Odisha State Board BSE Odisha 10th Class Physical Science Important Questions Chapter 7 ମାନବ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଓ ବର୍ଷଜଗତ Important Questions and Answers.
BSE Odisha 10th Class Physical Science Important Questions Chapter 7 ମାନବ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଓ ବର୍ଷଜଗତ
Objective Type Questions with Answers
A ଗୋଟିଏ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ଉତ୍ତର ଦିଅ ।
1. ଜଣେ ସୁସ୍ଥ ଓ ସ୍ବାଭାବିକ ଦୃଷ୍ଟି ସମ୍ପନ୍ନ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିର ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦର୍ଶନର ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ଦୂରତା କେତେ ?
ଉ –
25 ସେ.ମି.
2. ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସର ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା ବଢ଼ିଗଲେ କେଉଁ ପ୍ରକାର ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ହୋଇଥାଏ ?
ଉ –
ଦୂର ଦୃଷ୍ଟି
3. ଚମ୍ପୁ-ଲେନ୍ସର ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା କମିଗଲେ, କେଉଁ ପ୍ରକାର ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ହୋଇଥାଏ ?
ଉ –
ସମ1ପଦେ।ଷ
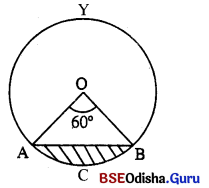
4. ଆଲୋକର କେଉଁ ପରିଘଟଣା ଯୋଗୁଁ ନିର୍ମଳ ଆକାଶର ରଙ୍ଗ ନୀଳ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
ଉ –
ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ
5. ସମୀପ-ଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଥିବା ଜଣେ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି 20 cm ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ଲେନ୍ସ୍ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରି ବସ୍ତୁଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟଭାବେ ଦେଖପାରନ୍ତି । ଡାୟୋପ୍ଟର୍ ଏକକରେ ସେହି ଲେନ୍ସ୍ର ପାୱାର୍ କେତେ ?
ଉ –
ପ୍ରତିସରଣ, ପ୍ରତିଫଳନ ଓ ପ୍ରକୀର୍ଣ୍ଣନ
6. ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରଧନୁ ସୃଷ୍ଟିରେ ଆଲୋକର କେଉଁ କେଉଁ ପରିଘଟଣା ଘଟିଥାଏ ?
ଉ –
– 5.0
7. ମାନବ ଚକ୍ଷୁର କେଉଁ ଅଂଶଟି ମିଞ୍ଜିମିଞ୍ଜି ଆଲୋକରେ ବସ୍ତୁଟିକୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟଭାବେ ଦେଖିବାରେ ସାହାଯ୍ୟ କରିଥାଏ ?
ଉ –
କନୀନିକା
8. ଗୋଟିଏ ବସ୍ତୁର ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ଚକ୍ଷୁର କେଉଁ ଅଂଶରେ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହୁଏ ?
ଉ –
ମୁକୁରିକା
9. ତାରାମାନେ ଦପ୍ଦପ୍ ହେବା ଆଲୋକର କେଉଁ ପରି ଘଟଣା ସହ ସମ୍ପର୍କିତ ?
ଉ –
ପ୍ରତିସରଣ
![]()
10. ଧୂଆଁପୂର୍ଣ ଏକ କୋଠରି ମଧ୍ୟକୁ ସୂକ୍ଷ୍ମ ରନ୍ଧ୍ର ଦେଇ ପ୍ରବେଶ କରୁଥିବା ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟାଲୋକର ଗତିପଥ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦିଶେ । ଏହାକୁ କ’ଣ କହନ୍ତି ?
ଉ –
ଟିଣ୍ଡଲ୍ ସିଦ୍ଧାନ୍ତ
11. ଅତି ସ୍ଵଚ୍ଛ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସ ଧଳା ଏବଂ ଧୂସର ହେବା ଅବସ୍ଥାକୁ କ’ଣ କହନ୍ତି ?
ଉ –
ମୋତିଆବିନ୍ଦୁ
12. ଚକ୍ଷୁର ନିକଟ ବିନ୍ଦୁ କେତେ ସେ.ମି. ?
ଉ –
25
13. ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନସ୍ ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତାକୁ ବଦଳାଇ ବିଭିନ୍ନ ଦୂରତାରେ ଥିବା ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ଫୋକସ୍ କରିବା କ’ଣ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
ଉ –
ସମାୟୋଜନ
14. ସିଲିଆରୀ ମାଂସପେଶୀ ସଙ୍କୁଚିତ ହେଲେ ଚକ୍ଷୁଲେନ୍ସର ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା କ’ଣ ହୁଏ ?
ଉ –
କମେ
15. ଛାତ୍ରଟି କଳାପଟାରେ ଲେଖାଥିବା ଅକ୍ଷରକୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଭାବରେ ଦେଖୁପାରୁ ନାହିଁ, ତେବେ ତାକୁ କେଉଁ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ହୋଇଛି ?
ଉ –
ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଦୋଷ
16. ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଗୋଲକ ଲମ୍ବିଗଲେ କେଉଁ ଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଦୋଷ ହୁଏ ?
ଉ –
ସମୀପ
17. ଜଣେ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିଙ୍କୁ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ଦୂର କରିବା ପାଇଁ ଲେନ୍ସର ପାୱାର- 2D । ଏହାକୁ କେଉଁ ଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଦୋଷ ହୋଇଛି କୁହାଯିବ ?
ଉ –
ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଦୋଷ
18. ମଧ୍ୟାହ୍ନରେ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟାଲୋକର କେଉଁ ବର୍ଷର ଆଲୋକ କମ୍ ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ ହୁଏ ?
ଉ –
ନୀଳ
19. ଦ୍ୱି-ଫୋକସୀ ଚଷମା କେଉଁ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ପାଇଁ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହୁଏ ?
ଉ –
ସମୀପ ଓ ଦୂର ଦୃଷ୍ଟି
20. ଜଣେ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ଗୋଟିଏ ଚକ୍ଷୁର ଭୂସମାନ୍ତର ଅଞ୍ଚଳର ପ୍ରାୟ କେଉଁ କୋଣରେ ଦେଖୁପାରେ ?
ଉ –
150°
21. ଉଭୟ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଖୋଲିଲେ ଜଣେ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ଭୂସମାନ୍ତର ଅଞ୍ଚଳର କେତେ ଡିଗ୍ରୀ ପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ ଦେଖୁପାରିବ ?
ଉ –
180°
![]()
22. କଲଏଡ଼ାଲ୍ କଣିକାଦ୍ଵାରା ଆଲୋକର ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣକୁ କ’ଣ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
ଉ –
ଟିଣ୍ଡଲ ସିଦ୍ଧାନ୍ତ
23. ମୁକୁରିକାରେ ପଡୁଥିବା ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ବସ୍ତୁ ତୁଳନାରେ କ’ଣ ହୁଏ ?
ଉ –
ବାସ୍ତବ, ଓଲଟା ଓ ସାମ
24. ଆଲୋକର ପ୍ରକୀର୍ଶନ ଯୋଗୁଁ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ଆଲୋକର ବର୍ଣ୍ଣପଟ୍ଟିକୁ କ’ଣ କହନ୍ତି ?
ଉ –
ବର୍ଣ୍ଣାଳୀ
25. ଅତି ବଡ଼ କଣିକାମାନ କେଉଁ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣର ଆଲୋକ ବିଛୁରଣ କରେ ?
ଉ –
ଧଳା
26. ପ୍ରିଜମ୍ରେ ନିର୍ଗତ ରଶ୍ମି ଓ ଆପତନ ରଶ୍ମି ସହିତ ସୃଷ୍ଟି କରୁଥିବା କୋଣକୁ କ’ଣ କହନ୍ତି ?
ଉ –
ବିଚଳନ କୋଣ
27. ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଉଦୟର କେତେ ମିନଟ୍ ପୂର୍ବରୁ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଦେଖାଯାଆନ୍ତି ?
ଉ –
2 ମିନିଟ୍
28. ଆଭାସୀ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟୋଦୟ ଓ ବାସ୍ତବ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟୋଦୟ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ସମୟ ପାର୍ଥକ୍ୟ କେତେ ?
ଉ –
2 ମିନିଟ୍
29. ଆଲୋକର ତୀବ୍ରତା ବୃଦ୍ଧି ଘଟିଲେ ନେତ୍ରପିତୁଳା କ’ଣ ହୁଏ ?
ଉ –
ସଙ୍କୁଚିତ
30. ସୋଡ଼ିୟମ୍ ଥାଓସଲ୍ଫେଟ୍ ଓ ଗାଢ଼ ସଲଫ୍ୟୁରିକ୍ ଏସିଡ୍ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ରାସାୟନିକ ପ୍ରତିକ୍ରିୟାରୁ କ’ଣ ଉତ୍ପନ୍ନ ହୁଏ ?
ଉ –
ସଲ୍ଫର୍
31. କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ର କଠିନ ସଲ୍ଫର୍ କଣିକା କେଉଁ ଆଲୋକ ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ କରେ ?
ଉ –
ନୀଳ
32. ଦୃଶ୍ୟମାନ ଆଲୋକ ମଧ୍ୟରୁ କେଉଁ ବର୍ଷ ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ ବର୍ଷ ଅଟେ ?
ଉ –
ଲାଲ୍
33. ଆଲୋକର କାହା ଯୋଗୁଁ ସଅଳ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟୋଦୟ ସମ୍ଭବ ହୋଇଥାଏ ?
ଉ –
ପ୍ରତିସରଣ
34. ତାରାମାନେ ଆକାଶରେ ପ୍ରକୃତ ଅବସ୍ଥାନଠାରୁ ଅଧିକ ଉଚ୍ଚ ସ୍ଥାନରେ ଦେଖାଯାଏ କାରଣ କ’ଣ ?
ଉ –
ଆଲୋକର ପ୍ରତିସରଣ
35. କେଉଁ କାରଣ ଯୋଗୁଁ ତାରାମାନେ ଦପ୍ଦପ୍ କରନ୍ତି ?
ଉ –
ବାୟୁମଣ୍ଡଳୀୟ ପ୍ରତିସରଣ
36. ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟୋଦୟ ଓ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟାସ୍ଥ ସମୟରେ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଲାଲ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣ ଦେଖାଯିବାର କାରଣ କ’ଣ ?
ଉ –
ନୀଳ ଆଲୋକର ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ
37. କାଚ ପ୍ରିଜଦ୍ଵାରା ବିଭିନ୍ନ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣର ରଶ୍ମିର ପୃଥକୀକରଣକୁ କ’ଣ କହନ୍ତି ?
ଉ –
ପ୍ରକୀର୍ତ୍ତନ
38. ଧଳା ଆଲୋକ କେତୋଟି ବର୍ଷର ମିଶ୍ରଣ ଅଟେ ?
ଉ –
7
39. ଧଳା ଆଲୋକର କେଉଁ ବର୍ଷର ଆଲୋକର ତରଙ୍ଗ ଦୈର୍ଘ୍ୟ କମ୍ ?
ଉ –
ବାଇଗଣୀ
![]()
40. କେଉଁ କାରଣ ଯୋଗୁଁ ଆକାଶ ନୀଳ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
ଉ –
ଆଲୋକ ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ
41. ପ୍ରିଜିମ୍ରେ ଆଲୋକ ପ୍ରତିସରଣରେ ତଳୁ ଉପରକୁ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣର କ୍ରମ କ’ଣ ?
ଉ –
VIBGYOR
42. 2D ପାୱାର ଥିବା ଲେନ୍ସର ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା କେତେ ସେ.ମି. ?
ଉ –
50
43. ଚକ୍ଷୁଦ୍ଵାରା ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ କେଉଁଠାରେ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହେଲେ ତାହାକୁ ଦେଖ୍ ହୁଏ ନାହିଁ ?
ଉ –
ଅନ୍ଧବିନ୍ଦୁ
44. ଆଲୋକ ଯେଉଁ ପତଳା ସ୍ଵଚ୍ଛଝିଲ୍ଲୀ ମଧ୍ୟଦେଇ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ମଧ୍ୟକୁ ପ୍ରବେଶ କରେ ତାକୁ କ’ଣ କହନ୍ତି ?
ଉ –
ସ୍ୱଚ୍ଛପଟ୍ଟଳ
45. ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଗୋଲକର ବ୍ୟାସ ପ୍ରାୟ କେତେ ସେ.ମି. ?
ଉ –
2.3
46. ସ୍ୱଚ୍ଛପଟ୍ଟଳ ପଛକୁ ଥିବା କଳା ମାଂସଳ ବସ୍ତୁକୁ କ’ଣ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
ଉ –
କନିନିକା
47. ନେତ୍ରପିତୁଳାର ଆକାର କାହାଦ୍ବାରା ନିୟନ୍ତ୍ରିତ ହୁଏ ?
ଉ –
କନିନିକା
48. ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସ ଓ ସ୍ଵଚ୍ଛପଟ୍ଟଳ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଥିବା ତରଳ ପଦାର୍ଥକୁ କ’ଣ କହନ୍ତି ?
ଉ –
ଜଳାଭରସ
49. ଆଲୋକ ସଂବେଦୀ କୋଷ କେଉଁଠାରେ ଥାଏ ?
ଉ –
ମୁକୁରିକା
50. ମାନବ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ମଧ୍ୟକୁ ପ୍ରବେଶ କରୁଥିବା ଅଧିକାଂଶ ଆଲୋକ କେଉଁଠାରେ ପ୍ରତିସୃତ ହୁଏ ?
ଉ –
ସ୍ୱଚ୍ଛପଟ୍ଟଳ ବାହ୍ୟପୃଷ୍ଠ
51. ମାନବ ଚକ୍ଷୁର କେଉଁଠାରେ ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ଗଠିତ ହେଲେ ବସ୍ତୁଟିକୁ ଦେଖ୍ ହେବ ?
ଉ –
ମୁକୁରିକା
52. କେଉଁଟି ମାନବ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ମଧ୍ୟକୁ ଆଲୋକର ପରିମାଣ ନିୟନ୍ତ୍ରଣ କରେ ?
