Odisha State Board BSE Odisha 8th Class Hindi Solutions Chapter 6 घोड़े ने जान बचाई (जीवनी)Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
BSE Odisha Class 8 Hindi Solutions Chapter 6 घोड़े ने जान बचाई (जीवनी)
1. निम्न प्रश्नों के उत्तर दीजिए ।
(क) राणा प्रताप सवेरा होते ही क्या करते थे ?
उत्तर:
राणा प्रताप सवेराहोते ही कवच पहनकर हाथ में तलवार लेकर निकल पड़ते थे । बादशाह अकबर की फौज से उनका मुकावला कहीं न-कहीं हो जाता था । अकबर राणा को कब्जे में लाना चाहता था । राणा प्रताप ने उससे मेवाड़ मुक्त करने की प्रतिज्ञा की थी ।
(ख) चेतक के रूप-गुणों का वर्णन कीजिए ?
उत्तर:
घोड़ा चेतक महाराणा प्रताप का लड़ाई के मैदान में प्राणप्यारा साथी था। उसका रंग चमचमाता काला था । शरीर गठा हुआ था। वह किसी वीर से कम नथा । वह जैसे युद्ध विद्या जानता था । दुश्मन की चाल पहचानता था, उछलकर दुश्मन का वार व्यर्थ करता था । कई बार राणा की जान बचाई थी ।
![]()
(ग) हल्दीयाटी में हुए युद्ध का वर्णन कीजिए ।
उत्तर:
हल्दीघाटी में महाराणा प्रताप के मुट्ठी भर सैनिक और शाहजादा सलीम के नेतृत्व में आई विशाल मुगल सेना के बीच घमासान लड़ाई हुई । युद्ध में सलीम का हाथी मारा गया, लेकिन वह बच गया ।महाराणा प्रताप ने अपनी तलवार से मुगल सैनिकों को मार गिराया । महाराणा के सिर पर मुकुट देखकर मुगल सौनिकों ने उन्हें घेर लिया, पर वे नहीं हटे ।
(घ) युद्ध में प्रताप ने क्या किया ?
उत्तर:
युद्ध में प्रताप ने अनंगिनत मुगल सौनिकों को मार गिराया । उनका मुकुट देखकर मुगल सैनिकों ने उनको घेर लिया । राणा अकेले पड़ गए। उनको कई चोटें आई, पर वे पीछे नहीं हटे । चेतक उन्हें युद्ध भूमि से ले जाते समय उन्होंने चेतक को रोकना चाहा । लोग उन्हें भगोड़ा न समझें इसलिए वे भागना नहीं चाहते थे ।
(ङ) चेतक प्रताप को लेकर कैसे भागा ?
उत्तर:
चेतक बहुत होशियार घोड़ा था । उसने भाँप लिया था राणा जख्मी हो गए हैं। वह मान्ना की बात सुन कर राणा को लेकर तेजी से भागा । राणा का हुक्म नहीं माना । उसे राणा को बचानाथा । दौड़ते – दौड़ते हाँफ़ने लगा। लड़खड़ाया, फिर उछला, नाला कूदकर पार किया पर धड़ाम् से गिरा और दम तोड़ दिए ।
(च) राणा चेतक की मौत से क्यों दु:खी हुए ?
उत्तर:
चेतक लड़ाई के मैदान में राणा का प्राण-प्यारा साथी था। वह दुश्मन की चाल समझता था। वह ऐन वक्त पर उछलकर दुश्मन का बार व्यर्थ कर देता था। कई बार राणा की जान बचाई थी । हल्दीघाटी से ले आकर उसने राणा को बचाया। राजपूती शान बचाई । उसकी छाती में तलवार भोंक दी गई थी। उसकी मौत हो गई तो राणा रोने लगे और शक्ति से कहा किमैं चेतक के बिना जी नहीं सकता ।
(छ) चेतक का नाम क्यों अमर हुआ ?
उत्तर:
चेतक एक विचक्षण घोड़ा था । लड़ाई के मैदान में वह राणा प्रताप का प्राण प्यारा साथी था; दुश्मन की चाल पहचानता था; उछलकर दुश्मन का वार व्यर्थ कर देता था । उसने कई बार राणा की जान बंचाई । हल्दीघाटी से राणा को ले आकर बचाया । राजपूती शान बचाई । अपनी वीरता, समझदारी और वफादारी के लिए उसका नाम अमर हो गया ।
![]()
(ज) आज चेतक की मूर्त्तियाँ कहाँ – कहाँ मिलती हैं ?
उत्तर:
आज राजस्थान के चौके-चौराहे, रास्ते, भवन- सब पर चेतक की मूर्त्तियाँ मिल जाती हैं ।
(क्ञ) शक्ति सिंह को किसे और क्या शिक्षा मिली ?
उत्तर:
महाराणा प्रताप का छोटा भाई शक्ति सिंह मुगलों के पक्ष में था । हल्दीघाटी युद्ध भूमि से चेतक राणा को लेकर भागा । शक्ति सिंह उनके पीछे-पीछे आकर उनके पास पहुँचा । उसने पहले मात्रा का मातृभूमि – प्रेम और वीरता देखी, अब चेतक का बलिदांन देखा । इन दोनों से उसे मातृभूमि – प्रेम की शिक्षा मिली ।
2. इन प्रश्नों का जवाब एक या दो वाक्यों में दीजिए ।
(क) राणा प्रताप का जीवन कैसा था ?
उत्तर:
राणा प्रताप का जीवन ही रणक्षेत्र था ।
(ख) लड़ाई में राणा का साथी कौन था ?
उत्तर:
लड़ाई में राणा का साथी चेतक था ।
(ग) चेतक युद्ध के मैदान में क्या करता था ?
उत्तर:
चेतक युद्ध के मैदान में उछल कर दुश्मन का वार व्यर्थ कर देता था। वह राणा की जान भी बचाता था ।
(घ) चेतक देखने में कैसा था ?
उत्तर:
चेतक का रंग चमचमाता काला था, शरीर गठा हुआ था।
(ङ) घोड़े का होशियार होना क्यों जरूरी है ?
उत्तर:
घुड़सवार के लिए उसके घोड़े का होशियार होना बहुत जरूरी है, क्योंकि वह अपने मालिक को ऐन वक्त पर बचा सकता है ।
(च) राणा ने चेतक की पीठ थपथपाई तो उसने क्या जवाब दिया ?
उत्तर:
राणा ने चेतक की पीठ थपथपाई तो चेतक ने कान फड़फड़ाए ।
![]()
(छ) झाला वीर ने मुकुट अपने सिर पर क्यों रखा ?
उत्तर:
मुकुट को देख मोगल फौजी राणा पर हमला करते थे । राणा को वे पहचान न सकें, इसलिए झाला वीर ने मुकुट अपने सिर पर रखा ।
(ज) प्रताप की तलवार फसल काट रही थी – इसका मतलब क्या है ?
उत्तर:
प्रताप बड़ी तेजी से अनगिनत मुगल सौनिकों को मार गिराते थे ।
(झ) मान्ना ने प्रताप से चले जाने को क्यों कहा ?
उत्तर:
मान्ना ने प्रताप के गहरे घाव देखकर उनसे चले जाने को कहा, क्योंकि वे जीवित रहेंगे तो लड़ाई चलती रहेगी ।
(ज) राणा चेतक को क्यों रोक रहे थे ?
उत्तर:
लोग राणा को भगोड़ा न समझें इसलिए राणा चेतक को रोक रहे थे ।
![]()
(ट) चेतक क्यों भागा ?
उत्तर:
चेतक महाराणा प्रताप की जान बचाने के लिए उनको लेकर भागा ।
(ठ) चेतक क्यों गिर पड़ा ?
उत्तर:
चेतक की छाती में तलवार भोंक दी गई थी। घाव से खून बह रहा था । वह हाँफ़ने लगा था । शक्तिहींन होकर वह गिर पड़ा ।
(ड) शक्ति सिंह प्रताप के पाँव क्यों पड़ा ?
उत्तर:
शक्ति सिंह ने अपनी आँखों से मात्रा का मातृभूमि प्रेम और वीरता तथा चेतक की प्रभु-भक्ति और बलिदान देखा तो उसने अपनी गलती समझी और माफी माँगकर प्रताप के पाँव पड़ा ।
3. सही विकल्प चुनकर लिखिए।
(क) महाराणा प्रताप का साथी कौन था?
(i) ज्ञान
(ii) संग्राम
(iii) पूजा
(iv) वार्तालाप
उत्तर:
(ii) संग्राम
(ख) प्रताप ने कहा – “प्राण दूँगा पर मुक्त करूँगा”, किससे ?
(i) चेतक
(ii) दुश्मन
(iii) मेवाड़
(iv) शक्ति सिंह
उत्तर:
(iii) मेवाड़
(ग) चेतक ने क्या फड़फड़ाए ?
(i) हाथ
(ii) पूँछ
(iii) कान
(iv) पीठ
उत्तर:
(iii) कान
(घ) सलीम का क्या मारा गया ?
(i) घोड़ा
(ii) कुत्ता
(iii) चेतक
(iv) हाथी
उत्तर:
(iv) हाथी
![]()
(ङ) कौन प्रताप के पाँवों पर गिरा?
