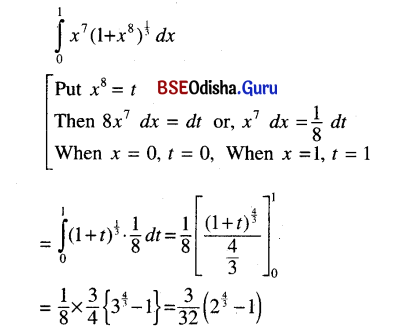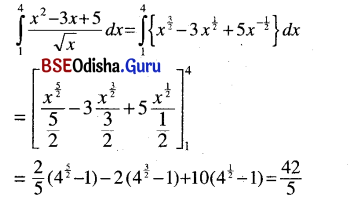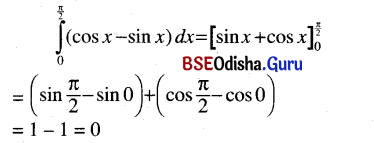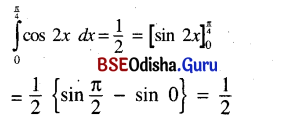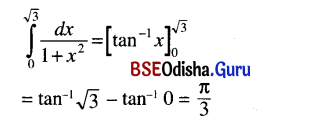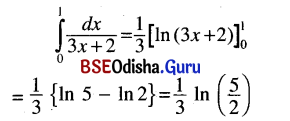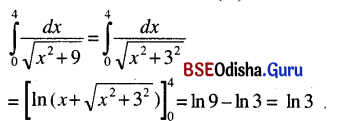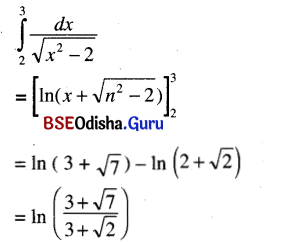Odisha State Board BSE Odisha Class 9 Sanskrit Grammar Book Solutions Chapter 10 କାରକ ଓ ବିଭକ୍ତି Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
BSE Odisha Class 9 Sanskrit Grammar Solutions Chapter 10 କାରକ ଓ ବିଭକ୍ତି
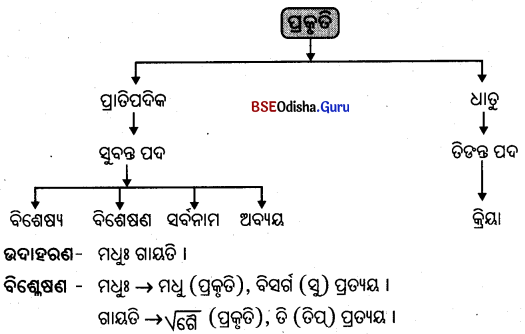
(କ) କାରକର ସାମାନ୍ୟ ଜ୍ଞାନ:
ନିମ୍ନଲିଖୁବାକ୍ୟାନି ପଠତ :
(କ) ଦେବଦତଃ ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟଂ ଗଚ୍ଛତ । (ଦେବଦତ୍ତ ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟକୁ ଯାଉଛି ।)
(ଖ) ସେବକୌ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କୁରୁତଃ । (ସେବକ ଦୁଇଜଣ କାମ କରୁଛନ୍ତି ।)
(ଗ) ଶିକ୍ଷକା କକ୍ଷାମ୍ ଆଗଛନ୍ତି । (ଶିକ୍ଷକମାନେ ଶ୍ରେଣୀକୁ ଆସୁଛନ୍ତି ।)
ଉପର୍ୟ୍ୟକ୍ତ ତିନିଗୋଟି ବାକ୍ୟରେ ‘ଗଚ୍ଛତି’, ‘କୁରୁତଃ’ ଓ ‘ଆଗଛନ୍ତି’ – ଏହି ତିନିଗୋଟି କ୍ରିୟାପଦ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହୋଇଛି । ଏହି କ୍ରିୟାଗୁଡ଼ିକର ବାକ୍ୟରେ ଥିବା ଅନ୍ୟାନ୍ୟା ପଦ; ଯଥା – ଦେବଦତ୍ତ, ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟ, କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ, କକ୍ଷ ଇତ୍ୟାଦି ପଦ ସହିତ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ରହିଛି । ତେଣୁ ପ୍ରଥମ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ‘ଦେବଦତ୍ତ’ ଓ ‘ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟ’ ପଦ କ୍ରିୟାପଦ ‘ଗଚ୍ଛତି’ ସହିତ ଅନ୍ବିତ ବା ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧିତ ହେଉଛନ୍ତି । ତେଣୁ ଏମାନେ ଗୋଟିଏ ଗୋଟିଏ ‘କାରକ’ ଅଟନ୍ତି ।
(ଖ) ସଂଜ୍ଞା ଓ ପ୍ରକାରଭେଦ:
‘କ୍ରିୟାନ୍ୱୟିତଂ କାରକତ୍ଵମ୍’ । କ୍ରିୟା ଜନକବଂ କାରକତ୍ଵମ୍ ଅର୍ଥାତ୍ ଯିଏ କ୍ରିୟାର ଜନକ ତାକୁ ମଧ୍ୟ ‘କାରକ’ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
ବାକ୍ୟରେ କ୍ରିୟାପଦ ସହିତ ଯେଉଁ ପଦର ପ୍ରତ୍ୟକ୍ଷ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ଥାଏ, ତାକୁ ‘କାରକ’ କୁହାଯାଏ । ଅତଏବ ଦେବଦତଃ, ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟମ୍, ସେବକୌ, କାର୍ଯ୍ୟମ୍, ଶିକ୍ଷକା ଓ କକ୍ଷାମ୍ – ଏହି ପଦଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ‘କାରକ’ ଅଟନ୍ତି । କ୍ରିୟାପଦ ସହ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ଥିବା ଅନ୍ୟପଦମାନଙ୍କର ଭିନ୍ନ ଭିନ୍ନ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ଥ୍ବାରୁ’ କାରକର ୧ ଭିନ୍ନ ଭିନ୍ନ ନ୍ନ ପ୍ରକାରଭେଦ ରହିଅଛି । ଯେପରି ରି ପ୍ରଥମ. ବାକ୍ୟରେ ।’ଗଚ୍ଛତି କ୍ରିୟା ସମ୍ପାଦନରେ ‘ଦେବଦତ୍ତ’ ସ୍ବତନ୍ତ୍ର ଅଟେ । ସେ କ୍ରିୟା ସମ୍ପାଦକ ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ କ୍ରିୟାପଦ ସହିତ ତା’ର କର୍ତ୍ତୃସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତ ହେଉଅଛି । ସୁତରାଂ ‘ଦେବଦତ୍ତ୍ୱ’ ବାକ୍ୟରେ କର୍ତ୍ତୃକାରକ ଅଟେ । ସେହିପରି ‘ସେବକୌ’ ଓ ‘ଶିକ୍ଷକାଂ’ ମଧ୍ୟ କର୍ତ୍ତୃକାରକ ଅଟନ୍ତି ।
‘‘କର୍ତ୍ତା କର୍ମ ଚ କରଣଂ ଚ ସମ୍ପ୍ରଦାନଂ ତଥୈବ ଚ ।
ଅପାଦାନମଧୂରଣମିତ୍ୟେବଂ କାରକାଣି ଷଟ୍ ।।’’

କାରକ ଛଅପ୍ରକାର; ଯଥା – କର୍ତ୍ତୃକାରକ, କର୍ମକାରକ, କରଣକାରକ, ସଂପ୍ରଦାନ କାରକ, ଅପାଦାନ କାରକ ଓ ଅଧିକରଣ କାରକ । ଏତଦ୍ଭିନ୍ନ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ‘ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ପଦ’ ମଧ୍ଯ ଥାଏ । ନିମ୍ନରେ ଗୋଟିଏ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ସମସ୍ତ ଛଅଗୋଟି କାରକ ଓ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧପଦର ଉଲ୍ଲେଖ କରାଯାଇଛି ।
ଅଯୋଧ୍ୟାର ରାଜା ଦଶରଥ ପ୍ରାତଃକାଳରେ ମାଗୁଥିବା ଲୋକଙ୍କୁ ରାଜକୋଷରୁ ଅମାତ୍ୟମାନଙ୍କ ଦ୍ୱାରା ଦାନକରୁଥିଲେ ।
ଅଯୋଧ୍ୟାୟା ରାଜା ଦଶରଥ ପ୍ରାତଃକାଳେ ଯାଚକେଭ୍ୟ ରାଜକୋଷାତ୍ ଅମାତ୍ୟେ ଦାନମ୍ ଅକରୋତ୍ ।
୧ । କିଏ ଦାନ କରୁଥିଲେ ? ଦଶରଥ –ଦଶରଥ-କର୍ତ୍ତୃକାରକ ଓ ପ୍ରଥମ ବିଭକ୍ତି ।
(କ୍ରିୟାକୁ ଧରି ପ୍ରଶ୍ନ ପଚାରିବ କିଏ ? ଉତ୍ତର ଦେବ ଯିଏ, କର୍ତ୍ତା ଜାଣିବ ସିଏ ।)
୨ । କ’ଣ ଦାନ କରୁଥିଲେ ? ଧନ-ଧନମ୍-କର୍ମକାରକ ଓ ଦ୍ୱିତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ।
(କ୍ରିୟାକୁ ଧରି ପ୍ରଶ୍ନ ପଚାରିବ କ’ଣ ବା କାହାକୁ ? ଉତ୍ତର ମିଳିବ ଯାହାକୁ, କର୍ମ ବୁଝିବ ତାହାକୁ ।)
୩। କାହାଦ୍ବାରା ଦାନ କରୁଥିଲେ ? ଅମାତ୍ୟମାନଙ୍କଦ୍ୱାରା – ଅମାତୌ-କରଣ କାରକ ଓ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ।
(କ୍ରିୟାକୁ ଧରି ପ୍ରଶ୍ନ ପଚାରିବ କାହାଦ୍ଵାରା ? ଉତ୍ତର ମିଳିବ ଯାହାଦ୍ୱାରା, କରଣ ଜାଣିବ ତାହାଦ୍ୱାରା ।)
୪ । କାହାକୁ ଦାନ କରୁଥିଲେ ? ମାଗୁଥିବା ଲୋକଙ୍କୁ – ଯାଚକେଭ୍ୟ-ସଂପ୍ରଦାନ କାରକ ଓ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ।
(କ୍ରିୟାକୁ ଧରି ପ୍ରଶ୍ନ ପଚାରିବ କାହାକୁ ? ଉତ୍ତର ମିଳିବ ଦାନ ଅର୍ଥରେ ଯାହାକୁ, ସମ୍ପ୍ରଦାନ ବୁଝିବ ତାହାକୁ ।)
୫ । କେଉଁଠାରୁ ଦାନ କରୁଥିଲେ ? ରାଜକୋଷରୁ – ରାଜକୋଷାତ୍ – ଅପାଦାନ କାରକ ଓ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ।
(କ୍ରିୟାକୁ ଧରି ପ୍ରଶ୍ନ ପଚାରିବ କେଉଁଠାରୁ ? ଉତ୍ତର ମିଳିବ ଯେଉଁଠାରୁ, ଅପାଦନ ସେହିଠାରୁ ।)
୬ । କେତେବେଳେ ଦାନ କରୁଥିଲେ ? ପ୍ରାତଃକାଳରେ-ପ୍ରାତଃକାଳେ- ଅଧିକରଣ କାରକ ଓ ସପ୍ତମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ।
(କ୍ରିୟାକୁ ଧରି ପ୍ରଶ୍ନ ପଚାରିବ କେତେବେଳେ ବା କେଉଁଠାରେ ? ଉତ୍ତର ମିଳିବ ଯେତେବେଳେ ବା ଯେଉଁଠାରେ, ଅଧ୍ୟାକରଣ ହେବ ସେତେବେଳେ ବା ସେହିଠାରେ ।)
୭ । କେଉଁ ଦେଶର ରାଜା ? ଅଯୋଧ୍ୟାର – ଅଯୋଧ୍ୟାୟା-ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧପଦ ଓ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ।
ତେଣୁ –
ଅଯୋଧ୍ୟାୟା ରାଜା ଦଶରଥ ପ୍ରାତଃକାଳେ ଅମାତୌ ରାଜକୋଷାତ୍ ଯାଚକେଭ୍ୟ ଧନମ୍ ଅଦଦାତ୍ । ଏହିପରି କାରକ ଛଅପ୍ରକାର ଅଟେ ।
(ଗ) ବିଭକ୍ତି:
“ସଂଖ୍ୟ।ଳାରକବୋଧୟିତ୍ରୀ ବଭକ୍ତିଃ’’
(୧) ସଂଖ୍ୟା ବା ବଚନ ଓ କାରକ ଯେଉଁ ସଂକେତଦ୍ୱାରା ଚିହ୍ନିତ ହୁଏ, ସେହି ସଂକେତଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ବିଭକ୍ତି କୁହାଯାଏ । ଯଥା : ବାଳକଃ ଗଚ୍ଛତି । ବାଳକୌ ପଶ୍ୟ । ବାଳକୈ ଗମ୍ୟତେ । ପ୍ରଥମ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ‘ସୁ’ ଦ୍ବାରା ‘ବାଳକ’ କର୍ତ୍ତୃକାରକ ଓ ଏକବଚନ, ଦ୍ୱିତୀୟ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ‘ଔ’ ଦ୍ଵାରା ‘ବାଳକୌ’ କର୍ମକାରକ ଓ ଦ୍ବିବଚନ ଏବଂ ତୃତୀୟ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ‘ଐ’ (ଭିସ୍) ଦ୍ଵାରା ‘ବାଳକୈ’ ଅନୁକ୍ତ କର୍ତ୍ତା ଓ ବହୁବଚନ ବୋଲି ଚିହ୍ନିତ ହୋଇଛି ।
(୨) ବିଭକ୍ତି ସାତପ୍ରକାର; ଯଥା- ପ୍ରଥମା, ଦ୍ୱିତୀୟା, ତୃ ତୀୟା, ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ, ପଞ୍ଚମୀ, ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ଓ ସପ୍ତମୀ ।
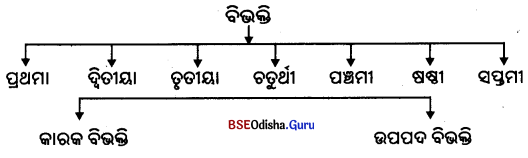
(୩) ଉକ୍ତ ସାତପ୍ରକାର ବିଭକ୍ତି କାରକ ବିଭକ୍ତି ଓ ଉପପଦ ବିଭକ୍ତ ଭେଦରେ ଦୁଇଭାଗରେ ବିଭକ୍ତ । ‘କ୍ରିୟା’ ଯୋଗରେ ହେଉଥିବା ବିଭକ୍ତିକୁ କାରକ ବିଭକ୍ତି ଓ ‘ଶବ୍ଦ’ ଯୋଗରେ ହେଉଥିବା ବିଭକ୍ତିକୁ ‘ଉପପଦ’ ବିଭକ୍ତି କୁହାଯାଏ; ଯଥା – (୧) ଶିବଂ ନମସ୍ତୁରୁ । ଏଠାରେ କର୍ତ୍ତୃପଦ ‘ତୁମ୍’ ଉହ୍ୟ ଅଛି । ତେବେ କ୍ରିୟାପଦ ‘କୁରୁ’ ପାଇଁ ‘ଶିବ’ ଶବ୍ଦ ‘କର୍ମପଦ’ ଅଟେ । କାରଣ ଏହା କର୍ତ୍ତାର ଈପ୍ସିତତମ । ତେଣୁ କର୍ମକାରକରେ କର୍ମଠାରେ (ଅନୁସ୍ତେ) କର୍ମଣି ଦ୍ୱିତୀୟା ସୂତ୍ରରେ ଦ୍ବିତୀୟାବିଭକ୍ତ ବିଧାନ କରାଗଲା । ଏହା ‘କାରକ ବିଭକ୍ତି’ ଅଟେ । କିନ୍ତୁ (୨) ଶିବାୟ ନମଃ । ଏଠାରେ କ୍ରିୟାପଦ ନଥିବାରୁ ଉପପଦ ବିଭକ୍ତି ଅନୁସାରେ ‘ନମଃ’ ଶବ୍ଦଯୋଗେ ‘ଶିବ’ ଶବ୍ଦରେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ବିଧାନ ହେଲା । ଏହାକୁ ‘ଉପପଦ ବିଭକ୍ତି’ କୁହାଯାଏ ।

(୪) ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ‘କାରକ’ ଗୋଟିଏ ଗୋଟିଏ ବିଭକ୍ତି ଗ୍ରହଣକରିଥା’ନ୍ତି । କିନ୍ତୁ ‘ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ପଦ’ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତିକୁ ଗ୍ରହଣ କରେ । ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତନ୍ତ ପଦର ‘କ୍ରିୟାପଦ’ ସହିତ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟକ୍ଷ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ନଥାଏ । ଏଠାରେ ଗୋଟିଏ ସଂଜ୍ଞାପଦର ଅନ୍ୟଏକ ସଂଜ୍ଞାପଦ ସହ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ଥାଏ । ତେଣୁ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତନ୍ତ ପଦ କାରକର ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକ୍ତ ହୁଏ ନାହିଁ । ଏହାକୁ ‘ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧପଦ’ କୁହାଯାଏ; ଯଥା – ରାଜଃ ପୁରୁଷା ଆଗଛନ୍ତି – ଏଠାରେ ‘ରାଜ୍ଞ’ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧପଦ ଅଟେ । କାରଣ ଏହାର ପ୍ରତ୍ୟକ୍ଷ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ‘ପୁରୁଷା’ ସହିତ ରହିଛି, ‘ଆଗଛନ୍ତି’ କ୍ରିୟାପଦ ସହିତ ଏହାର ପ୍ରତ୍ୟକ୍ଷ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ସ୍ଥାପିତ ହୋଇପାରୁ ନାହିଁ ।
(୫) ସମ୍ବୋଧନ – ଉପର୍ୟ୍ୟକ୍ତ ବିଭକ୍ତିଗୁଡ଼ିକ ବ୍ୟତୀତ ଏକ ସମ୍ବୋଧନ ପଦର ରୂପ ମଧ୍ଯ ରହିଥାଏ । ଏହାର ପ୍ରୟୋଗ କାହାକୁ ‘ଡାକିବା’ ରେ ଆବଶ୍ୟକ ହୁଏ । ଏହି ସମ୍ବୋଧନ ପଦର ରୂପ ପ୍ରଥମା ବିଭକ୍ତିପରି ହୋଇଥାଏ; ଅବଶ୍ୟ ସମ୍ବୋଧନ ଏକବଚନରେ ପ୍ରଥମ ବିଭକ୍ତି ଏକବଚନ ରୂପର ଅନେକ ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନ ହୋଇଯାଏ । କିନ୍ତୁ ଦ୍ବିବଚନ ଓ ବହୁବଚନରେ ରୂପ ପ୍ରଥମ ବିଭକ୍ତିର ଅବିକଳ ରୂପକୁ ଗ୍ରହଣ କରେ; ଯଥା – ଭୋ ବାଳକ, ଭୋ ବାଳକୌ, ଭୋ ବାଳକା ଇତ୍ୟାଦି । ନିମ୍ନରେ ଗୋଟିଏ ପଦର ସମସ୍ତ ବିଭକ୍ତିରେ ପ୍ରୟୋଗର ଉଦାହରଣ ଦିଆଗଲା ।
ରାମୋ ରାଜମଣି ସଦା ବିଜୟତେ ରାମଂ ରମେଶଂ ଭଜେ
ରାମେଣ ନିହତା ନିଶାଚରଚତୁଃ ରାମାୟ ତସ୍ମି ନମଃ ॥
ରାମାତ୍ର ନାସ୍ତି ପରାୟଣଂ ପରତରଂ ରାମସ୍ୟ ଦାସୋଽସ୍ଥ୍ୟହଂ
ରାମେ ଚିତ୍ତଲୟଃ ସଦା ଭବତୁ ମେ ହେ ରାମ ! ମାମୁଦ୍ଧର ॥
କଠିନ ଶବ୍ଦ : ଚତୁଃ – ଦଳପତି, ରମେଶଂ – ବିଷ୍ଣୁ (ଲକ୍ଷ୍ମୀପତି)
ଅଭ୍ୟାସଃ :
୧। କୋଷଶ୍ଠକାତ୍ବ ଯଥାର୍ଥପଦଂ ନିରୂପ୍ୟ ଶୂନ୍ଯସ୍ଥାନଂ ପୂରୟତ ।
ପିତା : ଅୟମ ଏକଃ ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟ । ଅତ୍ର _____________ ପଠନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଛାତ୍ରା
ପୁତ୍ରଃ : ଏଷ କଃ ଗଚ୍ଛତି ?
ପିତା : ଅୟଂ________________ ଗଚ୍ଛତି ।
Answer:
ଦେବଦତଃ
ପୁତ୍ରଃ : ତତ୍ର ବାଟିକାୟାଂ କେ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କୁର୍ବନ୍ତି ।
ପିତା : ତେ ____________________ ବାଟିକାୟାଂ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କୁର୍ବନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ସେବକା
ପୁତ୍ରଃ : ଏତୌ କୌ ଆଗଚ୍ଛତଃ ?
ପିତା : _________________ ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟମ୍ ଆଗଚ୍ଛତଃ ।
Answer:
ଶିକ୍ଷକୌ
ପୁତ୍ରଃ : ତତ୍ର କେ ଦଣ୍ଡାୟମାନଃ ସନ୍ତି ।
ପିତା : ତତ୍ର _______________ ଦଣ୍ଡାୟମାନଃ ସନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଅଭିଭାବକା
(ଅଭିଭାବକା, ସେବକା, ଛାତ୍ରା, ଦେବଦଭଃ, ଶିକ୍ଷକୌ)
୨। ‘କ’ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭସ୍ୟ କର୍ତ୍ତୃପଦାନାଂ ‘ଖ’ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭସ୍ୟ କ୍ରିୟାପଦୌ ସହ ମେଳନଂ କୃତ୍ୱା ‘ଗ’ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭେ ବାକ୍ୟାନି ଲିଖତ ।
| କ୍ |
ଖ |
ଗ |
|
| ଯଥା: ପବନଃ |
ବହତି |
ପବନଃ ବହତି । |
|
| ନଦ୍ୟଃ |
ଭାନ୍ତି |
__________________ । |
ଉ – ନଦ୍ୟଃ ବହନ୍ତି । |
| ଘନାଃ |
ସମାଶ୍ଵସନ୍ତି |
__________________ । |
ଉ – ଘନାଃ ବର୍ଷନ୍ତି । |
| ମତ୍ତଗଜାଃ |
ଧ୍ୟାୟନ୍ତି |
__________________ । |
ଉ – ମତ୍ତଗଜାଃ ନଦନ୍ତି । |
| ବନାନ୍ତାଃ |
ନୃତ୍ୟନ୍ତି |
__________________ । |
ଉ – ବନାନ୍ତାଃ ଭାନ୍ତି । |
| ପ୍ରିୟାବିହୀନାଃ |
ନଦନ୍ତି |
__________________ । |
ଉ – ପ୍ରିୟାବିହୀନାଃ ଧ୍ୟାୟନ୍ତି । |
| ଶିଖ୍ନଃ |
ବର୍ଷନ୍ତି |
__________________ । |
ଉ – ଶିଖ୍ନଃ ନୃତ୍ୟନ୍ତି । |
| ପ୍ଳବଙ୍ଗାଃ |
ବହନ୍ତି |
__________________ । |
ଉ – ପୃବଙ୍ଗାଃ ସମାଶ୍ବସନ୍ତି । |
ସୂଚନା : ବହନ୍ତି ବର୍ଷନ୍ତି ନଦନ୍ତି ଭାନ୍ତି ଧ୍ୟାୟନ୍ତି ନୃତ୍ୟନ୍ତି ସମାଶ୍ବସନ୍ତି ।
ନଦ୍ଯୋ ଘନାଃ ମତ୍ତଗଜାଃ ବନାନ୍ତାଃ ପ୍ରିୟାବିହୀନାଃ ଶିଖ୍ନଃ ପ୍ଲବଙ୍ଗାଃ ॥

