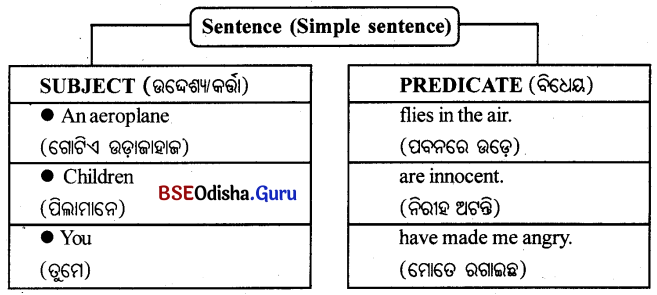
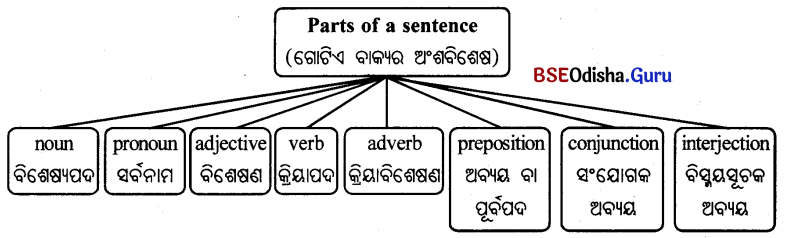
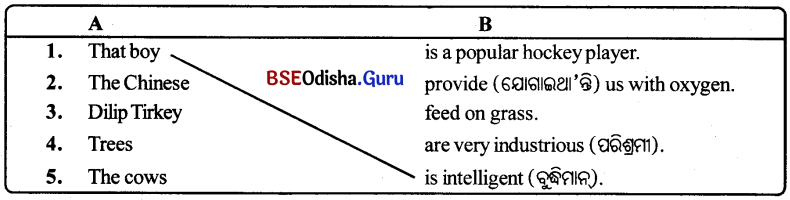
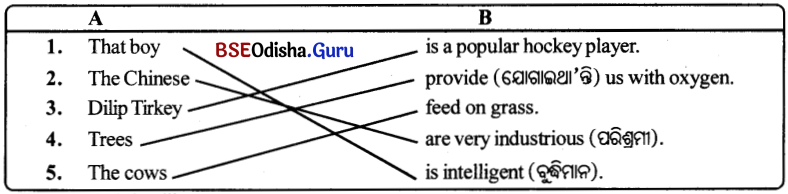
Odisha State Board BSE Odisha 8th Class Sanskrit Solutions Grammar ବ୍ୟାକରଣ ବିଭାଗ Questions and Answers.
BSE Odisha Class 8 Sanskrit Grammar ବ୍ୟାକରଣ ବିଭାଗ
संधिविधानम् (ସନ୍ଧିବିଧାନମ୍)
- ପ୍ର + ନମତି = ପ୍ରଣମତି
- ଇତି + ଆଦୟଃ = ଇତ୍ୟାଦୟ
- ଶିଳ୍ପ + ଆଗାରସ୍ୟ = ଶିଳ୍ପୀଗାରସ୍ୟ
- ଶିଳ୍ପା + ଆଗାରାନ୍ = ଶିଳ୍ପୀଗାରାନ୍
- ଇତଃ + ତତଃ = ଇତସ୍ତତଃ
- କଃ + ଅପି = କୋଽପି
- କିମ୍ + ତୁ = = କିନ୍ତୁ
- ଅତି + ଲବ = ଅତୀବ
- ଇତି + ଇବ = ଇତୀବ
- ନିଶା + ଅର୍ଧ = ନିଶାର୍ଧ
![]()
- ମରଣାତ୍ + ପରମ୍ = ମରଣାପୂରମ୍
- ଭୂଚରଣକ + ଆଦୀନି = ଭୂଚଣକାଦୀନି
- ପ୍ର + ଆରମଃ = ପ୍ରାରମଃ
- କଃ + ଚିତ୍ = କଶ୍ଚିତ୍
- କିମ୍ + ଅପି = କିମପି
- ପରଂ + ତୁ = ପରନ୍ତୁ
- ପ୍ର + ଆପ୍ତବାନ୍ = ପ୍ରାପ୍ତବାନ୍
- ପ୍ର + ଆପ୍ରୋତି = ପ୍ରାୟୋତି
- ଅତଃ + ଏବ = ଅତଏବ
- ସମ୍ + ଭଳ = ସମ୍ମିଳ
- ଅତି + ଅନ୍ତମ୍ = ଅତ୍ୟନ୍ତମ୍
- ପରି + ଅଟକା = ପର୍ଯ୍ୟଟକା
- ପୁଷ୍ପ + ଅର୍ଘ୍ୟମ୍ = ପୁଷ୍ପାର୍ଘ୍ୟମ୍
- କଃ + ଚିତ୍ର = କଶ୍ଚିତ୍
- ପ୍ର + ଆପ୍ରୋତି = ପ୍ରାପ୍ନାତି
- ଅତ୍ର + ଅପି = ଅତ୍ରାପି।
![]()
- ବୈଦିକଗୁରୁକୁଳ + ଆଶ୍ରମଃ = ବୈଦିକଗୁରୁକୁଳାଶ୍ରମଃ
- ଅର୍ଥ + ଉପାର୍ଜନମ୍ = ଅର୍ଥୋପାର୍ଜନମ୍
- ପ୍ର + ଆସୁବତି = ପ୍ରାପ୍ଲବନ୍ତ
- ଅତି + ଆବଶ୍ୟକ = ଅତ୍ୟାବଶ୍ୟକଃ
- ତତ୍ + ଅନନ୍ତରମ୍ = ତଦନନ୍ତମ୍
- ଉପନ୍ୟାସକାରଃ + ଚ = ଉପନ୍ୟାସକାରଷ୍ଟ
- ଅତି + ଲବ = ଅତୀବ
- ନାମ + ଅନୁସାରେଣ = ନାମାନୁସାରେଣ
- ସମ୍ + ଜାତଃ = ସଞ୍ଜାତଃ
- ସ୍ଵରଃ + ଲବ = ସ୍ଵର ଇବ
- ନ + ଅସ୍ଥି = ନାସ୍ତି
- ବିଦ୍ୟା + ଆଳୟେ = ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟ
- ଉତ୍ + ମୋଚୟତ = ଉନ୍ମୋଚୟତ
- ମୂଲ୍ୟ + ଅଙ୍କନମ୍ = ମୂଲ୍ୟାଙ୍କନମ୍ନୀ
- ତିରନ୍ + ଆବଳୀଭି = ନୀତିରଡା଼ବଳିଭି
- ଅତ୍ର + ଉପସ୍ୱାପିତା = ଅତ୍ରୋପସ୍ଥାପିତାଃ
- ବୃଦ୍ଧ + ଉପସେବିନଃ = ବୃଦ୍ଧାପସେବିନଃ
- ସର୍ପଦୁର୍ଜନୟୋ + ମଧେ = ସର୍ପଦୁର୍ଜନୟୋର୍ମଧେ
- ସର୍ପ + ନ = ସର୍ପା ନ
- ଦୁର୍ଜନଃ + ତୁ = ଦୁର୍ଜନସ୍ତୁ
- କାର୍ଯ୍ୟମ୍ + ଅଦ୍ୟ = କାର୍ଯ୍ୟମଧ୍ଯ
- ଚ + ଅପରାହ୍ନିକମ୍ = ଚାପରାନ୍ତ୍ରିକମ୍।
- କୃତମ୍ + ଅଦ୍ୟ = କୃତମଦ୍ୟ
- ପ୍ରତି + ଈକ୍ଷତେ = ପ୍ରତୀକ୍ଷତେ
- କିମ୍ + ଅପି = କିମପି
- ନ + ଏବ = : ନୈବ
- ତତ୍ + ଅପି = ତଦପି
- ଅଚ୍ଛାନାମ୍ + ଅପି = ଅଳ୍ପନାମପି
- ନାରଃ + ଅପି = ନାଗୋଽପି
- ଗୁଣବତ୍ + ଜନସୃକାଁତ୍ = ଗୁଣବଜନସୃକାଁତ୍ସ୍ଵ
- ନଃ + ଅପି = ସ୍କୋଽପି
- ପ୍ର + ଆପ୍ଳୁତି = ପ୍ରାପ୍ରୀତି
- ପୁଷ୍ପମାଳ + ଅନୁଷଙ୍ଗଣ = ପୁଷ୍ପମାଳାନୁଷଙ୍ଗଣ
- ପଞ୍ଚ + ଏବ = ପଞ୍ଚିବ
- ମନୁଷ୍ୟାନ୍ + ଚ = ମନୁଷ୍ୟ
- ଗୁରୂନ୍ + ଅତିଥୁପଞ୍ଚମାନ୍ = ଗୁରୂନତିଥପଞ୍ଚମାନ୍ତୃ
- ତିଃ + ଆରଭ୍ୟତେ = ତୃଣେରାରଭ୍ୟତେ
- ଉଦାରଚରିତାନାଂ + ତୁ = ଉଦାରଚରିତାନାନ୍ତୁ
- ବସୁଧା + ଏବ = ବସୁଧୈବ
- ହଂସ + ହି = ହଂସୋ ହି
- କ୍ଷୀରମ୍ + ଆଦରେ = କ୍ଷୀରମାଦରେ
- ତତ୍ + ମିଶ୍ରିତ୍ = ତନ୍ନିଶ୍ରାତ୍ଭ
- ବେତ୍ + ନ = ଭବେନ୍ନ
- କଦା + ଅପି = କଦାପି
- କଥମ୍ + ଅପି = କଥମପି
![]()
- ବର୍ଜୟତି + ଅପଃ = ବର୍ଜୟତ୍ୟପଃ
- ତଥା + ଏବ = ତଥୈବ
- କଃ + ବନ = କଷ୍ଟନ
- ସତ୍ + ଜନଃ = ସଜନଃ
- ପ୍ର + ଆପ୍ସ୍ୟାମି = ପ୍ରାପ୍ସ୍ୟାମି
- ନିଃ + କରୁନଃ = ନିଷ୍କରୁନଃ
- ଚ + ଆସୀତ୍ = ଚାସୀତ୍
- କଃ + ବନ = କଷ୍ଟନ
- ତତ୍ର + ଏବ = ତତ୍ରୈବ
- ସମ୍ + ଭବିଷ୍ୟତି = ସମ୍ଭବିଷ୍ୟତି
- ପ୍ର + ଆପ୍ତବାନ୍ = ପ୍ରାପ୍ତବାନ୍
- କଃ + ଚିତ୍ର = କଶ୍ଚିତ୍
- ସର୍ବ + ଆଦୌ = ସର୍ବାଦୌ
- ପ୍ର + ଆପ୍ଲୁୟାତ୍ = ପ୍ରାପ୍ତିତ୍ବ
- ହନଃ + ମଣ୍ଡୁକା = ବହବୋ ମଣ୍ଡୁକା
- ସମ୍ + ମିଳିତା = ସମ୍ମିଳିତ
- ଇତି + ଆଦିଭଃ = ଇତ୍ୟାଦିଭି
- ତଥା + ଅପି = ତଥାପି
- ପରଂ + ତୁ = ପରନ୍ତୁ
- ମନ + ବଳମ୍ = ମନୋବଳମ୍ପା
- ଦମ୍ + ଅପି = ପାଦମପି
- ପ୍ର + ଆପ୍ତବତଃ = ପ୍ରାପ୍ତବୟଃ
- କସ୍ୟ + ଅପି = କନ୍ୟାପି
- ଇତି + ଆଦୀନି = ଇତ୍ଯାଦୀନି
- ଶତଃ + ଇତି = ଶକ୍ତ ଇତି
- ପରଃ + ପରମ୍ = ପରସ୍ପରମ୍ବ
- ଚନ + ଅନୁସାରମ୍ଭ = ବଚନାନୁସାରମ୍କ
- ସ୍ୟ + ଅପି = କନ୍ୟାପି
- ସାଧୁ + ଉକ୍ତମ୍ = ସାଧୂକ୍ତମ୍ଅ
- ତି + ଉଜଃ = ଅତ୍ୟୁତଃ
- ପ୍ରଧାନ + ଅମାତ୍ୟ = ପ୍ରଧାନାମାତ୍ୟ
- ତଥା + ଏବ = ତଥୈବ
- କାଳ + ଅନ୍ତରେ = କାଳାନ୍ତରେ
- ଜନ୍ମଭୂମି + ଚ = ଜନ୍ମଭୂମିଣ୍ଟ
- ସ୍ଵର୍ଗତ୍ + ଅପି = ସ୍ବର୍ଗାଦପି
- ଭବତାଂ + ମମ = ଭବତାନୁମ
- ଯତ୍ର + ଅହିଂସା = ଯତ୍ରାହିଂସା
![]()
- ସ୍ଵତନ୍ତ୍ରତା ସାଧନମ୍ + ଅକରୋତ୍ = ସ୍ଵତନ୍ତ୍ରତାସାଧନମକରୋତ୍ର