ଉ –
କନୀନିକା
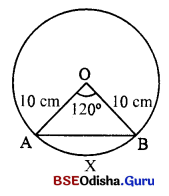
53. ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟି ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ଆଖ୍ୟାଠାରୁ 15cm ଦୂରତାରେ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ପଢ଼ିପାରନ୍ତି । 3 ମି. ଦୂରରେ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ପଢ଼ିବାପାଇଁ କେତେ ପାୱାରର ଚଷମା ଆବଶ୍ୟକ ?
ଉ –
-6.33D
54. ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟାଲୋକରେ କାମ କରୁଥିବାବେଳେ ନେତ୍ର ପିତୁଳାର ଆକାର ଘରେଥିବା ବେଳେ ନେତ୍ରପିତୁଳାର ଆକାର ତୁଳନାରେ କ’ଣ ହେବ ?
ଉ –
ପାନ
55. ଘନ ଜଙ୍ଗଲୀ ଚାନ୍ଦୁଆ (canopy) ମଧ୍ୟଦେଇ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟାଲୋକର ରଶ୍ମିଗୁଚ୍ଛ ଗତି କଲାବେଳେ କେଉଁ ସିଦ୍ଧାନ୍ତଟି କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରେ ।
ଉ –
ଟିଣ୍ଡାଲ ସିଦ୍ଧାନ୍ତ
56. ଚକ୍ଷୁରେ ଥିବା ଆଲୋକ ସଂବେଦୀ ପରଦାର ନାମ କ’ଣ ?
ଉ –
ମୁକୁରିକା
57. ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷର ପ୍ରତିକାର ପାଇଁ ଲେନ୍ସର ପାଓ୍ବାର କ’ଣ କରିବାକୁ ହେବ ?
ଉ –
ଜଣାଇବାକୁ
58. ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟାଲୋକ ସାତଟି ବର୍ଷର ଆଲୋକର ସମଷ୍ଟି – ଏହା କେଉଁ ବୈଜ୍ଞାନିକ ପ୍ରମାଣ କରିଥିଲେ ?
ଉ –
ନିଉଟନ୍
B ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନ ପୂରଣ କର ।
1. କନୀନିକା …………………….. ର ଆକାରକୁ ନିୟନ୍ତ୍ରଣ କରେ ।
2. ମୁକୁରିକାରେ ଅସଂଖ୍ୟ …………………. ସେଲ୍ ଥାଏ ।
3. ଆଲୋକ ମୁକୁରିକାରେ ପଡ଼ିଲେ ଆଲୋକ ସଂବେଦୀ ସେଲ୍ଗୁଡ଼ିକ କ୍ରିୟାଶୀଳ ହୋଇ ………………………….. ବଦଳିଲେ ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା ବଦଳେ ।
4. ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନସ୍ର …………………….. ବଦଳିଲେ ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା ବଦଳେ ।
5. ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦର୍ଶନର ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ଦୂରତାକୁ ମଧ୍ୟ …………………. କୁହାଯାଏ ।
6. ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନସ୍ ଏକ ………………. ଲେନସ୍ ।
7. କ୍ଷୀଣ ଆଲୋକର ଚକ୍ଷୁ ବା ନେତ୍ରପିତୁଳା ……………………… ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
8. ଚକ୍ଷୁ ସମାୟୋଜନ କ୍ଷମତା ହରାଇଲେ ……………………. ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
9. ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଦୋଷ ଥିବା ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ……………………… ବସ୍ତୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦେଖିପାରେ ନାହିଁ ।
10. ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ନିରାକରଣ ପାଇଁ …………………….. ଲେନସ୍ର ଚଷମା ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଏ ।
11. ଦୂର ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ଥିବା ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି …………………………. ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ଦେଖିପାରେ ନାହିଁ ।
12. ଦୂର ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ଥିବା ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ………………….
13. ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନସ୍ ଓ ମୁକୁରିକା ମଧ୍ୟରେ …………….. ଥାଏ ।
14. ପ୍ରକୃତ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟାସ୍ତ ଓ ଆଭାସୀ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟାସ୍ତ ମଧ୍ଯରେ ସମୟ ବ୍ୟବଧାନ ……………… ମିନିଟ୍ ।
15. ଅତ୍ୟଧ୍ଵକ କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ର କଣିକା …………………… ବର୍ଷର ଆଲୋକ ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ କରିନ୍ତି ।
16. ଅତ୍ୟଧିକ ବଡ଼ ଆକାରର କଣିକା ଗୁଡ଼ିକ …………………. ବର୍ଷର ଆଲୋକ ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ କରିଥାନ୍ତି ।
17. ଲାଲ୍ ଆଲୋକର ତରଙ୍ଗ ଦୈର୍ଘ୍ୟ ନୀଳ ଆଲୋକର ତରଙ୍ଗ ଦୈର୍ଘ୍ୟର ……………. ଗୁଣ ।
18. ଅତି ସୂକ୍ଷ୍ମ କଲଏଡ୍ ସଲଫର କଣିକାଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଦ୍ଵାରା ………………………… ଆଲୋକ ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ ହୁଏ ।
19. ପ୍ରିଜମ୍ରେ ଧଳା ଆଲୋକର ପ୍ରକୀର୍ଶନ ବେଳେ ……………………….. ବର୍ଣ୍ଣର ଆଲୋକ ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ବଙ୍କାଇଥାଏ ।
20. ପ୍ରିଜମ୍ର ଧଳା ଆଲୋକର ପ୍ରକୀର୍ତ୍ତନ ବେଳେ ……………………. ବର୍ଣ୍ଣର ଆଲୋକ ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ବଙ୍କାଇଥାଏ ।
21. ଜଳକଣା ଗୁଡ଼ିକର ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟାଲୋକ ପ୍ରକୀର୍ଶନ ଓ ………………….. ପ୍ରକ୍ରିୟା ଯୋଗୁଁ ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରଧନୁ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହୁଏ ।
22. ଟିଣ୍ଡଲ ସିଦ୍ଧାନ୍ତରେ ………………. କଣିକାଦ୍ଵାରା ଆଲୋକର ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
23. ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରଧନୁ …………………… ର ଏକ ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଘଟଣା ।
24. ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଦୋଷ ଦୂର କରିବା ପାଇଁ ……………….. ଲେନ୍ପର ଚଷମା ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଏ |
25. ପ୍ରିଜମ୍ର ……………. ଟି ପୃଷ୍ଠ ଅଛି ।
26. ବିପଦ ସଙ୍କେତ ସୂଚାଇବା ପାଇଁ ……………… ବର୍ଣ୍ଣର ଆଲୋକ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହୁଏ ।
27. ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ କରୁଥିବା କଣିକା ବଡ଼ଆକାରର ହେଲେ ……………………. ବର୍ଣ୍ଣର ଆଲୋକ ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ କରିବ ।
28. କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ର କଠିନ ସଲ୍ଫର୍ କଣିକା …………………… ଆଲୋକ ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ କରେ ।
29. ଜଳରେ ଆଲୋକର ବେଗ …………………. କିମି/ସେ. ।
30. ଧଳା ଆଲୁଅରେ ………………….. ଟି ବର୍ଷର ଆଲୋକ ଦୃଶ୍ୟ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣାଳୀରେ ଅଛି ।
31. ଉଭୟ ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଓ ଦୂରଦୃଷ୍ଟି ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ………………… ଚଷମା ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିବ ।
32. ଜଣେ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ଦୂରଦୃଷ୍ଟି ସଂଶୋଧ ପାଇଁ +2D ଚଷମା ବ୍ୟବହାର କରେ । ତେବେ ଲେନ୍ସର ଫୋକସ୍ର ଦୂରତା …………………. |
33. ଆଭାସୀ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟୋଦୟ ଓ ବାସ୍ତବ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟୋଦୟ ମଧ୍ଯରେ ସମୟ ପାର୍ଥକ୍ୟ ……………………. ମିନିଟ୍ ।
34. ସୋଡ଼ିୟମ୍ ଥାଓସଲ୍ଫେଟ୍ ଓ ଗାଢ଼ ସଲଫ୍ୟୁରିକ୍ ଏସିଡ୍ ମଧ୍ଯରେ ରାସାୟନିକ ପ୍ରତିକ୍ରିୟାରୁ ……………… ଉତ୍ପନ୍ନ ହୁଏ ।
Answer:
1. ନେତ୍ରପିତୁଳା
2. ଆଲୋକ ସଂବେଦୀ
3. ବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍
4. ବକ୍ରତା
5. ନିକଟବିନ୍ଦୁ
6. ଉତ୍ତଳ
7. ବଡ଼
8. ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ
9. ଦୂର
10. ଅବତଳ
11. ନିକଟ
12. ଉତ୍ତଳ
13. କାଚାଭରସ
14. ପ୍ରାୟ ଦୁଇ
15. ନୀଳ
16. ଧଳା
17. ପ୍ରାୟ 1.8 ଗୁଣ
18. ନୀଳ
19. ବାଇଗଣୀ
20. ଲାଲ୍
21. ଆଭ୍ୟନ୍ତରୀଣ ପ୍ରତିଫଳନ
22. କଲଏଡ଼ାଲ୍
23. ଆଲୋକ ପ୍ରକୀର୍ଶନ
24. ଅବତଳ
25. 5
26. ଲାଲ୍
27. ଧଳା
28. ନୀଳ
29. 2.25 x 105
30.7
31. ବାଇଫୋକାଲ | ସ୍ଵିଫୋକସୀ
32. +50 ସେ.ମି.
33. 2 ମିନିଟ୍
34. ସଲ୍ଫର୍
![]()
C ଠିକ୍ ଉକ୍ତି ପାଇଁ ( ✓) ବା ଭୁଲ ଉକ୍ତି ପାଇଁ (x) ଲେଖ ।
1. ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଭିତରେ ଥିବା କନୀନିକା ନେତ୍ରପିତୁଳାର ଆକାରକୁ ନିୟନ୍ତ୍ରଣ କରେ ।
2. ଚକ୍ଷୁର ସିଲିଆରୀ ମାଂସପେଶୀ ସଂକୁଚିତ ହେଲେ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସର ବକ୍ରତା କମିଯାଏ ।
3. କୌଣସି କାରଣରୁ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସର ବକ୍ରତା ବଢ଼ିଗଲେ ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
4. ମୋତିଆବିନ୍ଦୁ ଅସ୍ତ୍ରୋପଚାର କରିଥିବା ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିମାନେ ଚକ୍ଷୁଦାନ କରିପାରିବେ ।
5. ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରଧନୁ ଆଲୋକ ପ୍ରକୀର୍ତ୍ତନର ଏକ ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ଦୃଷ୍ଟାନ୍ତ ।
6. 2D ପାୱାର ଥିବା ଲେନ୍ସର ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା 50 ସେ.ମି. ।
7. ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦର୍ଶନର ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ଦୂରତା 25 ସେ.ମି. ।
8. ସିଲିଆରୀ ମାଂସପେଶୀଗୁଡ଼ିକ ହୁଗୁଳା ହେଲେ ଲେନ୍ସର ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା କମିଯାଏ ।
9. ନେତ୍ରପିତୁଳା ଚକ୍ଷୁଲେନ୍ସ ଓ ମୁକୁରିକା ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଅଛି ।
10. ଚକ୍ଷୁଦ୍ଵାରା ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ମୁକୁରିକାଠାରେ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହେଲେ ତାହାକୁ ଦେଖ୍ ହୁଏ ନାହିଁ ।
11. ଆଲୋକ ଯେଉଁ ପତଳା ସ୍ଵଚ୍ଛଝିଲ୍ଲୀ ମଧ୍ୟଦେଇ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ମଧ୍ୟକୁ ପ୍ରବେଶ କରେ ତାକୁ ସ୍ୱଚ୍ଛପଟ୍ଟଳ କହନ୍ତି ।
12. ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଗୋଲକର ବ୍ୟାସ ପ୍ରାୟ 2.3 ସେ.ମି. ।
13. ସ୍ଵଚ୍ଛପଟ୍ଟଳ ପଛକୁ ଥିବା କଳା ମାଂସଳ ଅଂଶକୁ କନୀନିକା କୁହାଯାଏ ।
14. ନେତ୍ରପିତୁଳାର ଆକାର ସ୍ଵଚ୍ଛପଟ୍ଟଳଦ୍ୱାରା ନିୟନ୍ତ୍ରିତ ହୁଏ ।
15. ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସ ଓ ସ୍ଵଚ୍ଛପଟ୍ଟଳ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଥିବା ତରଳ ପଦାର୍ଥକୁ ଜଳାଭରସ କହନ୍ତି ।
16. ଆଲୋକ ସଂବେଦୀ କୋଷ ମୁକୁରିକାଠାରେ ଥାଏ ।
17. ମାନବ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ମଧ୍ୟକୁ ପ୍ରବେଶ କରୁଥିବା ଅଧିକାଂଶ ଆଲୋକ ମୁକୁରିକାଠାରେ ପ୍ରତିସୃତ ହୁଏ ।
18. ମାନବ ଚକ୍ଷୁର ମୁକୁରିଗାଁଠାରେ ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ଗଠିତ ହେଲେ ବସ୍ତୁଟିକୁ ଦେଖ୍ ହେବ ।
19. କନୀନିକା ମାନବ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ମଧ୍ୟକୁ ଆଲୋକର ପରିମାଣ ନିୟନ୍ତ୍ରଣ କରେ ।
20. ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟି ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ଆଠାରୁ 15cm ଦୂରତାରେ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ପଢ଼ିପାରନ୍ତି । 3 ମି. ଦୂରରେ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ପଢ଼ିବାପାଇଁ –6.33D
21. ପ୍ରିଜମ୍ର ଭୂମିଆଡୁ ଉପରକୁ ତୃତୀୟ ସ୍ଥାନରେ ଥିବା ବର୍ଷଟି ହଳଦିଆ ।
22. ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦର୍ଶନର ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ଦୂରତାକୁ ନିକଟବିନ୍ଦୁ କହନ୍ତି ।
23. ଜଣେ ସୁସ୍ଥ ଓ ସ୍ଵାଭାବିକ ଦୃଷ୍ଟି ସମ୍ପନ୍ନ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିର ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦର୍ଶନର ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ଦୂରତା 25 ସେ.ମି. ।
24. ଗୋଟିଏ ବସ୍ତୁର ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ଚକ୍ଷୁର ମୁକୁରିକା ଅଂଶରେ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହୁଏ ।
25. ଅତି ବଡ଼ କଣିକାମାନ ନୀଳ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣର ଆଲୋକ ବିଛୁରଣ କରେ ।
26. ଗଭୀର ସମୁଦ୍ର ନୀଳ ଦେଖାଯିବାର କାରଣ ଆଲୋକର ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ ।
27. ଚକ୍ଷୁ-ଲେନ୍ସର ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା କମିଗଲେ, ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
Answer:
1. ✓
2. x
3. x
4. ✓
5. ✓
6. ✓
7. ✓
8. ✓
9. x
10. x
11. ✓
12. ✓
13. ✓
14. x
15.✔
16.✔
17. x
18.✔
19.✔
20. ✓
21. x
22. ✓
23. ✓
24. ✓
25. x
26. ✔
27. ✔
![]()
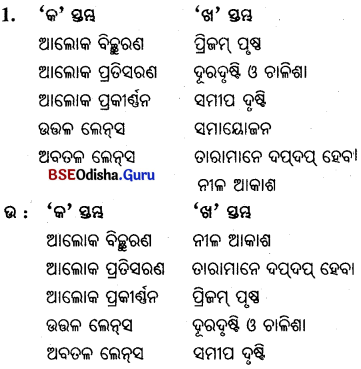
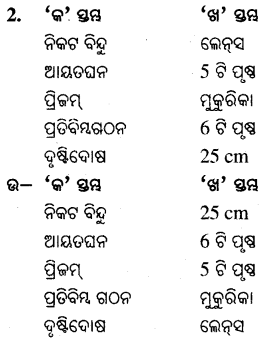
D ‘କ’ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭର ଶବ୍ଦକୁ ‘ଖ’ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭର ଶବ୍ଦ ସହ ମିଳନ କରି ଲେଖ ।


E ଗୋଟିଏ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ଉତ୍ତର ଦିଅ ।
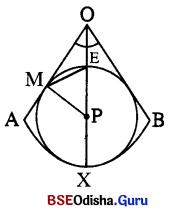
1. ସ୍ଵଚ୍ଛ ପଟ୍ଟଳ କାହାକୁ କହନ୍ତି ?