୩। କୋଷ୍ଠକାତ୍ କର୍ତ୍ତୃପୟଂ ନିରୂପ୍ୟ ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନଂ ପୂରୟତ ।
(କ) _______________________ ସାହିତ୍ୟ ପଠସି ।
Answer:
ଛାତ୍ରୀ
(ଖ) _______________ ସାହିତ୍ୟ ପଠସି ।
Answer:
ତ୍ୱଂ
(ଗ) _________________ ଫଳ ନେଷ୍ୟାମଃ ।
Answer:
ବୟଂ
(ଘ) ________________________ କଳହଂ ମା କୁରୁତମ୍ ।
Answer:
ଯୁବାଂ
(ଙ) ____________________ ଗ୍ରାମିଂ ଗଚ୍ଛାବାଃ ।
Answer:
ଆବାଂ
(ବୟମ୍, ତ୍ୱମ୍, ଛାତ୍ର, ଆବାମ୍, ଯୁବାମ୍)
କର୍ତ୍ତୃକାରକ ଓ ପ୍ରଥମ ବିଭକ୍ତି
୧। କିଏ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରୁଛନ୍ତି ?
(କ) ଛାତ୍ରୀ ପଠତି । (ଛାତ୍ରଟି ପଢ଼ୁଛି ।)
(ଖ) ବାଳକଃ ପଶ୍ୟତି । (ପିଲାଟି ଦେଖୁଛି ।)
(ଗ) ଦେବଦତଃ ଗଚ୍ଛତି । (ଦେବଦତ୍ତ ଯାଉଛି ।)
ସ୍ୱତନ୍ତଃ କର୍ତ୍ତାଃ
ଏଠାରେ ଛାତ୍ର ‘ପଠନ’ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ, ବାଳକ ‘ଦର୍ଶନ’ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଓ ଓ ଦେବଦତ୍ତ ‘ଗମନ’ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରୁଛନ୍ତି; ଅର୍ଥାତ୍ ଏମାନେ ସେହି ସେହି କ୍ରିୟାସାଧନ ପାଇଁ ସ୍ବତନ୍ତ୍ର ବା ପ୍ରଧାନ ଅଟନ୍ତି । ଅତଏବ ସେମାନେ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ‘କର୍ତ୍ତା’ ଅଟନ୍ତି । ତେଣୁ କ୍ରିୟାସାଧନପାଇଁ ଯେ ସ୍ବତନ୍ତ୍ର ବା ପ୍ରଧାନ, ତାକୁ ‘କର୍ତ୍ତା’ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
୨। ପ୍ରଧାନ = ମୁଖ୍ୟ = ବାଚ୍ୟ = ଭକ୍ତ – ଏହି ଚାରିଗୋଟି ଶବ୍ଦ ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବ୍ୟାକରଣଦୃଷ୍ଟିରୁ ପର୍ଯ୍ୟାୟବାଚୀ ଅଟନ୍ତି ।
ଉପର୍ୟ୍ୟକ୍ତ ବାକ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ କର୍ତ୍ତା ପ୍ରଧାନ ବା ବାଚ୍ୟ ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ ଏଗୁଡ଼ିକ କର୍ତ୍ତବାଚ୍ୟ ଅଟନ୍ତି । ‘କର୍ତ୍ତବାଚ୍ୟ’ ରେ କର୍ତ୍ତାଠାରେ ପ୍ରଥମା ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ଉକ୍ତ କର୍ତ୍ତାରେ ପ୍ରଥମ ବିଭକ୍ତିକୁ ସଂସ୍କୃତରେ ‘ଉଲ୍ଲେ କର୍ଭରି ପ୍ରଥମା’ କୁହାଯାଏ । ନିମ୍ନଲିଖ୍ ବାକ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ଦେଖ ।
(କ) ଛାତ୍ର ସଂସ୍କୃତଂ ପଠତି । (ଛାତ୍ରଟି ସଂସ୍କୃତ ପଢୁଛି ।)
(ଖ) ବାଳକ ଚନ୍ଦ୍ର ପଶ୍ୟତି । (ପିଲାଟି ଜହ୍ନ ଦେଖୁଛି ।)
(ଗ) ଦେବଦତଃ ଗ୍ରାମିଂ ଗଚ୍ଛତି । (ଦେବଦତ୍ତ ଗାଁକୁ ଯାଉଛି ।
ଉପର୍ୟ୍ୟକ୍ତ ବାକ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ‘କର୍ତ୍ତା’ ପ୍ରଧାନ ବା ଉକ୍ତ ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ ଏ ଗୁଡ଼ିକ କର୍ତ୍ତବାଚ୍ୟ ତେଣୁ ଉକ୍ତ କର୍ତ୍ତା ‘ଛାତ୍ର’, ‘ବାଳକ’ ଓ ‘ଦେବଦତ୍ତ’ ଠାରେ ‘ଉସ୍ତେ କଉଁରି ପ୍ରଥମା’ ବା ‘କଉଁରି ପ୍ରଥମା’ ସୂତ୍ରଦ୍ୱାରା ପ୍ରଥମ ବିଭକ୍ତି ବିଧାନ କରାଗଲା ।
୩। ନିମ୍ନଲିଖତ ବାକ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ପଢ଼ ।
(କ) ଛାତ୍ରେଣ ଇତିହାସ ପଠ୍ୟତେ । (ଛାତ୍ରଦ୍ୱାରା ଇତିହାସ ପଢ଼ାଯାଉଛି ।)
(ଖ) ବାଳକେନ ଚନ୍ଦ୍ର ଦୃଶ୍ୟତେ । ( ପିଲାଟିଦ୍ଵାରା ଚନ୍ଦ୍ର ଦେଖାଯାଉଛି ।)
(ଗ) ଦେବଦତ୍ତେନ ଗ୍ରାମ ଗମ୍ୟତେ । (ଦେବଦତ୍ତଦ୍ବାରା ଗାଁ ଯିବା ହେଉଛି । )
‘ଉଲ୍ଲେ କର୍ମଣି ପ୍ରଥମା’
ଉପର୍ୟ୍ୟକ୍ତ ବାକ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ କର୍ମପଦ ‘ଇତିହାସ’, ‘ଚନ୍ଦ୍ର’ ଓ ‘ଗ୍ରାମ’ ଉକ୍ତ ବା ପ୍ରଧାନ ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ, ଏହି ବାକ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକ କର୍ମବାଚ୍ୟରେ ଅଛନ୍ତି । ତେଣୁ କର୍ମବାଚ୍ୟରେ କର୍ମଠାରେ ପ୍ରଥମ ବିଭକ୍ତ ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
୪। (କ) ହେ ଛାତ୍ରା ! ଅଦ୍ୟ କିଂ ପଠିଷ୍ୟଥ ?
(ଖ) ଅରେ ବାଳକ ! ତବ ନାମ କିମ୍ ?
(ହେ ଛାତ୍ରମାନେ ! ଆଜି କ’ଣ ପଢ଼ିବ ?)
(ଆରେ ପିଲା ! ତୁମ ନାମ କ’ଣ ?)
ଏଠାରେ ହେ, ଅରେ ଇତ୍ୟାଦି ପଦରେ ଯଥାକ୍ରମେ ଛାତ୍ର, ବାଳକ ପ୍ରଭୃତିଙ୍କୁ ସମ୍ବୋଧନ କରଯାଇଛି । ତେଣୁ ‘ସମ୍ବୋଧନ’କୁ ବୁଝାଇଲେ ‘ପ୍ରଥମ ବିଭକ୍ତି’ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ସମ୍ବୋଧନର ଏକବଚନରେ ରୂପର ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନ ଦେଖାଯାଏ; ମାତ୍ର ଦ୍ବିବଚନ ଓ ବହୁବଚନ ପ୍ରଥମ ବିଭକ୍ତିପରି ହୋଇଥାଏ ।

‘ସଂବୋଧନେ ପ୍ରଥମା’
୫। (କ) ତୁମ୍ ଏବ ମମ ପରମ ବନ୍ଧୁ । (ତୁମେ ହିଂ ମୋର ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ ବନ୍ଧୁ ।)
(ଖ) ଆସୀତ୍ ପୁରା ବାଲ୍ମୀକି ନାମ ମହାନ୍ କବି । (ପୂର୍ବେ ବାଲ୍ମୀକି ବୋଲି ଜଣେ ବଡ଼ କବି ଥିଲେ ।)
(ଗ) ରାମ ଇତି ବାଳକ ଅତ୍ର ପଠତି । (ରାମ ବୋଲି ପିଲାଟି ଏଠାରେ ପଢ଼ୁଛି ।)
‘ଅବ୍ୟୟଯୋଗେ ପ୍ରଥମା’
ଏଠାରେ ଏବଂ (କେବଳ), ନାମ (ନାମକ), ଇତି (ବୋଲି) ପ୍ରଭୃତି ଅବ୍ୟୟପଦ ଅଟନ୍ତି । ‘ତୁମ୍’, ବାଲ୍ମୀକି ଓ ରାମଃ ପ୍ରଭୃତି ଶବ୍ଦର ଯେଉଁ ପ୍ରଥମ ବିଭକ୍ତ ହୋଇଛି, ତାହା ଉପର୍ୟ୍ୟକ୍ତ ଅବ୍ୟୟପଦଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଯୋଗରେ ହୋଇଛି । ଏହାକୁ ‘ଅବ୍ୟୟଯୋଗେ ପ୍ରଥମା’ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
ମନେରଖ :
- କ୍ରିୟାସାଧନରେ ଯେ ସ୍ବତନ୍ତ୍ର ବା ପ୍ରଧାନ, ତାକୁ କର୍ତ୍ତା କୁହାଯାଏ ।
- ଯେଉଁ ବାକ୍ୟରେ କର୍ତ୍ତାପ୍ରଧାନ, ତାହା କର୍ତ୍ତୃବାଚ୍ୟ ଏବଂ କର୍ତ୍ତୃବାଚ୍ୟରେ କର୍ତ୍ତାଠାରେ ପ୍ରଥମ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ ।
- ସମ୍ବୋଧନ ଏକ ସ୍ବତନ୍ତ୍ର ବିଭକ୍ତି ନୁହେଁ । ଏହା ପ୍ରଥମ ବିଭକ୍ତିର ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକ୍ତ ।
- ପ୍ରଥମ ବିଭକ୍ତି ଏକବଚନବ୍ୟତୀତ ସମ୍ବୋଧନର ରୂପ ପ୍ରଥମ ବିଭକ୍ତି ସଦୃଶ ।
- ସମ୍ବୋଧନକୁ ବୁଝାଇଲେ ପ୍ରଥମ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ ।
- କେତେକ ଅବ୍ୟୟଯୋଗେ ମଧ୍ୟ ପ୍ରଥମ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
ଗୀତ :
କରିବାଚ୍ୟ କର୍ତ୍ତା ପ୍ରଥମ ବିଭକ୍ତି ଆଉ ପୁଣି ସଂବୋଧନେ
କର୍ମ ଉକ୍ତ ହେଲେ ଅବ୍ୟୟ ଯୋଗରେ ମନେରଖ ପିଲାମାନେ ।
(i) କର୍ଭରି ପ୍ରଥମା
(ii) ସଂବୋଧନେ ପ୍ରଥମ
(iii) ଉକ୍ତ କର୍ମଣି ପ୍ରଥମା
(iv) ଅବ୍ୟୟଯୋଗେ ପ୍ରଥମା ବା ନିୟତ ଯୋଗେ ପ୍ରଥମା
ଅଭ୍ୟାସଃ :
୧। ଅଧୋଲିଖୂତପଦାନାଂ ସମ୍ବୋଧନେ ରୂପାଣି ଲିଖତ; ଯଥା – ମାତା – ହେ ମାତ !
(କ) ସୌରଭଃ __________________________।
Answer:
ହେ ସୌରଭ !
(ଖ) ଦେବୀ __________________________।
Answer:
ହେ ଦେବି !
(ଗ) ମୁନିଃ ___________________________।
Answer:
ହେ ମୁନଃ !
(ଘ) ପ୍ରଭୁଃ __________________________।
Answer:
ହେ ପ୍ରଭୋ !
(ଙ) ଲତା ___________________________।
Answer:
ହେ ଲତେ !
(ଚ) ଭ୍ରାତା __________________________।
Answer:
ହେ ଭ୍ରାତଃ !
(ଛ) ନମଃ __________________________।
Answer:
ହେ ନମଃ !

(ଜ) ବାଳିକେ __________________________।
Answer:
ହେ ବାଳିକେ !
(ଝ) ହରି __________________________।
Answer:
ହେ ହରଃ !
(ଞ) ପୁନଃ __________________________।
Answer:
ହେ ପୁତ୍ରା !
୨। ଅଧୋଲିଖନି ଅବ୍ୟୟପଦାନି ବ୍ୟବହୃତ୍ୟ ବାକ୍ୟାନି ରଚୟତ । ଯଥା : ଏବ – ସତ୍ୟମ୍ ଏବ ଜୟତେ ।
ଇତି _____________________________________।
Answer:
ସତ୍ୟମ୍ ଇତି ଜାନାମି ।
ଅପି _____________________________________।
Answer:
ତୁମପି ମମ ମାତା ।
ନାମ _____________________________________।
Answer:
ତବ ନାମ କିମ୍ ?
୩। କୋଷ୍ଠକାତ୍ ଯଥାର୍ଥ କର୍ତ୍ତୃପଦାନି ବ୍ୟବହୃତ୍ୟ ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନଂ ପୂରୟତ । ଯଥା : ଛାତ୍ରୀ ବ୍ୟାକରଣଂ ପଠତଃ ।
(କ) _____________________________________ ମାଂ ବଧୃତି ।
Answer:
ବୟମ୍
(ଖ)_____________________________________ ହରିଂ ଭଜତି ।
Answer:
ବାନୌ
(ଗ)_____________________________________ ଗୁରଂ ପ୍ରଣମାମି ।
Answer:
ଗୋପାଳ
(ଘ)_____________________________________ ଦୁଗ୍ଧ ପିବତଃ ।
Answer:
ବାନରୌ
(ଙ)_____________________________________ ଚିତ୍ରାଣି ପଶ୍ୟନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଅହମ୍
(ଚ) ____________________________________ଦେଶଂ ରକ୍ଷନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଶିଶନଃ
(ଛ)_________________________________ ବୃକ୍ଷମ୍ ଆରୋହତଃ ।
Answer:
ତୁମ୍
(ଜ) ___________________________________ମନ୍ଦିରଂ ଗମିଷ୍ୟତଃ ।
Answer:
ସୈନିକା
(ଝ) _________________________________ ପାଠ୍ୟ ସ୍ମରାମଃ ।
Answer:
ଯୁବାମ୍
(ଞ) __________________________________କୁତ୍ର ଗଚ୍ଛସି ?
Answer:
ଭକ୍ତ

୪। କୋଷ୍ଠକାତ୍ (ଉକ୍ତ) କର୍ମପଦାନି ବ୍ୟବହୃତ୍ୟ ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନଂ ପୂରୟତ । ଯଥା : ରମେଣ ରାବଶଃ ହତଃ ।
(କ) ଛାତ୍ରେଣ _______________________ ପଠ୍ୟତେ ।
Answer:
ପାଠ୍ୟ
(ଖ) ଭକ୍ତେନ _____________________________ ସେବ୍ୟତେ ।
Answer:
ଭଗବାନ୍
(ଗ) ରାମେଣ ____________________________ ଗମ୍ୟତେ ।
Answer:
ଗ୍ରାମଃ
(ଘ) ମୟା ________________________________ ଉନ୍ତଃ ।
Answer:
ଶିକ୍ଷକଃ
(ଙ) ରାଜ୍ଞା _________________________ ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଶ୍ୟତେ ।
Answer:
ଭୃତ୍ୟ
(ଚ) ମାତ୍ରା __________________________ ଉଚ୍ୟତେ ।
Answer:
କନ୍ଯା
(ଛ) ତ୍ୱୟା ___________________________ଦୃଷ୍ଟା ।
Answer:
କନ୍ଯା
(ଜ) କେନ _____________________________ କ୍ରିୟତେ ।
Answer:
କାର୍ଯ୍ୟମ୍
(ଝ) ବାଳିକୟା ____________________________ ନୀୟତେ ।
Answer:
ଜଳଂ
(ଞ) ଲକ୍ଷ୍ୟା ____________________________ ସେବ୍ୟତେ ।
Answer:
ଜଗନ୍ନାଥ
କର୍ମକାରକ ଓ ଦ୍ୱିତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି
୧। (କ) ଛାତ୍ର ସଂସ୍କୃତଂ ପଠତି । (ଛାତ୍ରଟି ସଂସ୍କୃତ ପଢୁଛି ।)
(କ) ଛାତ୍ର ସଂସ୍କୃତଂ ପଠତି। (ଛାତ୍ରଟି ସଂସ୍କୃତ ପଢୁଛି ।)
(ଖ) ବାଳକ ଚିତ୍ର ପଶ୍ୟତି। (ପିଲାଟି ଚିତ୍ର ଦେଖୁଛି ।)
(ଗ) ତ୍ୱମ୍ ଓଦନଂ ଖାଦସି । (ତୁମେ ଭାତ ଖାଉଛ ।)
ଉପନ୍ଯୁକ୍ତ ବାକ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ କର୍ତ୍ତା ‘ଛାତ୍ର’, ‘ଅହମ୍’ ଓ ‘ତୁମ୍’ ର ମୁଖ୍ୟ ଲକ୍ଷ୍ୟ ଯଥାକ୍ରମେ ‘ସଂସ୍କୃତମ୍’, ‘ଚିତ୍ରମ୍’, ଓ ‘ଓଦନମ୍’ ଅଟେ । କର୍ଭାର ଯାହା ଈପ୍ସିତତମ, ତାହା କର୍ମ । ତେଣୁ ସଂସ୍କୃତ, ଚିତ୍ର ଓ ଓଦନ ପଦଗୁଡ଼ିକ ‘କର୍ମପଦ’ ଅଟନ୍ତି ।୧ ବାକ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ କର୍ତ୍ତୃପଦ ଉକ୍ତ ବା ପ୍ରଧାନ ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ ‘କର୍ମ’ ଏଠାରେ ଅନୁକ୍ତ । ଅତଏବ ଅନୁକ୍ତ କର୍ମଠାରେ ଦ୍ଵିତୀୟା (ଅନୁସ୍ତେ କର୍ମଣି ଦ୍ୱିତୀୟା) ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୋଇଅଛି । ‘କରୁଁ ଈପ୍ସିତତମଂ କର୍ମ’
୨। ହରି ବୈକୁଣ୍ଠମ୍ ଅଧୂଶେତେ । (ଭଗବାନ୍ ବୈକୁଣ୍ଠରେ ଅଧ୍ୟୟନ କରନ୍ତି ।)
ଗୁରୁ ଆସନମ୍ ଅଧ୍ଯାସ୍ତେ । (ରାଜା ସିଂହାସନରେ ବସିଛନ୍ତି ।)
ଗୁରୁ ଆସନମ୍ ଅଧ୍ଯାସ୍ତେ । (ଗୁରୁ ଆସନରେ ବସିଛନ୍ତି ।)
ଏଠାରେ ‘ଅଧ୍’ ଉପସର୍ଗ ଯୁକ୍ତ ଶୀ (ଶାଢୀ଼), ସ୍ଥା, ଆସ୍ ଧାତୁର ପ୍ରୟୋଗରେ ଅଧୂକରଣ ସ୍ଥାନରେ କର୍ମସଂଜ୍ଞା ପ୍ରାପ୍ତ ହୋଇ ବୈକୁଣ୍ଠ, ସିଂହାସନ ଓ ଆସନ ପଦରେ ଦ୍ବିତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତ ହେଲା । ‘ଅସ୍ଥାସାଂ କର୍ମ’
୩ । ମୁନୟ କୁଟୀରମ୍ ଉପବସନ୍ତି । (ମୁନିମାନେ କୁଟୀରରେ ବାସ କରନ୍ତି ।)
ମୃଗ ବନମ୍ ଅନୁବସନ୍ତି । (ହରିଣମାନେ ବଣରେ ବାସ କରନ୍ତି ।)
ବିହଙ୍ଗ ନୀଡ଼ମ୍ ଅଧ୍ବସତି । (ଚଢ଼େଇ ବସାରେ ବାସକରେ ।)
କୃଷକଃ ଗ୍ରାମମ୍ ଆବସତି । (କୃଷକ ଗାଁରେ ବାସକରେ ।)
ଏଠାରେ ‘ଅଧ୍’ ଉପସର୍ଗ ଯୁକ୍ତ ଶୀ (ଶାଡ୍), ସ୍ଥା, ଆସ୍ ଧାତୁର ପ୍ରୟୋଗରେ ଅଧୂକରଣ ସ୍ଥାନରେ କର୍ମସଂଜ୍ଞା ପ୍ରାପ୍ତ ହୋଇ ବୈକୁଣ୍ଠ, ସିଂହାସନ ଓ ଆସନ ପଦରେ ଦ୍ବିତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତ ହେଲା । ‘ଅଧୂଶୀସ୍ଥାସାଂ କର୍ମ’‘ବସ୍’ ଧାତୁ ପୂର୍ବରେ ‘ଉପ’, ‘ଅନୁ’, ‘ଅଧ୍’ ଓ ‘ଆ’ ଉପସର୍ଗ ରହିଲେ ଅଧ୍ଯକରଣ କାରକ କର୍ମସଂଜ୍ଞା ପ୍ରାପ୍ତ ହୁଏ, ଏବଂ ସେଠାରେ ଦ୍ଵିତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତିର ପ୍ରୟୋଗ ହୁଏ । କିନ୍ତୁ ‘ଉପବସତି’ ର ଅର୍ଥ ଉପବାସ ବୁଝାଉଥିଲେ, ଆଧାର କର୍ମ ସଂଜ୍ଞା ପ୍ରାପ୍ତ ହୁଏ ନାହିଁ ଅର୍ଥାତ୍ ସପ୍ତମୀ ସ୍ଥାନରେ ଦ୍ୱିତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ ନାହିଁ । ‘ଉପାନ୍ସଧ୍ୟାହ୍ନ ବୟଃ’