- ବୀନ୍ଦ୍ର + ମଧୁରମ୍ = ରବୀନ୍ଦ୍ରା ମଧୁରମ୍
- କା + ଅପି = କାପି
- ସହ + ଉଦରା = ସହୋଦରଃ
- ବିହଙ୍ଗ + ଉତ୍ପତନେ = ବିହଙ୍ଗୋତ୍ପତନେ
संधिविच्छेद: (ସନ୍ଧିବିଚ୍ଛେଦଃ)
- ପ୍ରଣମତି = ପ୍ର + ନମତି
- ଇତ୍ୟାଦୟଃ = ଇତି + ଆଦୟ
- ଶିଳାଗାରସ୍ୟ = ଶିଳ୍ପ + ଆଗାରସ୍ୟ
- ଶିଳ୍ପୀଗାରାନ୍ = ଶିଳ୍ପ + ଆଗାରାନ୍
- ଇତସ୍ତତଃ = ଇତଃ + ତତଃ
- କୋଽପି = କଃ + ଅପି
- କିନ୍ତୁ = କିମ୍ + ତୁ
- ଅତୀବ = ଅତି + ଇବ
- ନିଶାର୍ଧ = ନିଶା + ଅର୍ଧ
- ମରଣାପୂରମ୍ = ମରଣାତ୍ + ପରମ୍
- ଭୂଚଣକାଦୀନି = ଭୂଚଣକ + ଆଦାନ
- ପ୍ରାରମ୍ଭ = ପ୍ର + ଆରମ୍ଭ
- ଶାକାଦିର୍ଭି = ଶାକ + ଆଦିରଃ
- କଶ୍ଚିତ୍ = କଃ + ଚିତ୍ର
- କିମପି = କିମ୍ + ଅପି
- ପରନ୍ତୁ = ପରଂ + ତୁ
- ପ୍ରାପ୍ତବାନ୍ = ପ୍ର + ଆପ୍ତବାନ୍
- ପ୍ରାଷ୍ଟୋତି = ପ୍ର + ଆପ୍ଳୁତି
- ଅତ ଏବ = ଅତଃ + ଏବ
- ସମୁଳ = ସମ୍ + ଉଚ୍ଚ
![]()
- ପର୍ଯ୍ୟଟକା = ପରି + ଅଟକା
- କଶ୍ଚିତ୍ର = କଃ + ଚିତ୍ର
- ପ୍ରାଷ୍ଟୋତି = ପ୍ର + ଆଜ୍ୟୋତି
- ଅତୀବ = ଅତି + ଇବ
- ପୁଷ୍ପାର୍ଘ୍ୟମ୍ = ପୁଷ୍ପ + ଅର୍ଘ୍ୟମ୍
- ଅତ୍ରାପି = ଅତ୍ର + ଅପି
- ବୈଦିକଗୁରୁକୁଳା ଶ୍ରମଃ = ବୈଦିକଗୁରୁକୁଳ + ଆଶ୍ରମ
- ଅର୍ଥୋପାର୍ଜନମ୍ = ଅର୍ଥ + ଉପାର୍ଜନମ୍
- ପ୍ରାପ୍ରୁବନ୍ତି = ପ୍ର + ଆସୁବନ୍ତି .
- ଅତ୍ୟାବଶ୍ୟକମ୍ = ଅତି + ଆବଶ୍ୟକମ୍
- ତଦନନ୍ତରଂ = ତତ୍ + ଅନନ୍ତରମ୍
- ଉପନ୍ୟାସକାରଷ୍ଟ = ଉପନ୍ୟାସକାରଃ + ଚ
- ଅତୀବ = ଅତି + ଇବ
- ପରନ୍ତୁ = ପରମ୍ + ତୁ
- ନାମାନୁସାରେଣ = ନାମ + ଅନୁସାରେଣ
- ସଞ୍ଜାତଃ = ସମ୍ + ଜାତଃ
- ସ୍ଵର ଇବ = ସ୍ଵରଃ + ଇବ
- ନାସ୍ତି = ନ + ଅସ୍ତି
- ନୀତିରନ୍ଧାବଳିଭଃ = ନୀତିରନ୍ + ଆବଳିଭିଂ
- ଅତ୍ରୋପସ୍ଥାପିତା = ଅତ୍ର + ଉପସ୍ଥାପିତା
- ପସେବିନଃ = ବୃଦ୍ଧ + ଉପବେସିନଃ
- ପ୍ରାଣମତ୍ = ପ୍ର + ଅନମତ୍
- ସର୍ପଦୁର୍ଜନୟୋର୍ମଧ୍ଯ = ସର୍ପଦୁର୍ଜନ + ମଧ୍ୟ
- ସର୍ପୋ ନ = ସପଃ + ନ
- ସର୍ପୋ ଦଶତି = ସପଃ + ଦଶତି
- ଦୁର୍ଜନସ୍ତୁ = ଦୁର୍ଜନଃ + ତୁ
- କାର୍ଯ୍ୟମଦ୍ୟ = କାର୍ଯ୍ୟମ୍ + ଅଦ୍ୟ
- ଚାପରାହ୍ନିକମ୍ = ଚ+ ଅପରାହ୍ନିକମ୍
- କୃତମସ୍ୟା = କୃତମ୍ + ଅଦ୍ୟ
- ପ୍ରତୀକ୍ଷତେ = ପ୍ରତି+ ଈକ୍ଷତେ
- କିମପି = କିମ୍ + ଅପି
- ଜୈବ = ନ + ଏବ
- ତଦପି = ତତ୍ + ଅପି
- ଅଜ୍ଞା ନାମପି = ଅଚ୍ଛାନାମ୍ + ଅପି
- ନାଗୋଽପି = ନାରଃ + ଅପି
- କିନ୍ତୁ = କିଂ + ତୁ
- ଗୁଣବଜନସ୍ମର୍କାତ୍ = ଗୁଣବତ୍ + ଜନସୃତ୍
- ସ୍ଵକପି = ସ୍ଵତଃ + ଅପି
- ପ୍ରାସ୍ମୋତି = ପ୍ର + ଆପ୍ରୋତି
- ପୁଷ୍ପମାଳା ନୁଷଙ୍ଗଣ = ପୁଷ୍ପମାଳ + ଅନୁଷଙ୍ଗଣ
- ପବ = ପଞ୍ଚ + ଏବ
- ଗୁରୂନତିଥପଞ୍ଚମାନ୍ = ଗୁରୂନ୍ + ଅତିଥପଞ୍ଚମାନ୍
- ତୃଣିରାରଭ୍ୟତେ = ତୃ + ଆରଭ୍ୟତେ
- ଉଦାରଚରିତାନାନ୍ତୁ = ଉଦାରଚରିତାନାଂ + ତୁ
- ବସୁଧୈବ = ବସୁଧା + ଏବ
- ହଂସୋ ହି = ‘ହଂସ + ହି
![]()
- କ୍ଷୀରମାଦରେ = କ୍ଷୀରମ୍ + ଆଦରେ
- ତନ୍ନିଶ୍ରାତ୍ = ତତ୍ + ମିଶ୍ରିତ୍ଭ
- ବେନ୍ସ = ଭବେତ୍ + ନ
- କଦାପି = କଦା + ଅପି
- କଥମପି = କଥମ୍ + ଅପି
- ବର୍ଜୟତ୍ୟପଃ = ବର୍ଜୟତି + ଅପ
- ତଥୈବ = ତଥା + ଏବ
- କଷ୍ଟନ = କଃ + ଚନ
- ସଜନଃ = ସତ୍ + ଜନଃ
- ନିଷ୍ଠାପ = ନିଃ + ପାପଃ
- .ନିଷ୍କରୁନଃ = ନିଃ + କରୁନଃ
- ପ୍ରାପ୍ସ୍ୟାମି = ପ୍ର + ଆପ୍ସ୍ୟାମି
- ପ୍ରଧାନାମାତ୍ୟ = ପ୍ରଧାନ + ଅମାତ୍ୟ
- ତଥୈବ = ତଥା + ଏବ
- କାଳାନ୍ତରେ = କାଳ + ଅନ୍ତରେ
- ଜନ୍ମଭୂମିଷ୍ଟ = ଜନ୍ମଭୂମି + ଚ
- ସ୍ବର୍ଗାଦପି = ସ୍ଵର୍ଗତ୍ + ଅପି
- କଶ୍ଚିତ୍ = କଃ + ଚିତ୍
- ସର୍ବାଦୌ = ସର୍ବ + ଆଦୌ
- ପ୍ରାପ୍ରୁୟାତ୍ = ପ୍ର + ଆପ୍ୟାତ୍
- ବହବୋ ମଣ୍ଡୁକା = ବହନଃ + ମଣ୍ଡୁକା
- ସମ୍ମିଳିତା = ସମ୍ + ମିଳିତଃ
- ଇତ୍ୟାଦିଭିଂ = ଇତି + ଆଦିଭି
- କ୍ରୋ ବା = କଃ + ବା
- ତଥାପି = ତଥା + ଅପି
- ମନୋବଳମ୍ = ମନଃ + ବଳମ୍
- ପୁନରପି = ପୁନଃ + ଅପି
- କୋଽପି = କଃ + ଅପି
- ପାଦମପି = ପାଦମ୍ + ଅପି
- ପ୍ରାପ୍ତିବତଃ = ପ୍ର + ଆୟୁବତଃ
- କସ୍ୟାପି = କସ୍ୟ + ଅପି
- ଇତ୍ୟାଦୀନି = ଇତି + ଆଦାନ
- ଶକ୍ତ ଇତି = ଶନ୍ତଃ + ଇତି
- ପରସ୍କରମ୍ = ପରଃ + ପରମ୍
- ବଚନାନୁସାରମ୍ = ବଚନ + ଅନୁସାରମ୍
- କନ୍ୟାପି = କସ୍ୟ + ଅପି
- ସାଧୁଲମ୍ = ସାଧୁ + ଉକ୍ତମ୍
- ଅତ୍ୟଚ୍ଚ = ଅତି + ଉଚ୍ଚ
- ବାସୀଙ୍କ = ଚ+ ଆସୀତ୍
- କଣ୍ଟନ = କଃ + ଚନ
- ଅତୀବ = ଅତି + ଇବ
- ତତ୍ରୈବ = ତତ୍ର + ଏବ
- ସମ୍ଭବିଷ୍ୟତି = ସମ୍ + ଭବିଷ୍ୟତି
- ପ୍ରାପ୍ତବାନ୍ = ପ୍ର + ଆପ୍ତବାନ୍
- ଭବତାନ୍କମ = ଭବତାଂ + ମମ
- ଯତ୍ରାହିଂସା = ଯତ୍ର + ଅହିଂସା
![]()
- ସ୍ଵତନ୍ତ୍ରତା ସାଧନମୂକରୋତ୍ = ସ୍ୱତନ୍ତ୍ରତାସାଧନମ୍ ଅକରୋତ୍
- ରବୀନ୍ଦ୍ରା ମଧୁରମ୍ = ରବୀନ୍ଦ୍ର + ମଧୁରମ୍
- କାପି = କା’ + ଅପି .
- ସହୋଦରଃ = ସହ + ଉଦରଃ
- ବିହଙ୍ଗୋପତନେ = ବିହଙ୍ଗ + ଉତ୍ପତନେ
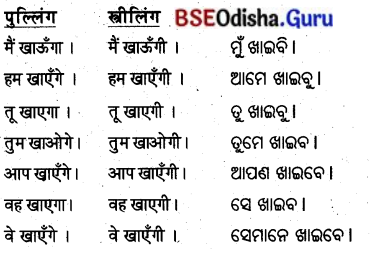
क्रियापदचयनम् (କ୍ରିୟାପଦଚୟନମ୍ )
प्रश्न 1.