ଉ –
ଆଲୋକ ଏକ ପତଳା ସ୍ଵଚ୍ଛ ଝିଲ୍ଲୀ ମଧ୍ୟ ଦେଇ ଚକ୍ଷୁକୁ ପ୍ରବେଶ କରେ । ଏହାକୁ ସ୍ବଚ୍ଛ ପଟ୍ଟଳ କହନ୍ତି ।
2. ସମାୟୋଜନ ପାୱାର କାହାକୁ କହନ୍ତି ?
ଉ –
ଚକ୍ଷୁଲେନସ୍ ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତାକୁ ଆବଶ୍ୟକତା ଅନୁଯାୟୀ ବଦଳାଇବା ସାମର୍ଥ୍ୟକୁ ସମାୟୋଜନ ପାୱାର କହନ୍ତି ।
3. ‘ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦର୍ଶନର ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ଦୂରତା’’ କ’ଣ ଲେଖ ।
ଉ –
ସାଧାରଣ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ପାଇଁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଭାବରେ କୌଣସି ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ଦେଖୁବାର ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ଦୂରତା 25 ସେ.ମି. ଅଟେ । ଏହି ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ଦୂରତାକୁ ‘‘ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦର୍ଶନର ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ଦୂରତା’’ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
4. ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ଦେଖୁବାପାଇଁ ଆଲୋକ ଚକ୍ଷୁର କେଉଁ ଅଂଶଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଦେଇ ଯାଏ ?
ଉ –
କୌଣସି ବସ୍ତୁରୁ ଆଲୋକ ରଶ୍ମିଗୁଚ୍ଛ ଆସି ସ୍ଵଚ୍ଛ ପଟ୍ଟଳ, ଜଳାଭରସ, ନେତ୍ରପିତୁଳା, ଚକ୍ଷୁଲେନସ୍ ଓ କାଚାଭରସ ଦେଇ ମୁକୁରିକାର ଆଲୋକ ସଂବେଦୀ ସେଲ୍ରେ ପଡେ ।
5. ନିକଟ ବିନ୍ଦୁ କାହାକୁ କହନ୍ତି ?
ଉ –
ଯେଉଁ ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ଦୂରତାରେ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦେଖିପାରେ ଉକ୍ତ ଦୂରତାକୁ ନିକଟ ବିନ୍ଦୁ କହନ୍ତି ।
6. ଦୂର ବିନ୍ଦୁ କାହାକୁ କହନ୍ତି ?
ଉ –
ଯେଉଁ ଦୂରତା ପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ୍ର ଚକ୍ଷୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଭାବରେ ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ଦେଖିପାରେ ତାହାକୁ ଦୂରବିନ୍ଦୁ କହନ୍ତି ।
7. ମୋତିଆ ବିନ୍ଦୁ କାହାକୁ କହନ୍ତି ?
ଉ –
ସମୟ ସମୟେ ବୟସ୍କ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିଙ୍କର ଅତି ସ୍ଵଚ୍ଛ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନସ୍ ଧଳା ଏବଂ ଧୂସର ହୋଇଯାଏ । ଚକ୍ଷୁର ଏହି ଅବସ୍ଥାକୁ ମୋତିଆ ବିନ୍ଦୁ କହନ୍ତି ।
8. ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ କାହାକୁ କହନ୍ତି ?
ଭ –
କୌଣସି କାରଣରୁ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ସମାୟୋଜନ ପାଓ୍ବାର ହରାଇଲେ । ସେହି ଚକ୍ଷୁର ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ଅଛି ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ ।
9. ସାଧାରଣ ଚକ୍ଷୁର ଦୃଷ୍ଟିସୀମା କେତେ ?
ଉ –
25 ସେ.ମି.ରୁ ଅନନ୍ତ ଦୂରତା ।
![]()
10. ଚାଳିଶା କାହାକୁ କହନ୍ତି ?
ଉ –
ବୟସ ପ୍ରାୟ ଚାଳିଶ ବର୍ଷ ପାଖାପାଖୁ ହେଲେ ସିଲିଆରୀ ମାଂସପେଶୀ ଦୁର୍ବଳ ହୋଇଯାଏ । ଏଥିଯୋଗୁଁ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନସ୍ ତାହାର ସମାୟୋଜନ କ୍ଷମତା ହରାଇବା ଫଳରେ ନିକଟ ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ଦେଖିବାରେ ଅସୁବିଧା ହୁଏ । ଏହାକୁ ଚାଳିଶା କହନ୍ତି ।
11. ବାଇଫୋକାଲ୍ ଚଷମା କାହାକୁ କହନ୍ତି ?
ଉ –
ଯେଉଁ ଚଷମାରେ ଦୁଇ ଭିନ୍ନ ପ୍ରକାର ଲେନସ୍ (ଉତ୍ତଳ ଓ ଅବତଳ) ବ୍ୟବହାର ହୋଇଥାଏ ତାକୁ ଦ୍ଵିଫୋକସୀ ବା ବାଇଫୋକାଲ୍ ଚଷମା କହନ୍ତି ।
12. ଜଣେ ଛାତ୍ର ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ ପଛ ବେଞ୍ଚରେ ବସି ବ୍ଲାକ୍ବୋର୍ଡରେ ଯାହା ଲେଖାଯାଉଛି ତାକୁ ଦେଖିପାରୁ ନାହିଁ । ପିଲାଟିର କେଉଁ ପ୍ରକାରର ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ଅଛି ? ଏହା କିପରି ଦୂର କରାଯାଇ ପାରିବ ?
ଉ –
ପିଲାଟିର ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଦୋଷ ଅଛି । ଏହି ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷକୁ ଦୂର କରିବା ପାଇଁ ଉପଯୁକ୍ତ ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ଅବତଳ ଲେନସ୍ ଚଷମା ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିବା ଉଚିତ ।
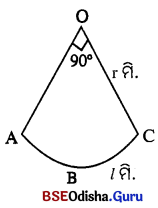
13. ବିଚଳନ କୋଣ କାହାକୁ କହନ୍ତି ।
ଉ –
ପ୍ରିଜମ୍ରେ ଆଲୋକ ପ୍ରତିସରଣ ହେତୁ ଆପତିତ ରଶ୍ମି ଓ ନିର୍ଗତ ରଶ୍ମି ମଧ୍ୟରେ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହେଉଥିବା କୋଣକୁ ବିଚଳନ କୋଣ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
14. ଆଲୋକର ପ୍ରକୀର୍ତ୍ତନ କାହାକୁ କହନ୍ତି ?
ଉ –
ମିଶ୍ରିତ ବର୍ଣ ଆଲୋକରୁ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣାଳୀ ସୃଷ୍ଟିର ପ୍ରକ୍ରିୟାକୁ ଆଲୋକର ପ୍ରକୀର୍ଣ୍ଣନ କହନ୍ତି ।
15. ଚଷମା ପିନ୍ଧିବା ବ୍ୟତୀତ ଚକ୍ଷୁଦୋଷ କେଉଁ ଉପାୟରେ ଦୂର କରାଯାଇ ପାରୁଛି ?
ଊ –
ଚଷମା ବ୍ୟବହାର ବ୍ୟତୀତ ସଂସ୍ପର୍ଶ ଲେନ୍ସ କିମ୍ବା ଶଲ୍ୟ ଉପଚାର ଦ୍ଵାରା ପ୍ରତିସରଣ ଜନିତ ତ୍ରୁଟି ଦୂର କରାଯାଇ ପାରୁଛି ।
16. ଟିଣ୍ଡଲ୍ ସିଦ୍ଧାନ୍ତ କାହାକୁ କହନ୍ତି ?
ଊ –
କଲଏଡାଲ୍ କଣିକାଗୁଡ଼ିକର ଆଲୋକ ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣକୁ ଟିଣ୍ଡଲ୍ ସିଦ୍ଧାନ୍ତ କହନ୍ତି ।
17. ବାଇଫୋକାଲ୍ ଚଷମାରେ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ଲେନସ୍ଗୁଡ଼ିକର କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଲେଖ ।
ଉ –
ବାଇଫୋକାଲ୍ ଚଷମାରେ ଦୁଇ ଭିନ୍ନ ପ୍ରକାରର ଲେନସ୍ ଏକାଠି ରହିଥାଏ । ତଳ ଲେନସ୍ରେ ନିକଟ ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ଦେଖନ୍ତି ବା ବହି ପଢନ୍ତି ଏବଂ ଉପର ଲେନସ୍ରେ ଦୂର ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ଦେଖନ୍ତି ।
18. ଚକ୍ଷୁରେ ମୋତିଆ ବିନ୍ଦୁର ଲକ୍ଷଣ କ’ଣ ?
ଉ –
ବୟସ୍କ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିର ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନସ୍ ବେଳେବେଳେ ଧଳା ଏବଂ ଧୂସର ହୋଇଯାଏ । ଚକ୍ଷୁର ଏହି ଅବସ୍ତାକୁ ମୋତିଆ ବିନ୍ଦୁ
19. ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ଥିବା ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି 1.2 m ରୁ ଅଧିକ ଦୂରରେ ଗୋଟିଏ ବସ୍ତୁ ଥିଲେ ସେ ଭଲ ଭାବରେ ତାକୁ ଦେଖୁ ପାରୁନାହିଁ । କେଉଁ ପ୍ରକାରର ଲେନସ୍ ବ୍ୟବହାର କଲେ ଏହିଦୋଷ ଦୂର ହେବ ବୁଝାଅ ।
ଉ –
ଦୁର ବିଦୁର ଦୁରତା = 1.2 ମି.
P = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) = \(\frac { -1 }{ 1.2 }\) = – 0.83 D
∴ ଅବତଳ ଲେନସ୍ର ଚଷମା ବ୍ୟବହାର କଲେ ଏହି ଦୋଷ ଦୂର ହେବ ।
20. ବିପଦ ସଙ୍କେତରେ ଲାଲବର୍ଣ ଆଲୋକ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଏ କାହିଁକି ?
ଉ –
ଲାଲ୍ ଆଲୋକ କୁହୁଡ଼ି କିମ୍ବା ଧୂଳିକଣା ଦ୍ବାରା ଖୁବ୍ କମ୍ ବିଚ୍ଛୁରିତ ହୁଏ । ଫଳରେ ଦୂରକୁ କେବଳ ଲାଲ ବର୍ଷ ଫିକା ନପଡ଼ି ସେମିତି ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
21. ପୃଥିବୀ ଚାରିପାଖେ ବାୟୁମଣ୍ଡଳ ନଥିଲେ କ’ଣ ହୁଅନ୍ତା ?
ଉ –
ବାୟୁମଣ୍ଡଳ ନଥୁଲେ କୌଣସି ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ ହୁଅନ୍ତା ନାହିଁ, ତେଣୁ ଆକାଶ ଅନ୍ଧକାରମୟ ହୋଇଥାନ୍ତା ।
22. ସମୁଦ୍ର ଜଳର ରଙ୍ଗ ନୀଳ ଦେଖାଯାଏ କାହିଁକି ?
ଉ –
ସମୁଦ୍ର କୂଳ ଅନ୍ୟ ବର୍ଷ ଅପେକ୍ଷା ନୀଳବର୍ଣ୍ଣର ଆଲୋକ ଅତିମାତ୍ରାରେ ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ କରେ । ତେଣୁ ସମୁଦ୍ର ଜଳ ନୀଳ ବର୍ଷ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
23. କେଉଁ ତିନୋଟି ପ୍ରକ୍ରିୟାରେ ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରଧନୁ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହୁଏ ?