ଯଥା ଦରିଦ୍ର୍ୟ ଗୃହେ ଉପବସନ୍ତି । (ଗରିବ ଲୋକଟି ଘରେ ଉପବାସ ଅଛି ।)
ଶ୍ରମିକଃ କୁଟୀରେ ଉପବସତି । (ଶ୍ରମିକ କୁଡ଼ିଆରେ ଉପବାସ ଅଛି ।)
ଉପ ଅନୁ ଅଧୂ ଆ ବସ୍ ଧାତୁ ମୂଳରେ ଥିଲେ ଆଧାରେ ହୁଏ ଦ୍ଵିତୀୟା ।
୪। ସାଧୁ ସନ୍ମାର୍ଗମ୍ ଅଭିନିବିଶତେ । (ସାଧୁଲୋକ ଭଲ ବାଟକୁ ମନ ଦେଉଛି ।)
ଅଭି ଓ ନି ଉପସର୍ଗ ପୂର୍ବକ ‘ବିଶ୍’ ଧାତୁର ଆଧାରରେ କର୍ମକାରକ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ସ୍ଥଳବିଶେଷରେ ଏହାର ବ୍ୟତିକ୍ରମ ମଧ୍ୟ ଦେଖାଯାଏ । ଯଥା : ବାଳକାନାଂ ପାଠେ ଅଭିନିବେଶ (ଆଗ୍ରହ) ଅସ୍ଥି । (ପିଲାମାନଙ୍କର ପାଠରେ ଆଗ୍ରହ ଅଛି ।) ୫। ହିରଣ୍ୟତଃ ନିର୍ଭୟଂ ସ୍ଥିତଃ । (ହିରଣ୍ୟକ ନିର୍ଭୟରେ ରହିଲା ।)
୫। ହିରଣ୍ୟତଃ ନିର୍ଭୟଂ ସ୍ଥିତଃ । (ହିରଣ୍ୟକ ନିର୍ଭୟରେ ରହିଲା ।)
ଗଜଃ ଧୀରଂ ଚଳତି । (ହାତୀ ଧୀରେ ଧୀରେ ଚାଲୁଛି ।)
ଦୀର୍ଘକଣ୍ଠୀ ସଭୟମ୍ ଆହ । (ଦୀର୍ଘକଣ୍ଠ ଭୟ ସହିତ କହିଲା ।)
ଶିଶୁ ସାଶ୍ଚର୍ଯ୍ୟ ପଶ୍ୟତି । (ଶିଶୁ ଆଶ୍ଚର୍ଯ୍ୟର ସହିତ ଦେଖୁଛି ।)
ଉପନ୍ଯୁକ୍ତ ଉଦାହରଣଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ‘ନିର୍ଭୟମ’, ‘ଧୀରମ୍’ ଓ ‘ସଭୟମ୍’ ବାକ୍ୟର କ୍ରିୟାକୁ ବିଶେଷିତ କରୁଥିବାରୁ, ଏମାନଙ୍କୁ କ୍ରିୟା ବିଶେଷଣ କୁହାଯାଏ । କ୍ରିୟାବିଶେଷଣଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଦ୍ବିତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ଓ କ୍ଲବଲିଙ୍ଗ ଏକବଚନ ହୁଅନ୍ତି । ଏହାକୁ ‘କ୍ରିୟା ବିଶେଷଣେ ଦ୍ଵିତୀୟା’ ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ ।
ଅହଂ ମାସଂ ବ୍ୟାକରଣଂ ପଠାମି । (ମୁଁ ମାସେ ହେଲା ବ୍ୟାକରଣ ପଢ଼ୁଛି ।)
ରାମଚନ୍ଦ୍ର ଚତୁର୍ଦ୍ଦଶବର୍ଷାଣି ବନେ ତିଷ୍ଠତି ସ୍ମ । (ରାମଚନ୍ଦ୍ର ଚଉଦବର୍ଷ ବଣରେ ରହିଥିଲେ ।)
ପର୍ବତଃ କ୍ରୋଶଂ ବର୍ଷତେ । (ପର୍ବତଟି କୋଣେ ବ୍ୟାପି ରହିଛି ।)
ଅତ୍ୟନ୍ତ ସଂଯୋଗ (ବ୍ୟାପି) ଅର୍ଥରେ କାଳବାଚକ ‘ମାସ’ ଓ ‘ବର୍ଷ’ଠାରେ ଓ ମାର୍ଗବାଚକ ‘କ୍ରୋଶ’ ଶବ୍ଦରେ ଦ୍ୱିତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୋଇଛି । ଏହାକୁ ‘ବ୍ୟାପ୍ୟର୍ଥେ ଦ୍ୱିତୀୟା’ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
୭। ମାନବାଃ ଦେବାନ୍ ଅନୁ । (ମନୁଷ୍ୟମାନେ ଦେବତାଙ୍କଠାରୁ ନିକୃଷ୍ଟ ।)
ଦୀନଂ ପ୍ରତି ଦୟାଂ କୁରୁ । (ଗରିବକୁ ଦୟା କର ।)
ମାଳାକାରଃ ବୃକ୍ଷ ବୃକ୍ଷ ପ୍ରତି ସିଞ୍ଚତି / ପରି ସିଞ୍ଚତି / ଅନୁ ସିଞ୍ଚତି । (ମାଳି ଗଛକୁ ଗଛ ପାଣି ଦେଉଛି ।)
ଏଠାରେ ଅନୁ, ପ୍ରତି, ପରି ପ୍ରଭୃତି କେତେକ ଉପସର୍ଗ ସ୍ବତନ୍ତ୍ର ପଦରୂପେ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହୋଇ ଗୋଟିଏ ଗୋଟିଏ ‘ସ୍ୱତନ୍ତ୍ର’ ଅର୍ଥକୁ ପ୍ରକାଶ କରୁଛନ୍ତି । ଏମାନଙ୍କୁ ‘କର୍ମପ୍ରବଚନୀୟ’ କୁହାଯାଏ । ସେହି କର୍ମପ୍ରବଚନୀୟ ଯୋଗେ ‘ଦେବାନ୍’, ‘ଦୀନଂ’, ‘ବୃକ୍ଷ’ ହରିମ୍ ପ୍ରଭୃତି ଦ୍ଵିତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୋଇଅଛି ।
୮। ଗୋପାଳ ରାଂ ପୟଃ ଦୋଷି । (ଗଉଡ଼ ଗାଈ ଦୁହୁଛି ।)
କୃଷକଃ ଅକ୍ଷାଂ ଗ୍ରାମିଂ ନୟତି । (କୃଷକ ଛେଳିଟିକୁ ଗ୍ରାମକୁ ନେଉଛି ।)
ବିଚାରପତିଃ ଚୋରଂ ଶତଂ ଦଣ୍ଡୟତି। (ବିଚାରପତି ଚୋରକୁ ଶହେଟଙ୍କା ଦଣ୍ଡ ହେଉଛନ୍ତି ।)
ପୟଃ – ମୁଖ୍ୟକର୍ମ, ଗ୍ରାମ – ଗୌଣକର୍ମ ।
ଅଜାମ୍ – ମୁଖ୍ୟକର୍ମ, ଗ୍ରାମମ୍ – ଗୌଣକର୍ମ ।
ଚୌରମ୍ – ମୁଖ୍ୟକର୍ମ, ଶତମ୍ – ଗୌଣକର୍ମ ।
ଦୁହ୍, ନୀ ଓ ଦଣ୍ଡ ପ୍ରଭୃତି ଧାତୁଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଦ୍ବିକର୍ମକ ଅଟନ୍ତି । ଏପରି ଧାତୁମାନଙ୍କର ପ୍ରୟୋଗରେ ଗୌଣ କର୍ମଠାରେ ଅନ୍ୟ କାରକ ସ୍ଥାନରେ କର୍ମସଂଜ୍ଞା ପ୍ରାପ୍ତ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଏହାକୁ ‘ଅକଥ୍ତଂ ଚ’ ସୂତ୍ରରେ କର୍ମ କୁହାଯାଏ । ‘ଗୋ’ ସ୍ଥାନରେ ‘ଗାମ୍’, ‘ଗ୍ରାମେ’ ସ୍ଥାନରେ ‘ଗ୍ରାମମ୍’, ‘ଶତେନ’ ସ୍ଥାନରେ ‘ଶତମ୍’ ହୋଇଛି ।
ସଂସ୍କୃତବ୍ୟାକରଣରେ ସାଧାରଣତଃ ୧୬ ଗୋଟି ଦ୍ବିକର୍ମକ ଧାତୁର ବ୍ୟବହାର ଦେଖାଯାଏ । ଯଥା : ଦୁହ୍, ଯାଚ୍, ପଚ୍, ଦଣ୍ଡ, ରୁଧ, ପ୍ରଚ୍ଛ, ଚି, ବୁ, ଶାସ୍ତ୍ର, ଜି, ମଥ୍, ମୁଷ୍କ, ନୀ, ହୃ, କୃଷ୍ ଓ ବହ୍ । ଏହି ଧାତୁଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଯୋଗରେ ଓ ତଦର୍ଥକ ଧାତୁରେ ମଧ୍ଯ ଅକଥ୍ତ ଗୌଣ କର୍ମର ପ୍ରୟୋଗ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
ଯଥା : ବଲିଂ ଭିକ୍ଷତେ ବସୁଧାମ୍ । (ବଳିରାଜାଙ୍କୁ ବସୁଧା ଭିକ୍ଷା କରୁଛନ୍ତି ।)
ଭିକ୍ଷୁକଃ ଗୃହିଣୀମ୍ ଅନଂ ପ୍ରାର୍ଥୟତେ । (ଭିକାରୀ ଗୃହିଣୀଙ୍କୁ ଭାତ ମାଗୁଛି ।)
ଏଠାରେ ‘ଯାତ୍’ ଅର୍ଥରେ ଭିକ୍ଷ୍ ଓ ପ୍ରାର୍ଥ ଧାତୁର ପ୍ରୟୋଗ ହୋଇଛି ।
୯ । ନିମ୍ନଲିଖତ ପଦଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଯୋଗରେ ଦ୍ଵିତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ ।
ସର୍ବତଃ – (ସବୁଆଡ଼େ)- ଦେଶଂ ସର୍ବତଃ ‘ସର୍ବଶିକ୍ଷା-ଅଭିଯାନଂ’ ପ୍ରଚଳତି ।
(ଦେଶର ସବୁଆଡ଼େ ସର୍ବଶିକ୍ଷା ଅଭିଯାନ ଚାଲୁଛି ।)
ପରିତଃ – (ଚାରିପାଖରେ) – ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟଂ ପରିତଃ ପ୍ରାଚୀରଂ ଶୋଭତେ ।
(ସ୍କୁଲ ଚାରିପଟେ ପାଚିରୀ ଶୋଭା ପାଉଛି ।)
ଅଭିତଃ – (ଆଗରେ ) – ମାତରମ ଅଭିତଃ ଶିଶୁ କ୍ରୀଡ଼ତି । (ମାଆ ଆଗରେ ପିଲା ଖେଳୁଛି ।)-
ଉଭୟତଃ – (ଉଭୟ ପାର୍ଶ୍ବରେ) – ନଦୀମ୍ ଉଭୟତଃ ବୃକ୍ଷା ସନ୍ତି । (ନଈ ଦୁଇପଟେ ଗଛ ଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଅଛନ୍ତି ।)
ଉପର୍ୟୁପରି – (ଉପରକୁ ଉପର) – ବାୟୁମଣ୍ଡଳମ୍ ଉପର୍ୟ୍ୟପରି ସ୍ତରଭେଦଃ ।
(ବାୟୁମଣ୍ଡଳ ଉପରକୁ ଉପରକୁ ସ୍ତରଭେଦ ଅଛି ।)
ଅଧ୍ୟଧୂ – (ଉପରକୁ ଉପର) – ବୃକ୍ଷମ୍ ଅଧଧ ଶାଖା ସନ୍ତି । (ଗଛ ଉପରକୁ ଉପରକୁ ଡାଳ ଅଛି ।)
ଅଧୋଽଧଃ – (ତଳକୁ ତଳ) – ଅଧୋଽଧଃ ଲୋକଂ ପାତାଳ । (ସଂସାରର ତଳକୁ ତଳ ପାତାଳ ।)
ଅନ୍ତରା – (ମଧ୍ୟରେ ) – ଜଗନ୍ନାଥ ବଳଭଦ୍ର ଚ ଅନ୍ତରା ସୁଭଦ୍ରା ବିରାଜତେ ।
(ଜଗନ୍ନାଥ ଓ ବଳଭଦ୍ରଙ୍କ ମଝିରେ ସୁଭଦ୍ରା ଅଛନ୍ତି ।)
ଅନ୍ତରେଣ– (ବିନା ) – ଜଳଂ ବିନା ଜୀବନମ୍ ଅସମ୍ଭବମ୍ । (ପାଣି ବିନା ଜୀବନ ଅସମ୍ଭବ ।)
ଧକ୍ – (ଧକ୍କାର) – ଚୌରଂ ଧକ୍ । (ଚୋରକୁ ଧକ୍ ।)
ଯାବତ୍ – (ପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ) – ନଦୀ ଯାବତ୍ ଗଚ୍ଛ । (ନଈ ପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ ଯାଅ ।)
ବିନା – (ବ୍ୟତୀତ) – ପରିଶ୍ରମଂ ବିନା ବିଦ୍ୟା ନ ଭବତି । (ପରିଶ୍ରମ ବିନା ପାଠ ହୁଏ ନାହିଁ ।)
(ବିନା ଯୋଗେ ୩ୟା / ୫ମୀ ମଧ୍ଯ ହୁଏ ।)
ଋତେ – (ବ୍ୟତୀତ ) – ଧର୍ମମ ରତେ ସୁଙ୍ଖ ନାସ୍ତି । (ଧର୍ମ ବିନା ସୁଖ ନାହିଁ ।)
(ଋତେ ଯୋଗେ ୫ମୀ ମଧ୍ଯ ହୁଏ ।)
ସମୟା / ନିକଷା – (ନିକଟରେ) – ଗ୍ରାମଂ ସମୟ। / ନିକଷା ନଦୀ ପ୍ରବହତି । (ଗାଁ ପାଖରେ ନଈ ବହୁଛି ।)
ହା – (ଦୁଃଖସୂଚକ ) – ହା ନାସ୍ତିକମ୍ । ହା – ମନ୍ଦଭାଗ୍ୟମ୍ଭ। (ହାୟରେ ନାସ୍ତିକ । ହାୟରେ ମନ୍ଦଭାଗ୍ୟ ।)
ଦକ୍ଷିଣେନ – (ଦକ୍ଷିଣରେ ) – ଅସ୍ମାଙ୍କ ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟ ରାଜମାର୍ଗ ଦକ୍ଷିଣେନ ଅସ୍ଥି । (ଆମ ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟ ସଡ଼କ ଦକ୍ଷିଣପଟେ ଅଛି ।)
ଉତ୍ତରେଣ – (ଉତ୍ତରରେ) – ତବ ଗୃହଂ ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟମ୍ ଉତ୍ତରେଣ ଅନ୍ତି । (ତୁମଘର ସ୍କୁଲ ଉତ୍ତରପଟେ ଅଛି ।)

ବି.ଦ୍ରା : ଅବ୍ୟୟାଦି ପଦ ଯୋଗରେ ଯେଉଁ ବିଭକ୍ତ ହୁଏ ତାହାକୁ ‘ଉପପଦ ବିଭକ୍ତି’ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
ମନେରଖ :
- କର୍ରାର କ୍ରିୟାଦ୍ବାରା ଯାହା ଅତ୍ୟନ୍ତ ଈପ୍ସିତ ତାହା କର୍ମକାରକ ଓ ଏହା ଦ୍ୱିତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତାନ୍ତ ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
- ବସ୍ ଧାତୁ ପୂର୍ବରେ ଉପ, ଅନୁ, ଅଧ୍ ଓ ଆ ଉପସର୍ଗ ରହିଲେ, ଆଧାରର କର୍ମସଂଜ୍ଞା ହୁଏ ।
- କ୍ରିୟାର ବିଶେଷଣଠାରେ ଦ୍ଵିତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ ଏବଂ ତାହା କ୍ଲବଲିଙ୍ଗ ଏକବଚନରେ ପ୍ରୟୋଗ ହୁଏ ।
- ଉଭୟତଃ, ପରିତଃ, ସମୟା, ନିକଷା, ହା, ପ୍ରତି, ଧ୍ୱକ୍ ପ୍ରଭୃତି କେତେକ ଅବ୍ୟୟପଦ ଯୋଗେ ଦ୍ଵିତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
- ବିନା ଯୋଗେ ଦ୍ୱିତୀୟା, ତୃତୀୟା ଓ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ ।
ଗୀତ :
କର୍ମ କାରକେ ଦ୍ବିତୀୟା
କାଳ ବାଚକରେ ତାହା
ଶୀ, ସ୍ଥା, ଅସ୍ ଧାତୁ ଅଧ୍ ଯୋଗରେ
ଉପ, ଅନୁ, ଅଧୂଗେ
ବସ୍ ଧାତୁର ସଙ୍ଗେ
ଦ୍ବିତୀୟା ହୁଅଇ ଅଭି, ନି, ବିଶ୍ ସଙ୍ଗରେ
ଅଧଧ ଓ ଉପସ୍ଥ୍ୟପରି
ଅଭିତଃ ପରିତଃ ଯୋଗେ ହୁଏ ସେପରି । ୧।
ହା, ପ୍ରତି, ଧୂକ ଓ ସମୟା
ରତେ ଯାବତ୍ ଅନ୍ତରା
ଅନ୍ତରେଣ ବିନା ଯୋଗେ ହୁଏ ଦ୍ବିତୀୟା
କ୍ରିୟା ବିଶେଷଣେ ଯାହା
ଅନୁ ପ୍ରତି ଯୋଗେ ତାହା
ସର୍ବତଃ ଯୋଗେ ମଧ୍ୟ ହୁଅଇ ଏହା
ମନେରଖ ବାଳକ ବାଳିକାଗଣ
ଦ୍ବିତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ପାଇଁ ନିୟମମାନ । ୨।
ଅଭ୍ୟାସଃ :
୧। ବନ୍ଧନୀମଧ୍ୟାତ୍ ଯଥାର୍ଥ-କର୍ମପଦଂ ନିରୂପ୍ୟ ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନଂ ପୂରୟତ ।
ଯଥା : ବାଳକ ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟଂ ଗଚ୍ଛତି ।
(କ) କୃଷକଃ _______________________ ନୟତି ।
Answer:
ଅଜାଂ
(ଖ) ପଥ୍ __________________________ ପିବତି ।
Answer:
ଜଳଂ
(ଗ) ଛାତ୍ରୀ __________________________ ସେବତେ ।
Answer:
ଗୁରୁଂ
(ଘ) ଭକ୍ତାଃ__________________________ ପୂଜୟନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଈଶ୍ୱରଂ
(ଙ) ଧନିକ __________________________ ଦଦାତି ।
Answer:
ଧନଂ
୨। ବନ୍ଧନୀସ୍ଥିତାନାଂ ଶବ୍ଦାନାଂ ଯଥାର୍ଥ-ବିଭରୌ ପ୍ରୟୋଗଂ କୁରୁତ ।
ଯଥା : ଡଃ ବରଂ ସଂସ୍କୃତଂ ପଠିଷ୍ୟତି (ବର୍ଷ) ।
(କ)_______________________ ଅନୁ ବସ୍ତ୍ର ଧାବତି । (ଗୋ)
Answer:
ଗାମ୍ଂ
(ଖ) ଅହଂ ___________________ ନମାମି । (ଗୁରୁ)
Answer:
ଗୁରୁଂ