ପ୍ରବହତି, ଗଙ୍ଗା, ଘୋଷିତବାନ୍, ଅକରୋତ୍, ପ୍ରବର୍ଗତେ, ଭବତି ।
उत्तर:
ପ୍ରବହତି, ଘୋଷିତବାନ୍, ଅକରୋଡ୍, ପ୍ରବର୍ଗତେ, ଭବତି।
प्रश्न 2.
ହଂସ, ଆଦତ୍ତ, ଦଶତି, ସ୍ୟାତ୍, ଭବେତ୍, କୁର୍ଥାତ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ଆଦରେ, ଦଶତି, ସ୍ୟାତ୍, ଭବେତ, କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟାତ୍।
प्रश्न 3.
ମୁଞ୍ଚତି, ପ୍ରାଷ୍ଟୋତି, ଧାର୍ଯ୍ୟ, ଯାତି, ଶିରସି, ବର୍ଣୟନ୍ତି ।
उत्तर:
ମୁଞ୍ଚତି, ପ୍ରାପ୍ନାତି, ଧାର୍ଯ୍ୟତେ, ଯାତି, ବର୍ଷୟନ୍ତି।
प्रश्न 4.
ଦଶତି, କୃତବାନ୍, ଅକରୋଡ୍, ପ୍ରଖରା, ଆସୀତ୍ବ, ଭବତି ।
उत्तर: ଦଶତି, କୃତବାନ୍, ଅକରୋତ, ଆସୀତ, ଭବତି ।
प्रश्न 5.
ନିବସନ୍ତି, ଭବତି, ଅସ୍ଥି, ଭୂମି, ପ୍ରାପ୍ରୁବନ୍ତି, ଆସୀତ୍।
उत्तर:
ନିବସ୍ତ୍ତି, ଭବତି, ଅସ୍ଥି, ପ୍ରାପ୍ତିବନ୍ତି, ଆସୀତ୍।
प्रश्न 6.
କୁର୍ବନ୍ତ, ଜାନାତି, ଅସ୍ଥି, ଅତ୍ର, ଭବତି, ପୋଷୟତି ।
उत्तर:
କୁର୍ବନ୍ତି, ଜାନାତି, ଅସ୍ଥି, ଭବତି, ପୋଷୟତି ।
![]()
प्रश्न 7.
ଅସ୍ଥି, ନିବସତି, ଲିଖୁତବାନ୍, ଭବତି, ସମର୍ପୟତି, ମାର୍ଗମ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ଅସ୍ଥି, ନିବସନ୍ତ, ଲିଖତବାନ୍, ଭବତି, ସମର୍ପୟନ୍ତି ।
प्रश्न 8.
ପ୍ରାଷ୍ଟୋତି, ସ୍ୟାତ୍, ପୃଷ୍ଟବାନ୍, ଭକ୍ତବାନ୍, ଭବାନ୍,ଅଗଚ୍ଛତ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ପ୍ରାଷ୍ଟୋତି, ସ୍ୟାତ, ପୃଷ୍ଟବାନ, ଉକ୍ତବାନ, ଅଗଚ୍ଛତ୍।
प्रश्न 9.
ଅସ୍ଥି, ପଠତି, ଇତି, ସ, ଆଗଚ୍ଛନ୍ତୁ, ହରଡି ।
उत्तर:
ଅଗ୍ନି, ପଠରି, ସରି, ଆଗଚ୍ଛନ୍ତୁ, ହରନ୍ତି ।
प्रश्न 10.
ମଣ୍ଡୟତି, ଜୀବନ୍ତ, ଭୂମି, କର୍ଷତି, କରୋତି, ଆନୟତି ।
उत्तर:
ମଣ୍ଡୟତି, ଜୀବନ୍ତି, କର୍ଷତି, କରୋତି, ଆନୟତି ।
प्रश्न 11.
କରିଷ୍ୟାମଃ, ଅଭବତ୍, କୃତବନ୍ତୀ, ନୀତବନ୍ତୀ, ଭାଷଣମ୍, ଆସୀତ୍ ।
उत्तर:
କରିଷ୍ୟାମଃ, ଅଭିବତ୍, କୃତବନ୍ତୀ, ନୀତବନ୍ତଃ, ଆସୀତ୍।
![]()
प्रश्न 12.
ହ୍ୟାମି, ଦୀୟତେ, ଦଣ୍ଡୟତି, ଇଚ୍ଛାମି, ପଠନ୍ତି ।
उत्तर:
ସ୍ମିଥ୍ୟାମି, ଦୀୟତେ, ଦଣ୍ଡୟତି, ଇଚ୍ଛାମି, ପଠନ୍ତି ।
प्रश्न 13.
ମମ, ଭବେୟୁ, ଭବିଷ୍ୟତି, ଅସ୍ଥି, ପାଳୟତି, ନେଷ୍ୟାମି |
उत्तर:
ଉବେୟୁ, ଭବିଷ୍ୟତି, ଅସ୍ଥି, ପାଳୟତି, ନେଷ୍ୟାମି।
प्रश्न 14.
ଭବତି, ପ୍ରୟଚ୍ଛନ୍ତି, ଆଗଳନ୍ତି, ସନ୍ତ, କୁର୍ବନ୍ତ, ତତ୍ର ।
उत्तर:
ଭବତି, ପ୍ରୟଚ୍ଛନ୍ତି, ଆଗଛନ୍ତି, ସନ୍ତ, କୁର୍ବନ୍ତି।
प्रश्न 15.
ରକ୍ଷତି, ନୟତି, କୁର୍ମ, ଜାନାତି, ପୁନଃ, ପ୍ରଣମତି।
उत्तर:
ରକ୍ଷତି, ନୟତି, କୁର୍ମୁ, ଜାନାତି, ପ୍ରଣମତି।
प्रश्न 16.
ଆସୀତ୍, ସୂତ୍ରମ୍, ଅଭିବତ୍, ଅପଶ୍ୟନ, ଅଭବନ, ଆଗଛନ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ଆସୀତ, ଅଭିବତ୍, ଅପଶ୍ୟନ୍, ଅଭବନ, ଆଗଚ୍ଛନ୍।
प्रश्न 17.
ଅପୀଡୟନ୍, ଅଭିବତ, ଦୁଃଖ୍ୟତଃ, ଆସୀତ, ଅଦଦାତ୍, ଅଚିନ୍ତୟତ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ଅପୀଡୟନ, ଅଭବତ, ଆସୀତ, ଅଦଦାତ, ଅଚିନ୍ତୟତ୍।
![]()
प्रश्न 18.
ଅପଶ୍ୟତ୍, ମରିଷ୍ୟତି, ଭବତି, କିମର୍ଥ୍ୟ, ରକ୍ଷତି, ଅଗଚ୍ଛତ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ଅପଶ୍ୟତ୍, ମରିଷ୍ୟତି, ଭବତି, ରକ୍ଷତି, ଅଗଚ୍ଛତ୍।
प्रश्न 19.
ଅବଦତ୍, ଭବତଃ, ଅଭିବତ୍, କାକ, ଅଗଚ୍ଛତ୍, ଆସୀତ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ଅବଦତ, ଭବତଃ, ଅଭିବତ୍, ଅଗଚ୍ଛିତ, ଆସୀତ୍।
प्रश्न 20.
ଦେହି, ଜଳମ୍, ରକ୍ଷ, ଆସୀତ୍, ଗତବାନ୍, ଭକ୍ତବାନ୍।
उत्तर:
ଦେହି, ରକ୍ଷ, ଆସୀତ, ଗତବାନ, ଉକ୍ତବାନ୍।
प्रश्न 21.
ରକ୍ଷତଃ, କରୋତି, ଛାତ୍ରା, ଭର୍ବତି, ଭବତଃ, ପଶ୍ୟତଃ ।
उत्तर:
ରକ୍ଷତଃ, କରୋତି, ଭବତି, ଭବତଃ, ପଶ୍ୟତଃ ।
प्रश्न 22.
କୁରୁତଃ, ପଶ୍ୟତଃ, ବର୍ଷୟତଃ, ଖ୍ରୀଷ୍ଟାବ୍ଦ, ପ୍ରାପ୍ତବାନ୍, ସ୍ମାରୟତି ।
उत्तर:
କୁରୁତଃ, ପଶ୍ୟତଃ, ବର୍ଷୟତଃ, ପ୍ରାପ୍ତବାନ, ସ୍ମାରୟତି ।
प्रश्न 23.
ଆଗତବନ୍ତଃ, ମୁଣ୍ଡୁକା, କୃତବତଃ, ବର୍ଷୟନ୍ତ, ଆସୀତ୍ବ, କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟାତ୍।
उत्तर:
ଆଗତବନ୍ତଃ, କୃତବତଃ, ବର୍ଷୟନ୍ତ, ଆସୀତ, କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟାତ୍ ।
प्रश्न 24.
କୃତବନ୍ତଃ, ପତିତବନ୍ତଃ, ମନୋବଳମ୍, କୁର୍ବନ୍ତ, ପ୍ରାପ୍ତବନ୍ତୀ, ଉଦ୍ଭବତୀ ।
उत्तर:
କୃତବନ୍ତଃ, ପତିତବନ୍ତଃ, କୁର୍ବନ୍ତି, ପ୍ରାପ୍ତବନ୍ତଃ, ଉଦ୍ଭବତୀ।
प्रश्न 25.
କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟା, ଶୃଣୁମା, ପ୍ରାପ୍ରୁୟା, ଭବେ, ଆଗଚ୍ଛତ, ଶିଶୁ ।
उत्तर:
କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟା, ଶୁଣୁୟଃ, ପ୍ରାପ୍ତି, ଭବେ, ଆଗଚ୍ଛିତ।
प्रश्न 26.
ଆଗଳତ୍ବ, ଭବତଃ, ପ୍ରାପ୍ତବାନ୍, ଅଭିବତ୍, କଥ୍ୟ, ଅବଦନ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ଆଗଚ୍ଛିତ, ଭବତଃ, ପ୍ରାପ୍ତବାନ୍, ଅଭିବତ୍, ଅବଦନ୍।
प्रश्न 27.
ଅବଦତ୍, ପ୍ରାପ୍ତବନ୍ତ, ଅଭବନ୍, ପ୍ରାପ୍ତବାନ୍, ପୁତ୍ର, ଭବେ ।
उत्तर:
ଅବଦତ୍, ପ୍ରାପ୍ତବନ୍ତଃ, ଅରବନ, ପ୍ରାପ୍ତବାନ୍, ଭବେ ।
प्रश्न 28.
କ୍ରନ୍ଦସି, କ୍ରନ୍ଦାମି, ଭବିଷ୍ୟତି, କରିଷ୍ୟାମି, ପୁତ୍ର, ଭବିଷ୍ୟାମି |
उत्तर:
କୁନ୍ଦସି, କ୍ରନ୍ଦାମି, ଭବିଷ୍ୟତି, କରିଷ୍ୟାମି, ଭବିଷ୍ୟାମି ।
![]()
प्रश्न 29.
ଜ୍ଞାତବତୀ, ଅସ୍ଥି, କ୍ରନ୍ଦସି, ଚିହ୍ନମ, ଭବନ୍ତି, ପୂଛନ୍ତି ।
उत्तर:
ଜ୍ଞାତବତୀ, ଅସ୍ଥି, କୁନ୍ଦସି, ଭବନ୍ତି, ପୂଛନ୍ତି ।
प्रश्न 30.
ଭବତି, ପୂଛନ୍ତି, ବିସ୍ମରନ୍ତି, ଦୁଃଖମ୍, କଥୟତ୍ତି, ଭବିଷ୍ଯତି ।
उत्तर:
ଭବନ୍ତି, ପୂଛନ୍ତି, ବିସ୍ମରନ୍ତି, କଥୟନ୍ତି, ଭବିଷ୍ୟତି।
प्रश्न 31.
ଭବିଷ୍ୟତି, ସ୍ଵାସ୍ୟତି, ସ୍ମରିଷ୍ୟତି, ଏତଦ୍, କଥୁତବତୀ, ଅଭିବତ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ଭବିଷ୍ୟତି, ସ୍ଵାସ୍ୟତି, ସ୍ମରିଷ୍ୟତି, କଥୁତବତୀ, ଅଭିବତ୍।
प्रश्न 32.
