେବେହେଲେ ମେଣ୍ଟେ ନାହିଁ ।
12. ବିଶ୍ବ କେଉଁମାନଙ୍କ ପାଇଁ ସୁନ୍ଦର ନୁହେଁ ?
Answer:
ନୈରାଶ୍ୟଦଗ୍ଧ ହୋଇ ସଂସାରକୁ ଧ୍ୱଂସାଭିମୁଖୀ ତଥା ଜୀବନକୁ ମୃତ୍ୟୁପଥର ଯାତ୍ରୀ ବୋଲି ବିବେଚନା କରୁଥିବା ମାନବ ପାଇଁ ଏ ବିଶ୍ଵ ସୁନ୍ଦର ନୁହେଁ ।
13. ବିଧାତାଙ୍କ ବିଚାରରେ କେଉଁ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଉଚିତ ନୁହେଁ ?
Answer:
ବିଶ୍ବକୁ ବିଳାସ କ୍ଷେତ୍ର ମନେକରି ଦୁର୍ବଳକୁ ପଦଦଳିତ କରି ନିଜକୁ ନିଜେ ବିନାଶ କରିବା ବିଧାତାଙ୍କ ବିଚାର ନୁହେଁ ।
![]()
14. କବି କିଭଳି ସଂସାରର ପରିକଳ୍ପନା କରିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
କବି ସଂସାରକୁ କର୍ମର ଶୁଭ ଭୁବନ ଭାବେ ପରିକଳ୍ପନା କରିଛନ୍ତି ।
15. ମଣିଷ କେତେବେଳେ ବୀରତ୍ଵର ଟୀକା ଲାଭ କରିପାରିବ ?
Answer:
ଲଜ୍ଜା, ଭୟ, ଅପମାନ ଓ ଅହଂକାରକୁ ତ୍ୟାଗକରି ପଶୁତ୍ଵ-ଦେବତ୍ଵ ପରୀକ୍ଷାରେ ବିଜୟୀ ହେବାପରେ ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ବୀରତ୍ଵର ଟୀକା ଲାଭ କରିପାରିବ ।
16. କବି ଏହି ପୃଥିବୀକୁ କାହାର ଭୁବନ ବୋଲି ଦର୍ଶାଇଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
କବି ଏହି ପୃଥିବୀକୁ କର୍ମର ଶୁଭ ଭୁବନ ବୋଲି
17. ମଣିଷକୁ କେଉଁ ପ୍ରବୃତ୍ତିଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ତ୍ୟାଗ କରିବାପାଇଁ କବି ଆହ୍ୱାନ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
କବି ଲଜ୍ଜା, ଭୟ, ଅପମାନ ଓ ଅହମିକା ପ୍ରଭୃତି କୁପ୍ରବୃତ୍ତିଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ତ୍ୟାଗ କରିବାପାଇଁ ମଣିଷକୁ ଆହ୍ଵାନ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି ।
18. ଭଗବାନଙ୍କୁ
ଋଣୀ କରାଯାଇପାରିବ ?
Answer:
ବିଶ୍ବ ଜୀବନର କଲ୍ୟାଣ ନିମନ୍ତେ ଆୟୋତ୍ସର୍ଗ କରିପାରିଲେ ହିଁ ଭଗବାନଙ୍କୁ ଋଣୀ କରାଯାଇପାରିବ ।
19. ମଣିଷ ଭାଇକୁ କବି ‘ଅରିନ୍ଦମ’ ବୋଲି କାହିଁକି ସମ୍ବୋଧନ କରିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ମାନବ ହିଁ କାମ, କ୍ରୋଧ, ଲୋଭ, ମୋହ, ମଦ ଓ ମାସ୍କର୍ଯ୍ୟ ପ୍ରଭୃତି ଷଡ଼ରିପୁଙ୍କୁ ଜୟ କରିପାରେ ବୋଲି କବି ତାକୁ ‘ଅରିନ୍ଦମ’ ବୋଲି କହିଛନ୍ତି ।
20. ମଣିଷ କେତେବେଳେ ଦେବତା ରୂପେ ପୂଜିତ ହୋଇପାରିବ ?
Answer:
ମାନବ ଯେତେବେଳେ କାମ-କ୍ରୋଧାଦି ଷଡ଼ରିପୁକୁ ଜୟକରି ବିଶ୍ୱଜୀବନର କଲ୍ୟାଣ ନିମନ୍ତେ ଆୟୋତ୍ସର୍ଗ କରିବାକୁ ସମର୍ଥ ହେବ, ସେତେବେଳେ ସେ ଦେବତାରୂପେ ପୂଜିତ ହୋଇପାରିବ ।
B ଗୋଟିଏ ଶବ୍ଦରେ ଉତ୍ତର ଲେଖ ।
1. ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ନିଜର ଭବିଷ୍ୟତକୁ କାହା ଉପରେ ଛାଡ଼ିଦିଏ ?
Answer:
ନିୟତି ଉପରେ
2. କିଏ ଝୁରି ମରିବାକୁ ବୁଡ଼ି ମରିବାକୁ ଜନମି ନାହିଁ ବୋଲି କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ମାନବ
3. ଏ ବିଶାଳ ଜଗତୀ କାହାର ଯାତ୍ରୀ ନୁହେଁ ?
Answer:
ଧ୍ବଂସର
4. ଏ ସଂସାରକୁ କବି କାହାର ଶୁଭ ଭୁବନ ବୋଲି ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନା କରିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
କର୍ମର
5. କେଉଁ ପରୀକ୍ଷାରେ ବିଜୟୀ ହୋଇ ବୀରତ୍ଵର ଟୀକା ଲାଭ କରିବାକୁ କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ପଶୁତ୍ଵ -ଦେବତ୍ୱ
6. ପଶଉତ୍ସ- ଦେବତ୍ୱ ପରୀକ୍ଷାରେ ବିଜୟୀ ହୋଇ କାହାକୁ ଋଣୀ କରିବାକୁ କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ଈଶ୍ବରଙ୍କୁ
7. ଏ ସାରା ସଂସାରର ରଚୟିତା କିଏ ?
Answer:
ଈଶ୍ବର
![]()
8. କବି କାହାକୁ ବିଧାତାର ବରପୁତ୍ର ବୋଲି କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ମଣିଷକୁ
9. କବି ମଣିଷ ଭାଇକୁ କେଉଁ ରଜ୍ଜୁ ଛିଣ୍ଡାଇବାକୁ କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ଯୁଗାନ୍ତ-ମୃତ୍ୟୁ ରଜ୍ଜୁ
10. କେଉଁ ସୂତ୍ର ଧରିବାକୁ କବି ମଣିଷ ଭାଇକୁ ନିବେଦନ କରିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ଜୀବନ ସୂତ୍ର
11. ଅମୃତ ଦୀପ୍ତି ସନ୍ତାନ ଭାବେ କବି କାହାକୁ ବର୍ଣନା କରିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ମଣିଷମାନଙ୍କୁ
12. କାହାକୁ କବି ଅନ୍ଧକାର ରୂପେ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନା କରିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ନୈରାଶ୍ୟ
13. ‘ନିକେତନ’ ଶବ୍ଦର ଅର୍ଥ କ’ଣ ?
Answer:
ଗୃହ
14. ବିଧାତାଙ୍କ ବିଚାରରେ କେଉଁ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଉଚିତ ନୁହେଁ ?
Answer:
ଆପଣାକୁ ଆପେ ବଧୂ
15. ଏ ସଂସାର କେଉଁମାନଙ୍କ ପାଇଁ ସୁନ୍ଦର ନୁହେଁ ?
Answer:
ଧ୍ଵଂସର ଯାତ୍ରୀ ଓ ମୃତ୍ୟୁର ଧାତ୍ରୀ
16. କାହାକୁ ଋଣୀ କରିବାକୁ କବି ମନୁଷ୍ୟମାନଙ୍କୁ କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ଭବରାଣଙ୍କୁ
17. ‘ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ’ କବିତାର କବି କିଏ ?
Answer:
କୁନ୍ତଳାକୁମାରୀ ସାବତ୍
18. ‘ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ’ କବିତାଟି କବିଙ୍କର କେଉଁ କବିତା ପୁସ୍ତକରୁ ଆସିଅଛି ?