(ଗ) ସଃ _______________________ ପିବତି । (ମଧୁ)
Answer:
ମଧୁଂ
(ଘ) ଭକ୍ତଃ ________________________ ଭଜତି । (ହରି)
Answer:
ହରିଂ
(ଙ) ବ୍ରାହ୍ମଣୀ _______________________ ପୂଜୟତି । (ଦେବ)
Answer:
ଦେବଂ
(ଚ) ଅଶ୍ଳୀ _______________________ ଧାବତି । (ଶୀଘ୍ର)
Answer:
ଶୀଘ୍ରଂ
(ଛ) ଛାତ୍ରା ___________________________ ପଠେୟୁ । (ପାଠ)
Answer:
ପାଠଂ
(ଜ) ଙ _____________________________ ଗଚ୍ଛସି । (ପାଠଶାଳା)
Answer:
ପାଠଶାଳାଂ
୩। ବାକ୍ୟାନି ସଂଶୋଧୟତ ।
ଯଥା – ଦୀନସ୍ୟ ପ୍ରତି ଦୟା କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟା-ଦୀନଂ ପ୍ରତି ଦୟା କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟା ।
(କ) ରାମଃ ଅଯୋଧ୍ୟାୟାମ୍ ଅଧ୍ଯାସ୍ତେ ।
Answer:
ରାମଃ ଅଯୋଧ୍ୟାମ୍ ଅଧ୍ଯସ୍ତେ ।
(ଖ) ପକ୍ଷିଣ ମଧୁରେଣ କୂଜନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ପକ୍ଷିଣ ମଧୁରଂ କୂଜନ୍ତି ।
(ଗ) ପ୍ରାକ୍ ଭରତେନ ଇତି ରାଜା ଆସୀତ୍ ।
Answer:
ପ୍ରାକ୍ ଭରତଃ ଇତି ରାଜା ଆସୀତ୍ ।
(ଘ) ମମ ପ୍ରତି ଦୟାଂ କୁରୁ ।
Answer:
ମାଂ ପ୍ରତି ଦୟାଂ କୁରୁ ।
(ଙ) ଗ୍ରାମାତ୍ ଅଭିତଃ ଗାପଃ ଚରନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଗ୍ରାମମ୍ ଅଭିତଃ ଗାପଃ ଚରନ୍ତି ।
(ଚ) ମନ୍ତ୍ରଣ ଦିଲ୍ୟାମ୍ ଉପବସନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ମନ୍ତ୍ରଣ ଦିଲ୍ଲୀମ୍ ଉପବସନ୍ତି ।
(ଛ) ମାନବାଃ ଦେବାନାମ୍ ଅନୁ ।
Answer:
ମାନବାଃ ଦେବାନ୍ ଅନୁ ।

(ଜ) ମୂଷିକାଂ ଗର୍ଭେ ଅଧ୍ଵସନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ମୂଷିକା ଗର୍ଭମ୍ ଅଧ୍ଵସନ୍ତି ।
୪। ଅଧୋଲିଖୁନି ପଦାନି ବ୍ୟବହୃତ୍ୟ ବାକ୍ୟାନି ରଚୟତ ।
ଯଥା : (ଅଭିତଃ-ମାତରମ୍ ଅଭିତଃ ଶିଶୁ କ୍ରୀଡ଼ତି ।)
ପ୍ରତି – ଗ୍ରାମଂ ପ୍ରତି ଗମିଷ୍ୟାମି ।
ଶୀଘ୍ରମ୍ – ଶୀଘ୍ରମାଗଚ୍ଛ ତୁମ୍ ।
ହା – ହା କଷ୍ଟମ୍ ।
ଅନ୍ତରା – ଗୃହମନ୍ତରା ଶିଶୁ କ୍ରନ୍ଦତି ।
ଅଭିନିବିଶେତେ – ଛାତ୍ରା ପାଠମ୍ ଅଭିନିବିଶେତେ ।
ଦିବସମ୍ – ଦିବସମହମତ୍ର ସ୍ଥାସ୍ୟାମି ।
ଧୂ – ଅସାରଂ ସଂସାରଂ ଧ୍ଵଂକ୍ ।
ସମୟା – ମାଂ ସମୟା ଆଗଚ୍ଛତଃ ।
ଉଭୟତଃ – ମାର୍ଗମ୍ ଉଭୟତଃ ବୃକ୍ଷା ସନ୍ତି ।
ଉପବସତି – ଦରିଦ୍ର୍ୟ ଗ୍ରାମମ୍ ଉପବସତି ।
୫। ସଂସ୍କୃତେନ ଅନୁବାଦଃ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ।
(କ) କେତେବର୍ଷ ହେଲା ତୁମେ ଖବରକାଗଜ ପଢୁଛ ।
Answer:
କତି ବର୍ଷାଣି ତଂ ସମ୍ବାଦପତ୍ର ପଠସି ।
(ଖ) ମୁଁ ଏଠାରେ ଦିନଟିଏ ରହିବି ।
Answer:
ଅହମତ୍ର ଦିବସଂ ସ୍ଥାସ୍ୟାମି ।
(ଗ) ରାସ୍ତାର ଉଭୟ ପାର୍ଶ୍ଵରେ ଗଛଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଅଛି ।
Answer:
ମାର୍ଗମ୍ ଉଭୟତଃ ବୃକ୍ଷା ସନ୍ତି ।
(ଘ) ଧନ ବିନା କିଏ ସୁଖୀ ହେବ ।
Answer:
ଧନଂ ବିନା କଃ ସୁଖୀ ଭବିଷ୍ୟତି ।
(ଙ) ମୃତ୍ୟୁ ପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ ପରିଶ୍ରମ କରିବା ଉଚିତ ।
Answer:
ମୃତ୍ୟୁ ଯାବତ୍ ପରିଶ୍ରମଂ କୁର୍ଥାତ୍ ।
(ଚ) ଦେଶର ସବୁଆଡ଼େ ପ୍ରଗତି ହେଉଛି ।
Answer:
ଦେଶଂ ସର୍ବତଃ ପ୍ରଗତିଃ ଭବତି ।
(ଛ) ଆଜିକାଲି ପିଲାଙ୍କର ପାଠରେ ଆଗ୍ରହ ନାହିଁ ।
Answer:
ଅଧୁନା ବାଳକାନାଂ ପାଠେ ଅଭିନିବେଶଃ ନାସ୍ତି।
୬। ରେଖାଙ୍କିତପଦାନାଂ ସକାରଣବିଭଣ୍ଡିଂ ନିରୂପୟତ ।
ଯଥା : ବିଦ୍ୟା ବିନା ଜୀବନଂ ବୃଥା । ଉତ୍ତର : ବିନା ଯୋଗେ ତୃତୀୟା
(କ) ଶିଶୁ ମାତରମ ଅନୁ ଧାବତି ।
Answer:
ଅନୁଯୋଗେ ଦ୍ଵିତୀୟା
(ଖ) ହସ୍ତୋ ପ୍ରକ୍ଷାଲ୍ୟ ଭୋଜନଂ କୁରୁତ ।
Answer:
କର୍ମଣି ଦ୍ବିତୀୟା ।
(ଗ) ସଦ୍ କୁର୍ନୀତ ସଙ୍ଗତିମ୍ ।
Answer:
କର୍ମଣି ଦ୍ବିତୀୟା ।
(ଘ) ତବ ଗୃହଂ ପ୍ରତି ମାର୍ଗ ଦର୍ଶୟ
Answer:
ପ୍ରତିଯୋଗେ ଦ୍ବିତୀୟା ।
(ଙ) ବ୍ଲକ୍ ତଂ ମିଥ୍ୟାବାଦିନମ ।
Answer:
ଧୂଯୋଗେ ଦ୍ଵିତୀୟା ।

୭। ବନ୍ଧନୀ ମଧ୍ଯସ୍ଥଶବ୍ଦାନାମ୍ ଉପଯୁକ୍ତ ବିଭକ୍ତି ପ୍ରୟୋଗଂ କୃତ୍ୱା ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନଂ ପୂରୟତ ।
ଯଥା :
ଶିକ୍ଷକଃ : ତଂ କିଂ ପଠସି ?
ଛାତ୍ରଃ : ଅହଂ ସାହିତ୍ୟ ପଠାମି । (ସାହିତ୍ୟ)
Answer:
ସାହିତ୍ୟ
(କ) ଶିକ୍ଷକଃ : ହାଃ ନଂ କୁତ୍ର ଅଗଚ୍ଛ ?
ଛାତ୍ରଃ : ହାଃ ଅହଂ ___________________ ଅଗଚ୍ଛମ୍ । (ମାତୁଳାଳୟ )
Answer:
ମାତୁଳାଳୟମ୍
(ଖ) ଶିକ୍ଷକ : ତତ୍ର ତଂ କମ୍ ଅପଶ୍ୟ ?
ଛାତ୍ରଃ : ତତ୍ର ଅହଂ _______________________ ଅପଶ୍ୟମ୍ ? (ସମୁଦ୍ର)
Answer:
ସମୁଦ୍ରମ୍
(ଗ) ଶିକ୍ଷକଃ : ଶ୍ୱ ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟସ୍ୟ ଅବକାଶ – ଦିବସ ।
ଛାତ୍ରଃ: ଅହଂ ଗୃହେ ______________________ ନାଗମିଷ୍ୟାମି । (ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟ)
Answer:
ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟଂ
(ଘ) ଶିକ୍ଷକଃ : ଗୃହେ ତଂ କିଂ କରିଷ୍ଯସି ?
ଛାତ୍ରଃ: ଅହଂ ଗୃହେ ___________________________ ପଠିଷ୍ୟାମି । (ପାଠ)
Answer:
ପାଠଂ
କରଣକାରକ ଓ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭଳି
୧। (କ) ଛାତ୍ର ଯାନେନ ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟଂ ଗଚ୍ଛତି । (ଛାତ୍ରଟି ଗାଡ଼ିରେ ସ୍କୁଲ ଯାଉଛି ।)
(ଖ) ବ୍ୟାଧଃ ଶରଣ ମୃଗଂ ହନ୍ତି । (ଶିକାରୀ ଶରରେ ହରିଣକୁ ମାରେ ।)
(ଗ) ବାଳକ ହସ୍ତେନ ଖାଦତି । (ପିଲାଟି ହାତରେ ଖାଏ ।)
(ଘ) ଅହଂ କଲମେନ ଲିଖାମି । (ମୁଁ କଲମରେ ଲେଖେ ।)
(ଙ) ତଂ ପାଦାଭ୍ୟ ଗୃହଂ ଗଚ୍ଛସି । (ତୁମେ ଦୁଇପାଦରେ ଘରକୁ ଯାଅ ।)
ଏଠାରେ କର୍ତ୍ତା ‘ଛାତ୍ର’ ର ‘ଗମନ’ କ୍ରିୟା ସାଧନରେ ‘ଯାନ’ ପ୍ରଧାନ ସହାୟକ ଅଟେ । ସେହିପରି କର୍ତ୍ତା ‘ବ୍ୟାଧ’ର ‘ମାରଣ’ କ୍ରିୟା ସମ୍ପାଦନରେ ‘ଶର’, ପ୍ରଧାନ ସହାୟକ, ବାଳକର ଭୋଜନ କ୍ରିୟାରେ ହସ୍ତ, ‘ଅହମ୍’ ର ଲେଖନ କ୍ରିୟାରେ କଲମ ଓ ‘ଡ଼ମ୍’ ର ଗମନକ୍ରିୟା ସମ୍ପାଦନରେ ‘ପାଦ’ ପ୍ରଧାନ ସହାୟକ ଅଟେ । ଅତଏବ ଯାନ, ଶର, ହସ୍ତ, କଲମ ଓ ପାଦ ଏମାନେ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ‘ କରଣ କାରକ’ ଅଟନ୍ତି । କାରଣ କ୍ରିୟା ସାଧନରେ କର୍ତ୍ତାର ପ୍ରଧାନ ସହାୟକକୁ ‘କରଣ’ କୁହାଯାଏ । କରଣ କାରକରେ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ‘ସାଧକତମଂ କରଣମ୍’
୨। (କ) ବାଳକେନ ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥ ପଠ୍ୟତେ । (ପିଲାଟି ପଢ଼ୁଛି ।)
(ଖ) ରାମେଣ ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟ ଗମ୍ୟତେ । (ରାମ ସ୍କୁଲ ଯାଉଛି ।)
(ଗ) ତ୍ରୟା ଲିଖ୍ଯତେ । (ତୁମେ ଲେଖୁଛ ।)
(ଘ) ମୟା କଥ୍ୟତେ । (ମୁଁ କହୁଛି ।)
ଯେଉଁ ବାକ୍ୟରେ କର୍ମ ମୁଖ୍ୟ ତାକୁ ‘କର୍ମବାଚ୍ୟ’ ଓ ଯେଉଁ ବାକ୍ୟରେ କ୍ରିୟା ମୁଖ୍ୟ ତାକୁ ‘ଭାବବାଚ୍ୟ’ କୁହାଯାଏ । ଏହି ଦୁଇପ୍ରକାର ବାକ୍ୟରେ ‘କର୍ତ୍ତା’ ଅପ୍ରଧାନ ବା ଅନୁକ୍ତ ଅଟେ । ଏହି ଅନୁକ୍ତ କର୍ରାଠାରେ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଏହାକୁ ‘ଅନୁସ୍ତେ କଉଁରି ତୃତୀୟା’ କହନ୍ତି । ଉପର୍ୟ୍ୟକ୍ତ ବାକ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ବାଳକେନ, ରାମେଣ, ତ୍ରୟା ଓ ମୟା ଅନୁକ୍ତ କର୍ତା ହୋଇ ତୃତୀୟ ବିଭକ୍ତିରେ ରହିଛନ୍ତି ।
୩। (କ) ଗବାଂ ପୟଃ ପ୍ରକୃତ୍ୟା ମଧୁରମ୍ । (ଗାଈର କ୍ଷୀର ପ୍ରକୃତିରେ ମିଠା ।)
(ଖ) ରାମଃ ସ୍ବଭାବେନ ସରଳୀ । (ରାମ ସ୍ବଭାବରେ ସରଳ ।)
(ଗ) ପବନଃ ବେଗେନ ବହତି । (ପବନ ଜୋରରେ ବହୁଛି ।)
(ଘ) ଦରିଦ୍ର୍ୟ ଦୁଃଖେନ କାଳଂ ଯାପୟତି । (ଗରିବ ଦୁଃଖରେ କାଳ କାଟୁଛି ।)
ପ୍ରକୃତି, ସ୍ଵଭାବ, ବେଗ ଓ ଦୁଃଖ ପ୍ରଭୃତି ଶବ୍ଦ ‘ପ୍ରକୃତି’ଗଣରେ ଆସୁଥିବାରୁ ଏହି ଶବ୍ଦଗୁଡ଼ିକର ତୃତୀୟାନ୍ତ ହୋଇ ପ୍ରୟୋଗ ହୁଏ । ଏହାକୁ ‘ପ୍ରାକୃତ୍ୟାଦିଭିଂ ତୃତୀୟା’ ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ । ଏହି ପ୍ରକୃତିଗଣରେ ଆସୁଥିବା ଅନ୍ୟଶବ୍ଦଗୁଡ଼ିକ; ଯଥା – ପ୍ରାୟ, ଗୋତ୍ର, ଜାତି, ନାମ, ସମ, ବିଷମ, ଆକୃତି, ଅବଲୀଳା ପ୍ରଭୃତି ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତାନ୍ତ ହୋଇ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହୁଅନ୍ତି । ଯଥା – ପ୍ରାୟଣ, ଗୋତ୍ରେଣ, ଜାତ୍ୟା, ନାମ୍ନା, ସମେନ, ବିଷମେନ, ଆକୃତ୍ୟା, ଅବଳୀଳୟା ।
୪। (କ) ଜଟାଭି ତାପରଃ । (ଜଟରେ ତପସ୍ବୀ ।)
(ଖ) ଉପବୀତେନ ବ୍ରାହ୍ମଶଃ । (ପଇତାରେ ବ୍ରାହ୍ମଣ ।)
(ଗ) ଧ୍ଵଜେନ ଦେବାଳୟଃ । (ପତାକାରେ ଦେଉଳ ।)
ଯେଉଁ ଲକ୍ଷଣ ବା ଚିହ୍ନଦ୍ୱାରା କୌଣସି ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ବା ବସ୍ତୁ ଚିହ୍ନିତ ହୁଏ, ସେହି ଚିହ୍ନବାଚକ ଶବ୍ଦରେ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ଏଠାରେ ‘ଜଟା’ ଦ୍ବାରା ତାପସ, ଉପବୀତ ଦ୍ବାରା ବ୍ରାହ୍ମଣ ଓ ଧ୍ଵଜା ଦ୍ବାରା ଦେବାଳୟ ଚିହ୍ନିତ ହୋଇଅଛି । ତେଣୁ ଜଟା, ଉପବୀତ ଓ ଧ୍ଵଜ ଶବ୍ଦର ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ବିଧାନ ହେଲା । ଏହାକୁ ‘ଉପଲକ୍ଷଣେ ତୃତୀୟା’ ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ ।