ଉ –
ପ୍ରକୀର୍ଶନ, ଆଭ୍ୟନ୍ତରୀଣ ପ୍ରତିଫଳନ ଓ ପ୍ରତିସରଣ ।
24. ପ୍ରିଜମ୍ ମଧ୍ୟଦେଇ ଆଲୋକ ଗତିକଲେ କେଉଁ ଆଲୋକର ପ୍ରତିସରଣାଙ୍କ ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ଓ କେଉଁ ଆଲୋକର ପ୍ରତିସରଣାଙ୍କ ସର୍ବାଧିକ ?
ଉ –
ଲାଲ୍ ଆଲୋକର ପ୍ରତିସରଣାଙ୍କ ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ଓ ବାଇଗଣୀ ଆଲୋକର ପ୍ରତିସରଣାଙ୍କ ସର୍ବାଧିକ ।
25. ପ୍ରକୀର୍ଶନ କଣ ?
ଭ –
ମିଶ୍ରିତ ବର୍ଣ ଆଲୋକରୁ ବିଭିନ୍ନ ବର୍ଷର ଆଲୋକକୁ ପ୍ରତିସରଣ ଦ୍ଵାରା ପୃଥକ କରିବା ପ୍ରକ୍ରିୟାକୁ ଆଲୋକର ପ୍ରକୀର୍ଣ୍ଣନ କହାନ୍ତି । ।
26. ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ଦେଖିବାପାଇଁ ଆଲୋକ ଚକ୍ଷୁର କେଉଁ ଅଂଶଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଦେଇ ଯାଏ ?
ଉ –
କୌଣସି ବସ୍ତୁରୁ ଆଲୋକ ରଶ୍ମିଗୁଚ୍ଛ ଆସି ସ୍ୱଚ୍ଛପଟଳ, ଜଳାଭରସ, ନେତ୍ରପିତୁଳା, ଚକ୍ଷୁଲେନ୍ସ ମୁକୁରିକାର ପୀତବିନ୍ଦୁ ଉପରେ ପଡ଼େ ଏବଂ ମୁକୁରିକାରେ ବାସ୍ତବ, କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ର ଓଲଟା ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ସୃଷ୍ଟି କରେ ।
27. ସମୁଦ୍ରର ରଙ୍ଗ ନୀଳ କାହିଁକି ?
ଉ –
ସମୁଦ୍ରର ଜଳ ଅନ୍ୟ ବର୍ଷ ଅପେକ୍ଷା ନୀଳବର୍ଣ୍ଣର ଆଲୋକ ଅତିମାତ୍ରାରେ ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ କରେ । ତେଣୁ ସମୁଦ୍ରର ଜଳ ନୀଳ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣ ଦେଖାଯାଏ |
28. ଅନ୍ଧବିନ୍ଦୁ କ’ଣ ?
ଉ –
ମୁକୁରିକାର ଏପରି ଏକ ଅଂଶ ଅଛି, ଯେଉଁଠାରେ ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହେଲେ ବସ୍ତୁ ଆଦୌ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ନାହିଁ । ସେହି ସ୍ଥାନକୁ ଅନ୍ଧବିନ୍ଦୁ କହନ୍ତି । ଏଠାରେ ଚକ୍ଷୁସ୍ନାୟୁ ମୁକୁରିକା ସହ ସଂଯୁକ୍ତ ହୋଇଛି ।
29. ପ୍ରିଜିମ୍ ମଧ୍ୟଦେଇ ଆଲୋକ ଗତି କଲେ କେଉଁ କେଉଁ ଆଲୋକର ପ୍ରତିସରଣାଙ୍କ ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ଓ ସର୍ବୋଚ୍ଚ ?
ଉ-
ଲାଲ୍ ଆଲୋକର ପ୍ରତିସରଣାଙ୍କ ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ଏବଂ ବାଇଗଣି ଆଲୋକର ପ୍ରତିସରଣାଙ୍କ ସର୍ବୋଚ୍ଚ ।
![]()
30. କେଉଁ ତିନୋଟି ପ୍ରକ୍ରିୟା ପାଇଁ ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରଧନୁ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହୁଏ ?
ଉ-
(a) ପ୍ରକୀର୍ଶନ (b) ଅନ୍ତଃପ୍ରତିଫଳନ (c) ପ୍ରତିସରଣ
31. ସମାୟୋଜନ ପାଓ୍ବାର କହିଲେ କ’ଣ ବୁଝ ?
ଉ –
ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସ ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତାକୁ ଆବଶ୍ୟକତା ଅନୁଯାୟୀ ବଦଳାଇବା ସାମର୍ଥ୍ୟକୁ ସମାୟୋଜନ ପାୱାର କହନ୍ତି ।
32. କାଚାଭରସ କହିଲେ କ’ଣ ବୁଝ ?
ଉ –
ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସ ଓ ମୁକୁରିକା ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଏକ ଜେଲିଭଳି ପଦାର୍ଥ ଥାଏ, ତାହାକୁ କାଚାଭରସ (Vitreous Humour) କହନ୍ତି । ଆଲୋକ ରଶ୍ମି କୌଣସି ବସ୍ତୁରୁ ଆସି ସ୍ୱଚ୍ଛପଟ୍ଟଳ, ଜଳାଭରସ, ନେତ୍ରପିତୁଳା, ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସ ଓ କାଚାଭରସ ମଧ୍ୟଦେଇ ମୁକୁରିକାରେ ପଡ଼େ ।
33. କନୀନିକା କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
ଉ–
ସ୍ୱଚ୍ଛପଟ୍ଟଳର ପଛରେ ଥିବା କଳା ମାଂସଳ ଅଂଶକୁ କନୀନିକା (Iris) କୁହାଯାଏ । ଏହା ନେତ୍ରପିତୁଳା (Pupil)ର ଆକାରକୁ ନିୟନ୍ତ୍ରଣ କରେ ।
34. ନେତ୍ରପିତୁଳା କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
ଉ –
କନୀନିକା କେନ୍ଦ୍ରରେ ଥିବା ରନ୍ଧ୍ରକୁ ନେତ୍ରପିତୁଳା କହନ୍ତି । ଉଜ୍ଜ୍ବଳ ଆଲୋକରେ ଏହାର ଆକାର ଛୋଟ ହୋଇଥାଏ ଏବଂ କ୍ଷୀଣ ଆଲୋକରେ ଆକାର ବୃଦ୍ଧି ଘଟିଥାଏ । ଏହା ଆବଶ୍ୟକ ପରିମାଣର ଆଲୋକ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ମଧ୍ୟକୁ ଛାଡ଼ିଥାଏ ।
35. ଜଳାଭରସ କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ?
ଉ –
ସ୍ୱଚ୍ଛପଟ୍ଟଳ ଓ କନୀନିକା ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଏକ ସ୍ଵଚ୍ଛ ତରଳ ପଦାର୍ଥ ଅଛି, ତାହାକୁ ଜଳାଭରସ (Aqueous Humour) କତନ୍ତ୍ର |
![]()
F ପ୍ରଥମଯୋଡ଼ିର ସମ୍ପର୍କକୁ ଲକ୍ଷ୍ୟ କରି ଦ୍ୱିତୀୟ ଯୋଡ଼ିର ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନ ପୂରଣ କର ।
1. ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସର ବକ୍ରତା ବୃଦ୍ଧି : ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା କମ୍ :: ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନସ୍ର ବକ୍ରତା ହ୍ରାସ : ……………. |
2. ନିକଟ ବିନ୍ଦୁ : 25 ସେ.ମି. :: ଦୂରବିନ୍ଦୁ : …………………. |
3. ଗୋଟିଏ ଚକ୍ଷୁ : 150° :: ଦୁଇଟି ଚକ୍ଷୁ : …………………. |
4. ଚକ୍ଷୁ ବନ୍ଦ : ଦ୍ୱି-ବିମିତୀୟ :: ଦୁଇଟି ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଖୋଲା : ……………………. |
5. ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟି : ଅବତଳ ଲେନସ୍ :: ଦୂରଦୃଷ୍ଟି : ……………… |
6. ଚାଳିଶା : ଉତ୍ତଳ ଲେନସ୍ :: ମୋତିଆ ବିନ୍ଦୁ : ……………………. |
7. ଦୂରଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସ୍ର ପାୱାର ହ୍ରାସ :: ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟି : ………………………. |
8. ସମୀପଦୃଷ୍ଟି : କାଚାଭରସ :: ଦୂରଦୃଷ୍ଟି : ………………… |
9. ପ୍ରିଜମ୍ର ତ୍ରିଭୁଜାକାର ପୃଷ୍ଠ : 2 ଟି :: ପ୍ରିଜିମ୍ ଆୟତଘନାକାର ପୃଷ୍ଠ : ………………… |
10. ବାଇଗଣୀ : ଅଧିକ ବଙ୍କାଇଥାଏ :: ଲାଲ୍ : ………………… |
11. ଆଲୋକର ପ୍ରତିସରଣ : ଲେନ୍ସ :: ଆଲୋକର ପ୍ରକୀର୍ତ୍ତନ : ……………….. |
12. ଟିଣ୍ଡଲ ସିଦ୍ଧାନ୍ତ : ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ :: ସଅଳ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟୋଦୟ : ………………. |
13. ସୂକ୍ଷ୍ମକଣିକା : ନୀଳ :: ବୃହତ୍ତର କଣିକା : ………………… |
14. ଆକାଶ ନୀଳ : ଆଲୋକର ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ :: ଟିଣ୍ଡଳ ସିଦ୍ଧାନ୍ତ : ………………….. |
15. ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟୋଦୟ : ଲାଲ୍ :: ମଧ୍ୟାହ୍ନ : ………………….. |
16. ଲାଲ୍ ଆଲୋକ : ଅଧିକ ତରଙ୍ଗ ଦୈର୍ଘ୍ୟ :: ନୀଳ ଆଲୋକ : ………………….. |
17. ଦପ୍ଦପ୍ ଆଲୋକ : ତାରା :: ସ୍ଥିର ଆଲୋକ : …………………. |
18. ପୃଥିବୀବାସୀ : ଆକାଶ ନୀଳ :: ମହାକାଶଚାରୀ : ………………….. |
19. ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା 1 ମି. : 1D :: ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା 25 ସେ.ମି. ::…………….. |
20. ତୁମ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର ପିଲା : ସମୀପଦୃଷ୍ଟି :: ଶିକ୍ଷକ ଶିକ୍ଷୟିତ୍ରୀ : ………………. |
21. ତୁମଶ୍ରେଣୀର ପିଲା : ଅବତଳ ଲେନସ୍ :: ଶିକ୍ଷକ : ……………… |
22. +2D: 0.50 m ::- 2.5 D : ……………… |
23. କାଚପ୍ଲାଟ୍ : ପାର୍ଶ୍ଵ ବିସ୍ଥାପନ :: ପ୍ରିଜମ୍ : ………………….. |
Answer:
1. ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା ବୃଦ୍ଧି
2. 25 ସେ.ମି.ରୁ ଅନନ୍ତ ଦୂରତା
3. 180°
4. ତୃତୀୟ ବିମିତି
5. ଉତ୍ତଳ ଲେନସ୍
6. ଶଲ୍ୟଚିକିତ୍ସା
7. ଲେନସ୍ ପାଓ୍ବାର ବୃଦ୍ଧି
8. ମୁକୁରିକା ପଛପାଖ
9. 3 ଟି
10. କମ୍ ବଙ୍କାଇଥାଏ
11. ପ୍ରିଜମ୍
12. ବାୟୁମଣ୍ଡଳୀୟ ପ୍ରତିସରଣ
13. ଧଳା
14. ଆଲୋକର ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ
15. ଧଳା
16. କମ୍ ତରଙ୍ଗ ଦୈର୍ଘ୍ୟ
17. ଗ୍ରହ
18. ଆକାଶ କଳା
19. 4D
20. ଦୂରଦୃଷ୍ଟି
21. ଉତ୍ତଳ ଲେନସ୍
22. 0.40 ମି.