ଅପଶ୍ୟତ୍, ମରିଷ୍ୟତି, ସଜ୍ଜନଃ, ରକ୍ଷତି, ଭବତି, ଅବଦତ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ଅପଶ୍ୟତ୍, ମରିଷ୍ୟତି, ରକ୍ଷତି, ଭବତି, ଅବଦତ୍।
प्रश्न 33.
ସମ୍ଭବିଷ୍ୟତି, ଭବତି, କୁରୁତଃ, ପଶ୍ୟତ, ବର୍ଷୟତ, ଫଳମ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ସମ୍ଭବିଷ୍ୟତି, ଭବତି, କୁରୁତଃ, ପଶ୍ୟତ, ବର୍ଷୟତ ।
प्रश्न 34.
ପ୍ରକଟିତବତୀ, ଉତ୍ପାଟିତବାନ୍, ଦୂରୀକୃତବାନ୍, ଅଭିବତ୍, ନୟନମଃ, ସ୍ଵାସ୍ୟତି ।
उत्तर:
ପ୍ରକଟିତବତୀ, ଉତ୍ପାଟିତବାନ୍, ଦୂରୀକୃତବାନ୍, ଅଭିବତ୍, ସ୍ଵାସ୍ୟତି |
प्रश्न 35.
ଭ୍ରମତି, ଖେଳତି, ଦୁଷ୍ୟନ୍ତ, ବାଳିକା, ପଶ୍ୟାମି, ଦ୍ରଷ୍ୟାମି ।
उत्तर:
ଭ୍ରମତି, ଖେଳନ୍ତି, ଦ୍ରଷ୍ୟାନ୍ତ, ପଶ୍ୟାମି, ଦ୍ରଷ୍ୟାମି ।
प्रश्न 36.
ଚିନ୍ତୟତି, ସ୍ତମଃ, ବର୍ଷୟତି, କୁର୍ଯାତ୍, ଗଚ୍ଛେତ୍, ପତେତ୍।
उत्तर:
ଚିନ୍ତୟତି, ବର୍ଷୟତି, କୁର୍ଯାତ, ଗଚ୍ଛେତ, ପତେତ୍।
प्रश्न 37.
ଦତ୍ଥ, କୁର୍ମ, ପ୍ରାପ୍ରୁଥ, ପିବାମଃ, ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟ, ଶୁଣୁଥ ।
उत्तर:
ଦତ୍ଥ, କୁର୍ମୁ, ପ୍ରାପ୍ରୁଥ, ପିବାମଃ, ଶୁଣୁଥ।
![]()
प्रश्न 38.
ଆଗଚ୍ଛିତ, କୁରୁତ, ରକ୍ଷତ, ନିୟୋଜିତଃ, ଯୁବକ, ସ୍ଥାପିତବାନ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ଆଗଚ୍ଛିତ, କୁରୁତ, ରକ୍ଷତ, ନିୟୋଜିତଃ, ସ୍ଥାପିତବାନ୍।
प्रश्न 39.
ତିଷ୍ଠତି, ତିଷ୍ଠତଃ, ତିଷ୍ଠନ୍ତି, ବାଳିକେ, ଦଦାତି, ଜାନାତି ।
उत्तर:
ତିଷ୍ଠତି, ତିଷ୍ଠତଃ, ତିଷ୍ଠନ୍ତି, ଦଦାତି, ଜାନାତି।
प्रश्न 40.
କରୋଷି, କୁରୁଥା, କୁରୁଥ, ବୟମ, ପଶ୍ୟସି, ପଶ୍ୟଥ ।
उत्तर:
କରୋଷି, କୁରୁଥ, କୁରୁଥ, ପଶ୍ୟସି, ପଶ୍ୟଥ ।
प्रश्न 41.
ସୁରିଷ୍ୟତି, ପୁତ୍ର, କଥୁତବତୀ, ରଚିତବାନ୍, କୃତବାନ୍, ଅର୍ପିତବାନ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ସ୍ମରିଷ୍ୟନ୍ତ, କଥୁତବତୀ, ରଚିତବାନ, କୃତବାନ୍, ଅର୍ପିତବାନ୍।
प्रश्न 42.
ବୃକ୍ଷ, ଆସୀତ୍ବ, ଅଭିବତ୍, ଅପଶ୍ୟନ୍, ଅଭବନ, ଆଗଚ୍ଛନ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ଆସୀତ, ଅଭିବତ, ଅପଶ୍ୟନ୍, ଅଭବନ, ଆଗର୍ଜନ।
प्रश्न 43.
ଦୃଶ୍ୟତେ, ଚାଣକ୍ୟ, ପୂଛନ୍ତି, ବିସ୍ମରନ୍ତି, ବିସ୍ମରିଷ୍ୟସି, କଥୟତି ।
उत्तर:
ଦୃଶ୍ୟତେ, ପୃଚ୍ଛନ୍ତି, ବିସ୍ମରତି, ବିସ୍ମରିଷ୍ୟସି, କଥୟତି।
प्रश्न 44.
ପ୍ରାପ୍ରୁୟାତ୍ର, ନିର୍ଣ୍ଣୀତବନ୍ତୀ, ମୟୂକ, ଆଗତବନ୍ତୀ, କୃତବନ୍ତଃ, ବର୍ଷୟନ୍ତ ସୁ ।
उत्तर:
ପ୍ରାପ୍ୟୟାତ, ନିର୍ଣ୍ଣୀତବନ୍ତଃ, ଆଗତବନ୍ତଃ, କୃତବନ୍ତଃ, ବର୍ଣ୍ଣୟନ୍ତ
प्रश्न 45.
କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟା, ଶୁଣୁୟଃ, ପ୍ରାପ୍ରୁୟା, ବାଳିକା, ଭବେ, ଆଗଚ୍ଛତ୍ ।
उत्तर:
କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟା, ଶୃଣୁୟାଁ, ପ୍ରାପ୍ତି, ଭବେ, ଆଗଚ୍ଛିତ୍।
![]()
प्रश्न 46.
ତ୍ୟଜସି, ଲିଖନ୍ତି, ଗଚ୍ଛତୁ, ଭବତଃ, ଆଗଚ୍ଛନ, ଅପଶ୍ୟନ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ତ୍ୟଜର୍ସି, ଲିଖନ୍ତି, ଗଛତୁ, ଆଗଚ୍ଛନ, ଅପଶ୍ୟନ୍।
प्रश्न 47.
ହସସି, ତୁମ୍, ହସ, ହସଥ, ଭବସି, ଭବତଃ ।
उत्तर:
ହସସି, ହସଥା, ହସଥ, ଭବସି, ଭବତଃ ।
प्रश्न 48.
ପତିତବନ୍ତଃ, କୁର୍ବନ୍ତ, ଦର୍ଶକା, ଆରୂଢ଼ବାନ, ପ୍ରାପ୍ତବତଃ, ଉଦ୍ଭବତୀ ।
उत्तर:
ପତିତବନ୍ତଃ, କୁର୍ବନ୍ତ, ଆରୂଢ଼ବାନ, ପ୍ରାପ୍ତିବନ୍ତୀ, ଉଦ୍ଭବତୀ।
प्रश्न 49.
ଅସ୍ତି, ନୟନ୍ତି, ସନ୍ତି, ସ୍ତ୍ରୀ, ମିତ୍ରାଣି, ତିଷ୍ଠତି ।
उत्तर:
ଅସ୍ତି, ନୟନ୍ତି, ସରି, ଡଃ, ତିଷ୍ଠତି।
प्रश्न 50.
ଧାବତି, ଧାବତଃ, ଧାବନ୍ତି, କୂଜନ୍ତି, କୋକିଳ, ନୃତ୍ୟନ୍ତ ।
उत्तर:
ଧାବତି, ଧାବତଃ, ଧାବନ୍ତି, କୂଜନ୍ତି, ନୃତ୍ୟନ୍ତି।
प्रश्न 51.
ଗଚ୍ଛାବ, ପଠାବ, ହସାବ, ଭବାନଃ, ଆବାମ୍, ପଶ୍ୟାବ
उत्तर:
ଗଚ୍ଛାବାଃ, ପଠାଦଃ, ହସାବ, ଭବାନଃ, ପଶ୍ୟାବ ।
प्रश्न 52.
ଗର୍ଜତି, ଦଶତି, ଆରୋହତି, ସ୍ନିହ୍ୟତି, କର୍ଷତି, କୃଷକ।
उत्तर:
ଗର୍ଜତି, ଦଶତି, ଆରୋହତି, ସ୍ପୃହ୍ୟତି, କର୍ଷତି ।
प्रश्न 53.
ପଠସି, ପଠଥ, ପଠଥ, ଯୁବାମ, ଭବସି, ଭବତଃ ।
उत्तर:
ପଠସି, ପଠଥ୍ୟ, ପଠଥ, ଭବସି, ଭବଥ ।
प्रश्न 54.
ଧାବନ୍ତି, ରଚୟତି, ଯାତି, ପାଳୟତି, କୂଜତି, ଅହମ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ଧାବନ୍ତି, ରଚୟତି, ଯାତି, ପାଳୟତି, କୂଜତି ।
![]()
प्रश्न 55.
ଉବେୟମ୍, ଶୁଣୁୟାମ୍, ନିଷ୍ପୀତବାନ୍, ସା, କ୍ରନ୍ଦସି, କ୍ରନ୍ଦାମି ।
उत्तर:
ରବେୟମ୍, ଶୃଣୁୟାମ, ନିଶ୍ଚିତବାନ, କ୍ରନ୍ଦସି, କ୍ରନ୍ଦାମି।
प्रश्न 56.
ଦେହି, ରକ୍ଷ, କୃତବତଃ, ସୈନ୍ୟା, ଗତବାନ୍, ଭକ୍ତବାନ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ଦେହି, ରକ୍ଷ, କୃତବନ୍ତୀ, ଗତବାନ୍, ଭକ୍ତବାନ୍।
प्रश्न 57.
ଯାପୟତି, ପଠତି, ମିତ୍ର, ହସ୍ପତି, ନୟତି, ଦଦାତି ।
उत्तर:
ଯାପୟତି, ପଠତି, ହସତି, ନୟତି, ଦଦାତି ।
प्रश्न 58.
ପଶ୍ୟସି, ପଶ୍ୟଥ, ପଶ୍ୟଥ, ନୟସି, ନୟଥ, ଛାତ୍ରା ।
उत्तर:
ପଶ୍ୟସି, ପଶ୍ୟଥ, ପଶ୍ୟଥ, ନୟସି, ନୟଥା ।
प्रश्न 59.
କୃଷକ, ବିକସତି, ରକ୍ଷତି, ପଠତି, ସ୍ନିହାତି, ଜଛତି ।
उत्तर:
ବିକସତି, ରକ୍ଷତି, ପଠତି, ସ୍ନିନ୍ଦ୍ୟତି, ଜତି।
प्रश्न 60.
କ୍ରୀଣୀତଃ, ଗୃହ୍ମୀତଃ, ଚିନୁତଃ, ତ୍ୱ, ରୁଦତଃ, ନୟାବ ।
उत्तर:
କ୍ରୀଣୀତଃ, ଗୃହ୍ମୀତଃ, ଚିନୁତଃ, ରୁଦତଃ, ନୟାବ ।
प्रश्न 61.
ଈଶ୍ୱରଃ, ଆଗଚ୍ଛତି, ପଶ୍ୟତି, ଚିନ୍ତୟତି, ଜନୟତି, କରୋତି ।
उत्तर:
ଆଗଚ୍ଛତି, ପଶ୍ୟତି, ଚିନ୍ତସ୍ଥତି, ଜନୟତି, କରୋତି।
![]()
प्रश्न 62.
ହସାମି, ପିତା, ପଠାମ, ଭବତି, ଦଦାସି, ଅସ୍ଥି ।
उत्तर:
ହସାମି, ପଠାମଃ, ଭବତି, ଦଦାସି, ଅନ୍ତି।
प्रश्न 63.
କ୍ରୀଣନ୍ତି, ଗୃହୁରି, ଚିନ୍ଧତି, ରୁଦନ୍ତି, ନୟାମଃ, ପିତା ।
उत्तर:
କ୍ରୀଣନ୍ତି, ଗୃହୁରି, ଚିନ୍ତି, ରୁଦନ୍ତି, ନୟାମଃ ।
प्रश्न 64.