୫। (କ) ଚକ୍ଷୁଷା କାଶଃ । (ଆଖରେ କଣା ।)
(ଖ) କର୍ଣ୍ଣାଭ୍ୟ ବଧୂ । (କାନରେ ବଧୂର ।)
(ଗ) ପାଦେନ ଖଞ୍ଜ । (ପାଦରେ ଛୋଟା ।)
୬। ବିକୃତ ଅଙ୍ଗବାଚକ ଶବ୍ଦର ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ଉପର ଉଦାହରଣ ଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ଚକ୍ଷୁ, କର୍ଣ୍ଣ ଓ ପାଦବିକୃତ ଅଙ୍ଗ ହୋଇଥବାରୁ, ସେହି ସେହି ଶବ୍ଦରେ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତ ହେଲା । ଏହାକୁ ‘ଅଙ୍ଗବିକାରେ ତୃତୀୟା’ ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ ।
(କ) ବୃଦ୍ଧା ଶୀତେନ କମ୍ପତେ । (ବୁଢ଼ାଟି ଶୀତରେ ଥରୁଛି ।)
(ଖ) ଅୟଂ ଶୋକେନ କ୍ରନ୍ଦତି । (ଇଏ ଦୁଃଖରେ କାନ୍ଦୁଛି ।)
(ଗ) ଅଧ୍ୟୟନେନ ଡଃ କଟକେ ତିଷ୍ଠତି । (ପାଠ ପଢ଼ିବାକୁ ସେ କଟକରେ ରହୁଛି ।)
ହେତୁ ବା କାରଣ ବୋଧକ ଶବ୍ଦରେର ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ଉପର ଉଦାହରଣ ଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ‘କମ୍ପନ’ କ୍ରିୟାର କାରଣ ‘ଶୀତ’, କ୍ରନ୍ଦନ କ୍ରିୟାର କାରଣ ‘ଶୋକ’ ଓ ରହିବା କ୍ରିୟାର କାରଣ ‘ଅଧ୍ୟୟନ’ ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ ଏଠାରେ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ହେଲା । ଏହାକୁ ହେତୌ ତୃତୀୟା କହନ୍ତି । ହେତୁ ବା କାରଣବୋଧକଶବ୍ଦ ପୁଂଲିଙ୍ଗ ବା କ୍ଲବଲିଙ୍ଗ ହୋଇଥିଲେ, ତା’ଠାରେ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ମଧ୍ୟ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଯଥା – ‘ବୃଦ୍ଧା ଶୀତାତ୍ କମ୍ପତେ’ – ଏପରି ମଧ୍ଯ ହୁଏ । ଏହାକୁ ହେତୌ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ କହନ୍ତି କିନ୍ତୁ ହେତୁବୋଧକଶବ୍ଦ ସ୍ତ୍ରୀଲିଙ୍ଗ ହୋଇଥିଲେ, କେବଳ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ; ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ହୁଏ ନାହିଁ । ଯଥା :
(ଘ) ଡଃ ବୃଦ୍ଧା ମୁକ୍ତା । (ସେ ବୁଦ୍ଧିବଳରେ ମୁକ୍ତ ହେଲା ।)
(ଙ) ବିଦ୍ୟୟା ବଦ୍ଧତେ ବୁଦ୍ଧି । (ବିଦ୍ୟାଦ୍ଵାରା ବୁଦ୍ଧି ବଢ଼େ ।)
୭ । କ) ସପ୍ତଭିଂ ଦିବସୈ ନୀରୋଗ ଜାତଃ । (ସାଦିନରେ ନୀରୋଗ ହେଲା ।)
(ଖ) ଡଃ ମାସେନ ବ୍ୟାକରଣମ୍ ଅପଠତ୍ । (ସେ ମାସକରେ ବ୍ୟାକରଣ ପଢ଼ିଲା ।)
(ଗ) ବର୍ଷେଣ ଗୃହଂ ନିର୍ମିତଂ ଭବେତ୍ । (ବର୍ଷକରେ ଘର ତିଆରି ହୋଇପାରେ ।)
ଅପବର୍ଗ ବା ଫଳପ୍ରାପ୍ତି ବୁଝାଇଲେ କାଳବାଚକ ଶବ୍ଦରେ ବ୍ୟାପ୍ତିର୍ଥ ଦ୍ବିତୀୟା ନ ହୋଇ ‘ଅପବର୍ଗେ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି’ ବିଧାନ କରାଯାଏ । ଉପର ଲିଖ୍ତ ଉଦାହରଣ ଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ସପ୍ତଦିବସ, ମାସ ଓ ବର୍ଷ ଶବ୍ଦରେ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତିର ପ୍ରୟୋଗ ହୋଇଛି । କାରଣ ସାତ ଦିନରେ ନୀରୋଗ ହେବା, ମାସକରେ ବ୍ୟାକରଣ ପଢ଼ିସାରିବା ଓ ବର୍ଷକରେ ଗୃହନିର୍ମାଣ ହେବା ସୂଚିତ ହେଉଥିବାରୁ ଏହା ଫଳପ୍ରାପ୍ତି ବା କାର୍ଯ୍ୟସିଦ୍ଧିକୁ ବୁଝାଉଅଛି । (ଅପବର୍ଗ ତୃତୀୟା)
୮। (କ) ଅନେକ ମାର୍ଗଣ ଗଛତୁ । (ଏହି ବାଟେ ଯାଆନ୍ତୁ ।)
(ଖ) ଚୌରଃ ଅନୟା ଦିଶା ଗତବାନ୍ । (ଚୋର ଏହି ଦିଗକୁ ଗଲା ।)
(ଗ) ପଞ୍ଚିଭିଂ ମୁଦ୍ରାଭିଂ ଅହଂ କଲମଂ କ୍ରୀତବାନ୍ । (ପାଞ୍ଚଟଙ୍କା ଦେଉ ମୁଁ କଲମ କିଣିଲି ।)
ମାର୍ଗବାଚକ, ଦିଗବାଚକ ଓ ମୂଲ୍ୟବାଚକ ଶବ୍ଦରେ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଉପର ବାକ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ମାର୍ଗଣ, ଅନୟା ଦିଶା ଓ ପଞ୍ଚତିଃ ମୁଦ୍ରାଭି ଇତ୍ୟାଦି ଶବ୍ଦଗୁଡ଼ିକ ମାର୍ଗ, ଦିଗ ଓ ମୂଲ୍ୟ ଅର୍ଥକୁ ବୁଝାଉଥିବାରୁ ଏଠାରେ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ପ୍ରୟୋଗ ହୋଇଛି ।
୯। (କ) ପିତ୍ରା ସହ ପୁନଃ ଆପଣଂ ଗଚ୍ଛତି । (ବାପାଙ୍କ ସହିତ ପୁଅ ଦୋକାନକୁ ଯାଉଛ ।)
(ଖ) ମୟା ସାନ୍ଧ୍ୟ ତୁମ୍ ଆଗଚ୍ଛ । (ମୋ ସହିତ ତୁମେ ଆସ ।)
(ଗ) କେନାପି ସାକଂ କଳହଂ ମା କୁରୁ । (କାହା ସାଙ୍ଗରେ କଳି କର ନାହିଁ ।)
(ଘ) ରାମେଣ ସମଂ ସୀତା ବନମ୍ ଅଗଚ୍ଛତ୍ । (ରାମଙ୍କ ସହିତ ସୀତା ବଣକୁ ଗଲେ ।)
ଉପରେ ପ୍ରଦତ୍ତ ଉଦାହରଣ ଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ସହାର୍ଥକ ସହ, ସାର୍ଶମ୍, ସାକମ୍ ଓ ସମମ୍ ଶବ୍ଦ ପ୍ରୟୋଗରେ ଯାହା ସହିତ ବୁଝାଉଛି ତା’ଠାରେ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୋଇଅଛି । ଏହାକୁ ‘ସହଯୁକ୍ତ ଅପ୍ରଧାନେ ତୃତୀୟା’ ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ । ବେଳେ ବେଳେ ‘ସହ’ ପ୍ରଭୃତି ଶବ୍ଦ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ପ୍ରୟୋଗ ନହୋଇ ମଧ୍ୟ, ସହ ଅର୍ଥକୁ ବୁଝାଇଥାଏ । ଏପରି ସ୍ଥଳେ ମଧ୍ଯ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତିରେ ପ୍ରୟୋଗ ହୁଏ । ଯଥା –
(ଙ) ପିତା ପୁତ୍ରେଣ ଗଚ୍ଛତି । (ପିତା ପୁତ୍ର ସହିତ ଯାଉଛନ୍ତି ।)
(ଚ) ମାତ୍ରା ଗଚ୍ଛତି ଶିଶୁ । (ମାଆ ସାଙ୍ଗରେ ଶିଶୁଟି ଯାଉଛି ।)
ଏହାକୁ ସାଧାରଣତଃ ‘ସହାର୍ଥେ ତୃତୀୟା’ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
୧୦ । (କ) ଗ୍ରୀଷ୍ମକାଳେ ଜଳାଶୟଃ ଜଳେନ ଶୂନ୍ୟ ଭବନ୍ତି । (ଖରାଦିନେ ପୋଖରୀ ଜଳଶୂନ୍ୟ ହୋଇଥାଏ ।)
(ଖ) କଳହେନ ଅଳମ୍ । (କଳି କର ନାହିଁ ।)
(ଗ) ମମ ବିଦ୍ୟୟା ପ୍ରୟୋଜନମ୍ । (ମୋର ବିଦ୍ୟା ଦରକାର ।)
(i) ଊନାର୍ଥକ ଶବ୍ଦ ଊନଃ (ଊଣା), ହୀନଃ, ଶୂନ୍ଯ ଓ ରହିତଃ ଶବ୍ଦଯୋଗେ
(ii) ବାରଣାର୍ଥକ (ନିଷେଧ) ଅଳମ୍, କୃତମ୍ ଓ କିମ୍ ଶବ୍ଦଯୋଗେ ଏବଂ
(iii) ପ୍ରୟୋଜନାର୍ଥକ (ଆବଶ୍ୟକ) ପ୍ରୟୋଜନମ, ଅର୍ଥ, ଲାଭ ଓ କିମ୍ ଶବ୍ଦଯୋଗେ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତ ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
ତେଣୁ ଉପର ପ୍ରଦତ୍ତ ଉଦାହରଣ ଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ଜଳେନ ଊନାର୍ଥେ ତୃତୀୟା, କଳହେନ ବାରଣାର୍ଥେ ଓ ବିଦ୍ୟାୟା ପ୍ରୟୋଜନାର୍ଥେ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୋଇଅଛି ।
୧୧। (କ) ରାମେଣ ସଦୃଶଃ ରାଜା ନାସ୍ତା । (ରାମଙ୍କ ପରି ରାଜା ନାହାଁନ୍ତି ।)
(ଖ) ଜ୍ୟେଷ୍ଠଭ୍ରାତା ପିତ୍ରା ସମଃ । (ବଡ଼ଭାଇ ପିତୃତୁଲ୍ୟ ।)
(ଗ) ମୟା ତୁଲ୍ୟ କୋଽପି ନାସ୍ତି । (ମୋ ଭଳି କେହି ନାହିଁ ।)
(ଘ) ଅର୍ଜୁନେନ ସମାନଃ ବୀରଃ ନାସ୍ତି । (ଅର୍ଜୁନଙ୍କ ପରି ବୀର ନାହିଁ ।)
ତୁଲ୍ୟାର୍ଥକ ସଦୃଶଃ, ସମଃ, ତୁଲ୍ୟ ଓ ସମାନଃ ଶବ୍ଦଯୋଗେ ଯାହା ସହିତ ତୁଲ୍ୟ ତା’ଠାରେ ତୃତୀୟା ଓ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ବିଧାନ କରାଯାଏ । ଏଠାରେ ସଦୃଶଃ ଶବ୍ଦଯୋଗ ରାମେଣ, ସମଃ ଶବ୍ଦଯୋଗେ ପିତ୍ରା, ତୁଲ୍ୟ ଶବ୍ଦଯୋଗେ ମୟା ଓ ସମାନଃ ଶବ୍ଦଯୋଗେ ଅର୍ଜୁନେନ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତାନ୍ତ ହୋଇଅଛି ।
୧୨ । ନିମ୍ନଲିଖ ପଦଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଯୋଗରେ ତୃତୀୟା ହୁଏ ନାହିଁ ।)
ନାନା – (ବିନା) – ଧର୍ମେଣ ନାନା ସୁଙ୍ଖ ନ ଲଭ୍ୟତେ । (ଧର୍ମ ବିନା ସୁଖ ମିଳେ ନାହିଁ ।)
ପୃଥକ୍ – (ଅଲଗା) – ଜଳେନ ପୃଥକ୍ ମତ୍ସ୍ୟ ନ ଭବତି । (ପାଣିରୁ ଅଲଗା ହୋଇ ମାଛ ବଞ୍ଚେ ନାହିଁ ।)
ବିନା – (ବ୍ୟତୀତ) – ଶ୍ରୀମେଣ ବିନା ବିଦ୍ୟା ନ ଜୀବତି । (ପରିଶ୍ରମ ବିନା ବିଦ୍ୟା ହୁଏ ନାହିଁ ।)
ପୂର୍ବଃ – (ବଡ଼) – ସ ମତ୍ ବର୍ଷେଣ ପୂର୍ବ । (ସେ ମୋଠାରୁ ବର୍ଷେ ବଡ଼ ।)
ଅବରଃ – (ସାନ) – ନଂ ରାମାତ୍ ମାସେନ ଅବରଃ । (ତୁମେ ରାମଠାରୁ ମାସେ ସାନ ।)

ମନେରଖ :
- କ୍ରିୟା ସାଧନରେ କର୍ତ୍ତାର ଯିଏ ପ୍ରଧାନ ସହାୟକ, ତାକୁ କରଣକାରକ କୁହାଯାଏ ଏବଂ ସେଠାରେ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ ।
- ଅଙ୍ଗ ବିକାର ବୁଝାଇଲେ ବିକୃତ ଅଙ୍ଗବାଚକ ଶବ୍ଦରେ ତୃତୀୟା ହୁଏ ।
- ଫଳପ୍ରାପ୍ତି ବୁଝାଇଲେ ସମୟ ବାଚକ ଶବ୍ଦ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତାନ୍ତ ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
- ‘ଉପଲକ୍ଷଣ’ – ଚିହ୍ନ ବୁଝାଇଲେ, ଚିହ୍ନବାଚକ ଶବ୍ଦଠାରେ ତୃତୀୟା ହୁଏ ।
- ନିଷେଧାର୍ଥକ ‘ଅଳମ୍’ ଯୋଗେ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତ ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
- ସାକମ୍, ସାର୍ଶମ୍, ସମମ୍ ଓ ସହ ଶବ୍ଦଯୋଗେ ତୃତୀୟା ହୁଏ ।
- ଯେଉଁ ମାର୍ଗରେ ଗମନ କରାଯାଏ ତା’ଠାରେ ମଧ୍ୟ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ ।
- ଊନ, ବାରଣ ଓ ପ୍ରୟୋଜନ ଅର୍ଥରେ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
ଗୀତ :
କରଣ କାରକରେ ତୃତୀୟା
ସ୍ବଭାବେ ପ୍ରକୃତି ଯୋଗେ ତାହା
ସୁଖେନ, ଦୁଃଖେନ, ସହ ସାକଂ ସାନ୍ଧ୍ୟ ସମଂ
ଯୋଗରେ ହୁଏ ଏହା । ୧।
ଅଙ୍ଗବିକାରରେ ଯେ ବିଭକ୍ତ
ଉପଲକ୍ଷଣରେ ସେଇ ନୀତି
ହେତୁ ଅର୍ଥେ ସଦା ସ୍ତ୍ରୀଲିଙ୍ଗ ଶବ୍ଦର
ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ ସାଥୀ । ୨।
ନିଶ୍ଚେ ହେବ ତୃତୀୟା
ବାରଣ, ହୀନ, ଊନ, ପ୍ରୟୋଜନରେ
ହୁଅଇ ତୃତୀୟା ଶିଖ ନୀତି । ୩।
ଅଭ୍ୟାସଃ :
୧ । ବନ୍ଧନୀଦତ୍ତଶ ବ୍ଦାନାଂ ଯଥା ର୍ଥବିଭଳ୍ତିଂ କୃତ୍ସା ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନଂ ପୂରୟତ ।
ଯଥା : ତେ ବନ୍ଧୁଭି ସହ ଗଛନ୍ତି । (ବନ୍ଧୁ)
(କ) ବାଳକଃ ________________________ କ୍ରୀଡ଼ତି । (କନ୍ଦୁକ)
Answer:
କନ୍ଦୁକେନ
(ଖ) ଧନିକଃ __________________________ ଖଲ୍ଟାଟିଂ (ଚନ୍ଦ୍ରାଲୋକ) ।(ଶିରସ୍)
Answer:
ଶିରସା
(ଗ) ମୂର୍ଖସ୍ୟ _______________________ କିମ୍ । (ଜୀବନମ୍ )
Answer:
ଜୀବନେନ
(ଘ)___________________________________ ସହ ତୁମ୍ ଆଗଚ୍ଛ । (ଅସ୍ମଦ୍-ଏକବଚନେ)
Answer:
ମୟା
(ଙ) ଶିଶୁ _____________________________ କ୍ରନ୍ଦତି । (ଦୁଃଖମ୍ )
Answer:
ଦୁଃଖେନ
(ଚ) ମମ _________________________________ ପ୍ରୟୋଜନମ୍ ଅସ୍ତ । (ବିଦ୍ୟା)
Answer:
ବିଦ୍ୟୟା
(ଛ)___________________________________ ସମାନଃ କବି ନାସ୍ତି । (କାଳିଦାସ)
Answer:
କାଳିଦାସେନ
୨। ବନ୍ଧନୀସ୍ଥିତେଷୁ ଯଥାର୍ଥ ପଦେନ ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନଂ ପୂରୟତ ।
(କ) ______________________ ବିନା ଜୀବନଂ ବୃଥା । (ଧର୍ମସ୍ୟ, ଧର୍ମାତ୍, ଧର୍ମେଣ)
Answer:
ଧର୍ମେଣ / ଧର୍ମାତ୍

(ଖ) ବାଳାନାଂ __________________ ପ୍ରୟୋଜନମ୍ । (ଦୁଗ୍ଧାୟ, ଦୁଗ୍ଧନ, ଦୁଗ୍ଧସ୍ୟ)
Answer:
ଦୁସ୍ପେନ
(ଗ) ରାଜନ୍ ! ତବ _________________________ ଅଳମ୍ । (ଶ୍ରମେଣ, ଶ୍ରମସ୍ୟ, ଶ୍ରମମ୍)
Answer:
ଶ୍ରମେଣ
(ଘ) ଛାତ୍ରଃ ______________________________ ଲିଖତି । (କଲମସ୍ୟ, କଲମେନ, କଲମାୟ)
Answer:
କଲମେନ
(ଙ) କୃପଣସ୍ଯ ______________________________ ପ୍ରୟୋଜନମ୍ ? (ଧନସ୍ୟ, ଧନାୟ, ଧନେନ)
Answer:
ଧନେନ
(ଚ) ରାଜକନ୍ୟା _____________________ ଆଗଚ୍ଛତି ? (ଲୀଜେନ, ଲୀଳୟା, ଲୀଳାୟା)
Answer:
ଲୀଳୟା
୩। ରେଖାଙ୍କିତାନାଂ ପଦାନାଂ ସକାରଣବିଭଣ୍ଡିଂ ଦର୍ଶୟତ ।
ଯଥା – ରାମ ଶରଣ ରାବଣଂ ହତବାନ୍ । ଶରଣ – କରଣେ ୩ୟା । ।
(କ) ପ୍ରାୟଣ ଗ୍ରାମାଂ କୃଷକୈ ଶୋଭନ୍ତେ ।
Answer:
ପ୍ରାୟଣ – ପ୍ରକୃତ୍ୟାଦିଭ୍ୟତୀୟ ।
(ଖ) ସୋପାନ-ମାର୍ଗେଣ ନଦୀ ପ୍ରବିଶ ।
Answer:
ସୋପାନ-ମାର୍ଗଣ – ମାର୍ଗବାଚକ ପଦରେ ତୃତୀୟା ।
(ଗ) ବାଳିକା କଳସେନ ଜଳମ୍ ଆନୟନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
କଳସେନ – କରଣେ ତୃତୀୟା ।
(ଘ) ଗ୍ରାମବାସିନଃ ସ୍ଵଭାବେନ ସରଳା
Answer:
ସ୍ଵଭାବେନ – ପ୍ରକୃତ୍ୟାଦିଭ୍ୟତୀୟା ।
(ଙ) ଧନେନ ହୀନାଃ ଦରିଦ୍ର୍ୟ ଭବନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଧନେନ – ହୀନପଦପ୍ରୟୋଗେ ତୃତୀୟା ।
(ଚ) ମୟା ସାକଂ ପଃ ଗମିଷ୍ୟତି ?
Answer:
ବର୍ଷେଣ – ଅବରାପଦପ୍ରୟୋଗେ ତୃତୀୟା
(ଛ) ସୀତା ମତ ବର୍ଷେଣ ଅବରା ।
Answer:
ମୟା – ସାକଂ ପଦଯୋଗେ ତୃତୀୟା ।
୪। ବନ୍ଧନୀସ୍ଥିତପଦାନାଂ ଯଥାର୍ଥବିଭଲ୍ତୌ ପ୍ରୟୋଗଂ କୁରୁତ ।
ଯଥା – ତେନ ଦୀପେନ ସିଂ ପ୍ରୟୋଜନମ୍ ଯତ୍ର ତୈଳଂ ନାସ୍ତି । (ଦୀପ)
ତେନ ଯାନେନ କୋ ଲାଭଃ ଯତ୍ ନ ଚଳତି । (ଯାନ)
(କ) ତେନ _________________________ କିଂ ଯତ୍ର ନ ଗମ୍ୟତେ । (ମାର୍ଗ)
Answer:
ମାର୍ଗେଣ
(ଖ) ତେନ _________________________ କିଂ ଯତ୍ର ନ ଦୃଶ୍ୟତେ ମୁଖମ୍ । (ଦର୍ପଣ)
Answer:
ଦର୍ପେଣନ

(ଗ) ତେନ _________________________ କିଂ ଯତ୍ ଭ୍ରାନ୍ତଃ ଜନୟତି । (ପୁସ୍ତକ)
Answer:
ପୁସ୍ତକେନ
(ଘ) ତେନ _________________________ କିଂ ଯତ୍ ଦରିଦ୍ରେଭ୍ୟ ନ ଦୀୟତେ । (ଧନ)
Answer:
ଧନେନ
(ଙ) ତେନ _________________________ କିଂ ଯେନ ପରହିତଂ ନ କ୍ରିୟତେ । (ଜୀବନ)
Answer:
ଜୀବନେନ
(ଚ) ତେନ _________________________ କିଂ ଯତ୍ ନ ଆଚର୍ଯ୍ୟତେ । (ଜ୍ଞାନ)
Answer:
ଜ୍ଞାନେନ
୫। ଅଧୋଲିଖୂପଦାନି ବ୍ୟବହୃତ୍ୟ ପୃଥକ୍ବାକ୍ୟାନି ରଚୟତ ।
ଯଥା- ଜଳେନ ବିନା ମସ୍ୟା ନ ଜୀବନ୍ତି ।
ନାନା: ଧର୍ମେ ନାନା ସୁଙ୍ଖ ନାସ୍ତି ।
କୃତମ୍: ବିବାଦେନ କୃତମ୍ ।
ପୃଥକ୍: ରାମଃ ଶ୍ୟାମାତ୍ ପୃଥକ୍ ।
କିମ୍: ବିବାଦେନ କିମ୍ ।
ଅବରା: ସା ମତ୍ ମାସେନ ଅବରା ।
ସାର୍ବମ୍ : ମୟା ସାନ୍ଧ୍ୟମ୍ ଆଗଚ୍ଛ ।
ଊନଃ: ନେନ ଊନଃ ଦରିଦ୍ର୍ୟ ।
ପୂର୍ବଃ: ରାମ ଶ୍ୟାମାତ୍ ପୂର୍ବ ।
ସ୍ଵେଚ୍ଛାୟା: ବାଳକଃ ସ୍ଵେଚ୍ଛାୟା ଭ୍ରମନ୍ତି ।
ଲୀଳୟା: ଶ୍ରମିକଃ ଲୀଳୟା କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରୋତି ।
୬। ବାକ୍ୟାନି ସଂଶୋଧୟତ ।
ଅଶୁଦ୍ଧ
ଯଥା – ଡଃ ଜାତୌ କ୍ଷତ୍ରିୟ ।
ଶୁଦ୍ଧ
ଡଃ ଜାତ୍ୟା କ୍ଷତ୍ରିୟ ।
(କ) ରାଜା ମନ୍ତ୍ରଣଂ ସାନ୍ଧ୍ୟ ଭବବିଷ୍ଟ
Answer:
ରାଜା ମନ୍ତ୍ରୀତିଃ ସାର୍ଶ୍ଵମ୍ ଉପବିଷ୍ଟ ।
(ଖ) ଗୁରୁଭକ୍ତେ ପଃ ସର୍ବାନ୍ ଅତିକ୍ରାମତି ।
Answer:
ଗୁରୁଭକ୍ତା ସ ସର୍ବାନ୍ ଅତିକ୍ରାମତି ।
(ଗ) କାଣସ୍ୟ ଚକ୍ଷୁଷ କିମ୍ ?
Answer:
କାଣସ୍ୟ ଚକ୍ଷୁଷ କିମ୍ ?
(ଘ) ଜନଃ ପରିବାରଂ ସହ ନିବସନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଜନଃ ପରିବାରେଣ ସହ ନିବସନ୍ତି ।
(ଙ) କଳହସ୍ୟ କଃ ଅର୍ଥା ।
Answer:
କଳହେନ କଃ ଅର୍ଥ ।