Answer:
ସ୍ଫୁଲିଙ୍ଗ
![]()
19. କୁନ୍ତଳାକୁ ମାରୀ କେଉଁ ଉପାଧ୍ଧରେ ଭୂଷିତ ହୋଇଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ଉତ୍କଳ ଭାରତୀ
20. କବିତାରେ କବି କାହାକୁ ଭାଇଁ ବୋଲି ସମ୍ବୋଧନ କରିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ମଣିଷକୁ
C ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନ ପୂରଣ କର ।
1. କବିଙ୍କ ମତରେ ମଣିଷ ହେଉଛି ବିଧାତାର _______________।
Answer:
ବରପୁତ୍ର
2. କବିଙ୍କ ମତରେ ପରମେଶ୍ବରଙ୍କ ସୃଷ୍ଟ ଏ ସଂସାର ଚିର ଆନନ୍ଦମୟ ଓ ________________ ।
Answer:
ମଙ୍ଗଳମୟ
3. କର୍ମର ଶୁଭ ଭୁବନ ବୋଲି କବି ____________ କୁ କହିଛନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ସଂସାର
4. କବି ଅରିନ୍ଦମ ବୋଲି __________________ କୁ ସମ୍ବୋଧନ କରିଛନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ମଣିଷ
5. __________________ ର ଆସନ ତାରା ଦଳେ ବୋଲି କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ମଣିଷ
6. _______________ ପ୍ରବୃତ୍ତିଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ତ୍ୟାଗ କରିବାକୁ କବି ମଣିଷକୁ ଆହ୍ବାନ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଲାଜ, ଭୟ, ଅପମାନ
7. ମଣିଷ ନିଜ ଭିତରେ ଥିବା _______________ ଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ଦମନ କଲେ ଦେବତାର ଆସନ ଲାଭ କରିପାରିବ ।
Answer:
ଅନ୍ତଃଶତ୍ରୁ
8. ଏ ପୃଥିବୀ ନିରନ୍ତର ________________ ପଥରେ ଆଗେଇ ଚାଲିଛି ।
Answer:
ଧ୍ବଂସ
![]()
9. ‘ଚରାଚର’ କହିଲେ _____________________ କୁ ବୁଝାଏ ।
Answer:
ସାରା ସଂସାର
10. କୁନ୍ତଳାକୁମାରୀଙ୍କର ବୃତ୍ତି ______________ ଥିଲା ।
Answer:
ଡାକ୍ତରି
11. ଦେବତା ପୂଜିତ ______________ ରେ ତବାସନ ବୋଲି କବି ମଣିଷକୁ କହିଛନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଆକାଶ
12. ________________ କାଳିରେ ଦୀନହୀନ ନ ହେବାକୁ କବି ମଣିଷ ଭାଇକୁ କହିଛନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
କଳୁଷର କଳଙ୍କ
13. କବିତାରେ କବି ______________ କୁ ଭାଇ ବୋଲି ସମ୍ବୋଧନ କରିଛନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ମଣିଷ
14. ମଣିଷ ______________ ପାଇଁ ଜନ୍ମଲାଭ କରିନାହିଁ ବୋଲି କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଝୁରି ମରିବାକୁ
15. କବି ନୈରାଶ୍ୟକୁ _____________ ରୂପରେ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନା କରିଛନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଅନ୍ଧାର
16. ମଣିଷର ନିୟତି _____________ ମଣିଷର ନିୟତି ବୋଲି କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
କଷଣ କାରା
17. ହତୋତ୍ସାହ ହୋଇପଡ଼ିଥି ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ପୃଥିବୀକୁ ___________ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିରେ ଦେଖନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ମୃତ୍ୟୁର ଧାତ୍ରୀ
18. କବି ______________ ମାନଙ୍କୁ ଅମୃତର ସନ୍ତାନ ବୋଲି କହିଛନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ମଣିଷ
19. ଏ ବିଶାଳ ଜଗତୀ ______________ ର ଧାତ୍ରୀ ନୁହେଁ ।
Answer:
ମୃତ୍ୟୁ
20. କବିଙ୍କ ମତରେ _______________ ର ମରଣ ନାହିଁ ।
Answer:
ଅମୃତଦୀପ୍ତ ସନ୍ତାନ
D ଠିକ୍ କିମ୍ବା ଭୁଲ୍ ଲେଖ ।
1. ପଶୁ ଝୁରି ମରିବାକୁ ବୁଡ଼ି ମରିବାକୁ ଜନମି ନାହିଁ ବୋଲି
Answer:
ଭୁଲ୍
![]()
2. ଏ ସଂସାରକୁ କବି ଭାଗ୍ୟର ଶୁଭ ଭୁବନ ବୋଲି ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନା କରିଛନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଭୁଲ୍
3. ପଶୁତ୍ଵ-ଦେବତ୍ୱ ପରୀକ୍ଷାରେ ବିଜୟୀ ହୋଇ ମଣିଷକୁ ଋଣୀ କରିବାକୁ କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଭୁଲ୍
4. କବି ମଣିଷକୁ ବିଧାତାର ବରପୁତ୍ର ବୋଲି କହିଛନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଠିକ୍
5. ଜୀବନ ସୂତ୍ର ଧରିବାକୁ କବି ମଣିଷ ଭାଇକୁ ନିବେଦନ କରିଛନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଠିକ୍
6. ନୈରାଶ୍ୟକୁ କବି ଅନ୍ଧକାର ରୂପେ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନା କରିଛନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଠିକ୍
7. ବିଧାତାଙ୍କ ବିଚାରରେ ଆପଣାକୁ ଆପେ ବାଧିବା କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଉଚିତ ନୁହେଁ ।
Answer:
ଠିକ୍
8. ଭବରାଣଙ୍କୁ ଋଣୀ କରିବାକୁ କବି ମନୁଷ୍ୟମାନଙ୍କୁ କହିଛନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଠିକ୍
9. କବିତାରେ କବି ଭଗବାନକୁ ଭାଇ ବୋଲି ସମ୍ବୋଧନ କରିଛନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଭୁଲ୍
10. କବିଙ୍କ ମତରେ ପରମେଶ୍ବରଙ୍କ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ଏ ସଂସାର ଚିର ଆନନ୍ଦମୟ ଓ ମଙ୍ଗଳମୟ ।
Answer:
ଠିକ୍
11. କବି ଅରିନ୍ଦମ ବୋଲି ଭଗବାନକୁ ସମ୍ବୋଧନ କରିଛନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଭୁଲ୍
12. ଲାଜ, ଭୟ, ଅପମାନ ପ୍ରବୃତ୍ତିଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ତ୍ୟାଗ କରିବାକୁ କବି ମଣିଷକୁ ଆହ୍ଵାନ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଠିକ୍
![]()
13. ଏ ପୃଥିବୀ ନିରନ୍ତର ଅଗ୍ରସର ପଥରେ ଆଗେଇ ଚାଲିଛି ।
Answer:
ଭୁଲ୍
14. କୁନ୍ତଳାକୁମାରୀଙ୍କର ବୃତ୍ତି ଚାକିରି ଥିଲା ।
Answer:
ଭୁଲ୍
E ଚାରୋଟି ବିକଳ୍ପ ମଧ୍ୟରୁ ଠିକ୍ ଉତ୍ତରଟି ବାଛି ଲେଖ ।
1. ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ନିଜର ଭବିଷ୍ୟତକୁ କାହା ଉପରେ ଛାଡ଼ି ଦିଅନ୍ତି ?
(A) କର୍ମ
(B) କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ଯ
(C) ନିୟତି
(D) ଭଗବାନ୍
Answer:
(C) ନିୟତି
2. କିଏ ଝୁରି ମରିବାକୁ ବୁଡ଼ି ମରିବାକୁ ଜନମି ନାହିଁ ବୋଲି କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
(A) ମାନବ
(B) ମହାମାନବ
(C) ପରମପୁରୁଷ
(D) ପୁରୁଷୋତ୍ତମ
Answer:
(A) ମାନବ
3. ଏ ବିଶାଳ ଜଗତୀ କାହାର ଯାତ୍ରୀ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ମୃତ୍ୟୁର
(B) ଧ୍ବଂସର
(C) ଦାରିଦ୍ର୍ୟର
(D) ଅନଟନର
Answer:
(B) ଧ୍ବଂସର
4. ଏ ସଂସାରକୁ କବି କାହାର ଶୁଭ ଭୁବନ ବୋଲି ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନା କରିଛନ୍ତି ?
