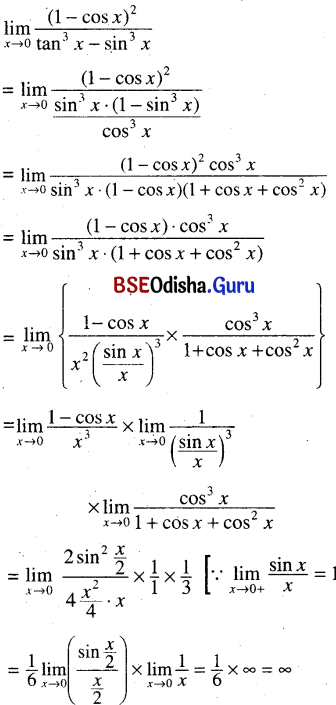
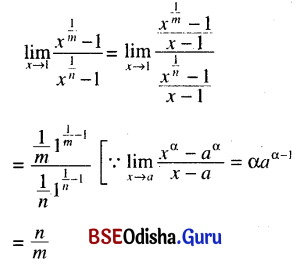
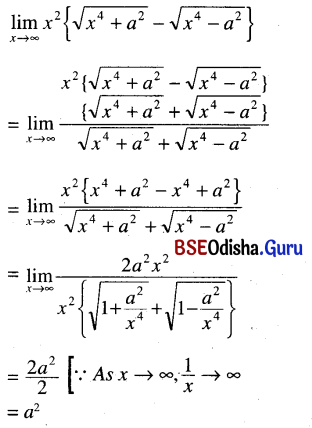
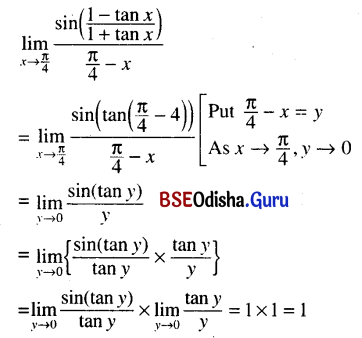
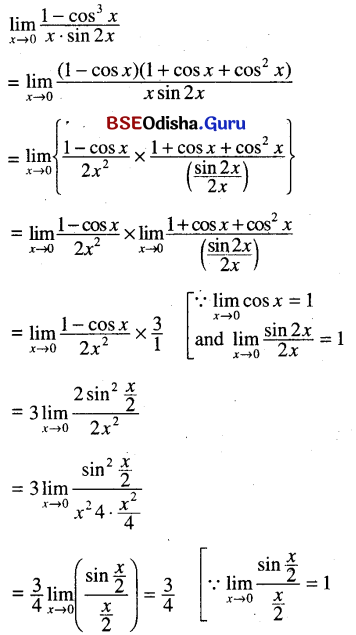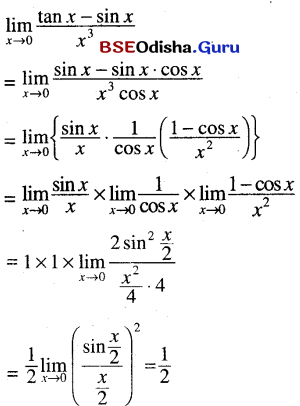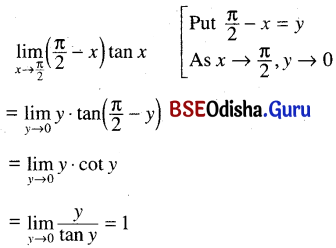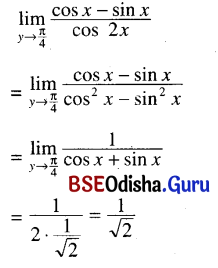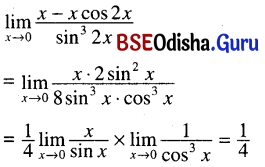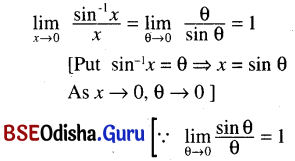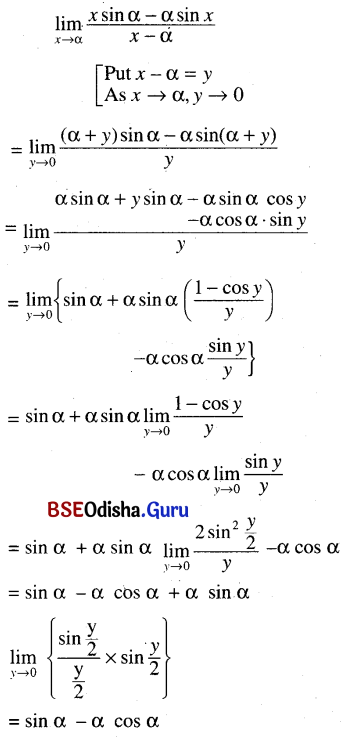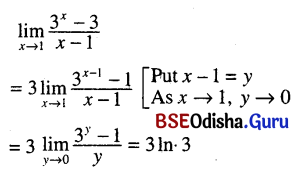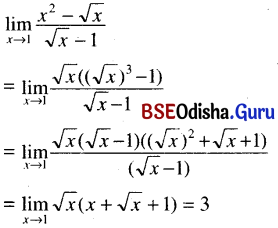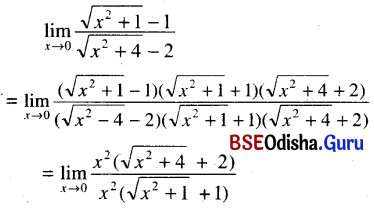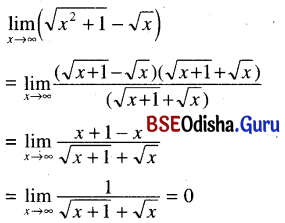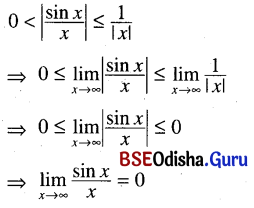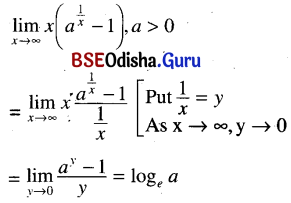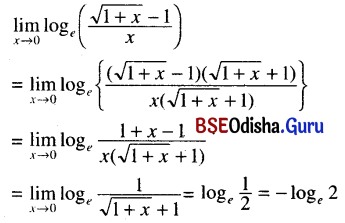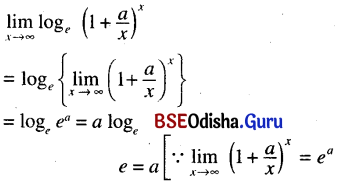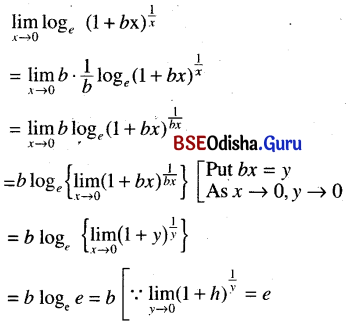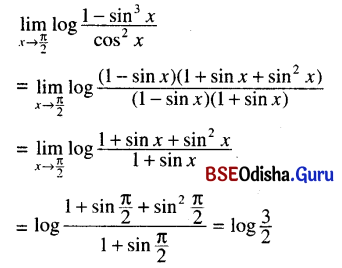Odisha State Board CHSE Odisha Class 11 Sanskrit Solutions Poem 1 सुभाषितावली Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
CHSE Odisha Class 11 Sanskrit Poem 1 सुभाषितावली Question Answer
GROUP – A
(क) बन्धनीमध्यात् शुद्धम् उत्तरं चित्वा लिखत –
1. भाषासु _______ मुख्या दिव्या गीर्वाणभारती ।
(रुचिरा, मधुरा, सरसा)
Answer:
मधुरा
2. भावासु मधुरा मुख्या _______ ग्रीप्वाणभारती ।
(दिव्या, सेव्या, योग्या)
Answer:
दिव्या
3. भाषासु मधुरा मुख्या दिव्या _______
(आङ्गलभाषा, हिन्दीभाषा, गीर्वाणभारती)
Answer:
गीर्वाणभारती
4. तत्रापि _______ मधुरम् ।
(नाट्यं, नृत्यं, काव्यं)
Answer:
काव्यं
5. तस्मादपि मधुरं _______ ।
(सुभाषितम्, सुभस्मितम्, सुचिन्तितम् )
Answer:
सुभाषितम्
6. _______ इन्द्रियसेनायाः नायकः ।
(चक्षुः, श्रोत्रम्, चित्तम्)
Answer:
चित्तम्
7. उपानद्गूढ़पादस्य _______ सर्वभूः ।
( रोमावृतेन, चर्मीवृतेव, वस्त्रावृतेव)
Answer:
चर्मावृतेव
8. _______ यः कुरुते साधोः तथा स्वं दूषयत्यसौ ।
( निन्दां, वाधां, पीड़ां)
Answer:
निन्दां

9. निन्दां यः कुरुते _______ तथा स्वं दूषयत्यसौ ।
(सिन्धोः, बन्धोः, साधोः)
Answer:
साधोः
10. केचिदज्ञानतो _______ ।
(नष्टा:, दुष्टाः, पिष्टा: )
Answer:
नष्टाः
11. केचित् _______ नष्टाः केचिन्नष्टाः प्रमादतः ।
(सुज्ञानतो, विज्ञानतो, अज्ञानतो )
Answer:
अज्ञानता
12. केचिन्नष्टैस्तु _______ ।
(शाशिताः, नाशिताः, वासिताः)
Answer:
नाशिता:
13. अभ्यासेन न लभ्यन्ते चत्वारः _______ गुणाः ।
(सरला:, सरसाः, सहजा:)
Answer:
सहजा:
14. अभ्यासेन न लभ्यन्ते _______ सहजा: गुणा: ।
(त्रयः, चत्वारः, पञ्च)
Answer:
चत्वारः
15. युक्तियुक्तं प्रगृहणीयाद्. _______ अपि विचक्षणः ।
(मूर्खात्, वालात्, वृद्धात्)
Answer:
वालात्
16. युक्तियुक्तं प्रगृहणीयाद् वालादपि _______ ।
( विचक्षणः, विलक्षण:, सुलक्षण:)
Answer:
विचक्षणः
17. पीत्वा कर्दमपानीयं _______ रटरटायते ।
(भीमो, सिंहो, भेको)
Answer:
भेको
18. पक्वं _______ पीत्वा गर्बं नायाति कोकिलः ।
( चूतरसं, इक्षुरसं, निम्बरसं)
Answer:
चूतरसं
19. पक्वं चूतरसं पीत्वा गर्वं नायाति _______ ।
(चातकः, वानरः, कोकिलः)
Answer:
कोकिलः
20. दैवं पुरुषकारणे यः _______ प्रवाधितुम् ।
(योग्य, समर्थः, दक्षः)
Answer:
समर्थः
21. न दैवेन विपन्नार्थः _______ सोऽवसीदति ।
( नर:, मानव:, पुरुषः)
Answer:
पुरुषः
22. अविज्ञाय फलं यो हि _______ त्वेवानुधावति ।
( धर्म, कर्म, चर्म)
Answer:
कर्म
23. _______ फलवेलायां यथा किंशुकसेचकः ।
(धावति, क्रीड़ति, शोचति )
Answer:
शोचति
24. नागुणी _______ वेत्ति ।
(ऋणिनं, गुणिनं, धनिनं)
Answer:
गुणिनं
25. _______ च गुणरागी च सरलो विरलो जनः ।
( धनी, ऋणी, गुणी )
Answer:
गुणी
26. गुणी च _______ च सरलो विरलो जनः ।
(गुणरागी, जनसेवी, धनरागी)
Answer:
गुणरागी
27. गुणी च गुणरागी च _______ विरलो जनः ।
(सरलो, तरलो, सवलो)
Answer:
सरलो
28. अनुष्ठानेन _______ पाठमत्रिण केवलम् ।
(सहिता, रहिता, वाहिता)
Answer:
रहिता
29. रञ्जयत्येव या _______ किं तया शुकविद्यया ।
(जनान्, नरान् लोकान् )
Answer:
लोकान्
30. गच्छत् _______ याति योजनानि शतान्यपि ।
(पिपीलिका, युका, भेका)
Answer:
पिपीलिका

31. तृणादुत्पद्यते _______ दुग्धादुत्पद्यते विषम् ।
(खाद्यं, शस्यं, दुग्धं )
Answer:
दुग्धं
32. तृणादुत्पद्यते दुग्धं दुग्धादुत्पद्यते _______ ।
(विषम्, रस, मधु )
Answer:
विषम्
33. न _______ युक्तं प्रदीप्ते वह्निना गृहे ।
(गर्तखननं, कूपखननं, क्षेत्रखननं )
Answer:
कूपखननं
34. _______ समं सख्यं प्रीतिं चापि न कारयेत् ।
(अञ्जनेन, सज्जनेन, दुर्जनेन )
Answer:
दुर्जनेन
35. _______ दहति चाङ्गारः ।
(कृष्णो, उष्णो, तप्तो)
Answer:
उष्णो
36. _______ कृष्णायते करम् ।
(शीतः, कृष्णः, उष्ण:)
Answer:
शीतः
37. अतः श्वः करणीयानि कुर्यादीद्यैव _______ ।
(वुद्धिमान्, शुद्धिमान्, सिद्धिमान् )
Answer:
वुद्धिमान्
38. आरोप्यते शिला _______ यत्नेन महता यथा ।
(पर्वते, शैले, समुद्रे)
Answer:
शैले
39. नाभिषेको न _______ सिंहस्य क्रियते वने ।
(विस्तार:, निस्तार:, संस्कार : )
Answer:
संस्कारः
40. विक्रमार्जितसत्वस्य स्वयमेव _______ ।
(मृगेन्द्रता, आत्मीयता, ईश्वरता )
Answer:
मृगेन्द्रता
41. _______ च प्रातरुत्थानं भोजनं सह बन्धुभिः ।
(भोग:, निद्रा, युद्धं )
Answer:
युद्धं
42. _______ आपद्गतां रक्षेत् ।
(स्त्रियम्, श्रियम्, प्रियम्)
Answer:
स्त्रियम्
43. _______ पृथिवीं चिन्वन्ति पुरुषास्त्रयः ।
(सुगन्धयुक्तां, सुवीरपुत्रां, सुवर्णपुष्पां )
Answer:
सुवर्णपुष्पां
44. उभयोर्नास्ति भोगेच्छा _______ धनसञ्चयः ।
(स्वार्थं, परार्थं, अन्वर्थं )
Answer:
परार्थं
45. _______ यदुत्थाय मूर्धानमधिरोहति ।
(पादाहतं, शराहतं, वलाहतं)
Answer:
पादाहतं
46. स्वस्थादेवाप्रमानेऽपि देहिनस्तद् वरं _______ ।
(सज:, व्रज:, रजः)
Answer:
रजः
47. येषां _______ नास्ति ।
(चन्द्रबलं, बाहुवलं, मनोबलं)
Answer:
बाहुवलं
48. तेषां _______ वापि किं कुर्यादम्बरस्थितम् ।
(मनोबलं, बाहुवलं, चन्द्रबलं )
Answer:
चन्द्रबलं
49. _______ प्रकृतिः शरीरिणाम् ।
(मरणं, गमनं, शयनं)
Answer:
मरणं
50. मरणं _______ शरीरिणाम् ।
(प्रकृति:, सुगतिः, विकृति:)
Answer:
प्रकृतिः
(ख) अतिसंक्षेपेण उत्तरं लिखत-
1. का भाषासु मधुरा मुख्या दिव्या च ?
Answer:
ଗୀର୍ବାଣଭ।ରତୀ
2. तत्रापि किं मधुरम् ?
Answer:
କାବ୍ୟମ୍
3. इन्द्रियसेनायाः कः नायक: ?
Answer:
ଚିତ୍ତମ୍
4. यः कस्य निन्दां कुरुते असौ तथा स्वं दूषयति ?
Answer:
ସାଧୋଃ
5. दातृत्वं, प्रियवक्तृत्वं, धीरत्वम् उचितज्ञता च केन न लभ्यन्ते ?
Answer:
ଅଭ୍ୟାସେନ
6. दातृत्वं प्रियवक्तृत्वं धीरत्वम् उचितज्ञता च किम्भूता: गुणा: ?
Answer:
ସହଜାଃ
7. कस्मात् विचक्षणः युक्तियुक्तं प्रगृह्णीयात् ?
Answer:
ବାଳାତ୍
8. विचक्षणः वालादपि किं प्रगृहणीयात् ?
Answer:
ଯୁକ୍ତିଯୁକ୍ତମ୍
9. कर्दमपानीयं पीत्वा कः रटरटायते ?
Answer:
ଭେକଃ
10. किं पीत्वा भेक: रटरटायते ?
Answer:
କର୍ଦମପାନୀୟମ୍
11. किं पीत्वा गर्वं नायाति कोकिलः ?
Answer:
ପକ୍ୱଂ ଚୂତରସମ୍
12. पक्वं चूतरसं पीत्वा क: गर्वं नायाति ?
Answer:
କେ।କିଳଃ
13. किम्भूतं चूतरसं पीत्वा गर्वं नायाति कोकिल: ?
Answer:
ପକ୍ବମ୍

14. कः फलवेलायां शोचति ?
Answer:
କିଂଶୁକସେଚକଃ
15. क: गुणं न वेत्ति ?
Answer:
ଅଗୁଣୀ
16. नागुणी किं वेत्ति ?
Answer:
ଗୁଣମ୍
17. गुणी गुणिषु किं भवति ?
Answer:
ମତ୍ସରୀ
18. का शतान्यपि योजनानि याति ?
Answer:
ଗଚ୍ଛତ୍ପିପୀଲିକା
19. कीदृश: वैनतेयोऽपि एकं पदं न गच्छति ?
Answer:
ଅଗଚ୍ଛନ୍
20. धेनुपन्नगयो : किमस्ति ?
Answer:
ପାତ୍ରାପାତ୍ରବିଶେଷଃ
21. तृणात् किम् उत्पद्यते ?
Answer:
ଦୁଗ୍ଧମ୍
22. कस्मात् विषम् उत्पद्यते ?
Answer:
ଦୁଗ୍ଧାତ୍
23. प्रदीप्ते वह्निना गृहे किं न युक्तम् ?
Answer:
କୂପଖନନମ୍
24. केन समं सख्यं प्रीतिञ्चापि न कारयेत् ?
Answer:
ଦୁର୍ଜନେନ
25. उष्णः अङ्गारः किं करोति ?
Answer:
କରଂ ଦହତି
26. कः श्वः करणीयानि अद्यैव कुर्यात् ?
Answer:
ବୁଦ୍ଧିମାନ୍
27. आत्मा कयो: आरोप्यते क्षणेन अधोनिपत्यते च ?
Answer:
ଗୁଣଦୋଷୟୋ
28. कस्य वने नाभिषेको न संस्कारः क्रियते ?
Answer:
ସିଂହସ୍ୟ
29. सिंहस्य कुत्र नाभिषेको न संस्कारः क्रियते ?
Answer:
ବନେ
30. कस्य स्वयमेव मृगेन्द्रता ?
Answer:
ବିକ୍ରମାର୍ଜିତସସ୍ୟ
31. पुरुषास्त्रय: किम्भूतां पृथिवीं चिन्वन्ति ?
Answer:
ସୁବର୍ଣ୍ଣପୁଷ୍ପମ୍
32. कयो: भोगेच्छा नास्ति ?
Answer:
କୃପଣୋଦାରୟୋଃ
33. किं वरम् ?
Answer:
ରଜଃ
34. शरीरिणां प्रकृति: किम् ?
Answer:
ମରଣମ୍
35. शरीरिणां विकृति: किम् ?
Answer:
ଜୀବିତମ୍
GROUP – B
(ग) संक्षेपेण (षड्भि: वाक्यै:/ पञ्चविंशत्यापदै:) उत्तरं लिखत –
1. संस्कृतभाषायाः सुभाषितस्य च किं महत्त्वम् ?
Answer:
ବିଶ୍ଵ ଯଃ ଭାଷା ବିଦ୍ୟନ୍ତେ ତାସୁ ମୁଖ୍ୟ ଭବତି ସଂସ୍କୃତଭାଷା । ଏଷା ଭାଷା ମଧୁରା ତଥା ଦିବ୍ୟା ଭବତି । ଏଷା ସୁରଭାରତୀ ଦେବଭାଷାରୂପେଣ ବା ଖ୍ୟାତା ଅସ୍ତା । ଅସ୍ୟା ସଂସ୍କୃତଭାଷାୟା ଯାନି କାବ୍ୟାନି ରଚିତାନି ତାନି ମଧୁରାଣି ଭବନ୍ତି । ସଂସ୍କୃତେନ ରଚିତକାଵେଷୁ ପ୍ରାପ୍ତାନି ସୁଭାଷିତାନି କାବ୍ୟଭ୍ୟଃ ଅପି ମଧୁରାଣି ସନ୍ତି ।
2. कथं चित्तविजय एव जय इत्युच्यते ?
Answer:
ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟସେନାୟଃ ନାୟକଃ ଭବତି ମନଃ । ଅତଃ ତଥ୍ୟ ଜୟ ଏବ ପ୍ରକୃତଜୟଃ । ଯେନ ପ୍ରକାରେଣ ପାଦୁକାବୃତପାଦଃ ଜନଃ ସମଗ୍ରା ଭୂମିଂ ଚର୍ମାବୃତାମ୍ ଇବ ଅନୁଭବତି, ଅସୌ ଜନଃ ଗମନସମୟେ ମାର୍ଗେ କଣ୍ଟକାଦୀନାମ୍ ଅନୁଭବମପି ନ କରୋତି । ତଥିବେ ମନମଃ ଜୟେନ ଏବ ନରଃ ଦୁଃଖସ୍ୟ ଅନୁଭବ ଅପି ନକରୋତି । ଚିତ୍ତଜୟୀ ତୁ ପ୍ରକୃତବିଜୟୀ ଇତି ।
3. यः साधोः निन्दां कुरुते तस्य का गतिर्भवति ?
Answer:
ଯଃ ସାଧୋ ନିତାଂ କୁରୁତେ, ସଃ ସ୍ୱୟମେବ ଦୂଷୟତି । ସାଧଃ ସଦୈବ ପରୋପକାରଂ କରୋତି । ପରନ୍ତୁ ଯଃ ଦୁଷ୍ଟଜନଃ ଡଃ ସଦୈବ ସାଧୋ ନିନ୍ଦନ୍ତି । ତଥା ଯଃ ଭୂତିମ୍ ଆକାଶେ ଉଚ୍ଚୈଃ କ୍ଷିପେଡ୍ ସା ତସ୍ୟ ମୂଷି ଏବଂ ପତେତ । ତେନ ପ୍ରକାରେଣ ସାଧୋ ନିନ୍ଦୟା ସ୍ଵସ୍ୟ ଦୂଷଣ୍ଡବ ଭବତି ।
4. के चत्वारगुणाः अभ्यासेन न लभ्यन्ते ?
Answer:
ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ଚରିତ୍ରେ ବୃହତଃ ଗୁଣା ଦୃଶ୍ୟନ୍ତେ। କେଚନ ଗୁଣା ଅଭ୍ୟାସେନ ପ୍ରାପ୍ୟନ୍ତେ ତଥା କେଚନ ଗୁଣା ସହଜାତଃ ଏବ। ଦାତୃତ୍ୱମ୍ (ଦାନଶୀଳତା), ପ୍ରିୟବକ୍ତତ୍ଵମ୍ (ପ୍ରିୟବଚନମ୍), ଧୀରତ୍ୱ (କାର୍ଯ୍ୟସମ୍ପାଦନେ ପ୍ରତିବଦ୍ଧତା) ତଥା ଉଚିତଜ୍ଞତା (କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟାକର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟଜ୍ଞାନେ ନିଷ୍ଠା) ଇତି ଚର୍ଚ୍ଚାରଃ ସହଜା ଗୁଣା କଦାପି ଅଭ୍ୟାସେନ ନ ଲଭ୍ୟନ୍ତେ ।
5. किंशुकसेचकः कथं शोचति ?
Answer:
ଯଥା କୋଽପି ଜନଃ ପରିଶ୍ରମପୂର୍ବକଂ ଜଳସେଚନଂ କୃତ୍ଵା ଫଳାଗମକାଳେ ଜଳସେଚନେନ ବର୍ଦ୍ଧିତଂ ଫଳହୀନଂ କିଂଶୁକବୃକ୍ଷ ପଲାଶବୃକ୍ଷ ବା ଦୃଷ୍ଟା ଶୋକଂ କରୋତି, ତଥା କାର୍ଯ୍ୟସ୍ୟ ଅନ୍ତିମପରିଣତିବିଷୟ ନ ବିଚାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଯଃ ଜନଃ କର୍ମଣି ନିରନ୍ତରଂ ରତଃ ଭବତି ଡଃ ଅନ୍ତେ ଦୁଃଖ୍ୟତଃ ଭବତ୍ୟେବ ।
6. कथं शुकविद्या अनुपयुक्ता ?
Answer:
ବିଦ୍ୟା ତଦା ଏବ ସଫଳା ଭବତି ଯଦା ସା ପ୍ରୟୋଗଯୁକ୍ତା ଭବତି । ପରନ୍ତୁ ଯଦି ସା ବିଦ୍ୟା ଅନୁଷ୍ଠାନେନ ରହିତା ଭବତି ତହିଁ ତସ୍ୟା ବିଦ୍ୟାୟଃ ପାଠମାତ୍ରେଣ କେବଳଂ ଲୋକରଞ୍ଜନଂ ଭବତ୍ୟେବ । ଅତଃ ଶୁକପଠିତ ବିଦ୍ୟାବତ୍ ପ୍ରୟୋଗହୀନୟା ତଯା ବିଦ୍ୟୟା କିଞ୍ଚିତ୍ ପ୍ରୟୋଜନଂ ନାସ୍ତ୍ୟବ । ଏତାଦୃଶ ଶୁକବିଦ୍ୟା ଅନୁପଯୁକ୍ତା ଭବତି ।
7. कीदृश: वैनतेयः एकं पदमपि न गच्छति ?
Answer:
ଅସ୍ମାନ୍ ସଂସାରେ ଯଃ ଆଳସ୍ୟରତଃ ସ୍ୱ କିମପି କର୍ତ୍ତୃ ନ ପାରୟତି ପରନ୍ତୁ ଯଃ ନିରନ୍ତରଂ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରୋତି ସ ସର୍ବପ୍ରକାରକଂ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରୁଁ ସାମର୍ଥ୍ୟ ପ୍ରାୟୋତି । ଯଥା କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ରା ପିପୀଲିକା ସର୍ବଦା ଚଳତି ଅତଃ ସା ଗଚ୍ଛନ୍ତୀ ଶତାନି ଯୋଜନାନି ଯାତି । ଅତ୍ୟନ୍ତସମର୍ଥ ବୈନତେୟ ନାମ ଗରୁଡଃ ଶତଯୋଜନଗମନେ ସାମର୍ଥ୍ୟ ବହନ୍ ଅପି ଯଦି ଗନ୍ତୁମ୍ ଇଚ୍ଛା ନ କରୋତି ତହିଁ ଏବଂ ପତ୍ରମ୍ ଅପି ଗତଂ ନ ପାରୟତି ।
8. वह्निप्रदीप्ते गृहे कूपखननं कथम् अनुचितम् ?