(i) सलीम
(ii) अकबर
(iii) शक्ति सिंह
(iv) चेतक
उत्तर:
(ii) शक्तिसिंह
भाषा ज्ञान
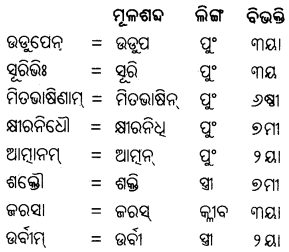
1. इन शब्दों के लिंग बताइए –
युद्ध, जंग, लड़ाई, संग्राम, जीवन, सैनिक, कवच, तलवार, मुकाबला, कब्जा, जान, फ़ौज, सेना, प्रतिज्ञा, देह, शरीर, हालत, पीठ, गर्दन, जीभं, पूँछ, जीत, हार,
गली, पहाड़ी, घाटी, फसले, आँधी, आवाज, जय, चोट, छाती, धारा, आँख, काम, मूर्ति, वीरता, वफादारी, समझ, समझदारी ।
उत्तर:
![]()
2. वचन बदलिए –
घोड़ा, आदमी, लड़ाई, आँख, कान, घाव, कवच
उत्तर:

3. समानार्थी शब्द लिखिए ।
युद्ध, प्रतिज्ञा, फौज, जान, छाती, वक्त, घाव
उत्तर:

4. ‘क’ विभाग के विशेषण शब्दों को ‘ख़’ विभाग के संज्ञा शब्दों से जोड़िए।
‘क’ विभाग — ‘ख’ विभाग
खाली — चाल
गठा हुआ — वक्त
हरा — सैनिक
ऐन — शरीर
विशाल — वार
मेरी — फौज
अनगिनत — गर्दन
बादशाही — सेना
उत्तर:
‘क’ विभाग — ‘ख’ विभाग
खाली– वार
गठा हुआ — शरीर
हर — चाल
ऐन — वक्त
विशाल — सेना
मेरी — गर्दन
अनगिनत — सैनिक
बादशाही — फौज
5. इन वाक्यों में एक-एक सर्वनाम है, उनको छाँटकर लिखिए।
(क) उन पर कई चोटें आईं ।
उत्तर: उन
(ख) आप रहेंगे तो लड़ाई चलती रहेगी ।
उत्तर: आप
(ग) मैं काफी हूँ।
उत्तर: मैं
(घ) उन्होंने बड़ी फुर्ती से हमला किया ।
उत्तर: उन्होंने
(ङ) वह बेतहाशा भागा ।
उत्तर: वह
6. निम्नलिखित शब्दों में से संज्ञाओं को छाँटिए ।
लड़ाई, खाली, लोहा, दुश्मन, खुश, घोड़ा, मूर्ति, वीरता, बोला, के साथ, उनके, हुक्म, गठा, प्यारा, प्राण, भाई, गर्दन, मेरी ।
उत्तर:
दुश्मन, घोड़ा, मूर्ति, वीरता, प्राण, भाई, गर्दन
![]()
7. कोष्ठक में से सही परसर्ग चुनकर शून्य स्थान भरिए। (ने, को, से, के लिए, में )
(क) प्रताप ………… प्रतिज्ञा की थी ।
उत्तर: ने
(ख) वह किसी वीर ………… कम न था ।
उत्तर: से
(ग) रण ………… उसने राजा की जान बचाई थी।
उत्तर: में
(घ) वह राणा ………… लेकर बेतहाशा भागा।
उत्तर: को
(ङ) में भी वतन ………… जान दूँगा ।
उत्तर: के लिए
जानिए :
इन वाक्यों को देखिए। कर्ता के साथ ‘ने’ विभक्ति लगी है तो वाक्य कैसे बदल जाते हैं। क्रिया कर्ता के अनुसार नहीं चलती । ‘ने’ विभक्ति भूतकाल में ही प्रयुक्त होती है ।
जैसे –
उत्तर:
राणा ने प्रतिज्ञा की थी ।
उन्होंने फुर्त्ती से हमला किया ।
उसने राणा की जान बचाई ।
चेतक ने दम तोड़ दिए।
राणा ने चेतक की पीठ थपथपाई।
चेतक ने मेरी आँखें खोल दीं ।
मान्ना ने प्रताप की बुरी हालत देखी ।
![]()
– इन विशेष कथनों को (मुहावरों को) शिक्षक समझा दें –
लोहा लेना, जान बचाना, पीठ थपथपाना, दम तोड़ देना
उत्तर:
लोहा लेना – लड़ाई करना ।
जान घचाना – प्राण रक्षा करना ।
पीठ थपथपाना – प्यार जताना ।
दम तोड़ देना – प्राण त्याग करना ।
परीक्षोपयोगी अतिरिक्त प्रश्नोत्तर
एक-एक वाक्य में उत्तर दीजिए :
प्रश्न 1.
संग्राम किसका साथी था ?
उत्तर:
संग्राम महाराणा प्रताप का साथी था।
प्रश्न 2.
राणा प्रताप का जीवन कैसा था ?
उत्तर:
राणा प्रताप का जीवन रणक्षेत्र था।
प्रश्न 3.
किसका जीवन रणक्षेत्र था ?
उत्तर:
महाराणा प्रताप का जीवन रणक्षेत्र था।
प्रश्न 4.
महाराणा के वीर सैनिक किससे नहीं छरते थे ?
उत्तर:
महाराणा के वीर सैनिक संग्राम से नहीं डरते थे ।
प्रश्न 5.
सवेरा होते ही महाराणा प्रताप क्या करते थे ?
उत्तर:
सवेरा होते ही महाराणा प्रताप कवच पहनकर, हाथ में तलवार लेकर निकल पड़ते थे ।
![]()
प्रश्न 6.
महाराणा प्रताप का किससे मुकावला हो जाता था ?
उत्तर:
महाराणा मताप का अकबर बादशाह की फैज से मुकाबला हो जाता था।
प्रश्न 7.
अकबर किसको अपने कब्दे में करना चाहते थे ?
उत्तर:
अकबर राणा को अपने कब्जे में करना चाहते थे।
प्रश्न 8.
प्रताप ने क्या प्रतिज्ञा की थी ?
उत्तर:
प्रताप ने प्रतिज्ञा की थी – प्राण दूँगा पर मेवाड़ को मुक्त करूँगा।
प्रश्न 9.
कौन लड़ाई के मैदान में राणा का प्रापा प्यारा साथी था?
उत्तर:
घोड़ा चेतक लड़ाई के मैदान में राणा का प्राणप्यारा साथी था।
प्रश्न 10.
चेतक का रंग कैसा था?
उत्तर:
चेतक का रंग चमचमाता श्याम था।
प्रश्न 11.
युद्ध के मैदान में चेतक क्या पहचान लेता था ?
उत्तर:
युद्ध के मैदान में चेतक दुश्मन की हर चाल को पहचान लेता था।
प्रश्न 12.
चेतक युद्ध के मैदान में क्या करता था ?
उत्तर:
चेतक युद्ध के मैदान में ऐन वक्त पर ऐसा उछलता कि दुश्मन का वार खाली जाता।
प्रश्न 13.
रण में चेतक ने राणा का क्या उपकार किया था?
उत्तर:
रण में चेतक ने कई बार राणा की जान बचाई थी ।
![]()
प्रश्न 14.
चेतक कब बहुत खुश हो जाता था ?
उत्तर:
चेतक तब बहुत खुश हो जाता था, जब राणा उस पर सवार हो जाते थे ।
प्रश्न 15.
घोड़े का होशियार होना किसके लिए जरूरी है ?
उत्तर:
घोड़े का होशियार होना घुड़सवार के लिए जरूरी है।
प्रश्न 16.
राणा लड़ाई के लिए कहाँ जा रहे थे ?
उत्तर:
राणा लड़ाई के लिए हल्दीघाटी की सैकरी गली में जा रहे थे।
प्रश्न 17.
राणा ने चेतक की पीठ थपथपाई तो उसने क्या जवाब दिया ?
उत्तर:
राणा ने चेतक की पीठ थपथपाई तो उसने अपने कान फड़फड़ाए।
प्रश्न 18.
राणा ने चेतक को पुचकारा तो चेतक क्या करने लगा?
उत्तर:
राणा ने चेतक को पुचकारा तो चेतक पूँछ हिलाने लगा।
प्रश्न 19.
चेतक जैसे हिनहिनाकर क्या बोल रहा था ?
उत्तर:
चेतक जैसे हिनहिनाकर बोल रहा था – राणा! मैं तो तुम्हें लेने को हर दम तैयार हूँ।
प्रश्न 20.
कितने सैनिक लेकर राणा हल्दीयाटी में उतरे ?
उत्तर:
अपनी मुट्ठी भर सैनिक लेकर राणा हल्दीघाटी में उतरे।
प्रश्न 21.
राणा ने हल्दीघाटी में माथे पर क्या लगाया ?
उत्तर:
राणा ने हल्दीघाटी में माथे पर चुटकी भर धूल लगाई।
प्रश्न 22.
राणा जब मातृभूमि को प्रणाम कर रहे थे, तब क्या हुआ ?
उत्तर:
राणा जब मातृभूमि को प्रणाम कर रहे थे, तब मुगलिया फौज टिड्डियों भी भाँति आ धमकी ।
![]()
प्रश्न 23.
कौन मुगलिया फौज लेकर जंग जीतने आया था ?
उत्तर:
शाहजादा सलीम मुगलिया फौज लेकर जंग जीतने आया था।
प्रश्न 24.
शाहजादा सलीम ने हल्दीघाटी में पहुँचकर क्या किया?
उत्तर:
शाहजादा सलीम ने हल्दीघाटी में पहुँचकर बड़ी फुर्ती से हमला किया।
प्रश्न 25.
युद्ध में किसका हाथी मारा गया ?
उत्तर:
युद्ध में सलीम का हाथी मारा गया।
प्रश्न 26.
मुगलिया फौज राणा पर कैसे टूट पड़ी ?
उत्तर:
मुगलिया फौज राणा पर आँधी-सी टूट पड़ी ।
प्रश्न 27.
क्या देखकर मुगलिया फौजी राणा पर हमला करते थे?
उत्तर:
राणा के सिर पर मुकुट देखकर मुगलियां फौजी राणा पर हमला करते थे ।
प्रश्न 28.
किसने राणा प्रताप की बुरी हालत देखी ?
उत्तर:
झाला वीर मान्ना ने दूर से राणा प्रताप की बुरी हालत देखी।
प्रश्न 29.
झाला वीर ने राणा की तरफ झपटकर क्या किया ?
उत्तर:
झाला वीर ने राणा’ की तरफ झपटकर पीछे से उनका मुकुट छीन कर अपने सिर पर रखा ।
प्रश्न 30.
झाला वीर ने राणा का मुकुट अपने सिर पर क्यों रखा?
उत्तर:
झाला वीर ने राणा का मुकुट अपने सिर पर रखा क्योंकि इससे मुगलिया सैनिक राणा को पहचान नहीं सकेंगे और राणा की जान बच जाएगी।
प्रश्न 31.
माना ने राणा से क्या अनुरोध किया ?
उत्तर:
मान्ना ने राणा से अनुरोध किया कि आप अपनी जान बचाइए, आप रहेंगे तो हमारी लड़ाई चलती रहेगी।
प्रश्न 32.
किसने कहा कि में मुगलिया फौज के लिए काफी हूँ?
उत्तर:
झाला वीर मात्रा ने कहा कि मैं मुगलिया फौज के लिए काफी हूँ।
प्रश्न 33.
चेतक पहले क्या भाँप चुका था ?
उत्तर:
चेतक पहले भाँप चुका था कि राणा जखी हो गए हैं।
![]()
प्रश्न 34.
चेतक ने राणा को बचाने के लिए क्या किया ?
उत्तर:
चेतक ने राणा को बचाने के लिए राणा को लेकर झाइ-झखाड़ों में बेतहाशा भागा ।
प्रश्न 35.
चेतक क्यों भागा ?
उत्तर:
चेतक राणा को बचाने के लिए भागा।
प्रश्न 36.
चेतक जब राणा को लेकर भाग रहा था, तब राणा क्या चिल्ला उठे ?
उत्तर:
चेतक जब राणा को लेकर भाग रहा था, तब राणा चिल्ला उठे – चेतक ! लोग मुझे भगोड़ा समझेंगे, रुक जा।
प्रश्न 37.
राणा चेतक को क्यों रोक रहे थे ?
उत्तर:
राणा लड़ाई का मैदान छोड़कर भागना नहीं चाहते थे, इसलिए वे चेतक को रोक रहे थे।
प्रश्न 38.
चेतक ने नाला कैसे पार किया ?