ଆରୋହତି, ବାନରଃ, ଦଶତି, ଗର୍ଜତି, ନିନ୍ଦତି, ସ୍ମରତି।
उत्तर:
ଆରୋହତି, ଦଶତି, ଗର୍ଜତି, ନିନ୍ଦତି, ସ୍ମରତି।
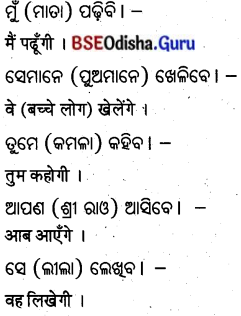
कर्तृ पदचयनम् (କର୍ତ୍ତୃପଦଚୟନମ୍ )
प्रश्न 1.
ଭାରତୀ, ମନୋଜଃ, ପ୍ରଣମତି, ସ୍ୱ, ମାତା, ପରିବେଶଃ ।
उत्तर:
ଭାରତୀ, ମନୋଜଃ, ସ, ମାତା, ପରିବେଶଃ ।
प्रश्न 2.
ବାୟୁ, କ୍ଷେତ୍ରାଣି, ଜୀବା, ଭବତି, ମେଘା, ପରିବେଶଃ ।
उत्तर:
ବାୟୁ, କ୍ଷେତ୍ରାଣି, ଜୀବା, ମେଘା, ପରିବେଶଃ ।
प्रश्न 3.
ଦେଶଃ, ରାଜ୍ୟ, ରାଜଧାନୀ, ରାଜାନୀ, କୁର୍ବନ୍ତ, ସରୋବରଃ ।
उत्तर:
ଦେଶ, ରାଜ୍ୟ, ରାଜଧାନୀ, ରାଜାନଃ, ସରୋବରଃ ।
प्रश्न 4.
ରାଜା, ପ୍ରଜାଃ, ସାଧବ, ତେ, ଭବାନ୍, ସ୍ୟାତ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ରାଜା, ପ୍ରଜାଃ, ସାଧବୀ, ତେ, ଭବାନ୍।
प्रश्न 5.
ଛାତ୍ରୀ, ଶିକ୍ଷକ, ସ୍ୱ, ସ୍ବୟଂ, ଆସୀତ୍ବ, ଗୋପାଳ ।
उत्तर:
ଛାତ୍ରୀ, ଶିକ୍ଷକଃ, ସ୍ୱ, ସ୍ଵୟଂ, ଗୋପାଳ ।
प्रश्न 6.
ବାଳକ, ଏଷ, ଅହଂ, ସେବକଃ, ବୟଃ, ନୀତବନ୍ତଃ ।
उत्तर:
ବାଳକଃ, ଏହିଃ, ଅହଂ, ସେବକଃ, ବୟମ୍ ।
प्रश्न 7.
ଗୁରୁ, ମୁକୁନ୍ଦଦେବୀ, ସୈନିକ, ଅଭବତ୍, ମାତୃଭୂମି ଭବାନ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ଗୁରୁ, ମୁକୁନ୍ଦଦେବାଃ, ସୈନିକ, ମାତୃଭୂମି, ଭବାନ୍ ।
प्रश्न 8.
ଜନା, ନଦ୍ୟ, ଭୂମି, ଶସ୍ୟାନି, କୃଷକ, ଭବତି ।
उत्तर:
ଜନଃ, ନଦ୍ୟ, ଭୂମି, ଶସ୍ୟାନି, କୃଷକ ।
प्रश्न 9.
ହରେକୃଷ୍ଣ, ଅହଂ, ଭବାନ୍, ପଠତି, ଛାତ୍ରା, ବୃକ୍ଷ ।
उत्तर:
ହରେକୃଷ୍ଣ, ଅହଂ, ଭବାନ, ଛାତ୍ରା, ବୃକ୍ଷା ।
प्रश्न 10.
ପଥଦଃ, ସ, ବୃଦ୍ଧ, ପୃଷ୍ଟବାନ୍, ଭବାନ୍, ଯଃ ।
उत्तर:
ପଥଦଃ, ସ, ବୃଦ୍ଧା, ଭବାନ୍, ଯଃ ।
प्रश्न 11.
ଭଲୁକ, ଗନ୍ଧମାଦନ, ପରିମଳଗିରି, ଏତତ୍ତ୍ଵ, ଭକ୍ତା, କରୋତି ।
उत्तर:
ଭଲୁକ, ଗନ୍ଧମାଦନ, ପରିମଳଗିରି, ଏତତ୍, ଭକ୍ତା|
![]()
प्रश्न 12.
ମହର୍ଷି, ସ୍ୱ, କ୍ଷେତ୍ର, ଅରଣ୍ୟ, ଜନା, ପୋଷୟତ୍ତି ।
उत्तर:
ମହର୍ଷି, ଡଃ, କ୍ଷେତ୍ର, ଅରଣ୍ୟମ୍, ଜନା ।
प्रश्न 13.
ପାଦପା, ମନ୍ଦିରମ, ଧୀବତି, ଯାତ୍ରିକା, ପର୍ଯଟକଃ, ପ୍ରାଚୀରମ୍ |
उत्तर:
ପାଦପା, ମନ୍ଦିରମ, ଯାତ୍ରିକା, ପର୍ଯଟକଃ, ପ୍ରାଚୀରମ୍।
प्रश्न 14.
ଗଙ୍ଗା, ଦେଶ, ତିଳକ, ରବୀନ୍ଦ୍ର, ପ୍ରବହିତ, ଜନଃ ।
उत्तर:
ଗଙ୍ଗା, ଦେଶଃ, ତିଳକ, ରବୀନ୍ଦ୍ର, ଜନଃ ।
प्रश्न 15.
ଆଦରେ, ହଂସ, ଦୀର୍ଘଦର୍ଶୀ, କୁଟୁମ୍ବକମ୍, ଅଙ୍ଗାରଃ, ପ୍ରତିକୂଳାନି।
उत्तर:
ହଂସ, ଦୀର୍ଘଦର୍ଶୀ, କୁଟୁମ୍ବକମ୍, ଅଙ୍ଗାରଃ, ପ୍ରତିକୂଳାନି।
प्रश्न 16.
ମୃତ୍ୟୁ, ବିଚକ୍ଷଣା, ସର୍ପ, ଦଶତି, ଦୁର୍ଜନୀ, ନରେଶଃ ।
उत्तर:
ମୃତ୍ଯୁ, ବିଚକ୍ଷଣା, ସର୍ପ, ଦୁର୍ଜନଃ, ନରେଶଃ ।
प्रश्न 17.
ସ୍ୱ, ତେ, ଗର୍ବାନ୍ଧ, ମହୀନ୍ଦ୍ର, ମହାପୁରୁଷା, ଜ୍ଞାତବାନ୍।
उत्तर:
ସ୍ୱ, ତେ, ଗର୍ବାନ୍ଧୀ, ମହୀନ୍ଦ୍ର, ମହାପୁରୁଷା ।
प्रश्न 18.
ଠାକୁରରାଜଃ, ମନ୍ତ୍ରୀ, ରାଜଗୁରୁ, ଜନା, ପ୍ରବିଷ୍ଟବତଃ, ନେତାରଃ ।
उत्तर:
ଠାକୁରରାଜଃ, ମନ୍ତ୍ରୀ, ରାଜଗୁରୁ, ଜନା, ନେତାରଃ ।
प्रश्न 19.
ଦେଶଃ, ଦାୟାଦଃ, ତେ, ଭାରତଂ, ନୀତବନ୍ତୀ, ଏଷା ।
उत्तर:
ଦେଶଃ, ଦାୟାଦଃ, ତେ, ଭାରତଂ, ଏଷା।
प्रश्न 20.
ବଟବୃକ୍ଷ, ପରିବାରଃ, ଶାବକ, ନୟତି, ମାତା, ଶୁକଃ ।
उत्तर:
ବଟବୃକ୍ଷ, ପରିବାରଃ, ଶାବକ, ମାତା, ଶୁକଃ ।
प्रश्न 21.
ସର୍ବେ, ବରଂ, ଶୁକଃ, ବ୍ୟାଧ୍ୟ, ପଶ୍ୟତି, ମାତା ।
उत्तर:
ସର୍ବେ, ବୟଂ, ଶୁକଃ, ବ୍ୟାଧ, ମାତା ।
प्रश्न 22.
ଆମ୍ରବୃକ୍ଷ, ଆସୀ, ସୂତ୍ର, କୋକିଳ, ସ, କାକଃ ।
उत्तर:
ଆମ୍ରବୃକ୍ଷ, ସୂତ୍ର, କୋକିଳୀ, ସ, କାକଃ ।
प्रश्न 23.
କାକା, ତେ, କ୍ରମେଣ, ସ୍ୱ, କୋକିଳ, ସଜନଃ ।
उत्तर:
କାକା, ତେ, ଡଃ, କୋକିନଃ, ସଜ୍ଜନଃ ।
प्रश्न 24.
ସୈନିକା, ଯୁବକ, ରକ୍ଷତ, ହେନେରୀ, ମାତା, ସେବିକା ।
उत्तर:
ସୈନିକଃ, ଯୁବକ, ହେନେରୀ, ମାତା, ସେବିକା।
प्रश्न 25.
ଜନମଃ, ହେନେରୀ, ଯୁବକ, ବ୍ୟବସାୟୀ, ଶ୍ରୁତମ, ସୈନିକା ।
उत्तर:
ଜନମଃ, ହେନେରୀ, ଯୁବକ, ବ୍ୟବସାୟୀ, ସୈନିକା।.
प्रश्न 26.
ଯଃ, ଭବେତ୍, ସର୍ବେ, ମଣ୍ଡୁକା, ଦର୍ଶକା, ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ।
उत्तर:
ଯଃ, ସର୍ବେ, ମଣ୍ଡୁକା, ଦର୍ଶକା, ସ୍ତମଃ ।
प्रश्न 27.
ସ୍ତତଃ, ଯଃ, ସ, ତ୍ୱ, ପତେତ, ଦର୍ଶକଃ ।
उत्तर:
ସ୍ତମଃ, ଯଃ, ସ, ବଂ, ଦର୍ଶକଃ ।
प्रश्न 28.
ପୁତ୍ର, ତ୍ୱ, ଏଷ, ଜନା, ଏଷା, ବିସ୍ମରିଷ୍ଯତି।
उत्तर:
ପୁନଃ, ବଂ, ଏଷ, ଜନଃ, ଏଷା ।
प्रश्न 29.
ବାଳ, ବାଣକ୍ୟ, ଏତତ୍ବ, ଏଷ, ଜନନୀ, ଅସ୍ଥି ।
उत्तर:
ବାଳ, ଚାଣକ୍ୟ, ଏତତ, ଏଷ, ଜନନୀ।
प्रश्न 30.
ଯୁବତଃ, ସୈନିକ, ଗ୍ରାମ, ପ୍ରାଣା, କୁରୁତ, ଧାର୍ମିକୀ ।
उत्तर:
ଯୁବତଃ, ସୈନିକ, ଗ୍ରାମଃ, ପ୍ରାଣୀ, ଧାର୍ମିକୀ।
प्रश्न 31
କୁର୍ଯ୍ୟାତ୍, ମଣ୍ଡୁକ, ଯଃ, ସ୍ତମଃ, ଶିଖରଃ, ବିଜୟୀ ।
उत्तर:
ମଣ୍ଡୁକଃ, ଯଃ, ସ୍ତମଃ, ଶିଖରଃ, ବିଜୟୀ ।
प्रश्न 32.
ବାଟିକା, ଭବତ, ଜନମଃ, ରତିଃ, ସରଳୀ, ମାର୍ଗ ।
उत्तर:
ବାଟିକା, ଜନମଃ, ରବି, ସରଜଃ, ମାର୍ଗ ।
प्रश्न 33.
କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ, ଏଷ, ପଶ୍ୟତ, ମହତ୍, ପୁରସ୍କାର, ମାନମଃ ।
उत्तर:
କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ, ଏଷ, ମହତ୍ବ, ପୁରସ୍କାରଃ, ମାନମଃ।
![]()
प्रश्न 34.
ଭାରତବର୍ଷମ, ଭବାନ୍, ଅକରୋତ୍, ତିଳକ, ଅହିଂସା, ସ୍ୱତନ୍ତ୍ରତା ।
उत्तर:
ଭାରତବର୍ଷମ, ଭବାନ, ତିଳକ, ଅହିଂସା, ସ୍ଵତନ୍ତ୍ରତା।
प्रश्न 35.