(A) କର୍ମର
(B) ଧର୍ମର
(C) ତ୍ଯାଗର
(D) ଉପକାରର
Answer:
(A) କର୍ମର
5. କେଉଁ ପରୀକ୍ଷାରେ ବିଜୟୀ ହୋଇ ବୀରତ୍ଵର ଟୀକା ଲାଭ କରିବାକୁ କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
(A) ପଶୁତ୍ଵ-ଦେବତ୍ଵ
(B) ଦେବତ୍ୱ-ମାନବତ୍ଵ
(C) ମାନବତ୍ବ-ପଶୁତ୍ଵ
(D) ଦେବତ୍ୱ-ଦାନବତ୍ୱ
Answer:
(A) ପଶୁତ୍ଵ-ଦେବତ୍ଵ
6. ପରୀକ୍ଷାରେ ବିଜୟୀ ହୋଇ କାହାକୁ ଋଣୀ କରିବାକୁ କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
(A) ପୃଥିବୀବାସୀଙ୍କୁ
(B) ଦେବତାଙ୍କୁ
(C) ଈଶ୍ବରଙ୍କୁ
(D) ସଂସାରକୁ
Answer:
(C) ଈଶ୍ବରଙ୍କୁ
![]()
7. ଏ ସାରା ସଂସାରର ରଚୟିତା କିଏ ?
(A) ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟ
(B) ଈଶ୍ବର
(C) କର୍ମ
(D) ଚନ୍ଦ୍ର
Answer:
(B) ଈଶ୍ବର
8. କବି କାହାକୁ ବିଧାତାର ବରପୁତ୍ର ବୋଲି କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
(A) ମହାପୁରୁଷମାନଙ୍କୁ
(B) ସଜ୍ଜନଙ୍କୁ
(C) ମଣିଷକୁ
(D) ଦେବତାଙ୍କୁ
Answer:
(C) ମଣିଷକୁ
9. କବି ମଣିଷ ଭାଇକୁ କେଉଁ ରଜ୍ଜୁ ଛିଣ୍ଡାଇବାକୁ କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
(A) ଜୀବନ ରଜ୍ଜୁ
(B) ବନ୍ଧୁତ୍ଵ ରଜୁ
(C) ଯୁଗାନ୍ତ-ମୃତ୍ୟୁ ରଜ୍ଜୁ
(D) ସମ୍ପର୍କ ରଜ୍ଜୁ
Answer:
(C) ଯୁଗାନ୍ତ-ମୃତ୍ୟୁ ରଜ୍ଜୁ
10. କେଉଁ ସୂତ୍ର ଧରିବାକୁ କବି ମଣିଷ ଭାଇକୁ ନିବେଦନ କରିଛନ୍ତି ?
(A) ସମ୍ପର୍କ ସୂତ୍ର
(B) ଜନ୍ମ ସୂତ୍ର
(C) ଜୀବନ ସୂତ୍ର
(D) ମୃତ୍ୟୁ ସୂତ୍ର
Answer:
(C) ଜୀବନ ସୂତ୍ର
11. କେଉଁ ଧରଣର ପିପାସା ମେଣ୍ଟେ ନାହିଁ ?
(A) ଜଳ ପିପାସା
(B) ସୁରା ପିପାସା
(C) ରକ୍ତ ପିପାସା
(D) କେଉଁଟି ନୁହେଁ
Answer:
(D) କେଉଁଟି ନୁହେଁ
12. କେଉଁଟି ମାନବର ଷଡ଼ରିପୁ ମଧ୍ୟରୁ ଏକ ଶତ୍ରୁ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) କାମ
(B) କ୍ରୋଧ
(C) ଲୋଭ
(D) କ୍ଷମା
Answer:
(D) କ୍ଷମା
13. କର୍ମର ଶୁଭ ଭୁବନ ବୋଲି କବି କାହାକୁ କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
(A) ସଂସାରକୁ
(B) ପାତାଳକୁ
(C) ସ୍ବର୍ଗକୁ
(D) ତ୍ରିଲୋକକୁ
Answer:
(A) ସଂସାରକୁ
14. କବି ଅରିନ୍ଦମ ବୋଲି କାହାକୁ ସମ୍ବୋଧନ କରିଛନ୍ତି ?
(A) ଈଶ୍ବରଙ୍କୁ
(B) ସବଳକୁ
(C) ଦୁର୍ବଳକୁ
(D) ମଣିଷକୁ
Answer:
(D) ମଣିଷକୁ
![]()
15. ତାରା ଦଳେ କାହାର ଆସନ ବୋଲି କବି କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
(A) ଚନ୍ଦ୍ରଙ୍କର
(B) ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟଙ୍କର
(C) ସପ୍ତର୍ଷିମଣ୍ଡଳର
(D) ମଣିଷର
Answer:
(D) ମଣିଷର
16. ମଣିଷର କେଉଁ ପ୍ରବୃତ୍ତିଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ତ୍ୟାଗ କରିବାକୁ କବି ଆହ୍ବାନ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି ?
(A) ସତ୍ୟ, ଧର୍ମ, ନ୍ୟାୟ
(B) କ୍ରୋଧ, ଲୋଭ, ମୋହ
(C) ଲାଜ, ଭୟ, ଅପମାନ
(D) ଦୟା, କ୍ଷମା, ସଂଯମ
Answer:
(C) ଲାଜ, ଭୟ, ଅପମାନ
17. ମଣିଷ କେତେବେଳେ ଦେବତାର ଆସନ ଲାଭ କରିପାରିବ ?
(A) ସ୍ଵର୍ଗଜୟ କଲେ
(B) ପୃଥିବୀର ରାଜା ହେଲେ
(C) ତା’ ଭିତରେ ଥିବା ଅନ୍ତଃ ଶତ୍ରୁଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ଦମନ କଲେ
(D) ସୁକାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କଲେ
Answer:
(C) ତା’ ଭିତରେ ଥିବା ଅନ୍ତଃ ଶତ୍ରୁଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ଦମନ କଲେ
18. ଏ ପୃଥିବୀ ନିରନ୍ତର କେଉଁ ପଥରେ ଆଗେଇ ଚାଲିଛି ?
(A) ଅବନତି ପଥରେ
(B) ଉନ୍ନତି ପଥରେ
(C) ଧ୍ବଂସପଥରେ
(D) ଗତିପଥରେ
Answer:
(C) ଧ୍ବଂସପଥରେ
19. ‘ରୋଚର’ କହିଲେ କ’ଣ ବୁଝ ?
(A) ଚାରଣ ଭୂମି
(B) ଗୋଚର ଭୂମି
(C) ମରୁଭୂମି
(D) ସାରା ସଂସାର
Answer:
(D) ସାରା ସଂସାର
20. କୁନ୍ତଳାକୁମାରୀଙ୍କର ବୃତ୍ତି କ’ଣ ଥିଲା ?