(ଚ) ଅଳମ୍ ଅତି ବିସ୍ତରସ୍ୟ ।
Answer:
ଅଳମ୍ ଅତିବିସ୍ତରଣ ।
(ଛ) ଡଃ ନାମେନ ମାଧବ ।
Answer:
ଡଃ ନାମ୍ନା ମାଧବ ।
୭। ଯଥା ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦେଶଂ ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନଂ ପୂରୟତ ।
ଯଥା – ଅୟଂ ପୁସ୍ତକାଳୟ । ଅଳଂ ବାର୍ତ୍ତାଳାପେନ । (ବାର୍ତ୍ତାଳାପ)
(କ) ଅୟଂ ଦେବାଳୟଃ । ________________________ । (କୋଳାହଳ)
Answer:
କୋଳାହଳେନ
(ଖ) ଅୟଂ ମାର୍ଗ । ________________________ । (କୋଳହ)
Answer:
କୋଳହେନ
(ଗ) ଅୟଂ ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟ । ________________________ । (ବିବାଦ)
Answer:
ବିବାଦେନ
(ଘ) ଏଷା ବାଟିକା । ________________________ । (ପୁଷ୍ପପ୍ରୋଟନ )
Answer:
ପୁଷ୍ପପ୍ରୋଟନେନ
(ଙ) ଏଷ ଚକିତ୍ସାଳୟ । ________________________ । (ହସନ)
Answer:
ହସନେନ
୮। ‘କ’ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭାତ୍ ଶବ୍ଦାନ୍ ଗୃହୀତ୍ବା ‘ଖ’ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭସ୍ୟ ଶନିଃ ସହ ମେଳନଂ କୃତ୍ୱା ‘ଗ’ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭେ ଯଥାନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ ଲିଖତ ।
table
୯। ସଂସ୍କୃତେନ ଅନୁବାଦଃ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ।
(କ) ମୋ ଭଉଣୀ ମୋଠାରୁ ବର୍ଷେ ବଡ଼ ।
Answer:
ମମ ଭଗିନୀ ମତ୍ ବର୍ଷେଣ ପୂର୍ବ ।
(ଖ) ଲୋକମାନେ ନୌକାରେ ନଦୀପାର ହୁଅନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଜନଃ ନୌକୟା ନଦୀ ତରନ୍ତି ।
(ଗ) ଗୋରୁମାନେ ପଡ଼ିଆରେ ନିଜ ଇଚ୍ଛାରେ ବୁଲୁଛନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଗାନଃ ପ୍ରାନ୍ତରେ ସ୍ୱେଚ୍ଛୟା ଭ୍ରମନ୍ତି ।
(ଘ) ଖୁସିରେ ତୁମର ସମୟ କଟିଯିବ ।
Answer:
ଆନନ୍ଦନ ତବ କାଳ ଯାସ୍ୟାତି ।
(ଙ) ମୁଁ ତୁମ ସହିତ ମେଳାକୁ ଯିବି ।
Answer:
ଅହଂ ତ୍ରୟା ସାକଂ ମେଳା ଗମିଷ୍ୟାମି ।
୧। ନିମ୍ନଲିଖତ ବାକ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ପଢ଼ ।
(କ) ରାଜା ବ୍ରାହ୍ମଣାୟ ଧନଂ ଦଦାତି । (ରାଜା ବ୍ରାହ୍ମଣକୁ ଧନ ଦେଉଛନ୍ତି ।)
(ଖ) ଭିକ୍ଷୁକାୟ ଭିକ୍ଷାଂ ଦେହି । (ଭିକ୍ଷୁକକୁ ଭିକ ଦିଅ ।)
(ଗ) ମାତା ପୁତ୍ରାୟ ଚନ୍ଦ୍ର ଦର୍ଶୟତି । (ମାଆ ପୁଅକୁ ଚନ୍ଦ୍ର ଦେଖାଉଛି ।)

‘ସମ୍ୟକ୍ ପ୍ରଦୀୟତେ ଅସ୍ମେ ଇତି ସମ୍ପ୍ରଦାନ । ’ କର୍ତ୍ତା ଯେଉଁ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିକୁ ଦେବାକୁ ଇଚ୍ଛା କରେ, ସେ ସମ୍ପ୍ରଦାନ କାରକ ଅଟେ । ପ୍ରଥମ ଦୁଇଟି ବାକ୍ୟରେ ‘ବ୍ରାହ୍ମଣ’ ଓ ‘ଭିକ୍ଷୁକ’ ସମ୍ପ୍ରଦାନ କାରକ ଅଟନ୍ତି । ‘କର୍ମଣା ଯମଭିପ୍ରେତି ସ ସମ୍ପ୍ରଦାନମ୍ ।’ ଦାନ କ୍ରିୟାର କର୍ତ୍ତା ରାଜା ‘ବ୍ରାହ୍ମଣ’ଙ୍କୁ ଦେବା ପାଇଁ ଇଚ୍ଛା କରୁଥିବାରୁ ତାହା ସମ୍ପ୍ରଦାନ କାରକ ଅଟେ । ‘କ୍ରିୟୟା ଯମଭିପ୍ରେତି ସୋଽପି ସମ୍ପ୍ରଦାନମ ।’ ପୁନଶ୍ଚ କର୍ତ୍ତା ଯେକୌଣସି କ୍ରିୟାଦ୍ଵାରା ଯାହାର ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ଇଚ୍ଛାକରେ (ଯାହାର ପ୍ରୀତି ସମ୍ପାଦନ କରେ) ସେ ମଧ୍ଯ ସମ୍ପ୍ରଦାନ କାରକ ହୁଏ । ତୃତୀୟ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ମାତା ଚନ୍ଦ୍ର ଦର୍ଶନ କ୍ରିୟାଦ୍ୱାରା ପୁତ୍ରକୁ ଖୁସି କରିବାକୁ ବା ପ୍ରୀତି ବର୍ଶନ କରୁଥିବାରୁ ‘ପୁତ୍ର’ଠାରେ ସମ୍ପ୍ରଦାନ ସଂଜ୍ଞା ହେଲା । ସମ୍ପ୍ରଦାନ କାରକ ଠାରେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭତ୍ତି ବିଧାନ କରାଯାଏ । ଏହାକୁ ‘ସମ୍ପ୍ରଦାନେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ’ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
୨। (କ) ଶିଶବେ କ୍ରୀଡ଼ା ରୋଚତେ । (ପିଲାଟିକୁ ଖେଳ ଭଲଲାଗେ ।)
(ଖ) ବାନରାୟ ଫଳାନି ସ୍ୱଦନ୍ତେ । (ମାଙ୍କଡ଼କୁ ଫଳ ଭଲଲାଗେ ।)
(ଗ) ସର୍ବେ ଧନାୟ ଗୃହୟନ୍ତି । (ସମସ୍ତେ ଧନ ଇଚ୍ଛା କରନ୍ତି ।)
‘ରୁଚ୍ୟର୍ଥନାଂ ପ୍ରୀୟମାଣ ।’ରୁଚି ଅର୍ଥକ (ରୁବ୍ ଓ ସ୍ୱଦ୍) ଧାତୁର ପ୍ରୟୋଗରେ କାହାକୁ ରୁଚେ, ତା’ଠାରେ ସମ୍ପ୍ରଦାନ ସଂଜ୍ଞା ହୋଇ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଶିଶୁକୁ କ୍ରୀଡ଼ା ଓ ବାନରକୁ ଫଳ ରୁଚୁଥିବାରୁ ‘ଶିଶୁ’ ଓ ‘ବାନର’ ଉଭୟଠାରେ ସମ୍ପ୍ରଦାନ ସଂଜ୍ଞା ହୋଇ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୋଇଛି । ‘ଗୃହେ ରୀପ୍ସିତଃ । ପୁନଶ୍ଚ ଇଚ୍ଛା କରିବା ଅର୍ଥରେ ଗୃହି (ସ୍ପୃହ୍+ଶିବ ସ୍ବାର୍ଥେ) ଧାତୁର ପ୍ରୟୋଗରେ କର୍ତ୍ତାର ଈପ୍ସିତ ବସ୍ତୁ ସମ୍ପ୍ରଦାନ ସଂଜ୍ଞା ପ୍ରାପ୍ତହୋଇ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୋଇଥାଏ । ତୃତୀୟ ବାକ୍ୟରେ କର୍ତ୍ତାର ଈପ୍ସିତ ବସ୍ତୁ ‘ଧନ’ ଠାରେ ସମ୍ପ୍ରଦାନ ସଂଜ୍ଞା ହୋଇ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୋଇଛି ।
୩। (କ) ଗୁରୁ ଶିଷ୍ୟୟ । କୁଧତି ।
(ଖ) ଦୁଷ୍ଟ ଶିଷ୍ଟାୟ ଦ୍ରୁଶ୍ୟତି / ଈଷ୍ୟତି / ଅସୂୟତି ।
(ଗ) ପ୍ରଭୁ ଭୃତ୍ୟ ସଂକୁଧତି ।
(ଘ) ସାଧୁ କୁରମ୍ ଅଭିଦ୍ରୁଶ୍ୟତି ।
‘କୁଧଦ୍ମହେଶ୍ୟାସୂୟାର୍ଥୀନାଂ ପଂପ୍ରତି କୋପଃ ।’କ୍ରୋଧାର୍ଥକ (କୁଧ୍ ଓ କୁପ୍) ରାଗିବା ଅର୍ଥରେ, ଦ୍ରୋହାର୍ଥକ ହିଂସା ବା ଅପକାର ଅର୍ଥରେ, ଈର୍ଷାର୍ଥକ ସହି ନ ପାରିବା ଅର୍ଥରେ ଓ ଅସୂୟାର୍ଥକ ଗୁଣକୁ ଦୋଷଦୃଷ୍ଟିରେ ଦେଖୁବା ଅର୍ଥରେ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ଧାତୁମାନଙ୍କର ପ୍ରୟୋଗରେ ଯାହା ପ୍ରତି କ୍ରୋଧାଦି ପ୍ରକାଶ ପାଏ, ସେଠାରେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଉପରିସ୍ଥିତ ଉଦାହରଣରେ ଗୁରୁଙ୍କର ‘ଶିଷ୍ୟ’ଠାରେ କ୍ରୋଧ ଓ ଦୁଷ୍ଟର ‘ଶିଷ୍ଟ’ ଠାରେ ଦ୍ରୋହ, ଈର୍ଷା ଓ ଅସୂୟା ବ୍ୟକ୍ତ ହେଉଥିବାରୁ ‘ଶିଷ୍ୟ’ ଓ ‘ଶିଷ୍ଟ’ ପଦଠାରେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତ ହେଲା । କିନ୍ତୁ କ୍ରୁଧ୍ ଓ ହୃଦ୍ ଧାତୁ ଉପସର୍ଗଯୁକ୍ତ ହେଲେ ସମ୍ପ୍ରଦାନର କର୍ମସଂଜ୍ଞା ହୁଏ । ଯଥା:-
୪। (କ) ବସ୍ତ୍ରାୟ ସୂତ୍ରମ୍ । (ଲୁଗାପାଇଁ ସୂତା)
(ଖ) ହାରାୟ ସୁବର୍ଣ୍ଣମ୍ । (ହାରପାଇଁ ସୁନା)
(ଗ) ଧର୍ମାୟ ପତ୍ନୀ । (ଧର୍ମପାଇଁ ପତ୍ନୀ)
‘ତାଦର୍ଥ୍ଯ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବାଚ୍ୟ ।’ ଉପର ଉଦାହରଣ ଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ଯାହା ଉଦ୍ଦେଶ୍ୟରେ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତି ବା ବସ୍ତୁ ଉଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ ହୋଇଛି, ତା’ଠାରେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୋଇଛି । ‘ବସ୍ତ୍ର’ ଉଦ୍ଦେଶ୍ୟରେ ସୂତ୍ର ଉଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ ‘ବସ୍ତ୍ର’ଠାରେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ହେଲା । ସେହିପରି ‘ହାର’ ଉଦ୍ଦେଶ୍ୟରେ ସୁବର୍ଣ୍ଣ ଓ ‘ଧର୍ମ’ ଉଦ୍ଦେଶ୍ୟରେ ପତ୍ନୀ ଉଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ ଉଭୟ ‘ହାର’ ଓ ‘ଧର୍ମ’ ଠାରେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୋଇଛି । ଏହାକୁ ସାଧାରଣତଃ ‘ନିମିତ୍ତାର୍ଥେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ’ କୁହାଯାଏ ।
୫। (କ) ମଶକାୟ ଧୂମଃ । (ମଶାକୁ ଧୂଆଁ ।)
(ଖ) ତାପାୟ ସ୍ନାନମ୍ । (ଉତ୍ତାପକୁ ସ୍ବାନ ।)
(ଗ) ଆତପାୟ ଛତ୍ରମ୍ । (ଖରାକୁ ଛତା ।)
‘ନିବୃନୌ ନିବର୍ତ୍ତନୀୟାତ୍ ।’ ନିବୃତ୍ତି ବୁଝାଇଲେ । ଯାହାର ନିବୃତ୍ତି ଉଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ, ସେହିଠାରେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ଉପର ଉଦାହରଣରେ ‘ମଶକ’, ‘ତାପ’ ଓ ‘ଆତପ’ର ନିବୃତ୍ତି ଉଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ ସେହି ସେହି ଶବ୍ଦରେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୋଇଛି ।
୬। (କ) ରାମ ଶ୍ୟାମାୟ ଶତଂ ରୂଦ୍ୟକାଣି ଧାରୟତି । (ରାମ ଶ୍ୟାମଠାରୁ ଶହେ ଟଙ୍କା ଧାର କରିଛି ।)
(ଖ) ଭକ୍ତି ଜ୍ଞାନାୟ କଳ୍ପତେ । (ଭକ୍ତିରୁ ଜ୍ଞାନ ଜାତ ହୁଏ ।)
(ଗ) ବାତାୟ କପିଳା ବିଦ୍ୟୁତ୍ ।
(ପବନ ବହିବ ତେଣୁ ବିଜୁଳି କପିଳରଙ୍ଗ ଦେଖାଯାଉଛି ।)
‘ଧାରେରୁତ୍ତମତଃ ’‘ଧାରି’ ଧାତୁର ପ୍ରୟୋଗରେ ବା ଧାର୍ କରିବା ଅର୍ଥରେ ଯିଏ ଋଣଦାତା (ଉତ୍ତମଣ୍ଡ) ତା’ଠାରେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ପ୍ରଥମ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ରାମ ଶ୍ୟାମ ଠାରୁ ଶହେ ଟଙ୍କା ଧାର କରିଥିବାରୁ ‘ଶ୍ୟାମ’ ମହାଜନ ବା ରଣଦାତା । ତେଣୁ ‘ଶ୍ୟାମ’ ଠାରେ ୪ର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତ ହେଲା । ‘କ୍ଲ ପି ସମ୍ପଦ୍ୟମାନେ ଚ।’ ସେହିପରି କଳ୍ପତେ, ସମ୍ପଦ୍ୟତେ ଓ ପରିଣମତେ -ଏହି କ୍ରିୟାଗୁଡ଼ିକ ପରିଣତ ହେବା ଅର୍ଥକୁ ବୁଝାଇଲେ ଯାହା ପରିଣତ ହୁଏ ତାହାର ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ଏହାକୁ ସମ୍ପଦ୍ୟମାନେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ କୁହାଯାଏ । ଦ୍ବିତୀୟ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ଭକ୍ତିକୁ ‘ଜ୍ଞାନ’ ଜାତ ହେଉଥିବାରୁ ସେଠାରେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହେଲା ।
‘ଉତ୍ପାତେନ ଜ୍ଞାପିତେ ଚ ।’ କୌଣସି ଉତ୍ପାତ ଜ୍ଞାପିତ ହେଉଥିଲେ ସେହି ଉତ୍ପାତବାଚୀ ଶବ୍ଦରେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ଏଠାରେ କପିଳବର୍ଷର ବିଜୁଳି ‘ବାତ’ ବା ‘ବାତ୍ୟା’ ର ସୂଚନା ଦେଉଥିବାରୁ, ସେଠାରେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତ ହେଲା ।
୭। ବାଳକେଭିଂ ଆୟୁଷ୍ୟ / ମଦ୍ରୀ / ଭଦ୍ର/ କଲ୍ୟାଣଂ/ କୁଶଳଂ/ ସୁଙ୍ଖ|ସମୃଦ୍ଧି / ହିତଂ ଭବତୁ ।
‘ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ଚାଷିଷ୍ୟାୟୁଷ୍ୟମଦ୍ରଭଦ୍ରକୁଶଳସୁଖାର୍ଥହିତଃ । ’ ଆର୍ଶୀବାଦ, ଆୟୁଷ୍ୟ, କଲ୍ୟାଣ, ମଦ୍ର, ଭଦ୍ର, କଲ୍ୟାଣ, କୁଶଳ, ଆରୋଗ୍ୟ, ସୁଖାର୍ଥକ ଶବ୍ଦ, ହିତ ପ୍ରଭୃତି ପଦଯୋଗରେ ଯାହା ପ୍ରତି ଶୁଭକାମନା କରାଯାଏ, ସେଠାରେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୋଇଥାଏ । ବିକଳ୍ପରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ମଧ୍ୟ ହୁଏ । ଯଥା : ବାଳକାନାମ୍ ଆୟୁଷ୍ୟ…. ଭବତୁ ।
୮। (କ) ଅହଂ ତାଂ ତୃଣାୟ । ତୃଣଂ ମନ୍ୟ ।
(ମୁଁ ତୁମକୁ ଘାସ ଭାବୁଛି ।)
(ଖ) ଡଃ ମାଂ କାକଂ ମନ୍ୟତେ ।
(ନ କାକାୟ) (ସେ ମୋତେ କାଉ ମନେ କରୁଛି ।)
‘ମନ୍ୟକର୍ମଣ୍ୟନାଦରେ ବିଭାଷା ଅପ୍ରାଣିଷ୍ଣୁ ।’ ମନ୍ୟତେ କ୍ରିୟାର (ମନ୍ ଧାତୁ ଯୋଗେ) ଅନାଦର ବୋଧକ କର୍ମ ଅପ୍ରାଣୀବାଚକ ଶବ୍ଦ ହେଲେ ତା’ଠାରେ ଦ୍ୱିତୀୟା ଓ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୋଇଥାଏ । କିନ୍ତୁ ଅନାଦର ବୋଧକ କର୍ମ ପ୍ରାଣୀବାଚକ ହେଲେ କେବଳ ଦ୍ଵିତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତ ହୁଏ, ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ହୁଏ ନାହିଁ ।