ରବୀନ୍ଦ୍ର, ମଧୁରଂ, ଗାନଂ, ଅତନୋତୁ, ଦେଶଃ, ଜନ୍ମ।
उत्तर:
ରବୀନ୍ଦ୍ର, ମଧୁରଂ, ଗାନଂ, ଦେଶଃ, ଜନ୍ମ।
प्रश्न 36.
ମନୁଜାଃ, ସର୍ବେ, ସହୋଦରା, ବିହଙ୍ଗା, ପ୍ରବର୍ତତେ, ଧର୍ମ ।
उत्तर:
ମନୁଜାଃ, ସର୍ବେ, ସହୋଦରା, ବିହଙ୍ଗା, ଧର୍ମ୍ଯ ।
प्रश्न 37.
ମନୋଜଃ, ଭବତି, ବାୟୁ, ପରିବେଶ, ମାତା, ଇୟମ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ମନୋଜଃ, ବାୟୁ, ପରିବେଶ, ମାତା, ଇୟମ୍।
प्रश्न 38.
ଇୟମ୍, କଃ, ବାୟୁ, ଜୀବା, ମେଘା, ପୂଚ୍ଛତି ।
उत्तर:
ଇୟମ୍, କଃ, ବାୟୁ, ଜୀବା, ମେଘା ।
प्रश्न 39.
ମେଘା, ବୃକ୍ଷା, ମାତା, ଭବତି, ବୃଦ୍ଧି, ରମା ।
उत्तर:
ମେଘା, ବୃକ୍ଷା, ମାତା, ବୃଦ୍ଧି, ରମା ।
प्रश्न 40.
ଦେଶଃ, ଏଷା, ପୁତ୍ର, କଥୟତି, ବାୟୁ, ସ୍ୱସାରଃ ।
उत्तर:
ଦେଶଃ, ଏଷା, ପୁନଃ, ବାୟୁ, ସ୍ଵରଃ ।
प्रश्न 41.
ସ୍ୱ, ସ୍ଵସା, ଦୁହିତା, କରୋତି, ପର୍ବତଃ, ମେଘା ।
उत्तर:
ସ, ସ୍ଵସା, ଦୁହିତା, ପର୍ବତଃ, ମେଘା ।
प्रश्न 42. ଜନଃ, ଜ୍ୟେଷ୍ଠା, ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ, ଭବନ୍ତି,ଏଷା, ବାଳ ।
उत्तर:
ଜନଃ, ଜ୍ୟେଷ୍ଠା, ଶ୍ଳେଷ୍ମା, ଏଷା, ବାଜଃ ।
प्रश्न 43.
ବୃକ୍ଷ, ଜୀବା, ମେଘା, ଭ୍ରମତି, ମନୋଜଃ, ଇୟମ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ବୃକ୍ଷ, ଜୀବା, ମେଘା, ମନୋଜଃ, ଇୟମ୍ ।
प्रश्न 44.
ନିର୍ମାଣମ୍, ଅହମ୍, ଭବିଷ୍ୟସି, ଦର୍ପଣମ୍, ଚିହ୍ନମ, ଏଷ ।
उत्तर:
ନିର୍ମାଣମ୍, ଅହମ୍, ଦର୍ପଣମ୍, ଚିହ୍ନମ, ଏଷ ।
![]()
प्रश्न 45.
ଲୋକା, ନୀତିଃ, ମତଃ, ଭରି, ଶତିଃ, କୃତବାନ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ଲୋକା, ନୀତିଃ, ମତିଃ, ଭଲ୍ଲି, ଶ ।
प्रश्न 46.
ପାଦଃ, ଦର୍ଶକଃ, ଏକା, କୁର୍ଯା, ପୁତ୍ର, ସଫଳ ।
उत्तर:
ପାଦଃ, ଏକା, ଦର୍ଶକଃ, ପୁନଃ, ସଫଳ ।
प्रश्न 47.
ମୂର୍ଖ, ସର୍ବେ, ମାତରଃ, ଶିଶୁ, ଅହମ୍, ପ୍ରାପ୍ତବାନ।
उत्तर:
ମୂର୍ଖ, ସର୍ବେ, ମାତରଃ, ଶିଶୁ, ଅହଂ ।
प्रश्न 48.
ଉଜଃ, ପତେ, ଯନ୍ତ୍ର, ବଚନମ୍, ତେ, କଃ ।
उत्तर:
ଉଚ୍ଚା, ଯନ୍ମ, ବଚନ, ତେ, କଃ ।
प्रश्न 49.
ଏତତ୍ କୌଟିଲ୍ୟ, ନେତ୍ରୀ, ମଙ୍ଗଳ, ପଶ୍ୟ, ମାତୃଭୂମି ।
उत्तर:
ଏତତ୍, କୌଟିଲ୍ୟ, ନେତ୍ରୀ, ମଙ୍ଗଳଂ, ମାତୃଭୂମି ।
प्रश्न 50.
ମାତରଃ, ଦୁହିତରଃ, ବାୟୁ, ଯାତି, କଃ, ମାତା ।
उत्तर:
ମାତରଃ, ଦୁହିତରଃ, ବାୟୁ, କଃ, ମାତା ।
प्रश्न 51.
ମାତରଃ, ରାମଃ, ମନୋଜଃ, କରୋତି, ବୟମ୍, ଅହମ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ମାତରଃ, ରାମଃ, ମନୋଜଃ, ବୟମ୍, ଅହମ୍ ।
प्रश्न 52.
ଭ୍ରମତି, ପରିବେଶ, ଜଳମ୍, ଗଗନମ୍, ଭୂମି, ହାଃ ।
उत्तर:
ପରିବେଶ, ଜଳମ୍ବ, ଗଗନମ, ଭୂମି, ଡଃ ।
प्रश्न 53.
ଯାତ୍ରା, ଦୁହିତା, ଦୁହିତରଃ, ନନାନ୍ଦା, କରୋତି, ସ୍ଵସା ।
उत्तर:
ଯାତ୍ରା, ଦୁହିତା, ଦୁହିତରଃ, ନନାନ୍ଦା, ସ୍ଵସା ।
प्रश्न 54.
ବଂଶଃ, ଚନ୍ଦ୍ରଗୁପ୍ତା, ରାମାୟଣମ୍, ବାକ୍ୟ, ସ୍ମରତି, ମଧୁ ।
उत्तर:
ବଂଶ, ଚନ୍ଦ୍ରଗୁପ୍ତ, ରାମାୟଣମ୍, ବାକ୍ୟ, ମଧୁ।
प्रश्न 55.
ରାଷ୍ଟ୍ରମ, ପ୍ରବହତି, ବିମଳା, ଗଙ୍ଗା, ବେଦଃ, ପବିତ୍ରମ୍ |
उत्तर:
ରାଷ୍ଟ୍ରମ, ବିମଳା, ଗଙ୍ଗା, ବେଦଃ, ପବିତ୍ରମ୍ ।
प्रश्न 56.
ପୁନଃ, ମାତରଃ, ଅହମ୍, ବୟମ୍, ଫଳମ୍ ପୃଚ୍ଛତି ।
उत्तर:
ପୁନଃ, ମାତରଃ, ଅହମ୍, ବୟମ୍, ଫଳମ୍ ।
प्रश्न 57.
ମାତା, ଭୂମି, ଭବତି, ଗଗନମ, ପରିବେଶଃ, ବୃକ୍ଷା ।
उत्तर:
ମାତା, ଭୂମି, ଗଗନମ, ପରିବେଶଃ, ବୃକ୍ଷା ।
![]()
प्रश्न 58.
ଏକା, ପୁତ୍ର, ଭବୋ, ବଧୂର, ବାଳକଃ, ପ୍ରୟାସ ।
उत्तर:
ଏକା, ପୁନଃ, ବଧୂରଃ, ବାଳକ, ପ୍ରୟାତଃ ।
प्रश्न 59.
କ୍ରନ୍ଦସି, ଚାଣକ୍ୟ, ଶିଶୁ, ପୁଂ, ହସ୍ତ, ମଗଧଃ ।
उत्तर:
ଚାଣକ୍ୟ, ଶିଶୁ, ବଂ, ହସ୍ତୀ, ମଗଧଃ ।
प्रश्न 60.
ଅସ୍ଥି, ମମ, ନଦୀ, ପ୍ରଜାଃ, ନରେଶଃ, ଗ୍ରାମାଧୀଶଃ ।
उत्तर:
ମମ, ନଦୀ, ପ୍ରଜାଃ, ନରେଶଃ, ଗ୍ରାମାଧୀଶଃ ।
प्रश्न 61.
ସା, କୃଷ୍ଣବହିଃ, ଈଶ୍ୱରଃ, ସୁନ୍ଦରଃ, ଅସୁନ୍ଦରା, ଭବତି ।
उत्तर:
ସା, କୃଷ୍ଣବର୍ଶୀ, ଈଶ୍ୱରଃ, ସୁନ୍ଦରଃ, ଅସୁନ୍ଦରଃ ।
प्रश्न 62.
ଈର୍ଷା, ଆଗଛତି, ସ, ଗାନମ୍, ନେତ୍ରମ, ତୃପ୍ତି ।
उत्तर:
ଈର୍ଷା, ସା, ଗାନମ୍, ନେତ୍ରମ୍, ତୃପ୍ତି ।
प्रश्न 63.
ସୁଙ୍ଖ, ଦୁଃଖ, ଆସୀତ୍ବ, ମିତ୍ର, ଫଳ, ବନମ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ସୁଖ, ଦୁଃଖ, ମିତ୍ର, ଫଳ, ବନମ୍।
प्रश्न 64.
ସର୍ବା, ଅଭବତ୍, ଭବାନ୍, ସୂତ୍ର, ଛିନ୍ନମ୍, ଶୀଘ୍ରମ୍ ।
उत्तर:
ସର୍ବା, ଭବାନ୍, ସୂତ୍ର, ଛିନ୍ନମ, ଶୀଘ୍ରମ୍ ।
प्रश्न 65.
ପିତା, ତେ, ବୟମ୍, ଭବତି, ବୃକ୍ଷ ।
उत्तर:
ପିତା, ତେ, ବୟମ୍, ବୃକ୍ଷ ।
प्रश्न 66.
ଭବତି, କୋକିଳ, ଶୁକ, କୃପା, ପରିବାରଃ, ସୁବର୍ଷବର୍ଷ ।
उत्तर:
କୋକିଳ, ଶୁକଃ, କୃପା, ପରିବାରଃ, ସୁବର୍ଣ୍ଣବହିଃ ।
प्रश्न 67.
ବ୍ୟାଧଃ, ପିଞ୍ଜରା, ଅହଂ, ବଦତି, ସୃଷ୍ଟି, ମନଃ ।
उत्तर:
ବ୍ୟାଧଃ, ପିଞ୍ଜରା, ଅହଂ, ସୃଷ୍ଟି, ମନଃ ।
प्रश्न 68.
ଯନଂ, ସୂତ୍ର, ବନ୍ଧ, କାକା, ଚଞ୍ଚୁ, ଅଭବନ୍।
उत्तर:
ଯନଂ, ସୂତ୍ର, ବନ୍ଧ୍ୟା, କାକା, ଚଞ୍ଚୁ
![]()
प्रश्न 69.