(A) ସାହିତ୍ୟ
(B) ସମାଜସେବା
(C) ଡାକ୍ତରି
(D) କାରିଗରି
Answer:
(C) ଡାକ୍ତରି
କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧରେ :
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ସାହିତ୍ୟରେ ନାରୀକବି ଉତ୍କଳଭାରତୀ କୁନ୍ତଳା କୁମାରୀ ସାବତ ଏକ ସୁଦୂରପ୍ରସାରୀ ନାମ । ଚିତ୍ତାକର୍ଷକ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିତ୍ଵ, ବିପ୍ଳବର ଅନିର୍ବାଣ ଅଗ୍ନିଶିଖା, ମାନବିକତାର ଏକ ପରିପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ ଉତ୍ସ ଏହି ମହୀୟସୀ କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ଲେଖନୀ କବିତା, ପ୍ରବନ୍ଧ, ଉପନ୍ୟାସ ପ୍ରଭୃତି ସାହିତ୍ୟର ବିଭିନ୍ନ ଦିଗକୁ ସ୍ପର୍ଶ କରିଛି । ପୂର୍ବ ଗୌରବାନୁଚିନ୍ତା, ଦେଶାତ୍ମବୋଧ ପ୍ରେମ, ପ୍ରକୃତି, ଭଗବାନ ପ୍ରଭୃତିଙ୍କୁ ଆଧାର କରି କାବ୍ୟ କବିତାର ବିଭିନ୍ନ ବିଭାଗ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ତାଙ୍କ ଲେଖନୀର ଜୟଯାତ୍ରା । ତାଙ୍କ କବିତାରେ ଓଡ଼ିଆ ପ୍ରୀତି ଓ ଓଡିଆ ଭାଷା ପ୍ରୀତିର ଅପୂର୍ବ ନମୁନା ପରିଦୃଷ୍ଟ ହୁଏ । କୁନ୍ତଳା କୁମାରୀଙ୍କ ଜନ୍ମ ୧୯୦୧ ଖ୍ରୀଷ୍ଟାବ୍ଦ ଫେବୃୟାରୀ ୮ ତାରିଖରେ ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ଏକ ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନାଞ୍ଚଳ ବସ୍ତର ଗଡ଼ଜାତରେ ।
ସାରସ୍ଵତ ପ୍ରତିଭାର ଉଜ୍ଜଳତର ସ୍ବାକ୍ଷର ଦେବାକୁ ଯାଉଥିଲାବେଳେ ୧୯୩୮ ମସିହାରେ ସେ ଇହଧାମରୁ ବିଦାୟ ନେଇଥିଲେ । ତେରବର୍ଷ ପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣ ପରିଚୟ ପାଇ ନ ଥିବା ଏହି ଅସାଧାରଣ ଧୀଶକ୍ତିସମ୍ପନ୍ନା ଅଳ୍ପ କେତୋଟି ଦିନ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଓଡ଼ିଆ ଭାଷା ଶିକ୍ଷା କରି ଓଡ଼ିଆ ସାହିତ୍ୟ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ଯେଉଁ ଗୌରବର ଅଧିକାରୀ ହୋଇପାରିଥିଲେ ତାହା ବାସ୍ତବିକ ବିସ୍ମୟକର । ବୃତ୍ତିରେ ଡାକ୍ତର ଥିଲେ ମଧ୍ୟ ତାଙ୍କ ପ୍ରବୃତ୍ତି ଥିଲା ସାରସ୍ବତ ସାଧନା । କେବଳ ଓଡ଼ିଆ ସାହିତ୍ୟ ନୁହେଁ ହିନ୍ଦୀ ସାହିତ୍ୟରେ ମଧ୍ୟ ତାଙ୍କର ଗଭୀର ପ୍ରବେଶ ଥିଲା । ହିନ୍ଦୀରେ ‘ବରମାଲା’ ନାମକ ଏକ ଗୀତିଗୁଚ୍ଛ ରଚନା କରି ତଥା ବହୁ ହିନ୍ଦୀ ପତ୍ରିକାର ସମ୍ପାଦନା ଦାୟିତ୍ଵରେ ରହି ସେ ହିନ୍ଦୀ ସାହିତ୍ୟ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ସୁପ୍ରତିଷ୍ଠିତା ହୋଇ ପାରିଥିଲେ ।
ଭାଷଣ ଦେବାର ଗୌରବ ଲାଭ କରିଥିଲେ ସେ । ପ୍ରତିଷ୍ଠାର ଉଚ୍ଚତମ ଶିଖରରେ ଥିଲାବେଳେ ତାଙ୍କୁ ସଂସାର ତ୍ୟାଗ କରିବାକୁ ପଡ଼ିଥିଲା । ମାତ୍ର ୩୮ ବର୍ଷର ସ୍ୱଳ୍ପ ଜୀବନକାଳ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ନିଜ ପ୍ରତିଭାର ସୁବିନିଯୋଗ କରି ସେ ଓଡ଼ିଆ ସାହିତ୍ୟ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ନିଜର ଅମଳିନ ପରିଚୟ ରଖ୍ଯାଇଛନ୍ତି । ‘ଅଞ୍ଜଳି’, ‘ଉଲ୍ଲାସ’, ‘ଅର୍ଜନା’, ‘ସ୍କୁଲିଙ୍ଗ’ ଓ ‘ଆହ୍ବାନ’ ଆଦି କବିତା ପୁସ୍ତକ; ‘ଭ୍ରାନ୍ତି’, ‘ନ’ ତୁଣ୍ଡୀ’, ‘ପରଶମଣି’, ‘ରଘୁ ଅରକ୍ଷିତ’, ‘କାଳୀବୋହୂ’ ଆଦି ଉପନ୍ୟାସ ତାଙ୍କ ଉଜ୍ଜ୍ଵଳ ପ୍ରତିଭାର ନିଦର୍ଶନ । ତାଙ୍କ ସାରସ୍ବତ କୃତି ପାଇଁ ପୁରୀର ‘ମହିଳା ବନ୍ଧୁ’ ଅନୁଷ୍ଠାନ ତାଙ୍କୁ ‘ଉତ୍କଳ ଭାରତୀ’ ଉପାଧ୍ ପ୍ରଦାନ କରିଥିଲେ । ବିଶ୍ୱଜନୀନତା, ସେବାପରାୟଣତା, ଭଗବତ୍ ବିଶ୍ଵାସ, ମାନବିକ ମୂଲ୍ୟବୋଧ ଓ କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟପରାୟଣତାକୁ ଆଧାର କରି ସାହିତ୍ୟ ସୃଷ୍ଟିରେ ତାଙ୍କ ଲେଖନୀ ଶତମୁଖ ହୋଇଉଠିଛି ।
କବିତାର ପୃଷ୍ଠଭୂମି :
ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ସ୍ଵାଧୀନତା ଲୋପଠାରୁ ନବ ସ୍ଵାଧୀନତା ଲାଭ ପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ ଉତ୍କଳୀୟମାନଙ୍କ ଜୀବନ ଥିଲା ଦୁର୍ଦ୍ଦିନ ରାତ୍ରିର ତିମିରିତ କାଳ । ବିକଟ ଦାରିଦ୍ର୍ୟ ଓ ନିପୀଡ଼ିତ ଜୀବନ ନେଇ ଓଡ଼ିଆ ଜାତି ନୈରାଶ୍ୟର ଘନ ଅନ୍ଧକାର ମଧ୍ଯରେ ହା-ହୁତାଶମୟ ଜୀବନ ଅତିବାହିତ କରୁଥିଲା । ଏହି ସମୟରେ କୁନ୍ତଳା କୁମାରୀ ଓଡ଼ିଆମାନଙ୍କ ମୁମୂର୍ଷୁ ଧମନୀକୁ ସ୍ପନ୍ଦିତ କରିବାପାଇଁ ଆଶାର ସଙ୍ଗୀତ ଶୁଣାଇଛନ୍ତି । ସେମାନଙ୍କ ନୈରାଶ୍ୟଦଗ୍ଧ ପ୍ରାଣରେ ଆଶାର ଅସୁମାରି ସ୍ବପ୍ନ ଭରିଦେଇ ଧୈର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଧାରଣପୂର୍ବକ କର୍ମମୟ ଜୀବନରେ ଉନ୍ମାଦନା ଓ ଆତ୍ମଚୈତନ୍ୟ ଜାଗରଣ କରିବାକୁ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ଆହ୍ବାନ ଜଣାଇଛନ୍ତି ।