उत्तर:
चेतक ने कूदकर नाला पार किया।
प्रश्न 39.
चेतक कब गिर पड़ा ?
उत्तर:
कूदकर सामने का नाला पार करके चेतक गिर पड़ा।
प्रश्न 40.
चेतक क्यों गिर पढ़ा ?
उत्तर:
चेतक की छाती में तलवार भाँक दी गई थी और घाव से खून की धारा बह रही थी, इसलिए वह शक्तिहीन होकर गिर पड़ा।
प्रश्न 41.
राणा प्रताप क्यों रोने लगे ?
उत्तर:
राणा प्रताप ने जब देखा कि चेतक की छाती में तलवार भोंक की गई है, और उससे खून की धारा बह रही है, तब वे रोने लगे।
प्रश्न 42.
राणा के भाई का नाम क्या था ?
उत्तर:
राणा के भाई का नाम शक्ति सिंह था ।
प्रश्न 43.
शक्ति सिंह किसके साथ था?
उत्तर:
शक्ति सिंह मुगलों के साथ था ।
प्रश्न 44.
शक्ति सिंह ने राणा को भागते हुए देखकर क्या किया?
उत्तर:
शक्ति सिंह ने राणा को भागते हुए देखकर उनका पीछा करके फौरन वहाँ पहुँचा गया, जहाँ चेतक ने दम तोड़ दिए थे।
प्रश्न 45.
शक्ति सिंह को देखकर राणा ने क्या कहा ?
उत्तर:
शक्ति सिंह को देखकर राणा ने कहा, “आ जा शक्ति, मेरी गर्दन उड़ा दे, अपने चेतक के बिना में जी नहीं सकता।”
![]()
प्रश्न 46.
शक्ति सिंह ने राणा प्रताप की बात सुनकर क्या किया?
उत्तर:
शक्ति सिंह ने राणा प्रताप की बात सुनकर उनके पाँव पर गिरा ।
प्रश्न 47.
शक्ति सिंह प्रताप के पाँव क्यों पड़ा ?
उत्तर:
झाला और चेतक ने शक्ति सिंह की आँखें खोल दीं, इसलिए वह प्रताप के पाँव पड़ा।
प्रश्न 48.
अपनी गलती समझने के बाद शक्ति सिंह ने क्या करने को कहा ?
उत्तर:
अपनी गलती समझे के बाद शक्ति सिंह ने वतन के लिए जान देना चाहा।
प्रश्न 49.
चेतक का नाम क्यों अमर हो गया ?
उत्तर:
अपनी वीरता, समझदारी और वफादारी के लिए चेतक का नाम अमर हो गया ।
प्रश्न 50.
चेतक ने क्या-क्या बचाया ?
उत्तर:
चेतक ने प्रताप की जान बचाई, राजपूती शान बचाई।
प्रश्न 51.
आज भी चेतक की मूर्तियाँ कहाँ-कहाँ खड़ी हैं ?
उत्तर:
आज भी चेतक की मूर्तियाँ राजस्थान के चौके-चौराहे, रास्ते, भवन सब पर खड़ी हैं ।
मे एक या दो शब्द में उत्तर दीजिए :
प्रश्न 1.
संग्राम किसका साथी था ?
उत्तर:
महाराणा प्रताप का
प्रश्न 2.
लड़ाई में जाने से पहले महाराणा प्रताप क्या पहन लेते थे ?
उत्तर:
कवच
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
कौन राणा को अपने कब में करना चाहता था ?
उत्तर:
अकबर
प्रश्न 4.
राणा ने किसे मुक्त करने की प्रतिज्ञा की थी ?
उत्तर:
मेवाड़ को
प्रश्न 5.
लड़ाई के मैदान में राणा का प्राणप्यारा साथी कौन था ?
उत्तर:
घोड़ा चेतक।
प्रश्न 6.
चेत्रक का रंग कैसा था ?
उत्तर:
काला
प्रश्न 7.
चेतक का क्या करने से दुश्मन का वार खाली जाता था?
उत्तर:
ऐन वक्त पर उछलने से
प्रश्न 8.
राणा किस की संकरी पहाड़ी गली में लड़ने निकले ?
उत्तर:
हल्दीघाटी की
प्रश्न 9.
हल्दीघाटी की लंड़ाई में उतरते समय राणा ने माथे पर क्या लगाया ?
उत्तर:
चुटकी भर धूल ।
प्रश्न 10.
राणा से लड़कर जंग जीतने कौन आया था ?
उत्तर:
शाहजादा सलीम
प्रश्न 11.
युद्ध में किसका हाथी मारा गया।
उत्तर:
सलीम का
प्रश्न 12.
क्या देखकर मुगल फौजी राणा पर हमला करते थे ?
उत्तर:
उनके सिर पर मुकुट
प्रश्न 13.
किसने राणा के सिर से मुकुट छीन लिया ?
उत्तर:
मान्ना ने
प्रश्न 14.
क्या पार करके चेतक गिर पड़ा ?
उत्तर:
नाला
प्रश्न 15.
चेतक के शरीर के किस स्थल से खून बह रहा था ?
उत्तर:
छाती से
प्रश्न 16.
मुगलों के साथ रहनेवाले राणा के भाई का नाम क्या था?
उत्तर:
शक्ति सिंह
![]()
प्रश्न 17.
शक्ति सिंह ने किससे कहा-मुझे माफ कर दो ।
उत्तर:
राणा प्रताप से
प्रश्न 18.
शक्ति सिंह की आँखें किन्होंने खोल दीं ?
उत्तर:
झाला और चेतक ने
प्रश्न 19.
किसने राणा की जान बचाई थी ?
उत्तर:
चेतक ने
प्रश्न 20.
आज कहाँ के चौके-चौराहों पर चेतक की मूर्तियाँ खड़ी हैं ?
उत्तर:
राजस्थान के
मातृभाषा में अनुवाद कीजिए :
प्रश्न 1.
संग्राम महाराणा प्रताप का साथी था ।
उत्तर:
ସଂଗ୍ରାମ ମହାରାଣା ପ୍ରତାପଙ୍କର ସାଥୀ ଥିଲା।
प्रश्न 2.
न तो वे कभी संग्राम से डरते थे, न उनके वीर सैनिक भी ।
उत्तर:
ନା ତ ସେ କେବେ ସଂଗ୍ରାମକୁ ଡରୁଥିଲେ, ନା ତାଙ୍କ ବୀର ସୈନିକ ମଧ୍ୟ ।
प्रश्न 3.
सवेरा हुआ नहीं कि वे कवच पहनकर, हाथ में तलवार लेकर निकल पड़ते थे ।
उत्तर:
ସକାଳ ନ ହେଉଣୁ ସେ କବଚ ପିନ୍ଧି ହାତରେ ଖଣ୍ଡା ଧରି ବାହାରିପଡ଼ୁଥଲେ।
प्रश्न 4.
अकबर बादशाह की फौज से कहीं-न-कहीं मुकाबला हो जाता था ।
उत्तर:
ବାଦଶାହ ଆକବରଙ୍କ ସେନା ସହିତ କେଉଁଠି ନା କେଉଁଠି
प्रश्न 5.
अकबर राणा को अपने कब्जे में करना चाहता था ।
उत्तर:
ଆକବର ରାଣାଙ୍କୁ ତାଙ୍କ ଅଧୀନକୁ ନେଇ ନେବାକୁ ଚାହୁଁଥିଲେ।
प्रश्न 6.
प्रताप ने प्रतिज्ञा की थी- प्राण दूँगा; पर मेवाड़ को मुक्त करूँगा ।
उत्तर:
ପ୍ରତାପ ପ୍ରତିଜ୍ଞା କରିଥିଲେ – ପ୍ରାଣ ଦେବି; କିନ୍ତୁ ମେଣ୍ଢାରକୁ ମୁକ୍ତ କରିବି ।
प्रश्न 7.
लड़ाई के मैदान में राणा का प्राणप्यारा साथी था उनका घोड़ा चेतक ।
उत्तर:
ଯୁଦ୍ଧକ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ରାଣାଙ୍କର ପ୍ରାଣପ୍ରିୟ ସାଥୀ ଥୁଲା – ତାଙ୍କ ଘୋଡ଼ା ଚେତକ ।
![]()
प्रश्न 8.
चमचमाता श्याम रंग, गठा हुआ शरीर ।
उत्तर:
ହଳଦୀଘାଟୀର ସଂକୀର୍ଣ୍ଣ ପାହାଡ଼ିଆ ଗଳି (ରାସ୍ତା) ।
प्रश्न 9.
वह भी जैसे युद्धविद्या जानता था ।
उत्तर:
ସେ ମଧ୍ଯ ସତେଯେପରି ଯୁଦ୍ଧବିଦ୍ୟା ଜାଣିଥିଲା ।
प्रश्न 10.
ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ହିଁ ଆମ ଗାଁ ଅଣୁ ଗ ମିଶା ଥ ।
उत्तर:
ଶତ୍ରୁର ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ଚାଲ (କୌଶଳକୁ) ୟେ ଜାଣିପାରୁଥିଲା।
प्रश्न 11.
ऐन वक्त पर ऐसा उछलता कि दुश्मन का वार खाली
उत्तर:
(ସେ) ଠିକ୍ ସମୟରେ ଏପରି ଡେଇଁପଡ଼ୁଥିଲା ଯେ ଶତ୍ରୁର ଆକ୍ରମଣ ନିଷ୍ଫଳ ହୋଇଯାଉଥିଲା ।
प्रश्न 12.
रण में उसने कई बार राणा की जान बचाई थी ।
उत्तर:
ରଣକ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ସେ ଅନେକଥର ରାଣାଙ୍କ ପ୍ରାଣରକ୍ଷା କରିଥିଲା ।
प्रश्न 13.
घुड़सवार के लिए उसके घोड़े का हाशियार होना बहुत जरूरी है ।
उत्तर:
ଅଶ୍ଵାରୋହୀ ପାଇଁ ତା’ ଅଶ୍ଵ ବୁଦ୍ଧିମାନ୍ ହେବା ଅତ୍ୟନ୍ତ ଆବଶ୍ୟକ ।
प्रश्न 14.
हल्दीघाटी की सँकटी पहाड़ी गली ।
उत्तर:
ଦୀପ୍ତିମାନ କଳାରଙ୍ଗ, ସୁଗଠିତ ଶରୀର।
![]()
प्रश्न 15.
विशाल मुगल सेना का यहीं आसानी से सामना किया जा सकता जा सकता है ।
उत्तर:
ବିଶାଳ ମୋଗଲ ସୈନ୍ୟବାହିନୀକୁ ଏହିଠାରେ ହିଁ ସହଜରେ ସମ୍ମୁଖୀନ (ସାମନା) କରାଯାଇପାରିବ ।
प्रश्न 16.
वैसे तो वे पहले कई बार बादशाही फौज से लोहा ले चुके थे ।
उत्तर:
ସେପରି ତ ସେ ଆଗରୁ ଅନେକଥର ବାଦଶାହଙ୍କ ସୈନ୍ୟବାହିନୀ ସହିତ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ କରିସାରିଥିଲେ।
प्रश्न 17.