Answer:
ଆସନ୍ନବିପଦଂ ପ୍ରତିକାରଃ ଆଦୌ ଏବ ଚିନ୍ତନୀୟଃ, ଅନ୍ୟଥା ଆପତ୍କାଳେ ଯଦି ତସ୍ୟ ପ୍ରତିକାରସ୍ୟ ବିଷୟେ ଚିନ୍ତା କ୍ରିୟତେ ତେନ କିମପି ନ ଭବତି । ଘେନ ପ୍ରକାରେଣ ଯଦା ଅଗ୍ନିନା ଗୃହଂ ପ୍ରଜ୍ବଳିତଂ ଭବତି ତଦା ଯଦି କୋଽପି କୂପଖନନବିଷୟ ଚିନ୍ତୟିଷ୍ୟତି ତହିଁ ଯେନ କିଂ ଗୃହଂ ସଂରକ୍ଷିତଂ ସ୍ୟାତ୍ ? ଅତଃ ସର୍ବଦା ସର୍ବତ୍ର ପ୍ରାର୍ଯୋଜନା ଏବଂ କର୍ଭବ୍ୟା । ଅତଃ ବହ୍ନିପ୍ରଦୀପ୍ତି ଗୃହେ କୂପଖନନମ୍ ଅନୁଚିତମ୍ । ଆଦୌ ଏବଂ କରଣୀୟମ୍ ।
9. बुद्धिमान् श्वः करणीयानि कथम् अद्य कुर्यात् ?
Answer:
ସଂସାରଃ ଖଳୁ ବିଚିତ୍ର । ଜୀବନଂ ଖଳୁ ଅଳିକମ୍ । କଦା କିଂ ଭବିଷ୍ୟତି କୋଽପି କଥୟିତଂ ନ ପାରୟିଷ୍ୟତି । ଶଃ କସ୍ୟ କିଂ ଭବିଷ୍ୟତି ଇତ୍ୟପି ବୟଂ ନ ଜାନୀମଃ । ଅତଃ ଯଃ ବୁଦ୍ଧିମାନ୍ ଡଃ ଅସ୍ୟ ବିଷୟସ୍ୟ ବିବେଚନାଂ କୃତ୍ୱା ଶଃ କରଣୀୟାନି କାର୍ଯ୍ୟାଣି ଯଥାଶୀଘ୍ର କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟାତ୍ । ଡଃ କରଣୀୟାନି ଅଦୈବ କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟାତ୍ ।
10. सिंहेन मृगेन्द्रता केन रूपेण अर्जिता ?
Answer:
ସ୍ଵପରାକ୍ରମବଳେନ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ଅସ୍ମିନ୍ ସଂସାରେ ପ୍ରତିଷ୍ଠା ଲଭତେ । ଯଥା ସିଂହଃ ସ୍ଵପରାକ୍ରମବଳେନ ଏବ ବନେ ରାଜା ଭବତି । ବନେ ତସ୍ୟ ସଂସ୍କାରଃ ଅଭିଷେକ ଚ ନ କ୍ରିୟତେ । ସ୍ଵକୀୟ ପରାକ୍ରମଶଲ୍ୟା ତୁ ସିଂହ ବନମଧ୍ୟ ପଶୁରାଜପଦଂ ପ୍ରାଷ୍ଟୋତି । ସର୍ବେ ପଶତଃ ସିଂହଂ ରାଜା ଇତି ସ୍ଵୀକୁର୍ବନ୍ତି ।
11. केषां चन्द्रवलं किमपि कर्तुं न शक्नोति ?
Answer:
ଯେତାଂ ବାହୁବଳଂ ନାସ୍ତି, ଯେତାଂ ମନୋବଳମପି ନାସ୍ତି ତେଷା କିମପି କାର୍ଯ୍ୟସିଦ୍ଧି ନ ଭବତି । କେବଳଂ ଭାଗ୍ୟସ୍ୟ ଆଧାରଣ କିମପି ନ ଭବତି । ଅତଃ ଯସ୍ୟ ନ ବାହୁବଳମସ୍ତ ନାପି ମନୋବଳମସ୍ତ କେବଳମ୍ ଆକାଶସ୍ଥିତେନ ଚନ୍ଦ୍ରବଳେନ ଅର୍ଥାତ୍ ଭାଗ୍ୟବଳେନ ତସ୍ୟ କିମପି ନ ଭବିଷ୍ୟତି । ତାଦୃଶଃ ଜନଃ କିମପି କରୁଁ ନ ଶକ୍ନୋତି ।
GROUP – C
(घ) प्रायश: चत्वारिंशता पदैः अष्टाभिः वाक्यैवी उत्तरं लिखत –
1. के के कथं नष्टाः भवन्ति ?
Answer:
ଅସ୍କ୍ରିନ୍ ସଂସାରେ ଜନଃ ବିବିଧପ୍ରକାରେଣ ନଶ୍ୟନ୍ତି । କେଚିତ୍ ଜନଃ ସ୍ବସ୍ୟ ଅଜ୍ଞାନକାରଣାତ୍ ନଷ୍ଟ ଭବନ୍ତି । କେଚିତ୍ ଜନାଃ ପ୍ରମାଦବଶତଃ ନାଶଂ ଲଭନ୍ତେ । ଅନ୍ୟ କେଚନ ଜନଃ ଜ୍ଞାନସ୍ୟ ଗର୍ବକାରଣାତ୍ ଏବଂ ନଷ୍ଟତଂ ଯାନ୍ତି । ଅପରେ କେଚନ ଜନଃ ନଷ୍ଟାନା ସଙ୍ଗେନ ଏବଂ ବିନାଶଂ ପ୍ରାପ୍ଲା ବନ୍ତି । ଅର୍ଥାତ୍ ନଷ୍ଟି ନାଶିତାଂ ଭବନ୍ତି । ଜନାନାଂ ନଷ୍ଟସ୍ୟ ରୂପଂ ପ୍ରକାରଂ ଯଥା ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତଂ ତଦେବ ଶିକ୍ଷଣୀୟଂ ଗ୍ରହଣୀୟଂ ଚ ଭବତି ।
2. विचक्षणः बालादपि कथं किं च गृहणीयात् ?
Answer:
ପଣ୍ଡିତଜନଃ ସର୍ବଦୈବ ପାଣ୍ଡିତ୍ୟପୂର୍ଣ ତଥା ଯୁକ୍ତିଯୁକ୍ତ ବଚନଂ ତୁ ବଦତ୍ୟେବ । କିନ୍ତୁ ଯଦି କୋଽପି ବାଳକ ଯୁକ୍ତିଯୁକ୍ତ ବାକ୍ୟ ବଦତି ତହିଁ ତତ୍ର ତସ୍ୟ ବଚନମ୍ ଅବଶ୍ୟମେବ ଗ୍ରହଣୀୟମ୍ । ଯଥା ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟ ସ୍ବପ୍ରକାଶେନ ସର୍ବଂ ପ୍ରକାଶୟତି । କିନ୍ତୁ ଯତ୍ର ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟାଲୋକଃ ନ ଗଚ୍ଛତି ତତ୍ର କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ର ଦୀପଃ ଏବ ଅପ୍ରକାଶିତଂ ପ୍ରକାଶୟତି । ବାଳସ୍ୟବଚଂ ହେୟଂ ନ କରଣୀୟମ୍ ।
3. दैवेन विपन्नार्थः पुरुषः कथं न अवसीदति ?
Answer:
ପୁରୁଷ ସ୍ଵସ୍ୟ ପୌରୁଷେଣ ସର୍ବଂ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ସାଧୟତି । ଦୈବେନ ଭାଗ୍ୟନ ବା ନଃ ପୁରୁଷ ବାଧ୍ୟତେ । ଅତଃ ଯ ଜନଃ ସ୍ଵସ୍ୟ ପୌରୁଷେଣ ସ୍ଵ କର୍ମଣା ଦୈବମପି ଦୂରୀକରୁଁ ବାସ୍ତୁ ବା ସମର୍ଥ୍ୟ ଭବତି ସ ଭବତି ତଦାଽପି ଅବସାଦଗ୍ରସ୍ତ ନ ଭବତି । ଭାଗ୍ୟସ୍ୟ ପ୍ରତିକୂଳେ ସତି ପୌରୁଷେଣ ସ୍ବସିଦ୍ଧି ଯତଃ ଉଦ୍ୟୋଗିନଂ ପୁରୁଷସିଂହମୁପୈତି ଲକ୍ଷ୍ମୀଃ ।

ଶ୍ଲୋକ – ୧
भाषासु मधुरा मुख्या दिव्या गीर्वाणभारती ।
तत्रापि काव्यं मधुरं तस्मादपि सुभाषितम् ॥ १ ॥
ଭାଷାସୁ ମଧୁରା ମୁଖ୍ୟା ଦିବ୍ୟା ଗୀର୍ବାଣଭାରତୀ ।
ତତ୍ରାପି କାବ୍ୟ ମଧୁରଂ ତସ୍ମାଦପି ସୁଭାଷିତମ୍ ॥ ୧ ॥
ଅନ୍ୱୟ – ଗୀର୍ବାଣଭାରତୀ ଭାଷାସୁ ମଧୁରା ମୁଖ୍ୟା ଦିବ୍ୟା (ଚ ଭବତି) । ତତ୍ରାଽପି ମଧୁରଂ କାବ୍ୟ ତସ୍ମାଦପି ସୁଭାଷିତଂ (ମଧୁରଂ ଭବତି) ।
ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ – ଗୀର୍ବାଣଭାରତୀ = ଦେବବାଣୀ, ସଂସ୍କୃତଭାଷା । ଭାଷାସୁ = ଭାଷାମାନଙ୍କ ମଧ୍ୟରେ । ସୁଭାଷିତମ୍ = ଉତ୍ତମ କଥା ।
ଅନୁବାଦ – ଦେବବାଣୀ ସଂସ୍କୃତଭାଷା ଭାଷାମାନଙ୍କ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ମଧୁରା, ମୁଖ୍ୟ ଓ ଦିବ୍ୟା ଅଟେ । ଏଠାରେ କାବ୍ୟ ହେଉଛି ମଧୁର, ତା’ଠାରୁ ଅଧ୍ଵ ସୁଭାଷିତ ବା ନୀତିବାଣୀ ।
ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶଂସିତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଃ ପଠିତଃ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ଥ ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗସ୍ଥିତଃ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ପଦ୍ୟାତ୍ ସଂଗୃହୀତଃ । ସଂସ୍କୃତବାମୟେ ଜୀବନେ ଶିକ୍ଷାର୍ଥୀ ସାମାଜିକନୀତିବଦ୍ଧନାର୍ଥ ଚ ଚରିତ୍ରନିର୍ମାଣାର୍ଥୀ କବୟଃ ସୁଭାଷିତରୂପେଣ ରତ୍ନାନି ପ୍ରଦତ୍ତବନ୍ତୀ । ଅତ୍ର ଅସ୍ମିନ୍ ଶ୍ଳୋକେ ଲୋକଶିକ୍ଷାର୍ଥୀ ସୁଭାଷିତାନାଂ ମହତ୍ତ୍ୱ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତମ୍।
ମନୁଷ୍ୟାନାଂ ଭାବସଂପ୍ରସାରଣାର୍ଥୀ ଯସ୍ୟା ପରମାବଶ୍ୟକତା ବିଦ୍ୟତେ ସା ଭାଷା । ଇୟଂ ଭାଷା ଭାବପରିପ୍ରକାଶନସ୍ୟ ମାଧ୍ୟମିଂ ଭବତି । ଭାଷାମାଂ ମୂଳଭୂତଃ ଆଦିଭାଷା ଭବତି ସଂସ୍କୃତଭାଷା । ସଂସ୍କୃତଭାଷା ସର୍ବାଷା ଭାଷାମାଂ ଜନନୀ ଭବତି । ଇୟଂ ଗୀର୍ବାଣଭାରତୀ ରୂପେଣ ଆଖ୍ୟାତା । ଅତୀବ ମଧୁରା ଅମୃବର୍ଷିଣୀ ଚ । ଦେବା ଅସ୍ୟା ଭାଷାୟାଂ କଥୋପକଥନଂ ଭବନ୍ତି । ବେଦମନ୍ତୋଽପି ସଂସ୍କୃତଭାଷାୟାଂ ରଚିତଃ ଭବତି ! ଭାଷାସୁ ମୁଖ୍ୟ ମଧୁରା, ଦିବ୍ୟା ଚ ଭବତି ସଂସ୍କୃତଭାଷା । ଇୟଂ ଭାଷା ସ୍ଵର୍ଗୀୟା ଭବତି । ତତ୍ରାଽପିମଧୁରଂ କାବ୍ୟ ତସ୍ମାଦପି ସୁଭାଷିତଂ ମଧୁରଂ ଭବତି । ଅତଃ ଏତତ୍ କାବ୍ୟ ପଠନଂ ପାଠନଂ ଚ କରଣୀୟମ୍ ।
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶଂସିତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଟି ପଠିତ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକର ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗସ୍ଥିତ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ରୁ ସଂଗୃହୀତ । ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବାଦ୍ୟରେ ଜୀବନରେ ଶିକ୍ଷା ନିମନ୍ତେ ଓ ସାମାଜିକ ନୀତିବର୍ଦ୍ଧନ ନିମନ୍ତେ ଚରିତ୍ର ନିର୍ମାଣ ପାଇଁ କବିମାନେ ସୁଭାଷିତ ରୂପରେ ରତ୍ନମାନ ପ୍ରଦାନ କରିଛନ୍ତି । ଏଠାରେ ଲୋକ ଶିକ୍ଷା ନିମନ୍ତେ ସୁଭାଷିତର ମହତ୍ତ୍ଵତା ପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତ ହୋଇଛି ।
ମନୁଷ୍ୟର ଭାବ ସମ୍ପ୍ରସାରଣ ନିମନ୍ତେ ଯାହାର ପରମ ଆବଶ୍ୟକତା ରହିଛି ତାହା ହେଉଛି ଭାଷା । ଏହି ଭାଷା ଭାବ ପରିପ୍ରକାଶନର ମାଧ୍ୟମ । ଯେତେ ଭାଷା ଅଛି ସେସବୁର ମୂଳ ହେଉଛି ସଂସ୍କୃତ । ସଂସ୍କୃତ ସବୁ ଭାଷାର ଜନନୀ । ଏହା ଗୀର୍ବାଣଭାରତୀ ରୂପେ ଆଖ୍ୟାୟିତ । ଏହା ଅତୀବ ମଧୁର ଅମୃତବର୍ଷିଣୀ । ଦେବତାମାନେ ଏହି ଭାଷାରେ କଥୋପକଥନ ହୁଅନ୍ତି । ବେଦମନ୍ତ୍ର ମଧ୍ୟ ଏହି ସଂସ୍କୃତ ଭାଷାରେ ରଚିତ ବା ଲିଖ୍ । ଭାଷାମାନଙ୍କ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଏହା ମୁଖ୍ୟା ଓ ଦିବ୍ୟା ତଥା ସ୍ଵର୍ଗୀୟା ଅଟେ । ଏହି ଭାଷାଠାରୁ ମଧୁର ହେଉଛି କାବ୍ୟ ଯାହା କବିର କୃତି ଅଟେ । ପୁନଶ୍ଚ ଏସବୁରୁ ଅଧ୍ଵ ମଧୁର ହେଉଛି ସୁଭାଷିତ ବା ନୀତିବାଣୀ । ଏଣୁ ଏସବୁର୍ ପଠନ ତଥା ପାଠନ ଏକାନ୍ତ ଆବଶ୍ୟକ ।
ବ୍ୟାକରଣ:
ସନ୍ଧିବିଚ୍ଛେଦ – ତନ୍ଦ୍ରାପି = ତତ୍ର + ଅପି । ତସ୍ମାଦପି = ତସ୍ମାତ୍ + ଅପି ।
ସମାସ – ଗୀର୍ବାଣଭାରତୀ = ଗୀର୍ବାଣୀ ଭାରତୀ (କର୍ମଧାରୟଃ) । ସୁଭାଷିତମ୍ = ସୁନଃ ଭାଷିତମ୍ (କର୍ମଧାରୟଃ )
ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତି – ଭାଷାସୁ = ନିର୍ଦ୍ଧାରଣେ ୭ମୀ । ତସ୍ମାତ୍ = ଅପାଦାନେ ୫ମୀ ।
ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ – ସୁଭାଷିତମ୍ = ସୁ + ଭାଷ୍ + ଣିଚ୍ + କ୍ତ ।
ଶ୍ଳୋକ – ୨
चित्तमिन्द्रियसेनाया नायकस्तज्जयाज्जयः ।
उपानद्गूढपादस्य चर्मवृतेव सर्वभूः ॥ २ ॥
ଚିତ୍ତମିନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟସେନାୟ ନାୟକସ୍ତଜୟାଜୟ ।
ଉପାନଦ୍ଗୂଢ଼ପାଦସ୍ୟ ଚର୍ମାବୃତେବ ସର୍ବଦୁଃ ॥ ୨ ॥
ଅନ୍ୱୟ – ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟସେନାୟଃ ନାୟକ ଚିତ୍ତମ୍, ତତ୍ ଜୟାତ୍ ଜୟଃ (ଭବତି) । ଉପାନତ୍ ଗୂଢ଼ପାଦସ୍ୟ ସର୍ବତଃ ଚର୍ମାବୃତେବ (ପଶ୍ୟତି) ।
ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ – ଚିଭମ୍ = ମନ । ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟସେନାୟା = ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟମାନଙ୍କର ସେନାପତି । ଉପାନହ୍ = ପାଦୁକା । ଚର୍ମାବୃତେବ = ଚର୍ମଦ୍ଵାରା ଆବୃତ ହେଲାପରି । ସର୍ବତଃ – ସମସ୍ତ ଭୂମିକୁ ।
ଅନୁବାଦ – ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟମାନଙ୍କ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ନାୟକ ବା ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ ହେଉଛି ମନ । ତା’ର ବିଜୟ ହିଁ ପ୍ରକୃତ ଜୟ । ଜୋତାରେ ଆବୃତ ହୋଇଥିବା ପାଦଦ୍ବାରା ସମସ୍ତ ଭୂମି ଚର୍ମରେ ଆବୃତ ହେବାଭଳି ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଉଦ୍ଧୃତଃ ଶ୍ଳୋକ ସଂସ୍କୃତବାମୟସ୍ୟ ରତ୍ନକଳ୍ପା ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ପଦ୍ୟାତ୍ ସଂଗୃହୀତଃ । ଅତ୍ର ଚିତ୍ତମ୍ ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟସେନାୟା ନାୟକଃ ରୂପେଣ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତମ୍।
ମନୁଷ୍ୟାନାମ୍ ଏକାଦଶଇନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟ ଯଥା – ପଞ୍ଚକର୍ମେନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟ, ପଞ୍ଚଜ୍ଞାନେନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟ ମନଶ୍ଚ । ମନଃ ଏକାଦଶଇନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟ ଭବତି । ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟାନାଂ ରାଜା, ନେତା ନାୟକୋ ବା ମନଃ । ମନମଃ ବିଜୟଂ ଜୟଂ ଭବତି । ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟା ଦୁଃଖସ୍ୟ କାରଣଂ ଭବତି । ଦୁଃଖସ୍ୟ ନିଦାନଂ ଜ୍ଞାତ୍ମା ସାକ୍ଷାତ୍ ଅନୁଭବଂ କୃଷ୍ଣା ପ୍ରତିକାରଂ କାରୟେତ୍ । ଇମଂ ପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗ କବି ଦୃଷ୍ଟାନ୍ତମାଧମେନ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣୟତି ଯତ୍ ଯସ୍ୟ ପାଦୌ ଉପାନହେନ ଆବୃତଃ ଭବତଃ ତସ୍ୟକୃତେ ସର୍ବଦୁଃ ଚର୍ମାବୃତେବ ଭବତି । କବି ଯଥାରୀତ୍ୟା ଏତଦେବ ପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତଂ ତଦେବ ଅତୀବ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନୀୟ ଭବତି ।
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଉଦ୍ଧୃତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଟି ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବାଡ଼ମୟର ରତ୍ନକଳ୍ପା ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ରୁ ସଂଗୃହୀତ । ଏଠାରେ ଚିତ୍ତକୁ ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟର ନାୟକ ଭାବେ ଅଭିହିତ କରାଯାଇଛି।
ମନୁଷ୍ୟର ଏକାଦଶ ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟ, ପଞ୍ଚ କର୍ମେନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟ, ପଞ୍ଚ ଜ୍ଞାନେନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟ ଓ ମନ । ମନ ଏହାର ଏକାଦଶ ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟ ଅଟେ । ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟମାନଙ୍କର ରାଜା, ନେତା ତଥା ନାୟକ ହେଉଛି ଏହି ମନ । ମନର ଜୟ ହିଁ ପ୍ରକୃତ ବିଜୟ । ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟମାନେ ଦୁଃଖର କାରଣ ହୋଇଥା’ନ୍ତି । ଦୁଃଖର ନିଦାନକୁ ଜାଣି ସାକ୍ଷାତ୍ ଅନୁଭବ କରି ପ୍ରତିକାର କରିବା ଉଚିତ । ଏ ପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗକୁ କବି ଏକ ସୁନ୍ଦର ଦୃଷ୍ଟାନ୍ତ ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ ପ୍ରତିପାଦନ କରିଅଛନ୍ତି । ତାହା ହେଉଛି ଯେ ଯାହାର ପାଦଦୁଇଟି ଉପାନହ ବା ପାଦୁକାଦ୍ଵାରା ଆବୃତ ହୋଇଛି, ସେ ସମସ୍ତ ଭୂମିକୁ ଚର୍ମଦ୍ଵାରା ଆବୃତ ହେବାଭଳି ଦେଖୁଛି ବା ଅନୁଭବ କରୁଛି । ମାର୍ଗରେ କଣ୍ଟକାଦି ସେ ଅନୁଭବ କରୁନାହିଁ ।
ବ୍ୟାକରଣ:
ସନ୍ଧିବିଚ୍ଛେଦ – ଚିତ୍ତମିନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟସେନାୟା = ଚିତ୍ତମ୍ + ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟସେନାୟା । ନାୟକସ୍ତଜୟାଜୟ = ନାୟକଃ + ତତ୍ + ଜୟାତ୍ + ଜୟଃ । ଉପାନଦ୍ଗୂଢ଼ପାଦସ୍ୟ = ଉପାନନ୍ଦ୍ + ଗୂଢ଼ପାଦସ୍ୟ । ଚର୍ମାବୃତେବ = ଚର୍ମ + ଆବୃତ + ଇବ ।
ସମାସ – ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟସେନାୟଃ = ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟାନାଂ ସେନା, ତସ୍ୟା (୬ଷ୍ଠୀ ତତ୍) । ଗୂଢ଼ପାଦସ୍ୟ = ଗୂଢ଼େ ପାଦୌ ଯସ୍ୟ ଡଃ; ତସ୍ୟ (ବହୁବ୍ରୀହିଃ) । ଚର୍ମାବୃତ = ଚର୍ମଣା ଆବୃତ (୩ୟା ତତ୍) । ସର୍ବଭୂ = ସର୍ବଃ ଭୂଃ ( କର୍ମଧାରୟଃ) ।
ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତି ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରିୟସେନାୟାଃ – ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ୬ଷ୍ଠୀ । ଜୟାତ୍ ହେତୌ ୫ମୀ । ଉପାନତ୍ = ହେତୌ ୫ମୀ ।
ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ – ଜୟ = ଜି + ଅଚ୍ ।
ଶ୍ଳୋକ – ୩
निन्दां यः कुरुते साधोः तथा स्वं दूषयत्यसौ ।
खे भूतिं यः क्षिपेदुच्चैमूर्ध्नि तस्यैव सा पतेत् ॥ ३ ॥
ନିନ୍ଦା ଯଃ କୁରୁତେ ସାଧୋ ତଥା ସ୍ଵଂ ଦୂଷୟତ୍ୟସୌ ।
ଖେ ଭୂତଂ ଯଃ କ୍ଷିପେଦୁର୍ଜେମୂର୍ତ୍ତି ତଥ୍ୟବ ସା ପତେତ୍ ॥ ୩ ॥
ଅନ୍ୱୟ – ଯଃ ସାଧୋ ନିନ୍ଦା କୁରୁତେ, ଅସୌ ତଥା ସ୍ଵଂ ଦୂଷୟତି । ଯଃ ଖେ ଭୂତିମ୍ ଉଲୈ କ୍ଷିପେଡ୍ ସା ତତ୍ସ୍ୟବ ମୂର୍ତ୍ତି ପତେତ୍ ।
ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ – ସାଧୋ = ସାଧୁବ୍ୟକ୍ତିଙ୍କର । ଦୂଷୟତି = ଦୂଷିତ କରିଥାଏ । ଖେ = ଆକାଶରେ । ଭୂତିମ୍ = ଭସ୍ମ । ମୂର୍ତ୍ତି = ମସ୍ତକରେ । କ୍ଷିପେଡ୍ = ଫୋପାଡ଼ିଥାଏ ।
ଅନୁବାଦ – ଯେ ସାଧୁମାନଙ୍କର ନିନ୍ଦା କରିଥାଏ, ସେ ସେହିପରି ନିଜକୁ ଦୂଷିତ କରିଥାଏ, ଯେପରି ଯେ ଭସ୍ମ ବା ପାଉଁଶକୁ ଉଚ୍ଚକୁ ପକାଇଥାଏ ସେହି ଭସ୍ମ ତା’ର ମସ୍ତକରେ ହିଁ ପଡ଼ିଥାଏ ।
ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶ୍ଳୋକୋଽୟଂ ପଠିତଃ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ୟ ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ପଦ୍ୟାତ୍ ଆନୀତଃ । ଅତ୍ର ସାଧୁଜନାନାଂ ନିନ୍ଦାହେତୋ କୀଦୃଶୀ ଦଶ ଭବତି ତଦେବ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତମ୍ ।
ଅସ୍ମିନ୍ ସଂସାରେ ସାଧୁ ସଜ୍ଜନଃ ଚ ଦୁର୍ଲଭପ୍ରାୟ ଭବତି । ତେଷା ନିନ୍ଦାକାରୀ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ଦୁର୍ଜନରୂପେଣ ପରିଚିତମ୍ । ସାଧବ ସଦା ଶୁଦ୍ଧସ୍ଵଭାବାଃ ଭବନ୍ତି । ତେଷା ଦୋଷଦର୍ଶନଂ ତୁ ସ୍ବସ୍ୟ ଦୋଷୀ ପ୍ରଦର୍ଶନମ୍ । ଯେ ତାବତ୍ ତେଷା ଦୂଷୟିତଂ ପ୍ରଯତଂ କୁର୍ବନ୍ତ ତେ ତୁ ସ୍ବୟମେବ ଦୂଷୟନ୍ତି । ଏତତ୍ ପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗମ୍ ଉଦାହରଣଛଳେନ କବି ପ୍ରଭୌତି ଯଥା – କେନାପି ଜନେନ ଭସ୍ମନି ଉର୍ଧ କ୍ଷିପ୍ରେ’ ତଜ୍ଜନସ୍ୟ ମସ୍ତକେ ପତତି ତଥୈବ ଯଃ ସାଧୁ ନିନ୍ଦତି ସ ସ୍ଵୟଂ ତନ୍ନିନ୍ଦୟା ଆତ୍ମାନଂ ପ୍ରଦୂଷୟତି ଏବ । ଅତଃ ସାଧୋ ନିନ୍ଦା ସଦୈବ ପରିହାର୍ଯ୍ୟା ।
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଉକ୍ତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଟି ପଠିତ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକର ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ରୁ ସଂଗୃହୀତ । ଏଠାରେ ସାଧୁମାନଙ୍କର ନିନ୍ଦା କରିବାରୁ କି ଦଶା ହୁଏ ତାହା ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନା କରାଯାଇଅଛି ।
ଏ ସଂସାରରେ ସାଧୁ ବା ସଜନ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ଦୁର୍ଲଭପ୍ରାୟ । ସେମାନଙ୍କର ନିନ୍ଦା କରୁଥିବା ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ଖଳ ବା ଦୁର୍ଜନରୂପେ ପରିଚିତ । ସାଧୁମାନେ ସଦା ଶୁଦ୍ଧ ସ୍ବଭାବ । ସେମାନଙ୍କର ଦୋଷ ଦର୍ଶନ ହିଁ କେବଳ ନିଜର ଦୋଷ ଦର୍ଶନ । ଯେ ସେମାନଙ୍କୁ ଦୂଷିତ ବା କଳଙ୍କିତ କରିବାକୁ ଇଚ୍ଛାକରେ ସେ ନିଜେ ହିଁ କଳଙ୍କିତ ବା ଦୂଷିତ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଏକଥାକୁ ସୁନ୍ଦର ଉଦାହରଣ ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ ଉଲ୍ଲେଖ କରାଯାଇଛି- ଆକାଶରେ ଭସ୍ମକୁ ଯେ ଉଚ୍ଚକୁ ନିକ୍ଷେପିତ କରେ ସେ ଭସ୍ମ ଆସି ତା’ରି ମସ୍ତକରେ ହିଁ ପଡ଼ିଥାଏ । ଏଣୁ ଅନ୍ୟ ପାଇଁ ଯେ ଗାତ ଖୋଳେ ସେ ଗାତରେ ସେ ନିଜେ ହିଁ ପଡ଼ିଥାଏ । ଏଣୁ ଅନ୍ୟର ନିନ୍ଦାରୁ ସଦା ବିରତ ରହିବା ଉଚିତ ।
ବ୍ୟାକରଣ:
ସନ୍ଧିବିଚ୍ଛେଦ – ଦୂଷୟତ୍ୟସୌ = ଦୂଷୟତି + ଅର୍ଥେ । କ୍ଷିପେଦୁଜୈମୂର୍ତ୍ତି = କ୍ଷିପେଡ୍ + ଉଚ୍ଚୈଃ + ମୂର୍ତ୍ତି । ତଦୈବ = ତଥ୍ୟ + ଏବ ।
ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତି – ସାଧୋ = ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ୬ଷ୍ଠୀ । ନିନ୍ଦାମ୍ = କର୍ମଣି ୨ୟା । ସ୍କୃ = କର୍ମଣି ୨ୟା । ଖେ = ସ୍ଥାନାଧ୍ଵରଣେ ୭ମୀ । ଭୂତିମ୍ = କର୍ମଣି ୨ୟା । ମୂର୍ତ୍ତି = ଅଧ୍ଵରଣେ ୭ମୀ ।
ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ – ଦୋଷ = ଦୁଷ୍ + ଘଞ୍ଚ୍ ।
ଶ୍ଳୋକ – ୪
केचिदज्ञानतो नष्टाः केचिन्नष्टाः प्रमादतः ।
केचिज्ज्ञानावलेपेन केचिन्नष्टैस्तु नाशिताः ॥ ४॥
କେଚିଦଜ୍ଞାନତଃ ନଷ୍ଟା କେଚିନ୍ନଷ୍ଟା ପ୍ରମାଦତଃ ।
କେଚିଜ୍ଞାନାବଲେପେନ କେଚିନଷ୍ଟିସ୍ତୁ ନାଶିତା ॥ ୪॥
ଅନ୍ବୟ – କେଚିତ୍ର/ଅଜ୍ଞାନତଃ ନଷ୍ଟା, କେଚିତ୍ ପ୍ରମାଦତଃ ନଷ୍ଟା । କେଚିତ୍ ଜ୍ଞାନାବଲେପେନ (ନଷ୍ଟା) କେଚିତ୍ ତୁ ନଷ୍ଟି ନାଶିତାଃ ।
ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ – କେଚିତ୍ର = କେତେକ । ଅଜ୍ଞାନତା = ଅଜ୍ଞାନତାବଶତଃ । ପ୍ରମାଦତଃ = ଅସାବଧାନତାବଶତଃ । ଜ୍ଞାନାବଲେପେନ = ଜ୍ଞାନର ଗର୍ବଦ୍ୱାରା ନାଶିତା = ନଷ୍ଟ ହୋଇଯାଆନ୍ତି ।
ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶଂସିତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଃ ପଠିତଃ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ୟ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ପଦ୍ୟାଭାଗାତ୍ ସଂଗୃହୀତଃ । ଅତ୍ର ଅସ୍ଥିନ୍ ଶ୍ଳୋକେ ମନୁଷ୍ୟ କଥ୍ୟ ନଶ୍ୟତି ତଦେବ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତମ୍ ।
ଯତ୍ର ସୃଷ୍ଟି ତତ୍ର ବିନାଶଂ, ଯତ୍ର ଜନ୍ମ ତତ୍ର ମୃତ୍ୟୁ ଭବତି । ଶ୍ରୀମଦ୍ଭଗବଦ୍ଗୀତାୟାମ୍ ଉକ୍ତ ଯତ୍ – ‘ଜାତସ୍ୟ ହି ମୃତ୍ୟୁ ଧ୍ରୁବଂ ଜନ୍ମ ମୃତସ୍ୟ ଚ ।’’ ଇତି । ସଂସାରେ ଅଜ୍ଞାନଂ ଘନଂ ତମଃ ଇବ ଭବତି । ଯଥା କୋଽପି ନରଃ ଘନେ ତମସି କି ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟତୟା ଦ୍ରଷ୍ଟୁମ୍ ଅଶତଃ ତଥୈବ ଅଜ୍ଞାନେନ ସମାୟୁକ୍ତ ଜନଃ ବିନାଶଂ ଭଜତି । ଜ୍ଞାନଂ ସୁମାର୍ଗଦ୍ୟୋତକମ୍ । ଅଜ୍ଞାନଂ ବିନାଶକାରଣମ୍ । ଅସ୍ଥିନ୍ ସଂସାରେ ତୁ ଅଜ୍ଞାନତଃ କେଚନ ଜନଃ ବିନଶ୍ୟନ୍ତି । କେଚିତ୍ ପ୍ରମାଦତଃ ଅପି ନଷ୍ଟ ଭବନ୍ତି । ପୁନଶ୍ଚ ଅପରେ କେଚନ ଜ୍ଞାନାବଲେପେନ ନବଂ ଯାନ୍ତି । ପରନ୍ତୁ କେଚିତ୍ର ନଷ୍ଟି ନାଶିତାଂ ଭବନ୍ତି । ଜ୍ଞାନଗର୍ବେଣ ମନସି ଅଭିମାନମ୍ ଅହଙ୍କାରଂ ଚ ଆୟାତି । ଅଳ୍ପଜ୍ଞାନଂ ଭୟଙ୍କରଂ ଭବତି । କୁସଙ୍ଗେଣ କୁପଥାଚାରୀ ଭବନ୍ତି । ଅତଃ ଅଜ୍ଞତା, ଅନବଧାନତା, ଗର୍ବମ୍ , ଅଭିମାନମ୍, ଅହଙ୍କାରଂ ଚ ସଦୈବ ତ୍ୟଜେତ୍ । ଯତ୍ନବାନ୍ ନରଃ ନାଶମୁଖ୍ୟତ୍ ଉଦ୍ଧୃତଃ ଭବତି ।
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶଂସିତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଟି ପାଠିତ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ଥ ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗର ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ସଂଗ୍ରହରୁ ଆନୀତ । ଏଠାରେ କିପରି ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ନାଶ ଯାଏ ତାହା ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତ ହୋଇଛି ।
ଯେଉଁଠି ସୃଷ୍ଟି ସେଇଠି ବିନାଶ, ଯେଉଁଠି ଜନ୍ମ ସେଇଠି ମୃତ୍ୟୁ । ‘ଜାତସ୍ୟ ହି ଧ୍ରୁବ ମୃତ୍ୟୁ ।’ ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ଜ୍ଞାନବଳରେ ସବୁକିଛି ସାଧ କରିଥାଏ । ଜ୍ଞାନ ହିଁ ତା’ର ତୃତୀୟ ନୟନ । ଜ୍ଞାନ ହିଁ ଆଲୋକ ହେଲେ କେତେକ ଅଜ୍ଞାନର ଅମାଅନ୍ଧକାରରେ ପଡ଼ି ବିନଷ୍ଟ ହୋଇଥା’ନ୍ତି । ଅଜ୍ଞାନରୁ କେତେକ ନଷ୍ଟ ହୋଇଥା’ନ୍ତି । କେତେକ ଅସାବଧାନତାବଶତଃ ମୃତ୍ୟୁମୁଖରେ ପଡ଼ିଥା’ନ୍ତି । ଆଉ କେତେକ ଜ୍ଞାନର ଗର୍ବରେ ଅଭିମାନ ଓ ଅହଂକାରଦ୍ବାରା ଉନ୍ମତ୍ତ ହୋଇ ବିନଷ୍ଟ ହୋଇଥା’ନ୍ତି । ଅଳ୍ପଜ୍ଞାନ ଭୟଙ୍କର । ହେଲେ କେତେକ କିନ୍ତୁ ଏହି ନଷ୍ଟଦ୍ୱାରା ହିଁ ନାଶ ଯାଇଥା’ନ୍ତି । କୁସଙ୍ଗରେ ପଡ଼ି ମନୁଷ୍ୟ କୁପଥାଚାରୀ ହୋଇଯାଏ, ସୁପଥ ଛାଡ଼ିଦିଏ । ଏହି କୁପଥ ହିଁ ତାକୁ ନାଶ କରିଦେଇଥାଏ । ଏଣୁ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ଅଜ୍ଞତା, ଅନବଧାନତା, ଗର୍ବ, ଅଭିମାନ, ଅହଂକାରାଦି ତ୍ୟାଗକରିବା ଉଚିତ । ଏଥପ୍ରତି ଯତ୍ନବାନ୍ ରହିଲେ ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ନାଶମୁଖରୁ ଉଦ୍ଧାର ପାଇପାରିବ ।
ବ୍ୟାକରଣ:
ସନ୍ଧିବିଚ୍ଛେଦ – କେଚିଦଜ୍ଞାନତୋ = କେଚିତ୍ + ଅଜ୍ଞାନତଃ । କେଚିନ୍ନଷ୍ଟା = କେଚିତ୍ + ନଷ୍ଟା । କେଚିଜ୍ଞାନାବଲେପେନ = କେଚିତ୍ + ଜ୍ଞାନ + ଅବଲେପେନ । କେଚିନ୍ନଷ୍ଟିସ୍ତୁ = କେଚିତ୍ + ନଷ୍ଟି + ତୁ ।
ସମାସ – ଅଜ୍ଞାନତଃ = ନ ଜ୍ଞାନମ୍, ତସ୍ମାତ୍ (ନଞ୍ଝ ତତ୍) । ଜ୍ଞାନାବଲେପେନ ଜ୍ଞାନସ୍ୟ ଅବଲେପମ୍, ତେନ (୬ଷ୍ଠୀ ତତ୍) ।
ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତି – ଅଜ୍ଞାନତଃ, ପ୍ରମାଦତଃ = ହେତୌ ୫ମୀ । ଜ୍ଞାନବଲେପେନ, ନଷ୍ଟି = ହେତୌ ୩ୟା ।
ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ – ନଷ୍ଠାଃ = ନଶ୍ + କ୍ତ (ବହୁବଚନ) । ନାଶିତା = ନଶ୍ + ଣିଚ୍ + କ୍ତ (ବହୁବଚନ) ।
ଶ୍ଳୋକ – ୫
दातृत्वं प्रियवक्तृत्वं धीरत्वमुचितज्ञता ।
अभ्यासेन लभ्यन्ते चत्वारः सहजा गुणाः ॥ ५ ॥
ଦାତୃତ୍ୱ ପ୍ରିୟବକ୍ତୃତ୍ୱ ଧୀରତ୍ଵମୁଚିତଜ୍ଞତା ।
ଅଭ୍ୟାସେନ ନ ଲଭ୍ୟନ୍ତେ ଚତ୍ବାରଃ ସହଜା ଗୁଣା ॥ ୫ ॥
ଅନ୍ବୟ – ଦାତୃତ୍ୱ ପ୍ରିୟବକ୍ତୃତ୍ୱ ଧୀରତ୍ଵମ୍ ଉଚିତଜ୍ଞତା ଚତ୍ବାରଃ ସହଜାଗୁଣା ଅଭ୍ୟାସେନ ନ ଲଭନ୍ତେ ।
ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ – ଦାତୃତ୍ଵମ୍ = ଦାନଶୀଳତା । ପ୍ରିୟବକ୍ତୃତ୍ୱମ୍ = ପ୍ରିୟବଚନ ସ୍ଵଭାବ । ଉଚିତଜ୍ଞାତା = ସମୀଚୀନ କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟାକର୍ଭବ୍ୟଜ୍ଞାନନିଷ୍ଠା ଅଭ୍ୟାସେନ = ବାରମ୍ବାର ପ୍ରୟୋଗ କରିବାଦ୍ୱାରା । ସହଜା = ସ୍ଵାଭାବିକ ।
ଅନୁବାଦ – ଦାନଶୀଳତା, ପ୍ରିୟବଚନସ୍ବଭାବ, କାର୍ଯ୍ୟସମ୍ପାଦନରେ ପ୍ରତିବଦ୍ଧତା ଏବଂ ସମୀଚୀନ କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟାକର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟ ଜ୍ଞାନନିଷ୍ଠା ଏ ଚାରୋଟି ସ୍ବାଭାବିକ ଗୁଣ ଅଭ୍ୟାସଦ୍ବାରା ଲାଭ କରାଯାଇପାରେ ନାହିଁ ।
ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶ୍ଳୋକୋଽୟଂ ପଠିତଃ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ୟ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗାତ୍ ଆନୀତଃ । ଅତ୍ର ଅସ୍ମିନ୍ ଶ୍ଳୋକେ କେ ସ୍ଵାଭାବିକଗୁଣା ଅଭ୍ୟାସେନ ନ ଲଭନ୍ତେ ତଦେବ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତମ୍ ।
ମନୁଷ୍ୟାନାଂ ସର୍ଜନକାଳେ ଈଶ୍ଵରଃ ତସ୍ମିନ୍ ମଧ୍ୟ କତିପୟ ସହଜାତଂ ସ୍ଵାଭାବିକଂ ସ ଗୁଣଂ ସୃଜତି । ବ୍ୟସ୍ତେ ସ୍ବଭାବେ ଚରିତ୍ରେ ଚ ଏମାଂ ଗୁଣାନାଂ ପ୍ରତିଫଳନଂ ତଥା ବିକଶନଂ ଭବନ୍ତି । କୋଽପି ଅଭ୍ୟାସବଳେନ ଏଷା ଗୁଣାନାମ୍ ଅଧିକାରୀ ନ ଭବେତ୍ । ତଦେବ ସହଜାତଂ ସ୍ଵାଭାବିକଂ ଗୁଣଂ ଯଥା – ଦାନଶୀଳତା, ପ୍ରିୟବଚନଂ, ଧୀରତ୍ଵ, ଉଚିତଜ୍ଞତାଦି । କଃ କଦାପି ପ୍ରଦାନେନ ଅଭ୍ୟାସମାଧମେନ ଦାନୀ ନ ଭବେତ୍ । ପ୍ରିୟକଥନସ୍ୟାଭ୍ୟାସେନ ପ୍ରିୟବାଦୀ ନ ଭବେତ୍ । କିମପି କାର୍ଯ୍ୟସଂପାଦନେନ ଧୀରତ୍ବ ନାୟାତି । ଉଚିତଜ୍ଞାତା ହିତାହିତଜ୍ଞାନସ୍ୟ ବିବେଚନାତ୍ ନାୟାତି । ଅଭ୍ୟାସବଳେନ ଏତେରାଂ ଗୁଣାନାଂ ସିଦ୍ଧି ନ ଭବେତ୍ । ଏତଦ୍ ତୁ ମନୁଷ୍ୟାନାଂ ସ୍ୱାଭାବିକା ଗୁଣା । ଅଭ୍ୟାସଂ ବିନା ଏଷା ଗୁଣାନାମ୍ ଅଧିକାରୀ ଭବେୟୁଃ ।
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶଂସିତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଟି ପଠିତ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକର ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ରୁ ସଂଗୃହୀତ ଏଠାରେ କ’ଣ କ’ଣ ସବୁ ସ୍ଵାଭାବିକ ଗୁଣ ଅଭ୍ୟାସଦ୍ୱାରା ଲାଭ କରାଯାଇପାରେ ନାହିଁ ତାହା ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତ ହୋଇଛି ।
ମନୁଷ୍ୟକୁ ସୃଷ୍ଟି କଲାବେଳେ ଈଶ୍ବର ତା’ଠାରେ କେତେକ ସହଜାତ ବା ସ୍ଵାଭାବିକ ଗୁଣକୁ ସୃଷ୍ଟି କରିଅଛନ୍ତି । ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିର ସ୍ଵଭାବ ତଥା ଚରିତ୍ରରେ ଏସବୁ ଗୁଣର ପ୍ରତିଫଳନ ତଥା ବିକାଶ ହୋଇଥାଏ । କେହି କେବେ ଅଭ୍ୟାସଦ୍ୱାରା ଏସବୁ ଗୁଣର ଅଧିକାରୀ ହୋଇପାରେ ନାହିଁ । ସେସବୁ ସହଜାତ ବା ସ୍ବାଭାବିକ ଗୁଣ ହେଉଛି; ଯଥା – ଦାନଶୀଳତା ପ୍ରିୟବଚନସ୍ଵଭ।ବ ଧୀରତା ଏବଂ ଉଚିତଜ୍ଞତା ଇତ୍ୟାଦି । କେହି କେବେ ପ୍ରଦାନ ରୂପକ ଅଭ୍ୟାସଦ୍ୱାରା ଦାନୀ ହୋଇପାରେ ନାହିଁ । ଭଲ କଥା କହିବାର ଅଭ୍ୟାସ କରି ପ୍ରିୟକଥା କହିପାରେନା, କୌଣସି କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ସମ୍ପାଦନରେ ଧୀରତା ଆସେ ନାହିଁ ଏବଂ ଉଚିତଜ୍ଞତା ଉପଯୁକ୍ତ ହିତାହିତଜ୍ଞାନର ବିବେଚନାରୁ ଆସେନାହିଁ । ଅଭ୍ୟାସକରି ଏସବୁ ସିଦ୍ଧ କରାଯାଇପାରେ ନାହିଁ । ଏସବୁ ସାଧାରଣତଃ ମନୁଷ୍ୟର ସ୍ଵାଭାବିକ ଗୁଣ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଆମେ ଅଭ୍ୟାସ ବିନା ଏସବୁର ଅଧିକାରୀ ହେବା ଉଚିତ ।
ବ୍ୟାକରଣ:
ସନ୍ଧିବିଚ୍ଛେଦ – ଧୀରତ୍ୱମୁଚିତଜ୍ଞ = ଧୀରତ୍ୱମ୍ + ଉଚିତଜ୍ଞତା ।
ସମାସ – ପ୍ରିୟବକ୍ତୃତ୍ୱମ୍ = ପ୍ରିୟଶ୍ଚାସୌ ବକ୍ତୃତ୍ୱ ଚେତି (କର୍ମଧାରୟ) । ଉଚିତଜ୍ଞତା = ଉଚିତଂ ଜ୍ଞାୟତେ ଇତି (ଉପପଦ ତତ୍) ।
ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତି – ଗୁଣା = କଉଁରି ୧ମା । ଅଭ୍ୟାସେନ = କରଣେ ୩ୟା ।
ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ – ପ୍ରିୟ = ପ୍ରୀ + କ । ଦାତୃତ୍ବ = ଦାତୃ + ତ୍ୱ । ଉଚିତଜ୍ଞତା = ଉଚିତଜ୍ଞ + ତଳ (ତା) ।
ଶ୍ଳୋକ – ୬
युक्तियुक्तं प्रगृहणीयाद् बालादपि विचक्षणः ।
रवेरविषयं वस्तु किं न दीपः प्रकाशयेत् ॥ ६ ॥
ଯୁକ୍ତିଯୁକ୍ତ ପ୍ରଗୃହଣୀୟାଦ୍ ବାଳାଦପି ବିଚକ୍ଷତଃ ।
ରବେରବିଷୟଂ ବସ୍ତୁ କିଂ ନ ଦୀପଃ ପ୍ରକାଶୟେତ୍ ॥ ୬ ॥
ଅନ୍ୱୟ – ବିଚକ୍ଷଣ ବାଳାଦପି ଯୁକ୍ତିଯୁକ୍ତ ପ୍ରଗୃହ୍ୟାଦ୍ । ରବେ ଅବିଷୟଂ ବସ୍ତୁ ଦୀପଃ କିଂ ନ ପ୍ରକାଶୟେତ୍ ?
ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ – ପ୍ରଗୃହ୍ୟାଦ୍ = ଗ୍ରହଣ କରିବା ଉଚିତ । ବାଳାଦପି = ବାଳକଠାରୁ ମଧ୍ୟ । ରବେରବିଷୟଂ ବସ୍ତୁ = ରବିଙ୍କର ଯାହା ଅବିଷୟ ବସ୍ତୁ ।
ଅନୁବାଦ – ବୁଦ୍ଧିମାନ୍ ବାଳକଠାରୁ ମଧ୍ୟ ଯୁକ୍ତିଯୁକ୍ତ କଥା ଗ୍ରହଣୀୟ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟ ପ୍ରକାଶିତ କରିପାରୁନଥିବା ବସ୍ତୁକୁ କ’ଣ ଦୀପ ପ୍ରକାଶିତ କରେ ନାହିଁ କି ? (ପ୍ରକାଶିତ କରିଥାଏ) ।
ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶ୍ଳୋକୋଽୟଂ ପଠିତଃ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ୟ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗାତ୍ ଆନୀତଃ । ଅସ୍ମିନ୍ ଶ୍ଳୋକେ ବିଚକ୍ଷତଃ ବାଳାତ୍ ଅପି ଯୁକ୍ତିଯୁକ୍ତ ପ୍ରଗୃହଣାୟାତ୍ ଇତି ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତମ୍ ।
ଅସ୍ଥିନ୍ ବ୍ୟବହାରିକେ ଜୀବନେ ମନୁଷ୍ୟାନାଂ ବୟଃକ୍ରମେଣ ତଥା ସମୟକ୍ରମେଣ ଏବଂ ବୁଦ୍ଧ ବିକଶନଂ ଭବତି । ବିଭିନ୍ନେଷୁ ବିଷୟେଷୁ ଯୁକ୍ତିଯୁକ୍ତ ବଚନଂ ଅନୁଭବତଃ ଏବଂ ଭବତି । ଏତତ୍ ସର୍ବଂ କେବଳଂ ବିବେକାନାଂ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରେ ପରିଦୃଷ୍ଟ ଭର୍ବତି, ପରନ୍ତୁ ଅବିବେକୀ ସ୍ବଭାବଂ ତୁ ଭିନ୍ନମେବ ଭବତି । ପରନ୍ତୁ କେଚନ ବିଚକ୍ଷଣା ବୁଦ୍ଧିମନ୍ତଃ ବାଳା ସନ୍ତି ଯେ ତାବତ୍ ସ୍ୱଳ୍ପ ବୟସି ସୀମିତଜ୍ଞାନେନ ଚ ଯୁକ୍ତିଯୁକ୍ତ ବଚନଂ ବଦନ୍ତି । ଏତେରାଂ ବାଳାନାଂ ଯୁକ୍ତିଯୁକ୍ତ ବଚନଂ ସର୍ବୋଦୌ ଗ୍ରହଣୀୟଂ ଭବତି । ଦୃଷ୍ଟାନ୍ତଡେନ ଉଲ୍ଲିଖ୍ ଭବତି ଯଥା – ଏକ କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ର ଦୀପଃ ରାଡ୍ରୋ ଅନ୍ଧକାରେ କାଳେଽପି ଆଲୋକଂ ପ୍ରଦଦାତି । ଅସ୍ଥିନ୍ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଭବତି ପ୍ରକାଶସ୍ୟ ପ୍ରତୀକଂ, ସ୍ଵକୀୟେନ ଆଲୋକେନ ‘ସର୍ବମ୍ ଉଦ୍ଭାସୟତି । ପରନ୍ତୁ ତଥ୍ୟ ଅନୁପସ୍ଥିତୌ ଏତତ୍ ସାମାନ୍ୟ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଦୀପଃ ସାଧୟତି । ଅତଃ ଅତ୍ର ବିଚକ୍ଷତଃ ବାଳ ଦୀପେନ ସାକଂ ତୁଳିତଂ ଭବତି । ଯଥାରୀତ୍ୟା କବିନା ପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗୋୟଂ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତଂ ତଦେବ ବଣ୍ଡନୀୟଂ ଭବତି ।
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶଂସିତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଟି ପଠିତ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକର ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗସ୍ଥିତ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ରୁ ଆନୀତ । ଏଠାରେ ବାଳକଠାରୁ ଯୁକ୍ତିଯୁକ୍ତ କଥା ଯେ ଗ୍ରହଣୀୟ ତାହା ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତ ହୋଇଛି ।
ଏ ବ୍ୟାବହାରିକ ଜୀବନରେ ମନୁଷ୍ୟର ବୟସକ୍ରମେ ତଥା ସମୟକ୍ରମେ ହିଁ ବୁଦ୍ଧିର ବିକାଶ ହୋଇଥାଏ ଓ ବିଭିନ୍ନ ବିଷୟରେ ଯୁକ୍ତିସଙ୍ଗତ କଥା ଅନୁଭବରୁ ହିଁ କହିଥାଏ । ଏସବୁ କେବଳ ବିବେକବାନ୍ଠାରେ ହିଁ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ହେଲେ ଅବିବେକୀ କିନ୍ତୁ ଭିନ୍ନଭାବ. ପ୍ରଦର୍ଶନ କରିଥାଏ । କିନ୍ତୁ କେତେକ ବୁଦ୍ଧିମାନ୍ ବିଚକ୍ଷଣ ବାଳକ ଅଛନ୍ତି ଯେଉଁମାନେ କି ଅଳ୍ପ ବୟସରେ ସୀମିତ ଜ୍ଞାନରେ ମଧ୍ୟ ଯୁକ୍ତିସଙ୍ଗତ କଥା କୁହନ୍ତି । ଏମାନଙ୍କର ବଚନ ସଦା ଗ୍ରହଣୀୟ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଯେପରିକି ଏକ କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ର ଦୀପ ରାତ୍ରକାଳରେ ଅନ୍ଧକାର ସମୟରେ ମଧ୍ୟ ଆଲୋକ ପ୍ରଦାନ କରିଥାଏ । ଏ ସୃଷ୍ଟିରେ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟ ହେଉଛନ୍ତି ପ୍ରକାଶର ପ୍ରତୀକ, ସେ ନିଜର ଆଲୋକରେ ସବୁକୁ ଉଦ୍ଭାସିତ କରନ୍ତି । ହେଲେ ତାଙ୍କର, ଅନୁପସ୍ଥିତିରେ ଏ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ସାମାନ୍ୟ ଦୀପ ହିଁ କରିପାରେ । ଏଣୁ ଏଠାରେ ଯେପରିଭାବେ ବିଚକ୍ଷଣ ବାଳକକୁ କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ର ଦୀପ ସହ ତୁଳନା କରାଯାଇଛି ତାହା ଅତ୍ୟନ୍ତ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନୀୟ ହୋଇଛି ।

ବ୍ୟାକରଣ:
ସନ୍ଧିବିଚ୍ଛେଦ – ବାଳାଦପି = ବାଳାତ୍ + ଅପି । ରବେରବିଷୟମ୍ = ରବେ + ଅବିଷୟମ୍ ।
ସମାସ – ଯୁକ୍ତିଯୁକ୍ତମ୍ =ଯୁକ୍ତା ଯୁକ୍ତମ୍ (୩ୟା ତତ୍) । ଅବିଷୟମ୍ = ନ ବିଷୟମ୍ (ନୡ ତତ୍) ।
ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତି – ବିଚକ୍ଷଣ, ବାଳାତ୍ = ଅପାଦାନେ ୫ମୀ । ରବେ = ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ୬ଷ୍ଠୀ । ଦୀପଃ = କଉଁରି ୧ମା ।
ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ – ଯୁକ୍ତି = ୟୁଜ୍ + ସ୍କ୍ରିନ୍ । ଯୁକ୍ତମ୍ = ୟୁଜ୍ + କ୍ତ । ଦ୍ଵୀପ = ଦ୍ବୀ + ପା + କ ।
ଶ୍ଳୋକ – ୭
पीत्वा कर्दमपानीयं भेको रटरटायते ।
पक्कं चूतरसं पीत्वा गर्वं नायाति कोकिलः ॥ ७ ॥
ପୀତ୍ବା କର୍ଦମପାନୀୟଂ ଭେକୋ ରଟରଟାୟତେ ।
ପକ୍ଵ ଚୂତରସଂ ପୀତ୍ବା ଗର୍ବ ନାୟାତି କୋକିଳ ॥ ୭ ॥
ଅନ୍ବୟ – ଭେକଃ କର୍ଦମପାନୀୟଂ ପୀତ୍ବା ରଟରଟାୟତେ । କୋକିନଃ ପକ୍ଵ ଚୂତରସଂ ପୀତ୍ବା ଗର୍ବଂ ନ ଆୟାତି ।
ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ – ଭେକଃ = ବେଙ୍ଗ । କର୍ଦମପାନୀୟମ୍ = ପଙ୍କପାଣି । ପୀଡ଼ା = ପିଇ । ପକ୍ୱମ୍ = ପାଚିଲା । ଚୂତରସଂ ଆମ୍ବରସ । ଆୟାତି = ଆସେ
ଅନୁବାଦ – ବେଙ୍ଗ ପଙ୍କିଳ ଜଳ ପାନ କରି କୈକଟର ରାବ କରିଥାଏ । କୋଇଲି ପାଚିଲା ଆମ୍ବରସ ପିଇ ମଧ୍ୟ ଗର୍ବ କରି ନ ଥାଏ ।
ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଉଦ୍ଧୃତଃ ଶ୍ଳୋକ ପଠିତଃ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ୟ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗାତ୍ ଆନୀତଃ । ଅସ୍ମିନ୍ ଶ୍ଳୋକେ ଭେକସ୍ୟ କୋକିଳସ୍ୟ ଚ ସ୍ଵାଭାବିକପ୍ରବୃତ୍ତି ବିଷୟ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତଂ ଭବତି ।
ପ୍ରକୃତିଃ ଅତୀବ ବିଚିତ୍ରା । ଅତ୍ର କଃ କୀଦୃଶମ୍ ଆଚରଣଂ କରୋତି ତଦେବ ଅବଗତଂ ନ ଶକ୍ୟତେ । ପରସ୍ପରୟୋ ମଧ୍ୟ ଭାବଂ ପ୍ରଭେଦଂ ଚ ପରିଲକ୍ଷ୍ୟତେ । ସାଧାରଣତଃ ଏକଃ ଭେକଃ କର୍ଦମପାନୀୟଂ ପୀଡ଼ା ରଟ୍ଟାୟତେ ପରନ୍ତୁ କୋକିଳୀ ପଚ୍ୟୁତରସଂ ପୀତ୍ବାପି ଗର୍ବ ନ କରୋତି । ସଦା ପୌନଃ ଏବ ତିଷ୍ଠତି । ଅତ୍ର ଭେକସ୍ୟ କୋକିଳସ୍ୟ ଚ ସ୍ବଭାବଂ ସଂପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ ଭିନ୍ନ ଭବତି । ଏତେ ତେରାଂ ସହଜାତଃ ପ୍ରବୃତିଃ । ତଥୈବ ଅସ୍ଥିନ୍ ସଂସାରେ ସର୍ବେ ସ୍ୱ ସ୍ୱ ପ୍ରକୃତି ସ୍ଵଭାବଂ ଚ ସ୍ବୀକୃତ୍ୟ ପରସ୍ପରୟୋନ ବ୍ୟବହ୍ରୁୟନ୍ତେ । ତସ୍ୟ ପ୍ରଭାବଂ ପ୍ରଭୃତି ଚ ପ୍ରତି କିମପି ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନଂ ନ ଦୃଶ୍ୟତେ । ଅତଃ କବେ ଏତାଦୃଶ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନସ୍ୟ ଉପାଦେୟତା ମନୁଷ୍ୟାନାଂ କୃତେ ବିଦ୍ୟତେ । ପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗୋଽୟମ୍ ଅତୀବ ସ୍ପୃହଣୀୟଂ ଗ୍ରହଣୀୟଂ ଚ ଭବତି ।
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଉଦ୍ଧୃତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଟି ପଠିତ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକର ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ରୁ ଆସିଅଛି । ଏଠାରେ ବେଙ୍ଗ ଓ କୋଇଲିର ସ୍ଵାଭାବିକ ପ୍ରବୃତ୍ତି ବିଷୟ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତ ହୋଇଛି ।
ପ୍ରକୃତି ବଡ଼ ବିଚିତ୍ର । ଏଠି କିଏ କିପରି ଆଚରଣ କରୁଛି ତାହା ଜାଣିବା କଷ୍ଟକର । ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ମଧ୍ୟରେ ପ୍ରଭେଦ ପରିଲକ୍ଷିତ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ସାଧାରଣରେ ଏକ ବେଙ୍ଗ ପଙ୍କିଳ ବା କାଦୁଅ ପାଣି ପିଇ କେଁକଟର ରାବ କରିଥାଏ । ହେଲେ କୋଇଲି ପାଚିଲା ଆମ୍ବର ମିଠାରସ ପାନକରି ମଧ୍ୟ ଗର୍ବିତ ହୋଇ ନଥାଏ । ସେ ସଦା ଯୌନ ହିଁ ରହିଥାଏ । ଏଠାରେ ବେଙ୍ଗ ଓ କୋଇଲିର ସ୍ଵଭାବ ସମ୍ପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ ବିପରୀତ ଅଟେ । ବେଙ୍ଗର କୈକଟର ରାବ ଓ କୋକିଳର ଗର୍ବଶୂନ୍ୟତା ଏସବୁ ସେମାନଙ୍କର ସହଜାତ ପ୍ରବୃତ୍ତି । ହେଲେ ଏହା କର୍ଦମାକ୍ତ ଜଳ ବା ପକ୍ବ ଆମ୍ରରସରେ ନ ଥାଏ । ସେହିପରି ଏ ସଂସାରରେ ସମସ୍ତେ ନିଜର ପ୍ରକୃତି ବା ସ୍ବଭାବାନୁସାରେ ହିଁ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିଥା’ନ୍ତି । ତା’ ଉପରେ ଭଲମନ୍ଦର ବିଚାର କିଛି ବି ପ୍ରଭାବ ପକାଇନଥାଏ । କବିଙ୍କର ଏ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନା ପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗ ଅତୀବ ଶିକ୍ଷଣୀୟ ତଥା ଗ୍ରହଣୀୟ ହୋଇଛି।
ବ୍ୟାକରଣ:
ସନ୍ଧିବିଚ୍ଛେଦ – ନାୟାତି = ନ + ଆୟତି ।
ସମାସ – କର୍ଦମପାନୀୟମ୍ = କର୍ଦମଂ ପାନୀୟମ୍ (କର୍ମଧାରୟ) । ଚୂତରସମ୍ = ଚୂତସ୍ୟ ରସମ୍ (୬ଷ୍ଠ ତତ୍) ।
ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତି – ଭେକଃ, କୋକିନଃ = କର୍ଭରି ୧ ମା । କର୍ଦମପାନୀୟଂ, ଚୂତରସମ୍ = କର୍ମଣି ୨ୟା । ଗର୍ବମ୍ = କର୍ମଣି ୨ୟା ।
ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ – ପୀତ୍ମା = ପା + କ୍ଵାଚ୍ । ପାନୀୟମ୍ ପା + ଅନୀୟ । ପକ୍ବମ୍ = ପଚ୍ + କ୍ତ ।
ଶ୍ଳୋକ – ୮
दैवं पुरुषकारेण यः समर्थः प्रबाधितुम् ।
न दैवेन विपन्नार्थ: पुरुष: सोऽवसीदति ॥ ८ ॥
ଦୈବଂ ପୁରୁଷକାରେଣ ଯଃ ସମର୍ଥୀ ପ୍ରବାଧୂମ୍ ।
ନ ଦୈବେନ ବିପନ୍ନାର୍ଥୀ ପୁରୁଷ ସୋଽବସୀଦତି ॥ ୮ ॥
ଅନ୍ୱୟ – ଯଃ ପୁରୁଷକାରେଣ ଦୈବଂ ପ୍ରବାସ୍ତୁ ସମର୍ଥ, ଡଃ ବିପନ୍ନାର୍ଥୀ ପୁରୁଷ ଦେବେନ ନ ଅବସୀଦତି ।
ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ – ଦୈବମ୍ = ଦୈବକୁ । ପ୍ରବାଧୁମ୍ = ବାଧା ଦେବାକୁ । ବିପନ୍ନାର୍ଥୀ = ବିପଦଗ୍ରସ୍ତ । ଅବସୀଦତି = ଦୁଃଖ ପାଇଥାଏ ।
ଅନୁବାଦ – ଯେ ପୌରୁଷଦ୍ୱାରା ଦେବଙ୍କୁ ବାଧାଦେବାକୁ ସମର୍ଥ, ସେ ବିପଦଗ୍ରସ୍ତ ପୁରୁଷ ଦୈବଦ୍ଵାରା ଦୁଃଖପାଏ ନାହିଁ । ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶ୍ଳୋକୋଽୟଂ ପଠିତଃ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ୟ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ପଦ୍ୟାତ୍ ସଂଗୃହୀତଃ । ଅତ୍ର ଅସ୍ମିନ୍ ଶ୍ଳୋକେ ଦୈବାପେକ୍ଷୟା ପୌରୁଷ ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠମ୍ ଇତି ପ୍ରତିପାଦିତମ୍ ।
ସଚାରାଚରସୃଷ୍ଟି ଇୟଂ ଦେବେନ କୃତା । ମନୁଷୋଽପି ଦେବେନ ସୃଷ୍ଟ । ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ସ୍ଵକର୍ମଣା ପୌରୁଷେଣ ଚ ସର୍ବକାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କର୍ଡିଂ ସମର୍ଥୀ ଭବତି । ଦୈବକୃତଂ ଦୁଃଖମପି ଶୋଇଂ ଶତି । ଯସ୍ୟ ପୌରୁଷ ଯତୋଧୀକଂ ଭବତି ତସ୍ୟ ଦୈବ କିମପି ନ କରୋତି । କୃତେ ସତି ଧଃ ସମ୍ମୁଖୀନଃ ଭବିତୁଃ ଶକ୍ୟ ଭବତି । ପୌରୁଷବଳେନ ଦୈବକୃତଂ ଦୁଃଖ୍ୟ ବିପରିଂ ଚ ଡଃ ଅନାୟାସେନ ସହଜେ ପାରଂ ଚ ଗଚ୍ଛତି । ଅତଃ ମହାଭାରତେ କର୍ଣ୍ଣଦ୍ୟୋତିଃ ଯଥା – ‘ଦୈବାୟତ୍ତକୁଳେ ଜାତଂ ମଦାୟତ୍ତ ତୁ ପୌରୁଷମ୍ ।’ ଅସ୍ଵାକଂ ଭାଗ୍ୟ ତୁ ଦୈବାଧୁନଂ ଭବତି ପରନ୍ତୁ ପୌରୁଷ ମନୁଷ୍ୟାଧୁନଂ ଭବତି । ପୌରୁଷସ୍ୟ ଉପରି ସର୍ବଦା ଆସ୍ଥାଭାଜନଂ ଭବେୟୁଃ ।
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶଂସିତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଟି ପଠିତ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକର ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗସ୍ଥିତ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ରୁ ସଂଗୃହୀତ । ଏଠାରେ ଦୈବଙ୍କଠାରୁ ପୌରୁଷ ଯେ ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ ତାହା ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତ ହୋଇଛି ।
ଏ ସଚରାଚର ସୃଷ୍ଟି ଦୈବକୃତ, ଏପରିକି ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ମଧ୍ୟ । ତଥାପି ଦୈବସୃଷ୍ଟ ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ନିଜ କର୍ମ ତଥା ପୌରୁଷ ବଳରେ ସବୁକିଛି କରିବାକୁ ସମର୍ଥ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ସେ ଦୈବୀକୃତ ଦୁଃଖ ଓ ବିପତ୍ତିକୁ ସହିବାକୁ ସମର୍ଥ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଯାହାର ପୌରୁଷ ଯେତେ ଅଧ୍ବକ ତା’ର ଦୈବ କିଛି ହେଲେ କରିବାକୁ ସମର୍ଥ ହୁଏନି । ନିଜର ପୌରୁଷବଳରେ ଦୈବଦତ୍ତ ଦୁଃଖ ବିପତ୍ତିକୁ ସେ ଅନାୟାସରେ ସହ୍ୟ କରିଥାଏ ଓ ପାର ହୋଇଯାଏ । ନିଜ ଭାଗ୍ୟ ଉପରେ ଅଧିକ ବିଶ୍ବାସ ନକରି ପୌରୁଷ ଉପରେ ଭରସିଥାଏ । କଣ୍ଠମୁଖର ଉକ୍ତି ଯେ, ‘ଦୈବାୟର କୁଳେ ଜାତଂ ମଦାୟତ୍ତ ତୁ ପୌରୁଷମ୍’’ ଅର୍ଥାତ୍ ପୌରୁଷ ହିଁ ମୋ ଅଧୀନରେ । ମନୁଷ୍ୟର ଭାଗ୍ୟ ଦୈବାଧୀନ କିନ୍ତୁ ପୁରୁଷାର୍ଥ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ଅଧୀନ ଅଟେ । ପୌରୁଷ ବଳରେ ଦୈବଦୁଃଖ ସହ୍ୟ ହୋଇଯାଏ । ଏଣୁ ନିଜର ପୌରୁଷ ଉପରେ ସଦା ଆସ୍ଥା ବା ବିଶ୍ଵାସ ରଖୁବା ଉଚିତ ।
ବ୍ୟାକରଣ:
ସନ୍ଧିବିଚ୍ଛେଦ – ବିପନ୍ନାର୍ଥୀ = ବିପନ୍ନ + ଅର୍ଥା । ସୋଽବସୀଦତି = ଡଃ + ଅବସୀଦତି ।
ସମାସ – ପୁରୁଷକାରେଣି = ପୁରୁଷ କରୋତି ଇତି, ତେନ (ଉପପଦ ତତ୍) । ବିପନ୍ନାର୍ଥ = ବିପନଃ ଅର୍ଥ ଯସ୍ୟ ଡଃ (ବହୁବ୍ରୀହିଃ) ।
ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତି – ଯଃ = କଉଁରି ୧ ମା । ଦେବମ୍ = କର୍ମଣି ୨ୟା । ପୁରୁଷକାରେଣ = କରଣେ ୩ୟା । ପୁରୁଷ=କର୍ଭରି ୧ମା । ଦେବେନ = କରଣେ ୩ୟା ।
ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ – ପ୍ରବାଧୁମ୍ = ପ୍ର – ବାଧ୍ + ତୁମୁନ୍ । ବିପନ୍ନ = ବି + ପଦ୍ + କ୍ତ ।
ଶ୍ଳୋକ – ୯
अविज्ञाय फलं यो हि कर्मत्वे वानुधावति ।
शोचति फलवेलायां यथा किंशुकसेचकः ॥ ९ ॥
ଅବିଜ୍ଞାୟ ଫଳ ଯୋ ହି କର୍ମତ୍ରେ ବାନୁଧାବତି ।
ଶୋଚତି ଫଳବେଳାୟା ଯଥା କିଂଶୁକସେଚକଃ ॥ ୯॥
ଅନ୍ବୟ – ଯଃ ଫଳମ୍ ଅବିଜ୍ଞାୟ କର୍ମଡ଼େ ବା ଅନୁଧାବତି ଫଳବେଳାୟାଂ ହି ଯଥା କିଂଶୁକସେଚକଃ ଶୋଚତି (ତଥା ଶୋଚତି) ।
ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ – ଅବିଜ୍ଞାୟ = ନଜାଣି । କର୍ମତ୍ତି = କର୍ମ ପଛରେ ବା କର୍ମରେ । ଅନୁଧାବତି = ଅନୁଧାବନ କରେ । କିଂଶୁକ = ଗନ୍ଧହୀନ । ସେଚକଃ = ସେଚନକାରୀ ।
ଅନୁବାଦ – ଯେ ଫଳକୁ ନଜାଣି ବୃଥା କର୍ମ କରିଥାଏ ତା’ର କର୍ମ ନିଶ୍ଚୟ ବିଫଳ ହୋଇଥାଏ, ଯେପରି ଗନ୍ଧହୀନ ବୃକ୍ଷରେ ଜଳସେଚନ ହିଁ ବୃଥା ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶ୍ଳୋକୋଽୟଂ ପଠିତଃ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ୟ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ପଦ୍ୟାତ୍ ଆନୀତଃ । ଅତ୍ର ଅସ୍ମିନ୍ ଶ୍ଳୋକେ କର୍ମଫଳ ପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗେ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତଂ ଭବତି।
ସଂସାରେଽସ୍ମିନ୍ ପ୍ରାଣିମାତ୍ରେଷୁ କର୍ମତତ୍ପରଃ । ‘ପ୍ରୟୋଜନମନୁଦିଶ୍ୟ ନାମନ୍ଦୋଽପି ପ୍ରବର୍ଗତେ ।’ – ଇତି ବାକ୍ୟାନୁସାରେଣ ନରଃ ସଦୈବ କର୍ମତତ୍ପରଃ ଭବତି । ପରନ୍ତୁ ଯଃ ଫଳବିଷୟମ୍ ଅବିଚାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କର୍ମକରୋତି ତଥ୍ୟ କର୍ମ ବିଫଳ ଯାତି । କାରଣ ଗନ୍ଧହୀନ ବୃକ୍ଷେବ ସେଚନସ୍ୟ କୋଽବା ଆବଶ୍ୟକତା ବିଦ୍ୟତେ ? କେବଳଂ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ବୃଥା ଯାତ୍ରା ନିଷ୍ଫଳଂ ଚ ଭବତି । ଅତଃ ଗୀତାକାର ସୁଶ୍ରୁତୟା ଉଚ୍ୟତେ ଯତ୍ – ‘କର୍ମଣ୍ୟବାଧିରସ୍ତେ ‘ମା ଫଳେଷୁ କଦାଚନ ।’’ ଅସ୍ମାକମ୍ ଅଧିକାରଂ ତୁ କେବଳଂ କର୍ମଣି ଅସ୍ତି । ଫଳପ୍ରାପ୍ତିଷ୍ଣୁ ନାସ୍ତି ଏବ । ଏତଦେବ ଭବତି ନିଷ୍କାମ କର୍ମଯୋଗୀ । ତଥାପି ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ପ….ଦନନ୍ତରମେବ କର୍ମ କରୋତି । ଅତଃ ଫଳ ବିଜ୍ଞାୟ କର୍ମତ୍ୱ ଅନୁଧାବନଂ କରଣୀୟମ୍ ଅନ୍ୟଥା କିଂଶୁକସେଚକସ୍ୟ ଦଶମଃ ଲଭତେ ।
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଉକ୍ତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଟି ପଠିତ ସଂସ୍କୃତ ପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକର ପଦ୍ୟ ଉ। ଗସ୍ଥ ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ ରୁ ଆସିଅଛି । ଏଠାରେ କର୍ମଫଳ ପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗରେ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତ ହୋଇଛି ।
ଏ ସଂସାରରେ ପ୍ରାଣୀମାତ୍ରକେ କର୍ମତତ୍ପର । ଆମେ ଯାହାବି କର୍ମ କରୁ କିଛି ପ୍ରୟୋଜନ ବା ଫଳରେ ଉଦ୍ଦେଶ୍ୟ ରଖ୍ ହିଁ କରିଥାଉ । ବିନା ପ୍ରୟୋଜନରେ ବା ଆଶାରେ କୌଣସି କର୍ମ ସମ୍ଭବ ହୁଏ ନାହିଁ । ଏଣୁ ଅଗ୍ନିପୁରାଣର ଯଥାର୍ଥ ଉକ୍ତି ଯେ – ‘‘ପ୍ରୟୋଜନମନୁଦିଶ୍ୟ ନ ମନ୍ଦୋଽପି ପ୍ରବର୍ଗତେ ।’’ ଅର୍ଥାତ୍ ବିନା ପ୍ରୟୋଜନରେ ମନ୍ଦକାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ମଧ୍ୟ କରାଯାଏ ନାହିଁ । ହେଲେ ଯେ ଫଳ ବିଷୟରେ ବିଚାର ନ କରି ବୃଥା କର୍ମ କରେ ତା’ର କର୍ମ ଅବଶ୍ୟ ବିଫଳ ହୋଇଥାଏ । କାରଣ କିଂଶୁକ ବା ଗନ୍ଧହୀନ ବୃକ୍ଷରେ ସେଚନ କରି କ’ଣ ବା-ଲାଭ ? ନିଷ୍ଫଳ ମାତ୍ର ଅଟେ । ତଥାପି ଗୀତାକାରଙ୍କର ଉକ୍ତି ଯେ- ‘କର୍ମଣ୍ୟବାଧ୍ଵରାସ୍ତୁ ମା ଫଳେଷୁ କଦାଚନ’’ ଅର୍ଥାତ୍ ଆମର କର୍ମ ଉପରେ ଅଧିକାର ଅଛି କିନ୍ତୁ ଫଳ ଉପରେ ନୁହେଁ । ଫଳ ଉପରେ ଆଶା ନରଖ୍ କର୍ମ କରିବା ଉଚିତ । ଏହାକୁ ନିଷ୍କାମ କର୍ମଯୋଗ କୁହାଯାଏ । ତଥାପି ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ପ୍ରଥମେ ଫଳର ସୂଚନା ବା ଜ୍ଞାନ ପାଇବା ପରେ ହିଁ କର୍ମ କରିଥାଏ ।
ବ୍ୟାକରଣ:
ସନ୍ଧିବିଚ୍ଛେଦ – ବାନୁଧାବତି = ବା + ଅନୁଧାବତି ।
ସମାସ – ଅବିଜ୍ଞାୟ : = ନ ବିଜ୍ଞାୟ (ନୡ ତତ୍) । ଫଳବେଳାୟାମ୍ = ଫଳସ୍ୟ ବେଳା, ତସ୍ୟାମ୍ (୬ଷ୍ଠ ତତ୍) । କିଂଶୁକସେଚକଃ = କିଂଶୁକାନାଂ ସେଚକ (୬ଷ୍ଠୀ ତତ୍) ।
ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତି – ଫଳମ୍ = କର୍ମଣି ୨ୟା । ଫଳବେଳାୟାମ୍ = କାଳାଧ୍ଵରଣେ ୭ମୀ । କିଂଶୁକସେଚକଃ = କଉଁରି ୧ ମା ।
ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ – ସେଚ = ସିଞ୍ଚ୍ + ଅଚ୍ ।
ଶ୍ଳୋକ – ୧୦
नागुणी गुणिनं वेत्ति गुणी गुणिषु मत्सरी ।
गुणी च गुणरागी च सरलो विरलो जनः ॥ १० ॥
ନାଗୁଣୀ ଗୁଣିନଂ ବେଭି ଗୁଣୀ ଗୁଣିଷୁ ମତ୍ସରୀ ।
ଗୁଣୀ ଚ ଗୁଣରାଗୀ ଚ ସରଳୋ ବିରଳୋ ଜନଃ ॥ ୧୦ ॥
ଅନ୍ବୟ – ଅଗୁଣୀ ଗୁଣିନଂ ନ ବେଭି, ଗୁଣୀ ଗୁଣିଷୁ ମତ୍ସରୀ । ଗୁଣୀ ଚ ଗୁଣରାଗୀ ଚ ସରକଃ ଜନଃ ବିରଜଃ (ଭବତି) ।
ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ – ଅଗୁଣୀ = ଗୁଣହୀନ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି । ଗୁଣିନମ୍ = ଗୁଣଗ୍ରାହୀକୁ । ବେଭି = ଜାଣେ । ମତ୍ସରୀ = ଅନ୍ୟର ଶୁଭରେ ଦୋଷ ଦର୍ଶନକାରୀ ବା ବିରାଗୀ ।
ଅନୁବାଦ – ଗୁଣହୀନ ଜନ ଗୁଣବାକୁ ଜାଣେ ନାହିଁ । ଗୁଣବାନ୍ ଗୁଣୀଠାରେ ପରଶ୍ରୀକାତର ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଗୁଣବାନ୍ ଓ ଗୁଣଗ୍ରାହୀ ଏବଂ ସରଳ ଲୋକ ଦୁର୍ଲଭ ହୋଇଥା ନ୍ତି ।
ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶଂସିତଃ ଶ୍ଳୋକ ପଠିତଃ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ୟ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ପଦ୍ୟାତ୍ ଆନୀତଃ । ଅତ୍ର ଅସ୍ମିନ୍ ଶ୍ଳୋକେ ସାଧାରଣତଃ ଗୁଣବାନ୍, ଗୁଣଗ୍ରାହୀ ଚ ଜନଃ କଅଂ ବିରଜଃ ଭବତି ତଦେବ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତମ୍ ।
ସଂସାରେଽସ୍ମିନ୍ ଦୃଶ୍ୟତେ ଯତ୍ – ଯଃ ଗୁଣବାନ୍ ଜନଃ ସ ଉତ୍ତମଗୁଣଯୁକ୍ତ ଜନଂ ଜ୍ଞାୟତେ । ପରନ୍ତୁ ଗୁଣହୀନଃ ଜନଃ କଦାପି ନ ଜାନାତି । ଏକ ଗୁଣୀ ଅପରଂ ଗୁଣୀଜନମପି ନ ଆଦ୍ରିୟତେ । ଗୁଣୀ ଗୁଣିଷୁ ମହରୀ ଭବତି । ଏକ ଗୁଣଜନଃ ଅପେରେରାଂ ଗୁଣୀଜନାନାଂ ଦୋଷ ଦର୍ଶନଂ କରୋତି । ପରନ୍ତୁ ଅସ୍ଥିନ୍ ସଂସାରେ ଏକାଧାରେଣ ଗୁଣୀ ଗୁଣାନୁରାଗୀ ସରକଃ ଜନଃ ଦୁର୍ଲଭଃ ଭବତି । ଅତଃ ଜନଃ ଯୁଗପତ୍ର ଗୁଣୀ ଗୁଣାନୁରାଗୀ ଭବିତଂ ଯତ୍ନ କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟାତ୍ । ସ୍ବୟମେବ ଗୁଣବାନ୍ ଜନଃ ଅନ୍ୱେଷା ଗୁଣିଜନାନାଂ ପ୍ରତି ଅନୁରାଗଂ ପ୍ରଦର୍ଶୟତି । ଏତାଦୃଶଃ ଜନଃ ସଂସାରେ ସ୍ୱଭୂତଜଂ ଭବତି । ଅତଃ ସଦୈବ ଗୁଣବାନ୍ ଗୁଣାନୁରାଗୀ ଚ ଭବେୟୁ ।. କବି ଯଥାରୀତ୍ୟା ପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗୋଽୟଂ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତଂ ତଦେବ ଅତୀବ ଶିକ୍ଷଣୀୟଂ ଗ୍ରହଣୀୟଂ ଚ ଭବତି ।
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶପିତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଟି ପଠିତ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକର ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭ।ଷିତାବଳୀ’ ରୁ ଆନୀତ ଏଠାରେ ଗୁଣବାନ୍ ଓ ଗୁଣଗ୍ରାହୀ ଲୋକଙ୍କର ବିରଳତା ପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତ ହୋଇଛି ।
ସାଧାରଣରେ ଲୋକୋକ୍ତି ଯେ – ‘ସୁନା ଚିହ୍ନେ ବଣିଆ ଓ ଗୁଣ ଚିହ୍ନେ ଗୁଣିଆ’’ । ପ୍ରକୃତରେ ଯେ ଗୁଣବାନ୍ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ସେ ହିଁ ଉତ୍ତମ ଗୁଣକୁ ବା ଜନକୁ ହିଁ ଜାଣିପାରେ । ହେଲେ ଯେ ଗୁଣହୀନ ସେ କେବେହେଲେ ଗୁଣବାନ୍ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିର ଗୁଣକୁ ଜାଣେନାହିଁ । ପୁନଶ୍ଚ ଯେ ଗୁଣୀ ସେ ଅନ୍ୟ ଏକ ଗୁଣବାନ୍ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିଠାରେ ମଧ୍ୟ ଆଦର କରେନାହିଁ କାରଣ ମତ୍ସରଭାବନା ବା ଅନ୍ୟପ୍ରତି ପରଶ୍ରୀକାତରତା ତାକୁ ଏପରି କରିଥାଏ । ସ୍ୱାର୍ଥପରତାର ଅମା ଅନ୍ଧକାରରେ ଦ୍ରବୀଭୂତ ବା ନିମଗ୍ନ ହୋଇ ଅନ୍ୟ ଗୁଣବାନ୍ଠାରେ ଦୋଷ ଦର୍ଶାଇଥାଏ । ଏଣୁ ଏକସଙ୍ଗରେ ଗୁଣବାନ୍ ଓ ଗୁଣଗ୍ରାହୀ ସରଳ ନିଷ୍କପଟ ସାଧାରଣ ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ଏ ସଂସାରରେ ବିରଳ। କଦବାକ୍ୱଚିତ୍ ଦେଖାଯା’ନ୍ତି । ଏହା ମହାପୁରୁଷମାନଙ୍କର ଲକ୍ଷଣରୂପେ ବିଦିତ । ଏହିପରି ଗୁଣର ଅଧ୍ୟାକାରୀ ଆମେ ହେବା ଉଚିତ । ଏହାହିଁ ଆମର କାମ୍ୟା ।
ବ୍ୟାକରଣ:
ସନ୍ଧିବିଚ୍ଛେଦ – ନାଗୁଣୀ = ନ + ଅଗୁଣୀ ।
ସମାସ – ଅଗୁଣା = ନ ଗୁଣୀ (ନୡ ତତ୍) । ଗୁଣରାଗୀ = ଗୁନଃ ରାଗ ଯସ୍ୟ ଡଃ (ବହୁବ୍ରୀହିଃ) ।
ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତି – ଗୁଣିନମ୍ = କର୍ମଣି ୨ୟା । ଗୁଣିଷୁ = ଅଧୂକରଣେ ୭ମୀ । ଜନଃ = କର୍ଭରି ୧ମା ।
ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ – ଗୁଣୀ = ଗୁଣ + ଇନ୍ । ରାଗ = ରଞ୍ଜ୍ + ଘଡ୍ ।
ଶ୍ଳୋକ – ୧୧
अनुष्ठानेन रहिता पाठमात्रेण केवलम् ।
रज्ञयत्येव या लोकान् किं तया शुकविद्यया ॥ ११ ॥
ଅନୁଷ୍ଠାନେନ ରହିତା ପାଠମାତ୍ରେଣ କେବଳମ୍ ।
ରଞ୍ଜୟତ୍ୟେବ ଯା ଲୋକାନ୍ କିଂ ତୟା ଶୁକବିଦ୍ୟୟ ॥୧୧॥
ଅନ୍ୱୟ – ଅନୁଷ୍ଠାନେନ ରହିତା କେବଳଂ ପାଠମାତ୍ରେଣ ଯା ଲୋକାନ୍ ଏବ ରଞ୍ଜୟତି ତୟା ଶୁକବିଦ୍ୟୟା କିମ୍ ? (କଃ ଲାଭଃ) ।
ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ – ରହିତା = ଶୂନ୍ୟ । ଲୋକାନ୍ = ଲୋକମାନଙ୍କୁ । ରଞ୍ଜୟତି = ରଞ୍ଜିତ ବା ଆନନ୍ଦିତ କରେ । ଶୁକବିଦ୍ୟୟା = ଶୁକବିଦ୍ୟାଦ୍ୱାରା ।
ଅନୁବାଦ – ଅନୁଷ୍ଠାନ ରହିତ କେବଳ ପାଠମାତ୍ରକେ ଯେ ଲୋକମାନଙ୍କୁ ହିଁ ଆନନ୍ଦିତ କରିଥାଏ ସେପରି ଶୁକ ପରି ରଟନରେ କି ଲାଭ ?
ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶ୍ଳୋକୋଽୟଂ ପଠିତଃ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ପଦ୍ୟାତ୍ ଆନୀତଃ । ଅତ୍ର ଅସ୍ମିନ୍ ଶ୍ଳୋକେ ଶୁକବିଦ୍ୟୟା କିଂ ବା ପ୍ରୟୋଜନମ୍ ? ଇତି ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତମ୍ ।
ଅଧୁନା ସମାଜଃ ପ୍ରଚାରଧର୍ମୀ । ଅତ୍ର କଥନସ୍ୟ ବଚନସ୍ୟ ବା ପ୍ରାବଲ୍ୟ ବିଦ୍ୟତେ, କାର୍ଯ୍ୟସ୍ୟ ନୂନତା ଚ ଅନୁଭୂୟତେ । ବାପାଟବସ୍ୟ ଚାଟୁକାରସ୍ୟ ଚ ପ୍ରାପ୍ତି ସର୍ବତ୍ର ସୁଲଭ ଏବ ଭବତି । ସୁଷୁବାଗାଳାପେନ ଏକ ଜନଃ ଅପରଂ ପ୍ରବଞ୍ଚନଂ କରୋତି । ସ୍ୱାସ୍ଥ୍ୟ ସ୍ଵାର୍ଥସାଧନାର୍ଥୀ ‘ବିଷକୁମ୍ଭପୟୋମୁଖମ୍’’ ଇବ ଆଚରତି । ବିଦ୍ୟାୟଃ ପ୍ରୟୋଗମ୍ ଅବଶ୍ୟ କରଣୀୟମ୍ । ଲୋକଚାରେଷୁ ନୈପୁଣ୍ୟ ଲ ଜନଃ ଜ୍ଞାନମ୍ ଅର୍ଜୟତି ବିଦ୍ୟାଧ୍ୟୟନଂ ଚ କରୋତି । ପରନ୍ତୁ ଯଦି ସା ବିଦ୍ୟା ଅନୁଷ୍ଠାନରହିତା ତହିଁ ବିଦ୍ୟାପଠନେନ କେବଳଂ ଜନରଞ୍ଜନଂ ସ୍ୟାତ୍ ନ ତୁ ପ୍ରୟୋଜନସିଦ୍ଧି ! କେବଳଂ ଶୁକପଠନଂ ସଦୃଶଂ ଭବତି । ଅତଃ ଶୁକପଠିତବିଦ୍ୟାବତ୍ ପ୍ରୟୋଗହୀନୟା ତୟା ବିଦ୍ୟାୟା କିଂ ବା ପ୍ରୟୋଜନମ୍ । ଅର୍ଥାତ୍ କିମପି ପ୍ରୟୋଜନଂ ନାସ୍ତି । ବିଦ୍ୟା ସର୍ବଦା ଅନୁଦାନଯୁକ୍ତ ଭବେତ୍ ।
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶଂସିତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଟି ପଠିତ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକର ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ରୁ ସଂଗୃହୀତ । ଏଠାରେ କେବଳ ଉଚ୍ଚାରଣ ନୁହେଁ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟାନୁଷ୍ଠାନ ଉପରେ ଗୁରୁତ୍ବ ଦିଆଯିବା ପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗ ବର୍ଣିତ ହୋଇଛି ।
ବର୍ତ୍ତମାନର ସମାଜ କେବଳ ପ୍ରଚାରଧର୍ମୀ । ଏଠି କଥା ବେଶି ଆଉ କାମ କମ୍ । କଥାକୁହା ଚାଟୁକାରଙ୍କର ସମାଗମରେ ପରିପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ ସମାଜ । ଯେ ଯାହାକୁ କଥା କହି ତା’ର ମନ ମୋହି ଠକିବାରେ ବ୍ୟସ୍ତ । ନିଜର ସ୍ବାର୍ଥସାଧନ ପାଇଁ ମୁଖରେ ଅମୃତବୋଳା କଥା କହି ଫାଇଦା ଉଠାଇବାରେ ବ୍ୟସ୍ତ । କାମ କରିବେନି ଆଉ ଖାଲି ଚିକ୍କଣିଆ କଥା କହିବେ ଅନ୍ୟର ମନ ମୋହିବେ ଯେପରି ଶୁକ ପଞ୍ଜୁରି ଭିତରେ ରହି ମିଟୁ ମିଟୁ କହୁଥାଏ । ଶୁକ କେବଳ ଶବ୍ଦକୁ ରଟନ କରି କରି ଅଭ୍ୟସ୍ତ ହୋଇଛି । ଏ ଶୁକ ବିଦ୍ୟାରେ କ’ଣ ଅବା ଲାଭ ଅଛି । ଏଣୁ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ କଥାର କାର୍ଯ୍ୟାନୁଷ୍ଠାନ ଏକାନ୍ତ ପ୍ରୟୋଜନ । କଥାରେ କହିଦେଲେ ହେବନି କାମରେ କରି ଦେଖାଇବାକୁ ହେବ । ତେବେ ଯାଇ ଏ ସମାଜ ଉନ୍ନତି ହୋଇପାରିବ ।
ବ୍ୟାକରଣ:
ସନ୍ଧିବିଚ୍ଛେଦ – ରଞ୍ଜୟତ୍ୟେବ = ରଞ୍ଜୟତି + ଏବ ।
ସମାସ – ପାଠମାତ୍ରେଣ = ପାଠ୍ଃ ଏବ ମାତ୍ରମ୍ ପାଠମାତ୍ରମ୍, ତେନ (ମୟୂର ବ୍ଯସକାଦି) । ଶୁକବିଦ୍ୟୟା = ଶୁକସ୍ୟ ବିଦ୍ୟା, ତୟା (୬ଷ୍ଠ ତତ୍) ।
ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତି – ପାଠମାତ୍ରେଣ, ଅନୁଷ୍ଠାନେନ = କରଣେ ୩ୟା । ଲୋକାନ୍ = କର୍ମଣି ୨ୟା । ତୟା, ଶୁକବିଦ୍ୟୟା = କରଣେ ୩ୟା ।
ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ – ଅନୁଷ୍ଠାନମ୍ = ଅନୁ + ସ୍ଥା + ଲୁଟ୍ । ପାଠ୍ୟ = ପଠ୍ + ଘଞ୍ଚ୍ ।
ଶ୍ଳୋକ – ୧୨
गच्छत्पिपीलिका याति योजनानि शतान्यपि ।
अगच्छन् वैनतेयोऽपि पदमेकं न गच्छति ॥ १२ ॥
ଗଚ୍ଛତ୍ପିପୀଲିକା ଯାତି ଯୋଜନାନି ଶତାନ୍ୟପି ।
ଅଗଚ୍ଛନ୍ ବୈନତେୟୋଽପି ପଦମେକଂ ନ ଗଚ୍ଛତି ॥ ୧୨ ॥
ଅନ୍ୱୟ – ଗଚ୍ଛତ୍ ପିପୀଲିକା ଶତାନି ଯୋଜନାନି ଯାତି, ଅଗଚ୍ଛନ୍ ବୈନତେୟଂ ଏବଂ ପଦମ୍ ଅପି ନ ଗଚ୍ଛତି ।
ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ – ପିପୀଲିକା = ପିମ୍ପୁଡ଼ି । ଗଚ୍ଛତ୍ = ସଦା ଗତିଶୀଳ । ବୈନତେୟଃ = ଗରୁଡ଼ । ଅଗଚ୍ଛନ୍ = ନ ଯାଇ ମଧ୍ଯ । ଯାତି = ଯାଇଥାଏ ।
ଅନୁବାଦ – ନିରନ୍ତର ଚାଲୁଥିବା ପିମ୍ପୁଡ଼ି ଶହେ ଯୋଜନ ଚାଲିଯାଏ, ଆଦୌ ଯାଉନଥିବା ଗରୁଡ଼ ମଧ୍ଯ ଏକପାଦ ଯାଇପାରେ ନାହିଁ ।
ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶ୍ଳୋକୋଽୟଂ ପଠିତଃ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ପଦ୍ୟାତ୍ ଆନୀତଃ । ଅତ୍ର ଅସ୍ମିନ୍ ଶ୍ଳୋକେ ପିପୀଲିକା ବୈନତେୟଃ ଗମନ ପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗେ ଆଳସ୍ୟରୂପ ରିପୁଂ ବର୍ଷୟତି ।
ସଂସାରୋଽୟଂ ଇଶଃ ସୃଷ୍ଟି । ପକ୍ଷୀ ପ୍ରାଣୀ ଚ ସର୍ବେ ପରମେଶ୍ୱରେଣ ସୃଷ୍ଟି । କଃ ପାଦେନ ଚଳତି ଅଥବା କଃ ସ୍ଵପକ୍ଷ୍ମଣା ଆକାଶ ଉଡ୍ଡୀୟମାନଃ ଗଚ୍ଛତି । ପିପୀଲିକା ପାଦେନ ଗଚ୍ଛତି । ଶତାନି ଅପି ଯୋଜନାନି ପିପୀଲିକା ଯାତି । ପରନ୍ତୁ ବୈନତେୟଃ ଏକପାଦମ୍ ଅପି ନ ଗଚ୍ଛତି । ସ ତୁ ଉଡ୍ଡୀୟମାନଂ ଗଚ୍ଛତି ନ ଚଳତି । ବିନତାନନ୍ଦନ ଗରୁଡ଼ ଶତଯୋଜନଗମନେ ସାମର୍ଥ୍ୟ ବହନ୍ ଅପି ଯଦି ଗତଂ ନ ଇଚ୍ଛତି ତହିଁ ଏବଂ ପଦମ୍ ଅପି ନ ଯାତି । ଅସ୍ମାତ୍ ଶ୍ଳୋକାତ୍ ଏତତ୍ ଜ୍ଞାୟତେ ଯତ୍ ଯଃ ଅସ୍କ୍ରିନ୍ ସଂସାରେ ଉଦ୍ୟୋଗ କରୋତି ପଃ ସର୍ବାଣି କାର୍ଯ୍ୟାଣି ସିଦ୍ଧତି । ଅତଃ ସୁଶ୍ରୁ ଉଦ୍ୟତେ – ‘ଉଦ୍ୟୋଗ ସମଃ ବନ୍ଧୁ ନାସ୍ତ ।’’ ସର୍ବଦା ଉଦ୍ୟୋଗ କରଣୀୟଃ ।
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶଂସିତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଟି ପଠିତ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକର ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ରୁ ସଂଗୃହୀତ । ଏଠାରେ ପିମ୍ପୁଡ଼ି ଓ ଗରୁଡ଼ର ଗତି ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧରେ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନ କରାଯାଇଅଛି ।
ଏ ସୃଷ୍ଟିରେ ସମସ୍ତେ ଈଶ୍ଵରସୃଷ୍ଟ ସେ ପକ୍ଷୀ ହେଉ ଅବା ପ୍ରାଣୀ ହେଉ । କିଏ ପାଦରେ ଚାଲେ ତ ପୁଣି କିଏ ପକ୍ଷ ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ ଉଡ଼ିଯାଏ । ପିମ୍ପୁଡ଼ି ସଦାସର୍ବଦା ପାଦଦ୍ୱାରା ଚାଲୁଥାଏ । ଚାଲି ଚାଲି ଶହେ ଯୋଜନ ଅତିକ୍ରମ କରିଯାଏ । କାରଣ ପ୍ରତିପଦରେ ଥାଏ ବାଧାବିଘ୍ନ । ଏତେ କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ରତା କାରଣରୁ କେବେ ସେ ପାଏ ଅନ୍ୟ ପଦାଘାତ ତ ପୁଣି କେବେ ଶକ୍ତିର ଅଭାବରୁ ଯିବାକୁ ହୁଏ ଅସମର୍ଥ । ହେଲେ ବୈନତେୟ ବା ଗରୁଡ଼ ଯେ କି ଆଦୌ ଗତିକରେ ନାହିଁ, ସେ ଏକ ପାଦ ମଧ୍ଯ ଅତିକ୍ରମ କରିପାରେ ନାହିଁ । ଏହା ହେଉଛି ଭଗବାନ୍ଙ୍କର କୃପା । ସ୍ଵୟଂ ବୈନତେୟ ହେଉଛି ଭଗବାନ୍ ନାରାୟଣଙ୍କର ବାହନ । ତେଣୁ ଈଶ୍ଵରକୃପା ଆମ ସମସ୍ତଙ୍କର ଏକାନ୍ତ କାମ୍ୟ ହେବା ଉଚିତ ।
ବ୍ୟାକରଣ:
ନ୍ଧିବିଚ୍ଛେଦ – ଶତାନ୍ୟପି = ଶତାନି + ଅପି । ବୈୟୋଽପି = ବୈନତେୟଃ + ଅପି । ପଦମେକମ୍ = ପଦମ୍ + ଏକମ୍ ।
ସମାସ – ଅଗଚ୍ଛନ୍ = ନ ଗଚ୍ଛନ୍ (ନୡ ତତ୍) । ଗଚ୍ଛତ୍ ପିପୀଲିକା = ଗଚ୍ଛନ୍ତୀ ପିପୀଲିକା (କର୍ମଧାରୟ ) । ପଦମେକମ୍ = ଏବଂ ପଦମ୍ (କର୍ମଧାରୟଃ) ।
ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତି – ପିପୀଲିକା, ବୈନତେୟଃ = କଉଁରି ୧ମା । ପଦମ୍ = କର୍ମଣି ୨ୟା ।
ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ – ଗଛତ୍ = ଗମ୍ + ଶତ୍ରୁ । ବୈନତେୟଃ = ବିନତା + ଢକ୍ ।
ଶ୍ଳୋକ – ୧୩
पात्रापात्रविशेषोऽस्ति धेनुपन्नगयोरिव ।
तृणादुत्पद्यते दुग्धं दुग्धादुत्पद्यते विषम् ॥ १३ ॥
ପାତ୍ରାପାତ୍ରବିଶେଷୋଽସ୍ତି ଧେନୁପନ୍ନଗୟୋରିବ ।
ତୃଣାଦୁପ୍ଦ୍ୟତେ ଦୁଗ୍ଧ ଦୁଗ୍ଧଦୁତେ ବିଷମ୍ ॥ ୧୩ ॥
ଅନ୍ବୟ – ପାତ୍ରାପାତ୍ରବିଶେଷ ଧେନୁପନ୍ନଗୟୋ ଇବ ଅସ୍ଥି । ତୃଣାତ୍ ଦୁଗ୍ଧ ଉତ୍ପଦ୍ୟତେ, ଦୁଗ୍ଧାତ୍ ବିଷମ୍ ଉତ୍ପଦ୍ୟତେ ।
ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ – ଧେନୁ = ଗାଈ । ପନ୍ନଗ ସର୍ପ । ଉତ୍ପଦ୍ୟତେ = ଜାତ ହୁଏ ।
ଅନୁବାଦ – ସାଧାରଣରେ ପାତ୍ର ଏବଂ ଅପାତ୍ର ବିଶେଷ ଗାଈ ଓ ସର୍ପ ପରି ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଗାଈ ପାତ୍ର ଏବଂ ସର୍ପ ଅପାତ୍ର ଅଟେ । ତୃଣରୁ ଦୁଗ୍ଧ ଉତ୍ପନ୍ନ ହୁଏ ଏବଂ ଦୁଗ୍ଧରୁ ବିଷ ଉତ୍ପନ୍ନ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଗାଈ ତୃଣ ଖାଇ ଦୁଗ୍ଧ ପ୍ରଦାନ କରେ । ସର୍ପ ଦୁଗ୍ଧ ପିଇ ବିଷ ଉତ୍ପନ୍ନ କରିଥାଏ ।
ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶ୍ଳୋକୋଽୟଂ ପଠିତଃ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ପଦ୍ୟାତ୍ ଆନୀତଃ । ଅତ୍ର ଅସ୍ଥିନ୍ ଶ୍ଳୋକେ ପାତ୍ରାପାତ୍ରବିଶେଷାନାଂ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନଂ ଭବତି ।
ଯୋଗ୍ୟଯୋଗ୍ୟୟୋର୍ଭେଦମ୍ ଅତ୍ର ବର୍ଣ୍ଣୟିତୁମାହ ଯତ୍ – ଅସ୍ଥିନ୍ ସଂସାରେ ଭକ୍ଷ୍ୟଭକ୍ଷ୍ୟୟୋ ବିବେଚନଂ ଭବତି । ଭକ୍ଷ୍ୟଭ୍ୟ ଅଭକ୍ଷ୍ୟମ୍, ଅଭଷ୍ୟତଃ ଭକ୍ଷ୍ୟ ଚ ଜାତଃ ଭବତି । ଯଃ ଯୋଗ୍ୟ ସ ସୁଫଳଂ ଦଦାତି ପୁନଶ୍ଚ ଯଃ ଅଯୋଗ୍ୟ ସ୍ୱ କୁଫଳ ଦଦାତି । ତୃଣଂ ଖାଦନ୍ ଅପି ଧେନୁଃ ଦୁଗ୍ଧ ପ୍ରଦଦାତି । ପୁନଶ୍ଚ ସର୍ପ ଦୁଗ୍ ପିବନ୍ ଅପି ବିଷମ୍ ଉତ୍ପାଦୟତି । ଅତଃ ଧେନୁପନ୍ନଗୟୋ ଇବ ପାତ୍ରାପାତ୍ରବିଶେଷ ଅସ୍ଥି । ଯଃ ଉପଯୁକ୍ତପାତ୍ର ସ ସର୍ବଦା ସର୍ବତ୍ର ସ୍ଵକୀୟ ଯୋଗ୍ୟତାଂ ପ୍ରଦର୍ଶୟତି । ଅତଃ ସର୍ପାଶାଂ ପୟଃ ପାନେନ ବିଷବର୍ଦ୍ଧନମିବ ଅପାତ୍ରସେବା କୁଫଳଂ ଜନୟତି । ଅତଃ ଶାସ୍ତ୍ରକାରେଣ ଯଥାରୀତ୍ୟା ପାତ୍ରାପାତ୍ରୟୋ ବିବେଚନ ପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗେ ଧେନୁପନ୍ନଗ ଉଦାହରଣଂ ପ୍ରଦତ୍ତବାନ୍ତଦେବ ଅତୀବ ସ୍ପୃହଣୀୟଂ ଗ୍ରହଣୀୟଂ ଶିକ୍ଷଣୀୟଂ ଚ ଭବତି ।
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶଂସିତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଟି ପଠିତ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକର ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ରୁ ଆନୀତ । ଏଠାରେ ପାତ୍ର ଓ ଅପାତ୍ର ବିଶେଷର ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନା କରାଯାଇଛି ।
ଏ ସଂସାରରେ ଭକ୍ଷାଭକ୍ଷ୍ୟ ବିବେଚନ କରାଯାଇଛି । ଭକ୍ଷ୍ୟରୁ ଅଭକ୍ଷ୍ୟ ଏବଂ ଅଭକ୍ଷ୍ୟରୁ ଭକ୍ଷ୍ୟର ଜାତ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଗୋଟିଏ ପାତ୍ର ଓ ଅନ୍ୟଟି ଅପାତ୍ର ଅଟେ । ଯେପରିକି ପାତ୍ର ହେଉଛି ଧେନୁ ଏବଂ ଅପାତ୍ର ହେଉଛି ପନ୍ନଗ ବା ସର୍ପ । ଗାଈ ସ୍ବୟଂ ତୃଣ ଭକ୍ଷଣ କରେ ହେଲେ ଅପରକୁ ଦୁଗ୍ଧ ପ୍ରଦାନ କରିଥାଏ । ଦୁଗ୍ଧ ଅମୃତତୁଲ୍ୟ ଅଟେ । ହେଲେ ସର୍ପ ଏହି ଅମୃତତୁଲ୍ୟ ଦୁଗ୍ଧକୁ ଭକ୍ଷଣ କରି ଅପରକୁ ବିଷ ହିଁ ପ୍ରଦାନ କରିଥାଏ । ଏଣୁ ଉପଯୁକ୍ତ ପାତ୍ରରେ ଅଦ୍ରବ୍ୟ ମଧ୍ଯ ଉପକାରକ ହୋଇଥାଏ ହେଲେ ଅନୁପଯୁକ୍ତ ଅପାତ୍ରରେ ଦ୍ରବ୍ୟ ମଧ୍ଯ ଅପକାରକ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଏଣୁ କାବ୍ୟକାର ଯେପରିଭାବେ ଧେନୁ ଓ ପନ୍ନଗର ଉଦାହରଣ ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ ପାତ୍ରାପାତ୍ର ବିଶେଷର ବିଶ୍ଳେଷଣ କରିଅଛନ୍ତି ତାହା ଅତ୍ୟନ୍ତ ଯୁକ୍ତିଯୁକ୍ତ ତଥା ଗ୍ରହଣୀୟ ହୋଇଛି ।
ବ୍ୟାକରଣ:
ସନ୍ଧିବିଚ୍ଛେଦ – ପାତ୍ରାପାତ୍ରବିଶେଷୋଽସ୍ତି = ପାତ୍ର + ଅପାତ୍ରବିଶେଷ + ଅସ୍ଥି । ଧେନୁପନ୍ନଗୟୋରିବ = ଧେନୁପନ୍ନଗୟୋଃ + ଇବ । ତୃଣାଦୁପ୍ଦ୍ୟତେ = ତୃଣାତ୍ + ଉତ୍ପଦ୍ୟତେ । ଦୁଗ୍ଧଦୁପ୍ଦ୍ୟତେ = ଦୁଗ୍ଧାତ୍ + ଉତ୍ପଦ୍ୟତେ ।
ସମାସ – ପାତ୍ରାପାତ୍ରବିଶେଷ = ପାରଂ ଚ ଆପାତ୍ର ଚ (ଦ୍ବନ୍ଦ୍ବ), ତଧେନୁଃ ବିଶେଷ (୬ଷ୍ଠୀ ତତ୍) । ଧେନୁପନ୍ନଗୟୋଃ = ଧେନୁଃ ଚ ପନ୍ନଶଃ ଚ, ତୟୋ (ଦ୍ବନ୍ଦ୍ବ) ।
ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତି – ଧେନୁପନ୍ନଗୟୋଃ = ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ୬ଷ୍ଠୀ । ତୃଣାତ୍, ଦୁଗ୍ଧାତ୍ = ‘ଜନିକର୍ତ୍ତା ପ୍ରକୃତି’ ଯୋଗେ ଅପାଦାନେ ୫ମୀ । ବିଷମ୍ = କର୍ମଣି ୨ୟା ।
ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ – ବିଶେଷ = ବି + ଶିଷ୍ + ଘଞ୍ଚ୍ ।
ଶ୍ଳୋକ – ୧୪
चिन्तनीया हि विपदामादावेव प्रतिक्रिया ।
न कूपखननं युक्तं प्रदीप्ते वह्निना गृहे ॥ १४ ॥
ଚିନ୍ତନୀୟା ହି ବିପଦାମାଦାବେବ ପ୍ରତିକ୍ରିୟା ।
ନ କୂପଖନନଂ ଯୁକ୍ତ ପ୍ରଦୀପ୍ତ ବହ୍ନିନା ଗୃହେ ॥ ୧୪ ॥
ଅନ୍ବୟ – ବିପଦାମ୍ ଆଦୌ ଏବ ପ୍ରତିକ୍ରିୟା ଚିନ୍ତନୀୟା, ହି ବହ୍ନିନା ଗୃହେ ପ୍ରଦୀପ୍ତ କୂପଖନନଂ ନ ଯୁକ୍ତ (ଭବତି) ।
ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ – ବିପଦାମ୍ = ବିପଦମାନଙ୍କର । ଚିନ୍ତନୀୟା = ଚିନ୍ତା କରାଯିବା ଉଚିତ । ବହ୍ନିନା = ଅଗ୍ନିଦ୍ଵାରା । ପ୍ରଦୀପ୍ତି = ପ୍ରଜ୍ୱଳିତ ହୁଅନ୍ତେ ।
ଅନୁବାଦ – ବିପଦ ଆପଦର ପ୍ରଥମରୁ ହିଁ ପ୍ରତିକ୍ରିୟା ଚିନ୍ତା କରାଯିବା ଉଚିତ । ଯେହେତୁ ଅଗ୍ନିଦ୍ଵାରା ଗୃହ ପ୍ରଜ୍ଜ୍ୱଳିତ ହୁଅନ୍ତେ କୂପର ଖନନ୍ ଯୁକ୍ତିଯୁକ୍ତ ନୁହେଁ ।
ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶଂସିତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଃ ପଠିତଃ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ପଦ୍ୟାତ୍ ସଂଗୃହୀତଃ । ଅତ୍ର ଅସ୍ମିନ୍ ଶ୍ଳୋକେ ଶାସ୍ତ୍ରକାରଃ ପ୍ରତିକାର ବିଧାନସ୍ୟ କାଳଂ ବିଷୟେ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣୟତି ।
ଅସ୍ଥିନ୍ ବ୍ୟସ୍ତବହୁଳେ ସଂସାରେ ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ଅଯଥାର୍ଥନ ବିପଦି ନିମଜ୍ଜିତଃ ଭବତି । ଚିନ୍ତୟିତଂ ଶୋଚିତୁଃ ଚ କାଳଂ ନାସ୍ତି । ପଶ୍ୟନ୍ ହି ନୟନୟୋ ସମୀପେ ଅଘଟଣଂ ଦୁର୍ଘଟଣଂ ଚ ପ୍ରତୀୟତେ । ଅଧୁନା ପ୍ରଯତ୍ନସ୍ୟ କାଳମ୍ ଆୟାତି । ସମୟାତ୍ ପ୍ରାକ୍ ଉଚିତାନୁଚିତଂ ବିଚାରଣୀୟମ୍ । କୋଽପି କର୍ମତତ୍ପରଃ ଜନଃ ସର୍ବଦା ଆସନ୍ନବିପଦଂ ପ୍ରତିକାରମ୍ ଆଦୌ ଏବ ଚିନ୍ତୟେତ୍ । ଅନ୍ୟଥା ଆପତ୍କାଳେ ପ୍ରତିକାରକରଣେ ନାବସରଃ ପ୍ରାପ୍ୟତେ । ଅଗ୍ନିନା ଗୃହେ ପ୍ରଦୀପ୍ତି ଯଥା କୂପଖନନମ୍ ଅଯୁକ୍ତ ତଥା ବିପଦି ଆଗତାୟାଂ ତପ୍ରତିକାରଚିନ୍ତନମ୍ ଅଯଥାର୍ଥମ୍ । ଅତଃ ସଦୈବ ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ବିପଦଃ ପ୍ରାକ୍ ଏବଂ ତଥ୍ୟ ପ୍ରତିକାର ବିଷୟମ୍ ଅବଶ୍ୟ ଶୋଚେତ୍ ।
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶଂସିତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଟି ପଠିତ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକର ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ରୁ ସଂଗୃହୀତ । ଏଠାରେ ବିପଦ ଆସିବା ପୂର୍ବରୁ ହିଁ ପ୍ରତିକ୍ରିୟା ଚିନ୍ତାକରିବା ପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତ ହୋଇଛି ।