ବୀର ଓଡ଼ିଆଜାତିର ସ୍ମାରକୀ ବାରବାଟୀ ଭାଙ୍ଗି ପଡ଼ିଥିଲେ ମଧ୍ୟ, ଓଡ଼ିଆ ଶିଳ୍ପୀ ଓ ସ୍ଥପତିଙ୍କ ଅତୁଳନୀୟ କାରୁକଳାର ପ୍ରତୀକ କୋଣାର୍କ ମାଟିରେ ଲୋଟିଥିଲେ ମଧ୍ୟ, ଓଡ଼ିଆ ସାଧବ ପୁଅର ନୌବାଣିଜ୍ୟ ବିଭବ ଲୋପ ପାଇଯାଇଥିଲେ ମଧ୍ୟ, ଏପରିକି ବନ୍ୟା, ବାତ୍ୟା ଓ ଦୁର୍ଭିକ୍ଷ ପରି ପ୍ରକୃତିର କ୍ରୂର ପରିହାସରେ ଜନଜୀବନ ବିପର୍ଯ୍ୟସ୍ତ ହୋଇପଡ଼ିଥିଲେ ମଧ୍ୟ ଉତ୍କଳରୁ ମନୁଷ୍ୟତା ନିଃଶେଷ ହୋଇଯାଇ ନାହିଁ । ଜାତିର ମାନବିକ ମୂଲ୍ୟବୋଧ ଉପରେ କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କର ନିବିଡ଼ ଆସ୍ଥା ରହିଛି ।
ଅସହାୟ ଓଡ଼ିଆ ଜାତିପ୍ରାଣରେ ଆଶା ଓ ଉଦ୍ଦୀପନାର ସୁଧାବାରି ସିଞ୍ଚନ କରିବାକୁ ଯାଇ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ସୃଷ୍ଟି କରିଛନ୍ତି କବିତା ‘ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ’। କବିତାଟି କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ କବିତା ପୁସ୍ତକ ସ୍ଫୁଲିଙ୍ଗ ରୁ ଉଦ୍ଧୃତ ହୋଇଛି, ଯାହାର ରଚନାକାଳ ୧୯୨୯ ମସିହା । ତତ୍କାଳୀନ ରାଜନୈତିକ ଓ ସାମାଜିକ ପରିସ୍ଥିତି ଥିଲା ଉତ୍ତେଜନାପ୍ରବଣ । ବିଦେଶୀ ଶାସକଙ୍କ ଅର୍ଥନୈତିକ ଶୋଷଣ, ନିପୀଡ଼ନ, ଦେଶବାସୀଙ୍କ ଉତ୍କଟ ଦାରିଦ୍ର୍ୟ, ରୋଗବ୍ୟାଧ, ରାଜା ଜମିଦାରଙ୍କ ବିଳାସବ୍ୟସନ, ବିଦେଶୀ ପଦଲେହନକାରୀଙ୍କର ବିଶ୍ୱାସଘାତୀ ଭୂମିକା ପ୍ରଭୃତି ଦେଶର ଘୋର ଅସହାୟ ଅବସ୍ଥାରେ ସାଧାରଣ ଜନଜୀବନ ବ୍ୟତିବ୍ୟସ୍ତ ହୋଇପଡ଼ିଥିଲା ।
ଧନୀ-ନିର୍ଜନ, ଶୋଷକ ଓ ଶୋଷିତ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଥିବା ଯୁଗ ‘ଯୁଗର ବ୍ୟବଧାନ ନାରୀକବିଙ୍କ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିକୁ ଏଡ଼ାଇ ଯାଇ ପାରି ନ ଥିଲା । ମଣିଷର ଦୁଃଖରେ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ କେଉଁଠାରେ ବ୍ୟଥ୍ତା ତ କେଉଁଠି ଜାତୀୟ ଜୀବନର ଦୁର୍ଗତି ଲକ୍ଷ୍ୟ କରି ଅବସାଦଗ୍ରସ୍ତା । ଶୋଷିତ, ଲାଞ୍ଛିତ ତଥା ଦାରିଦ୍ର୍ୟର କଷାଘାତରେ ଜର୍ଜରିତ ଜନତାର ଦୁର୍ଦ୍ଦଶା ମୋଚନ ପାଇଁ ତାଙ୍କ କାବ୍ୟସ୍ୱରରେ ଉଗ୍ରତା ନାହିଁ; ମାତ୍ର ଅଭିଯୋଗ ଅଛି । ଦୁର୍ଦ୍ଦଶାଗ୍ରସ୍ତ ଜନତାଙ୍କ ପାଇଁ କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ମନର କୋମଳ କାରୁଣ୍ୟ କବିତାରେ ରୂପାୟିତ ହୋଇଛି । ଏହି ଗ୍ଳାନିକର ପରିସ୍ଥିତି ଭିତରେ କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ଅନ୍ତରରେ ଆଶାର ଅସରନ୍ତି ବିଶ୍ବାସ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହୋଇପାରିଛି ଓ ମଣିଷର ମହାନତାକୁ ଘୋଷଣା କରି ସେ ଗାଇଛନ୍ତି –
‘ଶୁଣ ହେ ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ !
ଝୁରି ମରିବାକୁ ବୁଡ଼ି ମରିବାକୁ
ମଣିଷ ଜନମି ନାହିଁ ।”
![]()
କବିତାର ସାରମମ :
ନାରୀକବି କୁନ୍ତଳା କୁମାରୀଙ୍କ କାବ୍ୟସ୍ୱରରେ ମଣିଷ ପାଇଁ ଅଶେଷ ସ୍ନେହ ଓ ଦିବ୍ୟାଶୀର୍ବାଦର ଧାରା ଉତ୍ସାରିତ ହୋଇଛି । ସମାଜର ଦଳିତ, ଲାଞ୍ଛିତ, ପତିତ ଓ ନିପୀଡ଼ିତ ମଣିଷ ଜାତି ପାଇଁ ତାଙ୍କ ଚିତ୍ତର କୋମଳ କାରୁଣ୍ୟ କବିତାରେ ଭରିଦେଇଛି ଅଫୁରନ୍ତ ପ୍ରାଣପ୍ରାଚୁର୍ଯ୍ୟ । ମାନବ ସମାଜର ଐକ୍ୟ, ପ୍ରୀତି ଓ କଲ୍ୟାଣ କାମନାରେ କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ସାହିତ୍ୟରେ ଅମୃତର ବାର୍ତ୍ତା ପରିବେଷିତ ହୋଇଛି ।
କୁନ୍ତଳା କୁମାରୀଙ୍କ ସମ୍ଭୋଧୀ କବିତା ‘ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ’ ଅମୃତର ସନ୍ତାନ ମଣିଷ ପାଇଁ ଆତ୍ମବିଶ୍ଵାସଭରା ଆଶା, ଆଶ୍ୱାସନାର ଦିବ୍ୟବାଣୀ ଶୁଣାଇଛି । ସୁଖସ୍ଵପ୍ନଭରା ଅତୀତ ସ୍ମୃତିର ରୋମନ୍ଥନ କରି ତଥା ସାମ୍ପ୍ରତିକ ଦୁଃଖ, ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣାର କାରୁଣ୍ୟରେ ହୃଦୟକୁ ଅଯଥା ଭାରାକ୍ରାନ୍ତ ନ କରି ଉପସ୍ଥିତ ପରିସ୍ଥିତିକୁ ସାହସର ସହିତ ସାମନା କରିବା ବିବେକୀର କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ।