मगर आज की लड़ाई तो हर हालत में जीतनी होगी ।
उत्तर:
କିନ୍ତୁ ଆଜିର ଯୁଦ୍ଧକୁ ତ ଯେ କୌଣସି ଉପାୟରେ ଜିଣିବାକୁ ପଡ଼ିବ।
प्रश्न 18.
मुगल राजपूती शौर्य की शान देखें ।
उत्तर:
ମୋଗଲ ରାଜପୁତାମାନଙ୍କ ପରାକ୍ରମର ଶକ୍ତି ଦେଖନ୍ତୁ ।
प्रश्न 19.
राणा ने चेतक की पीठ थपथपाई ।
उत्तर:
ରାଣା ଚେତକର ପିଠିକୁ ଥାପୁଡ଼େଇଦେଲେ।
प्रश्न 20.
राणा ने पुचकारा तो वह पूँछ हिलाने लगा ।
उत्तर:
ରାଣା ସ୍ନେହରେ ଚୁ-ଚୁ କଲେ ତ ସେ ଲାଞ୍ଜ ହଲାଇବାକୁ ଲାଗିଲା ।
प्रश्न 21.
मैं तो तुम्हें लेने को हरदम तैयार हूँ.
उत्तर:
ମୁଁ ତ ତୁମକୁ ନେବାପାଇଁ ସଦାସର୍ବଦା ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ ଅଛି ।
प्रश्न 22.
अपनी मुट्ठी भर सैनिक लेकर राणा हल्दीघाटी में उतरे।
उत्तर:
ନିଜର ସୀମିତ ସୈନିକଙ୍କୁ ନେଇ ରାଣା ହଳଦୀଘାଟିରେ ପ୍ରବେଶ କଲେ।
प्रश्न 23.
(उन्होंने) माथे पर चुटकी भर धूल लगाई ।
उत्तर:
(ସେ) ଟିପେ ଧୂଳି ନେଇ ମସ୍ତକରେ ଲଗାଇଲେ ।
![]()
प्रश्न 24.
मुग़लिया फौज टिड्डियों की भॉति आ धमकी ।
उत्तर:
ମୋଗଲ ସୈନ୍ୟଦଳ ପଙ୍ଗପାଳ ଦଳ ଭଳି ଆସି ପହଞ୍ଚିଗଲେ।
प्रश्न 25.
राणा ने देखा-शाहजादा सलीम जंग जीतने आया है ।
उत्तर:
ରାଣା ଦେଖିଲେ ରାଜକୁମାର ସଲୀମ ଯୁଦ୍ଧରେ ଜିଣିବା ପାଇଁ ଆସିଛନ୍ତି ।
प्रश्न 26.
उन्होंने बड़ी फुर्ती से हमला किया ।
उत्तर:
ସେ ଖୁବ୍ ଶୀଘ୍ର ଆକ୍ରମଣ କରିଦେଲେ।
प्रश्न 27.
उसकी फौज राणा पर आँधी-सी टूट पड़ी ।
उत्तर:
ତାଙ୍କ ସୈନ୍ୟବାହିନୀ ରାଣାଙ୍କଉପରେ ଝଡ଼ ଭଳି ଆକ୍ରମଣ କରିଦେଲେ ।
प्रश्न 28.
प्रताप की तलवार मानों फसल काटने लगी।
उत्तर:
ପ୍ରତାପଙ୍କ ଖଣ୍ଡା ସତେଯେପରି ଫସଲ କାଟିଲା ଭଳି ଲାଗିଲା।
प्रश्न 29.
मुकुट को देख फौजी उन पर हमला करते थे ।
उत्तर:
ମୁକୁଟ ଦେଖୁ ସୈନ୍ୟମାନେ ତାଙ୍କ ଉପରେ ଆକ୍ରମଣ କରୁଥିଲେ ।
प्रश्न 30.
राणा अकेले पड़ गए।
उत्तर:
ରାଣା ଏକୁଟିଆ ପଡ଼ିଗଲେ (ହୋଇଗଲେ)।
प्रश्न 31.
उन पर कई चोटें आईं ।
उत्तर:
ତାଙ୍କ ଦେହରେ ଅନେକ ଆଘାତ ଲାଗିଲା।
प्रश्न 32.
दूर से झाला वीर मान्ना ने प्रताप की बुरी हालत देखी।
उत्तर:
ଦୂରରୁ ଝାଲା ବୀର ମାନ୍ନା ପ୍ରତାପଙ୍କର ଏହି ଖରାପ ଅବସ୍ଥା ଦେଖିଲେ ।
प्रश्न 33.
वह उनकी तरफ झपटा।
उत्तर:
ସେ ତାଙ୍କ ଆଡ଼କୁ ଜୋରରେ ମାଡ଼ିଆସିଲେ।
प्रश्न 34.
आवाज गूँज उठी।
उत्तर:
ଶବ୍ଦ ପ୍ରତିଧ୍ଵନିତ ହେଲା
प्रश्न 35.
मान्ना ने पीछे से मुकुट छीनकर अपने सिर पर रखा ।
उत्तर:
ମାନ୍ନା ପଛପଟୁ ମୁକୁଟ ଛଡ଼େଇ ନେଇ ନିଜ ମୁଣ୍ଡ ଉପରେ ରଖିଲେ ।
प्रश्न 36.
आपके घाव गहरे है ।
उत्तर:
ଆପଣଙ୍କ କ୍ଷତ ବହୁତ ଗଭୀର ହୋଇଛି।
प्रश्न 37.
आप रहेंगे तो हमारी लड़ाई चलती रहेगी।
उत्तर:
ଆପଣ ରହିଲେ ଆମ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ ଚାଲୁରହିବ।
प्रश्न 38.
अभी मैं इनके लिए काफी हैं।
उत्तर:
ଏବେ ମୁଁ ଏମାନଙ୍କ ପାଇଁ ଯଥେଷ୍ଟ ।
प्रश्न 39.
चेतक तो पहले भाँप चुका था कि राणा जख्मी हो गए हैं।
उत्तर:
ଚେତକ ତ ପ୍ରଥମରୁ ଅନୁମାନ କରିସାରିଥିଲା ଯେ ରାଣା ’ଆଘାତପ୍ରାପ୍ତ ହୋଇଯାଇଛନ୍ତି ।
![]()
प्रश्न 40.
अब वह राणा को लेकर बेतहाशा भागा ।
उत्तर:
ଏବେ ସେ ରାଣାକୁ ନେଇ ଖୁବ୍ ଜୋରରେ ଧାଇଁଲା ।
प्रश्न 41.
झाड़-इंखाड़ों में तेजी से भागना तो उसका खेल था ।
उत्तर:
କଣ୍ଟାବୁଦା ଭିତରେ ଜୋରରେ ଦୌଡ଼ିବା ତ ତା’ପାଇଁ ଖେଳ ଥିଲା ।
प्रश्न 42.
आज वह ऐसा कूद रहा था, जैसे कभी नहीं कूदा ।
उत्तर:
ଆଜି ସେ ଏପରି ଡେଉଁଥୁଲା, ଯେପରିକି କେବେହେଲେ ଡେଇଁନଥିଲା ।
प्रश्न 43.
लोग मुझे भगोड़ा समझेंगे।
उत्तर:
ଲୋକେ ମୋତେ ପଳାତକ ଭାବିବେ
प्रश्न 44.
इधर चेतक हाँफने लगा ।
उत्तर:
ଏପଟେ ଚେତକ ଧଇଁସଇଁ ହେବାକୁ ଲାଗିଲା ।
प्रश्न 45.
वह लड़खड़ाया ।
उत्तर:
ତା’ ପାଦ ଟଳମଳ ହେଲା।
प्रश्न 46.
सामने नाला था, उसे कूदकर पार किया, फिर धड़ाम से गिरा ।
उत्तर:
ଆଗରେ ନାଳ ଥୁଲା, ତାକୁ ଡେଇଁପଡ଼ି ପାର ହୋଇଗଲା ପୁଣି ହଠାତ୍ ତଳେ ପଡ଼ିଗଲା ।
प्रश्न 47.
राणा ने देखा, उसकी छाती में तलवार भोंक दी गई है।
उत्तर:
ରାଣା ଦେଖିଲେ, ତା’ ଛାତିରେ ଖଣ୍ଡା ଭୁସି ଦିଆଯାଇଛି।
![]()
प्रश्न 48.
खून की धारा बह रही है ।
उत्तर:
ରକ୍ତର ଧାରା ବହିଚାଲିଛି।
प्रश्न 49.
उनके सामने ही चेतक ने दम तोड़ दिए ।
उत्तर:
ତାଙ୍କ ଆଗରେ ହିଁ ଚେତକ ପ୍ରାଣତ୍ୟାଗ କଲା ।
प्रश्न 50.
उसने सारा माजरा देखा ।
उत्तर:
ସେ ସବୁ ଘଟଣା ଦେଖିଲା।
प्रश्न 51.
राणा का पीछा करके फौरन आ पहुँचा ।
उत्तर:
ରାଣାଙ୍କ ଅନୁଧାବନ କରି ଶୀଘ୍ର ଆସି ପହଞ୍ଚିଗଲା ।
प्रश्न 52.
(तू) मेरी गर्दन उड़ा दे ।
उत्तर:
ତୁ ମୋ ବେକ କାଟିଦେ ।
प्रश्न 53.
शक्ति प्रताप के पाँवों पर गिरा ।
उत्तर:
ଶକ୍ତି ପ୍ରତାପଙ୍କ ପାଦତଳେ ପଡ଼ିଗଲା ।
प्रश्न 54.
मुक्षे माफ कर दो ।
उत्तर:
ମୋତେ କ୍ଷମା କରିଦିଅ ।
प्रश्न 55.
झाला और चेतक ने मेरी आँखें खोल दीं ।
उत्तर:
ଝାଲା ଓ ଚେତକ ମୋ ଆଖୁ ଖୋଲିଦେଲେ
प्रश्न 56.
मैं भी वतन के लिए ही जान दूँगा ।
उत्तर:
ମୁଁ ମଧ୍ୟ ଦେଶ ପାଇଁ ହିଁ ଜୀବନ ଦେବି
![]()
प्रश्न 57.
दोनों फूट-फूट कर रोने लगे ।
उत्तर:
ଦୁହେଁ କଇଁକଇଁ ହୋଇ କାନ୍ଦିବାକୁ ଲାଗିଲେ।
प्रश्न 58.
अपनी वीरता समझदारी और बफादारी के लिए चेतक नाम अमर हो गया ।
उत्तर:
ନିଜ ବୀରତ୍ଵ, ବୁଦ୍ଧିମତ୍ତା ଓ କୃତଜ୍ଞତା ପାଇଁ ଚେତକ ନାମ ଅମର ହୋଇଗଲା ।
प्रश्न 59.