ଏ ବ୍ୟସ୍ତବହୁଳ ଦୁନିଆରେ ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ଅଯଥାରେ ବିପଦରେ ପଡ଼ୁଛି । ଭାବିବାକୁ ସମୟ ନାହିଁ, ଦେଖୁ ଦେଖୁ ଆଖୁଗରେ ଅଘଟଣ ଘଟିଯାଉଛି । ଆଜି ସତର୍କ ହେବାର ବେଳ ଆସିଛି । ସମୟ ପୂର୍ବରୁ ଭଲମନ୍ଦ ବିଚାରିବା ଉଚିତ । ଏଣୁ ବିପଦ ଆପଦର ପ୍ରଥମରୁ ହିଁ ପ୍ରତିକ୍ରିୟା ଚିନ୍ତା କରିନେବା ଉଚିତ । ଯଦି ଏଭଳି ହୁଏ ତେବେ କ’ଣ କରାଯିବା ଉଚିତ । ଯେହେତୁ ବିପଦ ଆସିଲେ ଆଉ ଚିନ୍ତା କରି ଲାଭ ହୁଏ ନାହିଁ । ଅଗ୍ନିଦ୍ଵାରା ଗୃହ ସଂଦୀପିତ ହୋଇଯା’ନ୍ତେ କୂପଖନନରେ କ’ଣ ବା ଲାଭ । ଘର ଜଳିପୋଡ଼ି ଭସ୍ମ ହୋଇଯିବ କୂପଖନନ ହେବାବେଳକୁ । ଏହାକୁ କହନ୍ତି ‘ବାହାଘରବେଳେ ବାଇଗଣ ରୁଆ’ । ଏହା ସମ୍ପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ ଅସଫଳ ବା ନିରର୍ଥକ ହୁଏ । ସର୍ବଦା ସମୟ ଥାଉ ଥାଉ ଯତ୍ନବାନ୍ ହେବା ଉଚିତ ।
ବ୍ୟାକରଣ:
ସନ୍ଧିବିଚ୍ଛେଦ – ବିପଦାମାଦାବେବ = ବିପଦାମ୍ + ଆଦୌ + ଏବ ।
ସମାସ – ପ୍ରତିକ୍ରିୟା = କ୍ରିୟା ପ୍ରତି (ଅବ୍ୟୟୀଭାବ) । କୂପଖନନମ୍ = କୂପସ୍ୟ ଖନନମ୍ (୬ଷ୍ଠୀ ତତ୍) ।
ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତି – ବିପଦାମ୍ = ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ୬ଷ୍ଠୀ । କୂପଖନନମ୍ = କର୍ମଣି ୨ୟା । ପ୍ରଦୀପ୍ତେ, ଗୃହେ = ଭାବେ ୭ମୀ । = କରଣେ ୩ୟା ।
ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ – ଚିନ୍ତନୀୟା = ଚିନ୍ତ୍ + ଅନୀୟ + ଟାପ୍ । ଖନନମ୍ = ଖନ୍ + ଲ୍ୟୁଟ୍ । ଯୁକ୍ତମ୍ = ଯୁଜ୍ + କ୍ତ । ପ୍ରଦୀପ୍ତ = ପ୍ର + ଦୀପ୍ + କ୍ତ ।
ଶ୍ଳୋକ – ୧୫
दुर्जनेन समं सख्यं प्रीतिं चापि न कारयेत् ।
उष्णो दहति चाङ्गरः शीतः कृष्णायते करम् ॥ १५ ॥
ଦୁର୍ଜନେନ ସମଂ ସଖ୍ୟ ପ୍ରୀତଂ ଚାପି ନ କାରୟେତ୍ ।
ଉଷୋ ଦହତି ଚାଙ୍ଗାରଃ ଶୀତଃ କୃଷ୍ଣାୟତେ କରମ୍ ॥୧୫ ॥
ଅନ୍ବୟ – ଦୁର୍ଜନେନ,ସମମ୍ ଅପି ସଖ୍ୟ ପ୍ରୀତଂ ଚ ନ କାରୟେତ୍ । ଅଙ୍ଗାରଃ ଉଷ୍ଣ ଦହତି ଶୀତଃ କରଂ କୃଷ୍ଣାୟତେ ଚ ।
ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ – ଦୁର୍ଜନେନ = ଖଳ ବା ଦୁର୍ଜନ ସହିତ । ସଖ୍ୟ = ବନ୍ଧୁତା । ପ୍ରୀତି = ସ୍ନେହ । ଦହତି = ପୋଡ଼ିଦିଏ । ଶୀତଃ = ଶୀତଳ । କରମ୍ ହସ୍ତ ।
ଅନୁବାଦ – ଖଳ ବା ଦୁର୍ଜନ ସହିତ ମିତ୍ରତା ଓ ସ୍ନେହ ବା ପ୍ରେମ କରିବା ଉଚିତ ନୁହେଁ । କାରଣ ଅଙ୍ଗାର ଉଷ୍ଣ ହେଲେ ପୋଡ଼ିପକାଏ ଓ ଶୀତଳ ହେଲେ ହାତକୁ କଳା କରିଦିଏ ।
ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶଂସିତଃ ଶ୍ଳୋକଃ ପଠିତଃ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ପଦ୍ୟାତ୍ ଆନୀତଃ । ଅସ୍ମିନ୍ ଶ୍ଳୋକେ ଦୁର୍ଜନସ୍ୟ ସ୍ବଭାବଂ ପ୍ରଭାବଂ ଚ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତଂ ଭବତି ।
ଖଳଜନେନ ଦୁର୍ଜନେନ ବା ମୈତ୍ରୀ ନ କରଣୀୟା । ତେନ ସାକଂ ସଖ୍ୟ ପ୍ରୀତଂ ଚ ନ କାରୟେତ୍ । ପଦେ ପଦେ ତେ ଦୁର୍ଜନାଃ ଅନିତଂ ସାଧୟନ୍ତି । ତେଷା ସ୍ଵଭାବାଃ ମଶଃ ଭବତି । ଏତତ୍ ପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗ କବିନା ଦୃଷ୍ଟାନ୍ତମାଧମେନ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତଃ ଯଥା – ଭଷ୍ଷଃ ଅଙ୍ଗାରଃ ହସ୍ତଂ ଦହତି ପୁନଶ୍ଚ ଶୀତଳ କରଂ କୃଷ୍ଣାୟତେ ଚ । ଅତଃ ଦୁର୍ଜନଃ ସର୍ବଦା ପରିହର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟ । ସୁହୃଦ୍ରୂପେନ ଅସୌ ଅହିତଂ କରୋତି । ଶତ୍ରୁରୂପେଣ ବିନାଶକାରଣଂ ଭବତି । ଅତ୍ର ଦୁର୍ଜନଃ ଅଙ୍ଗାରଣ ସାକଂ ତୁଳିତଂ ଭବତି । ଅତଃ ଅଙ୍ଗାରଃ ଦୁର୍ଜନଃ ଚ ସଦୈବ ବର୍ଜନୀୟ ଭବତି ।
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶଂସିତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଟି ପଠିତ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକର ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ରୁ ସଂଗୃହୀତ । ଏଠାରେ ଦୁର୍ଜନର ନିବାରଣ ପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗ ଉଲ୍ଲେଖ କରାଯାଇଅଛି ।
ଖଳ ବା ମନ୍ଦବୁଦ୍ଧି ଲୋକଙ୍କୁ ଦୂରୁ ଜୁହାର। ସେମାନଙ୍କ ସହ ମିତ୍ରତା ଏବଂ ସ୍ନେହ ବା ପ୍ରେମ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ କରିବା ଆଦୌ ଉଚିତ ନୁହେଁ । ପ୍ରତି ପଦେ ପଦେ ସେମାନେ ମନୁଷ୍ୟର ଅନିଷ୍ଟ ସାଧନ କରିଥା’ନ୍ତି । ଭଲମନ୍ଦ ସବୁ ସମୟରେ ସେମାନଙ୍କର ସ୍ବଭାବ ଖରାପ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ସତେ ଅବା ଏମାନଙ୍କର ସ୍ବଭାବ ଏକ କାଠର କୋଇଲା ବା ଅଙ୍ଗାର ପରି । ଅଙ୍ଗାର ଉଷ୍ଣ ହେଲେ ଲାଲ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ଏହାକୁ ସ୍ପର୍ଶମାତ୍ରକେ ଜାଳିପୋଡ଼ିଦିଏ । ଯଦି ପୁଣି ଏହା ଶୀତଳ ବା ଥଣ୍ଡା ହୋଇଯାଏ ତେବେ ହାତକୁ କଳୁଷିତ ବା କାଳିମା ପୂର୍ବ କରିଦିଏ । ଏଠାରେ ଖଳଜନକୁ ଅଙ୍ଗାର ଭଳି ତୁଳନା କରାଯାଇ ଦୃଷ୍ଟାନ୍ତ ଛଳରେ ଏହାହିଁ ଶିକ୍ଷା ମିଳୁଛି ଯେ ଦୁର୍ଜନ ଏବଂ ଅଙ୍ଗାର ଏହା ସର୍ବଦା ବର୍ଜନୀୟ ଅଟନ୍ତି ।

ବ୍ୟାକରଣ:
ସନ୍ଧିବିଚ୍ଛେଦ – ଚାଙ୍ଗାରଃ = ଚ + ଅଙ୍ଗାରଃ ।
ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତି – ଦୁର୍ଜନେନ = ସମଂ ଯୋଗେ ୩ୟା । ସଖ୍ୟ, ପ୍ରୀତିମ୍ = କର୍ମଣି ୨ୟା । ଅଙ୍ଗାରଃ = କଉଁରି ୧ ମା । କରମ୍ = କର୍ମଣି ୨ୟା ।
ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ – ପ୍ରୀତି = ପ୍ରୀଣ୍ + ସ୍କ୍ରିନ୍ ।
ଶ୍ଳୋକ -୧୬
न कश्चिदपि जानाति किं कस्य श्वे भविष्यति ।
अत: श्वः करणीयानि कुर्यादद्यैव वुद्धिमान् ॥ १६ ॥
ନ କଶ୍ଚିଦପି ଜାନାତି କିଂ କସ୍ୟ ଶ୍ରେ ଭବିଷ୍ୟତି ।
ଅତଃ ଡଃ କରଣୀୟାନି କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟାଦଦୈବ ବୁଦ୍ଧିମାନ୍ ॥ ୧୬ ॥
ଅନ୍ୱୟ – ଡଃ କସ୍ୟ କିଂ ଭବିଷ୍ୟତି କଶ୍ଚିତ୍ ଅପି ନ ଜାନାତି । ଅତଃ ବୁଦ୍ଧିମାନ୍ ଶୃ କରଣୀୟାନି ଅଦୈବ କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟାତ୍ ।
ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ – ଶଃ = ଆସନ୍ତାକାଲି । ଭବିଷ୍ୟତି = ହେବ ବା ଘଟିବ । ଅତଃ = ଏଣୁ । କରଣୀୟାନି = କରିବାକୁ ଥିବା କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ । କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟାତ୍ = କରିବା ଉଚିତ ।
ଅନୁବାଦ – ଆସନ୍ତାକାଲି କାହାର କ’ଣ ହେବ କେହିହେଲେ ମଧ୍ୟ ଜାଣିନାହାଁନ୍ତି । ଏଣୁ ବୁଦ୍ଧିମାନ୍ (ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ) ଆସନ୍ତାକାଲିର କାର୍ଯ୍ୟକୁ ଆଜି ହିଁ କରିବା ଉଚିତ ।
ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶ୍ଳୋକୋଽୟଂ ପଠିତଃ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ପଦ୍ୟାତ୍ ଆନୀତଃ । ଅତ୍ର ଅସ୍ମିନ୍ ଶ୍ଳୋକେ ମନୁଷ୍ୟଜୀବନସ୍ୟ ବିନଶ୍ବରତାଂ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତମ୍ ।
ଅସ୍ମିନ୍ ସଂସାରେ ପ୍ରତିକ୍ଷଣଂ କିଂ ଭବତି, କିଂ ଭବିଷ୍ୟତି ଚ ଇତି ଏତତ୍ ନ କୋଽପି ଜାନାତି । ଏତତ୍ ବିଷୟଂ ତୁ ଭଗବତଃ ଜ୍ଞାନଗୋଚରଂ ଭବତି । ଅସ୍ଥିନ୍ ବିଷୟ ସାଧାରଣନରଃ ଅଜ୍ଞ ଭବତି । କୋଽପି ଜନଃ ଶଃ ତସ୍ୟ କିଂ ଭବିଷ୍ୟତି ନ ଜାନାତି । ତସ୍ୟ ଜୀବନଂ କ୍ଷଣିକମ୍ । ଅତଃ ବୁଦ୍ଧିମାନ୍ ନରଃ ଡଃ କରଣୀୟଂ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଯଥାଶୀଘ୍ର କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟାତ୍ । ଆଳସ୍ୟ ପରିତ୍ୟଜେତ୍ । ଆଳସ୍ୟ ପରିତ୍ୟଜ୍ୟ ଯଃ ଜନଃ କର୍ମକରଣେ ଯତ୍ନ କରୋତି ସ ଏବଂ କୃତାର୍ଥ ସଫଳଜନ୍ମା ଚ ଭବତି । ଅଦ୍ୟ କରଣୀୟଂ ନୂନଂ ସମାପିତବ୍ୟମ୍ । ଯଦି ସମ୍ଭବେତ୍ ଡଃ କରଣୀୟମ୍ ଅଦ୍ୟ କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟମ୍ । ଅଳୀକତାଂ କ୍ଷଣିକତାଂ ଚ ଉପଲବିଂ କୃତ୍ରା ନରଃ ସଦୈବ ଡଃ କରଣୀୟାନି ଅଦୈବ କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟାତ୍ । ପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗୋଽୟମ୍ ଅତୀବ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନୀୟ ଭବତି ।
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶଂସିତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଟି ପଠିତ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକର ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗସ୍ଥିତ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ରୁ ଆନୀତ । ଏଠାରେ ବୁଦ୍ଧିମାନର କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟ ବିଷୟରେ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନା କରାଯାଇଅଛି ।
ଏ ସଂସାରରେ ପ୍ରତିକ୍ଷଣରେ କ’ଣ ଘଟୁଛି, ଆଗକୁ କ’ଣ ଘଟିବ ତାହା ସୃଷ୍ଟିକର୍ତ୍ତା ପରମେଶ୍ୱର ହିଁ ଜାଣନ୍ତି । ଏ ବିଷୟରେ କିନ୍ତୁ ସାଧାରଣ ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ସମ୍ପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ ଅଜ୍ଞ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଆସନ୍ତାକାଲି ତା’ର କ’ଣ ହେବ କେହି ହେଲେ ଜାଣନ୍ତି ନାହିଁ । ସୁତରାଂ କାଲିର ସ୍ଥିତି କେହି ଜାଣନ୍ତି ନାହିଁ । କେବଳ ବର୍ତ୍ତମାନ ଉପରେ ଏ ଜଗତ ଚାଲିଛି । ଆସନ୍ତାକାଲି ଆସିପାରେ ଆସି ବି ନପାରେ କିଏ କହିବ ସେ କଥା । ଏଣୁ ବୁଦ୍ଧିମାନ୍ ଏ ଅଳୀକତାକୁ ଉପଲବ୍ଧି କରି କାଲିର କାମକୁ ଆଜି କରିନେବା ଉଚିତ । ଏହାହିଁ ହେବ ତା’ର ପ୍ରକୃଷ୍ଟ ବୁଦ୍ଧିମତାର ପରିଚୟ ।
ବ୍ୟାକରଣ:
ସନ୍ଧିବିଚ୍ଛେଦ – କଶ୍ଚିଦପି = କଶ୍ଚିତ୍ + ଅପି । କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟାଦଦୈବ = କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟାତ୍ + ଅଦ୍ୟ + ଏବ ।
ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତି – କସ୍ୟ = ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ୬ଷ୍ଠୀ । କିମ୍ = କର୍ମଣି ୨ୟା । ବୁଦ୍ଧିମାନ୍ = କଉଁରି ୧ ମା ।
ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ – ବୁଦ୍ଧିମାନ୍ = ବୁଦ୍ଧି + ମତୃପ୍ । କରଣୀୟାନି = କୃ + ଅନୀୟର୍ ।
ଶ୍ଳୋକ – ୧୭
आरोप्यते शिला शैले यत्नेन महता यथा ।
निपात्यते क्षणेनाधस्तथात्मा गुणदोषयोः ॥ १७ ॥
ଆରୋପ୍ୟତେ ଶିଳା ଶୈଳେ ଯତ୍ନନ ମହତା ଯଥା ।
ନିପାତ୍ୟତେ କ୍ଷଣେନାଧସ୍ତଥାତ୍ମା ଗୁଣଦୋଷୟୋ ।। ୧୭ ।।
ଅନ୍ବୟ – ଯଥା ଶୈଳେ ଶିଳା । ମହିତା ଯତ୍ନନ ଆରୋପ୍ୟତେ । ତଥା ଆତ୍ମା ଗୁଣଦୋଷୟୋ କ୍ଷଣେନ ଅଧଃ ନିପାତ୍ୟତେ ।
ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ – ଶୈଳେ – ପର୍ବତରେ । ଶିଳା = ପଥର । ଆରୋପ୍ୟତେ = ଆରୋପିତ ହୋଇଥାଏ । କ୍ଷଣେନ = ମୁହୂର୍ତ୍ତକରେ ।
ଅନୁବାଦ – ଯେପରି ପର୍ବତରେ ପଥରଖଣ୍ଡମାନ ଅତୀବ ଯତ୍ନସହକାରେ ଆରୋପିତ ହୋଇଥାଏ ଓ କ୍ଷଣକରେ ଅଧୋପତିତ ହୋଇଥାଏ, ସେହିପରି ଆତ୍ମା ଗୁଣ ଓ ଦୋଷରୁ ଉନ୍ନତ ଓ କ୍ଷଣକରେ ନିମ୍ନକୁ ନିପତିତ ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶ୍ଳୋକୋଽୟଂ ପଠିତଃ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ପଦ୍ୟାତ୍ ଆନୀତଃ । ଅତ୍ର ଅସ୍ଥିନ୍ ଶ୍ଳୋକେ ଗୁଣଦୋଷ ପ୍ରଭାବଂ ପ୍ରଦର୍ଶିତମ୍ ।
ଭଗବତଃ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ଇୟଂ ବିଚିତ୍ରା ଖଳୁ । ଅତ୍ର ପର୍ବତେ ମହତା ଯତ୍ନନ ଶିଳା ସ୍ଥାପ୍ୟତେ । ଏତତ୍ ଶିଳାସ୍ଥାପନଂ ବହୁଶ୍ରମସାପେକ୍ଷ କଷ୍ଟକରଞ୍ଚ ଭବତି । ପରନ୍ତୁ ସ୍ଥାପିତ ଶିଳା ଅନାୟାସେନ କ୍ଷଣମାତ୍ରେଣ ଚ ଅଧଃ ପାତୟିତୁଃ ଯଃ କୋଽପି ସମର୍ଥ ଭବତି । ତାଦୃକ୍ ଏବ ଜନଃ ମହତା କଷ୍ଟେନ ପ୍ରଯତ୍ନନ ଚ ସ୍ବଗୁଣାନ୍ ଆଧାୟ କୀର୍ତ୍ତି ଲଭତେ । ଏକମାତ୍ର ଦୋଷେଣ ତଥ୍ୟ ଜନସ୍ୟ ଅଧଃ ପତନମ୍ ଏବ ଜାୟତେ । ଅତଃ ଦୋଷାଦୋଷ ପରୀକ୍ଷ୍ୟ ଜନଃ କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟ କର୍ମ କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟାତ୍ । ନୋଚେତ୍ ସହସ୍ରଗୁଣି ପ୍ରାପ୍ତ ଯଶଃ ଏକେନାପି ଦୋଷେଣ କ୍ଷଣେନ ଭଗ୍ନ ଧ୍ୟାତ୍ । ଆତ୍ମା ସ୍ୱଗୁଣଦୋଷ ଅଧଃ ପତିତଃ ଭବତି । ଅତଃ ସର୍ବଦା ଯତ୍ନବାନ୍ ଭବେତ୍ ।
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଉଦ୍ଧୃତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଟି ପଠିତ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକର ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତ।ବଳୀ’ ରୁ ଆସିଅଛି ଏଠାରେ ଆତ୍ମାର ନିପତନ ପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତ ହୋଇଛି।
ପୃଥିବୀର ମାନଦଣ୍ଡରୂପେ ନଗାଧାଜ ହିମାଳୟ ପ୍ରତିଷ୍ଠିତ । ଏହି ପର୍ବତରେ ପଥରଖଣ୍ଡମାନ ସତେ ଅବା ସୁସଜ୍ଜିତ ହୋଇ ରଖାଯାଇଛି । କେହି ଯେପରି ଅତି ଯତ୍ନସହକାରେ ପଥରଖଣ୍ଡମାନଙ୍କୁ ପର୍ବତରେ ଆରୋପିତ କରିଅଛି । ହେଲେ କ୍ଷଣମାତ୍ରକେ ଏହା ନିପତିତ ହୁଏ । ଖଣ୍ଡବିଖଣ୍ଡିତ ହୋଇ ମାଟିରେ ମିଶିଯାଏ । ଏ ପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗକୁ ଦୃଷ୍ଟାନ୍ତ ଛଳରେ ଆତ୍ମାର ଉଲ୍ଲେଖ କରାଯାଇଛି । ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ଶରୀରରେ ପରମେଶ୍ୱର ଅତି ଯତ୍ନରେ ଆତ୍ମାକୁ ଆରୋପଣ କରିଅଛନ୍ତି । ଆଉ ଏହି ଆତ୍ମା ଗୁଣ ଏବଂ ଦୋଷ କାରଣରୁ ହିଁ କ୍ଷଣାମାତ୍ରକେ ଅଧପତିତ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଗୁଣରେ ଉତ୍କର୍ଷତା ଓ ଦୋଷରେ ନିମ୍ନଗାମୀ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଏଠାରେ ପର୍ବତକୁ ଶରୀର ଏବଂ ଶିଳାକୁ ଆମ୍ବରୂପେ ବିବେଚନା କରାଯାଇଛି ।
ବ୍ୟାକରଣ:
ସନ୍ଧିବିଚ୍ଛେଦ – କ୍ଷଣେନାଧସ୍ତଥାତ୍ମା = କ୍ଷଣେନ + ଅଧଃ + ତଥା + ଆତ୍ମା ।
ସମାସ – ଗୁଣଦୋଷୟୋ = ଗୁନଃ ଚ ଦୋଷୀ ଚ, ତୟୋ (ଦ୍ବନ୍ଦ୍ବ) ।
ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତି – ଶୈଳେ = ଅଧିକରଣେ ୭ମୀ । ଯତ୍ନନ = ପ୍ରକୃତ୍ୟାଦିଭ୍ୟଶ୍ଚ ୩ୟା । ଗୁଣଦୋଷ = ‘ଅଧଃ’ ଯୋଗେ ୬ଷ୍ଠୀ । କ୍ଷଣେନ = କରଣେ ୩ୟା ।
ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ – ଦୋଷ = ଦୁଷ୍ + ଘଞ୍ଚ୍ ।
ଶ୍ଳୋକ – ୧୮
नाभिषेको न संस्कारः सिंहस्य क्रियते वने ।
विक्रमार्जितसत्वस्य स्वयमेव मृगेन्द्रता ॥ १८ ॥
ନାଭିଷେକୋ ନ ସଂସ୍କାରଃ ସିଂହସ୍ୟ କ୍ରିୟତେ ବନେ ।
ବିକ୍ରମାର୍ଜିତସତ୍ଵସ୍ୟ ସ୍ୱୟମେବ ମୃଗେନ୍ଦ୍ରତା ॥୧୮ ॥
ଅନ୍ବୟ – ସିଂହସ୍ୟ ବନେ ନ ଅଭିଷେକଃ ନ ସଂସ୍କାରଃ କ୍ରିୟତେ । ବିକ୍ରମାଜିତସତ୍ଵସ୍ୟ ସ୍ଵୟଂ ମୃଗେନ୍ଦ୍ରତା ଏବ (ଆଗଚ୍ଛତି) ।
ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ – ଅଭିଷେକଃ = ରାଜସିଂହାସନାରୋହଣ । ବିକ୍ରମ = ବଳ । ସତ୍ଵ = ପ୍ରାଣୀ । ମୃଗେନ୍ଦ୍ରତା = ପଶୁରାଜତ୍ଵ ।
ଅନୁବାଦ – ସିଂହର ବଣରେ ଅଭିଷେକ ଓ ସଂସ୍କାର କରାଯାଇ ନଥାଏ । କାରଣ ସିଂହ ସ୍ବକୀୟ ପରାକ୍ରମ ବଳରେ ହିଁ ନିଜେ ପଶୁମାନଙ୍କର ରାଜା ବୋଲାଏ ।
ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶ୍ଳୋକୋଽୟଂ ପଠିତଃ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ପଦ୍ୟାତ୍ ସଂଗୃହୀତଃ । ଅତ୍ର ଅସ୍ମିନ୍ ଶ୍ଳୋକେ ପରାକ୍ରମମହତ୍ତ୍ୱ ବଣ୍ଡିତଂ ଭବତି ।
ମହିର୍ଷି – ମନୁନା ଉକ୍ତ ଯତ୍ – ଭାରତୀୟପରମ୍ପରାୟାଂ ଯଃ ରାଜା ଅତ୍ର-ଭବିତୁମ୍ ଅର୍ହତି ତସ୍ୟ ରାଜ୍ୟାଭିଷେକ ସଂସ୍କାରାଦି କ୍ରିୟା ଭବିଷ୍ୟତି । କୁଳପୁରୋହିତଃ ବେଦମନ୍ତ୍ରସ୍ୟ ଉଚ୍ଚାରଣଂ କୃତ୍ୱା ସପ୍ତତୀର୍ଥନାଂ ଜଳଂ, ମୃତ୍ତିକା, ପୁଷ୍ପମ୍, ନୈବେଦ୍ୟାଦି ଅର୍ପଣପୂର୍ବକଂ ରାଜ୍ୟାଭିଷେକ ପାଳନଂ ଭବତି । ଏସା ବିଧଃ ପରିଚାଳିତଃ । ରାଜ୍ୟାଭିଷେକାଦନନ୍ତରମେବ ପ୍ରଜାପାଳନଂ କରଗ୍ରହଣଂ ଚ ରାଜ୍ଞ ପ୍ରମୁଖ କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟଂ ଭବତି । ବନେ ସିଂହସ୍ୟ ଅଭିଷେକଃ ସଂସ୍କାରଃ ଚ ନ କ୍ରିୟତେ । ପରନ୍ତୁ ସ୍ବକୀୟପରାକ୍ରମେଣ ବଳମ୍ ଅର୍ଜିତସ୍ୟ ତସ୍ୟ ପଶୁରାଜପଦଂ ସ୍ୱୟମେବ ଆଗଚ୍ଛତି । ଏବମପି ଇହ ଜନଃ ଯଦି ସ୍ଵଚେଷ୍ଟୟା ପ୍ରଯତ୍ନନ ବା କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରଂ ସମର୍ଥ ସ୍ୟାତ୍ ତହିଁ ତଥ୍ୟ ଜୀବନସ୍ୟ ସଫଳତା ସ୍ଵୟମେବ ହି ଆଗମିଷ୍ୟତି । ପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗୋଽୟମ୍ ଅତୀବ ଶିକ୍ଷଣୀୟଂ ଗ୍ରହଣୀୟଂ ଚ ଭବତି ।
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶଂସିତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଟି ପଠିତ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକର ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ରୁ ଆନୀତ । ଏହି ଶ୍ଳୋକରେ ପରାକ୍ରମର ମହତ୍ତ୍ବ ବିଷୟ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତ ହୋଇଛି ।
ଭାରତୀୟ ପ୍ରାଚୀନ ପରମ୍ପରାରେ ରାଜା ହେବାପାଇଁ ହେଲେ ରାଜ୍ୟାଭିଷେକ ତଥା ସଂସ୍କାରାଦି କ୍ରିୟା କରାଯାଇଥାଏ । କୁଳପୁରୋହିତ ବେଦମନ୍ତ୍ରର ଉଚ୍ଚାରଣ କରି ସପ୍ତତୀର୍ଥର ଜଳ, ମୃତ୍ତିକା, ପୁଷ୍ପ, ନୈବେଦ୍ୟାଦି ଅର୍ପଣପୂର୍ବକ ରାଜାଙ୍କର ରାଜ୍ୟାଭିଷେକ ପର୍ବ ପାଳନ କରିଥା’ନ୍ତି । ଏସ୍ରେ ସମସ୍ତ ଗଣ୍ୟମାନ୍ୟ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ତଥା ସାଧାରଣ ପ୍ରଜାମାନେ ମଧ୍ଯ ସମ୍ମିଳିତ ହୋଇଥା’ନ୍ତି । ଏହାପରେ ରାଜସିଂହାସନରେ ଆସୀନ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ହିଁ ରାଜା ବୋଲାଏ ଓ ପ୍ରଜାପାଳନ ତଥା ଶତ୍ରୁସହ ଯୁଦ୍ଧାଦି କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରିଥାଏ । ହେଲେ ବଣର ରାଜା ସିଂହ ଯେକୌଣସି ଅଭିଷେକ ଓ ସଂସ୍କାର ବିନା ସ୍ଵକୀୟ ପରାକ୍ରମ ବଳରେ ରାଜପଦାଳଂକୃତ କରେ । ଏଣୁ ସିଂହ ପଶୁରାଜ ରୂପେ ସମ୍ବୋଧୃତ ହୋଇଥାଏ
ବ୍ୟାକରଣ:
ସନ୍ଧିବିଚ୍ଛେଦ – ନାଭିଷେକୋ = ନ + ଅଭିଷେକଃ । ବିକ୍ରମାର୍ଜିତସତ୍ଵସ୍ୟ = ବିକ୍ରମ + ଅର୍ଜିତସସ୍ୟ । ସ୍ୱୟମେବ = ସ୍ବୟମ୍ + ଏବ । ମୃଗେନ୍ଦ୍ରତା = ମୃଗ + ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରତା ।
ସମାସ – ବିକ୍ରମାର୍ଜିତସସ୍ୟ = ବିକ୍ରମେଣ ଅର୍ଜିତମ୍ (୩ୟା ତତ୍), ବିକ୍ରମାର୍ଜିତଂ ସବଂ ଯସ୍ୟ (ବହୁବ୍ରୀହିଃ) । ମୃଗେନ୍ଦ୍ରତା = ମୃଗାଣାମ୍ ଇନ୍ଦ୍ର ତସ୍ୟା ଭାବ (୬ଷ୍ଠୀ ତତ୍)।
ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତି – ସିଂହସ୍ୟ = ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ୬ଷ୍ଠୀ । ବନେ = ଅଧ୍ଵରଣେ ୭ମୀ । ଅଭିଷେକଃ, ସଂସ୍କାରଃ = ଉକ୍ତ କର୍ମଣି ୧ ମା ।
ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ – ଅଭିଷେକଃ = ଅଭି=ଷିଚ୍ + ଘଞ୍ଜ୍ ।
ଶ୍ଳୋକ – ୧୯
युद्धं च प्रातरुत्थानं भोजनं सह बन्धुभिः ।
स्त्रियमापद्गतां रक्षेच्चतुशिक्षेत कुक्कुटात् ॥ १९ ॥
ଯୁଦଂ ଚ ପ୍ରାତରୁତ୍ଥାନଂ ଭୋଜନଂ ସହ ବନ୍ଧୁଭଃ ।
ସ୍ତ୍ରିୟମାପଦ୍ଗତାଂ ରକ୍ଷେଚ୍ଚତୁଶ୍ଶିକ୍ଷେତ କୁକ୍କୁଖାତ୍ ॥ ୧୯ ॥
ଅନ୍ବୟ – କୁକ୍କୁଟାତ୍ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ, ପ୍ରାତରୁତ୍ଥାନଂ, ବନ୍ଧୁଭିଂ ସହ ଭୋଜନଂ, ଆପଦଗତାଂ ପ୍ରିୟଂ ରକ୍ଷେତ୍ ଚ ଚତୁଃ ଶିକ୍ଷେତ ।
ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ – କୁକ୍କୁଟାତ୍ = କୁକୁଡ଼ାଠାରୁ । ପ୍ରାତରୁତ୍ଥାନମ୍ = ସକାଳୁ ଉଠିବା । ବନ୍ଧୁଭି = ବନ୍ଧୁମାନଙ୍କ ସହ । ଆପଦ୍ଗତାମ୍ ବିପଦଗ୍ରସ୍ତା । ଶିକ୍ଷେତ = ଶିକ୍ଷା କରାଯିବା।
ଅନୁବାଦ – କୁକୁଡ଼ାଠାରୁ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ, ସକାଳୁ ଉଠିବା, ବନ୍ଧୁମାନଙ୍କ ସହ ଭୋଜନ ଏବଂ ବିପଦକାଳରେ ସ୍ତ୍ରୀର ରକ୍ଷଣାଦି ଚାରୋଟି ବିଷୟ ଶିକ୍ଷା କରାଯାଇଥାଏ ।
ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶ୍ଳୋକୋଽୟଂ ପଠିତଃ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ପଦ୍ୟାତ୍ ଆନୀତଃ । ଅତ୍ର ଅସ୍ମିନ୍ ଶ୍ଳୋକେ କୁକ୍କୁଟାତ୍ କିଂ କିଂ ଶିକ୍ଷେତ୍ର ତଦେବ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତମ୍ ।
ସଂସାରୋଽୟଂ ସହାବସ୍ଥାନସ୍ୟ । ଅତ୍ର ମନୁଷ୍ୟ, ପଶୁପକ୍ଷିଣ, ଇତରେ ପ୍ରାଣିନଃ ଚ ଏକତ୍ର ତିଷ୍ଠନ୍ତି । ଏତଃ ଅପରେଭ୍ୟ ଶିକ୍ଷାଲାଭିଂ କରୋତି । ସଂସ୍କୃତ କଥାସାହିତ୍ୟ ପଶୁପକ୍ଷୀଭ୍ୟ କଥା ଶିକ୍ଷଣଂ ପ୍ରଥା ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଗୋଚରଃ ଭବତି । ବିଷ୍ଣୁଶର୍ମା ସ୍ଵରଚିତ ପଞ୍ଚତନ୍ତ୍ର ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥେ ବହୁଳତୟା କଥା ପଶୁପକ୍ଷିନାଂ ଚ ଶିକ୍ଷଣୀୟ ବିଷୟଂ ପ୍ରତିପାଦିତମ୍ । ଅତଃ କୁକ୍କୁଟାତ୍ କିଂ କିଂ ଶିକ୍ଷଣୀୟଂ ତତ୍
ପ୍ରଦର୍ଶିତମ୍ ଯଥା – କୁକ୍କୁନଃ କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ର ଗୃହପାଳିତଃ ପକ୍ଷିବିଶେଷ । ପରନ୍ତୁ ସ ଏବ ପ୍ରାତଃ ଯଥାକାଳମ୍ ଉତ୍ତିଷ୍ଠତି । ଆବଶ୍ୟକସ୍ଥଳେ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ କରୋତି । ସ୍ଵବନ୍ଧୁଭି ସହ ଭୋଜନମ୍ ଅପି କରୋତି। ପୁନଶ୍ଚ ଆପଦଗତାଂ ପ୍ରିୟଂ ରକ୍ଷତି । କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ରେଽପି ତସ୍ମାତ୍ କୁକ୍କୁଟାତ୍ ଏତେ ଚତ୍ବାରଃ ଗୁଣା ଅବଶ୍ୟ ଶିକ୍ଷଣୀୟ । ଆଧୁନିକାନାଂ ଜନାନାଂ ସମୀପେ ଏତାଦୃଶାନାଂ ଗୁଣାନାମ୍ ଅଭାବଂ ପରିଲକ୍ଷ୍ୟତେ । ଅତଃ ସର୍ବେ ମାନବାଃ କୁକ୍କୁଟାତ୍ ତଦେବ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଷୟାନାଂ ଶିକ୍ଷଣମ୍ ଅବଶ୍ୟ କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟ ।
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶଂସିତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଟି ପଠିତ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକର ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ରୁ ଆନୀତ । ଏହି ଶ୍ଳୋକରେ କୁକୁଡ଼ାଠାରୁ କ’ଣ କ’ଣ ଶିକ୍ଷାକରିବା ଉଚିତ ତାହା ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତ ହୋଇଛି ।
ଏ ସଂସାର ହେଉଛି ସହାବସ୍ଥାନର ସ୍ଥଳ । ଏଠି ମନୁଷ୍ୟ, ପଶୁପକ୍ଷୀ ଜଣେ ଅନ୍ୟ ଜଣଙ୍କଠୁ ଶିକ୍ଷା କରିଥାଏ । ବିଶେଷତଃ ପଶୁପକ୍ଷୀମାନଙ୍କଠାରୁ ଶିକ୍ଷା କରିବା ବିଧୂ ସଂସ୍କୃତ କଥାସାହିତ୍ୟରେ ଉପଲବ୍ଧ ହୁଏ । ବିଷ୍ଣୁଶର୍ମା ପଞ୍ଚତନ୍ତ୍ରରେ ଏହିପରି ଅନେକ କାହାଣୀରେ ପଶୁପକ୍ଷୀଙ୍କର ବିଷୟ ଓ ସେମାନଙ୍କଠାରୁ ଶିକ୍ଷା କଥା ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନା କରିଛନ୍ତି । ତେବେ କୁକୁଡ଼ାଠାରୁ ମଧ୍ୟ କିଛି ଶିକ୍ଷା କରିବାର ଅଛି । କୁକୁଡ଼ାଠାରୁ ଚାରୋଟି କଥା ଶିକ୍ଷା କରିବା ଉଚିତ; ଯେପରିକି ଅନ୍ୟ ସହ କିପରି ଯୁଦ୍ଧ କରିବା ତାହା ତା’ଠାରୁ ହିଁ ଶିଖୁହୁଏ । ସେହିପରି ପ୍ରାତକାଳରୁ ଉଠିବା ମଧ୍ଯ କୁକୁଡ଼ାଠୁ ଶିଖ୍ । ବନ୍ଧୁମାନଙ୍କ ସହ ଭୋଜନ କରିବାର କଳା ମଧ୍ଯ କୁକୁଡ଼ାଠାରୁ ଶିକ୍ଷାକରିବା ଉଚିତ । ଶେଷରେ ସ୍ତ୍ରୀ ବିପଦରେ ପଡ଼ିଲେ ତାକୁ କିପରି ରକ୍ଷାକରାଯାଏ ଏ କଥା ମଧ୍ୟ କୁକୁଡ଼ା ଅନ୍ୟମାନଙ୍କୁ ଶିକ୍ଷାଦିଏ । ସୁତରାଂ ସବୁ ମଣିଷ କୁକୁଡ଼ାଠରୁ ଏ ଚାରୋଟି କଥା ନିଶ୍ଚୟ ଶିକ୍ଷାକରିବା ଉଚିତ ।
ବ୍ୟାକରଣ:
ପ୍ରାତରୁତ୍ଥାନମ୍ = ପ୍ରାତଃ + ଉତ୍ + ସ୍ଥାନମ୍ । ସିୟମାପଦ୍ଗତାମ୍ = ସିୟମ୍ + ଆପଦଗତାମ୍ । ରକ୍ଷେତୁଶ୍ଶିକ୍ଷେତ = ରକ୍ଷେତ୍ + ଚତୁଃ + ଶିକ୍ଷେତ ।
ସମାସ – ପ୍ରାତରୁତ୍ଥାନମ୍ = ପ୍ରାତଃ ଉତ୍ଥାନମ୍ (କର୍ମଧାରୟ) ।
ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତି – କୁକ୍କୁଟାତ୍ ଅପାଦାନେ ୫ମୀ । ବନ୍ଧୁଭି = ‘ସହ’ ଯୋଗେ ୩ୟା । ସିୟମ୍ = କର୍ମଣି ୨ୟା ।
ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ – ଉତ୍ଥାନମ୍ = ଉତ୍ + ସ୍ଥା + ଲ୍ୟୁଟ୍ । ଭୋଜନମ୍ = ଭୁଜ୍ + ଲୁଟ୍ ।
ଶ୍ଳୋକ – ୨୦
सुवर्णपुष्पां पृथिवीं चिन्वन्ति पुरुषास्त्रयः ।
शूरश्च कृतविद्यश्च यश्च जानाति सेवितुम् ॥ २० ॥
ସୁବର୍ଣ୍ଣପୁଷ୍ପ ପୃଥିବୀ ଚିନ୍ଧନ୍ତି ପୁରୁଷାସ୍ତ୍ରୟଃ ।
ଶୂରଶ୍ଚ କୃତବିଦ୍ୟଶ୍ଚ ଯଶ୍ଚ ଜାନାତି ସେବିତୁମ୍ ॥ ୨୦ ॥
ଅନ୍ବୟ – ତ୍ରୟଂ ପୁରୁଷା ସୁବର୍ଣ୍ଣପୁଷ୍ପ ପୃଥିବୀ ଚିନ୍ଧନ୍ତି । ଶୂରଃ ଚ କୃତବିଦ୍ୟ ଚ, ଯଃ ସେବିତୁଃ ଜାନାତି ଚ ।
ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ – ଚିନ୍ବନ୍ତି = ସଂଗ୍ରହ କରନ୍ତି । ଶୂରଃ = ବୀର । କୃତବିଦ୍ୟା = କୃତକର୍ମା । ଜାନାତି = ଜାଣିଛି ।
ଅନୁବାଦ – ତିନିଜଣ ପୁରୁଷ ସବୁର୍ଣ୍ଣପୁଷ୍ପ ପୃଥିବୀକୁ ଜୟ କରନ୍ତି । ବୀର, କୃତକର୍ମା ଓ ଯେ ସେବା କରିବାକୁ ଜାଣେ (ସେବକ) ।
ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶ୍ଳୋକୋଽୟଂ ପଠିତଃ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ପଦ୍ୟାତ୍ ସମୁଦ୍ଧତଃ । ଅସ୍ଥିନ୍ ଶ୍ଳୋକେ କେ ସୁବର୍ଣ୍ଣପୁଷ୍ପ ପୃଥିବୀ ଚିନ୍ଧନ୍ତି ବା କିଂ ତାବତ୍ ଅନୁଜୀବି ଧର୍ମମ୍ ଇତି ବଣ୍ଠିତମ୍ ।
ଇୟଂ ପୃଥିବୀ ଶସ୍ୟଶ୍ୟାମଳା । ଅସ୍ୟା କ୍ରୋଡ଼େ ଅଙ୍କେ ବା ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ଲାଳିତଃ ପାଳିତା ବଦ୍ଧତାଶ୍ଚ । ସମଗ୍ରଜୀବନଂ ମାତୃରୂପେ ମାତ୍ରାଙ୍କ ଚ ପରିପାଳିତାଂ ଭବତି । ସ ସର୍ବମେବ ସଂଗୃହ୍ୟତି ପୃଥିବ୍ୟା । ସଂସାରେ ବୀରଃ, ବିଦ୍ଵାନ୍, ସେବକ ଏତେ ତ୍ରୟଂ ଜନଃ ସୁବର୍ଣ୍ଣପୁଷ୍ପ ପୃଥିବୀ ଚିନ୍ଧନ୍ତି । ‘ବୀରଭୋଗ୍ୟ ବସୁନ୍ଧରା’ – ରାଜ୍ୟଭୋଗ କେବଳଂ ବୀରେଣ ବିଦୁଷ ସେବକେନ ଚ କ୍ରିୟତେ । ସ୍ଵପରାକ୍ରମେଣ ବୀରପୁରୁଷ ଅପରେଷା ବଶୀକରୋତି । ସର୍ବମେବ ସ୍ୱୟଭିକରୋତି । କୃତଃ କର୍ମଶଃ ସର୍ବମେବ ପ୍ରାପ୍ତି ବନ୍ତି । ସେବା ହି ପରମୋ ଧର୍ମ । ଅନୟା ସେବୟା ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ସର୍ବେରାଂ ହୃଦୟଂ ଜୟତି କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଚ ସାଧୟତି । ଏତାଦୃଶାନି ଜନାନାଂ ଚରିତ୍ରମ୍ ଅବଶ୍ୟ ଶିକ୍ଷଣୀୟଂ ଗ୍ରହଣୀୟଂ ଗୃହଣୀୟଂ ଚ ଭବତି ।
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବ୍ୟ।ଗ୍ୟା – ସଂସିତ ଶ୍ଲୋକଟି ପଠିତ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକର ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗସ୍ଥ ସୁଭ।ଷିତାବଳୀ ରୁ ଆନୀତ । ଏଠାରେ କେଉଁମାନେ ଏ ସୁବର୍ଣ୍ଣପୁଷ୍ପ ପୃଥିବୀକୁ ଜୟକରନ୍ତି ତାହା ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନା କରାଯାଇଅଛି ।
ଏ ପୃଥିବୀ ଶସ୍ୟଶ୍ୟାମଳା, ଏହାର କୋଳରେ ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ଲାଳିତପାଳିତ ଓ ବର୍ଷିତ ହୁଏ । ସମଗ୍ର ଜୀବନ ତା’ର ମାଟି ମା’ର କୋଳରେ କଟିଯାଏ । ସେ ତୋଳିଧରେ ସବୁକିଛି ଏ ପୃଥିବୀ ପୃଷ୍ଠରୁ । ସୁବର୍ଣ୍ଣପୁଷ୍ପତୁଲ୍ୟ ଏ ପୃଥିବୀ । ଆଉ ତାକୁ ତୋଳିବାକୁ ସକ୍ଷମ ସେହି ଯେ ବୀର, ଯେ କୃତକର୍ମା ଏବଂ ଯେ ସେବାକାରୀ ବା ସେବକ । ଏହି ତିନିଜଣ ପୁରୁଷ ହିଁ ପୃଥିବୀତୁଲ୍ୟ ସୁବର୍ଣ୍ଣ ପୁଷ୍ପ ତୋଳିବାକୁ ସମର୍ଥ । ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ପରାକ୍ରମ ବା ବୀରତ୍ୱଦ୍ୱାରା ଅନ୍ୟକୁ ବଶ କରେ । ସବୁକିଛି ନିଜର ଆୟତ୍ତ କରେ । ଯେ କୃତକର୍ମା, କର୍ମ ବଳରେ ସେ ସବୁକିଛି ପାଇଥାଏ । ସେବାକାରୀ ଅନ୍ୟର ସେବାକରି ସବୁର ହୃଦୟକୁ ଜିଣିବାକୁ ସମର୍ଥ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଏହିଭଳି ଲକ୍ଷଣଯୁକ୍ତ ପୁରୁଷଙ୍କର ଚରିତ୍ର ଆମର ଏକାନ୍ତ ଶିକ୍ଷଣୀୟ ତଥା ଗ୍ରହଣୀୟ ହେବା ଉଚିତ ।
ବ୍ୟାକରଣ:
ସନ୍ଧିବିଚ୍ଛେଦ – ପୁରୁଷାସ୍ତ୍ରୟଃ = ପୁରୁଷ + ତ୍ରୟଃ । ଶୂରଶ୍ଚ = ଶୂରଃ + ଚ । କୃତବିଦ୍ୟଶ୍ଚ = କୃତବିଦ୍ୟା + ଚ । ଯଶ୍ଚ = ଯଃ ଚ ।
ସମାସ – ସୁବର୍ଣ୍ଣପୁଷ୍ପମ୍ = ସୁବର୍ଣ୍ଣ ପୁଷ୍ପମ୍ ଯସ୍ୟା ସା (ବହୁବ୍ରୀହିଃ) । କୃତବିଦ୍ୟା = କୃତଂ ବିଦନ୍ତି ଯେ ତେ (ଉପପଦ୍ ତତ୍) ।
ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତି – ପୁରୁଷୋ = କଉଁରି ୧ମା । ସୁବର୍ଣ୍ଣପୁଷ୍ପ, ପୃଥ୍ବୀମ୍ = କର୍ମଣି ୨ୟା । ସେବିତୁମ୍ = କର୍ମଣି ୨ୟା ।
ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ – କୃତ = କୃ + କ୍ତ । ବିଦ୍ୟଃ = ବିଦ୍ + ଲ୍ୟାପ୍ । ସେବିତୁମ୍ = ସେବ୍ + ତୁମୁନ୍ ।
ଶ୍ଳୋକ – ୨୧
उभयोर्नासि भोगेच्छा परार्थं धनसञ्चयः ।
कृपणदारयोः पश्य पथाऽपि महदन्तरम् ।। २१ ।।
ଉଭୟୋର୍ନାସି ଭୋଗେଚ୍ଛା ପରାର୍ଥୀ ଧନସଞ୍ଚୟଃ ।
କୃପଣୋଦାରୟୋ ପଶ୍ୟ ପଥାଽପି ମହଦନ୍ତରମ୍ ॥ ୨୧ ॥
ଅନ୍ବୟ – କୃପଣୋଦାରୟୋ ଭୋଗେଚ୍ଛା ନାସ୍ତି (ଉଭୟୋ) ଧନସଞ୍ଚୟ ପରାର୍ଥମ୍ । ଉଭୟୋ ପଥା ମହତ୍ ଅନ୍ତରମ୍ ଅପି ପଶ୍ୟ ।
ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ – କୃପଣ = କଞ୍ଜୁସ୍, ଲୋଭୀ । ଉଦାରଃ = ଦାନଶୀଳ, ଦୟାବନ୍ତ । ପରାର୍ଥମ୍ = ପର ପାଇଁ । ପଥା = ମାର୍ଗରେ ।
ଅନୁବାଦ – କୃପଣ ଓ ଦାନଶୀଳଙ୍କର ଭୋଗର ଇଚ୍ଛା ନାହିଁ । ଉଭୟଙ୍କର ଧନସଞ୍ଚୟ ପର ନିମନ୍ତେ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଉଭୟଙ୍କର ମାର୍ଗରେ ବଡ଼ ପ୍ରଭେଦ ମଧ୍ୟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶ୍ଳୋକୋଽୟଂ ପଠିତଃ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ପଦ୍ୟାତ୍ ଆନୀତଃ । ଅତ୍ର ଅସ୍ଥିନ୍ ଶ୍ଳୋକେ କୃପଣୋଦାରୟୋ ପାର୍ଥକ୍ୟ ପ୍ରଦର୍ଶିତମ୍ ।
ସାଂସାରିକଃ ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ସ୍ଵପ୍ରକୃତିଃ ପ୍ରବୃତିଃ ଚ ମାଧ୍ୟମେନ କୃପନଃ ଉଦାରଃ ଚ ଭେଦେନ ଦ୍ବିଧା ବିଭଜ୍ୟତେ । ସଂସାରେ କୃପଣସ୍ୟ ଦାନଶୀଳସ୍ୟ ଚ ଭୋଗେଚ୍ଛା ନାସ୍ତି । ତୟୋ ଧନସଂଗ୍ରହଃ ପରନିମିତ୍ତକଃ ଭବତି । ପରନ୍ତୁ ଉଭୟୋ ମଧ୍ୟ ଧନସଂଗ୍ରହସ୍ୟ ମାର୍ଗେଣ ମହତ୍ ଅନ୍ତରଂ ପରିଲକ୍ଷ୍ୟତେ । ଦାନଶୀଳ ସ୍ବଜୀବଦଶାୟାଂ ଧନଂ ପରାର୍ଥେ ବିନିଯୋଗ୍ୟ ଯଶଃ ଲଭତେ । ପରନ୍ତୁ କୃପଣୀ ଜୀବନଂ ବ୍ୟାପୀ ସତ୍ତ୍ୱେ ଧନଂ ନ ସ୍ବକୀୟାର୍ଥେ ନ ପରାର୍ଥେ ବା ବିନିଯୋଗ୍ୟ ଅକୀର୍ତିମେବ ପ୍ରାଷ୍ଟୋତି । ଅତଃ ଦାନୋପଭୋଗହୀନେନ ଧନେନ କିଞ୍ଚିତ୍ ପ୍ରୟୋଜନଂ ନାସ୍ତି । ଏତତ୍ ବିଚାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ତୁ ସଦୈବ ଉଦାରସ୍ୟ ଚରିତ୍ର ଗ୍ରହଣୀୟଂ ଭବେତ୍ ।