ବଟବୃକ୍ଷ, ଏକ, ନୂତନଃ, ଶାବକ, ସା, ଅଛି ।
उत्तर:
ବଟବୃକ୍ଷ, ଏକ, ନୂତନଃ, ଶାବୟଃ, ସା।
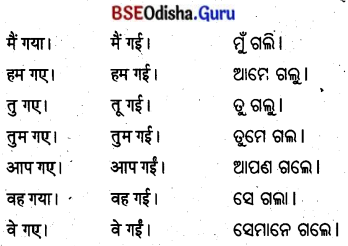
वाक्यगठनम् (ବାକ୍ୟଗଠନମ୍)
- ଇଣ୍ଡିଂ – (ଇଏ) ଇୟଂ ମମ ଜନନୀ।
- ପ୍ରତିଦିନ – (ପ୍ରତିଦିନ) ପ୍ରତିଦିନଂ ପାଠ୍ୟ ପଠ।
- ଏକଦା – (ଥରେ) ଏକଦା ତତ୍ର ବନମ୍ ଆସୀତ୍
- ସହ – (ସହିତ) ମାତ୍ରା ସହ ମନୋଜଃ ଭ୍ରମତି ।
- ତଦା – (ସେତେବେଳେ) ତଦା ମାତ୍ରେ ନିବେଦୟତି।
- କୃପୟା – (ଦୟାକରି) କୃପୟା ବଦତୁ।
- ପରିତଃ – (ଚାରିପଟେ) ଅମ୍ଳାନ୍ ପରିତଃ ଯଃ ଦୃଶ୍ୟମାନଃ ଅସ୍ତି ଡଃ ପରିବେଶଃ ।
- ପୁନଃ – (ପୁଣି) ପୁନଃ ପୁନଃ ପୃଚ୍ଛତି।
- ଭବତି – (ହୁଏ) ଭୂମି ଦୂଷିତା ଭବତି ।
- କୁର୍ମ – (କରିବା) ବୃୟଂ ବୃକ୍ଷଣା ରୋପଣଂ କୁର୍ମା।
- ତହିଁ – (ତେବେ) ତହିଁ ପରିବେଶଃ ସୁରକ୍ଷିତଃ ଭବେତ୍।
- ବିଶ୍ଵାସ – (ବିଶ୍ଵାସ) ମାତରି ତଥ୍ୟ ବିଶ୍ୱାସ ଅସ୍ତି।
- ଇତି – (ବୋଲି) ଇତି ଡଃ ଶପଥ୍ୟ ନୟତି ।
- ଆନନ୍ଦେନ – ( ଖୁସିରେ) ମାତା ଆନନ୍ଦେନ ଆଲିଙ୍ଗତି।
- ରକ୍ଷତି – (ରକ୍ଷାକରେ) ବୃକ୍ଷ ରକ୍ଷତି ରକ୍ଷିତଃ ।
- ସୂୟଂ – (ତୁମ୍ଭେମାନେ) ପୂୟଂ ସର୍ବେ ପଠତ।
- ଛାତ୍ରା – (ଛାତ୍ରମାନେ) ଛାତ୍ରା ପାଠ୍ୟ ପଠନ୍ତୁ ।
- ଆସୀତ୍ – (ଥିଲେ) ସ୍ୱୀ ରାଜା ଆସୀତ୍।
- ଆଗଳ୍ପ – (ଆସ) ତୁମ ଅତ୍ର ଆଗଛ ।
- ସମ୍ୟକ୍ – (ଭଲ) ଅହଂ ସମ୍ୟକ୍ ପଠାମି।
- ଅଧୂକମ୍ – (ବେଶି) ତୁମ୍ ଅଧୂକଂ ଜାନାସି।
- କିନ୍ତୁ – (କିନ୍ତୁ) କିନ୍ତୁ ମନସି ସୁଙ୍ଖ ନାସ୍ତି ।
- କଥ୍ତବାନ୍ – (କହିଲେ) ଗୁରୁଦେବ କଥ୍ତବାନ୍।
- ଉଚ୍ଚୈଃ – ( ବଡ଼ପାଟିରେ) ଛାତ୍ରା ଉଜଃ ପଠନ୍ତି ।
- ସାଧୁ – (ଧନ୍ୟବାଦ) ସାଧୁ ବାଳକ ସାଧୁ।
- କୃତେ – (ପାଇଁ) ତବ କୃତେ ନାସ୍ତି ।
- ଅତୀବ – (ଅତ୍ୟନ୍ତ) ଅହଂ ତ୍ବ ଅତୀବ ସୁହ୍ୟାମି ।
- ଏବଂ – (ହିଁ) ଏଷ ଏବ ଇଛତି।
- ତୁମ୍ – (ଦେବାକୁ) ପୁରସ୍କାରଂ ଦାତୁମ୍ ଇଚ୍ଛାମି ।
- କିଂ – (କଣ) ବଂ କିଂ ଖାଦସି ?
- ଏଷା – (ଇଏ) ଏଷା ମମ ଜନନୀ।
- ଉପରି – (ଉପରେ) ମମ ଉପରି ବଂ ତଃ ?
- ଅତ୍ର – (ଏଠାରେ) ଅତ୍ର କଃ ତିଷ୍ଠତି ?
- କ୍ରମଶଃ – (କ୍ରମେ) କ୍ରମଶଃ ଛାତ୍ରା ଗଛନ୍ତି ।
- ବହନଃ – (ବହୁତ) ବହବ ଜନଃ ଗଛନ୍ତି ।
- ଅଗ୍ରେ – (ଆଗରେ) ଅଗ୍ରେ ଅଗ୍ରେ ଆଗଛ ।
- ତଦାନୀ – (ସେତେବେଳେ) ତଦାନୀ ତୁମ୍ ଆଗଛ।
- ନୀତବାନ୍ – (ନେଉଥିଲେ) ବିଦ୍ରୋହସ୍ୟ ନେତୃତ୍ୱ ସ୍ୱ ନୀତବାନ୍ ।
- ତତଃ – (ତେଣୁ) ତତଃ ଅହଂ କଥୟାମି ।
- ଅଭବତ୍ – (ହେଲା) ଅଦ୍ୟ ଦୃଷ୍ଟି ଅଭବତ୍।
- ପ୍ରାୟତଃ – (ପ୍ରାୟ) ପ୍ରାୟତଃ ଶିକ୍ଷକ ଅସ୍ଥି ।
- ଜୀବନ୍ତ – (ବଞ୍ଚନ୍ତି) ଜନା କୃଷିଦ୍ୱାରା ଜୀବନ୍ତି ।
- ନାମ – (ନାଆଁ) ତବ ନାମ କିମ୍ ?
- କରୋତି – (କରେ) କୃଷକ କଷ୍ଟ କରୋତି।
- ନମଃ – (ନମସ୍କାର) କୃଷ୍ଣକାୟ ନମଃ ।
- ଏତସ୍ମିନ୍ – (ଏହି) ଏତସ୍ମିନ୍ ଗ୍ରାମେ କୃଷକ ତିଷ୍ଠନ୍ତି ।
- ହଳଂ – (ହଳ) ହଳଂ ନାମ ଲାଙ୍ଗଳମ୍।
- ଏତେନ – (ଏହାଦ୍ଵାରା) ଏତେନ ଭୂମି ଉର୍ବରା ଭବତି ।
- ଅସ୍ଵାକଂ – (ଆମର) ଅସ୍ମାକଂ ଦେଶସ୍ୟ ନାମ ଭାରତମ୍।
![]()
- ଭାବନ୍ତି – (ଅଟନ୍ତି) ତେ ଛାତ୍ରା ଭବନ୍ତି ।
- କଶ୍ଚିତ୍ – (କେହିଜଣେ) କଶ୍ଚିତ୍ ବୃଦ୍ଧ ଗଛତି।
- ଅଭବତ୍ – (ହେଲା) ଅଧୁନା ସୃଷ୍ଟି ଅଭବତ୍।
- ଅପଶ୍ୟତ୍ – (ଦେଖିଲା) ସା ଚନ୍ଦ୍ରମ୍ ଅପଶ୍ୟତ୍ ।
- ପୃଷ୍ଟବାନ୍ – (ପଚାରିଲା) ପୁନଃ ଜନକଂ ପୃଷ୍ଟବାନ୍ ।
- ଇତଃ – (ଏଠାରୁ) ଇତଃ କେନ୍ଦ୍ରାପଡ଼ା କିୟତ୍ ଦୂରମ୍ ?
- କିମପି – (କିଛି) ସାଂ କିମପି ନ ବଦତି।
- ପ୍ରାପ୍ତବାନ୍ – (ପାଇଲା) ଡଃ ପୁରସ୍କାରଂ ପ୍ରାପ୍ତବାନ୍।
- ଦୂରେ – (ଦୂରରେ) ଦୂରେ ପର୍ବତଃ ଅସ୍ଥି ।
- ତହିଁ – (ତେବେ) ତହିଁ ତ୍ରିଂ କଥୟ ।
- ପ୍ରାସ୍ମୋତି – (ପାଏ) ଶ୍ରମିକ ପାରିଶ୍ରମିକଂ ପ୍ରାପ୍ନାତି ।
- ଏତସ୍ୟ – (ଏହାର) ଏତସ୍ୟ ପୁସ୍ତକସ୍ୟ ନାମ ଭାଷାଜନନୀ ।
- ହରତି – (ହରଣକରେ) ପ୍ରାକୃତିକଶୋଭା ମନଃ ହରତି ।
- ଏକା – (ଗୋଟିଏ) ଏକା ବାଳିକା ଧାବତି ।
- ଆଗଚ୍ଛତି – (ଆସୁଛି) ସା ଅତ୍ର ଆଗଛତି ।
- ପ୍ରଣମନ୍ତି – (ପ୍ରଣାମ କରନ୍ତି) ଭକ୍ତା ଦେବଂ ପ୍ରଣମନ୍ତି ।
- ଉଭୟତଃ – ( ଉଭୟପଟେ) ମାର୍ଗମ୍ ଉଭୟତଃ ବୃକ୍ଷା ସତ୍ତ୍ୱେ ।
- ମନୋହରମ୍ – (ସୁନ୍ଦର) ତସ୍ୟ ଦୃଶ୍ୟ ମନୋହରମ୍ ।
- ବିନା – (ବିନା) ଧନଂ ବିନା ସୁଙ୍ଖ ନାସ୍ତି ।
- ଦର୍ଶନୀୟମ – (ଦର୍ଶନଯୋଗ୍ୟ) ଏତତ୍ ସର୍ବେଷା ଦର୍ଶନୀୟମ୍ ।
- ଅନ୍ତରେଣ – (ବିନା) ଜଳମ୍ ଅନ୍ତରେଣ ବୟଂ ନ ଜୀବାମଃ ।
- ଭକ୍ତା – ( ଭକ୍ତିରେ) ଭକ୍ତ ଭକ୍ତ ପ୍ରଣମନ୍ତି ।
- କ୍ରମେଣ – (କ୍ରମରେ) ଛାତ୍ରା କ୍ରମେଣ ଆଗଛନ୍ତି ।
- କୁଧତି – (ରାଗୁଛନ୍ତି) ପିତା ପୁତ୍ରାୟ କୃଧତି ।
- ସାକମ୍ – ( ସହିତ) ମୟା ସାକମ୍ ଆଗଛ। .
- ଅଭିତଃ – (ଆଗରେ) ପିତରମ୍ ଅଭିତଃ ସତ୍ୟ ବଦତୁ।
- ବା – (କି) ଙ୍ ପଠସି ବା ?
- ନ – (ନାହିଁ) ଅହଂ ନ ପଠାମି।
- ମହତ୍ – (ବଡ଼) ଅତ୍ର ମହତ୍ ଅରଣ୍ୟମ୍ ଆସୀତ୍ ।
- କ୍ରମଶଃ – (କ୍ରମେ) କ୍ରମଶଃ ଜଳ ବଦ୍ଧତେ।
- କୁର୍ବନ୍ତ – (କରନ୍ତି) ଜନଃ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କୁର୍ବନ୍ତି ।
- ତେନ – ( ତାହାଦ୍ୱାରା) ତେନ ପରିବାରାନ୍ ପୋଷୟନ୍ତି ।
- ଦ୍ରଷ୍ଟବ୍ୟ – (ଦେଖୁବାଉଚିତ)ଇସ୍ପାତନଗରୀ ଅବଶ୍ୟ ଦ୍ରଷ୍ଟବ୍ୟ।
- ଅବଶ୍ୟମ୍ – (ନିଶ୍ଚୟ) ତୁମ୍ ଅବଶ୍ୟମ୍ ଆଗଛ ।
- ନିବସନ୍ତି – (ରୁହନ୍ତି) ଅତ୍ର ଜନଃ ନିବସନ୍ତି।
![]()
- ଚ – (ଏବଂ) ତ୍ୱମେବ ମାତା ଚ ପିତା ତ୍ଵମ୍ ଏବ।
- ଅଭବତ୍ – (ହୋଇଥିଲେ) ଡଃ ପ୍ରଧାନମନ୍ତ୍ରୀ ଅଭବତ୍।
- ପ୍ରାପ୍ତବାନ୍ – (ପାଇଲେ) ଡଃ ପୁରସ୍କାରଂ ପ୍ରାପ୍ତବାନ୍ ।
- ଅନନ୍ତରମ୍ – (ପରେ) ଅନନ୍ତରମ୍ ଆଗଚ୍ଛତୁ।
- ପ୍ରଥମତଃ – (ପ୍ରଥମେ) ପ୍ରଥମତଃ ସ୍ଵଂ ତତ୍ର ଗଛ।
- ତସ୍ୟ – (ତାଙ୍କ) ତଥ୍ୟ ନାମ କିମ୍ ?