उसने प्रताप की जान बचाई,राजपूती शान बचाई ।
उत्तर:
ସେ ପ୍ରତାପଙ୍କ ଜୀବନ ରକ୍ଷାକଲା, ରାଜପୁତ ଜାତିର ସମ୍ମାନ ରକ୍ଷାକଲା ।
प्रश्न 60.
(उसने)खुद प्राण दे दिए ।
उत्तर:
(ସେ) ନିଜେ ପ୍ରାଣବଳି ଦେଇଦେଲା ।
मे सही उत्तर चूनिए :
प्रश्न 1.
राणा का प्राण-प्यारा साथी कौन था ?
(A) संग्राम
(B) हल्दीघाटी
(C) मेवाड़
(D) घोड़ा चेतक
उत्तर:
(D) घोड़ा चेतक
प्रश्न 2.
महाराणा प्रताप का जीवन क्या था ?
(A) हल्दी घाटी
(B) रणक्षेत्र
(C) संकरी पहाड़ी
(D) अपने वीर सैनिक
उत्तर:
(B) रणक्षेत्र
प्रश्न 3.
अकबर किसे कबे में लाना चाहता था ?
(A) मेवाड़ को
(B) हल्दीघाटी को
(C) राणा को
(D) सलीम को
उत्तर:
(C) राणा को
![]()
प्रश्न 4.
प्रताप की प्रतिज्ञा क्या थी ?
(A) मेवाड़ को मुक्त करना
(B) अकबर से लड़ना
(C) घोड़े चेतक को न छोड़ना
(D) सलीम को हराना
उत्तर:
(A) मेवाड़ को मुक्त करना
प्रश्न 5.
चेतक किस रंग का घोड़ा था ?
(A) श्याम
(B) श्वेत
(C) लाल
(D) चितकबरा
उत्तर:
(A) श्याम
प्रश्न 6.
वह भी जैसे युद्ध-विद्या जानता था – ‘वह’ किसके लिये आया है ?
(A) शाहजादा सलीम
(B) राणा के सैनिक
(C) मह्नराणा प्रताप
(D) घोड़ा चेतक
उत्तर:
(D) घोड़ा चेतक
प्रश्न 7.
चेतक क्या पहचान लेता था ?
(A) अपने मालिक का आदेश
(B) हल्दीघाटी का मार्ग
(C) ऐनवक्त पर उछलना
(D) दुशमन की चाल
उत्तर:
(D) दुशमन की चाल
प्रश्न 8.
चेतक ऐन वक्त पर उछल पढ़ने का परिणाम क्या होता था?
(A) दुशमन भाग जाते थे
(B) राणा प्रताप बच जाते थे
(C) दुश्मन का वार खाली हो जाता था
(D) मुगल-सेना हार जाती थी
उत्तर:
(C) दुश्मन का वार खाली हो जाता था
प्रश्न 9.
चेतक अपनी पूँछ क्यों हिलाने लगा ?
(A) राणा ने पुचकारा
(B) राणा ने चेतक की पीठ थप्थपाइ
(C) कान फड़फड़ाने से
(D) महाराणा प्रताप की आवाज सुनकर
उत्तर:
(A) राणा ने पुचकारा
प्रश्न 10.
चेतक हिनहुनिाकर क्या बता रहा था ?
(A) मैं तुम्हें लेने तैयार हूँ
(B) मैं बहुत थक गया हूँ
(C) मैं तुम्हें प्यार करता हूँ
(D) मैं तुम्हारे लिए प्राण दे दूँगा
उत्तर:
(A) मैं तुम्हें लेने तैयार हूँ
![]()
प्रश्न 11.
युद्ध करने से पहले राणा ने माथे पर क्या लगाया ?
(A) कवच
(B) मेवाड़ की धूल
(C) मुकुट
(D) हल्दीघाटी की धूल
उत्तर:
(D) हल्दीघाटी की धूल
प्रश्न 12.
मुगलिया फौज के पहुँच जाने के समय राणा क्या करते थे?
(A) सैन्य-संचालन
(B) मातृभूमि को प्रणाम करते थे
(C) संकरी पहाड़ी गली पार होते थे
(D) मातृभूमि की धूल को देखते थे
उत्तर:
(B) मातृभूमि को प्रणाम करते थे
प्रश्न 13.
मुगलिया फौज किस की भाँति आ पहुँची ?
(A) ज्वाला की भाँति
(B) तूफान की भाँति
(C) उनचास पवन की भाँति
(D) टिड्डियों की भाँति
उत्तर:
(D) टिड्डियों की भाँति
प्रश्न 14.
जंग जीतने कौन’आया था ?
(A) शाहजादा सलीम
(B) महाराणा प्रताप
(C) सम्राट अकबर
(D) शक्ति सिंह
उत्तर:
(A) शाहजादा सलीम
![]()
प्रश्न 15.
सलीम की फौज राणा पर कैसे टूट पड़ी ?
(A) तूफान-सी
(B) आँधी-सी
(C) कुत्तों-सी
(D) आग-सी
उत्तर:
(B) आँधी-सी
प्रश्न 16.
मुगल फौजी राणा पर हमला करने में कैसे समर्थ होते शे?
(A) युद्ध क्षेत्र में चेतक को देखकर
(B) राणा को सेनापति जानकर
(C) राणा के सिर पर मुकुट देखकर
(D) सैन्यों से पूछकर
उत्तर:
(C) राणा के सिर पर मुकुट देखकर
प्रश्न 17.
चोटें खाए राणा प्रताप की बुरी हालत किसने देखी?
(A) शाहजादा सलीम ने
(B) झाला वीर मान्रा ने
(C) मुगल सैनिकों ने
(D) शक्ति सिंह ने
उत्तर:
(B) झाला वीर मान्रा ने
प्रश्न 18.
महाराणा का मुकुट किसने छीन लिया ?
(A) झाला वीर मान्रा ने
(B) शाहजादा सलीम ने
(C) सैनिकों ने
(D) मुगलों ने
उत्तर:
(A) झाला वीर मान्रा ने
प्रश्न 19.
अभी मै इनके लिए काफी हैं। कौन किसके लिए काफी है ?
(A) झालावीर मान्ना मुगलों के लिए
(B) राणा प्रताप सलीम के लिए
(C) शक्ति सिंह राणा के लिए
(D) शक्ति सिंह मुगलों के लिए
उत्तर:
(A) झालावीर मान्ना मुगलों के लिए
प्रश्न 20.
लोग मुझे भगोड़ा समझेंगे । यह किसने कहा ?
(A) राषा मताप ने
(B) झाला वीर मान्ना ने
(C) शाहजादा सलीम
(D) शक्ति सिंह ने
उत्तर:
(A) राषा मताप ने
प्रश्न 21.
चेतक कहाँ गिर पड़ा ?
(A) नाले के पास
(B) झाड़-झंखाड़ों में,
(C) जहाँ उसे तलवार भोंक दी गई थी
(D) युद्ध के मैदान में
उत्तर:
(A) नाले के पास
![]()
प्रश्न 22.
राणा प्रताप क्यों रोने लगे ?
(A) चेतक के मर जाने से
(B) चेतक की छाती से खून की धारा बहने से
(C) चेतक के गिर पड़ने से
(D) शक्ति सिंह के मुगलों के साथ रहने से
उत्तर:
(B) चेतक की छाती से खून की धारा बहने से
प्रश्न 23.
युद्ध-क्षेत्र से राणा का पीछा किसने किया ?
(A) झाला वीर मान्ना ने
(B) शाहजादा सलीम ने
(C) शक्ति सिंह ने
(D) मुगल सैनिक ने
उत्तर:
(C) शक्ति सिंह ने
प्रश्न 24.
झाला और चेतक ने किसकी आँखें खोल दीं ?
(A) सलीम की
(B) मान्ना ने
(C) शक्ति सिंह की
(D) राणा प्रताप की
उत्तर:
(C) शक्ति सिंह की
प्रश्न 25.
शक्तिसिंह के मन में अंत में कौन-सा भाव जगा?
(A) चेतक के प्रति प्रेम
(B) देशप्रेम
(C) वीरत्व
(D) देशद्रोह
उत्तर:
(B) देशप्रेम
प्रश्न 26.
इनमें से कौन-सा चेतक में नहीं था ?
(A) वफादारी
(B) समझदारी
(C) वीरता
(D) दौड़ने में शिथिलता
उत्तर:
(D) दौड़ने में शिथिलता
प्रश्न 27.
कहाँ के चौके-चौराहों पर चेतक की मूर्त्तियाँ खड़ी हैं?
(A) गुजरात
(B) महाराष्ट्र
(C) राजस्थान
(D) पंजाब
उत्तर:
(C) राजस्थान
![]()
प्रश्न 28.
अकबर बादशाह की फौज से महाराजा प्रताप का मुकाबला हो जाता था, क्योंकि –
(A) राणा सवेरा होते ही कवच पहन और हाथ में तलवार लेकर निकल पड़ते थे
(B) युद्ध के मैदान में लड़ना महाराणा प्रताप की शौकथी
(C) अकबर राणा को अपने कब्जे में करना चाहता था
(D) अकबर वीर से लड़ना चाहता था
उत्तर:
(C) अकबर राणा को अपने कब्जे में करना चाहता था
प्रश्न 29.
चेतक घोड़ा किसी वीर से कम न था, क्योंकि –
(A) वह साहसी और स्वामी-भक्त था
(B) वह दुश्मन की हर चाल को पहचान लेता था
(C) लड़ाई के मैदान में वह राणा का प्राणप्यारा साथी था
(D) वह वीरों के साथ रहता था
उत्तर:
(B) वह दुश्मन की हर चाल को पहचान लेता था
प्रश्न 30.
झाला वीर मान्ना ने महाराणा प्रताप के पीछे से उनका मुकुट छीनकर अपने सिर पर रखा, क्योंकि –
(A) उनके मुकुट को देखकर मुगल फौजी उन पर हमला करते थे
(B) मुकुट मुगल लेना चाहते थे
(C) झाला-बीर मान्ना को मुकुट पहनने की इच्छा हुई
(D) मुकुट के कारण महाराणा प्रताप वार से बच जाते था
उत्तर:
(A) उनके मुकुट को देखकर मुगल फौजी उन पर हमला करते थे
प्रश्न 31.
चेतक राणा को युद्ध के मैदान से लेकर भागा, क्योंकि-
(A) झाला वीर मान्ना ने उससे ऐसा करने को कहा
(B) वह भाँप चुका था कि राणा जख्मी हो गए हैं और उनको बचाना है
(C) राणा ने उसे भागने का संकेत दिया
(D) राणा ने उसे रोकना नहीं चाहा
उत्तर:
(D) राणा ने उसे रोकना नहीं चाहा
![]()
प्रश्न 32.