23. ବିଚଳନ କୋଣ
SUBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS
1. ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ କ’ଣ ? ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷର କାରଣ ଓ ପ୍ରତିକାର ଚିତ୍ର ସହ ଦର୍ଶାଅ ।
ଉ–
ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ – କୌଣସି କାରଣରୁ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଯଦି କ୍ରମଶଃ ସମାୟୋଜନ ପାଓ୍ବାର ହରାଏ ତେବେ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ହୋଇଛି ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ । ଏହାଫଳରେ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟଭାବରେ ଦେଖିପାରେ ନାହିଁ । ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସର ପ୍ରତିସରଣ ତ୍ରୁଟିଯୋଗୁଁ ବସ୍ତୁ ଝାପ୍ସା ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ :
- ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ଥିବା ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ଦୂର ବସ୍ତୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦେଖିପାରେ ନାହିଁ । ମାତ୍ର ନିକଟରେ ଥିବା ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦେଖାରେ ।
- ଏହି ଦୋଷ ଥିବା ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିର ଦୂର-ବିନ୍ଦୁ ଅନନ୍ତ ଦୂରତାଠାରୁ କମିଯାଏ, କେବଳ କେତେ ମିଟର ଦୂରତାରେ ଥିବା ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟଭାବରେ ଦେଖୁହୁଏ ।
କାରଣ :
କୌଣସି କାରଣରୁ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସର ବକ୍ରତା ବଢ଼ିଗଲେ କିମ୍ବା ଚକ୍ଷୁଗୋଲକ ଲମ୍ବିଗଲେ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସର ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା କମିଯାଏ । ଫଳରେ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେସର ପାୱାର ବଢ଼ିଯାଏ ତେବେ ଦୂରବସ୍ତୁରୁ ଆସୁଥିବା ଆଲୋକ ରଶ୍ମିଗୁଚ୍ଛ ମୁକୁରିକା ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତେ ତା ପୂର୍ବରୁ କାଚାଭରସ ଭିତରେ ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ସୃଷ୍ଟିକରେ । ତେଣୁ ଦୂର =ବସ୍ତୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ନାହିଁ । ଅପେକ୍ଷାକୃତ ନିକଟରେ ଥିବା ବସ୍ତୁର ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ମୁକୁରିକାରେ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହୋଇ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦେଖାଯାଇପାରେ ।
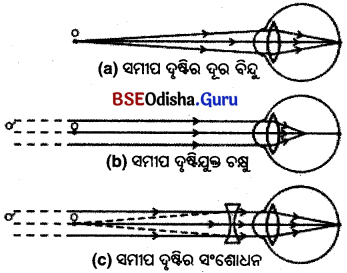
ପ୍ରତିକାର :
ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିର ପ୍ରତିକାର ପାଇଁ ଲେନ୍ସର ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା ବଢ଼ାଇବା ବା ପାୱାର କମାଇବା ଆବଶ୍ୟକ । ଏଥିପାଇଁ ଉପଯୁକ୍ତ ଅବତଳ ଲେନ୍ସର ଚଷମା ବ୍ୟବହାର କଲେ ଅବତଳ ଲେନ୍ସ ଓ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସର ସମାହାରର ପାୱାର ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସର ପାୱାରଠାରୁ କମ୍ ହେବ ଓ ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା ବଢ଼ିଯିବ । ଫଳରେ ଦୂରବସ୍ତୁର ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ମୁକୁରିକାରେ ପଡ଼ିବ ଏବଂ ବସ୍ତୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦେଖାଯିବ |
2. ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ କ’ଣ ? ଦୂରଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଦୋଷର କାରଣ ଓ ପ୍ରତିକାର ଚିତ୍ର ସହ ଦର୍ଶାଅ ।
ଉ–
ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ – କୌଣସି କାରଣରୁ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଯଦି କ୍ରମଶଃ ସମାୟୋଜନ ପାୱାର ହରାଏ ତେବେ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ହୋଇଛି ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ । ଏହାଫଳରେ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଭାବରେ ଦେଖିପାରେ ନାହିଁ । ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସର ପ୍ରତିସରଣ ତ୍ରୁଟିଯୋଗୁଁ ବସ୍ତୁ ଝାପ୍ସା ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
ଦୂର ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ :
ଦୂର ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ଥିବା ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ଦୂରବସ୍ତୁକୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦେଖ୍ପାରେ କିନ୍ତୁ ନିକଟ ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟଭାବରେ ଦେଖୁରେ ନାହିଁ । ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିର ନିକଟ ବିନ୍ଦୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦର୍ଶନର ନିମ୍ନତମ ଦୂରତା ଅର୍ଥାତ୍ 25 ସେ.ମି.ଠାରୁ ଅଧ୍ଵ ଦୂରରେ ରଖ୍ ପଢ଼ିପାରନ୍ତି ।
କାରଣ : – କୌଣସି କାରଣରୁ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେ ନ୍ ସର ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା ବଢ଼ିଗଲେ ଅର୍ଥାତ୍ ଚକ୍ଷୁର ଲେନ୍ସର ପାୱାର କମିଗଲେ ନିକଟ ବସ୍ତୁର ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ମୁକୁରିକା ପଛପଟେ ଗଠିତ ହୁଏ । ନିକଟ ବସ୍ତୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ନାହିଁ ।
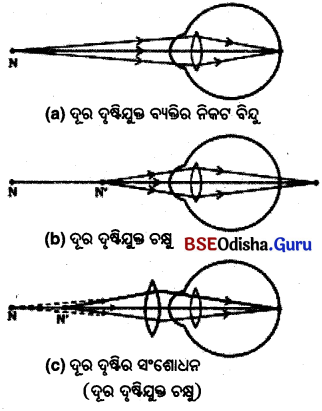
ନିରାକରଣ : ଚକ୍ଷୁ ପରୀକ୍ଷା କରାଇ ଉପଯୁକ୍ତ ମାପର ଉତ୍ତଳ ଲେନ୍ସର ଚଷମା ପିନ୍ଧିଲେ ଏହି ଉତ୍ତଳ ଲେନ୍ସ ଓ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସର ସମାହାରର ପାୱାର ଅଧିକ ହୁଏ ଏବଂ ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା କମିଯାଏ । ଫଳରେ ନିକଟ ବସ୍ତୁର ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ମୁକୁରିକାରେ ପଡ଼େ ଓ ବସ୍ତୁଟି ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
3. ବିଭିନ୍ନ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷର କାରଣ ଓ ନିରାକରଣ ବିଷୟରେ ଆଲୋଚନା କର । (ଚିତ୍ର ଅନାବଶ୍ୟକ)
ଢ –
ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ମୁଖ୍ୟତଃ ତିନି ପ୍ରକାର । ଯଥା- (a) ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ, (b) ଦୂରଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଦୋଷ, (c) ଚାଳିଶା ।
(a) ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିର କାରଣ ଓ ଲକ୍ଷଣ :
- ଏହି ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷରେ ନିକଟ ବସ୍ତୁ ଦେଖାଯାଏ କିନ୍ତୁ ଦୂରବସ୍ତୁ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ନାହିଁ ।
- ଏହି ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷରେ ଚକ୍ଷୁଲେନ୍ସର ବଜ୍ରତା ବଢ଼ିଯାଏ କିମ୍ବା ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଗୋଲକ ଲମ୍ବିଯାଏ । ଏହାଦ୍ଵାରା ଦୂର ବସ୍ତୁରୁ ଆସୁଥିବା ଆଲୋକ ରଶ୍ମିଗୁଚ୍ଛ ମୁକୁରିକା ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତେ କାଚାଭରସରେ ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ସୃଷ୍ଟି କରେ । ତେଣୁ ଦୂରବସ୍ତୁ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ନାହିଁ । କିନ୍ତୁ ନିକଟ ବସ୍ତୁର ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ମୁକୁରିକାରେ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହୁଏ, ତେଣୁ ନିକଟ ବସ୍ତୁ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
ନିରାକରଣ :
- ଏହି ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷର ପ୍ରତିକାର ପାଇଁ ଲେନ୍ସର ଫୋକ୍ସ ଦୂରତା ବଢ଼ାଇବା କିମ୍ବା ପାୱାର କମାଇବା ଆବଶ୍ୟକ ।
- ଏଥପାଇଁ ଉପଯୁକ୍ତ ପାୱାରର ଅବତଳ ଲେନ୍ସର ଚଷମା ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଏ । ଏହାଦ୍ଵାରା ଚକ୍ଷୁଲେ ନ୍ସ ଓ ଅବତନ ଲେନ୍ସର ସମାହାର ପାୱାର ଚକ୍ଷୁଲେନ୍ସର ପାୱାରଠାରୁ କମ୍ ହେବ ଓ ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ପୁନର୍ବାର ମୁକୁରିକାରେ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହେବ ।
(b) ଦୂରଦୃଷ୍ଟିର ଲକ୍ଷଣ : ଏହି ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷରେ ଦୂର ବସ୍ତୁ ଦେଖାଯାଏ କିନ୍ତୁ ନିକଟ ବସ୍ତୁ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ନାହିଁ ।
କାରଣ :
- ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସର ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା ବଢ଼ିଗଲେ ବା ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସର ପାୱାର କମିଗଲେ ଏହି ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
- ଏହି ଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଦୋଷରେ ନିକଟ ବସ୍ତୁର ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ମୁକୁରିକାର ପଛପଟେ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହୁଏ, ତେଣୁ ନିକଟ ବସ୍ତୁ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ନାହିଁ ।
ନିରାକରଣ :
- ଉପଯୁକ୍ତ ପାୱାର ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ଉତ୍ତଳ ଲେନ୍ସ ବ୍ୟବହାର କଲେ ଚକ୍ଷୁଲେନ୍ସ ଓ ଉତ୍ତଳ ଲେନ୍ସର ମିଳିତ ପାଓ୍ବାର ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଯୁକ୍ତର ପାୱାରଠାରୁ ଅଧିକ ହେବ ।
- ଫଳତଃ ନିକଟ ବସ୍ତୁର ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ମୁକୁରିକାରେ ସୃଷ୍ଟିହୋଇ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦେଖାଯିବ ।
(c) ଚାଳିଶା :
- ଚାଳିଶ ବର୍ଷ ପାଖାପାଖ୍ ବୟସର ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିଙ୍କର ଚକ୍ଷୁର ସିଲିଆରୀ ମାଂସପେଶୀ ଦୁର୍ବଳ ହୋଇଯିବାରୁ ଏହି ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ
- ଏହି ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷକୁ ନିରାକରଣ କରିବାପାଇଁ ଉପଯୁକ୍ତ ପାୱାରର ଉତ୍ତଳ ଲେନ୍ସ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଏ ।
![]()
4. ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟାଲୋକ ସାତଟି ବର୍ଷର ସମାହାର ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନା କର ।
ଉ –
ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟାଲୋକ ଭଳି ଧଳା ଆଲୋକ ସାତଟି ସ୍ୱତନ୍ତ୍ର ବର୍ଣ୍ଣର ମିଶ୍ରଣ ଅଟେ ।
- ପ୍ରଥମେ ବୈଜ୍ଞାନିକ ସାର୍ ଆଇଜାକ୍ ନିଉଟନ୍ ପ୍ରିଜଦ୍ୱାରା ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟାଲୋକର ପ୍ରତିସରଣ କରାଇ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣାଳୀ ସୃଷ୍ଟି କରିଥଲେ ।
- ଧଳା ଆଲୋକକୁ ପ୍ରିଜମ୍ର ଗୋଟିଏ ପ୍ରତିସରଣ ପୃଷ୍ଠ ଉପରେ ପକାଇଲେ ପ୍ରିଜମ୍ର ଅପର ପ୍ରତିସରଣ ପୃଷ୍ଠଦେଇ ଧଳା ଆଲୋକରେ ଥିବା ମୂଳ ମିଶ୍ରବର୍ଷର ଆଲୋକ ଅଂଶସବୁ ବିଭିନ୍ନ କୋଣରେ ବାହାରି ଆସିବ । ପ୍ରିଜମ୍ଠାରୁ ଅଳ୍ପ ଦୂରରେ ଖଣ୍ଡିଏ ଧଳା କାଗଜରେ ବା ଧଳା କାନ୍ଥରେ ଏହି ବର୍ଣ୍ଣାଳୀକୁ ପକାଇ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ଅନୁଧ୍ୟାନ କରାଯାଇପାରିବ ।
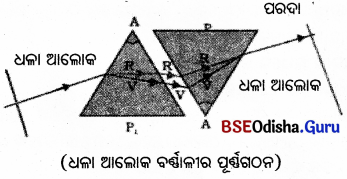
- ପ୍ରିଜମ୍ର ଭୂମି ଆଡୁ ଉପରକୁ ଦେଖିଲେ ଆଲୋକଗୁଡ଼ିକର ବର୍ଣ୍ଣ ବାଇଗଣି, ଘନନୀଳ, ନୀଳ, ହଳଦିଆ, ନାରଙ୍ଗୀ ଓ ଲାଲ୍ (VIBGYOR)
- ଏହି ସପ୍ତବର୍ଣ୍ଣର ଆଲୋକରୁ ଆଉ ଗୋଟିଏ ଏକା ପ୍ରକାରର ପ୍ରିଜମ୍ବୁକୁ ଓଲଟାଇ ରଖ୍ ତା’ ଭିତରକୁ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣାଳୀକୁ ପ୍ରବେଶ କରାଇଲେ, ଯେଉଁ ଆଲୋକ ଦ୍ଵିତୀୟ ପ୍ରିଜ୍ମରୁ ନିର୍ଗତ ହେବ ତାହା ମୂଳ ଆଲୋକଟି ଭଳି ଧଳା !
- ଏହି ପରୀକ୍ଷଣରୁ ନିଉଟନ୍ ପ୍ରମାଣ କଲେ ଯେ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟାଲୋକ ସାତଟି ବର୍ଷର ଆଲୋକର ସମଷ୍ଟି ଏବଂ ପ୍ରିଜମ୍ କେବଳ ବର୍ଷଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ପୃଥକ୍ କରି (ପ୍ରକୀର୍ଣ୍ଣନଦ୍ଵାରା) ବର୍ଣ୍ଣାଳୀ ସୃଷ୍ଟିରେ ସହାୟକ ହୁଏ ।
ସଂକ୍ଷିପ୍ତ ଭତ୍ତରମୂଳକ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନୋତ୍ତର
1. ଧଳା ଆଲୋକ ଏକ ସପ୍ତବର୍ତ୍ତୀ ଆଲୋକ ବୋଲି କିପରି ପ୍ରମାଣ କରାଯାଏ ଲେଖ । (ଚିତ୍ର ଅନାବଶ୍ୟକ ।)
ଉ –
- ଧଳା ଆଲୋକ ଏକ ସପ୍ତବର୍ତ୍ତୀ ଆଲୋକ ବୋଲି କିପରି ପ୍ରମାଣ କରାଯାଏ ଲେଖ । (ଚିତ୍ର ଅନାବଶ୍ୟକ ।) ଧଳା ଆଲୋକକୁ ପ୍ରିଜମ୍ର ଗୋଟିଏ ପ୍ରତିସରଣ ପୃଷ୍ଠ ଉପରେ ପକାଇଲେ ପ୍ରିଜମ୍ର ଅପର ପ୍ରତିସରଣ ପୃଷ୍ଠ ଦେଇ ଧଳା ଆଲୋକରେ ଥିବା ମୂଳ ମିଶ୍ରବଣ୍ଡର ଆଲୋକ ଅଂଶ ସବୁ ବିଭିନ୍ନ କୋଣରେ ବାହାରି ଆସିବେ । ପ୍ରିଜମ୍ଠାରୁ ଅଳ୍ପ ଦୂରରେ ଖଣ୍ଡିଏ ଧଳା କାଗଜରେ ବା ଧଳା କାନ୍ଥରେ ଏହି ବର୍ଣ୍ଣାଳୀକୁ ପକାଇ ବର୍ଷଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ଅନୁଧ୍ୟାନ
କରାଯାଇପାରେ । - ପ୍ରିଜମ୍ର ଭୂମିଆଡୁ ଉପରକୁ ଦେଖିଲେ ଆଲୋକଗୁଡ଼ିକର ବର୍ଣ୍ଣହେବ ବାଇଗଣି, ଘନନୀଳ, ନୀଳ, ସବୁଜ, ହଳଦିଆ, ନାରଙ୍ଗୀ ଓ ଲାଲ୍ ।
- ଏହି ସପ୍ତବର୍ତ୍ତୀ ଆଲୋକକୁ ଆଉ ଗୋଟିଏ ଏକା ପ୍ରକାର ପ୍ରିଜମ୍କୁ ଓଲଟା ରଖ୍ ତାହା ମଧ୍ୟକୁ ପ୍ରବେଶ କରାଇଲେ ଦେଖାଯିବ ଯେ ଯେଉଁ ଆଲୋକ ଦ୍ଵିତୀୟ ପ୍ରିଜମ୍ବୁରୁ ନିର୍ଗତ ହେବ ତାହା ମୂଳ ଆଲୋକ ଭଳି ଧଳା । ତେଣୁ ଧଳା ଆଲୋକ ଏକ ସପ୍ତବର୍ତ୍ତୀ ଆଲୋକ ।
ନିଉଟନ୍ ପ୍ରମାଣ କଲେ ଯେ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟାଲୋକ ସାତଟି ବର୍ଷର ଆଲୋକର ସମଷ୍ଟି ଏବଂ ପ୍ରିଜମ୍ କେବଳ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ପୃଥକ କରି ବର୍ଣ୍ଣାଳୀ ସୃଷ୍ଟିରେ ସହାୟକ ହୁଏ ।
2. ଟିଣ୍ଡଲ୍ ସିଦ୍ଧାନ୍ତ କ’ଣ ? ଦୈନନ୍ଦିନ ଜୀବନରେ ଟିଣ୍ଡଲ୍ ସିଦ୍ଧାନ୍ତର ଉଦାହରଣ ଦିଅ । କେଉଁ କେଉଁ କାରଣ ଉପରେ ଏହି ସିଦ୍ଧାନ୍ତ ନିର୍ଭର କରେ ?