୯। (କ) ପିତା ପୁତ୍ରାୟ କ୍ରୀଡ଼ନକଂ ପ୍ରତିଶୃଣୋତି ।
(ବାପା ପୁଅକୁ ଖେଳଣା ପ୍ରତିଶ୍ରୁତି ଦେଉଛନ୍ତି ।)
(ଖ) ରାଜା ବ୍ରାହ୍ମଣାୟ ଧନମ୍ ଆଶୃଣୋତି ।
(ରାଜା ବ୍ରାହ୍ମଣକୁ ଧନ ପ୍ରତିଶ୍ରୁତି ହେଉଛନ୍ତି ।)
‘ପ୍ରତ୍ୟାପ୍ରତ୍ୟା ଶୁନଃ ପୂର୍ବସ୍ୟ କର୍ତ୍ତା ।” ପ୍ରତି | ଆ ଉପସର୍ଗଯୁକ୍ତ ‘ଶୁ’ ଧାତୁ ଯୋଗରେ ଯାହାକୁ ପ୍ରତିଶ୍ରୁତି ଦିଆଯାଏ, ତାହାଠାରେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ଉପଯୁକ୍ତ ଉଦାହରଣ ଦ୍ଵୟରେ ପୁତ୍ରକୁ ପିତା ଓ ବ୍ରାହ୍ମଣଙ୍କୁ ରାଜା ପ୍ରତିଶ୍ରୁତି ଦେଇଥିବାରୁ ପୁତ୍ର ଓ ବ୍ରାହ୍ମଣ ଶବ୍ଦରେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୋଇଛି ।
୧୦ । (କ) ବାଳିକା ଜଳାୟ (ଜଳମ୍ ଆନେତୁମ୍) ନଦୀ ଗଚ୍ଛତି ।
(ଝିଅଟି ପାଣି ଅଣିବାକୁ ନଈକୁ ଯାଉଛି ।)
(ଖ) ଛାତ୍ରୀ (ପଠିତୁମ) ପଠନାୟ ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟଂ ଗଛତି ।
(ଛାତ୍ର ପଢ଼ିବାକୁ ସ୍କୁଲ ଯାଉଛି ।)
‘କ୍ରିୟାଥୋପଦଦସ୍ୟ ଚ କର୍ମଣି ସ୍ଥାନିନଃ ।’ ପ୍ରଥମ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ‘ତୁମୁନ୍’ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟାନ୍ତ ପଦ ଉହ୍ୟଥିବାରୁ କର୍ମ (ଜଳ) ଠାରେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତ ହେଲା । ‘ତୁମର୍ଥାଚ୍ଚ ଭାବବଚନାତ୍ ।’ ଦ୍ଵିତୀୟ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ‘ତୁମୁନ୍’ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତେ ଧାତୁଟି କ୍ରିୟାବାଚକ ବିଶେଷ୍ୟ (ପଠନ) ହୋଇ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହେଲା ।
୧୧। କୃଷକଃ ଗ୍ରାମିଂ/ଗ୍ରାମାୟ ଗଚ୍ଛତି ।
(ଚାଷି ଗାଁକୁ ଯାଉଛି ।)
ଭକ୍ତ ମନସା ବୈକୁଣ୍ଠ ଗଚ୍ଛତି । (ନ ବୈକୁଣ୍ଠାୟ)
(ଭକ୍ତ ମନେ ମନେ ବୈକୁଣ୍ଠ ଯାଉଛି ।)
ଡଃ ମାର୍ଗ ଗଚ୍ଛତି । (ନ ମାର୍ଗାୟ) ।
(ସେ ବାଟକୁ ଯାଉଛି ।)
‘ଗତ୍ୟର୍ଥକର୍ମଣି ଦ୍ଵିତୀୟା ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ଚେଷ୍ଟାୟାମନଧ୍ଵନି ।’ ଶରୀରଦ୍ଵାରା ଗମନ ବ୍ୟାପାର ବୁଝାଉଥିଲେ, ଗତ୍ୟର୍ଥକଧାତୁମାନଙ୍କର (ଯଥା- ଗମ୍, ଚଳ୍ ଓ ଯା ପ୍ରଭୃତି) କର୍ମସ୍ଥାନରେ ବିକଳ୍ପରେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଅଧ୍ଵବାଚକ (ମାର୍ଗ) ଶବ୍ଦ କର୍ମ ହୋଇଥିଲେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ନ ହୋଇ କେବଳ ଦ୍ଵିତୀୟା ହେବ । ପ୍ରଥମ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ଗତ୍ୟର୍ଥକ ‘ଗମ୍’ ଧାତୁ ଯୋଗେ କର୍ମ ‘ଗ୍ରାମ’ ଠାରେ ବିକଳ୍ପରେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ହୋଇ ‘ଗ୍ରାମାୟ’ ହେଲା । କିନ୍ତୁ ଦ୍ବିତୀୟ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ‘ଗମନ’ କ୍ରିୟାର ଶରୀର ଦ୍ଵାରା ଗମନ ବ୍ୟାପାର (ଚେଷ୍ଟା କିମ୍ବା ମାର୍ଗ ଅତିକ୍ରମ) ବୁଝାଉଥିବାରୁ କର୍ମର ବିକଳ୍ପରେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ହେଲାନାହିଁ । ପୁନଶ୍ଚ ତୃତୀୟବାକ୍ୟରେ ଅଧ୍ଵବାଚକ (ମାର୍ଗ) ଶବ୍ଦ କର୍ମ ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ନ ହୋଇ କେବଳ ଦ୍ଵିତୀୟା ହେଲା ।
୧୨। (କ) ଶିକ୍ଷକାୟ ନମଃ । (ଶିକ୍ଷକଙ୍କୁ ପ୍ରଣାମ ।)
(ଖ) ପ୍ରଜାତଃ ସ୍ବସ୍ତି ଭବତୁ । (ପ୍ରଜାମାନଙ୍କ ମଙ୍ଗଳ ହେଉ ।)
(ଗ) ଅଗ୍ନେୟେ ସ୍ୱାହା । (ଅଗ୍ନିଦେବତାଙ୍କୁ ଅର୍ପଣ କରାଗଲା ।)
(ଘ) ପିତୃଭ୍ୟ ସ୍ଵଧା । (ପିତୃପୁରୁଷଙ୍କୁ ଅର୍ପଣ କରାଗଲା ।)
(ଙ) ଭୀମଃ ଦୁଃଶାସନାୟ ଅଳମ୍ । (ଭୀମ ଦୁଃଶାସନକୁ ସମର୍ଥ ।)
(ଚ) ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରାୟ – ପୁଷ୍ପାଣି ବଷଟ୍ । (ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରଙ୍କୁ ଫୁଲ ଅର୍ପଣ କରାଗଲା ।)
‘ନମଃ-ସ୍ୱସ୍ତି-ସ୍ବାହା-ସ୍ଵଧାଳଂ ବଷଟ୍ ଯୋଗାଇ ।’ ନମଃ (ନମସ୍କାର), ସ୍ଵସ୍ତି (ମଙ୍ଗଳ), ସ୍ଵାହା (ଦେବତାଙ୍କ ଉଦ୍ଦେଶ୍ୟରେ), ସ୍ଵଧା (ପିତୃପୁରୁଷଙ୍କ ଉଦ୍ଦେଶ୍ୟରେ ସମର୍ପଣ), ଅଳମ୍ (ସମର୍ଥବାଚକ), ବଷଟ୍ (ସମର୍ପଣବାଚକ) – ଏହି ଶବ୍ଦମାନଙ୍କ ଯୋଗରେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତ ହୋଇଥାଏ । କିନ୍ତୁ ‘ନମଃ’ କ୍ରିୟାଯୁକ୍ତ ହେଲେ, ନମଃ ଶବ୍ଦ ଯୋଗେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ନ ହୋଇ ଦ୍ବିତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତ ହୁଏ । କାରଣ ଉପପଦ ଯୋଗୁ ଯେଉଁ ବିଭକ୍ତ ହୁଏ, ତା’ଠାରୁ କ୍ରିୟାଯୋଗେ ହେଉଥିବା ବିଭକ୍ତିର ଗୁରୁତ୍ଵ ବେଶି । ଯଥା –
(ଛ) ଶିକ୍ଷକଂ ନମସ୍କରୁ । (ନମଃ + କୁରୁ = ନମସ୍ତୁରୁ ଏହା କ୍ରିୟାପଦ)
(ଜ) ଭକ୍ତ ଈଶ୍ଵରଂ ନମସ୍କରୋତି । (ନମଃ + କରୋତି = ନମସ୍କରୋତି ଏହା କ୍ରିୟାପଦ)
‘ଉପପଦବିଭକ୍ତେ କାରକବିଭର୍ତ୍ତି ବଳୀୟସୀ ।’ ଉପର୍ୟ୍ୟକ୍ତ ବାକ୍ୟଦ୍ୱୟରେ ‘କର୍ମଣି ଦ୍ୱିତୀୟା’ ସୂତ୍ରରେ ‘ଶିକ୍ଷକ’ ଓ ‘ଈଶ୍ବର’ ଶବ୍ଦରେ ଦ୍ଵିତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତ ହେଲା । କାରଣ ଉପପଦ ବିଭକ୍ତିଠାରୁ କାରକବିଭକ୍ତିର ବଳ ବେଶି । ନମଃ – ଉପପଦ ମାତ୍ର ନମସ୍କୁରୁ, ନମସ୍କରୋତି କ୍ରିୟାପଦ ।
ମନେରଖ :
- କର୍ତ୍ତା ଯେଉଁ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିକୁ ଦେବାକୁ ଇଛାକରେ ଅଥବା କ୍ରିୟାଦ୍ବାରା ଯାହାର ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ଇଚ୍ଛାକରେ (ଯାହାର ପ୍ରୀତି ସମ୍ପାଦନ କରେ) ସେ ସମ୍ପ୍ରଦାନ କାରକ ହୁଏ ।
- କଚ୍ଛତେ, ସମ୍ପାଦ୍ୟତେ, ଜାୟତେ ଓ ଭବତି- ଏହି କ୍ରିୟାଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଯୋଗରେ ଯାହା ‘ଜାତ’ ହୁଏ, ତା’ର ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ ।
- ଯାହାକୁ ରୁଚେ, ତା’ଠାରେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ।
- ନମଃ, ସ୍ଵସ୍ଥି, ସ୍ୱାହା, ସ୍ଵଧା, ଅଳମ୍ (ସାମର୍ଥ୍ୟର୍ଥକ), ବଷଟ୍ ଯୋଗେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ।
- କୁଧ, ଦୁହ, ଈର୍ଷ ଓ ଅସୂୟ ପ୍ରଭୃତି ଧାତୁ ଯୋଗେ ଯାହାଠାରେ କ୍ରୋଧ, ଦ୍ରୋହ ତା’ଠାରେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ।
- ‘ତୁମୁନ୍’ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ ଲୋପ କଲେ, ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ ।
ଗୀତ :
ସଂପ୍ରଦାନେ ହୁଏ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ
ରୁଟ୍ ଧାତୁ ଯୋଗରେ
ଗୃହ, କୁଧ, ଦୃଶ୍ୟ ଅର୍ଥକ
ଧାତୁ ସେହି ପ୍ରକାରେ । ୧।
ଧାରି ଧାତୁ ଯୋଗେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ
ପ୍ରତ୍ୟାପୂର୍ବକ ଶ୍ରୁର
ତାଦ୍ୟାର୍ଥ ନିବୃତ୍ତି ଅର୍ଥରେ
ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବ୍ୟବହାର । ୨ ।
ନମଃ, ସ୍ଵସ୍ଥି, ସ୍ୱାହା, ବଷଟ୍
ଅଳଂ ସୁଧା ସଂଯୋଗେ
ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ କଳ୍ପତେ ଯୋଗରେ
ମନୋ ବିକଳେ ଲାଗେ । ୩ ।
ଡୁମୁନ୍ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟାୟନ୍ତ ପଦର
କ୍ରିୟା ବାଚକ ହେଲେ
ବିଶେଷ୍ୟ ହୁଅଇ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ
ପାଣିନି କହିଥିଲେ । ୪ ।

ଅଭ୍ୟାସଃ :
୧। ବନ୍ଧନୀମଧ୍ଯସ୍ଥ ଶବ୍ଦାନାଂ ଯଥାର୍ଥବିଭଣ୍ଡିଂ କୃତ୍ୱା ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନଂ ପୂରୟତ ।
ଯଥା – ଅହଂ ତୁଭ୍ୟମ ଦିବ୍ୟଚକ୍ଷୁଃ ଦଦାମି । (ଯୁଷ୍ପଦ୍)
(କ) _____________________________ ପୁରସ୍କାରଂ ଦଦାତି । (ଛାତ୍ର)
Answer:
ଛାତ୍ରାୟ
(ଖ) _____________________________ ଔଷଧ୍ୱଂ ନ ରୋଚତେ । (ଶିଶୁ)
Answer:
ଶିଶବେ
(ଗ) ଭୃତ୍ୟ __________________________ ତୃଣାନି ଆନୟତି । (ଅଶ୍ଵ)
Answer:
ଅଶ୍ରାୟ
(ଘ) ପିତା ___________________________ କ୍ରୀଡ଼ନକଂ ପ୍ରତିଶୃଣୋତି । (ପୁତ୍ର)
Answer:
ପୁତ୍ରାୟ
(ଙ) ସର୍ବେ _____________________ ଗୃହୟନ୍ତି । (ଧନ)
Answer:
ଧନାୟ
(ଚ) ରାଜା ______________________ କୁଧତି । (ଶତ୍ରୁ)
Answer:
ଶତ୍ରବେ
(ଛ) ଦ୍ବୟୋବିବାଦଃ ତୃତୀୟସ୍ୟ ________________________ ଭବତି । (ଲାଭ)
Answer:
ଲାଭାୟ
୨। ବନ୍ଧନୀସ୍ଥିତଯଥାର୍ଥପଦେନ ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନଂ ପୂରୟତ ।
ଯଥା – ପରଧନାୟ ମା ଗୃହୟ । (ପରଧନେନ, ପରଧନାୟ, ପରଧନାତ୍)
(କ) _________________________ ଫଳାନି ସ୍ୱଦନ୍ତେ । (ବାନରାୟ, ବାନରେଣ, ବାନରମ୍ )
Answer:
ବାନରାୟ
(ଖ) ଅହଂ ___________________________ ନ ଧାରୟାମି । (କେନ, କସ୍ମାତ୍, କମ୍ପ୍ଲେ)
Answer:
କହ୍ନେ
(ଗ) ମାର୍ଜାରାଃ _____________________ ସ୍ପୃହୟନ୍ତି । (ମତ୍ସ୍ୟମ୍, ମତ୍ସ୍ୟନ, ମଧ୍ୟାୟ)
Answer:
ମତ୍ସ୍ୟୟ
(ଘ) ପିତା _____________________ ଦଦାତି । (ପୁତ୍ରେଣ, ପୁତ୍ରମ, ପୁତ୍ରାୟ)
Answer:
ପୁତ୍ରାୟ
(ଡ) ଭକ୍ତଃ _________________________ ନମସ୍କରୋତି । (ଈଶ୍ବରାୟ, ଈଶ୍ୱରମ୍, ଈଶ୍ବରେଣ)
Answer:
ଈଶ୍ବରଂ
(ଚ) ___________________________ ପୁଷ୍ପାଣି ବଷଟ୍ । (ଗଣେଶାୟ, ଗଣେଶାୟ, ଗଣେଶନ)
Answer:
ଗଣେଶାୟ
(ଛ) ସୈନିକାଃ _______________________ ଅଗଚ୍ଛନ୍ । (ଯୁଦ୍ଧମ୍, ଯୁଦ୍ଧନ, ଯୁଦ୍ଧାୟ)
Answer:
ଯୁଦ୍ଧାୟ

୩। ରେଖାଙ୍କିତପଦାନାଂ ସକାରଣବିଭଣ୍ଡିଂ ଦର୍ଶୟତ ।
ଯଥା – ବାଳିକା ପୁଶେଭ୍ୟ ଗୃହଯନ୍ତି । ‘ଗୃହ’ ଧାତୁ ଯୋଗେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ।
(କ) ଜ୍ଞାନାୟ ବିଦ୍ୟାମ୍ ଅଧୀତେ ।
Answer:
ନିମିଭାର୍ଥେ ୪ର୍ଥୀ
(ଖ) ଶିଶବେ ଦୁଗ୍ଧ ରୋଚତେ ।
Answer:
ରୋଚତେ କ୍ରିୟାଯୋଗେ ୪ର୍ଥୀ
(ଗ) ଶବରୀ ଫଳାୟ ଯାତି ।
Answer:
ପୁଂଲୋପେ କର୍ମଣି ୪ର୍ଥୀ
(ଘ) ଛାତ୍ରେଭିଂ ସ୍ବସ୍ତି ଭବତୁ ।
Answer:
ସ୍ବସ୍ତିପଦ ଯୋଗେ ୪ର୍ଥୀ
(ଙ) ଶିଷ୍ୟା ଗୁରୁନ୍ ନମସ୍ଫୁର୍ବନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଉପପଦବିଭନ୍ତଃ କାରକ ବିଭକ୍ତି ବଳୀୟସୀ
(ଚ) ରମେଶଃ ପାଠ୍ଯୟ ଗଚ୍ଛତି ।
Answer:
ତୁମର୍ଥେ ୪ର୍ଥୀ
(ଛ) ଅହଂ ତୁଭ୍ୟ ନ ଈଶ୍ୟାମି ।
Answer:
ଈଷ୍ୟଧାତୁ ଯୋଗେ ୪ର୍ଥୀ
୪। ବନ୍ଧନୀମଧ୍ଯସ୍ଥଧାତୁନାଂ କ୍ରିୟାବାଚକବିଶେଷ୍ୟପଦେନ ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନଂ ପୂରୟତ ।
ଯଥା – ବାଳକଃ ପଠନାୟ ଯାତି । (ପଠ୍)
(କ) ବୃଦ୍ଧା _________________ ମନ୍ଦିରଂ ଗଛନ୍ତି । (ଭଜ୍)
Answer:
ଭଜନାୟ
(ଖ) ପ୍ରିୟ __________________________ ଗଚ୍ଛନ୍ତି । (ସ୍ନା)
Answer:
ସ୍ନାନାୟ
(ଗ) ପାଚକ _________________ ଚେଷ୍ଟତେ । (ପଚ୍)
Answer:
ପାଚନାୟ
(ଘ) କ୍ଷୁଧାର୍ୟ୍ଯ ________________ ଯାତି । (ଭୁଜ୍)
Answer:
ଭୋଜନାୟ
(ଙ) ______________________ ଧନମ୍ ଅର୍ଜୟ । (ଦା)
Answer:
ଦାନାୟ
(ଚ) ଚୌରଃ କାରାଗାରାତ୍ ______________________ ଇଚ୍ଛତି । (ଗମ୍)
Answer:
ଗମନାୟ
(ଛ) ଭକ୍ତ ମନ୍ଦିରସ୍ୟ _____________________ ବ୍ୟଗ୍ର ଭବତି । (ଦୃଶ୍ୟ)
Answer:
ଦର୍ଶନାୟ

୫। ନିମ୍ନଲିଖତପଦାନି ବ୍ୟବହୃତ୍ୟ ପୃଥକ୍ ବାକ୍ୟାନି ରଚୟତ ।
ଯଥା – ବଷଟ୍ : ଇନ୍ଦ୍ରାୟ ପୁଷ୍ପାଣି ବଷଟ୍ ।
ଦଦତି – ତେ ମହଂ ଖାଦ୍ୟ ଦଦତି ।
ଅସୂୟତି – ସା ମହ୍ୟମ୍ ଅସୂୟତି ।
ସ୍ୱସ୍ଥି – ପ୍ରଜାଭ୍ୟ ସ୍ୱସ୍ଥି ଭବନ୍ତୁ ।
ସ୍ୱାହା – ଅଗ୍ନେୟେ ସ୍ୱାହା ।
ଆଶୃଣୋତି – ପିତା ପୁତ୍ରାୟ ଆଶୃଣୋତି ।
ମନ୍ୟତେ – ସଂ ମାଂ କାକଂ ମନ୍ୟତେ ।
ରୋଚତେ – ତୁଭ୍ୟ କିଂ ରୋଚତେ ।
ନମସ୍କର୍ଯ୍ୟାତ୍ – ଭକ୍ତ ହରିଂ ନମସ୍କର୍ଯାତ୍ ।
ଅଳମ୍ – ମଲ୍ଟି ମଲ୍ଟିୟ ଅଳମ୍ ।
ସ୍ଵଧୀ – ପିତୃଭ୍ୟ ସ୍ଵଧୀ ।
ସମ୍ପଦ୍ୟତେ – ଭକ୍ତି ଜ୍ଞାନାୟ ସମ୍ପଦ୍ୟତେ ।
ହିତମ୍ – ତୁଭ୍ୟ/ତବ ହିତଂ ଭବତୁ
୬। ଅଧସ୍ତନବାକ୍ୟାନି ସଂଶୋଧୟତ ।
ଅହଂ ଶିକ୍ଷକାୟ ନମସ୍କରୋମି । ଅହଂ ଶିକ୍ଷକଂ ନମସ୍କରୋମି ।
(କ) ଙ ମାଂ କାକାୟ ମନ୍ୟସେ ।
Answer:
ବଂ ମାଂ କାକମ୍ ମନ୍ୟସେ ।
(ଖ) ଶିକ୍ଷକ ଛାତ୍ର ଆଶୃଣୋତି ପୁସ୍ତକମ୍ ।
Answer:
ଶିକ୍ଷକ ଛାତ୍ରାୟ ଆଶୃଣୋତି ପୁସ୍ତକମ୍ ।
(ଗ) ହାରସ୍ୟ ସ୍ଵଣ୍ଟିଂ ପ୍ରଦେୟମ୍ ।
Answer:
ହାରାୟ ସ୍ଵୟଂ ପ୍ରଦେୟମ୍ ।
(ଘ) ମାତରଂ ଦୁର୍ଗା ନମଃ ।
Answer:
ମାତ୍ରେ ଦୁର୍ଗାୟୈ ନମଃ
(ଙ) ସ୍ଵାମୀ ଭୃତ୍ୟାୟ ଅଭିକୁଧତି ।
Answer:
ସ୍ଵାମୀ ଭୃତ୍ୟମ୍ ଅଭିକୁଧତି ।
(ଚ) ପ୍ରଜାନାଂ ସ୍ବସ୍ତି ଭବତି ।
Answer:
ପ୍ରଜାଭ୍ୟ ସ୍ୱସ୍ତି ଭବତ ।
(ଛ) ରାମଃ ଶ୍ୟାମାତ୍ ଶତଂ ରୂପ୍ୟକାଣି ଧାରୟତି ।
Answer:
ରାମଃ ଶ୍ୟାମାୟ ଶତଂ ରୂପ୍ୟକାଣି ଧାରୟତି ।
୭। ଅଲିଖୂତେଷୁ ବାକ୍ୟଷୁ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀନ୍ତପଦାନି ରେଖାଙ୍କିତାନି କୁରୁତ ।
ଯଥା – ଦୁର୍ଜନଃ ସଜନେଭ୍ୟ ଦ୍ରୁଶ୍ୟନ୍ତ । (ଦୁଷ୍ଟଲୋକ ସାଧୁଲୋକଙ୍କ ଦ୍ରୋହ କରନ୍ତି ।)
(କ) ବଂ ମାଂ କାକାୟ ମନ୍ୟସେ । (ଶିବଙ୍କୁ ପ୍ରଣାମ ।)
Answer:
କାକାୟ
(ଖ) ଗୁରବେ ନମଃ । (ଗୁରୁଙ୍କୁ ପ୍ରଣାମ ।)
Answer:
ଗୁରବେ
(ଗ) ବାଳିକା ପୁଷ୍ପାୟ ଗୃହମ୍ମତି । (ଝିଅଟି ଫୁଲକୁ ଭଲପାଏ ।)
Answer:
ପୁଷ୍ପାୟ
(ଘ) କଃ ଧନଂ ସ୍ଵେଚ୍ଛାୟା କହ୍ନେ ଦଦାତି । (କିଏ ପଇସା ନିଜ ଇଚ୍ଛାରେ ଦାନ କରେ ।)
Answer:
କହ୍ନେ
(ଙ) ସର୍ବେଭ୍ୟ ପ୍ରାଣିଭିଂ ସ୍ବସ୍ତି ଭବତୁ । (ସବୁ ପ୍ରାଣୀଙ୍କର ମଙ୍ଗଳ ହେଉ ।)
Answer:
ପ୍ରାଣିଭ୍ୟ
(ଚ) ଶକ୍ତି ପରେରାଂ ପରିପୀଡ଼ନାୟ । (ଶତ୍ରୁର ଶକ୍ତି ଶତ୍ରୁକୁ କଷ୍ଟଦେବାପାଇଁ ।)
Answer:
ପୀଡ଼ନାୟ
(ଛ) ପରୋପକାରଃ ପୁଣ୍ୟାୟ ପାପାୟ ପରପୀଡ଼ନମ୍ । (ପରୋପକାର ପୁଣ୍ୟପାଇଁ ପରକୁ କଷ୍ଟଦେବା ପାପ ପାଇଁ ।)
Answer:
ପୁଣ୍ୟାୟ