प्रताप रोने लगे, क्योंकि –
(A) चेतक की छाती में तलवार भोंक दी गई थी और उससे खून की धारा बह रही थी
(B) चेतक नाला पार न कर सका और गिर पड़ा
(C) उनको भय था कि पीब्छे से मुगल सैनिक आकर पहुँच जाएँगे
(D) वे युद्ध में हार गए थे
उत्तर:
(A) चेतक की छाती में तलवार भोंक दी गई थी और उससे खून की धारा बह रही थी
प्रश्न 33.
शक्ति सिंह ने कहा, “मैं भी वतन के लिए ही जान दूँगा’ , क्योंकि –
(A) वह मुगलों के साथ था
(B) झाला और चेतक ने उसकी आँखें खोल दी थीं
(C) राणा चेतक की मौत हो जाने से रो रहे थे
(D) वह प्रताप का भाई था
उत्तर:
(B) झाला और चेतक ने उसकी आँखें खोल दी थीं
प्रश्न 34.
आज भी राजस्थान के चौके-चौराहे, रास्ते, भवन सब पर चेतक की मूर्तियाँ खड़ी हैं, क्योंकि –
(A) चेतक ने राजपूती शान बचाई थी
(B) सरकार ने विभिन्न पशुओं की मूर्तियाँ चौराहों पर स्थापित करने का निर्णय लिया था
(C) मूर्तिकार घोड़े की मूर्ति बनाना जानते थे
(D) वह बहुत होशियार था
उत्तर:
(A) चेतक ने राजपूती शान बचाई थी
मे शून्यस्थानों की पूर्ति कीजिए
1. संग्राम महाराणा प्रताप का ………… था।
उत्तर: साथी
2. महाराणा प्रताप का जीवन ही ………… था।
उत्तर: रणक्षेत्र
3. ………… राणा को अपने कबे में करना चाहता था।
उत्तर: अकबर
4. प्रताप ने प्रतिक्षा की थी, प्राण दूँगा, पर ………… को मुक्त करूँगा।
उत्तर: मेवाड़
5. चेतक घोड़ा किसी ………… से कम नथा।
उत्तर: वीर
6. चेतक दुश्मन की हर ………… को पहचान लेता था।
उत्तर: चाल
7. उसने वक्त पर ऐसा उछलता कि दुश्मन का ………… खाली जाता।
उत्तर: वार
![]()
8. घुड़सवार के लिए उसके घोड़े का ………… होना बहुत जरूरी है।
उत्तर: होशियार
9. वे पहले कई बार बादशाही फौज से ………… ले चुके थे।
उत्तर: लोहा
10. मुगल राजपुती ………… की शान देखें ।
उत्तर: शौर्य
11. राणा ने चेतक की पीठ ………… |
उत्तर: थपथपाई
12. चेतक ने कान ………… |
उत्तर: फड़फड़ाए
13. अपनी मुट्ठी भर सैनिक लेकर राणा ………… में उतरे ।
उत्तर: हलदीघाटी
14. मुगलिया फौज ………… की भाँति आ धमकी ।
उत्तर: टिड्डियों
15. शाहजादा ………… जंग जीतने आया है ।
उत्तर: सलीम
16. सठीम का ………… मारा गया ।
उत्तर: हाथी
17. सलीम की फ़ौज राणा पर ………… सी टूट पड़ी।
उत्तर: आँधी
18. झाला वीर ………… ने प्रताप की बुरी हालत देखी ।
उत्तर: मात्रा
19. ………… ने पीछे से मुकुट छीन कर अपने सिर प्र रखा ।
उत्तर: मात्रा
20. चेतक राणा को लेकर ………… भागा।
उत्तर: बेतहाशा
21. ………… में तेजी से भागना तो चेत्रक का खेल था।
उत्तर: झाड़-झंखाड़ों
22. राणा ने देखा ………… की छाती में तलवार भोंक दी गई है।
उत्तर: चेतक
![]()
23. उनके सामने ही चेतक ने ………… तोड़ दिए ।
उत्तर: दम
24. राणा का भाई ………… मुगलों के साथ था।
उत्तर: शक्तिसिंह
25. शक्ति ………… के पाँवो पर गिरा ।
उत्तर: प्रताप
26. झाला और ………… ने मेरी आँखें खोलं दीं ।
उत्तर: चेतक
27. शक्ति बोला, मैं भी ………… के लिए ही जान दूँगा ।
उत्तर: वतन
28. अपनी वीरता, समझदारी और ………… के लिए चेतक का नाम अमर हो गया।
उत्तर: वफादारी
29. चेतक ने ………… शान बचाई ।
उत्तर: राजपूती
30. आज भी ………… के चौके-चौराहे, रास्ते भवन सब पर चेतक की मूर्त्तियाँ खड़ी है ।
उत्तर: राजस्थान
उपयुक्त शब्द ले कर खाली जगह भरिए :
1. संग्राम महाराणा प्रताप …………….. साथी था। (का, को, में)
उत्तर: का
2. न तो वे कभी संग्राम …………….. डरते थे। (को, से, में)
उत्तर: से
3. वे हाथ …………….. तलवार लेकर निकल पड़ते थे। (पर, में, से)
उत्तर: में
![]()
4. प्रताप …………….. प्रतिज्ञा की थी। (को, से, ने)
उत्तर: ने
5. घोड़ा किसी वीर …………….. कम नहीं था। (को, से, ने)
उत्तर: से
6. वह ऐन वक्त …………….. उछलता था।.(पर, से, को)
उत्तर: पर
7. उसने कई बार राणा …………….. जान बचाई थी। (का, के, की)
उत्तर: की
8. घुड़सवार …………….. उसके घोड़े का होशियार होना जरूरी है। (को, केलिए, में)
उत्तर: केलिए
9. वे बादशाही फौज …………….. लोहा ले चुकेथे। (को,में,से)
उत्तर: से
10. हल्दीघाटी …………….. सँकरी पहाड़ी गली। (का, के, की)
उत्तर: की
11. मुगल राजपूती शौर्य …………….. शान देखें। (का, के, की)
उत्तर: की
12. मैं तुम्हें लेने …………….. तैयार हूँ। (का, को, ने)
उत्तर: को
13. चेतक …………….. कान फड़फड़ाए। (ने, से, में)
उत्तर: ने
14. राणा हल्दीघाटी …………….. उतरे। (पर, में, को)
उत्तर: में
15. उन्होंने बड़ी फूर्ती …………….. हमला किया। (ने, से, केलिए)
उत्तर: से
16. उन …………….. सिर पर मुकुट था। (का, के, को)
उत्तर: के
17. उन …………….. कई चोटें आई। (का, पर, से)
उत्तर: पर
18. जय, महाराणा …………….. जय। (का, की, को)
उत्तर: की
19. उस …………….. ये बातें सुनीं। (को, ने; से)
उत्तर: ने
20. आप …………….. घाव गहरे हैं। (के, में, से)
उत्तर: के
![]()
21. उसकी छाती …………….. तलवार भोंक दी गई है।(पर, में, से)
उत्तर: में
22. चेतक …………….. दम तोड़ दिए। (ने, को, पर)
उत्तर: ने
23. वह राणा …………….. पीछा करके पहुँचा । (का, के, पर)
उत्तर: का
24. प्रताप …………….. उसे देखा। (को, ने; से)
उत्तर: ने
25. मैं भी वतन …………….. जान दूँगा । (केलिए, को, से)
उत्तर: केलिए
26. वफादारी …………….. ‘चेतक’ नाम अमर हो गया। (को, केलिए, ने)
उत्तर: केलिए
27. चौराहे …………….. चेतक की मूर्तियाँ खड़ी हैं । (को, पर, केलिए)
उत्तर: पर
28. उसने प्रताप …………….. जान बचाई। का, के, की)
उत्तर: की
![]()
वर्तनी शुद्ध कीजिए :
1. लड़ाइ
2. तलबार
3. वादशाह
4. घोड़सवार
5. बिसाल
6. पुँछ
7. शलीम
8. बेतहासा
9. गरदन
10. आँखे
11. मुर्तियाँ
12. बफादारी
13. लड़ाई
उत्तर:
1. लड़ाई
2. तलवार
3. बादशाह
4. घुड़सवार
5. विशाल’
6. पूँछ
7. सलीम
8. बेतहांशा
9. गर्दन
10. आँखें
11. मूर्तियाँ
12. वफादारी
![]()
वाक्यों को शुद्ध कीजिए :
1. उनका जीवन ही रणक्षेत्र थी।
2. प्रताप ने प्रतिज्ञा किया था।
3. दुश्मन के हर चाल को यह पहचान लेता था ।
4. राणा प्रताप बड़े लंड़ाई में जा रहे थे ।
5. आज की लड़ाई हर हालत में जीतना होगी।
6. मुगल राजपूती शौर्य का शान देखें।
7. मुगलिया फौज टिड्डियों की भाँति आ धमका ।
8. प्रताप की तलवार मानों फसल काटने लगा ।
9. मान्ना प्रताप की बुरी हालत देखा ।
10. आपके घाव गहरा है।
11. वह ये बातें सुनीं।
12. उसने ऐसा कूद रहा था।
13. खून का धारा बह रहा था।
14. राणा का भाई शक्ति सिंह मुगलों का साथ था ।
15. चेतक ने खुद प्राण दे दिया ।
उत्तर:
1. उनका जीवन ही रणक्षेत्र था।
2. प्रताप ने प्रतिज्ञा की थी।
3. दुश्मन की हर चाल को यह पहचान लेता था।
4. राणा प्रताप बड़ी लड़ाई में जा रहे थे ।
5. आज की लड़ाई हर हालत में जीतनी होगी।
6. मुगल राजपूती शौर्य की शान देखें।
7. मुगलिया फौज टिड्डियों की भाँति आ धमकी।
8. प्रताप की तलवार मानों फसल काटने लगी।
9. मान्ना ने प्रताप की बुरी हालत देखी।
10. आपके घाव गहरे हैं।
11. उसने ये बातें सुनीं।
12. वह ऐसा कूद रहा था।
13. खून की धारा बह रही थी।
14. राणा का भाई शक्ति सिंह मुगलों के साथ था।
15. चेतक ने खुद प्राण दे दिए।
![]()
लिंग बदलिए :
बादशह – बेगम
हाथी – हथिनी
घोड़ा – घोड़ी
शाहजादा – शाहजादी
वचन बदलिए :
लड़ाई – लड़ाइयाँ
सैनिक – सैनिक
सड़क – सड़के
घोड़ा – घोड़े
चाल – चालें
घाटी – घाटियाँ
सेना – सेनाएँ
पूँछ – पूँछें
माथा – माथे
टिड्डी – टिड्डियाँ
हाथी – हाथी
भगोड़ा – भगोड़े
चोट – चोटें
घाव – घाव
नाला – नाले
युद्ध – युद्ध
तलवार – तलवारें
मैदान – मैदान
विद्या – विद्याएँ
जान – जानें
पहाड़ी – पहाड़ियाँ
कान – कान
मुट्ठी – मुट्ठियाँ
धूल – धूलें
जंग – जंग
आँधी – आँधियाँ
फसल – फसलें
आवाज – आवाजें
हमला – हमले
खून – खून
धारा – धाराएँ
गर्दन – गर्दनें
वतन – वतन
मूर्त्ति – मूर्त्तियाँ
सेना – सेनाएँ
माथा – माथे
हाथी – हाथी
चोट – चोटें
तलवार – तलवारें
नाला – नाले
गर्दन – गर्दनें
हाथ – हाथ
रानी – रानियाँ
रात – रातें
माजरा – माजरे
आँख – आँखें
चौराहा – चौराहे
घाटी – घाटियाँ
पूँछ – पूँछें
टिड्डी – टिड्टियाँ
भगोड़ा – भगोड़े
युद्ध – युद्ध
फैज – फौजें
धारा – धाराएँ
मूर्ति – र्तियाँ
खान – खानें
लकीर – लकीरें
रास्ता – रास्ते
![]()
अव्ययों से रिक्त स्थान भरिए :
1. ………… वे ………… संग्राम से डरते थे ।
उत्तर: न तो, कभी
2. बादशाह की फ़ौज से ………… मुकाबला हो जाता था।
उत्तर: कहीं न कहीं
3. प्राण दूँगा ………… मेवाड़ को मुक्त करूँगा।
उत्तर: पर
4. वह …………… युद्ध विद्या जानता था।
उत्तर: भी, जैसे
5. राणा उस पर सवार होते ………… वह बहुत खुश होता।
उत्तर: तो
6. सेना का कहीं ………… सामना किया जा सकता है।
उत्तर: आसानी से
7. ………… आज की लड़ाई जीतनी होगी।
उत्तर: मगर
8. ………… वह बच गया।
उत्तर: लेकिन
9. प्रताप की तलवार ………… फसल काटने लगी।
उत्तर: मानो
10. वह उन ………… झपटा।
उत्तर: की तरफ
11. ………… मैं इनके लिए काफी हूँ।
उत्तर: अभी
12. ………… वह राणा को लेकर भागा ।
उत्तर: अब
13. झाड़-झंखाड़ों में ………… भागना तो उसका खेल था।
उत्तर: तेजी से
14. आज वह ………… कूद रहा था, …………कूदा।
उत्तर: ऐसा, जैसे, कभी, नहीं
15. वह लड़खड़ाया, ………… उछला ।
उत्तर: फिर भी
16. ………… नाला था।
उत्तर: सामने
17. वह ………… गिरा ।
उत्तर: फिर, धड़ाम से
![]()
18. उन ………… चेतक़ ने दम तोड़ दिए ।
उत्तर: के सामने
19. वह राणा का पीछा करके ………… आ पहुँचा ।
उत्तर: फौरन
20. अपने चैतक ………… मैं जी ………… सकता।
उत्तर: के बिना, नहीं
21. झाला ………… चेतक ने मेरी आँखें खोल दीं ।
उत्तर: और
22. मैं ………… वतन के लिए ………… जान दूँगा।
उत्तर: भी, ही
३० शब्दों/दो-तीन वाक्यों में उत्तर दीजिए :
प्रश्न 1.