ଉ-
ଟିଣ୍ଡଲ୍ ସିଦ୍ଧାନ୍ତ : କଲଏଡ୍ ଏକ ବିଷମ ଜାତୀୟ କଣିକାଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ନେଇ ଗଠିତ । କଲଏଡାଲ୍ କଣିକାଗୁଡ଼ିକ କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ର (10-9 ମି. ରୁ 10-6 ମି.) । ତେଣୁ କଣିକାଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଆଲୋକ ରଶ୍ମି ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ କରନ୍ତି । ଏପରି ଆଲୋକର ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣକୁ ଟିଣ୍ଡଲ୍ ସିଦ୍ଧାନ୍ତ କଦ୍ଧାନ୍ତ
ଦୈନନ୍ଦିନ ଜୀବନରେ ଟିଣ୍ଡଲ୍ ସିଦ୍ଧାନ୍ତ :
- ଧୂଆଁପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ ଏକ କୋଠରି ମଧ୍ୟକୁ ଏକ ସୂକ୍ଷ୍ମ ରନ୍ଧ୍ର ସାହାଯ୍ୟରେ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟାଲୋକ ପ୍ରବେଶ କରାଇଲେ ଆଲୋକର ଗତିପଥ ଦେଖାହୁଏ ।
- ଘନ ଜଙ୍ଗଲର ଚାନ୍ଦୁଆ ବା ବିତାନ ମଧ୍ୟଦେଇ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟାଲୋକର ରଶ୍ମିଗୁଚ୍ଛ ଗତିକଲାବେଳେ କୁହୁଡ଼ି ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଥିବା କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ର ଜଳବିନ୍ଦୁସମୂହ ଆଲୋକକୁ ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ କରନ୍ତି ।
ଟିଣ୍ଡଲ୍ ସିଦ୍ଧାନ୍ତ କଣିକାର ଆକାର ଉପରେ ନିର୍ଭର କରେ –
- ଅତ୍ୟଧ୍ଵକ କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ରକଣିକା ନୀଳ ଆଲୋକ ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ କରିଥାଏ ।
- କଣିକାଗୁଡ଼ିକର ଆକାର ବଡ଼ ହେଲେ ଅତ୍ୟଧିକ ତରଙ୍ଗ ଦୈର୍ଘ୍ୟ ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ଆଲୋକ ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ କରିଥାଏ ।
- କଣିକାଗୁଡ଼ିକର ଆକାର ଅତ୍ୟଧିକ ବଡ଼ ଆକାରର ହୋଇଥିଲେ ତାହା କେବଳ ଧଳା ଆଲୋକ ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ କରିଥାଏ ।
3. ସଅଳ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟୋଦୟ ଓ ବିଳମ୍ବ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟାସ୍ତ କାହିଁକି ହୁଏ ବୁଝାଅ ।
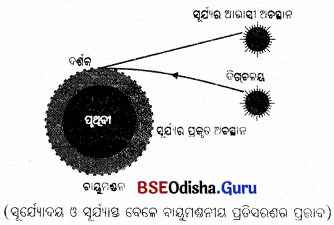
ଉ –
- ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟୋଦୟର ପ୍ରାୟ ଦୁଇ ମିନିଟ୍ ପୂର୍ବରୁ ଏବଂ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟାସ୍ତର ପ୍ରାୟ ଦୁଇ ମିନିଟ୍ ପରେ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଆମକୁ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
- ଏହା ମଧ୍ୟ ଆଲୋକର ବାୟୁମଣ୍ଡଳୀୟ ପ୍ରତିସରଣ ଯୋଗୁଁ ସମ୍ଭବ ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
- ବାୟୁମଣ୍ଡଳର ଉପର ବାୟୁ ସ୍ତର ଅପେକ୍ଷା ନିମ୍ନ ବାୟୁସ୍ତର ଅଧ୍ଵ ଘନ ।
- ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟଠାରୁ ଆସୁଥିବା ରଶ୍ମି ଭିନ୍ନ ଘନତା ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ଅନେକ ବାୟୁସ୍ତର ଦେଇ ପ୍ରତିସୃତ ହେବାରୁ କିଛି ପରିମାଣରେ ତା’ର ଦିଗ ବଦଳାଇ ଥାଏ ।
- ଏହା ଭୂପୃଷ୍ଠରେ ପହଞ୍ଚିବା ପରେ ଆମେ ସେହି ପ୍ରତିସୃତ ରଶ୍ମି ସିଧାରେ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟଙ୍କୁ ଦିଗ୍ବଳୟ ଉପରେ ଅଳ୍ପସମୟ ପାଇଁ ଦେଖୁ ।
4. ଜଣେ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ପାଖରେ ଥିବା ବହି ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ପଢ଼ି ପାରୁନାହାନ୍ତି କିନ୍ତୁ କଳାପଟାରେ ଥିବା ଲେଖାକୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଭାବରେ ପଢ଼ିପାରୁଛନ୍ତି । ତାଙ୍କର କି ପ୍ରକାର ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ଅଛି ଲେଖ । ଏହାର କାରଣ ଓ ପ୍ରତିକାର ଲେଖ ।
ଉ –
ବ୍ୟକ୍ତଙ୍କର ଦୂରଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଦୋଷ ଅଛି । ତେଣୁ ଖାଲି ଆସ୍ରେ ନିଜ ବହି ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଭାବରେ ପଢ଼ି ପାରୁନାହାନ୍ତି । କିନ୍ତୁ ଶ୍ରେଣୀର କଳାପଟାରେ ଲେଖାଗୁଡ଼ିକ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଭାବରେ ପଢ଼ିପାରୁଛନ୍ତି ।
- ଲକ୍ଷଣ : ଦୂରଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଦୋଷରେ ନିକଟ ବସ୍ତୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦିଶେ ନାହିଁ ଏବଂ ଦୂରବସ୍ତୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦିଶେ ।
- କାରଣ : କୌଣସି କାରଣରୁ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସର ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା ବଢ଼ିଗଲେ ବା ଚକ୍ଷୁଲେନ୍ସର ପାୱାର କମିଗଲେ ନିକଟ ବସ୍ତୁର ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ମୁକୁରିକାରେ ନ ପଡ଼ି ତା’ ପଛରେ ପଡ଼େ । ତେଣୁ ନିକଟ ବସ୍ତୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦିଶେ ନାହିଁ ।
- ନିରାକରଣ : ଦୂରଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଦୋଷ ନିରାକରଣ ପାଇଁ ଚକ୍ଷୁଲେନ୍ସର ପାୱାର ବଢ଼ାଇବା ଦରକାର । ତେଣୁ ଉତ୍ତଳ ଲେନ୍ସର ଚଷମା ପିନ୍ଧିଲେ ଉତ୍ତଳ ଲେନ୍ସ ଓ ଚକ୍ଷୁଲେନ୍ସର ସମାହାରର ପାଓ୍ବାର ଅଧ୍ଵ ହେବ ଓ ନିକଟ ବସ୍ତୁର ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ମୁକୁରିକାରେ ପଡ଼ି ବସ୍ତୁଟି ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦେଖାଯିବ ।
5. ସମାୟୋଜନ ପାୱାର କାହାକୁ କହନ୍ତି । ସ୍ଵାଭାବିକ ଚକ୍ଷୁର ସମାୟୋଜନ କ୍ଷମତା କ’ଣ ବୁଝାଅ ।
ଉ –
- ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନସ୍ ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତାକୁ ଆବଶ୍ୟକତା ଅନୁଯାୟୀ ବଦଳାଇବା ସାମର୍ଥ୍ୟକୁ ସମାୟୋଜନ ପାୱାର କହନ୍ତି ।
- ଗୋଟିଏ ସୁସ୍ଥ ଓ ସ୍ଵାଭାବିକ ଚକ୍ଷୁର ଲେନସ୍ ଦୂର ଓ ନିକଟ ବସ୍ତୁର ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବକୁ ମୁକୁରିକା ଉପରେ ପକାଇ ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ଦେଖିବାରେ ସାହାଯ୍ୟ କରେ ।
- ଦୂର ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ଦେଖୁବାକୁ ହେଲେ ଲେନ୍ସକୁ ଧରି ରଖିଥିବା ମାଂସପେଶୀଗୁଡ଼ିକ ହୁଗୁଳା ହୋଇ ଲେନ୍ସଟି ସରୁ ହୋଇଯାଏ ଏବଂ ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା ବଢ଼ିଯାଏ, ଫଳରେ ଦୂରବସ୍ତୁକୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଭାବରେ ଦେଖ୍ହୁଏ ।
- ନିକଟ ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ଦେଖିଲାବେଳେ ସିଲିଆରୀ ମାଂସପେଶୀ ସଂକୁଚିତ ହୁଏ ଓ ଚକ୍ଷୁଲେନସ୍ର ବକ୍ରତା ବୃଦ୍ଧି ପାଏ ଏବଂ ଏହା ମୋଟା ହୋଇଯାଏ । ଫଳରେ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସର ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା କମିଯାଏ ଏବଂ ଆମେ ନିକଟ ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଭାବରେ ଦେଖିପାରୁ । ଏହି ପ୍ରକ୍ରିୟାକୁ ସମାୟୋଜନ ପ୍ରକ୍ରିୟା କହନ୍ତି ।
6. ଜଣେ ଛାତ୍ର ଖାଲି ଆସ୍ରେ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଭାବରେ ନିଜ ବହି ପଢ଼ିପାରୁଛି; କିନ୍ତୁ ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ କଳାପଟାରେ ଲେଖା ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଭାବରେ ପଢ଼ିପାରୁ ନାହିଁ । ତା’ର କେଉଁ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ହୋଇଛି ଲେଖ । ଏହାର କାରଣ ଓ ପ୍ରତିକାର ଲେଖ ।
ଭ –
ଛାତ୍ରଟିର ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ହୋଇଛି । ତେଣୁ ଛାତ୍ରଟି ଖାଲିଆସ୍ରେ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଭାବରେ ନିଜ ବହି ପଢ଼ିପାରୁଛି; କିନ୍ତୁ ଶ୍ରେଣୀରେ କଳାପଟାରେ ଲେଖା ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଭାବେ ପଢ଼ିପାରୁ ନାହିଁ !
କାରଣ : କୌଣସି କାରଣରୁ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସ ବକ୍ରତା ବଢ଼ିଗଲେ କିମ୍ବା ଚକ୍ଷୁଗୋଲକ ଲମ୍ବିଗଲେ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସର ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା କମିଯାଏ । ଫଳତଃ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସର ପାୱାର ବଢ଼ିଯାଏ । ତେଣୁ ଦୂରବସ୍ତୁରୁ ଆସୁଥିବା ଆଲୋକ ରଶ୍ମିଗୁଚ୍ଛ ମୁକୁରିକା ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତେ ତା ପୂର୍ବରୁ କାଚାଭରସ ଭିତରେ ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ସୃଷ୍ଟିକରେ । ତେଣୁ ଦୂରବସ୍ତୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ନାହିଁ । ଅପେକ୍ଷାକୃତ ନିକଟରେ ଥିବା ବସ୍ତୁର ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ମୁକୁରିକାରେ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହୋଇ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
ପ୍ରତିକାର : ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷର ପ୍ରତିକାର ପାଇଁ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନସ୍ର ପାୱାର କମାଇବା ଆବଶ୍ୟକ । ଏଥିପାଇଁ ଉପଯୁକ୍ତ ଅବତଳ ଲେନ୍ସର ଚଷମା ବ୍ୟବହାର କଲେ ଅବତଳ ଲେନ୍ସ ଓ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସର ସମାହାରର ପାୱାର ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନ୍ସର ପାୱାରଠାରୁ କମ୍ ହେବ ଓ ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା ବଢ଼ିଯିବ । ଫଳରେ ବସ୍ତୁର ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ମୁକୁରିକାରେ ପଡ଼ିବ । ବସ୍ତୁଟି ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦେଖାଯିବ ।
![]()
7. ଜଣେ ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ସମ୍ପନ୍ନ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ପାଇଁ – 5.5 D ର ଲେନ୍ସ ପାୱାର ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ଲେନ୍ସ ଆବଶ୍ୟକ ହୁଏ ଏବଂ ଏବଂ ଜଣେ ଦୂରଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଦୋଷସମ୍ପନ୍ନ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିପାଇଁ (+ 1.5 D) ପାୱାର ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ଲେନ୍ସ ଦରକାର ହୁଏ । ସେମାନଙ୍କର (i) ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଦୋଷ ଓ (ii) ଦୂର ଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଦୋଷ ଦୂର କରିବା ପାଇଁ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ଲେନ୍ସ ଦ୍ବୟର ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା ନିର୍ଣ୍ଣୟ କର ।
ଉ –
(i) ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଦୋଷ ସମ୍ପନ୍ନ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ପାଇଁ ଲେନ୍ସର ପାୱାର P1 = – 5.5 D
![]()
= \(\frac { -2 }{ 11 }\) x 100 ସେ.ମି. = – 18.18 ସେ.ମି. = – 18.2 ସେ.ମି.