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶସିତ ଶ୍ଲୋକଟି ସଠିତ ସଂସ୍କତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ରୁ ସଂଗୃହାତା ଏହି ଶ୍ଳୋକରେ କୃପଣ ଓ ଦାନଶୀଳଙ୍କ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ସମାନତା ଓ ବୈଷମ୍ୟ ପ୍ରଦର୍ଶିତ ହୋଇଛି ।
ସାଂସାରିକ ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ନିଜର ପ୍ରକୃତି ଓ ପ୍ରବୃତ୍ତିଦ୍ଵାରା କୃପଣ ଓ ଦାନଶୀଳ ଭାବେ ଦ୍ଵିଧା ବିଭକ୍ତ ହୋଇଥାଏ । କୃପଣର ଓ ଦାନଶୀଳର ଭୋଗରେ ଇଚ୍ଛା ନଥାଏ । ଉଭୟଙ୍କର ଧନସଂଗ୍ରହ ପର ଉଦ୍ଦେଶ୍ୟରେ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ସେମାନଙ୍କ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଧନସଂଗ୍ରହର ମାର୍ଗରେ ଅନେକ ପାର୍ଥକ୍ୟ ପରିଲକ୍ଷିତ ହୁଏ । ଦାନଶୀଳ ସ୍ବଜୀବଦଶାରେ ପର ପାଇଁ ଧନକୁ ବିନିଯୋଗ କରି ଯଶ ବା କୀର୍ତ୍ତି ଲାଭ କରିଥାଏ । କୃପଣ କଦର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଜୀବନ ନିର୍ବାହ କରି ଧନ ସଂଗ୍ରହ କରିଥାଏ । ତା’ର ମୃତ୍ୟୁ ପରେ ହିଁ ବିନିଯୋଗର ସମ୍ଭାବନା କରାଯାଇଥାଏ । ଆଉ ସେ କେବଳ ଜୀବନରେ ଅପଯଶ ହିଁ ଲାଭ କରିଥାଏ । ଏ ଉଭୟ ପ୍ରକାର ଜୀବନକୁ ଲକ୍ଷ୍ୟକରି ଆମ୍ଭେମାନେ ଦାନଶୀଳର ଜୀବନକୁ ଆପଣେଇବା ଉଚିତ ।
ବ୍ୟାକରଣ:
ସନ୍ଧିବିଚ୍ଛେଦ – ଉଭୟୋର୍ନାସି = ଉଭୟୋ + ନ + ଅସି । ଭୋଗେଚ୍ଛା = ଭୋଗ + ଇଚ୍ଛା । କୃପଣୋଦାରୟୋ : କୃପଣ + ଉଦାରୟୋ । ପଥାଽପି = ପଥ + ଅପି । ମହଦନ୍ତରମ୍ = ମହତ୍ + ଅନ୍ତରମ୍ ।
ସମାସ – ଭୋଗେଚ୍ଛ = ଭୋଗସ୍ୟ ଇଚ୍ଛା (୬ଷ୍ଠ ତତ୍)। ପରାର୍ଥମ୍ = ପରାୟ ଇଦମ୍ (ନିତ୍ୟ) । ଧନସଞ୍ଚୟ = ଧନାନାଂ ସଞ୍ଚୟଂ (୬ଷ୍ଠୀ ତତ୍ତ୍ଵ) । କୃପଣୋଦାରୟୋ = କୃପଣଂ ଚ ଉଦାରଂ ଚ ତୟୋ (ଦ୍ବନ୍ଦ୍ବ) ।
ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତି – କୃପଣେ।ଦାରୟୋଃ = ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ୬ଷ୍ଠୀ । ଯଥା = କରଣେ ୩ୟା ।
ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ – ଭୋଗ = ଭୁଞ୍ଜ୍ + ଘଞ୍ଚେ । ସଞ୍ଚୟ = ସମ୍ + ଚି + ଅଚ୍ ।
ଶ୍ଳୋକ – ୨୨
पादाहतं यदुत्थाय मूर्धानमधिरोहति ।
स्वस्थादेवापमानेडपि देहिनस्तद् वरं रज: ।। २२ ।।
ପାଦାହତଂ ଯଦୁକ୍ତାୟ ମୂର୍ଧାନମଧୂରୋହତି ।
ସ୍ଵସ୍ଥାଦେବାପମାନେଽପି ଦେହିନସ୍ତଦ୍ ବରଂ ରଜଃ ॥ ୨୨ ॥
ଅନ୍ୱୟ – ଅପମାନେ ଅପି ସ୍ଵସ୍ଥାତ୍ ଦେହିନଃ ତତ୍ ରଜଃ ବରମ୍, ଯତ୍ ଏବ ପାଦାହତମ୍ ଉତ୍ଥାୟ ମୂର୍ଧାନମ୍ ଅଧ୍ହତି ।
ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ – ସ୍ଵସ୍ଥାତ୍ = ନିଶ୍ଚିନ୍ତ । ଦେହିନଃ = ପୁରୁଷ । ରଜଃ = ଧୂଳି । ବରମ୍ = ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ ।
ଅନୁବାଦ – ଅପମାନରେ ମଧ୍ୟ ନିଶ୍ଚିନ୍ତ ବା ସନ୍ତୁଷ୍ଟ ପୁରୁଷ ଅପେକ୍ଷା ସେହି ଧୂଳି ହେଉଛି ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ, ଯାହା ହିଁ ପାଦର ଆଘାତରେ ଉଠି ମସ୍ତକକୁ ଅଧ୍ହଣ କରିଛି ।
ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶ୍ଳୋକୋଽୟଂ ପଠିତଃ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ପଦ୍ୟାତ୍ ଆନୀତଃ । ଅସ୍ମିନ୍ ଶ୍ଳୋକେ ରଜସ୍ୱ ପ୍ରଶଂସ୍ୟ ସନ୍ତୁଷ୍ଟ ଦେହିନଃ ନିନ୍ଦା କ୍ରିୟତେ ।
ପ୍ରାଫ୍ସ୍ୟତେ । ସଂସାରେଽସ୍ମିନ୍ ଅପମାନେ ସତି କୋଽପି ଦେହୀ ସନ୍ତୁଷ୍ଟ ସନ୍ ନ ତିଷେତ୍ । ଯସ୍ୟ ସ୍ବାଭିମାନମ୍ ଅସ୍ତି ତଥ୍ୟ ଜନସ୍ଯ ଅପମାନମ୍ ଅସହ୍ୟ ଭବତି । ସ୍ବଚେଷ୍ଟୟା ଅପମାନକାରଣଂ ସମୂଳମ୍ ଉତ୍ପାଟୟିତ୍ୱ ଚେଷ୍ଟତେ ଏବ । ପରନ୍ତୁ ଯଦି ଅପମାନିତଃ ନରଃ ସନ୍ତୁଷ୍ଟ ସନ୍ ତଷ୍ଠତି ତହିଁ ତସ୍ମାତ୍ ସନ୍ତୁଷ୍ଟାତ୍ ଜନାତ୍ ପାଦାହତେନ ଉତ୍ଥୁତା ଧୂଳି ଯା ମୂର୍ଧାନମ୍ ଆରୋହତି ସା ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ ଭବତି । ଅନେନ ଅପମାନେ ସନ୍ତୁଷ୍ଟସ୍ୟ ଜନସ୍ୟ ଦୀନତା ହୀନତା ଚ ସୂଚିତା ଭବତି । ଅତ୍ର ଅପମାନିତଜନେଭ୍ୟ ଧୂଳି ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ ଇତି ସୂଚିତଂ ଭବତି । କବେ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନା ଅତୀବ ମନୋମୁଗ୍ଧକରଃ ଭବତି ।
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶଂସିତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଟି ପଠିତ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକର ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ରୁ ଆନୀତ । ଏଠାରେ ଅପମାନରେ ସନ୍ତୁଷ୍ଟ ପୁରୁଷ ଧୂଳିର ମହତ୍ତ୍ଵ ତଥା ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠତା ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତ ହୋଇଛି ।
ସଂସାରରେ ମାନ ଅପମାନ ଲାଗି ରହିଥାଏ । ନିଜର ବ୍ୟବହାର ଅନୁସାରେ କେହି ସମ୍ମାନ ପାଇଥାଏ ତ କେହି ଅପମାନ ପାଇଥାଏ । ଏହି ସଂସାରରେ ଅପମାନ ପାଇ କେହି ପୁରୁଷ ସନ୍ତୁଷ୍ଟ ରହି ନଥା’ନ୍ତି । ଯାହାର ସ୍ଵାଭିମାନ ଅଛି ତା’ ପାଇଁ ଅପମାନ ଅସହ୍ୟ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ସେ ନିଜ ଚେଷ୍ଟାରେ ଅପମାନର କାରଣକୁ ଉତ୍ପାଟନ କରିବାକୁ ଚେଷ୍ଟା କରିଥାଏ । ପରନ୍ତୁ ଯଦି ଅପମାନିତ ପୁରୁଷ, ସନ୍ତୁଷ୍ଟ ରହେ ତେବେ ସେହି ସନ୍ତୋଷ ଅପେକ୍ଷା ଲୋକମାନଙ୍କ ପଦାଘାତରେ ମସ୍ତକ ଆରୋହଣ କରୁଥିବା ଧୂଳି ହିଁ ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ । ଏହାଦ୍ଵାରା ଅପମାନରେ ସନ୍ତୁଷ୍ଟ ରହୁଥିବା ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିର ଦୀନତା ଓ ହୀନତା ଜଣା ପଡ଼ୁଛି । ଏଠାରେ ଅପମାନିତ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିଠାରୁ ଧୂଳି ହିଁ ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ ବୋଲି ସୂଚିତ ହୋଇଛି । କବିଙ୍କର ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନା ଅତୀବ ଚିତ୍ତାକର୍ଷକ ହୋଇଛି ।
ବ୍ୟାକରଣ:
ସନ୍ଧିବିଚ୍ଛେଦ – ଯଦୁଡା଼ୟ = ଯତ୍ + ଉତ୍ଥାୟ । ମୂର୍ଧାନମଧୂରୋହତି = ମୂଧାନମ୍ + ଅଧ୍ହତି । ସ୍ୱସ୍ଥାଦେବାପମାନେଽପି ସ୍ଵସ୍ଥାତ୍ + ଏବ + ଅପମାନେ + ଅପି । ଦେହିନସ୍ତଦ୍ = ଦେହିନଃ + ତଦ୍ ।
ସମାସ – ପାଦାହୃତମ୍ = ପଦ୍ଭ୍ଯାମ୍ ଆହତମ୍ (୩ୟା ତତ୍) ।
ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତି – ଅପମାନେ = ଅଧିକରଣେ ୭ମୀ । ସ୍ବସ୍ଥାତ୍ = ଅପାଦାନେ ୫ମୀ । ମୂର୍ଧାନମ୍ କର୍ମଣି ୨ୟା ।
ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ – ରଜଃ = ରଞ୍ଜ୍ + ଘଞ୍ଚ୍ । ହତମ୍ = ହନ୍ + କ୍ତ । ଉତ୍ଥାୟ = ଉତ୍ + ସ୍ଥା + ଲ୍ୟାପ୍ ।
ଶ୍ଳୋକ – ୨୩
येषां वाहुबलं नास्ति येषां नास्ति मनोबलम् ।
तेषां चन्द्रवलं वापि किं कुर्यादम्बरस्थितम् ॥ २३ ॥
ଯେଷା ବାହୁବଳଂ ନାସ୍ତି ଯେତାଂ ନାସ୍ତି ମନୋବଳମ୍ ।
ତେଷା ଚନ୍ଦ୍ରବଳଂ ବାପି କିଂ କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟାଦମ୍ବରସ୍ଥିତମ୍ ।। ୨୩ ।।
ଅନ୍ୱୟ – ଯେତାଂ ବାହୁବଳଂ ନ ଅସ୍ଥି, ଯେତାଂ ମନୋବଳଂ ନ ଅସ୍ଥି, ତେଷାମ୍ ଅମ୍ବରସ୍ଥିତମ୍ ଅପି ଚନ୍ଦ୍ରବଳଂ କିଂ ବା କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟାତ୍ ।
ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ – ବାହୁବଳମ୍ = ପରାକ୍ରମ/ଶକ୍ତି । ମନୋବଳମ୍ = ମାନସିକ ଶକ୍ତି ବା ଦୃଢ଼ତା । ଅମ୍ବରସ୍ଥିତମ୍ = ଆକାଶସ୍ଥ । କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟାତ୍ = କରିପାରେ ।
ଅନୁବାଦ – ଯେଉଁମାନଙ୍କର ବାହୁବଳ ନାହିଁ ଓ ମନୋବଳ ମଧ୍ଯ ନାହିଁ; ସେମାନଙ୍କର ଆକାଶରେ ସ୍ଥିତ ଚନ୍ଦ୍ରବଳ କ’ଣ ବା କରିପାରେ ।
ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶ୍ଳୋକୋଽୟଂ ପଠିତଃ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ପଦ୍ୟାତ୍ ଆନୀତଃ । ଅତ୍ର ଅସ୍ଥିନ୍ ଶ୍ଳୋକେ ବଳପ୍ରଶଂସା ବିଷୟେ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତମ୍ ।
ଅସ୍ମାନ୍ ସଂସାରେ ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ଯଥା ବୁଦ୍ଧିମାନ୍ ତଥା ଅପି ବଳବାନ୍ ଭବତି । ବଳଂ ଦ୍ବିବିଧମ୍ – (୧) ଶାରୀରିକ ବଳମ୍, (୨) ମାନସିକ ବଳମ୍ ଇତି । ସଂସାରେ ଯସ୍ୟ ଜନସ୍ୟ ବାହୁବଳଂ ନାସ୍ତି, ଯସ୍ୟ ମନୋବଳଂ ଚ ନ ଦୃଶ୍ୟତେ ତସ୍ୟ ଆକାଶସ୍ଥିତଂ ଚନ୍ଦ୍ରବଳଂ କିଞ୍ଚିତ୍ କର୍ଡିଂ ନ ପାରୟତି । ଅତଃ ଜୀବନେ ସଫଳତାର୍ଥ ବାହୁବଳଂ ମନୋବଳଂ ଚ ପରମାବଶ୍ୟକଂ ଭବତି । ଏତତ୍ ବିଷୟଂ ଜ୍ଞାତ୍ମା ସର୍ବେ ପ୍ରଯତ୍ନଶୀଳଂ ଭବେୟୁଃ।
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶଂସିତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଟି ପଠିତ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକର ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗସ୍ଥିତ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ରୁ ଆନୀତ । ଏହି ଶ୍ଳୋକରେ ବିଭିନ୍ନ ବଳ ପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗରେ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତ ହୋଇଛି ।
ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ଯେତିକି ବୁଦ୍ଧିମାନ୍ ସେତିକି ବଳବାନ୍ ମଧ୍ୟ । ଏହି ବଳ ପୁନଶ୍ଚ ଦୁଇଭାଗରେ ବିଭକ୍ତ; ଯଥା – ଶାରୀରିକ ବଳ ଓ ମନୋବଳ । ଯେଉଁମାନଙ୍କର ବାହୁବଳ ନାହିଁ କି ଯେଉଁମାନଙ୍କର ମନୋବଳ ନାହିଁ ସେମାନଙ୍କର ଆକାଶରେ ସ୍ଥିତ ଚନ୍ଦ୍ରବଳ କ’ଣ ବା କରିପାରେ ? କିଛିହେଲେ କରିପାରେ ନାହିଁ । ଏଣୁ ଜୀବନରେ ସଫଳତା ପାଇଁ ବହୁବଳ ଓ ମନୋବଳ ଏକାନ୍ତ ଆବଶ୍ୟକ । ଏହି କଥା ମନେରଖି ସମସ୍ତେ ପ୍ରଯତ୍ନଶୀଳ ହେବା ଉଚିତ । ସୁଭାଷିତକାରଙ୍କର ଏତାଦୃଶ ଉକ୍ତି ଏକାନ୍ତ ଯଥାର୍ଥତାପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ ଅଟେ ।
ବ୍ୟାକରଣ:
ସନ୍ଧିବିଚ୍ଛେଦ – ନାସ୍ତି = ନ + ଅସ୍ତି । ବାପି = ବା + ଅପି । କିଂ କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟାଦମ୍ବରସ୍ଥିତମ୍ = କିଂ କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟାତ୍ + ଅମ୍ବରସ୍ଥିତମ୍ ।
ସମାସ – ବାହୁବଳମ୍ = ବାକ୍ସୋ ବଳମ୍ (୬ଷ୍ଠୀ ତତ୍) । ମନୋବଳମ୍ = ମନମଃ ବଳମ୍ (୬ଷ୍ଠ ତତ୍) । ଚନ୍ଦ୍ରବଳମ୍ = ଚନ୍ଦ୍ରସ୍ୟ ବଳମ୍ (୬ଷ୍ଠ ତତ୍) ଅମ୍ବରସ୍ଥିତମ୍ = ଅମ୍ବରେ ସ୍ଥିତମ୍ (୭ମୀ ତତ୍) ।
ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତି – ଯେଷାଂ = ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ୬ଷ୍ଠୀ |
ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ – ସ୍ଥିତମ୍ = ସ୍ଥା + କ୍ତ + ଅମ୍ ।
ଶ୍ଳୋକ – ୨୪
मरणं प्रकृतिः शरीरिणां विकृतिर्जीवितमुच्यते बुधैः ।
क्षणमप्यवतिष्ठते श्वसन् यदि जन्तुर्ननु लाभवानसौ ॥ २४ ॥
ମରଣଂ ପ୍ରକୃତିଃ ଶରୀରିଣା ବିକୃତିର୍ଜୀବିତମୁଚ୍ୟତେ ବୁଧଃ ।
କ୍ଷଣମପ୍ୟବତିଷ୍ଠତେ ଶ୍ଵାସନ୍ ଯଦି ଜନ୍ତୁର୍ମନୁ ଲାଭବାନସୌ ॥ ୨୪ ॥
ଅନ୍ବୟ – ଶରୀରିକ୍ଷାଂ ମରଣଂ ପ୍ରକୃତିଃ ଜୀବିତଂ ବିକୃତିଃ (ଇତି) ବୁଧଃ ଉଚ୍ୟତେ । ଯଦି ଜନ୍ତୁ କ୍ଷଣମ୍ ଅପି ଶ୍ବସନ୍ ଅବତିଷ୍ଠତେ, ନନୁ ଅସୌ ଲାଭବାନ୍ ।
ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ – ଶରୀରିକ୍ଷାଂ = ଦେହଧାରୀମାନଙ୍କର । ଜୀବିତମ୍ = ଜୀବନ । ବୁଧୈ = ପଣ୍ଡିତମାନଙ୍କଦ୍ୱାରା । ଜନ୍ତୁଃ = ମନୁଷ୍ୟ । କ୍ଷଣମ୍ = କ୍ଷଣିକେ, ମୁହୂର୍ଭେ । ଶ୍ଵାସନ୍ = ନିଃଶ୍ବାସ ନେଇ ।
ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶ୍ଳୋକୋଽୟଂ ପଠିତଃ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ ପଦ୍ୟାତ୍ ଆନୀତଃ । ଅତ୍ର ଅସ୍ମିନ୍ ଶ୍ଳୋକେ ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ଜୀବନଂ କଳଂ ଶ୍ରେୟସ୍କରଂ ଲାଭବାନ୍ ଚ ଭବତି ତଦେବ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତମ୍ ।

ଅସ୍ମିନ୍ ସଂସାରେ ମନୁଷ୍ୟତାଂ ଜୀବନଂ କ୍ଷଣସ୍ଥାୟୀ । ଯଃ ଜାୟତେ ତସ୍ୟ ମରଣ ସୁନିଶ୍ଚିତମ୍ । ପରନ୍ତୁ ମନୁଷ୍ୟସ୍ୟ ଏତତ୍ ମରଣଂ ସ୍ଵାଭାବିକମ୍ ଏବ । ଗୀତାକାରସ୍ୟ ଉକ୍ତି – ‘ଜାତସ୍ୟ ହି ଧ୍ରୁନଃ ମୃତ୍ୟୁ ।’’ ପଣ୍ଡିତାଃ ଜୀବନଂ ବିକାରଃ ଇତି କଥୟନ୍ତି । ଜୀବଦ୍ଦଶାୟାଂ ଯଦି କୋଽପି ଜନଃ କ୍ଷଣଂ ଶ୍ଵାସନ୍ ତିଷ୍ଠତି ତହିଁ ଅର୍ଥେ ପୁଣ୍ଯାଦିକର୍ମକରଣେନ ଲାଭବାନ୍ ଭବତି ଏବ । ଅତଃ ଜୀବନମରଣଚକ୍ର ସନ୍ନପି ନରଃ ପ୍ରତିକ୍ଷଣଂ ସୁକର୍ମ କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟାତ୍ । ଯଥାରୀତ୍ୟା ଅତ୍ର ଜୀବନସ୍ୟ ଚରମଂ ତଥା ପରମାଂ ରହସ୍ୟମ୍ ଉଦ୍ଘାଟିତଂ ତଦେବ ଅତୀବ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନୀୟ ଭବତି । ମନୁଷ୍ୟଜୀବନସ୍ୟ ମହାର୍ଘ୍ୟମ୍ ଅତ୍ର ସ୍ଵୀକ୍ରିୟତେ । ଜୀବନସ୍ୟ ମହାମୂଲ୍ୟ ଜ୍ଞାତ୍ମା ଏକ ସର୍ବେ ଜୀବେଯୁଃ ।
ଓଡ଼ିଆ ବ୍ୟାଖ୍ୟା – ଶଂସିତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଟି ପଠିତ ସଂସ୍କୃତପ୍ରଭା ପୁସ୍ତକର ପଦ୍ୟଭାଗସ୍ଥ ‘ସୁଭାଷିତାବଳୀ’ରୁ ଆନୀତ । ଏଠାରେ କିଭଳି ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ଜୀବନ ଶ୍ରେୟସ୍କର ବା ଲାଭବାନ୍ ହୋଇଥାଏ ତାହା ବର୍ଣ୍ଣିତ ହୋଇଛି ।
ପ୍ରାଣୀମାତ୍ରକେ ଜୀବନ ଓ ମୃତ୍ୟୁର ଚକ୍ରରେ ଘୂର୍ଣାୟମାନ ହେଉଥାଏ । ଦେହଧାରୀମାନଙ୍କର ମରଣ ହେଉଛି ପ୍ରକୃତି ଏବଂ ଜୀବନ ହେଉଛି ବିକୃତି ଏହା ପଣ୍ଡିତମାନେ କହିଅଛନ୍ତି । ପ୍ରକୃତି ବିକୃତିର ସମାହାର ସଂସାର ରୂପେ ଆଖ୍ୟାୟିତ । ଏଭଳି ସ୍ଥିତିରେ ଯଦି ପ୍ରାଣୀ କ୍ଷଣେମାତ୍ର ନିଃଶ୍ବାସ ନେଇ ଅବସ୍ଥାନ କରେ ନିଶ୍ଚୟ ଏହା ପୁଣ୍ୟାଦି କର୍ମ କରିବା ଦୃଷ୍ଟିରୁ ଲାଭବାନ୍ । ଏଣୁ ଜୀବନ ମରଣ ଚକ୍ରରେ ଥାଇ ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ସର୍ବଦା ସୁକର୍ମ କରିବା ଉଚିତ । ଏଠାରେ ଜୀବନର ଚରମ ରହସ୍ୟ ଉଦ୍ଘାଟିତ ହୋଇଛି । ମନୁଷ୍ୟ ଜୀବନର ମହାର୍ଘତା ସ୍ବୀକୃତ ହୋଇଛି । ତେଣୁ ଜୀବନର ମହାର୍ଘତାକୁ ଜାଣି ସମସ୍ତେ ଜୀବନ ଧାରଣ କରନ୍ତୁ ।
ବ୍ୟାକରଣ:
ସନ୍ଧିବିଚ୍ଛେଦ – ବିକୃତିର୍ଜୀବିତମୁଚ୍ୟତେ = ବିକୃତିଃ + ଜୀବିତମ୍ + ଉଚ୍ୟତେ । କ୍ଷଣମପ୍ୟବତିଷ୍ଠତେ = କ୍ଷଣମ୍ + ଅପି + ଅବତିଷ୍ଠତେ । ଲାଭବାନସୌ = ଜୀଭବାନ୍ + ଅସୌ ।
ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତି – ଶରୀରିଣାମ୍ = ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ୬ଷ୍ଠୀ । ବୁଧୈ = ଅନୁକ୍ତ କର୍ଭରି ୩ୟା ।
ପ୍ରକୃତିପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ – ପ୍ରକୃତିଃ = ପ୍ର + କୃ + ସ୍କ୍ରିନ୍ । ବିକୃତି = ବି + କୃ + ସ୍କ୍ରିନ୍ । ମରଣମ୍ = ମୃ + ଲ୍ୟୁଟ୍ । ଲାଭବନ୍ = ଲାଭ + ବତୁମ୍ !
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()