राणा प्रताप सवेरा होते ही क्या करते थे ?
उत्तर:
राणा प्रताप मेवाड़ को मुक्त करना चाहते थे और अकबर राणा प्रताप को अपेने कबें में लाना चाहते थे। राणा प्रताप का जीवन ही रणक्षेत्र था, इसलिए वे सवेरा होते ही कवच पहनकर, हाथ में तलवार लेकर युद्ध करने निकल पड़ते थे ।
प्रश्न 2.
चेतक के रूप-गुणों का वर्णन कीजिए ।
उत्तर:
चेतक चमकीले रंग का घोड़ा था । वह मानो युद्धविद्या जानता था, वीर था, वह युद्धभूमि में युद्धविद्या – विशारद की तरह बड़ी होशियारी से काम करता था। वह दुश्मन की चाल पहचानकर सही वक्त पर उछलकर दुश्मन के वार से राणा को बचा लेता था ।
प्रश्न 3.
हल्दीघाटी में हुए युद्ध का वर्णन कीजिए।
उत्तर:
राणा प्रताप और सलीम के बीच घमासान लड़ाई हुई । अनगिनत सैनिक मारे गए । सलीम का हाथी मारा गया । मुगल राणा को अकेला पाकर घेर गए। राणा पर कई चोटें आई ।
![]()
प्रश्न 4.
युद्ध में प्रताप ने क्या किया ?
उत्तर:
प्रताप ने सामने मुगल सेना देखकर तुरंत उन पर हमला कर दिया । उन्होंने युद्ध में अपनी तलवार से मुगल सैनिकों को मार गिराया । उनको अकेले पाकर मुगल सैनिकों ने उन पर कई चोटें कीं, पर प्रताप पीछे नहीं हटे ।
प्रश्न 5.
चेतक प्रताप को लेकर क्यों और कैसे भागा ?
उत्तर:
चेतक जान गया था कि राणा युद्द में जख्मी हो गए हैं । झाला वीर मात्रा ने राणा से युद्ध का मैदान छोड़कर चले जाने को कह्न । यह सुनते ही चेतक राणा को लेकर झाड़-झंखाडों में तेजी से कूदते हुए भागा ।
प्रश्न 6.
राणा चेतक की मौत से क्यों दुःखी हुए ?
उत्तर:
चेतक राणा को जख्मी की ह्हलत में लेकर युद्ध के मैदान से भागते समय एक गाला कूदकर पार करने के बाद गिर पड़ा । उसकी छाती में तलवार भोंक दी गई थी और उससे खून की धारा बह रही थी। राणा के सामने वहीं चेतक की मौत हो गई; इससे राणा दु:खी हुए ।
प्रश्न 7.
चेतक का नाम क्यों अमर हुआ ?
उत्तर:
चेतक ने राणा को युद्ध क्षेत्र से ले आकर उनको बचाया था । खुद प्राण दे दिए और उसकी वीरता, समझदारी और वफादारी के लिए राजपूती शान ब्रच गई ।इसी कारण उदका नाम अमर हो गया।
प्रश्न 8.
आज चेतक की मूर्तियाँ कहाँ-कहाँ मिलती है ?
उत्तर:
चेतक ने हल्दीघाटी के युद्ध क्षेत्र से राणा को दूर लेकर उनके प्राण बचाए थे । वह वीरता, समझदारी और वफादारी का प्रतीक बन गया । राजस्थान के चैके चौराहों, सड़कों, भवनों पर उसकी मूर्तियाँ मिलती हैं ।
प्रश्न 9.
शक्ति सिंह को किनसे और क्या शिक्षा मिली ?
उत्तर:
राणा प्रताप को युद्ध से भागते हुए देखकर शक्तिसिंह भाई के पीछे-पीछे नाले के पास पहुँचा, जहाँ चेतक की मौत हो गई थी। उसने झाला और चेतक का देशप्रेम देखा था। शक्तिसिंह को इन दोनों से देश-प्रेम की शिक्षा मिली ।
प्रश्न 10.
झाला वीर मान्ना प्रताप का मुकुट छीनकर क्या बोला ?
उत्तर:
राणा कां मुकुट छीनकर झाला बोला – राणा, आपके घाव नहरे हैं। मेरी बात मानकर अब आप अपनी जान बचाइए। आप रहेंगे तो हमारी लड़ाई चलती रहेगी ।अभी में इनके लिए काफी हूँ, ।
प्रश्न 11.
हल्दीघाटी के युद्धक्षेत्र में चेतक राणा की सहायता कैसे कर रहा था ?
उत्तर:
हल्दीघाटी के युदक्षेत्र में वेतक ने राणा का पूरा साथ दिया । अंत में उसने घायल राणा को युद्ध-क्षेत्र से दूर ले जाकर उनके प्राण बचाए। एक नाला कूटकर पार करने के बाद खुद घोड़े ने दम तोड़ दिए।
प्रश्न 12.
महाराणा प्रताप का संग्राम से कैसा संबंध था?
उत्तर:
संग्राम महाराणा प्रताप का साथी था। उनका जीवन ही रणक्षेत्र था। वे संग्राम से कभी नहीं डरते थे।
![]()
प्रश्न 13.
महाराणा प्रताप का अकबर बादशाह की फौज से क्यों मुकाबला हो जाता था?
उत्तर:
अकबर राणा को अपने कब्जे में करना चाहता था। प्रताप ने प्रतिज्ञा की थी – प्राण दूँगा, पर मेवाड़ को मुक्त करूँगा। इसलिए उनका अकबर बादशाह की फौज से मुकाबला हो जाता था।
प्रश्न 14.
चेतक क्यों खुश हो जाता था ?
उत्तर:
राणा चेतक पर सवार होते ही चेतक खुश हो जाता था। उसने रण में होशियारी से कई बार राणा की जान बचाई थी। वह किसी वीर से कम न था।
प्रश्न 15.
हल्दीयाटी की क्या विशेषता थी ?
उत्तर:
हल्दीघाटी की संकरी पहाड़ी गली में विशाल मुगल सेना से सामना किया जा सकता है। शाहुजादा सलीम के नेतृत्व में आई मुगल सेना से महाराणा म्रताप ने अपनी मुट्ठी भर सैनिक लेकर लड़े थे।
![]()
प्रश्न 16.
राणा चिल्लाकर चेतक से क्या बोले ?
उत्तर:
राणा चिल्लाकर चेतक से बोले, “चेतक ! चेतक ! यह क्या कर रहा है ? लोग मुझे भगोड़ा समझेंगे। रूक जा।”
प्रश्न 17.
शक्ति सिंह को देखकर राणा ने क्या कहा?
उत्तर:
शक्ति सिंहको देखकर रापा ने कहा, “आ जा शक्ति! मेरी गर्दन उड़ा दे। अपने चेतक के बिना में जी नहीं सकता।”
विचार बिन्दु :
यह घोड़े ेेतक की समझदारी, बफादारी और बलिदान की कहानी है । राजपूत वीर महाराणा प्रताप मुगल सम्राट अकबर की वशता स्वीकार न करके बराबर उनका मुकावला करते रहे । चेतक महाराणा प्रताप का हर लड़ाई में साथी रहा । वह तो जैसे दुश्मन की हर चाल को पहचान लेता था। वह अपने मालिक से बेहद प्यार करता था । एक बार जख्मी मालिक के प्राण बचाने के लिए चेतक दुश्मनों की भीड़ से तेज रफ्तार से भागा और एक नाला पार करते ही गिर पड़ा और अपने प्राण त्याग दिए। प्रभु-पशु-प्रेम की यह कहानी ऐतिहासिक अमर कहानी है ।
शब्दार्थ


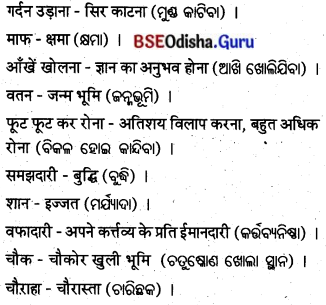
सारांश
मेवाड़ के राणा महाराणा प्रताप मुगल सम्राट अकबर के कबे में नहीं आए। अकबर ने मेवाड़ का अधिकार कर लिया था। मेवाड़ को मुक्त करने के लिए महाराणा प्रताप को अकबर की फौज से बारबार मुकाबला करना पड़ता था । उनके वीर सौनिक और जान से प्यारा घोड़ा चेतक उनका साथ दे रहे थे ।
चेतक बहुत होशियारथा । लड़ाई के मैदान में अपने मालिक के साथ रहकर दुश्मन की चाल को पहचान लेने की शक्ति उसमें आ गई थी। कई बार युद्ध में उसने राणा की जान बचाई थी ।
![]()
एक बार मुगली फौज से लड़ने राणा हलदीघाटी में उतरे । एकाएक सलीम के नेतृत्व में मुगलिया फैज पहुँच गई। भीषण लड़ाई हुई । सलीम का हाथी मारा गया, पर वह बच गया । महाराणा प्रताप अपनी तलवार से शत्रु सैनिकों को मारने लगे ।उनको भी कई चोटें लगीं । राणा के सिर पर मुकुट देख कर मुगलों ने राणा को घेर लिया।
दूर से झाला वीर मात्रा ने यह हालत देखी । उसने झपटकर पीछे से राणा का मुकुट छीन लिया और मुगलों को भ्रम में डालने के लिए मुकुट अपने सिर पर धारण कर लिया । उसने राणा से लड़ाई छोड़कर चले जाने की विनती की और खुद लड़ाई जारी रखने का वचन दिया ।
चेतक ने भाँप लिया कि राणा को बचाना है । अंब उसने रांणा का हुक्म नहीं माना । वह राणा को लेकर झाड़-झंखाडों में तेजी से भागा। वह हाँफने लगा ।आगे एक नाला था। वह कूटकर तो नाला पार हो गया, पर वहीं धड़ाम् से गिर पड़ा । उसकी छाती में तलवार भोंक दी गई थी। खून की धारा बह रही थी। वहीं चेतक ने दम तोड़ दिये । राणा प्रताप रोने लगे ।
इतने में राणा का भाई शक्ति सिंह जो मुगलों के साथ था, उनका पीछा करता हुआ वहीं आ पहुँचा । उसको देखते ही राणा बोले – तू मेरी गर्दन उड़ा दे । मैं चेतक के बिना जी नहीं सकूँगा ।
झाला और चेतक ने शक्ति सिंह की आँखें खोल दी थीं । शक्ति सिंह ने भैया से माफी माँगी; मुगल-पक्ष छोड़कर मातृभूमि के लिए जान देने को वचन-बद्ध हुआ, फूट-फूटकर रोने लगा ।
चेतक ने तो खुद जान दे दी । पर उसने महाराणा प्रताप की जान बचाई । राजपूती शान बचाई । अपनी वफादारी के लिए चेतक अमर हो गया ।आज राजस्थान के चौराहों और भवनों पर चेतक की मूर्त्तियाँ उस शान की याद दिलाती हैं।
ସାରାଂଶ
ମେଣ୍ଢାର ରାଣା ମହାରାଣା ପ୍ରତାପ ମୋଗଲ ସମ୍ରାଟ ଆକବରଙ୍କ ବଶତା ସ୍ଵୀକାର କରିନଥୁଲେ । ଆକବର ମେୱାର ଅଧିକାର କରି ନେଇଥିଲେ । ମେୱାରକୁ ମୁକ୍ତ କରିବା ପାଇଁ ମହାରାଣା ପ୍ରତାପଙ୍କୁ ଆକବରଙ୍କ ସୈନ୍ୟବାହିନୀ ସହିତ ବାରମ୍ବାର ସମ୍ମୁଖୀନ ହେବାକୁ ପଡ଼ୁଥିଲା । ତାଙ୍କର ବୀର ସୈନିକଗଣ ଓ ପ୍ରାଣପ୍ରିୟ ଘୋଡ଼ା ଚେତକ ତାଙ୍କୁ ସହାୟତା କରୁଥିଲେ ।
ଚେତକ ବହୁତ ବୁଦ୍ଧିମାନ ଥଲା । ଯୁଦ୍ଧ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ନିଜ ପ୍ରଭୁଙ୍କ ସହିତ ରହି ଶତ୍ରୁର କୌଶଳକୁ ଜାଣିପାରିବାର ଶକ୍ତି ତା’ର ଆସିଯାଇଥିଲା । ଅନେକ ଥର ସେ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ମହାରାଣାଙ୍କ ଜୀବନ ମଧ୍ୟ ରକ୍ଷା କରିଥିଲା । ଏକଦା ମୋଗଲ ସୈନ୍ୟଙ୍କ ସହିତ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ କରିବାପାଇଁ ମହାରାଣା ପ୍ରତାପ ହଳଦୀଘାଟିରେ ପହଞ୍ଚିଲେ । ସେଠାରେ ଚାହୁଁଚାହୁଁ ସଲୀମଙ୍କ ନେତୃତ୍ବରେ ମୋଗଲ ବାହିନୀ ମଧ୍ୟ ପହଞ୍ଚିଗଲେ । ଭୀଷଣ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ ହେଲା । ଯୁଦ୍ଧରେ ସଲୀମଙ୍କ ହାତୀ ମରିଗଲା | କିନ୍ତୁ ସଲୀମ ରକ୍ଷା ପାଇଗଲେ । ରାଣା ପ୍ରତାପ ତାଙ୍କ ତରବାରୀରେ ଶତ୍ରୁ ସୈନ୍ୟଙ୍କୁ ହତ୍ୟା କରି ଚାଲିଲେ । ତାଙ୍କୁ ମଧ୍ଯ ଅନେକ ଆଘାତ ଲାଗିଲା । ରାଣା ପ୍ରତାପଙ୍କ ମସ୍ତକରେ ରାଜମୁକୁଟ ଦେଖି ମୋଗଲ ସୈନ୍ୟ ତାଙ୍କୁ ଘେରିଗଲେ ।
ଦୂରରୁ ଝାଲାବୀର ମାନ୍ନା ଏହି ଅବସ୍ଥା ଦେଖି ପକାଇଲେ । ସେ ଜୋର୍ରେ ଆସି ରାଣା ପ୍ରତାପଙ୍କ ପଛରୁ ମୁକୁଟ ଝି ନେଲେ ଓ ମୋଗଲ ସୈନ୍ୟଙ୍କୁ ସନ୍ଦେହରେ ପକାଇବା ପାଇଁ ମୁକୁଟ ନିଜେ ପିନ୍ଧି ପକାଇଲେ । ସେ ରାଣା ପ୍ରତାପଙ୍କୁ ଯୁଦ୍ଧକ୍ଷେତ୍ର ଛାଡ଼ି ଚାଲିଯିବା ପାଇଁ ବିନୀତ ପ୍ରାର୍ଥନା କଲେ । ସେ ନିଜେ ଯୁଦ୍ଧସଂଚାଳନ କରିବେ ବୋଲି ମଧ୍ୟ କଥାଦେଲେ ।
ଚେତକ ଠଉରେଇ ନେଲା ଯେ ରାଣା ପ୍ରତାପଙ୍କୁ ବଞ୍ଚାଇବାକୁ ହେବ । ସେ ଆଉ ରାଣା ପ୍ରତାପଙ୍କ ଆଦେଶ ମାନିଲା ନାହିଁ । ସେ ରାଣା ପ୍ରତାପଙ୍କୁ ନେଇ କଣ୍ଟା ବୁଦା, ଜଙ୍ଗଲ ଭିତରେ ଜୋର୍ରେ ଦୌଡ଼ିବାକୁ ଲାଗିଲା । ସେ ଧଇଁ ସଇଁ ହୋଇଗଲା । ତା’ ସମ୍ମୁଖରେ ନାଳଟିଏ ପଡ଼ିଲା । ଚେତକ ଡେଇଁ ନାଳ ପାରି ହୋଇଗଲା । କିନ୍ତୁ ସେ ସେହିଠାରେ ଟଳି ପଡ଼ିଲା । ତା’ ଛାତିରେ ମଧ୍ୟ ତରବାରୀ ବିଦ୍ଧ ହୋଇଥିଲା । ରକ୍ତର ସୁଅ ଛୁଟୁଥୁଲା ଚେତକର ସେହିଠାରେ ପ୍ରାଣବାୟୁ ଉଡ଼ିଗଲା । ରାଣା ପ୍ରତାପ ଜୋରରେ କାନ୍ଦିବାକୁ ଲାଗିଲେ । ଏହି ସମୟରେ ମୋଗଲ ପକ୍ଷରେ ଯୋଗ ଦେଇଥିବା ରାଣା
![]()
ପ୍ରତାପଙ୍କ ସାନ ଭାଇ ଶକ୍ତି ସିଂହ ତାଙ୍କ ଅନୁଧାବନ କରି ସେଠାରେ ଆସି ପହଞ୍ଚିଲା । ତାଙ୍କୁ ଦେଖୁଦେଖୁ ରାଣା ପ୍ରତାପ କହିଲେ, ଶକ୍ତି, ତୁ ବର୍ତ୍ତମାନ ମୋର ଶିରଛେଦ କର । ମୁଁ ଚେତକ ବିନା ବଞ୍ଚି ପାରିବି ନାହିଁ । ଝାଲା ଏବଂ ଚେତକ ଦୁହେଁ ଶକ୍ତି ସିଂହଙ୍କ ଆଖି ଖୋଲିଦେଲେ । ଶକ୍ତି ସିଂହ ଭାଇଙ୍କୁ କ୍ଷମା ପ୍ରାର୍ଥନା କଲେ । ସେ ମୋଗଲ୍ ପକ୍ଷ ତ୍ୟାଗ କରି ନିଜ ମାତୃଭୂମି ପାଇଁ ଜୀବନ ଉତ୍ସର୍ଗ କରିବାପାଇଁ ପ୍ରତିଜ୍ଞା କଲେ ଓ ଖୁବ୍ ଜୋର୍ରେ କାନ୍ଦିବାକୁ ଲାଗିଲେ ।
ଚେତକ ନିଜେ ପ୍ରାଣବଳି ଦେଇଦେଲା । କିନ୍ତୁ ସେ ମହାରାଣା, ପ୍ରତାପଙ୍କ ଜୀବନ ରକ୍ଷା କଲା । ରାଜପୁତ ସମ୍ମାନ ରକ୍ଷା କଲା | ନିଜର କର୍ମବ୍ୟନିଷ୍ଠା ପାଇଁ ଚେତକ ଅମର ହୋଇଗଲା । ଏବେ ରାଜସ୍ଥାନର ଛକ ଓ ଭବନମାନଙ୍କ ଉପରେ ଚେତକର ମୂର୍ତ୍ତିଗୁଡ଼ିକ ସେହି ସମ୍ମାନକୁ ସ୍ମରଣ କରେଇ ଦିଅନ୍ତି ।