ସମୟ ଚକ୍ରରେ ଚିର ଘୂର୍ଣ୍ଣନଶୀଳ ଦୁଃଖର ଅମାରାତ୍ରି ପରେ ନବ ପ୍ରଭାତର ନବୀନ ସୁଖ-ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟର ଉଦୟ ଅବଶ୍ୟମ୍ଭାବୀ । ତେଣୁ ଦୁଃଖ-ଦୁର୍ଦ୍ଦଶାକୁ କପାଳ ଲିଖନ ବୋଲି ବିବେଚନା ନ କରି ଓ ଭାଗ୍ୟକୁ ସ୍ଵୀକାର କରି ଶତ ହତଶ୍ଵାସରେ ଜୀବନକୁ ଅଧିକ ଜନ୍ତ୍ରଣାଜର୍ଜର ନ କରିବାକୁ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ସମ୍ବେଦନଶୀଳ ଆଶ୍ୱାସନା ବାଣୀ ଶୁଣାଇଛନ୍ତି । କାରଣ ଅନାଗତ ଭବିଷ୍ୟତ ନିଶ୍ଚିତଭାବେ ଜୀବନକୁ ନୂତନ ଆଶା ଓ ନିବ ଉନ୍ମାଦନାରେ ସ୍କନ୍ଦିତ କରିବ । ଯେହେତୁ ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନ ଧାରାର ପ୍ରବହମାନତାରେ ବିଧାତାଙ୍କ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ଚିର ମଙ୍ଗଳମୟ, ମାନବ ଜୀବନ ,ଯେ ନିୟତିର ଅଧୀନ, ଏକଥା ସତ୍ୟ । ମାତ୍ର ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣା ପରିପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ କାରାଗାରରେ ଚିର ଶୃଙ୍ଖଳିତ ଜୀବନ ଧରି ମାନବ ଯେ କେବଳ । ଲାଞ୍ଛନା, ଦୁଃଖ, ଅପମାନ ଓ ଅତ୍ୟାଚାରକୁ ନୀରବରେ ସହ୍ୟ କରି ଚାଲିଥିବ ଏହା କଦାପି ନିୟତିର ବିଧାନ ନୁହେଁ । ମାନବ ଜାତି କେବେ ବି ଧ୍ୱଂସପଥର ଯାତ୍ରୀ ନୁହେଁ କି ଏ ସଂସାର ତା’ ପାଇଁ ମୃତ୍ୟୁର ମହାକାଳ ନୁହେଁ ।
ଈଶ୍ବର ସୃଷ୍ଟ ଏ ବିଶାଳ ଜଗତ ହେଉଛି ଅମୃତ ସନ୍ତାନ, ମାନବର ଲୀଲାକ୍ଷେତ୍ର, ଯେଉଁଠି ତା’ ଜୀବନର ସୁଖ -ଦୁଃଖ, ହସ – କାନ୍ଦ ଗୋଟିଏ ଘୂର୍ଣାୟମାନ ମୁଦ୍ରାର ଦୁଇପାର୍ଶ୍ଵ ସଦୃଶ । ସମୟାନୁକ୍ରମେ ମୁଦ୍ରାର ପଟ ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନରେ ଦୁଃଖ – ଦୁର୍ଦ୍ଦଶାର ପତନ ଘଟିବ ଏବଂ ସୁଖ-ସମୃଦ୍ଧିର ପ୍ରାଚୁର୍ଯ୍ୟରେ ଜୀବନପାତ୍ର ଭରିଉଠିବ । ପରମେଶ୍ଵରଙ୍କ ଅମୃତମୟ ସୃଷ୍ଟିରେ ଏ ଜଗତ ମଧ୍ଯ କାହାରି ପାଇଁ ଚିର ବିଳାସର ମଧୁକୁଞ୍ଜ ନୁହେଁ । ଧନ, ସମ୍ପଦ ଓ କ୍ଷମତାରେ ମଦମତ୍ତ ହୋଇ ଦଳେ ବିଳାସ, ବ୍ୟସନ ଓ ସୁଖ ସମ୍ଭୋଗରେ ଚିର ମତୁଆଲା ହେଉଥିବେ ଅଥଚ ଅନ୍ୟ ଦଳକ ଶୋଷଣ, କଷଣ, ଅତ୍ୟାଚାର ଓ ଦାରିଦ୍ର୍ୟର କଷାଘାତରେ ଚିର ଜର୍ଜରିତ ହୋଇ ଭାଗ୍ୟ ଆଦରି ନୀରବରେ ସବୁ ସହ୍ୟ କରି ଚାଲିଥିବେ, ଏହା କଦାପି ନିୟତିର ବିଧାନ ନୁହେଁ ।
ଧନୀ, ପୁଞ୍ଜିପତି, ସ୍ୱେଚ୍ଛାଚାରୀ ଶାସକ ସଦାବେଳେ ଦୁର୍ବଳ, ନିରୀହ ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ଉପରେ ଚିର ଆଧୂପତ୍ୟ ବିସ୍ତାର କରି କଷଣ, ପେଷଣରେ ତା’ର ଜୀବନକୁ ଦୁର୍ବିଷହ କରି ଚାଲିଥିବ; ଏହାକୁ ବିଧ୍ଵନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ ବୋଲି କଦାପି କୁହାଯାଇ ନ ପାରେ । ଦୁଃଖ, ବେଦନା ଓ ଅନୁଶୋଚନାର ତୀବ୍ର ତାଡ଼ନା ମଧ୍ୟରେ ସବୁ ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣାକୁ ନତଶିରେ ସହ୍ୟ କରି ମନୁଷ୍ୟ କେବଳ ଲୋତକ ବର୍ଷଣ କରିଚାଲିଥବ ଓ ଜୀବନ ଯୁଦ୍ଧରେ ପରାଜିତ ସୈନିକ ପରି ହତଭାଗ୍ୟ ବୋଲି ନିଜକୁ ଶତ ଧକ୍କାର କରି ଚାଲିଥବ, ଏହାକୁ ଭାଗ୍ୟଲିପି ବୋଲି କହି ମୃତ୍ୟୁ ଅପେକ୍ଷାରେ ପଡ଼ିରହିବାକୁ ଶ୍ରେୟ ମନେକରୁଥିବା ମଣିଷ ମନରେ ଆଶା ଓ ବିଶ୍ୱାସ ଭରିଦେବାକୁ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ଆପ୍ରାଣ ଉଦ୍ୟମ କରିଛନ୍ତି । କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ମତରେ ଈଶ୍ବରଙ୍କ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ଏ ସଂସାର ସଦା ଶୋଭାମୟ ଓ ଚିର ଆନନ୍ଦମୟ ।
ମଙ୍ଗଳମୟଙ୍କ ସୃଷ୍ଟିରେ ଏ ସଂସାରବାସୀ ହେଉଛନ୍ତି ବିଶ୍ଵନିୟନ୍ତାଙ୍କ ଅମୃତ ସନ୍ତାନ । ତେଣୁ ଭାଗ୍ୟକୁ ଆଦରି ମାନବ ନିଜକୁ କେବଳ ମୃତ୍ୟୁପଥର ଯାତ୍ରୀ ବୋଲି ଭାବି ସ୍ଵକର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟ ସମ୍ପାଦନରୁ ନିବୃତ୍ତ ରହିବା ସର୍ବାଦୌ ଅନୁଚିତ । କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ମତରେ ଏ ବିଶାଳ ଜଗତ କଦାପି ହଂସାଭିମୁଖୀ ନୁହେଁ ଏବଂ ଅମୃତର ସନ୍ତାନ ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ମୃତ୍ୟୁ-ପଥର ଯାତ୍ରୀ ନୁହେଁ । କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ମତରେ ଏ ବିଶାଳ ଜଗତ କଦାପି ଧ୍ୱଂସାଭିମୁଖୀ ନୁହେଁ ଏବଂ ଅମୃତର ସନ୍ତାନ ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ମୃତ୍ୟୁ-ପଥର ଯାତ୍ରୀ ନୁହେଁ । କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ଭାଷାରେ –
‘ନତଶିରେ ସୁଖେ ଶ୍ରୀପାଦେ ଅରପି ଆପଣାକୁ ଆପେ ବଧୂବ
ଏ ନୁହେଁ ବିଧାତା ବିଚାର,
ଧ୍ଵଂସର ଯାତ୍ରୀ, ମୃତ୍ୟୁର ଧାତ୍ରୀ ନୁହେଁ ଏ ସୁନ୍ଦର ସଂସାର ।’’
![]()
କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ବିଶ୍ବବାସୀଙ୍କୁ ସଦା କର୍ମତତ୍ପର ରହି କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟ ସମ୍ପାଦନ କରିଯିବାପାଇଁ ଉପଦେଶ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି । କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ମତରେ ଏ ଜଗତ ହେଉଛି କର୍ମମୟ । ଏହି କର୍ମମୟ ଜଗତରେ ମାନବ ନିଜକୁ ଜଣେ ସଟ କର୍ମୀ ମନେକରି କର୍ମକୁ ଜୀବନର ମାନଦଣ୍ଡ ଭାବେ ଗ୍ରହଣ କରିବା ଉଚିତ ବୋଲି କହି କବୟିତ୍ରୀ କର୍ମର ଜୟଗାନ କରିଛନ୍ତି । କର୍ମରେ ନିମଜ୍ଜିତ ରହିଲେ ମନରୁ ନୈରାଶ୍ୟ ଓ ହତାଶାବୋଧ ଆପେ ଦୂରେଇଯିବ । ମାନସିକ ଗ୍ଳାନିର ବିସ୍କରଣ ପାଇଁ କର୍ମତତ୍ପର ଜୀବନ ହିଁ ପ୍ରକୃଷ୍ଟ ମାର୍ଗ ବୋଲି କବୟିତ୍ରୀ କହିଛନ୍ତି ।
ନିଜକୁ ଅସହାୟ ମନେକରୁଥିବା ଚିର ନିଷ୍ପେଷିତ, ଲାଞ୍ଛିତ, ବଞ୍ଚିତ ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ ଯେତେବେଳେ ନିଜକୁ ଧ୍ବଂସ ପଥର ଯାତ୍ରୀ ବୋଲି ଚିନ୍ତାକରି ଆତ୍ମଗ୍ଳାନିରେ ମ୍ରିୟମାଣ ହୋଇପଡ଼ିଛି, ସେତେବେଳେ ମାନବିକ ଦରଦ ନେଇ ଭରିଦେବାକୁ କବି ମଣିଷ ଭାଇକୁ କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟ କର୍ମରେ ବୁଡ଼ି ରହିବାକୁ ଉପଦେଶ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି । ଅନନ୍ତ ମରଣ ଯେ ମାନବର ଶେଷଗତି ନୁହେଁ ଏହି ଭାବନାକୁ ମାନବ ହୃଦୟରେ ଭରିଦେବାକୁ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ଆପ୍ରାଣ ଉଦ୍ୟମ କରିଛନ୍ତି । ତାଙ୍କ ମତରେ ସବୁ ଲାଜ, ଭୟ, ଅପମାନ ଆଦି ମାନସିକ ଗ୍ଳାନିର ବିସ୍କରଣ ପାଇଁ ତାକୁ କର୍ମଯୋଗୀର ଜୀବନ ଆଦରି ନେବାକୁ ହେବ ।
ମନରେ ଅହମିକା ପୋଷଣ କରି କ୍ରୋଧ ଓ ପ୍ରତିଶୋଧପରାୟଣ ହେବା ପଶୁତ୍ଵର ପରିଚାୟକ । ଅପରନ୍ତୁ ଜୀବନର ସବୁ ମାନ-ଅପମାନ, ଲଜ୍ଜା-ଭୟ, ଅଶ୍ରୁ-ଅଭିଳାଷ, ହା-ହତାଶ, ଦୁଃଖ – ଅବସୋସକୁ ବିଭୁଙ୍କ ପଦାରବିନ୍ଦରେ ସମର୍ପଣ କରିଦେଇ ପରମେଶ୍ଵରଙ୍କ କର୍ମମୟ ସଂସାରରେ କେବଳ କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟ ସମ୍ପାଦନରେ ବ୍ରତୀ ହେବା ହିଁ ମାନବିକତାର ପରିଚାୟକ । ଫଳପ୍ରାପ୍ତିରେ ଆଶା ନ ରଖ୍ କର୍ମରେ ଲିପ୍ତ ହେବାରେ ଜୀବନର ସାର୍ଥକତା ବିଦ୍ୟମାନ ।
ତଦ୍ବାରା ହିଁ ଈଶ୍ଵରଙ୍କ ଇଚ୍ଛା ପୂର୍ଣ ହୋଇପାରିବ ଓ ମଣିଷ ପଶୁତ୍ଵ- ଦେବତ୍ଵର ଭୀଷଣ ପରୀକ୍ଷାରେ ସସମ୍ମାନେ ଉତ୍ତୀର୍ଣ୍ଣ ହୋଇ ମାନବିକ ମୂଲ୍ୟବୋଧର ବିଜୟ ବୈଜୟନ୍ତୀ ଉଡ଼ାଇ ପାରିବ । ପରମେଶ୍ଵର ମଧ୍ଯ ତାଙ୍କ ସୃଷ୍ଟିର ସାର୍ଥକତାରେ ଚିରସନ୍ତୁଷ୍ଟ ହୋଇ ମାନବ ଜାତି ନିକଟରେ ଚିର ଋଣୀ ରହିବେ । ତେଣୁ ତାଙ୍କ ରଚିତ ଅନୁପମ ସୃଷ୍ଟିକୁ ସୁନ୍ଦରତର କରିବାପାଇଁ ମଣିଷ ଭାଇ ନିଜକୁ ଉତ୍ସର୍ଗ କରୁ ବୋଲି କବୟିତ୍ରୀ କାମନା କରିଛନ୍ତି । କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ଭାଷାରେ –
‘‘ପଶୁତ୍ବ ଦେବତ୍ୱ ପରୀକ୍ଷାରେ ଜୟୀ ଲଭ ବୀରତ୍ଵର ଟୀକା
ଋଣୀ କର ଭବରାଣେ
ତା’ଙ୍କ ରଚା ଚରାଚର ପରାଣରେ ବଳି ଦିଅ ନିଜ ପ୍ରାଣେ ।’’
ବୁଦ୍ଧି ଓ ବିବେକର ଅଧିକାରୀ ମାନବ ହିଁ ବିଧାତାଙ୍କ ସୃଷ୍ଟିରେ ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ ପ୍ରାଣୀ । ତା’ ଜୀବନର ଚିର ଶତ୍ରୁ କାମ, କ୍ରୋଧ, ଲୋଭ, ମୋହ, ମଦ, ମାତ୍ସର୍ଯ୍ୟକୁ ଦୃଢ଼ତାର ସହ ଦମନ କଲେ ହିଁ ସେ ଜୀବନର ସାର୍ଥକତା ପ୍ରତିପାଦନ କରିପାରେ ଓ ତା’ ଜୀବନ ଧନ୍ୟ ହୁଏ । ଶତ୍ରୁଞ୍ଜୟ ଜୀବନ ତା’ର ଦିବ୍ୟତାରେ ଭରିଉଠେ, ଶାଶ୍ବତ ଜ୍ଞାନରେ ମାନବାତ୍ମା ତା’ର ଦୀପ୍ତିମନ୍ତ ହୋଇଉଠେ । ତା’ର ପ୍ରତିଟି କର୍ମରେ ସେ ଅନୁଭବ କରେ ଈଶ୍ବରସତ୍ତା । ସାତ୍ତ୍ଵିକ ଜୀବନାଦର୍ଶକୁ ପାଥେୟ କରୁଥିବା ମାନବାତ୍ମା ପରିଣତ ହୁଏ ଦିବ୍ୟାତ୍ମାରେ । ମୃତ୍ୟୁ ପରେ ସେହି ଜୀବାତ୍ମା ଅନନ୍ତ ଗଗନରେ ସୁଦୀପ୍ତ ତାରକାର ଆସନ ଅଳଙ୍କୃତ କରେ । କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ମତରେ –
‘ଶୁଣ ଶୁଣ ଅରିନ୍ଦମ ! ଷଡ଼ରିପୁଜିତ, ଦେବତା ପୂଜିତ
ତାରାଦଳେ ତବାସନ ।’’
କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ମତରେ ମାନବ ହେଉଛି ବିଧାତାର ବରପୁତ୍ର । ତେଣୁ କୌଣସି ପରିସ୍ଥିତିରେ ସେ ନିଜକୁ ପରାଜିତ ମନେକରିବା ଅନୁଚିତ୍ । ଜୀବନ ଯୁଦ୍ଧରେ କ୍ଷତାକ୍ତ ହୋଇଗଲେ ମଧ୍ଯ ସାହସ ଓ ବିକ୍ରମ ସହ ଶତ୍ରୁର ମୁକାବିଲା କରିବା ହେଉଛି ବୀରୋଚିତ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ । ସାମାନ୍ୟ ରକ୍ତପାତରେ ସେ ନିଜକୁ କ୍ଷୀଣ ବା ଦୁର୍ବଳ ମନେକରିବା ଅନୁଚିତ । କଳୁଷିତ ଜୀବନର କଳଙ୍କ କାଳିମାରେ ଦୀନହୀନ ହୋଇଯାଏ ନାହିଁ । ଦେବତ୍ୱର ମହିମାରେ ଦୀପ୍ତିମନ୍ତ ହୋଇ ତା’ର ପୁନରୁତ୍ଥାନ ଅବଶ୍ୟ ଘଟିଥାଏ ।
![]()
କାରଣ ବିଶ୍ଵନିୟନ୍ତା ପରମେଶ୍ଵର ତାଙ୍କ ଅମୃତମୟ ସୃଷ୍ଟିର ଅଭିନବ ବିକାଶ ଦର୍ଶନରେ ତୃପ୍ତ ହୁଅନ୍ତି । ତେଣୁ ମଣିଷ ଜୀବନର ସମସ୍ତ ବିଷାଦ, ବ୍ୟର୍ଥତା, ଦୁଃଖ, କାତରତା ତଥା ଯାବତୀୟ ହୀନମନ୍ୟତାକୁ ଧୋଇଦେଇ କ୍ଷତାକ୍ତ ଶରୀରକୁ ତାଙ୍କ ସୁଧାସ୍ପର୍ଶରେ ନବ ରୂପ ପ୍ରଦାନପୂର୍ବକ ତାକୁ ଅମୃତପିପାସୀ କରାଇବେ । ତେଣୁ ଭାଗ୍ୟବାଦୀ ମୃତ୍ୟୁକାମୀ ମାନବ ନିଜ ମନରୁ ଅସହାୟବୋଧତାକୁ ପରିହାର କରି ଜୀବନ ସୂତ୍ର ଧାରଣରେ ବ୍ରତୀ ହେବାକୁ କବୟିତ୍ରୀ ଆହ୍ବାନ ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି । କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ଆୟୋପଲବ୍ଧି ଓ ଜୀବନ ଦର୍ଶନ ଯେ ଗଭୀର ଆଶାବାଦିତାର ଉଜ୍ଜ୍ବଳ ମୟୂଖରେ ଚିର ଦୀପ୍ତିମାନ, ଆଲୋଚ୍ୟ କବିତାରୁ ତାହା ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ପରିଦୃଷ୍ଟ ହୁଏ । ଆବେଗଧର୍ମୀ ପ୍ରାଣବନ୍ତ ଭାଷାବିନ୍ୟାସ କବୟିତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ଭାବୋଚ୍ଛାସକୁ ଅଧିକ ଜୀବନ୍ତ କରିଛି ଏଥରେ ଦ୍ବିମତ ନାହିଁ ।
ବିଷୟଗତ ଶବ୍ଦ ଓ ଅର୍ଥ :
- ଝୁରି ମରିବା – ଶୋକ କରିବା / ଗୁଣ ସ୍ମରଣ କରି ଦୁଃଖ
- ନିରାଶେ – ଦୁଃଖରେ / ଆଶାଶୂନ୍ୟ ଭାବରେ ।
- ଲାଞ୍ଛିତ – ଅପମାନିତ ।
- ପୀଡ଼ିତ – ରୋଗଗ୍ରସ୍ତ / ଦୁଃଖୁତ ।
- କାରାରେ – ବନ୍ଦୀଶାଳରେ / ଜେଲଖାନାରେ ।
- ଧ୍ୱଂସର ଯାତ୍ର। – ନଷ୍ଟ ପଥର ପଥୁ ।
- ବିଶାଳ ଜଗତ – ବିରାଟ ପୄଥ୍କ
- ସନ୍ତ।ନ – ପୁତ୍ର ।
- ବିଳାସ – ସୁଖ ଭୋଗ ।
- ବିଶ୍ୱ – ପୃଥିବୀ ।
- କୂ୍ର – ନିଷ୍ଠୁର ।
- ଦଳିବ – ଚାପିଦେବା, ଦମନ କରିବା ।
- ରକ୍ତପିପାସା – ରକ୍ତତୃଷ୍ଣା ।
- ନତଶିରେ – ମଥା ନୁଆଇଁ ।
- ବଧ୍ବ – ମାରିବ ।
- ଭୁବନ – ଘର ।
- ଦେବ ତେଜେ – ପରାକ୍ରମରେ
- ଅହମିକା – ଅହଂଭାବ / ଗର୍ବ ।
- ଦେବତ୍ୱ – ଦେବଭାବ ସ୍ବଭାବ ।
- ଭବଗ।ଣ – ଈଶ୍ବର, ଭଗବାନ୍ ।
- ରଚା – ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହୋଇଥବା, ରଚିତ ହୋଇଥିବା ।
- ଚର।ଚର – ସାରା ସଂସାର ।
- ଅରିଦମ – ଶତ୍ରୁ ଦମନକାରୀ ।
- ପ୍ର।ଣ – ଜୀବନ ।
- ଷଡ଼ରିପୁ – କାମ, କ୍ରୋଧ, ଲୋଭ, ମୋହ, ମଦ, ମାସ୍କର୍ଯ୍ୟ ପ୍ରଭୃତି ମାନବର ଛଅଗୋଟି ଶତ୍ରୁ ।
- ତବାସନ – ତୁମରି ଆସନ ବା ସ୍ଥାନ ।
- ଶୋଣିତ ଶ୍ରାବ – ରକ୍ତଧାର
- ହତଶ୍ୱ।ସେ- ହତାଶ ଭାବରେ ।
- ନିବିଡ଼ – ଘନ ।
- ବୟତି – ବାଦ୍ ଯିବା, ଅପ୍ରାପ୍ତି ।
- କଷଣ – କଷ୍ଟ ।
- ନିୟତି – ଭାଗ୍ୟ ।
- ମୃତ୍ୟୁର ଧାତ୍ରୀ – ମରଣର ସହଚରୀ ।
- ଅମୃତ ଦୀପ୍ତି – ଅମୃତର ତେଜ, ଜ୍ୟୋତି, ଉଜ୍ଜ୍ବଳତା ।
- ନର-ନାରୀ – ପୁରୁଷ -ସ୍ତ୍ରୀ ।
- ନିକେତନ – ଗୃହ ।
- ସତତ – ସବୁବେଳ ପାଇଁ ।
- ଅତ୍ୟ।ଚାର – ଅମାନୁଷିକ ଆଚରଣ ।
- ଦୁର୍ବଳେ – ବଳହୀନରେ ।
- ଶମିବ – ଶାନ୍ତ ହେବ ।
- ଅରପି – ଅର୍ପଣ କରି ।
- ବିଧାତା ବିଚାର – ନିୟତିର ବିଚାର ବା ଇଚ୍ଛା ।
- ବିଶ୍ୱବାସୀ- ପୃଥିବୀର ଜୀବଗଣ ।
- ଶ୍ରମ – ପରିଶ୍ରମ ।
- ଶୌର୍ଯ୍ୟ – ଶକ୍ତି, ବୀରତ୍ଵ।
- ପଶୁତ୍ୱ – ପଶୁବୃତ୍ତି ବା ସ୍ଵଭାବ ।
- ପୀକା – ସଙ୍କେତ, ଚିତା
- ପରାଣେ – ପ୍ରାଣରେ ।
- ବଳିଦିଅ – ଉତ୍ସର୍ଗ କରିବା ।
- କ୍ଷତଶିରେ – ଖଣ୍ତିଆ ମଥାରେ
- କ୍ଳୀଷ୍ନ – ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣାପୀଡ଼ିତ, କ୍ଳେଶଜର୍ଜରିତ
- କ୍ଷୀଣ – କମିଯିବା, ପତଳା ହେବା ।
- କଳଙ୍କ – ଅପଯଶ
- ଦୀନ – ଦରିଦ୍ର (ଏଠାରେ ଦୈନ୍ୟ -ନିକୃଷ୍ଟ) ।
- ଯୁଗ।ନ୍ତ – ଯୁଗ ଯୁଗ ଧରି ।
- ଛିଣ୍ଡ।ଇ – ନଷ୍ଟ କରି ।
- କଳୁଷ – ପାପ ।
- ହୀନ – ସାନ ।
- ବିଧାତାର ବରପୁତ୍ର – ଈଶ୍ବରଙ୍କ ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ ସନ୍ତାନ ।
- ମୃତୁ୍ୟରତୁ – ମରଣର ଡୋରି ।
- ଜୀବନସୂତ୍ର – ବଞ୍ଝାର ଡୋର ।
- ନିୟତି – ଭାଗ୍ୟ ।
- ଧାତ୍ରି – ଧାଈ / ଉପମାତା ।
- ଜଗତୀ – ଅଟ୍ଟାଳିକା / ଭବନ । (ଏଠାରେ ଏ ଶବ୍ଦଟି ପୃଥିବୀ ଅର୍ଥରେ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହୋଇଛି ।)
- ଦୀପ୍ତି – ତେଜ ।
- ପିପ।ସା – ପିଇବାର ଇଚ୍ଛା/ଶୋଷ ।
- ନତ – ନଇଁବା ।
- ଭବରାଣ – ଈଶ୍ବର ।
- ଯୁଗ।ନ୍ତ – ଯୁଗର ଅନ୍ତ ।
- ରଜୁ – ଦଉଡ଼ି ।
- ଶୃଙ୍ଖଳିତ – ଶୃଙ୍ଖଳରେ ବନ୍ଦୀ ।
- ଶୋଣିତ – ରକ୍ତ ।
- ନିରାଶେ – ଆଶାଶୂନ୍ୟ ଭାବରେ ।
- ପୀଡ଼ିତ – ରୋଗଗ୍ରସ୍ତ, ଦୁଃଖ୍