୮। ଯଥାନିର୍ଦେଶଂ ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନଂ ପୂରୟତ ।
ଯଥା : ଭୀମଃ ଯୁଦ୍ଧାୟ ଅଳମ୍ । (ଯୁଦ୍ଧ)
(କ) ଗୋବିନ୍ଦ __________________ ଅଳମ୍ । (ତର୍କ)
Answer:
ତର୍କୀୟ
(ଖ) ପାଚକଃ _______________________ ଅଳମ୍ । (ପାକ/ପାଚନ)
Answer:
ପାକାୟ / ପାଚନାୟ
(ଗ) ଶିଷ୍ଯ __________________________ ଅଳମ୍ । (ବେଦପଠନ)
Answer:
ବେଦପଠନାୟ
(ଘ) ଦୁଗ୍ଧଂ _______________________ ଅଳମ୍ । (ଶିଶୁ)
Answer:
ଶିଶବେ
(ଙ) ରାମଃ ______________________ ଅଳମ୍ । (ରାବଣ)
Answer:
ରାବଣାୟ
(ଚ) ଏତତ୍ ବେତନଂ _______________________ ଅଳମ୍ । (ଭୃତ୍ୟ )
Answer:
ଭୃତ୍ଯାୟ
୯। ସଂସ୍କୃତେନ ଅନୁବାଦଃ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ।
(କ) ମୁଁ ପୁଅକୁ ବହିଟିଏ ଦେବି ।
ଅନୁ : ଅହଂ ପୁତ୍ରାୟ ପୁସ୍ତକଂ ଦାସ୍ୟାମି ।
(ଖ) ବଗଗୁ ମାଛ ଭଲ ଲାଗେ ।
ଅନୁ : ବକାୟ ମୀନଃ ରୋଚତେ ।
(ଗ) ଶିକ୍ଷକ ଛାତ୍ରକୁ ପୁସ୍ତକ ପ୍ରତିଶ୍ରୁତି ଦେଉଛନ୍ତି ।
ଅନୁ : ଶିକ୍ଷକ ଛାତ୍ରାୟ ପୁସ୍ତଙ୍କ ପ୍ରତିଶୃଣୋତି
(ଘ) ରୋଗୀକୁ ଔଷଧ ରୁଚେ ନାହିଁ ।
ଅନୁ : ରୋଗିଣେ ଔଷଧ୍ୱଂ ନ ରୋଚତେ ।
(ଙ) ଭଲପିଲାମାନେ ଜ୍ଞାନପାଇଁ ପଢ଼ନ୍ତି ।
ଅନୁ : ଉତ୍ତମଃ ଛାତ୍ରା ଜ୍ଞାନୀୟ ପଠନ୍ତି ।
(ଚ) ମୂର୍ଖମାନେ ପଣ୍ଡିତଙ୍କୁ ଈର୍ଷା କରନ୍ତି ।
ଅନୁ : ମୁର୍ଖ ପଣ୍ଡିତେଭ୍ୟ ଈର୍ଷାନ୍ତି ।
(ଛ) ଖରାପାଇଁ ଛତା ନିଅ ।
ଅନୁ : ଆତପାୟ ଛତ୍ର ନୟ ।
(ଜ) ସୈନିକମାନେ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ କରିବାକୁ ଗଲେ ।
ଅନୁ : ସୈନିକା ଯୁଦ୍ଧାମ୍ଭ ପ୍ରସ୍ଥିତଃ ।
(ଝ) ସେମାନେ ଆମକୁ ଘାସଭଳି ମନେ କରନ୍ତି ।
ଅନୁ : ତେ ଅସ୍ମାନ୍ ତୃତଂ।ତୃଣାୟ ମନ୍ୟନ୍ତେ ।
(ଞ) ତୁମର ମଙ୍ଗଳ ହେଉ ।
ଅନୁ : ତୁଭ୍ୟ ମଙ୍ଗଳମସ୍ତୁ ।
ଅପାଦାନକାରକ ଓ ପଞ୍ଚମା ବିଭକ୍ତି
୧। (କ) ବୃକ୍ଷାତ୍ ଫଳଂ ପତତି । (ଗଛରୁ ଫଳ ପଡ଼ୁଛି ।)
(ଖ) ପ୍ରାସାଦାତ୍ ବାଳକଃ ଅପତତ୍ । (କୋଠାଉପରୁ ପିଲାଟି ପଡ଼ିଗଲା ।)
(ଗ) ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟାତ୍ର ଛାତ୍ରା ଆଗଛନ୍ତି । (ସ୍କୁଲରୁ ଛାତ୍ରମାନେ ଆସୁଛନ୍ତି ।)
‘ଧ୍ରୁବମପାୟେଽପାଦାନମ୍ ।” ଉପରିଲିଖ ଉଦାହରଣ ଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ବୃକ୍ଷରୁ ଫଳ, ପ୍ରାସାଦରୁ ବାଳକ ଓ ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟରୁ ଛାତ୍ରମାନଙ୍କର ବିଚ୍ଛେଦ ଘଟୁଛି । ଯାହାଠାରୁ ବସ୍ତୁ ବା ବାକ୍ତିର ବିଚ୍ଛେଦ ହୁଏ, ତାହା ‘ଅପାଦାନ କାରକ’ ଅଟେ । ‘ବିଶ୍ଳେଷାବଧୌ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ।’ଏଠାରେ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ଏହାକୁ ‘ଅପାଦାନେ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ’ କୁହାଯାଏ । ବୃକ୍ଷାତ୍, ପ୍ରାସାଦାତ୍ ଓ ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟାତ୍ ପଦଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଅପାଦାନ କାରକ ଓ ସେଗୁଡ଼ିକ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତାନ୍ତ ହୋଇଛନ୍ତି ।

୨। (କ) ମୃଗ ବ୍ୟାଘ୍ରାତ ବିଭେତି । (ହରିଣ ବାଘକୁ ଡ଼ରୁଛି ।)
(ଖ) ଛତ୍ରମ୍ ଆତପାତ୍ର ତ୍ରାୟତେ|ରକ୍ଷତି । (ଛତା ଖରାରୁ ରକ୍ଷାକରେ ।)
‘ଭୀତ୍ରାର୍ଥୀନାଂ ଭୟହେତୁଃ ।’ ‘ଭୀ’ ଧାତୁ ଭୟକରିବା ଓ ‘ତ୍ରୈ’ ଧାତୁ ରକ୍ଷାକରିବା ଅର୍ଥରେ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହୁଅନ୍ତି । ଏହି ଅର୍ଥକୁ ବୁଝାଉଥବା ଧାତୁର ପ୍ରୟୋଗରେ ଭୟର କାରଣଠାରେ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ଏଠାରେ ଭୟର କାରଣ ‘ବ୍ୟାଘ୍ର’ ଓ ‘ଆତପ’ ଶବ୍ଦରେ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହେଲା ।
୩। (କ) ଧାର୍ମିକଃ ପାପାତ୍ର ପରାଜୟତେ । (ଧାର୍ମିକ ପାପକୁ ସହିପାରେ ନାହିଁ ।)
(ଖ) ଅଧ୍ୟୟନାତ୍ର ପରାଜୟତେ ଜାତିଃ । ଜାତିଃ (ଠକ, ମୂର୍ଖ) ଠକ ପାଠପଢ଼ାକୁ ସହିପାରେ ନାହିଁ ।)
‘ପରାଜେରସୋରଃ ।’ ପରା + ଜି (ପରାଜୟତେ) ଅନୁଯୋଗରେ ଯାହାକୁ ସହିହୁଏ ନାହିଁ, ତାହା ଅପାଦାନ ସଂଜ୍ଞକ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ସୁତରାଂ ‘ପାପାତ୍’ ଓ ‘ଅଧ୍ୟୟନାତ୍’ ଠାରେ ଅପାଦାନ ସଂଜ୍ଞା ହୋଇ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତ ହେଲା । କିନ୍ତୁ ‘ପରାଜୟତେ’ ହରାଇବା ଅର୍ଥରେ ପ୍ରଯୁକ୍ତ ହେଲେ ଯିଏ ପରାଜିତ ହୁଏ, ସେଠାରେ କର୍ମ ସଂଜ୍ଞା ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଯଥା – ମଗଧ୍ୟ ପରାଜୟତେ କଳିଙ୍ଗଃ ।
୪। (କ) ଧାନ୍ୟଭ୍ୟ ମାଂ ବାରୟ । (ଧାନରୁ ଗାଈମାନଙ୍କୁ ବାରଣ କର ।)
(ଖ) ପିତା ପୁତ୍ର ଚଳଚ୍ଚିତ୍ରଦର୍ଶନାତ୍ ବାରୟତି । (ପିତା ପୁତ୍ରକୁ ସିନେମାଦେଖାରୁ ବାରଣ କରୁଛି ।)
‘ବାରଣାର୍ଥନାମୀପ୍ସିତଃ ।’ ବାରଣାର୍ଥକ ଧାତୁ ଯୋଗରେ ନିବାର୍ଯ୍ୟମାଣର ଅଭିଳଷିତ ଅପାଦାନକାରକ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଉପର୍ୟ୍ୟକ୍ତ ଉଦାହରଣ ଦ୍ଵୟରେ ‘ଧାନ୍ୟ’ ଓ ଚଳଚ୍ଚିତ୍ର ଦର୍ଶନରୁ ଯଥାକ୍ରମେ ଗାଈ ଓ ପୁତ୍ରକୁ ବାରଣ କରାଯାଉଥିବାରୁ ବାରଣର ଈପ୍ସିତ ‘ଧାନ୍ୟ’ ଓ ‘ଚଳଚ୍ଚିତ୍ର ଦର୍ଶନ’ ଠାରେ ଅପାଦାନ ସଂଜ୍ଞା ହୋଇ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତ ହେଲା ।
୫। (କ) ଚୌରଃ ରକ୍ଷିତଃ ନିଲୀୟତେ । (ଚୋର ପୋଲିସକୁ ଲୁଚୁଛି ।)
(ଖ) କୃଷ୍ଣ ମାତୁଃ ନିଲୀୟତେ । (କୃଷ୍ଣ ମାଆଙ୍କୁ ଲୁଚୁଛନ୍ତି ।)
‘ଅନ୍ତର୍ଥେ ଯେନାଦର୍ଶନମିକୃତି ।’ ନି+ ଲୀ (ନିଲୀୟତେ) ଅର୍ଥାତ୍ ଲୁଚିବା । କୌଣସି ବ୍ୟବଧାନରେ ରହି ଯାହାଠାରୁ ନିଜକୁ ଲୁଚାଇ ରଖିବାକୁ ଇଚ୍ଛାକରେ, ସେ ଅପାଦାନକାରକ ହୁଏ । ଚୋର ପୋଲିସ୍ରୁ ଓ କୃଷ୍ଣ ମା’ଙ୍କଠାରୁ ନିଜକୁ ଲୁଚାଇ ରଖୁଛନ୍ତି, ତେଣୁ ରକ୍ଷୀ ଓ ମାତାଠାରେ ଅପାଦାନ ସଂଜ୍ଞା ହେଲା ।
୬। (କ) କାମାତ୍ର କ୍ରୋଧଃ ଅଭିଜାୟତେ । (କାମନାରୁ କ୍ରୋଧ ଜାତ ହୁଏ ।)
(ଖ) ନବନୀତାତ୍ର ଘୃତମ୍ ଉତ୍ପଦ୍ୟତେ । (ଲହୁଣୀରୁ ଘିଅ ଉତ୍ପନ୍ନ ହୁଏ ।)
(ଗ) ଅମରକଣ୍ଟକାତୁ ମହାନଦୀ ପ୍ରଭବତି । ଅମର କଣ୍ଟକରୁ ମହାନଦୀ ପ୍ରବାହିତ ହେଉଛି ।
‘ଜନିକର୍ତ୍ତା ପ୍ରକୃତିଃ ।’ ଜାତ ବା ଉତ୍ପତ୍ତି ହେବା ଅର୍ଥରେ ଜନ୍ମର ମୂଳକାରଣଠାରେ ଏବଂ ‘ଭୁନଃ ପ୍ରବୟଃ’ ପ୍ର + ଭୂ ଧାତୁ ପ୍ରୟୋଗରେ ବୁଝାଉଥବା ପ୍ରଥମ ଆବିର୍ଭାବସ୍ଥଳରେ ଅପାଦାନସଂଜ୍ଞା ହୁଏ । କାମନାରୁ କ୍ରୋଧର ଜନ୍ମ ଓ ନବନୀତରୁ ଘୃତର ଉତ୍ପତ୍ତି ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ ‘କାମ’ ଓ ନବନୀତ, ଯଥାକ୍ରମେ କ୍ରୋଧ ଓ ଘୃତ ଉତ୍ପତ୍ତି ମୂଳକାରଣ ଅଟେ ଏବଂ
ହୋଇଛି ।
୭ । (କ) ସାଧଃ ପାପାତ୍ର ଜୁଗୁପ୍ତେ । (ସାଧୁ ଲୋକ ପାପକୁ ଘୃଣାକରେ ।)
(ଖ) ଛାତ୍ରୀ ପଠନାତ୍ର ବିରମତି । (ଛାତ୍ର ପଠନରୁ ନିବୃତ ହେଉଛି ।)
(ଗ) ଧର୍ମାତ୍ର ନ ପ୍ରମଦିତବ୍ୟମ୍ । (ଧର୍ମପ୍ରତି ଅମନଯୋଗୀ ହେବା ଅନୁଚିତ ।)
(ଘ) ଛାତ୍ରୀ ଅଧ୍ୟୟନାତ ପ୍ରମାଦ୍ୟତି । (ଛାତ୍ର ଅଧ୍ୟୟନରୁ ବିମୁଖ ହେଉଛି ।)
‘ଜୁଗୁପ୍ବିରାମ ପ୍ରମାଦାର୍ଥନାମୁପସଂଖ୍ୟାନମ୍ ।’ ଜୁଗୁପ୍ସା (ଘୃଣା), ବିରାମ (ନିବୃଦ୍ଧି) ଓ ପ୍ରମାଦ (ଅନବଧାନତା) ବୋଧକ ଧାତୁ ଯୋଗରେ କର୍ମକାରକ ସ୍ଥାନରେ ଅପାଦାନକାରକ ହୁଏ ।
୮। (କ) ହିମାଳୟ ବିନ୍ଧ୍ୟାତ୍ମ ଉଚ୍ଚତରଃ । ହିମାଳୟ ବିନ୍ଧ୍ୟଠାରୁ ଉଚ୍ଚତର ।
(ଖ) ଜ୍ଞାନଂ ଧନାତ୍ର ବିଶିଷ୍ୟତେ । ଧନଠାରୁ ଜ୍ଞାନ ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ ।
(ଗ) ଖଳ ସର୍ପାତ୍ର କ୍ରୁରତରଃ । ଦୁଷ୍ଟଲୋକ ସାପଠାରୁ ଭୟଙ୍କର ।
‘ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତେ ।’ ଦୁଇଟି ମଧ୍ୟରୁ ଗୋଟିକର ଉତ୍କର୍ଷ ବା ଅପକର୍ଷ ବୁଝାଇଲେ ନିକୃଷ୍ଟଠାରେ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ଏହାକୁ ‘ଅପେକ୍ଷାର୍ଥେ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ’ ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ । ଏଠାରେ ହିମାଳୟ ଓ ବିନ୍ଧ୍ୟ ମଧ୍ୟରୁ ‘ବିନ୍ଧ୍ୟ’ ଉଚ୍ଚତାରେ ହିମାଳୟଠାରୁ ନିକୃଷ୍ଟ, ସେହିପରି ବୈଶିଷ୍ଟ୍ୟ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ଧନ ଓ ଦୂରତାରେ ସର୍ପ ନିକୃଷ୍ଟ ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ, ସେଗୁଡ଼ିକଠାରେ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହେଲା । କେହି କେହି ଏହାକୁ ‘ତୁଲ୍ୟାର୍ଥେ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ’ ବୋଲି ମଧ୍ୟ କହନ୍ତି । ଏଠାରେ ବିନ୍ଧ୍ୟ ଅପେକ୍ଷା ହିମାଳୟ, ଧନ ଅପେକ୍ଷା ଜ୍ଞାନ ଓ ସର୍ପ ଅପେକ୍ଷା ଖଳ ବୋଲି ବୁଝିବାକୁ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଅର୍ଥାତ୍ ଦୁଇଟି ମଧ୍ୟରେ ତୁଳନା କରାଯାଇଛି ।
୯। (କ) ରମେଶଃ (ଛାତ୍ରାବାସେ ସ୍ଥିତ୍ଵା) ଛାତ୍ରାବାସାତ୍ ପତ୍ର ଲିଖତି । ରମେଶ ହଷ୍ଟେଲରୁ ଚିଠି ଲେଖୁଛି ।
(ଖ) ବାନରଃ (ବୃକ୍ଷମ୍ ଆରୁହ୍ୟ) ବୃକ୍ଷାତ୍ ପଶ୍ୟତି । ମାଙ୍କଡ଼ ଗଛକୁ ଚଢ଼ି ଚାହୁଛି ।
‘ ଲ୍ୟବ୍ଲୋପେ କର୍ମଣ୍ୟଧ୍ଵରଣେ ଚ ।’‘କ୍ସା’ ଏବଂ ‘ଲ୍ୟପ୍’ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟାନ୍ତ ପଦ ବ୍ୟବହାର ନ କରି ଉକ୍ତ କ୍ରିୟାପଦର ‘କର୍ମ’ ଓ ‘ଆଧାର’ ସ୍ଥାନରେ ‘ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି’ ହୁଏ । ଏହାକୁ ‘ଲ୍ୟବ୍ଲୋପେ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ’ କୁହାଯାଏ । ଏଠାରେ ‘ସ୍ଥିତ୍ଵା’ ଓ ‘ଆରୁହ୍ୟ’ କ୍ରିୟାପଦକୁ ଉହ୍ୟ କରି ଅଧ୍ଵକରଣ ‘ଛାତ୍ରାବାସ’ ଠାରେ ଓ ‘କର୍ମ’ ବୃକ୍ଷଠାରେ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୋଇଛି ।
୧୦ । (କ) ଶିଷ୍ୟ ଆଚାର୍ଯ୍ୟାତୁ ଶାସ୍ତ୍ରମ୍ ଅଧୀତେ । ଶିଷ୍ୟ ଗୁରୁଙ୍କଠାରୁ ଶାସ୍ତ୍ର ଅଧ୍ୟୟନ କରୁଛି ।
(ଖ) ବଧୂ ଶ୍ଵଶୁରାତ୍ ଲଜ୍ଜତେ । ବୋହୂ ଶ୍ୱଶୁରକୁ ଲାଜ କରୁଛି ।
‘ଆଖ୍ୟାତୋପଯୋଗେ ।’ ନିୟମପୂର୍ବକ ବିଦ୍ୟାଗ୍ରହଣରେ ଗୁରୁଙ୍କୁ ‘ଆଖ୍ୟାତ’ କୁହାଯାଏ । ସେଠାରେ ଅପାଦାନ ସଂଜ୍ଞା ହୁଏ । ‘ତ୍ରପାର୍ଥନାଂ ଯତଃ ତ୍ରପା ।’ ଲଜ୍ଜା କରିବା ଅର୍ଥରେ ଯାହାକୁ ଲଜ୍ଜା କରାଯାଏ ସେଠାରେ ମଧ୍ୟ ଅପାଦାନ ସଂଜ୍ଞା ହୋଇ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ଏଠାରେ ଆଚାର୍ଯ୍ୟଙ୍କଠାରୁ ନିୟମ ପୂର୍ବକ ଶାସ୍ତ୍ର ଅଧ୍ୟୟନ ହେତୁ ‘ଆଚାର୍ଯ୍ୟ’ ଆଖ୍ୟାତା ଓ ବଧୂ ଶ୍ୱଶୁରଙ୍କୁ ଲାଜ କରୁଥିବାରୁ ଉଭୟ ଆଚାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଓ ଶ୍ୱଶୁରଠାରେ ଅପାଦାନ ସଂଜ୍ଞା ହେଲା ।
୧୧ । (କ) ବାଳକ ଦୁଃଖେନ । ଦୁଃଖାତ୍ କ୍ରନ୍ଦତି । ପିଲାଟି ଦୁଃଖରେ କାନ୍ଦୁଛି ।
(ଖ) ପଥ୍ଅଃ ତୃଷୟା ଅପତତ୍ । ବାଟୋଇ ଶୋଷରେ ପଡ଼ିଗଲା ।
‘ହେତୌ ବିଭାଷା ଗୁଣେଽପ୍ରିୟାମ୍ । ’ସ୍ତ୍ରୀଲିଙ୍ଗ ଭିନ୍ନ ଅନ୍ୟଲିଙ୍ଗର ଗୁଣବାଚକ ଶବ୍ଦ ହେତୁ ବା କାରଣ ଅର୍ଥକୁ ବୁଝାଇଲେ ତା ସ୍ଥାନରେ ତୃତୀୟା ବା ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ହେତୁବୋଧକ ଶବ୍ଦ ସ୍ତ୍ରୀଲିଙ୍ଗ ହୋଇଥିଲେ, ତା’ଠାରେ କେବଳ ତୃତୀୟା ହୁଏ (ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ହୁଏ ନାହିଁ ) । କ୍ରନ୍ଦନ କ୍ରିୟାର କାରଣ ‘ଦୁଃଖ’ କ୍ଲବଲିଙ୍ଗ ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ ହେତୁ ