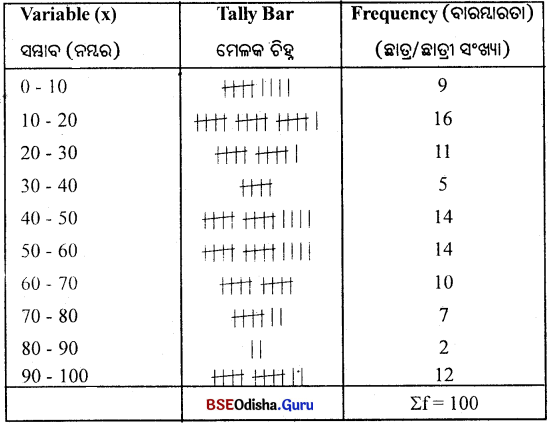
Odisha State Board CHSE Odisha Class 11 Economics Solutions Unit 6 ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ Questions and Answers.
CHSE Odisha 11th Class Economics Unit 6 Question Answer ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ
I. ନିମ୍ନୋକ୍ତ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନଗୁଡ଼ିକର ଉତ୍ତର ପ୍ରଦତ୍ତ ବିକଳ୍ପଗୁଡ଼ିକ ମଧ୍ୟରୁ ଚୟନ କର।
[Choose the Correct answer of the followings from the alternatives as given]
Question ୧।
କେଉଁ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ପଦ୍ଧତିରେ ଗୋଟିଏ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱସୀମା ତା ର ଠିକ୍ ପରବର୍ତୀ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ନିମ୍ନସୀମା ହୋଇଥାଏ ?
(A) ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ପଦ୍ଧତି
(B) ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ପଦ୍ଧତି
(C) ଉଭୟ (A) ଓ (B)
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ କୌଣସିଟି ନ ନୁହେଁ
Answer:
(A) ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ପଦ୍ଧତ
Question ୨।
ଗୋଟିଏ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ମଧ୍ୟବିନ୍ଦୁର ମୂଲ୍ୟ କେତେ ହେବା ଉଚିତ୍ ?
(A) 5
(B) 10
(C) 5 ଦ୍ବାରା ଛିଣ୍ଡଥୁବା ସଂଖ୍ୟା
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ ସମସ୍ତ
Answer:
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ ସମସ୍ତ
Question ୩।
ନିମ୍ନଲିଖୂତ ମଧ୍ୟରୁ କେଉଁଟି ବିବିକ୍ତ ଚଳର ବୈଶିଷ୍ଟ ?
(A) ସମସ୍ତ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ଧାରଣା କରିପାରେ
(B) ସମସ୍ତ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଅଟେ
(C) ଦୁଇଟି ମୂଲ୍ୟ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ବ୍ୟବଧାନ ଥାଏ
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ ସମସ୍ତ
Answer:
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ ସମସ୍ତ
Question ୪।
ଗୋଟିଏ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ବ ସୀମା ଓ ନିମ୍ନ ସୀମାର ଅନ୍ତର ଫଳକୁ କ’ଣ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
(A) ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ସଂଖ୍ୟା
(B) ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଅନ୍ତରାଳ
(C) ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ବିସ୍ତାର
(D) ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ମଧ୍ୟବିନ୍ଦୁ
Answer:
(B) ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଅନ୍ତରାଳ
![]()
Question ୫।
20 – 30 ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ମଧ୍ୟବିନ୍ଦୁର ମୂଲ୍ୟ କେତେ ?
(A) 5
(B) 10
(C) 15
(D) 25
Answer:
(D) 25
Question ୬।
50 -60 ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଅନ୍ତରାଳ (Class Interval) କେତେ ?
(A) 10
(B) 5
(C) 20
(D) 6
Answer:
(A) 10
Question ୭.।
ଗୋଟିଏ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଅନ୍ତରାଳର ମୂଲ୍ୟ କେତେ ହେବା ଉଚିତ୍ ?
(A) 0
(B) 5
(C) ପାଞ୍ଚ ଦ୍ବାରା ଛିଷ୍ଣୁଥିବା ସଂଖ୍ୟା
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ ସମସ୍ତ
Answer:
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ ସମସ୍ତ
Question ୮।
ନିମ୍ନଲିଖୂତ ମଧ୍ୟରୁ କେଉଁଟି ଗୋଟିଏ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳର ବୈଶିଷ୍ଟ୍ୟ ?
(A) ସମସ୍ତ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ଧାରଣ କରିପାରେ
(B) ଦୁଇଟି ଚଳ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ବ୍ୟବଧାନ ନ ଥାଏ
(C) ଉଭୟ (A) ଓ (B)
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ କୌଣସିଟି ନୁହେଁ
Answer:
(C) ଉଭୟ (A) ଓ (B)
Question ୯।
20 – 30 ଶ୍ରେଣୀର 20 ର ମୂଲ୍ୟକୁ କ’ଣ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
(A) ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱସୀମା
(B) ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଅନ୍ତରାଳ
(C) ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ନିମ୍ନସୀମା
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ ସମସ୍ତ
Answer:
(C) ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ନିମ୍ନସୀମା
Question ୧୦।
ଗୋଟିଏ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱସୀମା 40 ଏବଂ ନିମ୍ନସୀମା 30 ତେବେ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ମଧ୍ୟବିନ୍ଦୁର ମୂଲ୍ୟ କେତେ ହେବ ?
(A) 15
(B) 25
(C) 35
(D) 4
Answer:
(C) 35
![]()
Question ୧୧।
ବିସ୍ତାର ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଥିବା ସମସ୍ତ ମୂଲ୍ୟକୁ ଧାରଣ କରୁ ନ ଥିବା ବିତରଣ ହେଉଛି
(A) ବିବିକ୍ତ ବିତରଣ
(B) ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବିତରଣ
(C) ଏକକ ବିତରଣ
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ ସମସ୍ତ
Answer:
(A) ବିବିକ୍ତ ବିତରଣ
Question ୧୨।
କୌଣସି ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱସୀମା ଜିମ୍ବା ନିମ୍ନସୀମା ଦିଆଯାଇ ନଥୁଲେ ତାହାକୁ କ’ଣ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
(A) ମୁକ୍ତ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ
(C) ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ
(B) ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ ସମସ୍ତ
Answer:
(A) ମୁକ୍ତ ସଂଭାଗ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ
Question ୧୩।
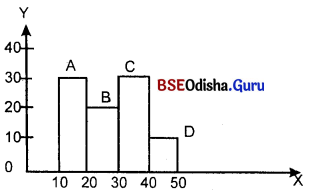
ଅଙ୍କିତ ହୋଇଥିବା ସମସ୍ତ ଆୟତକ୍ଷେତ୍ରର ସମାହାରକୁ କ’ଣ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
(A) ହିଷ୍ଟୋଗ୍ରାମ୍
(B) ସମୟାନୁକ୍ରମୀ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଲେଖ
(C) ରାଶୀକୃତ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ ସମସ୍ତ
Answer:
(A) ହିଷ୍ଟୋଗ୍ରାମ୍
Question ୧୪।
ନିମ୍ନୋକ୍ତ ମଧ୍ଯରୁ କେଉଁଟି ସାରଣୀର ଅଂଶ ?
(A) ସାରଣୀର ସଂଖ୍ୟା
(B) ସାରଣୀର ଶୀର୍ଷକ
(C) ଶିରୋନାମା
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ ସମସ୍ତ
Answer:
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ ସମସ୍ତ
Question ୧୫।
ଗୋଟିଏ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ଚିତ୍ରରେ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭଗୁଡ଼ିକର ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁ :
(A) ସମାନ
(B) ଅସମାନ
(C) ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନୀୟ
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ କୌଣସିଟି ନୁହେଁ
Answer:
(A) ସମାନ
![]()
Question ୧୬।
ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା ଅଧିକ ଓଜିଭ ଏକ :
(A) ନିମ୍ନଗାମୀ ବକ୍ରରେଖା
(B) ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱଗାମୀ ବକ୍ରରେଖା
(C) ଉଲୁମ୍ବ ରେଖା
(D) ଅନୁଭୂମିକ ରେଖା
Answer:
(A) ନିମ୍ନଗାମୀ ବକ୍ରରେଖା
Question ୧୭।
ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା କମ୍ ରାଶୀକୃତ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ଏକ :
(A) ନିମ୍ନଗାମୀ ବକ୍ର
(B) ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱଗାମୀ ରେଖା
(C) ଉଲୁମ୍ବ ରେଖା
(D) ଆନୁଭୂମିକ ରେଖା
Answer:
(B) ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱଗାମୀ ରେଖା
Question ୧୮।
ସମସ୍ତ ବୃତ୍ତକାଳର କେନ୍ଦ୍ରୀୟ କୋଣମାନଙ୍କର ସମଷ୍ଟି କେତେ ହେବ ?
(A) 360°
(B) 90°
(C) 180°
(D) 60°
Answer:
(A) 360°
Question ୧୯।
ତଥ୍ୟ ପରିପ୍ରକାଶର ଏକ ସରଳ ଓ ଯୁକ୍ତିଯୁକ୍ତ ମାଧ୍ଯମ ହେଲା :
(A) ସାରଣୀ
(B) ରେଖାଚିତ୍ର
(C) ଗ୍ରାଫ୍
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ ସମସ୍ତ
Answer:
(A) ସାରଣୀ
Question ୨୦।
ନିମ୍ନୋକ୍ତ ମଧ୍ୟରୁ କେଉଁଟି ଲେଖଚିତ୍ର ବିଷୟରେ ସଠିକ୍ ସୂଚନା ?
(A) ହାରାହାରି କଳନା
(B) ବିଶ୍ଳେଷଣ ଖୁବ୍ କମ୍ ସମୟରେ କରିହୁଏ
(C) ସବୁ ବର୍ଗର ପର୍ଯ୍ୟବେକ୍ଷକଙ୍କ ଦ୍ଵାରା ଆଦୃତ
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ ସମସ୍ତଟି
Answer:
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ ସମସ୍ତଟି
![]()
Question ୨୧।
ନିମ୍ନଲିଖୁତ ମଧ୍ୟରୁ କେଉଁଟି ସାରଣୀ ବିଷୟରେ ସଠିକ୍ ତଥ୍ୟ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ତଥ୍ୟର ସାଂଖ୍ୟକ ପରିପ୍ରକାଶ
(B) ଏକାଧିକ ତଥ୍ୟ ପ୍ରଦାନ କରାଯାଇପାରେ
(C) ବିଶ୍ଳେଷଣ ସହଜ ସାଧ୍ଯ ଅଟେ
(D) ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ ବର୍ଗର ପର୍ଯ୍ୟବେକ୍ଷକଙ୍କ ଦ୍ବାରା ଆଦୃତ
Answer:
(C) ବିଶ୍ଳେଷଣ ସହଜ ସାଧ୍ୟ ଅଟେ
Question ୨୨।
ତଥ୍ୟ ପରିପ୍ରକାଶର ଏକ ସରଳ ଓ ଯୁକ୍ତି ଯୁକ୍ତ ମାଧ୍ୟମ ହେଲା :
(A) ସାରଣୀ
(B) ରେଖାଚିତ୍ର
(C) ଗ୍ରାଫ୍
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ ସମସ୍ତ
Answer:
(A) ସାରଣୀ
Question ୨୩ ।
ପଂକ୍ତି ଓ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ଆକାରରେ ସଂଗୃହୀତ ତଥ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ଯେଉଁଥରେ ସଜାଡ଼ି ଲେଖାଯାଏ, ତାହାକୁ କ’ଣ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
(A) ରେଖାଚିତ୍ର
(B) ଗ୍ରାଫ୍
(C) ସାରଣୀ
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ କୌଣସିଟି ନୁହେଁ
Answer:
(C) ସାରଣୀ
Question ୨୪।
ଯେଉଁଥିରେ ତଥ୍ୟକୁ ପଂକ୍ତି ଓ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ଆକାରରେ ପ୍ରକାଶ କରାଯାଏ, ତାହାକୁ କ’ଣ କୁହାଯାଏ?
(A) ସାରଣୀ
(B) ଲେଖଚିତ୍ର
(C) ବିସ୍ତାର
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ ସମସ୍ତ
Answer:
(A) ସାରଣୀ
Question ୨୫।
ବୃତ୍ତ କଳାର କେନ୍ଦ୍ରୀୟ କୋଣ ନିର୍ଦ୍ଧାରଣ ପଦ୍ଧତି ଲେଖ।

Answer:

![]()
Question ୨୬।
ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭର :
(A) ପ୍ରସୁ ସମାନ
(B) ଦୈର୍ଘ୍ୟ ସମାନ
(C) ଉଚ୍ଚତା ସମାନ
(D) ସମସ୍ତଟି
Answer:
(A) ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁ ସମାନ
Question ୨୭।
କେତେକ ଆୟାତକ୍ଷେତ୍ରର ସମାହାର :
(A) ହିଷ୍ଟୋଗ୍ରାମ୍
(B) ସ୍ତମ୍ଭଚିତ୍ର
(C) ବୃତ୍ତଚିତ୍ର
(D) ସମସ୍ତବି
Answer:
(A) ହିଷ୍ଟୋଗ୍ରାମ୍
Question ୨୮।
ସାରଣୀର ଅଂଶ ନୁହେଁ :
(A) ସାରଣୀ ସଂଖ୍ୟା
(B) ବାରମ୍ବାରତା
(C) ଶିରୋନାମା
(D) ସମସ୍ତଟି
Answer:
(B) ବାରମ୍ବାରତା
Question ୨୯।
ଗୋଟିଏ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକ୍ତ ଲବ୍ଧାଙ୍କ ସଂଖ୍ୟାକୁ କ’ଣ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
(A) ବାରମ୍ବାରତା
(B) ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା
(C) ଚଳ
(D) ସମସ୍ତଟି
Answer:
(B) ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା
Question ୩୦।
୨୦-୩୦ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଅନ୍ତରାଳ କେତେ?
(A) ୧୦
(B) ୭୦
(C) ୫୦
(D) ୫
Answer:
(A) ୧୦
Question ୩୧।
୫୦ – ୬୦ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ମଧ୍ୟବିନ୍ଦୁ କେତେ ହେବ ?
(A) ୫୫
(C) ୪୫
(B) ୬୫
(D) ୭୫
Answer:
(A) ୫୫
Question ୩୨।
ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳର ଉଦାହରଣ :
(A) ପରୀକ୍ଷାରେ ନମ୍ବର
(B) ଶ୍ରମିକମାନଙ୍କର ମଜୁରି
(C) ଉଭୟ (A) ଓ (B)
(D) କୌଣସିଟି ନୁହେଁ
Answer:
(C) ଉଭୟ (A) ଓ (B)
Question ୩୩।
କେଉଁ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ପ୍ରଥମ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱସୀମା ପରବର୍ତି ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ନିମ୍ନ ସୀମାରେ ମିଶିଥାଏ ?
(A) ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ
(C) ବାରମ୍ବାରତା
(B) ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ
(D) ସମସ୍ତଟି
Answer:
(A) ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ
Question ୩୪।
ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳର ଉଦାହରଣ :
(A) ଶ୍ରମିକମାନଙ୍କର ମଜୁରି
(B) କୋଠରୀର ସଂଖ୍ୟା
(C) ପରୀକ୍ଷାର ନମ୍ବର
(D) ସମସ୍ତଟି
Answer:
(B) କୋଠରୀର ସଂଖ୍ୟା
![]()
Question ୩୫।
କେଉଁ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ଉଭୟ ପୂର୍ବ ସଂଖ୍ୟା ଓ ଦଶମିକ ସଂଖ୍ୟା ରେଖାଯାଏ ?
(A) ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ
(B) ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳ
(C) ପ୍ରାଥମିକ ତଥ୍ୟ
(D) ସମସ୍ତଟି
Answer:
(A) ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ
Question ୩୬।
୧୫-୨୦ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ମଧ୍ୟବିନ୍ଦୁ :
(A) ୧୭.୫
(B) ୧୫
(C) ୨୦
(D) ୧୮,୫
Answer:
(A) ୧୭.୫
Question ୩।
ଯଦି ଗୋଟିଏ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ନିମ୍ନ ସୀମା କିମ୍ବା ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱସୀମା ନ ଦିଆଯାଏ, ତେବେ ତାହାଙ୍କୁ କ’ଣ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
(A) ମୁକ୍ତ ସମ୍ବାର ଶ୍ରେଣୀ
(B) ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ସେବା
(C) ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ
(D) ସମସ୍ତଟି
Answer:
(A) ମୁକ୍ତ ସମ୍ବାଗ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ
Question ୩୯।
ବିସ୍ତାର ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଥିବା ସମସ୍ତ ମୂଲ୍ୟକୁ ଧାରଣ କରିପାରୁଥିବା ବିତରଣକୁ କ’ଣ କହନ୍ତି ?
(A) ବିବିକ୍ତ ବିତରଣ
(B) ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବିତରଣ
(C) ଏକକ ବିତରଣ
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ କେଉଁଟି ବି ନୁହେଁ
Answer:
(A) ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବିତରଣ
Question ୪୦।
ଗୋଟିଏ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱସୀମା ଓ ନିମ୍ନ ସୀମାର ଅନ୍ତର ଫଳକୁ କ’ଣ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
(A) ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ସଂଖ୍ୟା
(C) ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଅନ୍ତରାଳ
Answer:
(C) ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଅନ୍ତରାଳ
Answer: ୪୧।
ଯଦି ଗୋଟିଏ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ (10-20) ଏହି ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ମଧ୍ୟବିନ୍ଦୁ କେତେ ହେବ ?
(A) 15
(B) 2
(C) 5
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ କେଉଁଟି ନୁହେଁ
Answer:
(A)15
(B) ଶ୍ରେଣୀସୀମା
(D) ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ମଧ୍ୟବିନ୍ଦୁ
Question ୫୦।
ବିସ୍ତାର ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଥିବା ସମସ୍ତ ମୂଲ୍ୟକୁ ଧାରଣ କରୁ ନଥିବା ବିତରଣ ହେଉଛି ?
(A) ବିବିକ୍ତ ବିତରଣ
(B) ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବିତରଣ
(C) ଏକକ ବିତରଣ
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ କେଉଁଟି ନୁହେଁ
Answer:
(A) ବିବିକ୍ତ ବିତରଣ
Question ୫୧।
ଯଦି ଏକ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ ମଧ୍ୟବିନ୍ଦୁଗୁଡ଼ିକ 5, 10, 15, 25 ଓ 25 ଏହାର ଶ୍ରେଣୀଗୁଡ଼ିକ କେତେ ହେବ ?
(A) 10-5,5-10, 10-15, 15-20
(B) 10-20, 20-30, 30-40, 40-50
(C) 0-10, 10-20, 20-30, 30-40
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ କୌଣସିଟି ନୁହେଁ
Answer:
(C) 0-10, 10-20, 20-30, 30-40
Question ୫୨।
ଯଦି ଏକ ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ବାରମ୍ବାରତା 100- 199, 200 299, 300- 399, 400-499, ସେଗୁଡ଼ିକ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ପ୍ରକାଶ କଲେ କେତେ ହେବ ?
(A) 100.5-200.5, 200.5-300.5, 300.5-400.5, 400.5-500.5
(B) 99.5-199.5, 199.5-299.5, 299.5-399.5, 499.5
(C) 100-200, 200-300, 300-400, 400-500.
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ କେଉଁଟି ନୁହେଁ
Answer:
(B) 99.5-199.5, 199.5-299.5, 299.5-399.5, 499.5
Question ୫୩।
ସମୟାନୁକ୍ରମରେ ଲବ୍ଧାଙ୍କମାନଙ୍କର ଉପସ୍ଥାପନ :
(A) ସମାନୁକ୍ରମିକ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ
(B) ଓଜିଭ
(C) ବିସ୍ତାର
(D) ସାରଣୀ
Answer:
(A) ସମାନୁକ୍ରମିକ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ
Question ୫୪।
ଯେଉଁ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ଚିତ୍ରରେ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭମାନଙ୍କର କ୍ଷେତ୍ରଫଳ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ସହ ସମାନୁପାତୀ ତାହା ?
(A) ଲେଖଚିତ୍ର
(B) ହିଷ୍ଟୋଗ୍ରାମ
(C) ଓଜିଭ୍
(D) ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବକୁ
Answer:
(B) ହିଷ୍ଟାଗ୍ରାମ
![]()
Question ୫୫।
ବୃତ୍ତଚିତ୍ର ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ଅଂଶ ବୃତ୍ତକଳାର କେନ୍ଦ୍ରୀୟ କୋଣମାନଙ୍କ ସହ –
(A) ସମାନ
(B) ଅସାମାନୁପାତୀ
(C) ସମାନୁପାତୀ
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ କେଉଁଟି ନୁହେଁ
Answer:
(C) ସମାନୁପାତୀ
Question ୫୬।
ସମୟାନୁକ୍ରମୀ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଲେଖର ଅନ୍ୟନାମ କ’ଣ ?
(A) ଓଜିଭ୍
(B) ସ୍ତମ୍ଭଚିତ୍ର
(C) ରେଖାଲେଖ
(D) ଉପରୋକ୍ତ କେଉଁଟି ନୁହେଁ
Answer:
(C) ରେଖାଲେଖି
Question ୫୭।
ନିମ୍ନୋକ୍ତ କେଉଁଟି ସାରଣୀ ଅଂଶ ବିଶେଷ ନୁହେଁ ?
(A) ଶୀର୍ଷଟୀକା
(B) ପଂକ୍ତିନାମା
(C) ଶିରୋନାମା
(D) ବିସ୍ତାର
Answer:
(D) ବିସ୍ତାର
Question ୫୮।
ନିମ୍ନୋକ୍ତ ମଧ୍ୟରେ କେଉଁଟି ମୁକ୍ତ ସଂଭାଗ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ :
![]()
(B) ୧୦-୨୦
(C) ୩୦- ୪୦
(D) ୧୫-୨୦
Answer:
![]()
Question ୫୯।
ପ୍ରାଥମିକ ତଥ୍ୟ :
(A) ସମୟ ସାପେକ୍ଷୀ ନୁହେଁ
(B) ଶ୍ରମଅପଚୟକାରୀ
(C) ବ୍ୟୟବହୁଳ ନୁହେଁ
(D) ସମସ୍ତଟି
II. ନିମ୍ନୋକ୍ତ ଉକ୍ତିଗୁଡ଼ିକର ସଠିକତା ପ୍ରମାଣ କର। ଆବଶ୍ୟକ ସ୍ଥଳେ ରେଖାଙ୍କିତ ଅଂଶଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ନ ବଦଳାଇ ଭ୍ରମ ସଂଶୋଧନ କର।
[Prove the correctness of the followings correct then if neces you that changing words underlined.]
Question ୧।
ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ତଥ୍ୟାବଳୀର ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନତା ଦର୍ଶାଇଥାଏ। .
Answer:
ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ତଥ୍ୟାବଳୀର ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନତା ଦର୍ଶାଇଥାଏ।
Question ୨।
ଏକ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳ ପ୍ରଦତ୍ତ ବିସ୍ତାର ମଧ୍ୟରେ ସମସ୍ତ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ଗ୍ରହଣ କରିପାରେ ନାହିଁ।
Answer:
ଏକ ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳ ପ୍ରଦତ୍ତ ବିସ୍ତାର ମଧ୍ୟରେ ସମସ୍ତ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ଗ୍ରହଣ କରିପାରେ ନାହିଁ।
Question ୩।
ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିବରଣରେ କୌଣସି ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକ୍ତ ଲବ୍ଧାଙ୍କଗୁଡ଼ିକର ସଂଖ୍ୟାକୁ ସେହି ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ଚଳ କୁହାଯାଏ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୪।
ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ପଦ୍ଧତିରେ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱସୀମା ସେହି ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକ୍ତ ହୋଇଥାଏ।
Answer:
ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ପଦ୍ଧତିରେ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱସୀମା ସେହି ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକ୍ତ ହୋଇଥାଏ।
Question ୫ ।
ଶ୍ରେଣୀମଧ୍ୟବିନ୍ଦୁ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ସୀମା ଦ୍ଵୟର ମାଧ୍ୟମାନ ଅଟେ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୬।
ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ବିସ୍ତାର ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ସୀମା ଦ୍ବୟର ସମଷ୍ଟି ଅଟେ।
Answer:
ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଅନ୍ତରାଳ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ସୀମା ଦ୍ଵୟର ଅନ୍ତରଫଳ ଅଟେ।
Question ୭।
ଆଧାର ସାରଣୀରେ ତଥ୍ୟର ତୁଳନାତ୍ମକ ଚିତ୍ର ପ୍ରଦାନ କରାଯାଏ।
Answer:
ବିଶ୍ଳେଷଣାତ୍ମକ ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ତୁଳନାତ୍ମକ ଚିତ୍ର ପ୍ରଦାନ କରାଯାଏ।
Question ୮।
ଶୀର୍ଷଟୀକା ସାରଣୀର ଶୀର୍ଷରେ ଥାଏ ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୯।
ହିଷ୍ଟୋଗ୍ରାମ ଅଙ୍କନ କରି ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦେଶକ ଲେଖଚିତ୍ର ଅଙ୍କନ କରାଯାଇପାରେ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୧୦।
ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା କମ୍ ଓଜିଭ୍ ଏକ ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱଗାମୀ ବଜ୍ର ଅଟେ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
![]()
Question ୧୧।
ବୃତ୍ତଚିତ୍ରର ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ଅଂଶ ବୃତ୍ତକଳାର କେନ୍ଦ୍ରୀୟ କୋଣ ସହିତ ସମାନୁପାତ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୧୨।
ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା କମ୍ ଓଜିଭ୍ ରେଖା ନିମ୍ନଗାମୀ ଗତି କରିଥାଏ।
Answer:
ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା କମ୍ ଓଜିଭ୍ ରେଖା ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱଗାମୀ କରିଥାଏ ।
Question ୧୩।
ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା ଅଧିକ ଓଜିଭରେ ନିମ୍ନଗାମୀ ଗତି କରିଥାଏ ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୧୪।
Histogram ଦୁଇ ଦିଗ ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ରେଖାଚିତ୍ର ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୧୫।
Bar Diagram ଏକ ଦିଗ ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ରେଖାଚିତ୍ର।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୧୬।
ସାରଣୀ ଜଟିଳ ତଥ୍ୟାବଳୀକୁ ସରଳୀକରଣ କରିଥାଏ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୧୭।
ଏକ ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳ ପ୍ରଦତ୍ତ ବିସ୍ତାର ମଧ୍ୟରେ ସମସ୍ତ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ଧାରଣ କରିଥାଏ।
Answer:
ଏକ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳ ପ୍ରଦତ୍ତ ବିସ୍ତାର ମଧ୍ୟରେ ସମସ୍ତ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ଧାରଣ କରିଥାଏ।
Question ୧୮।
ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକ୍ତ ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ଏବଂ ସର୍ବବୃହତ୍ ମୂଲ୍ୟକୁ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍ ସୀମା କୁହାଯାଏ ।
Question ୧୯।
ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱ ସୀମା ଓ ନିମ୍ନସୀମାର ଠିକ୍ ମଝିରେ ଥିବା ମୂଲ୍ୟ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ମଧ୍ୟବିନ୍ଦୁ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୨୦।
ଗୋଟିଏ ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକ୍ତ ଲବ୍ଧାଙ୍କ ସଂଖ୍ୟା ସେହି ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ବାରମ୍ବାରତା କୁହାଯାଏ ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
![]()
Question ୨୧।
ପଂକ୍ତି ଓ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ଆକାରରେ ସଂଗୃହିତ ତଥ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ଯେଉଁଥିରେ ସଜାଡ଼ି ଲେଖାଯାଏ, ତାହାକୁ ସାରଣୀ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୨୨।
ସାରଣୀ ସଂଖ୍ୟା ସାରଣୀରେ ଏକ ଅଂଶ ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୨୩।
ଗୋଟିଏ ରେଖଚିତ୍ରରେ ଅନେକ ତଥ୍ୟ ପ୍ରଦାନ କରାଯାଏ।
Answer:
ଗୋଟିଏ ରେଖାଚିତ୍ରରେ ଗୋଟିଏ ତଥ୍ୟ ପ୍ରଦାନ କରାଯାଏ।
Question ୨୪।
ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ମାନଙ୍କର ଦୈର୍ଘ୍ୟ ଓ ଲବ୍ଧଙ୍କ ପରସ୍ପର ସମାନୁପାତ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୨୫।
ହିଷ୍ଟୋଗ୍ରାମ୍ କେତେକ ଆୟତ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରର ସମାହାର।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୨୬।
ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ସାହାଯ୍ୟରେ ତଥ୍ୟାବଳୀକୁ ସଂକୁଚିତ କରି ଉପସ୍ଥାପନା କରାଯାଏ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୨୭।
ଯାହାର ମୂଲ୍ୟ ସ୍ଥିର ରହିଥାଏ ତାହାକୁ ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନଶୀଳ ଚଳ କୁହାଯାଏ।
Answer:
ଯାହାର ମୂଲ୍ୟ ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନ ହୋଇଥାଏ ତାହାକୁ ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନଶୀଳ ଚଳ କୁହାଯାଏ।
Question ୨୮।
ଏକ ବିବିକ୍ତ ଚଳ ବିସ୍ତାର ମଧ୍ୟରେ ସମସ୍ତ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ଧାରଣ କରିପାରେ।
Answer:
ଏକ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳ ବିସ୍ତାର ମଧ୍ଯରେ ସମସ୍ତ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ଧାରଣ କରିପାରେ।
Question ୨୯।
ଏକ ବିବିକ୍ତଚଳ ପ୍ରଦତ୍ତ ବିସ୍ତାରର ସମସ୍ତ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ଧାରଣ କରିପାରେ ନାହିଁ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୩୦।
ଗୋଟିଏ ଦପ୍ତରର କର୍ମଚାରୀ ସଂଖ୍ୟା ବିର୍ବିକ୍ତ ଚଳର ଉଦାହରଣ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
![]()
Question ୩୧।
ଉଚ୍ଚତା ବିବକ୍ତ ବଳର ଉଦାହରଣ।
Answer:
ଉଚ୍ଚତା ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳର ଉଦାହରଣ।
Question ୩୨।
ଏକ ବିବନ୍ତ ଚଳ ଦ୍ୱାରା ପର୍ଯ୍ୟବସିତ ବିତରଣକୁ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ କୁହାଯାଏ।
Answer:
ଏକ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳଦ୍ଵାରା ପର୍ଯ୍ୟବସିତ ବିତରଣକୁ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା କୁହାଯାଏ।
Question ୩୩।
ଗୋଟିଏ ବିବକ୍ତ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିଚରଣରେ ତଥ୍ୟାବଳୀକୁ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଓ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ଦ୍ଵାରା ଉପସ୍ଥାପନ କରାଯାଏ।
Answer:
ଗୋଟିଏ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣରେ ତଥ୍ୟାବଳୀକୁ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଓ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ଉପସ୍ଥାପନ କରାଯାଏ।
Question ୩୪।
ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱସୀମା – ନିମ୍ନସୀମା = ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ମଧ୍ୟବିନ୍ଦୁ।
Answer:
ଉଦ୍ଧସୀମା – ନିମ୍ନ ସୀମା = ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଅନ୍ତରାଳ
Question ୩୫।
ଗୋଟିଏ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ମଧ୍ୟବିନ୍ଦୁ ଶ୍ରେଣୀକୁ ପ୍ରତିନିଧୁଗ୍ଧ କରେ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୩୬।
ଗୋଟିଏ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଊର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱସୀମା ଓ ନିମ୍ନସୀମାର ଠିକ୍ ମଝିରେ ଥିବା
Answer:
ଗୋଟିଏ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱସୀମା ଓ ନିମ୍ନସୀମାର ଠିକ୍ ମଝିରେ ଥିବା ମୂଲ୍ୟକୁ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଅନ୍ତରାଳ କୁହାଯାଏ। ମୂଲ୍ୟକୁ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ମଧ୍ୟବିନ୍ଦୁ କୁହାଯାଏ।
Question ୩୭।
ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ପଦ୍ଧତିରେ ଗୋଟିଏ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱସୀମା ତାର ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ନିମ୍ନ ସୀମା ହୋଇଥାଏ।
Answer:
ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ପଦ୍ଧତିକର ଗୋଟିଏ ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱସୀମା ସେହି ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକ୍ତ ହୋଇଥାଏ।
Question ୩୮।
ଗୋଟିଏ ବିତରଣର ଚଳର ମୂଲ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକ ବାମପାର୍ଶ୍ବରେ ସୂଚିତ କରାଯାଏ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୩୯।
ଗୋଟିଏ ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ମଧ୍ୟନ୍ତରର ମୂଲ୍ୟ ୦, ୫ କିମ୍ବା ୫ ଦ୍ବାରା ଛିଷ୍ଣୁଥିବା ଯେକୌଣସି ସଂଖ୍ୟା ହେବା ଉଚିତ୍।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୪୦।
ଗୋଟିଏ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ ପ୍ରଥମ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ନିମ୍ନସୀମାର ମୂଲ୍ୟ ୧ କିମ୍ବା ୫ ଦ୍ଵାରା ଛିଷ୍ଣୁଥିବା ସଂଖ୍ୟା ହେବା ଉଚିତ୍।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
![]()
Question ୪୧।
ମୁକ୍ତ ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ଉଭୟ ନିମ୍ନସୀମା ଓ ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱସୀମା ଦିଆଯାଇଥାଏ।
Answer:
ମୁକ୍ତ ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ନିମ୍ନସୀମା କିମ୍ବା ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱସୀମା ଦିଆଯାଇନଥାଏ।
Question ୪୨।
ସ୍ତମ୍ଭମାନଙ୍କର ଦୈର୍ଘ୍ୟ ଓ ଲଛାଙ୍କ ପରସ୍ପର ସମାନୁପାତ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍.
Question ୪୩।
ସମସ୍ତ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭମାନଙ୍କ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ବ୍ୟବଧାନ ସମାନ ରଖାଯାଏ ନାହିଁ।
Answer:
ସମସ୍ତ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭମାନଙ୍କ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ବ୍ୟବଧାନ ସମାନ ରଖାଯାଏ।
Question ୪୪।
ରେଖାଚିତ୍ର ତଥ୍ୟର ସାଂଖ୍ୟକ ପରିପ୍ରକାଶ।
Answer:
ସାରଣୀ ତଥ୍ୟର ସାଂଖ୍ୟକ ପରିପ୍ରକାଶ।
Question ୪୫।
କୌଣସି ଏକ ରେଖାଚିତ୍ରରେ ଗୋଟିଏ ତଥ୍ୟ ପ୍ରଦାନ କରାଯାଇଥାଏ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୪୬।
ସାରଣୀର ବିଶ୍ଳେଷଣ ଖୁବ୍ କମ୍ ସମୟରେ କରିହୁଏ।
Answer:
ଲ୍ଲେଖଚିତ୍ରର ବିଶ୍ଳେଷଣ ଖୁବ୍ ସମୟ ମଧ୍ୟରେ କରି ହୁଏ।
Question ୪୭।
ଲେଖଚିତ୍ର ଏକ ହାରାହାରି କଳନା।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୪୮।
ସାରଣୀ ଏକ ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ ବର୍ଗର ପର୍ଯ୍ୟବେକ୍ଷଙ୍କ ଦ୍ବାରା ଆଦୃତ ହୋଇଥାଏ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୪୯।
ପଂକ୍ତି ଓ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ଆକାରରେ ସଂଗୃହୀତ ତଥ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକର ଉପସ୍ଥାନକୁ ସାରଣୀ କୁହାଯାଏ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୫୦।
ପଂକ୍ତି ତଥ୍ୟମାନଙ୍କର ଉଲୁମ୍ବ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନାକୁ ବୁଝାଏ।
Answer:
ସ୍ତମ୍ଭତଥ୍ୟମାନଙ୍କର ଉଲ୍ଲମ୍ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନାକୁ ବୁଝାଏ।
![]()
Question ୫।
ବିଶ୍ଳେଷଣାତ୍ମକ ସାରଣୀ ତଥ୍ୟମାନଙ୍କର ତୁଳନାତ୍ମକ ଚିତ୍ର ପ୍ରଦାନ କରାଯଇଥାଏ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୫୨।
ପଂକ୍ତି ନାମ ପଂକ୍ତିର ମୁଖ୍ୟର ଶୀର୍ଷକ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୫୩।
ଶିରୋମାନା ପଂକ୍ତିର ମୁଖ୍ୟ ଶୀର୍ଷକ।
Answer:
ଶିରୋମାନା ସ୍ତମ୍ଭର ମୁଖ୍ୟ ଶୀର୍ଷକ।
Question ୫୪।
ସାରଣୀ ସଂଖ୍ୟାର ଠିକ୍ ତଳେ ସାରଣୀର ଶୀର୍ଷକ ଲେଖାଯାଏ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
Question ୫୫।
ସାରଣୀର ସନ୍ନିବେସିତ କୌଣସି ଅଂଶ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧରେ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟିକରଣ ଶିରୋନାମାରେ ଉଲ୍ଲେଖ କରାଯାଏ।
Answer:
ସାରଣୀରେ ସନ୍ନିବେଶିତ କୌଣସି ଅଂଶ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧରେ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟିକରଣ ପାଦଟୀକାରେ ଉଲ୍ଲେଖ କରାଯାଏ।
Question ୫୬।
ଶୀର୍ଷଟୀକା ଶୀର୍ଷକ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧରେ ଅତିରିକ୍ତ ସୂଚନା ଦିଏ।
Answer:
ସଠିକ୍
III. ନିମ୍ନୋକ୍ତ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନଗୁଡ଼ିକର ଉତ୍ତର ଦୁଇଟିରୁ ତିନୋଟି ବାକ୍ୟରେ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଲେଖ।
[Answer the following questions within 2 to 3 sentences in each case.]
Question ୧।
ଚଳ (Variable) କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଯାହାର ମୂଲ୍ୟରେ ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନ ହୁଏ ତାହାକୁ ବଳ ବା ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନଶୀଳ ଉପାଦାନ କୁହାଯାଏ। ଏହା ଦୁଇ ପ୍ରକାରର; ଯଥା- ବିବିକ୍ତ ବା ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳ (Discrete variable) ଏବଂ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳ (continuous variable)।
Question ୨।
ଶ୍ରେଣୀସୀମା (Class Limits) କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକ୍ତ ହୋଇ ପାରୁଥିବା ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ଓ ସର୍ବବୃହତ୍ ମୂଲ୍ୟକୁ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ସୀମା କୁହାଯାଏ। ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ନିମ୍ନସୀମା ଏପରି ଏକ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ଯାହାଠାରୁ କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ର ମୂଲ୍ୟ ସେହି ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକ୍ତ ହୋଇପାରେ ନାହିଁ। ସେହିପରି ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱସୀମା ଏପରି ଏକ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ଯାହାଠାରୁ ବୃହତ୍ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ସେହି ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକତ ହୋଇପାରେ ନାହିଁ।
Question ୩ ।
ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ (Frequency Distribution) କହିଲେ କ’ଣ ବୁଝ ?
Answer:
ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ କହିଲେ ଏକ ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନଶୀଳ ଚଳ ଓ ବିଭିନ୍ନ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ଓ ତାହାର ସଂପୃକ୍ତ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିନ୍ୟାସକୁ ବୁଝାଏ। ଏହା ଏକ ଗାଣିତିକ ସାରଣୀ ଯେଉଁଥିରେ ତଥ୍ୟାବଳୀକୁ ବିଭିନ୍ନ ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ବିଭକ୍ତ କରାଯାଇଥାଏ।
Question ୪।
ବିବିକ୍ତ ବା ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ (Discrete Frequency Distribution) କ’ଣ ?
Answer:
ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ ଏକ ବିବିକ୍ତ ଚଳ ଦ୍ଵାରା ପର୍ଯ୍ୟବସିତ ବିତରଣ । ଏକ ବିବିକ୍ତ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ କରିବାପାଇଁ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ଲବ୍ଧାଙ୍କ କେତେ ଥର ଆବିର୍ଭାବ ହେଉଛି, ତାହା ଗଣନା କରିବାକୁ ହୁଏ।
Question ୫।
ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ବିସ୍ତାର ବା ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଅନ୍ତରାଳ (Class Interval) କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଗୋଟିଏ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱସୀମା ଓ ନିମ୍ନସୀମାରେ ଅନ୍ତର ଫଳକୁ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ବିସ୍ତାର ବା ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଅନ୍ତରାଳ କୁହାଯାଏ । ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଅନ୍ତରଳ ନିର୍ଣ୍ଣୟ କରିବାପାଇଁ ପ୍ରଫେସର ଷ୍ଟେସ୍ ଏକ ସୂତ୍ର ଦେଇଛନ୍ତି।
![]()
Question ୬।
ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳ (Continuous Variable) କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଯେଉଁ ଚଳ ପ୍ରଦତ୍ତ ବିସ୍ତାର ମଧ୍ୟରେ ସମସ୍ତ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ଧାରଣ କରିପାରେ, ତାହାକୁ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳ କୁହାଯାଏ। ଉଚ୍ଚତା, ଓଜନ, ବୟସ, ଇତ୍ୟାଦି ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳର ଉଦାହରଣ।
Question ୭।
ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ (Continuous Frequency Distribution) କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଏକ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳ ଦ୍ୱାରା ପର୍ଯ୍ୟବେସିତ ବିତରଣକୁ ଏକ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାର ବିତରଣ କୁହାଯାଏ। ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣରେ ତଥ୍ୟାବଳୀକୁ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଓ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ଦ୍ଵାରା ଉପସ୍ଥାପନା କରାଯାଏ।
Question ୮।
ବିବିକ୍ତ ବା ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳ (Discrete Variable) କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଯେଉଁ ଚଳ ପ୍ରଦତ୍ତ ବିସ୍ତାର ମଧ୍ୟରେ ସମସ୍ତ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ଧାରଣ କରି ନଥାଏ, ତାହାକୁ ବିବିକ୍ତ ବା ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳ କୁହାଯାଏ। ଗୋଟିଏ ଦପ୍ତରର କର୍ମଚାରୀ, ଘରର କୋଠରି ସଂଖ୍ୟା, ପଶୁପକ୍ଷୀଙ୍କ ସଂଖ୍ୟା ଇତ୍ୟାଦି ବିବିକ୍ତ ଚଳର ଉଦାହରଣ।
Question ୯।
ହିଷ୍ଟୋଗ୍ରାମ (Historgram) କ’ଣ ?
Answer:
ହିଷ୍ଟୋଗ୍ରାମ୍ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣରେ ଏକ ଚିତ୍ର (Graph) ଯାହା ବିତ୍ରରଣକୁ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନ କରାଯାଏ। ଏହା କେତୋଟି ସନ୍ନିହିତ ଭୂଲମ୍ବ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ବା ଆୟତକ୍ଷେତ୍ରମାନଙ୍କର କ୍ଷେତ୍ରଫଳ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ସହିତ ସମାନୁପାତୀ।
Question ୧୦।
ସାରଣୀ (lable) କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ? ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ଆୟତକ୍ଷେତ୍ରର ସମାହାର ଯାହାର
Answer:
ପଂକ୍ତି ଓ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ଆକାରରେ ସଂଗୃହୀତ ତଥ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ଯେଉଁଥରେ ସଜାଡ଼ି ଲେଖାଯାଏ; ତାହାକୁ ସାରଣୀ ବା ତାଲିକା କୁହାଯାଏ। ଏହା ଦୁଇପ୍ରକାରର; ଯଥା– ଆଧାର ସାରଣୀ ଓ ବିଶ୍ଳେଷଣତ୍ମକ ସାରଣୀ। ସାରଣୀ ତଥ୍ୟର ସାଂଖ୍ୟକ ପରିପ୍ରକାଶ ଅଟେ।
Question ୧୧।
ସମୟାନୁକ୍ରମୀ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ (Time series graph) ଲେଖ କ’ଣ ?
Answer:
ସମୟାନୁକ୍ରମୀ ଶ୍ରେଣୀକୁ ଏକ ଗ୍ରାଫ୍ କାଗଜରେ ପରିପ୍ରକାଶ କଲେ ସମୟାନୁକ୍ରମୀ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଲେଖ (Time Series Grap) ମିଳିଥାଏ। ସମୟାନୁକ୍ରମୀ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଲେଖକୁ ‘ରେଖାଲେଖ’ ମଧ୍ୟ କୁହାଯାଏ।
Question ୧୨।
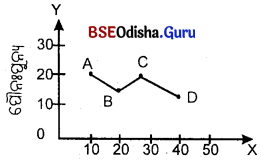
ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦେଶକ ଲେଖଚିତ୍ର (Frequeney polygon) କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଲବ୍ଧାଙ୍କ ଓ ତାହାର ବାରମ୍ବାରତାର କ୍ରମିକ ଯୋଡ଼ିମାନଙ୍କୁ ବିନ୍ଦୁ ଆକାରରେ ଗ୍ରାଫ୍ କାଗଜରେ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନ କରାଯାଏ। ଏହି ବିନ୍ଦୁ ଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ କ୍ରମାନ୍ଵୟରେ ସରଳରେଖାମାନଙ୍କ ଦ୍ଵାରା ସଂଯୋଗ କରି ଅଙ୍କିତ ହେଉଥିବା ରେଖାକୁ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦେଶକ ଲେଖଚିତ୍ର କୁହାଯାଏ।
Question ୧୩।
ବୃତ୍ତ ଚିତ୍ର (Pie Diagram) କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ତଥ୍ୟକୁ ଏକ ବୃତ୍ତାକାର କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ଆନୁପାତିକ ଅଂଶ ରୂପେ ଗ୍ରହଣ କରାଯାଇ ଚିତ୍ର ଅଙ୍କନ କରାଗଲେ, ତାହାକୁ ବୃତ୍ତଚିତ୍ର ବା ବୃତ୍ତଲେଖ କୁହାଯାଏ। ସମସ୍ତ ବୃତ୍ତକଳାର କେନ୍ଦ୍ରୀୟ କୋଣମାନଙ୍କର ସମଷ୍ଟି 360° ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ ଏହାର କେନ୍ଦ୍ରୀୟ କୋଣର ପରିମାଣ ନିମ୍ନଲିଖତ ସୂତ୍ର ସାହାଯ୍ୟରେ ନିର୍ଦ୍ଧାରଣ କରାଯାଇଥାଏ । ଯଥା-
![]()
Question ୧୪।
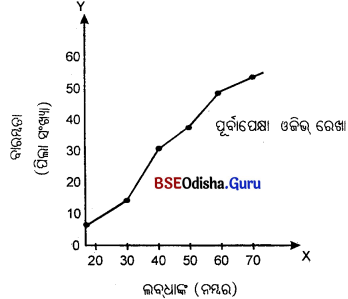
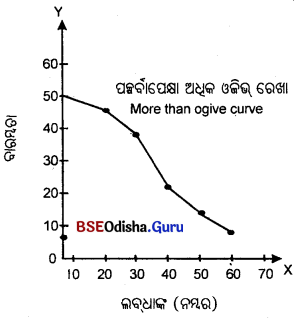
ରାଶିକୃତ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦେଶକ ବକ୍ର ବା ଓଭିଜ୍ (Cumulative Frequency Curve or Ogive)କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
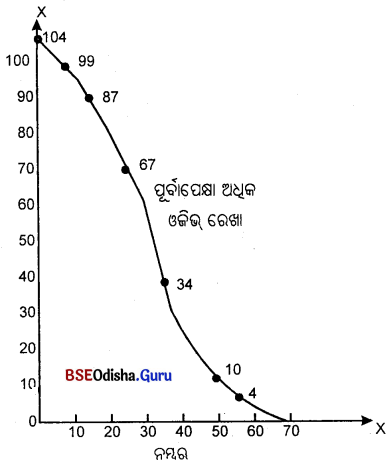
ରାଶିକୃତ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣର ଲେଖଚିତ୍ର ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ ପରିପ୍ରକାଶକୁ ଓଜିଭ କୁହାଯାଏ । ଓଜିଭ୍ ଦୁଇ ପ୍ରକାରର; ଯଥା– ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା କମ୍ ଓଜିଭ୍ ଏବଂ ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା ଅଧିକ ଓଜିଭ୍।
![]()
Question ୧୫।
ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ଚିତ୍ର (Bar Diagram) କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
କେତୋଟି ସମପ୍ରଭୁ ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ବା ଆୟତାକାର କ୍ଷେତ୍ରର ସମାହାରକୁ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭଚିତ୍ର କୁହାଯାଏ। ରେଖାଚିତ୍ର ଅନ୍ତର୍ଗତ ସମସ୍ତ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭର ପ୍ରସୁ ସମାନ ଥିବାବେଳେ ସେମାନଙ୍କ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ବ୍ୟବଧାନ ସମାନ ଥାଏ। ଏକ ସମୟରେ କେବଳ ଗୋଟିଏ ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନଶୀଳ ଚଳଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ପ୍ରଦର୍ଶନ କରୁଥିବାରୁ ଏହାକୁ ବିର୍ମିତୀୟ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭଚିତ୍ର ବା ଏକ ଆୟତନ ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭଚିତ୍ର କୁହାଯାଏ।
Question ୧୬।
ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ (Frequency Distribution) କହିଲେ କ’ଣ ବୁଝ ?
Answer:
ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ କହିଲେ ଏକ ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନଶୀଳ ଚଳ (variable) ର ବିଭିନ୍ନ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ଓ ତାହାର ସଂପୃକ୍ତ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିନ୍ୟାସକୁ ବୁଝାଏ। ଏହା ଏକ ଗାଣିତିକ ସାରଣୀ ଯେଉଁଥରେ ତଥ୍ୟାବଳୀକୁ ବିଭିନ୍ନ ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ବିଭକ୍ତ କରାଯାଇଥାଏ।
Question ୧୭ ।
ଚଳ (Variable) କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଯାହାର ମୂଲ୍ୟରେ ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନ ହୁଏ ତାହାକୁ ଚଳ ବା ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନଶୀଳ ଉପାଦାନ କୁହାଯା,। ଏହା ଦୁଇ ପ୍ରକାରର; ଯଥା – ବିବିକ୍ତ ବା ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳ (Discrete Variable), ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳ (Continuous Variable)।
Question ୧୮।
ବିବିକ୍ତ ବା ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ (Discrete Frequency Distribution) କ’ଣ ?
Answer:
ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ ଏକ ବିବିକ୍ତ ଚଳଦ୍ଵାରା ପର୍ଯ୍ୟବସିତ ବିତରଣ। ଏକ ବିବିକ୍ତ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ କରିବା ପାଇଁ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ଲବ୍ଧାଙ୍କ କେତେଥର ଆବିର୍ଭାବ ହେଉଛି, ତାହା ଗଣନା କରିବାକୁ ହୁଏ।
Question ୧୯। ସମୟାନୁକ୍ରମୀ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଲେଖ କ’ଣ ଲେଖ ?
Answer:
ସମୟାନୁକ୍ରମୀ ଶ୍ରେଣୀକୁ ଏକ ଗ୍ରାଫ୍ କାଗଜରେ ପରିପ୍ରକାଶ କଲେ ସମୟାନୁକ୍ରମୀ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଲେଖ (Time Series Graph) ମିଳିଥାଏ । ସମୟାନୁକ୍ରମୀ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଲେଖକୁ ‘ରେଖାଲେଖ’ (Line Graph) ମଧ୍ୟ କୁହାଯାଏ।
Question ୨୦।
ହିଷ୍ଟୋଗ୍ରାମ୍ (Histogram) କ’ଣ ?
Answer:
ହିଷ୍ଟୋଗ୍ରାମ୍ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣର ଏକ ଚିତ୍ର (graph) ଯାହା ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣକୁ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନ କରାଯାଏ। ଏହା କେତୋଟି ସନ୍ନିହିତ ଭୂଲମ୍ବ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ବା ଆୟତକ୍ଷେତ୍ରର ସମାହାର ଯାହାର ଆୟତକ୍ଷେତ୍ର ମାନଙ୍କର କ୍ଷେତ୍ରଫଳ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ସହିତ ସମାନୁପାତୀ।
![]()
Question ୨୧।
ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦେଶକ ଲେଖଚିତ୍ର (Frequency Polygon) କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ଲବ୍ଧାଙ୍କ ଓ ତାହାର ବାରମ୍ବାରତାର କ୍ରମିକଯୋଡ଼ିମାନଙ୍କୁ ବିନ୍ଦୁ ଆକାରରେ ଗ୍ରାଫ୍ କାଗଜରେ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନ କରାଯାଏ । ଏହି ବିନ୍ଦୁଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ କ୍ରମାନ୍ୱୟରେ ସରଳରେଖାମାନଙ୍କ ଦ୍ଵାରା ସଂଯୋଗ କରି ଅଙ୍କିତ ହେଉଥିବା ରେଖାକୁ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦେଶକ ଲେଖଚିତ୍ର (Frequency Polygon) କୁହାଯାଏ।
Question ୨୨।
ରାଶୀକୃତ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦେଶକ ବକ୍ର ବା ଓଜିଭ୍ (Cumulative Freuency curve or Ogive) କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ରାଶୀକୃତ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣର ଲେଖଚିତ୍ର ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ ପରିପ୍ରକାଶକୁ ଓଲିଭ୍ କୁହାଯାଏ। ଓଲିଭ୍ ଦୁଇପ୍ରକାରର; ଯଥା- ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା କମ୍ ଓଲିଭ୍ ଏବଂ ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା ଓଜିଭ୍।
Question ୨୩।
ସାରଣୀର ଦୁଇଟି ଅଂଶ (Part)ଲେଖ।
Answer:
ସାରଣୀର ଦୁଇଟି ଅଂଶ ହେଲା
(i) ସାରଣୀର ସଂଖ୍ୟା
(ii) ସାରଣୀର ଶୀର୍ଷକ
Question ୨୪।
ସରଳ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ଚିତ୍ର (Simple Bar Diagram) କ’ଣ ?
Answer:
ସରଳ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭଚିତ୍ର ହେଉଛି କେତୋଟି ସମପ୍ରଭୁ ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ବା ଆୟତକ୍ଷେତ୍ରର ସମାହାର। ଏହା ଅନ୍ତର୍ଗତ ସମସ୍ତ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭର ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁ ସମାନ ଥିବାବେଳେ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ବ୍ୟବଧାନ ସମାନ ଥାଏ।
Question ୨୫।
ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ମଧ୍ୟବିନ୍ଦୁ (Mid point of a class) କ’ଣ ?
Question
ଗୋଟିଏ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଦୁଇଟି ସୀମାର ଠିକ୍ ମଝିରେ ଥିବା ମୂଲ୍ୟକୁ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ମଧ୍ୟବିନ୍ଦୁ କୁହାଯା। ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ମଧବିନ୍ଦୁ ନିର୍ଧାରଣର ପଦ୍ଧତି ହେଲା
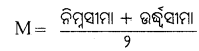
Question ୨୬।
ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଅନ୍ତରାଳ (Class interval) କ’ଣ ?
Answer:
ଗୋଟିଏ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଦୁଇଟି ସୀମାର ଅନ୍ତର ଫଳକୁ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଅନ୍ତରାଳ କୁହାଯାଏ। ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଅନ୍ତରାଳର ମୂଲ୍ୟ ସର୍ବଦା ଶୂନ୍ୟ, ୫ କିମ୍ବା ୫ ଦ୍ଵାରା ଛିଷ୍ଣୁଥିବା ସଂଖ୍ୟା ହେଲେ ସୁବିଧା ଜନକ ହୁଏ। ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଅନ୍ତରାଳ ନିର୍ଦ୍ଧାରଣ ପଦ୍ଧତି ହେଲା
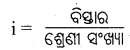
Question ୨୭।
ଓଜିଭ୍ (Ogive) କ’ଣ ?
Answer:
ରାଶିକୃତ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣର ଲେଖଚିତ୍ର ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ ପରିପ୍ରକାଶକୁ ଓଜିଭ୍ କୁହାଯାଏ। ଏହା ଦୁଇ ପ୍ରକାରର; ଯଥା- ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା କମ୍ ଓଜିଭ୍ ଏବଂ ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା ଅଧିକ ଓଜିଭ୍।
Question ୨୮।
ସାରଣୀ ଓ ଲେଖଚିତ୍ର ମଧ୍ୟରେ ପାର୍ଥକ୍ୟ (difference) ଦର୍ଶାଅ।
Answer:
(i) ଏଥିରେ ଥିବା ସମସ୍ତ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ଆକ୍ଷରିକ, କିନ୍ତୁ ଲେଖଚିତ୍ର ଏକ ହାରାହାରି କଳନା।
(ii) ଏକ ସାରଣୀରେ ଏକଧୂକ ତଥ୍ୟ ପ୍ରଦାନ କରାଯାଇପାରେ, କିନ୍ତୁ ଗୋଟିଏ ଲେଖାଚିତ୍ରରେ ଗୋଟିଏ ତଥ୍ୟ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନ କରାଯାଇପାରେ।
IV. ପାର୍ଥକ୍ୟ ଦର୍ଶାଅ ।
[Distinguish between]
Question ୧।
ରେଖାଚିତ୍ର ଏବଂ ଲେଖଚିତ୍ର (Diagram and Graphs)
Answer:
| ରେଖାଚିତ୍ର : | ଲେଖଚିତ୍ର : |
| i. ରେଖାଚିତ୍ର ଅଙ୍କନ କରିବା ପାଇଁ ସାଧା କାଗଜର ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଏ। | i. ଲେଖଚିତ୍ର ଅଙ୍କନ ଗ୍ରାଫ୍ ପେପର ସାହାଯ୍ୟୟ କରାଯାଏ। |
| ii. ଏହା ଗାଣିତିକ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ସ୍ଥାପନରେ ସହାୟକ ହୋଇନଥାଏ। | ii. ଏହା ଦୁଇଟି ଚଳ ମଧ୍ୟରୁ ଗାଣିତିକ ସଂପର୍କ ସ୍ଥାପନ କରିବାରେ ସହାୟକ ହୁଏ। |
| iii. ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ ଏବଂ ସମୟାନୁକ୍ରମୀ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଲେଖ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନ ପାଇଁ ଏହା ଉପୟୁକ୍ତ ନୁହେଁ। | iii. ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ ଏବଂ ସମୟାନୁକ୍ରମୀ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଲେଖ। ଉପସ୍ଥାପନରେ ଏହା ଉପଯୋଗୀ ହୁଏ। |
Question ୨।.
ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା କମ୍ ଓଜିଭ୍ ଏବଂ ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା ଅଧୂକ ଓଜିଭ୍ (Less than Ogive and Morc than Ogive)
Answer:
ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା କମ୍ ଓଜିଭ୍ :
i. ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା କମ୍ ଓଜିଭ୍ ସାରଣୀ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ ସମୟରେ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ଉଦ୍ଧସୀମା ନିଆଯାଇଥାଏ।
ii. ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା କମ୍ ଓଜିଭ୍ ରେଖା ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱଗାମୀ ଗତି କରିଥାଏ।
ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା ଅଧିକ ଓଜିଭ:
i. ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା ଅଧିକ ଓକିଭରେ ଶ୍ରେଣୀଗୁଡ଼ିକର ନିମ୍ନ ସୀମାକୁ ନିଆଯାଏ।
ii. ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା ଅଧିକ ଓଜିଭ୍ ରେଖା ନିମ୍ନଗାମୀ ଗତି କରିଥାଏ।
Question ୩।
ସାରଣୀ ଏବଂ ଲେଖଚିତ୍ର: (lable and Graph)
Answer:
ସାରଣୀ
i. ସାରଣୀର ସମସ୍ତ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ଆକ୍ଷରିକ।
ii. ଏଥିରେ ଅନେକ ତଥ୍ୟ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନ କରାଯାଇପାରେ।
iii. ଏହାର ବିଶ୍ଳେଣେ କଷ୍ଟକର ଓ ସମୟ ସାପେକ୍ଷ।
ଲେଖଚିତ୍ର :
i. ଲେଖଚିତ୍ରର ଏକ ହାରାହାରି କଳନା।
ii. ଏଥୁରେ କେବଳ ଗୋଟିଏ ତଥ୍ୟ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନ କରାଯାଇପାରେ।
iii. ଏହାର ବିଶ୍ଳେଷଣ ସରଳ ଓ କମ୍ ସମୟ ସାପେକ୍ଷ।
![]()
Question ୪।
ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବଳ ଓ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳ (Discrete Variable and Continuus Variable)
Answer:
ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳ:
i. ଏକ ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳ ପ୍ରଦତ୍ତ ବିସ୍ତାର ମଧ୍ୟରେ ସମସ୍ତ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ଧାରଣ କରିପାରେ ନାହିଁ।
ii. କୋଠରୀର ସଂଖ୍ୟା ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳର ଉଦାହରଣ।
iii. ଏ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ଚଳଗୁଡ଼ିକ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଧାରାବାହିକତା ନ ଥାଏ।
ନିରବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳ:
i. ଏକ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳ ପ୍ରଦତ୍ତ ବିସ୍ତାର ମଧ୍ୟରେ ସମସ୍ତ ଚଳ ଧାରଣ କରିପାରେ।
ii. ଉଚ୍ଚତା ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳର ଉଦାହରଣ।
iii. ଏ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ଚଳଗୁଡ଼ିକ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଧାରାବାହିକତା ଥାଏ।
VI ଦୀର୍ଘଧର୍ମୀ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନୋତ୍ତର।
[Long Answer type Questions]
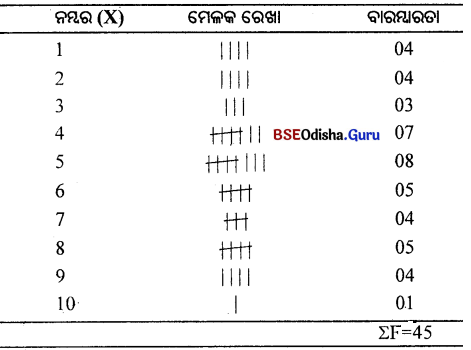
Question ୧।
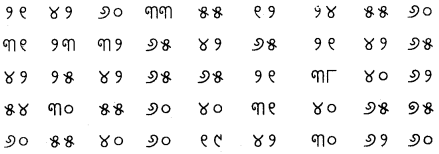
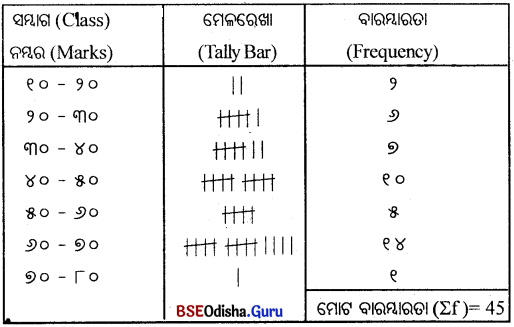
ନମ୍ବର (X) ଏକ ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ ଗଠନ କର ।
(Construct a Discrete Frequency distributor.)
1. 2, 4, 3, 5, 7, 6, 8, 9. 4, 3, 6, 2, 1, 7, 8, 5, 4. 2, 3. 5, 1, 4, 7, 5, 9, 8. 10, 4, 6, 5, 8,
9, 6, 4, 5, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5, 8, 7, 6, 5
ମୋଟ ସଂଖ୍ୟା = 45
ଏକ ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତଃ ବିତରଣ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ କର।
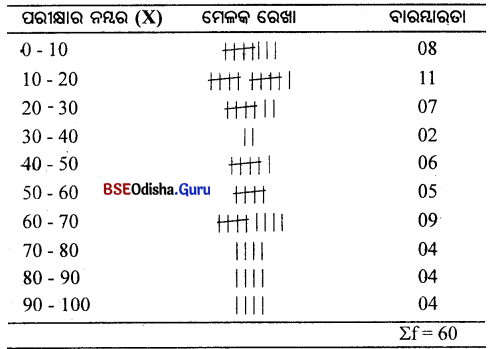
Question ୨।
ଗୋଟିଏ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ ଗଠନ କର।
(Construct a Continuous Frequency distribution.)
Answer:
ପରୀକ୍ଷାର ନମ୍ବର (X): 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 2, 5, 8, 7, 6, 18, 20, 11, 10, 12, 17, 13, 20, 22, 24, 26, 21, 28, 19, 30, 35, 40, 55, 60, 70, 60, 60, 62, 75, 61, 81, 85, 75, 73, 81, 90, 40, 50, 40, 60, 10, 91, 98, 99, 40, 50, 43, 48, 50, 51, 62, 68, 64, 60
ମୋଟ ସଂଖ୍ୟା = 60
ଏକ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ ଗଠନ କର।
Question ୩।
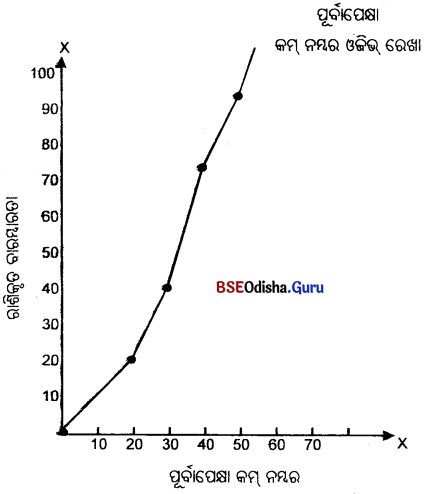
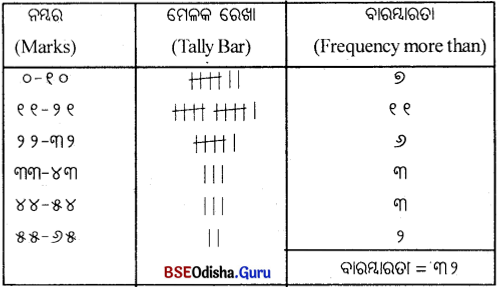
ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା କମ୍ ଓଜିଭ୍ ଏବଂ ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା ଅଧିକ ଓଜିଭ ନିର୍ଣ୍ଣୟ କର।
(Determine less than Ogive and more than Ogive.)
| ନମ୍ବର (X): | 0-10 | 10-20 | 20-30 | 30-40 | 40-50 | 50-60 |
| ଛାତ୍ର ସଂଖ୍ୟା (F) ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା : | 5 | 12 | 20 | 33 | 24 | 6 |
| ନମ୍ବର (X): | ଛାତ୍ର ସଂଖ୍ୟା (F) ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା : | ନମ୍ବର ବାରମ୍ବାରତା | ରାଶିକୃତ |
| 0-10 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| 10-20 | 12 | 20 | 17 |
| 20-30 | 20 | 30 | 37 |
| 30-40 | 33 | 40 | 70 |
| 40-50 | 24 | 50 | 94 |
| 50-60 | 6 | 60 | 100 |
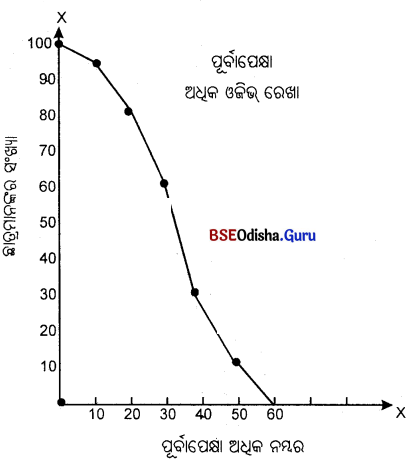
| ନମ୍ବର (X) | ଛାତ୍ରସଂଖ୍ଯା (F) | ନମ୍ବର ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା ଅଧକ | ରାଶିକୃତ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା |
| 0 – 10 | 5 | 0 | 100 |
| 10 – 20 | 12 | 10 | 95 |
| 20 – 30 | 20 | 20 | 83 |
| 30 – 40 | 33 | 30 | 63 |
| 40 – 50 | 24 | 40 | 30 |
| 50 – 60 | 6 | 50 | 6 |
| 60 – 70 | 60 | 0 |
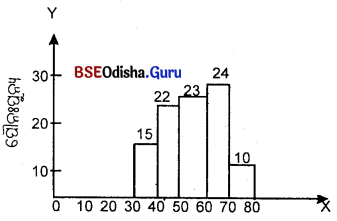
୪। ହିଷ୍ଟୋଗ୍ରାମ ଗଠନ କର।
(Construct a Histrogram.)
| Marks | 0-10 | 10-20 | 20-30 | 30-40 | 40-50 | 50-60 | 60-70 |
| No. of students | 5 | 10 | 20 | 40 | 30 | 20 | 5 |
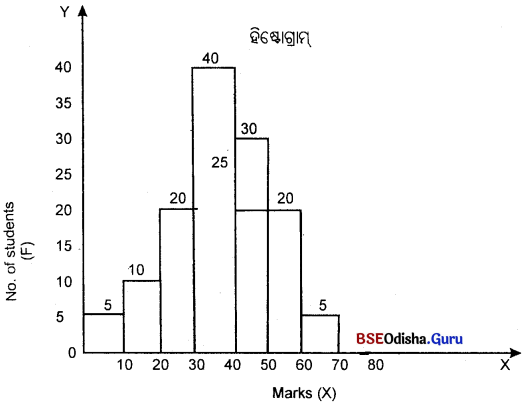
Question ୫।
ଗୋଟିଏ ହିଷ୍ଟୋଗ୍ରାମ୍ ଗଠନ କର।
(Construct a Histogram.)
| ପରୀକ୍ଷାରେ ନମ୍ବର (X) | 0-10 | 10-20 | 20-30 | 30-40 | 40-60 | 60-70 | 70-100 |
| ଛାତ୍ରମାନଙ୍କର ସଂଖ୍ୟା (F) | 5 | 10 | 15 | 25 | 40 | 10 | 15 |
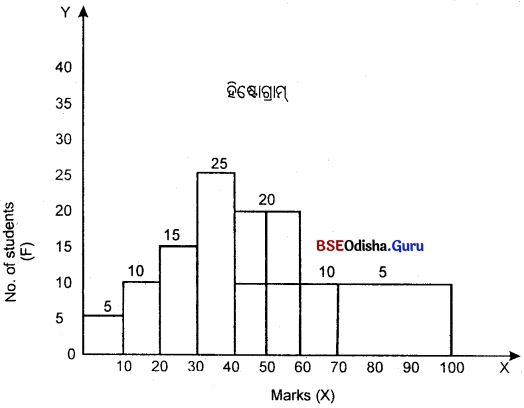
ଅସମାନ ଶ୍ରେଣୀକୁ ସମାନ କରିବାର ପଦ୍ଧତି :
40 – 60 ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ବାରମ୍ବାରତା 40, ତେଣୁ
\(\frac{40}{2}\) = 20, 40- 50 – 20,50 – 60 = 20
ସେହିପରି, 70 – 100 ର ବାରମ୍ବାରତା
ଏହି ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ଉଚ୍ଚତା 3, \(\frac{15}{3}\) = 5
ତେଣୁ 70 – 80 – 5, 80 – 90 – 5, 90 – 100 = 5
Question ୬। .
ଗୋଟିଏ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦେଶକ ରେଖା ଅଙ୍କନ କର।
(Construct a Frequency Polygon.)
| ଛାତ୍ରମାନଙ୍କର ସଂଖ୍ୟା ଆୟ (X) | 0 – 10 | 10 – 20 | 20 – 30 | 30 – 40 | 40 – 50 | 50 – 60 | 60 – 70 | 70 – 80 |
| କର୍ମଚାରୀଙ୍କ ସଂଖ୍ୟା (F) | 5 | 10 | 15 | 25 | 20 | 11 | 5 | 3 |
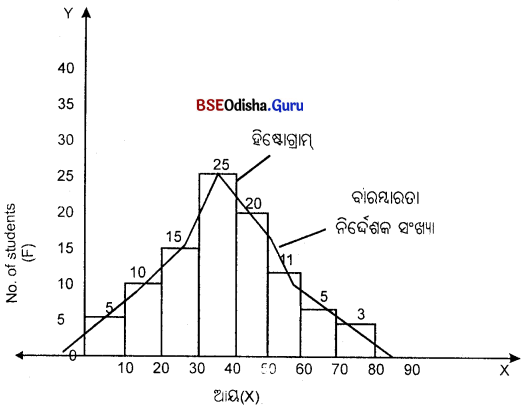
Question ୭।
100 ଜଣ ଛାତ୍ର-ଛାତ୍ରୀ ପରିକ୍ଷାରେ ରଖିଥିବା ନମ୍ବର ନିମ୍ନରେ ଦିଆଯାଉଛି। ଗୋଟିଏ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ କର।
(Construct a Continuous Frequency Distribution.)
1, 2, 1, 30, 50, 42, 98, 53, 73, 55, 42, 4, 9, 11, 20, 60, 88, 58, 32, 65, 11, 6, 25, 25, 28, 70, 80, 66, 11, 62, 48, 74, 19, 15, 40, 50, 59, 79, 72, 25, 65, 21, 92, 42, 9, 92, 11, 18, 42, 55, 58, 64, 63, 49, 76, 11, 31, 98, 11, 21, 36, 44, 52, 53, 62, 93, 18, 16, 99, 91, 62, 59, 32, 48, 20, 28, 92, 18, 16, 92, 47, 49, 52, 59, 66, 48, 98, 79, 2, 9, 15, 16, 28, 92, 29, 25, 43, 56, 16
Answer:
ନରିବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ ସୂଚୀ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତି (Continuous Frequency Distribution)
Question ୮।
ନିମ୍ନଲିଖୂତ ତଥ୍ୟାବଳୀର ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା କମ୍ ଓଳିଭ୍ ଓ ପୂର୍ବପେକ୍ଷା ଅଧିକ ଓଜିଭ୍ ଅଙ୍କନ କର ଓ ନିମ୍ନଲିଖୁତ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନର ଉତ୍ତର ଦିଅ।
(Draw Less than Ogive and More than Ogive curve.)
(a) କେତେଜଣ ଛାତ୍ର 45 ରୁ କମ୍ ନମ୍ବର ରଖୁଛନ୍ତି ?
(b) କେତେଜଣ ଛାତ୍ର 15 ରୁ ଅଧିକ ନମ୍ବର ରଖୁଛନ୍ତି ?
| ନମ୍ବର (X) | 0 – 10 | 10 – 20 | 20 – 30 | 30 – 40 | 40 – 50 | 50 – 60 | 60 – 70 |
| ଛାତ୍ରସଂଖ୍ଯା (F) | 5 | 12 | 20 | 33 | 24 | 6 | 4 |
ତଥ୍ୟାବଳୀର ଉପସ୍ଥାପନ
ସମାଧାନ :
ପୂର୍ବପେକ୍ଷା କମ୍ ଓଜିଭ୍ :
| ନମ୍ବର (X) | ଛାତ୍ରସଂଖ୍ଯା (F) | ନମ୍ବର ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା କମ୍ | ପୂର୍ବ ଅପେକ୍ଷା ଅଧୂକ | ରାଶିକୃତ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା |
| 0 – 10 | 5 | 0 | 100 | 5 |
| 10 – 20 | 12 | 10 | 95 | 17 |
| 20 – 30 | 20 | 20 | 83 | 37 |
| 30 – 40 | 33 | 30 | 63 | 70 |
| 40 – 50 | 24 | 40 | 30 | 94 |
| 50 – 60 | 6 | 50 | 6 | 100 |
| 60 – 70 | 4 | 60 | 0 | 104 |
| 70 |
ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା ଅଧା୍କ ଓ ଜିଉ:
| ନମ୍ବର (X) | ଛାତ୍ରସଂଖ୍ଯା (F) | ନମ୍ବର ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା ଅଧା୍କ | ପୂର୍ବ ଅପେକ୍ଷା ଅଧୂକ ରାଶିକୃତ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା (C.f) | |
| 0 – 10 | 5 | 0 | 100 | 104 |
| 10 – 20 | 12 | 10 | 95 | 99 |
| 20 – 30 | 20 | 20 | 83 | 87 |
| 30 – 40 | 33 | 30 | 63 | 67 |
| 40 – 50 | 24 | 40 | 30 | 34 |
| 50 – 60 | 6 | 50 | 6 | 10 |
| 60 – 70 | 4 | 60 | 0 | 4 |
| 70 | ||||
Question ୯।
ବିବିକ୍ତ ବା ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା କର।
(Define discrete Frequency Distribution)
Answer:
ଏକ ବିବିକ୍ତ ଚଳଦ୍ଵାରା ପର୍ଯ୍ୟବସିତ ବିତରଣକୁ ବିବିକ୍ତ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ କୁହାଯାଏ। ଏକ ବିବିକ୍ତ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ କରିବାପାଇଁ ଆମେ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ଲବ୍ଧାଙ୍କ କେତେଥରର ଆବିର୍ଭାବ ହୋଇଛି। ତାହା ଗଣନା କରୁ। ନିମ୍ନଲିଖତ ପ୍ରଣାଳୀ ଦ୍ଵାରା ଏ ପ୍ରକାର ବିତରଣ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ କରାଯାଏ।
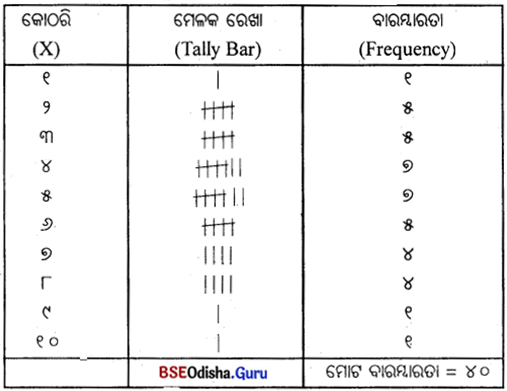
(i) ତିନୋଟି ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ କରାଯାଏ। ପ୍ରଥମ ଚଳର ବିଭିନ୍ନ ମୂଲ୍ୟ (ଲବ୍ଧାଭକ) ନିମନ୍ତେ; ଦ୍ଵିତୀୟ, ମେଳକ ରେଖା ବା ମେଳକ ଚିହ୍ନ (tally hars) ନିମନ୍ତେ ଓ ତୃତୀୟ, ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ନିମନ୍ତେ।
(ii) ପ୍ରଥମ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭରେ ଚଳର ମୂଲ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ବକ୍ରମରେ ଲେଖାଯାଏ।
(iii) ଦ୍ଵିତୀୟ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭରେ, ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ମୂଲ୍ୟର ଥରେ ଆର୍ବିଭାବ ପାଇଁ ଗୋଟିଏ ମେଳକ ରେଖା ଦିଆଯାଏ।
(iv) କୌଣସି ମୂଲ୍ୟର ପଞ୍ଚମ ଥର ଆବିର୍ଭାବ ପାଇଁ ମେଳକ ରେଖା ଉପରେ ଗୋଟିଏ ଛେଦରେଖା ଦିଆଯାଏ। ଏହିପରି ପାଞ୍ଚଟିକିଆ ମେଳକ ରେଖା ପୁଞ୍ଜି ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ କରାଯାଏ। ଦୁଇଟି ମେଳକ ରେଖା ପୁଞ୍ଜି ମଧ୍ୟରେ କିଛି ବ୍ୟବଧାନ ରଖାଯାଏ।
(v) ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ଲବ୍ଧାଙ୍କ ପାଇଁ ଦିଆଯାଇଥିବା ମେଳକ ରେଖା ଗଣନ କରାଯାଏ। ଏହାକୁ ସେହି ଲବ୍ଧାଙ୍କର ବାରମ୍ବାରତା କୁହାଯାଏ । ତୃତୀୟ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭରେ ‘ବାରମ୍ବାରତା’ ଲେଖାଯାଏ।
ଉଦାହରଣ – 1:
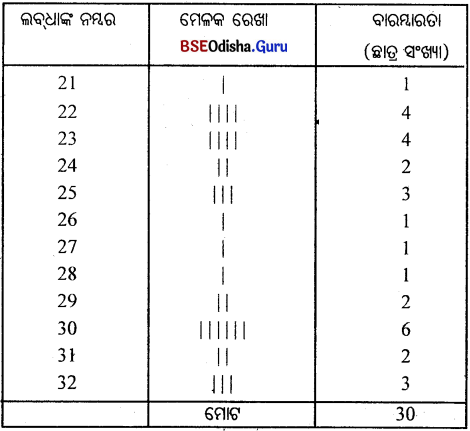
30 ଜଣ ଛାତ୍ର ପରୀକ୍ଷାରେ ରଖୁଥିବା ନମ୍ବର ନିମ୍ନରେ ଦିଆଗଲା। ଗୋଟିଏ ବିବିକ୍ତ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ।
23 22 21 30 32 24 25 23 22 23 32 32 25 27 28 30 22 29 31 31 30 24 22 25 29 26 30 23 30 30
ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ
ସମାଧାନ :
ପ୍ରଥମେ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭରେ ଲବ୍ଧାଙ୍କଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ଉକ୍ରମରେ ଲେଖାଯାଉ।
Question ୧୦।
ପୌନଃପୁନ୍ୟ ବିତରଣ କ’ଣ ? ପୌନଃପୁନ୍ୟ ବିତରଣ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ସାଧାରଣ ନିୟମଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଆଲୋଚନା କର।
(What is Frequency distribution? Explain diferent rules for constructing a Frequency distribution.)
Answer:
ଗୋଟିଏ ସେଟ୍ରେ ଯେତେଗୁଡ଼ିଏ ଉପାଦାନ-ଗ୍ରହଣ କରାଯାଏ ଓ ଉପାଦାନ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧୀୟ ତଥ୍ୟ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନା କଲାବେଳେ ସମ ତଥ୍ୟ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନା କରୁଥିବା ଉପାଦାନମାନଙ୍କୁ କ୍ରମାନ୍ୱୟରେ ସଜାଡ଼ି ଉପସ୍ଥାପନା କରିବାକୁ ପୌନଃପୁନ୍ୟ ବିନ୍ୟାସ (Frequency Array) କୁହାଯାଏ। ମାତ୍ର ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧୀୟ ତଥ୍ୟ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନା କରିବା ବେଳେ ତଥ୍ୟର ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ବିଭାଗ କରାଯାଇ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକ୍ତ ଉପାଦାନମାନଙ୍କୁ ସଜାଡ଼ି, ଉପସ୍ଥାପନା କରିବାକୁ ପୌନଃପୁନଃ ବିତରଣ (Frequency distribution) ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ। ତେଣୁ ପୌନଃପୁନ୍ୟ ବିନ୍ୟାସ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ଉପାଦାନମାନଙ୍କର ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ସୂଚିତ ହେଉଥିବା ବେଳେ ପୌନଃପୁନଃ ବିତରଣ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ଉପାଦାନର ମୂଲ୍ୟ କେଉଁ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଅନ୍ତର୍ଗତ ତାହା ଜଣାପଡ଼େ। ଉଦାହରଣସ୍ୱରୂପ ଇଂରାଜୀ ପରୀକ୍ଷାରେ ୪୦ ନମ୍ବର ରଖୁଥିବା ଛାତ୍ରଛାତ୍ରୀ ସଂଖ୍ୟା, ଅଷ୍ଟମ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ବାର୍ଷିକ ପରୀକ୍ଷାରେ ୧୦ ଜଣ। ଏହା ପୌନଃପୁନ୍ୟ ବିନ୍ୟାସ। ମାତ୍ର ୩୦ ରୁ ୪୦ ମଧ୍ଯରେ ରଖିଥିବା ଛାତ୍ରଛାତ୍ରୀ ସଂଖ୍ୟା ଯଦି ୧୫ ବୋଲି ଉପସ୍ଥାପନା କରାଯାଏ, ଏହା ପୌନଃପୁନଃ ବିତରଣ ଅଟେ।
ତେଣୁ ପ୍ରଥମେ ତଥ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକର ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ବିଭାଗ କରିବାକୁ ପଡ଼େ। ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ବିଭାଗ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ଶ୍ରେଣୀକୁ ଦୁଇଟି ସଂଖ୍ୟା ମଧ୍ୟରେ ସୀମାବଦ୍ଧ କରି ରଖାଯାଏ। ଗୋଟିଏ କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ର ସଂଖ୍ୟା ଓ ଅନ୍ୟଟି ବୃହତ୍ତମ ସଂଖ୍ୟା। ଏହାକୁ ନିମ୍ନ ସୀମା ଓ ଊର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱସୀମା ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ। ନିମ୍ନ ସୀମା ଯେଉଁ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ପ୍ରଦର୍ଶନ କରେ, ଏହାଠାରୁ କମୂଲ୍ୟର ତଥ୍ୟ ଏହି ଶ୍ରେଣୀଭୁକ୍ତ ହୋଇପାରନ୍ତି ନାହିଁ। ଊର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ବ ସୀମାର ମୂଲ୍ୟଠାରୁ ଅଧିକ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ପ୍ରଦର୍ଶନ କରୁଥିବା ତଥ୍ୟ ମଧ୍ଯ ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକ୍ତ ହୋଇପାରନ୍ତି ନାହିଁ। ତେଣୁ ଦୁଇସୀମା ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକ୍ତ ମୂଲ୍ୟର ତଥ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକ ‘କେବଳ ସେହି ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକ୍ତ ହୁଅନ୍ତି।
ନିମ୍ନ ସୀମା ଓ ଊର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ବ ସୀମା ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଦୂରତାକୁ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଦୂରତା କୁହାଯାଏ ଓ ଏକ ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ଯେଉଁ ସଂଖ୍ୟାରେ ଉପାଦାନଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଉପସ୍ଥାପିତ ହୁଅନ୍ତି, ତାକୁ ସେହି ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ପୌନଃପୁନଃ ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ। ଯେଉଁ କାଗଜ ଫର୍ଦ୍ଦରେ ବିଭିନ୍ନ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ପୌନଃପୁନ୍ୟତା ହିସାବ କରାଯାଏ, ତାହା ଅବମେଳନ ଫର୍ଦ କୁହାଯାଏ ଏବଂ ଯେଉଁ ଫର୍ଦ୍ଦରେ ପୌନଃପୁନଃ ବିତରଣକୁ ଉପସ୍ଥାନା କରାଯାଏ ତାକୁ ପ୍ରବେଶ ପତ୍ର କୁହାଯାଏ। ପୌନଃପୁନ୍ୟ ବିତରଣ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନା ଏକ ସାରଣୀର ରୂପ ନିଏ ଓ ତାକୁ ପୌନଃପୁନଃ ବିତରଣ ସାରଣୀ ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ।
ତଥ୍ୟ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧୀୟ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନା ବେଳେ ସେହି ମୂଲ୍ୟକୁ ମାପ କରାଗଲେ ତାହା ଅବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳସଂଖ୍ୟା ଓ ଗଣନା କରାଗଲେ ତାହା ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ଚଳସଂଖ୍ୟା ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ। ଗୋଟିଏ ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ନିମ୍ନ ସୀମା ଉର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱସୀମାକୁ ମିଶାଇ ୨ରେ ଭାଗ କଲେ ମଧ୍ୟ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ମିଳେ ଯାହା ହାରାହାରି ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିଗତ ଉପାଦାନର ତଥ୍ୟ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନା କରେ। ଉଦାହରଣ ସ୍ୱରୂପ ୧୮ଟି କାରଖାନାରେ ୫୦ ରୁ ୧୦୦ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଶ୍ରମିକ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରନ୍ତି। ମାତ୍ର ଏଥରେ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ କାରଖାନାର ଶ୍ରମିକ ସଂଖ୍ୟା ଜଣାପଡ଼େ ନାହିଁ। ତେଣୁ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ କାରଖାନାର ଶ୍ରମିକ ସଂଖ୍ୟାକୁ ଏକ ହାରାହାରି ହିସାବରେ ନିର୍ଣ୍ଣୟ କରାଯାଏ। ତାହାହେଲା ମାଧ୍ୟମାନ ଅଟେ। ମାତ୍ର ଏହାର ସଠିକତା କମ୍ ଅଯେ।
ସାଧାରଣ ନିୟମ :
(କ) ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ବିଭାଗ ସାଧାରଣତଃ ୫ ରୁ ୨୦ ମଧ୍ଯରେ ବା ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ସଂଖ୍ୟା ସାଧାରଣତଃ ୫ ରୁ ୨୦ ମଧ୍ଯରେ ରଖାଯାଏ। ଏହା ତଥ୍ୟ ପରିମାଣ ଉପରେ ନିର୍ଭରଶୀଳ।
(ଖ) ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଦୂରତା ସାଧାରଣତଃ ୫ ବା ଏହାର ଗୁଣାତ୍ମକ ହୋଇଥାଏ; ଯଥା ୫, ୧୦, ୧୫ ଇତ୍ୟାଦି। ମାତ୍ର ଏହି କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ଏକ ସାଧାରଣ ନିୟମ ହେଲା-
i = \(\frac{L-S}{k}\)
i = ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ହରତ।
s = ଉପସ୍ଥାପିତ ତଥ୍ୟର ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ମୂଲ୍ୟ
C = ଉପସ୍ଥାପିତ ତଥ୍ୟର ସର୍ବାଧିକ ମୂଲ୍ୟ
K = ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ସଂଖ୍ୟା
ଉଦାହରଣସ୍ୱରୂପ 100 ଜଣ କର୍ମଚାରୀଙ୍କ ଦରମା ୫୦୦ ରୁ ୫୫୦୦ ଟଙ୍କା ମଧ୍ଯରେ ଦର୍ଶାଗଲେ ଆମେ ୧୦ଟି ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ବିଭକ୍ତ କରିବାକୁ ଚାହିଁଲେ, ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଦୂରତା ହେବ = \(\frac{5500-500}{10}\) = 500
(ଗ) ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ନିମ୍ନ ସୀମା ଆରମ୍ଭରୁ ୦ ବା ୫ ରୁ ଆରମ୍ଭ ହୋଇଥାଏ।
(ଘ) ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ବିଭାଗ ବହିଃସ୍କରଣ ନୀତି ଓ ଅନ୍ତଃକରଣ ନୀତି ଅଧୀନରେ ଗଠନ କରାଯାଇପାରେ। ବହିଃସ୍କରଣ ନୀତି କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଊର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱସୀମାର ମୂଲ୍ୟ ପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ ସେହି ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକ୍ତ କରାଯାଏ ଓ ଊର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ସହ ସମାନ ମୂଲ୍ୟରେ ତଥ୍ୟକୁ ପର ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକ୍ତ କରାଯାଏ। ଅନ୍ତସ୍କରଣନୀତି ଅଧୀନରେ ଊର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱସୀମା ମୂଲ୍ୟ ସହ ସମାନ ତଥ୍ୟକୁ ସେହି ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ଓ ତା’ଠାରୁ ଅଧିକ ମୂଲ୍ୟଇ ତଥ୍ୟକୁ ପର ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକ୍ତ କରାଯାଏ। ବହିଃସ୍କରଣ ନୀତି ଅଧୀନରେ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ବିଭାଗକୁ ଉପାଦେୟତା ଅଧୂକ ଅଟେ । ଅନ୍ତଃସ୍କରଣ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ବିଭାଗକୁ ବହିଃସ୍କରଣ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ବିଭାଗରେ ପରିଣତ କରିବାକୁ ହେଲେ ଗୋଟିଏ ସାଧାରଣ ସୂତ୍ର ହେଲା-
n = \(\frac{\mathrm{L}_1-\mathrm{U}_2}{2}\)
ଏହି ସଂଶୋଧୂତ ମୂଲ୍ୟ (~)କୁ ଶ୍ରେଣୀଗୁଡ଼ିକର ନିମ୍ନ ସୀମାରୁ ବିୟୋଗ ଏବଂ ଊର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱ ସୀମାରେ ଯୋଗ କରାଯାଏ।
n = ସଂଶୋଧୃତ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ
L<sub>1<sub> = ଦ୍ଵିତୀୟ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ନିମ୍ନ ସୀମା
L<sub>2<sub> = ପ୍ରଥମ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଊର୍ଦ୍ଧ୍ୱସୀମା
(ଙ) ଯେତେବେଳେ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ସଂଖ୍ୟା ଅନେକ ଓ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଦୂରତା ବୃଦ୍ଧି ଘଟାଇ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ସଂଖ୍ୟା ହ୍ର.ସ କଲେ, ଉଚିତ ବିଶ୍ଳେଷଣ ହୋଇପାରେ ନାହିଁ। ସେହି କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ବିଭାଗ କରିବା ବେଳେ ଖୋଲା ମୁହଁ ନୀତି ଅବଲମ୍ବନ କରାଯାଏ, ଯଥା- ୧୦୦ ରୁ କମ୍, ୧୦୦-୨୦୦, ୨୦୦-୩୦୦, ୩୦୦-୪୦୦, ୪୦୦-୫୦୦, ୫୦୦ ରୁ ଅଧିକ ଇତ୍ୟାଦି ଭଳି। ଏହା ଲେଖଚିତ୍ର ଉପସ୍ଥାପନା ଲାଗି ସମସ୍ୟା ସୃଷ୍ଟି କରେ।
(ଚ) ପୌନଃପୁନଃ ବିତରଣ ସ୍ଥଳେ ଉପାଦାନ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧୀୟ ତଥ୍ୟ ବା ମୂଲ୍ୟ ବାମ ପଟରେ ଓ ସେହିତଥ୍ୟ ବା ମୂଲ୍ୟ ଅଧୀନରେ ଆସୁଥୁବା ଉପାଦାନ ସଂଖ୍ୟା ବା ପୌନଃପୁନଃ ବିତରଣ ସାରଣୀ ଗଠନ କରାଯାଏ। ତେଣୁ ପୌନଃପୁନଃ ବିତରଣ ସ୍ଥଳେ କେତେଗୁଡ଼ିଏ ସାଧାରଣ ନିୟମ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହେଲେ ହେଁ ଏହା ଲାଗି ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ ନୀତିନିୟମ ସେପରି କିଛି ନାହିଁ ଓ ଏହା ପୌନଃପୁନ୍ୟ ସାରଣୀରେ ଗଠନ ଓ ବ୍ୟବହାର ଉପରେ ନିର୍ଭରଶୀଳ ଅନୁସରଣ କରାଯାଇଥାଏ।
![]()
Question ୧୧୮
ଆୟତ ରେଖାଚିତ୍ର (Histogram) କ’ଣ ? ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ଲେଖଚିତ୍ର ଓ ଆୟତ ରେଖାଚିତ୍ର ମଧ୍ୟରେ ପାର୍ଥକ୍ୟ ଦର୍ଶାଅ।
(What is Histogram ? Distinguish between Histogram and Bar Diagram.)
Answer:
ପୌନଃପୁନଃ ବିତରଣ ସାରଣୀକୁ ରେଖାଚିତ୍ରରେ ପ୍ରକାଶ କଲେ ତାକୁ ପୌନଃପୁନ୍ୟ ରେଖାଚିତ୍ର କୁହାଯାଏ। ପୌନଃପୁନ୍ୟ ବିତରଣକୁ ରେଖାଚିତ୍ର ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ ପ୍ରକାଶ କରିବାର ବିଭିନ୍ନ ମାଧ୍ୟମ ମଧ୍ଯରୁ, ବିଶେଷ ଆଦୃତ ଓ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ମାଧ୍ୟମଟିକୁ ଆୟତ ରେଖାଚିତ୍ର ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ। ଏହାର ଆବୃତି ସ୍ତମ୍ଭାକାର ଆୟତ କ୍ଷେତ୍ର ସଦୃଶ। ପୌନଃପୁନ୍ୟ ବିତରଣ ସାରଣୀରେ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ବିଭାଗ ଓ ପ୍ରତିଶ୍ରେଣୀର ପୌନଃପୁନଃ ଉପସ୍ଥାପିତ ହୋଇଥାଏ। ତେଣୁ ରେଖା ଚିତ୍ରରେ ସେହିଭଳି ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଓ ପୌନଃପୁନ୍ୟ ପ୍ରଦର୍ଶିତ ହୁଅନ୍ତି। ରେଖାଚିତ୍ରରେ ଭୂଲମ୍ବରେ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଦୂରତା ସବୁ ମାପ କରାଯିବାବେଳେ ଏହି ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଦୂରତାକୁ ଭୂମି ରୂପେ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରି ଆୟତ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରମାନ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହୁଅନ୍ତି ଓ ଏହି ଆୟତ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରର ଉଚ୍ଚତା ପୌନଃପୁନଃ ପ୍ରଦର୍ଶନ କରି ଉଲମ୍ବ ବାହୁରେ ପ୍ରଦର୍ଶନ କରାଯାଇଥାନ୍ତି। ଏହିଭଳି ଯେତୋଟି ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଥାଏ ସେତେଗୋଟି ଆୟତ କ୍ଷେତ୍ର ଗଠିତ ହୁଏ; ଯାହାର ଭୂମି ଓ ଓସାର ହେଲା ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଦୂରତା ଓ ଉଚ୍ଚତା ପୌନଃପୁନ୍ୟ ସଂଖ୍ୟା ଦ୍ୱାରା ନିରୂପଣ କରାଯାଇଥାଏ। ଯଦି ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଦୂରତା ସମାନ ରୁହେ ତେବେ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ଆୟତକ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ଓସାର ସମାନ ଓ ସେହି କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ସମୁଦାୟ ଆୟତକ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରଫଳ ପୌନଃପୁନ୍ୟର ଅନୁପାଳିକ ହୁଏ। ଯଦି ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଦୂରତା ଅସମାନ ହୁଏ ତେବେ ଆୟତ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରଗୁଡ଼ିକର ଓସାର ସମାନ ରହେ ନାହିଁ। ଯେତେବେଳେ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଦୂରତା ଅସମାନ, ସେତେବେଳେ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଦୂରତାକୁ ସମାନ କରି ରେଖାଚିତ୍ର ଅଙ୍କନ କରାଯାଏ। ଏହି କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ଯେଉଁ ସୂତ୍ର ପ୍ରୟୋଗ କରାଯାଏ, ତାହା ହେଲା-
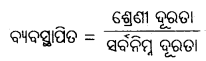
ଏହି ସୂତ୍ରର ପ୍ରୟୋଗ କରାଯାଇ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ସମଦୂରତା ଓ ପୌନଃପୁନ୍ୟତା ମାପ କରାଯାଏ।
ଉଦାହରଣ ସ୍ବରୂପ :
୩୦ – ୪୦ – ୧୫
୪୦ – ୫୫ – ୩୩
୫୫ – ୭୦ – ୩୬
ଏହାଙ୍କୁ ସମଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଦୂରତାରେ ପ୍ରକାଶ କରିବାକୁ ହେଲା;
ଶ୍ରେଣୀ – ପୌନଃପୁନ୍ୟତା – ବ୍ୟବସ୍ଥାପିତ ଉପାଦାନ – ବ୍ୟବସ୍ଥାପିତ ପୌନଃପୁନ୍ୟ

ଏହାର ଅର୍ଥ ୬୦ – ୭୦ର ପୌନଃପୁନ୍ଯ = ୨୪
ତେଣୁ ଜଣାଯାଏ ଯେ ୫୦ ରୁ ୬୦ ପୌନଃପୁନଃ = ୨୩
ନିମ୍ନରେ ଏହି ସାରଣୀକୁ ଆୟତ ରେଖାଚିତ୍ର ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ ପ୍ରକାଶ କରାଗଲା।
ଆୟତ ରେଖା ଚିତ୍ର ଓ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ଲେଖ ଚିତ୍ର ମଧ୍ୟରେ ପାର୍ଥକ୍ୟ :
ଆୟତ ରେଖା ଚିତ୍ର ଦ୍ବିମୁଖୀ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନା ବେଳେ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ଲେଖାଁ ଚିତ୍ର ଏକମୁଖୀ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନା ଅଟେ। ଆୟତ ରେଖା ଚିତ୍ରରେ ଉଭୟ ଲମ୍ବ ଓ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁକୁ ବିଶ୍ଳେଷଣାତ୍ମକ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ପ୍ରଦାନ କରାଯିବା ବେଳେ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ଲେଖ ଚିତ୍ରର କେବଳ ଲମ୍ବର ବିଶ୍ଳେଷଣାତ୍ମକ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ଥାଏ। ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ଲେଖ ଚିତ୍ର କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ପ୍ରସୁର ବ୍ୟବହାର କେବଳ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭର ସୁସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଅବସ୍ଥାର ପ୍ରକାଶନ ଲାଗି ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଇଥାଏ।
Question ୧୨।
Ù_ø Ü_êý ^òÿg K aj b R (Frequency Polygon) କ’ଣ ? ଏହାର ସୁଗୁଣଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନ କର।
(What is Frequency Polygon ? Explain its merits.)
Answer:
ପୌନଃପୁନ୍ୟ ବିତରଣ ରେଖା ଚିତ୍ରମାନଙ୍କ ମଧ୍ୟରୁ ପୌନଃପୁନଃ ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦେଶକ ବହୁଭୁଜ ଏକ ରେଖାଚିତ୍ର ଅଟେ। ଯାହାର ୪ଟି ପାର୍ଶ୍ବ ଥାଏ, ଯେତେବେଳେ ପୌନଃପୁନଃ ବିତରଣ ଦୁଇରୁ ଅଧିକ ସେତେବେଳେ ଏହା ତୁଳନାତ୍ମକ ଆଲୋଚନାରେ ବିଶେଷ ଉପଯୋଗୀ ଅଟେ।ଏହାର ଗଠନକୁ ଦେଖିଲେ ସତେଯେପରି ଏହା ଏକ ଆୟତ ରେଖା ଚିତ୍ର ଉଦ୍ଧୃତ ହୋଇଅଛି। ଏହାର ଗଠନ ସାଧାରଣତଃ ଦୁଇଟି ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ ହୋଇଥାଏ।
(କ) ସିଧାସଳଖ ଆୟତ ରେଖାଚିତ୍ରରୁ ଉଦ୍ଧୃତ କରି।
(ଖ) ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଦୂରତାର ମଧ୍ୟମା ନିର୍ଣ୍ଣୟ କରି।
ପ୍ରଥମ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ସାରଣୀର ଅନୁସରଣରେ ଏକ ଆୟତ ରେଖା ଚିତ୍ର ଅଙ୍କନ କରାଯାଇ ଆୟତ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଗଠନ ହେବ, ସେଗୁଡ଼ିକର ଉପରିଭାଗ ଭୂଲମ୍ବରେ ମଧ୍ଯ ବିନ୍ଦୁ ଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ସରଳ ରେଖାରେ ଯୋଗ କରି ଏହି ପୌନଃପୁନ୍ୟ ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦେଶକ ବହୁଭୁଜ ଗଠନ କରିବା ସରଳ ରେଖାଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଦ୍ଵାରା ଯୋଗ କଲାପରେ ଏହି ଯୋଗରେଖାର ଆକୃତି ହିଁ ପୌନଃପୁନ୍ୟ ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦେଶକ ବହୁଭୁଜ ଅଟେ।
ଦ୍ଵିତୀୟ ପ୍ରକାରରେ, ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଦୂରତାକୁ ଦୁଇ ଭାଗ କରି ସେହି ମଧ୍ୟବିନ୍ଦୁରୁ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ପୌନଃପୁନ୍ୟ ସଂଖ୍ୟା ମାପକରେ ଉଲମ୍ବ ଦିଗରେ ବିନ୍ଦୁ ନିରୂପଣ କରି ସେହି ବିଯୁଗୁଡ଼ିକ ସରଳ ରେଖାରେ ଯୋଗ କରିବା। ପ୍ରଥମ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ନିମ୍ନରେ ଏକ ଆୟତ ରେଖାଚିତ୍ର ଅଙ୍କନ କରାଯାଇ ତହିଁରୁ ବହୁଭୁଜ ରେଖାଚିତ୍ର ଅଙ୍କନ କରାଗଲା। ଏହି ଉପ ରେଖାଚିତ୍ରରେ A, B, C, D ବିନ୍ଦୁଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ଯୋଗ କରି ବହୁଭୁଜ ରେଖାଚିତ୍ର ଗଠନ କରାଯାଇଅଛି।
ଦ୍ବିତୀୟ ପ୍ରକାର ବହୁଭୁଜଅଙ୍କନ:
ପୂର୍ବୋକ୍ତ ରେଖାଚିତ୍ରରେ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଦୂରତାର ମଧ୍ୟବିନ୍ଦୁ ଓ ପୌନଃପୁନ୍ୟ ସଂଖ୍ୟାର ସହାୟତାରେ A, B, C, D ବିନ୍ଦୁ ନିରୂପଣ କରାଯାଇ ବହୁଭୁଜ ରେଖାଚିତ୍ର ଅଙ୍କନ କରାଯାଇଅଛି।
ବହୁଭୁଜ ରେଖା ଚିତ୍ର କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ମଧ୍ୟ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଦୂରତାର ଅସମାନତା ଦେଖାଦେଲେ ଏହାକୁ ଆୟତରେଖା ଚିତ୍ର କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ବ୍ୟବସ୍ଥାପିତ କରାଯିବା ଭଳି ବ୍ୟବସ୍ଥାପିତ କରାଯାଇ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ଦୂରତାକୁ ସମାନକରି, ବହୁଭୁଜ ଅଙ୍କନ କରାଯାଏ। କିନ୍ତୁ ଏହା ଆୟତ ରେଖା ଚିତ୍ରରୁ ଉଦ୍ଧୃତ ହେଲେ ମଧ୍ୟ ଗୋଟିଏ ରେଖା ଚିତ୍ରରେ ଦୁଇ ସେଟ୍ ଆୟତ ରେଖା ଚିତ୍ର ସମ୍ଭବ ହେଉ ନଥିବା ବେଳେ ଗୋଟିଏ ରେଖା ଚିତ୍ରରେ ଦୁଇ-ସେଟ୍ ବହୁଭୁଜ ଗଠନ ସମ୍ଭବ ହୁଏ ଓ ଏହା ତୁଳନାତ୍ମକ ବିଶ୍ଳେଷଣରେ ବିଶେଷ ସହାୟକ ହୋଇଥାଏ।
ଏହାର ଅନ୍ୟ ଏକ ବୈଶିଷ୍ଟ୍ୟ ହେଲା ବହୁଭୁଜ ଗଠନ ସମ୍ଭବ ହୁଏ ଓ ଏହା ତୁଳନାତ୍ମକ ବିଶ୍ଳେଷଣରେ ବିଶେଷ ସହାୟକ ହୋଇଥାଏ। ସେହି ବିନ୍ଦୁରୁ ଭୂମିକୁ ସରଳରେଖାରେ ଯୋଗ କରିବାର ଅର୍ଥ ଏହା ଆୟତ ରେଖାଚିତ୍ରମାନଙ୍କର କ୍ଷେତ୍ରଫଳ ସହ ସମାନ କରି ବହୁଭୁଜ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରଫଳ ପ୍ରଦର୍ଶନ କରିଥାଏ।
ସୁବିଧା :
(କ) ବହୁଭୁଜ ସ୍ଥଳେ ଦୁଇ ସେଟ୍ର ଆଲୋଚନା ଓ ତୁଳନା ଗୋଟିଏ ରେଖା ଚିତ୍ରରେ ସମ୍ଭବ ହୁଏ।
(ଖ) ଆୟତ ରେଖାଚିତ୍ର ତୁଳନାରେ ବହୁଭୂଜର ଗଠନ ସହଜ।
(ଗ) ଏହା ତଥ୍ୟ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନାକୁ ଅତ୍ୟନ୍ତ ସରଳ କରେ।
(ଘ) ଅଧିକ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ବିଭାଗ ସ୍ଥଳେ ଏହା ରେଖାର ବକ୍ରତାକୁ ଅଧିକ ମସୃଣ କରେ।
୧୩ । ନିମ୍ନରେ ୪୫ ଜଣ ପିଲାଙ୍କର ନମ୍ବର ପ୍ରଦାନ କରାଯାଇଛି । ଉପରୋକ୍ତ ସାଂଖ୍ୟକ ତଥ୍ୟକୁ ଆଧାରକରି ଏକ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ (Continuous Frequency Distribution) ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ କର।
(Construct a Continuous Frequency Distribution of the following Data of the marks of 45 students.)
ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ ଗଠନ
ଉପରୋକ୍ତ ସାରଣୀରେ ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ମୂଲ୍ୟାଙ୍କ ୧୨ ଏବଂ ସର୍ବାଧିକ ମୂଲ୍ୟାଙ୍କ ୭୫ ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ ସମ୍ଭୋଗ ବିସ୍ତାର ୧୦ ନେଇ ୧୦ – ୨୦ ପ୍ରଥମ ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ କରାଯାଏ ଏବଂ ଏହିପରି ୭ଟି ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ କରାଯାଏ। ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ଥିବା ମୂଲ୍ୟାଙ୍କକୁ ଗୋଟିଏ ଗୋଟିଏ ମେଳକ ରେଖା ଦ୍ଵାରା ଉପସ୍ଥାପନ କରାଯାଏ। ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ଥିବା ମୋଟ ମୂଲ୍ୟାଙ୍କ (ମେଳକ ରେଖା)କୁ ଯୋଗକରି ଶ୍ରେଣୀ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ନିର୍ଣ୍ଣୟ କରାଯାଏ।
୧୪। ନିମ୍ନରେ ଏକ ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ ଅଞ୍ଚଳର କୋଠରିରେ ସଂଖ୍ୟା ଦିଆଯାଇଛି। ଏକ ବିଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ସାରଣୀ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ କର। (Below give a number of rooms of a house. Construct a discrete Frequency distribution.)
କୋଠରିର ସଂଖ୍ୟା (Number of rooms)
୫, ୮, ୬, ୨, ୪, ୭, ୧, ୨, ୪, ୫
୭, ୬, ୪, ୩, ୫, ୮, ୬, ୪, ୫, ୩
୨, ୮, ୭, ୬, ୧୦, ୫, ୪, ୩, ୨, ୬
୧୪, ୭, ୮, ୪, ୫, ୩, ୨, ୪, ୫, ୩
Answer:
ଏକ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବିତରଣ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତି (Construction of a Discrete F.D.) ;
Question ୧୫।
ନିମ୍ନ ପ୍ରଦତ୍ତ ତଥ୍ୟାବଳୀକୁ ଉପଯୋଗକରି ରାଶିକୃତ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ରେଖା ଅଙ୍କନ କର।
(By using the data as give below. Construct a cumulative Frequency Curve.)
| ଲବ୍ଧାଙ୍କ (ନମ୍ବର) | ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ( ପିଲାସଂଖ୍ୟା) |
| ୧୦ – ୨୦ | ୫ |
| ୨୦ – ୩୦ | ୮ |
| ୩୦ – ୪୦ | ୮ |
| ୪ – ୫୦ | ୧୯ |
| ୫୦ – ୬୦ | ୬ |
Answer:
ପୂର୍ବାପେକ୍ଷା କମ୍ ରାଶିକୃତ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ସାରଣୀ
| ଲବ୍ଧାଙ୍କ (ନମ୍ବର) | ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ( ପିଲାସଂଖ୍ୟା) | ନମ୍ବର ( ପୂର୍ବପେକ୍ଷା କମ୍) | ରାଶିକୃତ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା |
| ୧୦ – ୨୦ | ୫ | ୨୦ | ୫ |
| ୨୦ – ୩୦ | ୮ | ୩୦ | ୧୩ |
| ୩୦ – ୪୦ | ୧୫ | ୪୦ | ୨୮ |
| ୪ – ୫୦ | ୧୦ | ୫୦ | ୩୮ |
| ୫୦ – ୬୦ | ୬ | ୬୦ | ४४ |
| ୬୦ – ୭୦ | ୬ | ୭୦ | ୫୦ |
Question ୧୬।
ପୂର୍ବପେକ୍ଷା ଅଧୂକ ଓଜିଭ୍ ସାରଣୀ ଗଠନ କର। (Construct More than Ogive lable.)
Answer:
| ଲବଙ୍କ (ନମ୍ବର) | ବାରମ୍ବାରତା (ପିଲା ସଂଖ୍ୟା) (Marks more than) | ପୂର୍ଦାପେକ୍ଷା ଅଧୂକ ନମ୍ବର (C.F.) | ରାଶିକୃତ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା |
| ୧୦ – ୨୦ | ୫ | ୧୦ | ୫୦ |
| ୨୦ – ୩୦ | ୮ | ୨୦ | ୪୫ |
| ୩୦ – ୪୦ | ୧୫ | ୩୦ | ୩୭ |
| ୪୦ – ୫୦ | ୧୦ | ୪୦ | ୨୨ |
| ୫୦ – ୬୦ | ୬ | ୫୦ | ୧୧ |
| ୬୦ – ୭୦ | ୬ | ୬୦ | ୬ |
| ୭୦ | ୦ |
Question ୧୭।
ନିମ୍ନରେ ୩୨ ଜଣ ପିଲାଙ୍କର ନମ୍ବର ପ୍ରଦାନ କରାଯାଇଛି। ଉପରୋକ୍ତ ସାଂଖ୍ୟକ ତଥ୍ୟାବଳୀକୁ ଆଧାର କରି ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକ୍ତ ପ୍ରଣାଳୀ (Inclusive Method) ରେ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ କର।
(Construct a Frequency with the help of Inclusive Method.)
ନମ୍ବର (Marks) :
୨, ୪, ୧୦, ୮, ୫, ୧୧,୧୯
୨୫, ୨୧ ୨୨, ୧୮, ୧୬, ୧୫, ୧୧, ୩୦
୩୨, ୩୬, ୪୨, ୩୧ ୪୮, ୫୦, ୫୨, ୪୧
୫୮, ୬୦, ୩୧, ୨୦, ୧୮, ୪, ୬, ୧୨
Answer:
ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକ୍ତ ପଦ୍ଧତିରେ ନିରବଚ୍ଛିନ୍ନ ବାରମ୍ବାରତା ବିତରଣ ଗଠନ
Question ୧୮।
ସାରଣୀ କ’ଣ ? ଏହାର ବିଭିନ୍ନ ଅଂଶ ଲେଖ।
(What is a Table ? Explain its different parts.)
Answer:
ପଂକ୍ତି ଓ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ଆକାରରେ ସଂଗୃହୀତ ତଥ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ଯେଉଁଥରେ ସଜାଡ଼ି ଲେଖାଯାଏ ତାହାକୁ ସାରଣୀ ବା ତାଲିକା କୁହାଯାଏ। ପଂକ୍ତି ଆନୁଭୂମିକ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନର ଏକ ବ୍ୟବସ୍ଥା ହୋଇଥିଲାବେଳେ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ଉଲମ୍ବ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନାର ଏକ ବ୍ୟବସ୍ଥା ତଥ୍ୟର ସରଳ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନ ଓ ତଥ୍ୟମାନଙ୍କ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଥିବା ପ୍ରଭେଦ ନିରୂପଣ ସାରଣୀ ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ ହୋଇଥାଏ। ସାରଣୀ ମୁଖ୍ୟତଃ ଦୁଇ ପ୍ରକାରର। ସେଗୁଡ଼ିକ ହେଲା ଆଧାର ସାରଣୀ ଓ ବିଶ୍ଳେଷଣାତ୍ମକ ସାରଣୀ। ଯେଉଁ ସାରଣୀରେ ତଥ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକର କେବଳ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନ କରାଯାଏ ତାହାକୁ ଆଧାର ସାରଣୀ କୁହାଯାଏ। ଯେଉଁ ସାରଣୀରେ ଉପସ୍ଥାପିତ ତଥ୍ୟମାନଙ୍କର ତୁଳନାତ୍ମକ ଚିତ୍ର ପ୍ରଦାନ କରାଯାଇ ବିଶ୍ଳେଷଣ କରାଯାଇଥାଏ, ତାହାକୁ ବିଶ୍ଳେଷଣାତ୍ମକ ସାରଣୀ କୁହାଯାଏ।
ସାରଣୀର ବିଭିନ୍ନ ଅଂଶ – ସାରଣୀ କେତେକ ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ ଅଂଶକୁ ନେଇ ଗଠିତ। ସେଗୁଡ଼ିକ ହେଲା
(୧) ସାରଣୀର ସଂଖ୍ୟା : ସାରଣୀର ଶୀର୍ଷରେ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ସାରଣୀର କ୍ରମିକ ସଂଖ୍ୟା ଉଲ୍ଲେଖ କରାଯାଇଥାଏ। ଏହାଦ୍ଵାରା ସାରଣୀକୁ ଖୋଜି ପାଇବା ଓ ଆଲୋଚନାରେ ଉଲ୍ଲେଖ କରିବା ସହଜ ହୁଏ।
(୨) ସାରଣୀର ଶୀର୍ଷକ : ସାରଣୀ ସଂଖ୍ୟାର ଠିକ୍ ତଳ ସାରଣୀର ଶୀର୍ଷକ ଲେଖାଯାଏ। ଏହା ସାରଣୀର ବିଷୟବସ୍ତୁ। ଏହାକୁ ପଢ଼ି ପାଠକ ସାରଣୀରେ କ’ଣ ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକ୍ତ ତାହା ଜାଣିପାରନ୍ତି। ଏହା ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ପୂର୍ଣାଙ୍ଗ ଓ ସଂକ୍ଷିପ୍ତ ହେବା ଉଚିତ।
(୩) ଶୀର୍ଷ ଟୀକା : ଶୀର୍ଷଟିକା ଶୀର୍ଷକ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧରେ ଅତିରିକ୍ତ ସୂଚନା ଦେଇଥାଏ। ଏହା ଶୀର୍ଷକର ତଳେ ଏକ ଚନ୍ଦ୍ର ବନ୍ଧନୀ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଲେଖାଯାଏ । ଏହା ଶୀର୍ଷଟୀକା । ଏହା ବିଭିନ୍ନ ରାଷ୍ଟ୍ରର ମୁଣ୍ଡପିଛା ଆୟ କାହା ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ ସାରଣୀରେ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତ କରାଯାଇଛି ତାହା ବ୍ୟକ୍ତ କରୁଛି।
(୪) ପଂକ୍ତିନାମା : ପଂକ୍ତିନାମା ପଂକ୍ତିର ମୁଖ୍ୟ ଶୀର୍ଷକ। ଏହାର ତଳକୁ ପଂକ୍ତି ଉଲ୍ଲେଖ ରହିଥାଏ। ‘ବର୍ଷ’ ପଂକ୍ତିନାମା ଓ ‘୧୯୦୫-୫୧’, ‘୧୯୦୬-୬୧’ ଇତ୍ୟାଦି ପଂକ୍ତି ଉଲ୍ଲେଖ।
(୫) ଶିରୋନାମା : ଶିରୋନାମା ସ୍ତମ୍ଭର ମୁଖ୍ୟ ଶୀର୍ଷକ। ଏଥିରେ ଲେଖାଥିବା ‘ମୁଣ୍ଡପିଛା ଆୟ’ ସାରଣୀରେ ଶିରୋନାମା ଏବଂ ‘୨୦୩’ ଓ ‘୨୦୧୦’ ଉପଶିରୋନାମା।
(୬) କ୍ଷେତ୍ର : ସାରଣୀର ଯେଉଁ ଅଂଶରେ ତଥ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଉପସ୍ଥାପିତ ହୋଇଥାଏ ତାହାକୁ କ୍ଷେତ୍ର କହନ୍ତି । ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ତଥ୍ୟ ଗୋଟିଏ ଗୋଟିଏ କୋଠରିରେ ଲେଖାଯାଏ ଏବଂ ତାହା ପଂକ୍ତି ଓ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ସହିତ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ରହିଥାଏ।
(୭) ପାଦଟୀକା : ସାରଣୀରେ ସନ୍ନିବେଶିତ କୌଣସି ଅଂଶ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧରେ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟିକରଣ ପାଦଟୀକାରେ ଉଲ୍ଲେଖ କରାଯାଏ। ଏହା ସାରଣୀର ନିମ୍ନରେ ବାମ ପାର୍ଶ୍ଵରେ ଲେଖାଯାଏ।
(୮) ଉତ୍ସଟୀକା : ତଥ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକ କେଉଁ ଉତ୍ସ ବା ସୂତ୍ରରୁ ଉଦ୍ଧାର କରାଯାଇଛି, ତାହା ସାରଣୀର ନିମ୍ନରେ ଥିବା ଉତ୍ସଟୀକାରେ ଉଲ୍ଲେଖ କରାଯାଇଥାଏ। ଏହା ‘ବିଶ୍ବ ଉନ୍ନୟନ ରିପୋର୍ଟ – ୨୦୧୦।