- ବାଲ୍ୟାତ୍ – (ପିଲାଦିନୁ) ବାଲ୍ୟାତ୍ ଅହଂ ଦୁଃଖୀ ।
- ପ୍ରଚାରାୟ – (ପ୍ରଚାରପାଇଁ) ସ୍ତ ଧର୍ମସ୍ୟ ପ୍ରଚାରାୟ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରୋତି।
- ଅପି – (ମଧ୍ୟ) ମାତା ଅପି ଅହସତ୍ ।
- ଅତୀବ – (ଅତ୍ୟନ୍ତ) ଅହମ୍ ଅତୀବ ଦୁଃଖୀ ।
- କୃତବାନ୍ – (କରିଥିଲେ) ଡଃ ଦେଶସେବାଂ କୃତବାନ୍
- ଗତଃ – (ଗଲେ) ରାମଃ ବରଂ ଗତଃ ।
- ସମୀପେ – (ପାଖରେ) ଗ୍ରାମସ୍ୟ ସମୀପେ ବନମ୍ ଅଛି ।
- ପ୍ରତିବର୍ଷ – (ପ୍ରତିବର୍ଷ) ପ୍ରତିବର୍ଷମତ୍ର ମେଳା ଭବତି ।
- ନାମ୍ନା – (ନାମରେ) ଅହଂ ନାମ୍ନା ଶୁଭାଶିଷ ।
- ମହାନ୍ – (ବଡ଼) ମହାନ୍ ବଟବୃକ୍ଷ ଅନ୍ତି।
- ସାନନ୍ଦ – (ଆନନ୍ଦରେ) ଡଃ ସାନନ୍ଦ ନିବସତି ।
- ନୟତି – (ନିଏ) ଶାବକ ଜନ୍ମ ନୟତି ।
- ତସ୍ମି – (ତାକୁ) ତସ୍ମି ଭୋଜନଂ ଦଦାତି ।
- କୀଦୃଶ – (କିପରି) ଈଶ୍ଵରସ୍ୟ ପକ୍ଷପାତଃ କୀଦୃଶଃ ?
- ନାସ୍ତି – (ନାହିଁ) ମମ ସ୍ଵତଃ ନାସ୍ତି ।
- ତହିଁ – (ତେବେ) ତହିଁ ତୁମ୍ ଆଗଛ।
- କର୍ତ୍ତୃ – (କରିବାକୁ) ବରଂ ଗର୍ବଂ କର୍ଡିଂ ପାରୟାମଃ ।
- ପ୍ରତିଦିନମ୍ – (ପ୍ରତିଦିନ) ପ୍ରତିଦିନଂ ବ୍ୟାୟାମଂ କୁରୁ।
- ତତ୍ର – (ସେଠାକୁ) ଶୁନଃ ତତ୍ର ଆଗଛତି।
- ତଦା – (ସେତେବେଳେ) ତଦା ତସ୍ୟା ଈର୍ଷା ଆଗଛତି ।
- ତତ୍ – (ତାହା) ତତ୍ ମୟି ନାସ୍ତି ।
- କୃତେ – (ପାଇଁ) ଈଶ୍ଵରସ୍ୟ କୃତେ ଧନ୍ୟବାଦମ୍ ଅର୍ପୟତି ।
- ଏବଂ – (ହି) ମନଃ ଅବ୍ୟବସ୍ଥିତମ୍ ଏବ।
- ସମମ୍ – ( ସହିତ) ପରିବାରେଣ ସମଂ ତିଷ୍ଠତି।
- ନିତ୍ୟ – (ପ୍ରତିଦିନ) ନିତ୍ୟ ପାଠ୍ୟ ପଠ।
- ବରଂ – (ଭଲ) ବରମ୍ ଏକ ଗୁଣୀପୁନଃ ।
- ଦଶତି – (ଦର୍ଶନ କରେ) ସର୍ପ ଦଶତି କାଳେନ ।
- ଶଃ – (ଆସନ୍ତାକାଲି) ଶଃ ତୁମ୍ ଆଗଛ।
- ହ୍ୟୁ – (ଗତକାଲି) ହ୍ୟୁ ପିତା ଆଗଛତ୍।
- କୃତମ୍ – (କରିଛ) କୃତଂ ନ ବା ?
- ନୈବ – (କେବେନୁହେଁ) ନୈବ ତୁଲ୍ୟ କଦାଚନ।
![]()
- ଯାତି – (ଯାଏ) ଛାତ୍ର ପାଠଶାଳା ଯାତି ।
- ପ୍ରାସ୍ମୋତି – (ପାଏ) କେବଳଂ ଯଶଃ ପ୍ରାପ୍ଳୁତି ।
- ପଞ୍ଚ – (ପାଞ୍ଚ) ପଞ୍ଚ ଫଳାନି ସନ୍ତି ।
- ସମାର୍ଚ୍ଚରେଡ୍ – (କରଣୀୟ) ପରେରାଂ ନ ସମାଚରେତ୍।
- ମୁଞ୍ଚତି – (ଛାଡେ) ମଳିନବଂ ନ ମୁଞ୍ଚତି ।
- ତି– (ହିଁ) ନଂ ହି ଦୁର୍ଗା ।
- ଆତ୍ମନଃ – (ନିଜର) ଆତ୍ମନଃ ବୁଦ୍ଧି ନାସ୍ତି ।
- ଆଦରେ – (ଗ୍ରହଣ କରେ) ହଂସ କ୍ଷୀରମ୍ ଆଦରେ
- କଷ୍ଟନ – (କୌଣସି) କଣ୍ଟନ ଜନଃ ଆୟାତି ।
- ଆସୀତ୍ – (ଥ୍ଲା) ଡଃ ରାଜା ଆସୀତ୍।
- ଅଭବତ୍ – (ହେଉଥୁଲା) ଡଃ ମୁକ୍ତା ନ ଅଭିବତ୍।
- କେଚନ – (କେତେକ) କେଚନ କାମଃ ଅପଶ୍ୟନ୍।
- କ୍ରମେଣ – (କ୍ରମେ) ଛାତ୍ରା କ୍ରମେଣ ଗଛନ୍ତି ।
- ଅଧ୍ବକଂ – (ବେଶି) ଡଃ ଅଧିକାଂ ଦୁଃଖମ୍ ଅଦଦାତ୍।
- କୃପୟା – (ଦୟାକରି) କୃପୟା ବଦତୁ।
- ଅକରୋତ୍ – (କଲା) କୋକିଳସ୍ୟ ଉପରି ଆକ୍ରମଣମ ଅକରୋତ୍ ।
- ନୂନମ୍ – (ନିଶ୍ଚୟ ) ଅହଂ ନୂନଂ ପ୍ରାପ୍ସ୍ୟାମି ।
- ଭବାନ୍ – (ଆପଣ) ଭବାନ୍ ନିଷ୍କରୁନଃ ଭବତି।
- କିମର୍ଥମ୍ – (କାହିଁକି) ଭବାନ୍ କିମର୍ଥ୍ୟ ନ ରକ୍ଷତି ?
- ଦୂରମ୍ – (ଦୂର) ଦୂରଂ ଗଛତୁ ଭବାନ୍।
- ଶୀଘ୍ରମ୍ – (ଶୀଘ୍ର) ଶୀଘ୍ରମ୍ ଅତ୍ର ଆଗଛ।
- ଶ୍ରୁତମ୍ – (ଶୁଣାଗଲା) ଘୋରଗର୍ଜନଂ ଶ୍ରୁତମ୍।
- ଅନେକେ – (ଅନେକ) ଅନେକେ ସୈନ୍ୟା ଆହତା
- ଦେହି – (ଦିଅ) ଜଳଂ ଦେହି ।
- ଅତୀବ – (ଅତ୍ୟନ୍ତ) ବ୍ୟବସାୟୀ ଅତୀବ ଦୁଃଖ୍ୟତଃ ।
- ଗତବାନ୍ – (ଗଲେ) ରାମଃ ବରଂ ଗତବାନ୍।
- ରକ୍ଷ – (ରକ୍ଷାକର) ରକ୍ଷ ରକ୍ଷ ମାତରମ୍ ।
- କୁରୁତ – (କର) ଜନସେବାଂ କୁରୁତ।
- ଋତଃ – (ଗଲେ) ପିତା କଟକଂ ଗତଃ ।
- ସତତମ୍ – (ସର୍ବଦା) ମନସା ସତତଂ ସ୍ମରଣୀୟମ୍ ।
- ସର୍ବେ – ( ସମସ୍ତେ) ସର୍ବେ ତତ୍ତ୍ବ ଗଛନ୍ତି ।
![]()
- ବହନଃ – (ବହୁତ) ବହବ ଛାତ୍ରା ପଠନ୍ତି ।
- ଅସ୍ତି – (ଅଛି) ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ଚିକ୍କଶଃ ଅସ୍ଥି ।“
- ଅଧଃ – (ତଳେ) ସ ନୂନମ୍ ଅଧଃ ପତେତ୍ ।
- ତଥାପି – (ତଥାପି) ତଥାପି ଡଃ ନ ପଠତି।
- ଶୁକ୍ଳା – (ଶୁଣି) ଅନ୍ୟତାଂ ବଚନଂ ଶ୍ରୁତ୍ବା ଅଧଃ ପତିତବହିଃ ।
- ପୁତ୍ର – (ହେ ପୁତ୍ର) ପୁତ୍ର ! ପାଠ୍ୟ ପଠ।
- ଭବେ – (ହେବାଉଚିତ) ରଂ ନୂନଂ ସଫଳଂ ଭବେ ।
- ଅତଃ – (ଏଣୁ) ଅତଃ ଡଃ ନ ପଠତି।
- ଅନ୍ୟ – (ଅନ୍ୟମାନେ) ଅନ୍ୟ ନ ଆଗଛନ୍ତି ।
- ଇତି – (ଶେଷ) ଇତି ବାହାଁ ।
- ମାତଃ – (ହେ ମା’) ମାତଃ ! ବଂ କ୍ରନ୍ଦସି ?
- କୀ ଦୃଶମ୍ – (କିପରି) କୀଦୃଶଂ ସୌଭାଗ୍ୟମ୍ ?
- କଥମ୍ – (କାହିଁକି) କଣଂ କ୍ରନ୍ଦତି ପୁନଃ ?
- ଜ୍ଞାତବତୀ – (ଜାଣିଲେ) ମାତା ସର୍ବଂ ଜ୍ଞାତବତୀ ।
- ଏଵମ୍ – (ଏହିପରି) ସମାଜେ ଏବଂ ଦୃଶ୍ୟତେ |
- ମଙ୍ଗଳମ୍ – (ମଙ୍ଗଳ) ମାତୃଭୂମେ ମଙ୍ଗଳଂ ଭବିଷ୍ୟତି |
- ଗରୀୟସୀ – (ବଡ଼) ଜନନୀ ଜନ୍ମଭୂମି ଚ ସ୍ବର୍ଗାଦପି ଗରୀୟସୀ ।
- ଭବିଷ୍ୟସି – (ହେବ) ତୁମ୍ ଅମାତ୍ୟ ଭବିଷ୍ୟସି ।
- ହସ୍ତେନ – (ହାତରେ) ଶିଶୁ ହସ୍ତେନ ଖାଦତି ।
- ପଶ୍ୟ – (ଦେଖ) ବଂ ଚନ୍ଦ୍ର ପଶ୍ୟ।
- ବିମଳା – (ନିର୍ମଳ) ଗଙ୍ଗା ବିମଳା ଅଣ୍ଡି।
![]()
- ପବିତ୍ରମ୍ – (ପବିତ୍ର) ସଂସ୍କୃତଂ ସଦା ପବିତ୍ରମ୍ ।
- ମଧୁରମ୍ – (ମିଠା) ରବୀନ୍ଦ୍ରଗାନଂ ମଧୁରମ୍ ଅସ୍ତି ।
- ମତମ୍ – (ମତ) ଅତ୍ର ସମସ୍ତଂ ମତଂ ସମାନମ୍ ।
- କାପି – (କିଛିହେଲେ) କାପି ବାଧା ନାସ୍ତି ।