∴ 18.2 ସେ.ମି. ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ଅବତଳ ଲେନ୍ସ ଆବଶ୍ୟକ ।
(ii) ଦୂରଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଦୋଷସମ୍ପନ୍ନ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ପାଇଁ ଲେନ୍ସର ପାୱାର
P2 = + 1.5D
ଦୂରଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଦୋଷ ଦୂର କରିବା ପାଇଁ ଆବଶ୍ୟକ ଲେନ୍ସର ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା
![]()
∴ 66.67 ସେ.ମି. ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ଉତ୍ତଳ ଲେନ୍ସର ଚଷମା ଆବଶ୍ୟକ ।
8. ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିର ଦୂରବିନ୍ଦୁ କହିଲେ କ’ଣ ବୁଝ ? ଜଣେ ପିଲା 2 ମିଟର ଦୂରତାରୁ ଅଧିକ ଦୂରରେ ଥିବା ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ଦେଖାରୁନାହିଁ – ତା’ର କି ପ୍ରକାର ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ହୋଇଛି ? ସେ କେଉଁ ପ୍ରକାରର ଚଷମା ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିବ ? ଏହି ଲେନ୍ସର ପାୱାର କଳନା କର ।
ଉ –
- ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଦୋଷ ଥିବା ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ସର୍ବାଧିକ ଯେତିକି ଦୂରତାରୁ ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ଦେଖ୍ ପାରନ୍ତି ତାହାକୁ ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିର ଦୂରବିନ୍ଦୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
- ଜଣେ ପିଲା 2 ମିଟରରୁ ଅଧିକ ଦୂରର ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ଦେଖିପାରୁ ନାହିଁ । ତାହାକୁ ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟି ହୋଇଛି, ସେ ଅବତଳ ଲେନ୍ସର ଚଷମା ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିବ ।
- ଏହି ଚଷମାରେ ଥିବା ଲେନ୍ସର ପାୱାର P = \(\frac { 1 }{ -f }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ -2 }\) D = – 0.5 D
9. ତାରାଗୁଡ଼ିକ କାହିଁକି ଦପ୍ଦପ୍ ହୁଅନ୍ତି ?
ଉ –
(i) ପୃଥିବୀର ବାୟୁମଣ୍ଡଳର ଉଚ୍ଚତର ସ୍ତର ସମୁଦ୍ର ପତ୍ତନ ଆଡ଼କୁ ଥିବା ବାୟୁସ୍ତର ଅପେକ୍ଷା କମ୍ ଘନ । ତାରାମାନଙ୍କଠାରୁ ଆସୁଥିବା ଆଲୋକ ରଶ୍ମି କ୍ରମାଗତ ଭାବେ କମ୍ ଘନ ମାଧ୍ୟମରୁ ବେଶୀ ଘନ ମାଧ୍ୟମ ଆଡ଼କୁ ଗତି କରିଥାଏ
(ii) ବାୟୁମଣ୍ଡଳର କ୍ରମ ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତିତ ପ୍ରତିସରଣାଙ୍କ ଯୋଗୁଁ ଆଲୋକ ରଶ୍ମି ଅଭିଲମ୍ବ ଆଡ଼କୁ ଅନବରତ ବଙ୍କେଇ ହେଉଥାଏ ଏବଂ କ୍ରମାଗତ ଭାବରେ ପ୍ରତିସ୍ମୃତ ହୋଇ ଆମ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ନିକଟରେ ପହଞ୍ଚେ । ଫଳରେ ତାରାର ଆଭାସୀ ଅବସ୍ଥାନ ତାହାର ପ୍ରକୃତ ଅବସ୍ଥାନ ଅପେକ୍ଷା ଭିନ୍ନ ହୋଇ ସାମାନ୍ୟ ଉପରକୁ ହୁଏ ।
(iii) ବାୟୁସ୍ତରର ଅବସ୍ଥାର ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନ ହେଉଥିବାରୁ ବହୁଦୂରର ବିନ୍ଦୁ ଉତ୍ସ ପ୍ରାୟ ତାରାର ଆଭାସୀ ଅବସ୍ଥାନ ସାମାନ୍ୟ ଉପର ତଳ ହୋଇ ବଦଳୁଥାଏ । ଫଳରେ ତାରାମାନେ ଦପ୍ ଦପ୍ ହେଲା ପରି ଦିଶେ ।
10. ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟୋଦୟ ଓ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟାସ୍ତ ସମୟରେ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟ କାହିଁକି ଗାଢ଼ ଲାଲ୍ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
ଊ–
- ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟୋଦୟ ଓ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟାସ୍ତ ସମୟରେ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଦିଗ୍ବଳୟରେ ଥାଆନ୍ତି । ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟଠାରୁ ଆସୁଥିବା ଆଲୋକ ଦିଗବଳୟରେ ଥିବା ବାୟୁସ୍ତର ଦେଇ ବାୟୁମଣ୍ଡଳରେ ଅଧ୍ଵ ଦୂରତା ଗତିକରେ ।
- ଫଳରେ ଅଧିକାଂଶ କମ୍ ତରଙ୍ଗ ଦୈର୍ଘ୍ୟ ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ନୀଳ ଆଲୋକ କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ର କଣିକାଗୁଡ଼ିକଦ୍ୱାରା ବିଚ୍ଛୁରିତ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଅଧୂକ ତରଙ୍ଗ ଦୈର୍ଘ୍ୟ ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ଆଲୋକ ଅତି କମ୍ ମାତ୍ରାରେ ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
- ଅଧୂକ ତରଙ୍ଗ ଦୈର୍ଘ୍ୟ ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ଲାଲ୍ ଆଲୋକ ଆମ ଆଖରେ ପଡ଼େ । ତେଣୁ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟୋଦୟ ଓ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟାସ୍ତ ସମୟରେ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟର ବର୍ଣ୍ଣ ଲାଲ୍ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
ଅତିସଂଯିପ୍ର ଉତ୍ତରମ୍ଜଲକ ପ୍ରଣ୍ଟୋତ୍ତର
1. ମୋତିଆ ବିନ୍ଦୁ କ’ଣ ? ଏହାର ଚିକିତ୍ସା କିପରି କରାଯାଏ ?
ଊ –
- ବେଳେବେଳେ ବୟସ୍କ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିଙ୍କ ଚକ୍ଷୁଲେନ୍ସ ଧଳା ଏବଂ ଧୂସର ହୋଇଯାଏ । ଏହାଦ୍ୱାରା ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ସମ୍ପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ ବା ଆଂଶିକ ଭାବରେ ଦେଖ୍ଯାରନ୍ତି ନାହିଁ । ଚକ୍ଷୁର ଏହିପରି ଅବସ୍ଥାକୁ ମୋତିଆ ବିନ୍ଦୁ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
- ଶଲ୍ୟ ଚିକିତ୍ସା ଦ୍ଵାରା ମୋତିଆବିନ୍ଦୁର ଚିକିତ୍ସା କରାଯାଏ ।
2. ଚକ୍ଷୁର ସମାୟୋଜନ କ୍ଷମତା କ’ଣ ? ଏହା କିପରି ହୋଇଥାଏ ?
ଊ –
- ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନସ୍ ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତାକୁ ଆବଶ୍ୟକତା ଅନୁଯାୟୀ ବଦଳାଇବା ସାମର୍ଥ୍ୟକୁ ସମାୟୋଜନ କ୍ଷମତା କହନ୍ତି ।
- ସିଲିଆରି ମାଂସପେଶୀର ସଙ୍କୋଚନ ପ୍ରସାରଣ ଫଳରେ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନସ୍ର ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା ବଦଳେ । ତେଣୁ ବସ୍ତୁର ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ସର୍ବଦା ମୁକୁରିକାରେ ପଡେ ।
3. ଆଲୋକର ବିଭିନ୍ନ ବର୍ଷ ପାଇଁ କାଚର ପ୍ରତିସରଣାଙ୍କ ଭିନ୍ନ ହୁଏ କାହିଁକି ?
ଊ –
- ବିଭିନ୍ନ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣର ଆଲୋକ କାଚ ମଧ୍ଯରେ ଭିନ୍ନ ଭିନ୍ନ ବେଗରେ ଗତି କରିଥାଏ ।
- ତେଣୁ ଧଳା ଆଲୋକ ପ୍ରକୀର୍ତ୍ତନରେ ଭିନ୍ନ ଭିନ୍ନ ଆଲୋକର ବିଚ୍ୟୁତି ଭିନ୍ନ ଭିନ୍ନ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ତେଣୁ ବିଭିନ୍ନ ବର୍ଷ ପାଇଁ କାଚର ପ୍ରତିସରଣାଙ୍କ ଭିନ୍ନ ଭିନ୍ନ ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
4. ସ୍ଵାଭାବିକ ଚକ୍ଷୁର 25 ସେ.ମି.ରୁ କମ୍ ଦୂରତାରେ କୌଣସି ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ରଖେ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ବସ୍ତୁଟିକୁ କାହିଁକି ଦେଖିପାରେ ନାହିଁ ?
ଊ –
- ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦର୍ଶନର ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ଦୂରତା 25 ସେ.ମି. ଅଟେ । ଚକ୍ଷୁଠାରୁ ବସ୍ତୁର ଅବସ୍ଥାନ 25 ସେ.ମି.ରୁ କମ୍ ହେଲେ ସିଲିଆରି ମାଂସପେଶୀ ଚକ୍ଷୁଲେନସ୍ର ବକ୍ରପୃଷ୍ଠକୁ ଆଉ ଅଧିକ ବକ୍ର କରିପାରେ ନାହିଁ ।
- ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନସ୍ର ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା ହ୍ରାସ ପାଏ ନାହିଁ ଅର୍ଥାତ୍ ସମାୟୋଜନ କ୍ଷମତା ହରାଏ । ତେଣୁ ବସ୍ତୁର ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ମୁକୁରିକାରେ ଗଠିତ ହୋଇପାରେ ନାହିଁ, ଫଳରେ ବସ୍ତୁର ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ଅସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଭାବରେ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
5. ମହାକାଶଚାରୀ ମାନଙ୍କୁ ଆକାଶ କାହିଁକି ନୀଳ ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତେ ଅନ୍ଧାରୁଆ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
ଊ –
- ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟାଲୋକ ବାୟୁମଣ୍ଡଳ ଦେଇ ଗତି କଲାବେଳେ ବାୟୁର ସୂକ୍ଷ୍ମକଣିକାଗୁଡ଼ିକ ନୀଳ ଆଲୋକ ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ କ ରି ଥା’ନ୍ତି ।
- କିନ୍ତୁ ମହାକାଶରେ ବାୟୁମଣ୍ଡଳ ପ୍ରାୟ ନଥାଏ । ତେଣୁ ଟିଣ୍ଡଲ ପଦ୍ଧତି ଜନିତ ଆଲୋକର ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ ଘଟେ ନାହିଁ । ତେଣୁ ମହାକାଶ ଅନ୍ଧକାର ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
6. ବାହାରର ଅଧ୍ଵ ଉଜ୍ଜ୍ୱଳ ଆଲୋକରୁ ଘର ଭିତରକୁ ଆସିଲେ କିଛି ସମୟ ପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ କୌଣସି ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ଦେଖିପାରୁ ନାହୁଁ କାହିଁକି ?
ଊ –
- ଉଜ୍ଜ୍ବଳ ଆଲୋକରୁ ଘର ଭିତରକୁ ଆସିଲେ କିଛି ସମୟ ପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ କିଛି ଦେଖାରୁ ନାହିଁ କାରଣ କନୀନିକା ପ୍ରସାରିତ ହୋଇ ଅଧ୍ଵ ଆଲୋକ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ମଧ୍ୟକୁ ଛାଡ଼ିବାକୁ କିଛି ସମୟ ନେଇଥାଏ ।
- ସେହିପରି ଯେତେବେଳେ କମ୍ ଉଜ୍ଜ୍ବଳ ଆଲୋକରୁ ଅଧିକ ଉଜ୍ଜ୍ୱଳ ଆଲୋକକୁ ଯାଇଥାଉ ସେତେବେଳେ କନୀନିକା ନେତ୍ର ପିତୁଳାକୁ ସଙ୍କୁଚିତ କରି କମ୍ ଆଲୋକ ରଶ୍ମି ଚକ୍ଷୁ ମଧ୍ୟକୁ ଛାଡ଼ିବା ପାଇଁ କିଛି ସମୟ ନେଇଥାଏ ।
7. ଆକାଶ କାହିଁକି ନୀଳ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ?
ଊ –
- ବାୟୁମଣ୍ଡଳରେ ଥିବା ବାୟୁର ଅଣୁଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଏବଂ ଅନ୍ୟ ସୂକ୍ଷ୍ମକଣିକା ଗୁଡ଼ିକର ଦୈର୍ଘ୍ୟ ଦୃଶ୍ୟମାନ ଆଲୋକର ତରଙ୍ଗ ଦୈର୍ଘ୍ୟଠାରୁ କମ୍ ।
- ଏହି କଣିକାଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଅଧୂକ ତରଙ୍ଗ ଦୈର୍ଘ୍ୟ ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ଲାଲ୍ ଆଲୋକ ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ ନକରି କମ୍ ତରଙ୍ଗ ଦୈର୍ଘ୍ୟ ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ନୀଳ ଆଲୋକ ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ କରିଥାନ୍ତି । ଏହି ବିଚ୍ଛୁରିତ ନୀଳ ଆଲୋକ ଆମ ଚକ୍ଷୁରେ ପ୍ରବେଶ କରୁଥିବାରୁ ଆକାଶ ନୀଳ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
![]()
8. ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦର୍ଶନର ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ଦୂରତା କହିଲେ କ’ଣ ବୁଝ ? ସ୍ଵାଭାବିକ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ପାଇଁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦର୍ଶନର ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ଦୂରତା କେତେ ?
ଊ –
- ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟଭାବେ ଦେଖିବା ପାଇଁ ହେଲେ ତାକୁ ଚକ୍ଷୁଠାରୁ ଏକ ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ଦୂରତାରେ ରଖିବାକୁ ହେବ । ଏହାକୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦର୍ଶନର ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ଦୂରତା କୁହାଯାଏ ।
- ସ୍ଵାଭାବିକ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ପାଇଁ ଏହି ଦୂରତା 25 ସେ.ମି. ।
9. ସାଧାରଣ ଚକ୍ଷୁର ଦୂରବିନ୍ଦୁ ଓ ନିକଟବିନ୍ଦୁ କାହାକୁ କହନ୍ତି ?
ଊ –
- ଯେଉଁ ଦୂରତା ପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟଭାବରେ ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ଦେଖୁପାରେ ତାହାକୁ ଦୂର ବିନ୍ଦୁ କୁହାଯାଏ । ସାଧାରଣ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ପାଇଁ ଏହା ଅନନ୍ତ ଦୂରତା ।
- ଯେଉଁ ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ଦୂରତା ପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟଭାବେ ଦେଖିପାରେ ତାହାକୁ ନିକଟ ବିନ୍ଦୁ କହନ୍ତି । ସାଧାରଣ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ପାଇଁ ଏହା 25 ସେ.ମି. ।
10. ଚକ୍ଷୁ ନିକଟରେ ଥିବା ଗୋଟିଏ ବସ୍ତୁର ଦୂରତାକୁ ବଢାଇଲେ ତାହାର ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ଦୂରତା କ’ଣ ହେବ
ଊ –
- ଚକ୍ଷୁ ନିକଟରେ ଥିବା ଗୋଟିଏ ବସ୍ତୁର ଦୂରତାକୁ ବଢାଇଲେ ତାହାର ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବର ଦୂରତା ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନ ହୁଏ ନାହିଁ ।
- ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବର ଦୂରତା, ଚକ୍ଷୁଲେନସ୍ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଥିବା ଦୂରତା ସହିତ ସମାନ । କାରଣ ବସ୍ତୁର ଦୂରତା ବୃଦ୍ଧି ଘଟିଲେ ଲେନସ୍ ଧରି ରଖୁଥିବା ମାଂସପେଶୀଗୁଡ଼ିକ ହୁଗୁଳା ହୋଇଯାଏ ଓ ଲେନସ୍ ସରୁ ହୋଇଯାଏ । ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା ବଢ଼େ ଓ ବସ୍ତୁର ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ମୁକୁରିକାରେ ପଡେ ଫଳରେ ବସ୍ତୁଟି ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
11. ନିକଟବସ୍ତୁ ଓ ଦୂରବସ୍ତୁକୁ ଦେଖିବା ପାଇଁ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନସ୍ର କିପରି ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନ ହୁଏ ?
ଊ –
- ବସ୍ତୁଟି ଦୂରରେ ଥିଲେ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନସ୍ ଧରି ରଖୁବା ମାଂସପେଶୀ ହୁଗୁଳା ହୁଏ । ଲେନସ୍ ସରୁ ହେବାରୁ ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା ବଢ଼ିଯାଏ, ଫଳରେ ଦୂରବସ୍ତୁକୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦେଖ୍ ହୁଏ ।
- ନିକଟ ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ଦେଖିବାପାଇଁ ସିଲିଆରୀ ମାଂସପେଶୀ ସଂକୁଚିତ ହୁଏ ଓ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନସ୍ର ବକ୍ରତା ବୃଦ୍ଧି ଘଟେ ଓ ମୋଟା ହୋଇଯାଏ ଏବଂ ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା କମିଯାଏ । ଫଳରେ ନିକଟ ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଭାବରେ ଦେଖ୍ହୁଏ ।
12. ଚକ୍ଷୁର ଅତି ନିକଟରେ କାହିଁକି ବହି ପଢ଼ିପାରିବା ନାହିଁ ?
ଊ –
- ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଦର୍ଶନର ସର୍ବନିମ୍ନ ଦୂରତା 25 cm |
- 25 cm ରୁ କମ୍ ଦୂରତାରେ ବସ୍ତୁକୁ/ବହିକୁ ରଖିଲେ ସିଲିଆରି ମାଂସପେଶୀ ଆଉ ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନସ୍ର ବକ୍ରତା ବୃଦ୍ଧି କରିପାରେ ନାହିଁ । ଫଳରେ ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା ହ୍ରାସ ପାଏ ନାହିଁ । ତେଣୁ ଚକ୍ଷୁର ଅତି ନିକଟରେ ବହି ରଖୁ ପଢିହୁଏ ନାହିଁ ।
13. ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ଦେଖୁବାପାଇଁ ବସ୍ତୁର ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବ ମୁକୁରିକାରେ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହେବା ଆବଶ୍ୟକ, କାହିଁକି ?
ଊ –
- ମୁକୁରିକାରେ ଅସଂଖ୍ୟ ଆଲୋକ ସମ୍ବେଦୀସେଲ୍ ଥାଆନ୍ତି । ଆଲୋକ ମୁକୁରିକା ଉପରେ ପଡ଼ିଲେ ଆଲୋକ ସମ୍ବେଦୀ ସେଲ୍ଗୁଡ଼ିକ କ୍ରିୟାଶୀଳ ହୋଇ ବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ସଙ୍କେତ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହୁଏ ।
- ଏହି ବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ସଙ୍କେତ ନେତ୍ରସ୍ନାୟୁ ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ ମସ୍ତିଷ୍କକୁ ଯାଏ । ଏହାପରେ ଆମେ ବସ୍ତୁକୁ ଦେଖିପାରୁ ।
14. ଚକ୍ଷୁର ଉତ୍ତଳ ଲେନସ୍ ଓ ସାଧାରଣ ଉତ୍ତଳ ଲେନସ୍ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ପାର୍ଥକ୍ୟ କ’ଣ ?
ଉ –
- ଚକ୍ଷୁ ଲେନସ୍ ଜେଲି ଭଳି ତନ୍ତୁ ଜାତୀୟ ପଦାର୍ଥରେ ଗଠିତ କିନ୍ତୁ ସାଧାରଣ ଉଭଳ ଲେନସ୍ କାଚ କିମ୍ବା ପ୍ଲାଷ୍ଟିକ୍ରେ ତିଆରି ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
- ବସ୍ତୁର ଅବସ୍ଥାନ ଅନୁଯାୟୀ ଚକ୍ଷୁଲେନସ୍ର ଆକାର ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନ ହୋଇ ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନ ହୁଏ । କିନ୍ତୁ ସାଧାରଣ ଉଭଳ ଲେନସ୍ର ଆକାର ଅପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନୀୟ । ତେଣୁ ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା ସ୍ଥିର ।
15. ଲାଲ୍ ବଣ୍ଣକୁ କାହିଁକି ବିପଦ ସଙ୍କେତ ରୂପେ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରାଯାଏ ?
ଭ –
- ଦୃଶ୍ୟ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣାଳୀରେ ଲାଲ୍ ବର୍ଣ୍ଣର ଆଲୋକ ତରଙ୍ଗର ଦୈର୍ଘ୍ୟ ସର୍ବାଧ୍ଵ ।
- ଲାଲ୍ ବର୍ଷର ଆଲୋକ କୁହୁଡ଼ି, ଧୂଳିକଣା କିମ୍ବା କଲଏଡ୍ କଣିକାମାନଙ୍କ ଦ୍ବାରା ବିଚ୍ଛୁରଣ ହୁଏ ନାହିଁ । ଫଳରେ ଲାଲ୍ ଆଲୋକ ଅଧିକ ଦୂର ପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ ଗତି କରେ ।
16. ବସ୍ତୁ ଯେପରି ଅଛି ସେହିପରି ଧାରଣା ଦେବାରେ ଚକ୍ଷୁ କିପରି ସାହାଯ୍ୟ କରେ ଆଲୋଚନା କର ।
ଉ –
- କୌଣସି ବସ୍ତୁର ଆଲୋକ ରଶ୍ମିଗୁଚ୍ଛ ଆସି ସ୍ଵଚ୍ଛ ପଟ୍ଟଳ, ଜଳାଭରସ, ନେତ୍ରପିତୁଳା, ଚକ୍ଷୁଲେନସ୍ ଓ କାଚାଭରସ ଦେଇ ମୁକୁରିକାର ଆଲୋକ ସଂବେଦୀ ସେଲ୍ଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଉପରେ ପଡେ ।
- ଆଲୋକ ସଂବେଦୀ ସେଲ୍ରୁ ବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ସଂକେତ ନେତ୍ରସ୍ନାୟୁ ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ ମସ୍ତିଷ୍କକୁ ଯାଏ । ମସ୍ତିଷ୍କ ହିଁ ଓଲଟା ପ୍ରତିବିମ୍ବକୁ ସଳଖକରି ବସ୍ତୁ ଯେପରି ଅଛି ସେହିପରି ଧାରଣା ଦେବାରେ ସହାୟକ ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
17. ଗୋଟିଏ ଚକ୍ଷୁର ନିକଟବିନ୍ଦୁ 40 ସେ.ମି. । ଖବର କାଗଜ 25 ସେ.ମି. ଦୂରରେ ପଢ଼ିବା ପାଇଁ କେଉଁ ଲେନସ୍ ଓ କେତେ ପାୱାରର ଲେନସ୍ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିବ ?
ଉ –
u = – 25 cm, v = – 40 cm
\(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ -40 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ -25 }\) = – \(\frac { 1 }{ 40 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 25 }\) = \(\frac { 3 }{ 200 }\) ⇒ f = \(\frac { 200 }{ 3 }\)cm = + \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)m, p = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) = + \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\) = + 1.5 D
∴ 1.5 D ପାୱାର ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ଉତ୍ତଳ ଲେନସ୍ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିବ ।
![]()
18. ଦୂରଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଦୋଷ ଥିବା ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିର ନିକଟ ବିନ୍ଦୁ 1ମି ହେଲେ, ଏହାକୁ ଦୂର କରିବା ପାଇଁ କେତେ ପାୱାରର ଲେନ୍ସ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିବେ ? (ମନେକର ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟଦର୍ଶନର ନିମ୍ନତମ ଦୂରତା 25 ସେ.ମି.) ।
ଉ –
ଏଠାରେ v = 1 ମିଟର = – 100 ସେ.ମି., u = − 25 ସେ.ମି.
ଲେନ୍ସସର ପୂତ୍ର
\(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) ⇒ \(\frac { 1 }{ -100 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ -25 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) ⇒ \(\frac { -1+4 }{ 100 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) ⇒ \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) = \(\frac { 3 }{ 100 }\)
⇒ f = \(\frac { 100 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac { 100 }{ 3 }\) x \(\frac { 1 }{ 100 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) ମିଟର ∴ P = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) = \(\frac{1}{\frac{1}{3}}\) D = 3D = + 3.0D
∴ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ଜଣକ + 3.D ପାୱାର ଲେନସ୍ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିବେ ।
19. ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଥିବା ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିର ଚକ୍ଷୁ ସମ୍ମୁଖ ଦୂରବିନ୍ଦୁ ୫୦ ସେ.ମି. ଅଟେ । ଏହି ଦୋଷ ଦୂରୀକରଣ ପାଇଁ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ଲେନସ୍ର ପ୍ରକୃତି ଓ ପାଓ୍ବାର କ’ଣ ହେବ ?
ଉ –
f = – 80 cm = – \(\frac { 8 }{ 10 }\) ମି., P = – \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) = – \(\frac { 10 }{ 8 }\) = – 1.25D
ଏହି ଦୋଷ ଦୂର କରିବାପାଇଁ −1.25D ପାୱାର ଥିବା ଅବତଳ ଲେନସ୍ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିବାକୁ ହେବ ।
20. ଜଣେ ସମୀପ ଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଥିବା ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିଙ୍କ ପାଇଁ -5.5D ପାୱାରର ଲେନସ୍ ଏବଂ ତାଙ୍କର ଦୂରଦୃଷ୍ଟି ପାଇଁ +1.5D ପାୱାରର ଲେନ୍ସ ଆବଶ୍ୟକ ହୁଏ । ଏହି ଲେନ୍ସ ଦ୍ବୟର ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା କେତେ ନିର୍ଣ୍ଣୟ କର ।
ଊ –
- ଅବତଳ ଲେନ୍ସର ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା f1 = \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{P}_1}\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ -5.5 }\) ମି. = – 0.18 ମି.
- ଉତ୍ତଳ ଲେନ୍ସର ଫୋକସ୍ ଦୂରତା f2 = \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{P}_2}\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ +1.5 }\) ମି. = 0.67 ମି.







 ୧୯୩୬ ମସିହା ଏପ୍ରିଲ୍ ୧ ତାରିଖରେ ମଧୁସୂଦନ ଦାସ ଓ ମହାରାଜା କୃଷ୍ଣଚନ୍ଦ୍ର ଗଜପତିଙ୍କର ସ୍ଵପ୍ନ ବାସ୍ତବରେ ପରିଣତ ହୋଇଥିଲା ।
୧୯୩୬ ମସିହା ଏପ୍ରିଲ୍ ୧ ତାରିଖରେ ମଧୁସୂଦନ ଦାସ ଓ ମହାରାଜା କୃଷ୍ଣଚନ୍ଦ୍ର ଗଜପତିଙ୍କର ସ୍ଵପ୍ନ ବାସ୍ତବରେ ପରିଣତ ହୋଇଥିଲା ।


 α କଣିକା ।
α କଣିକା ।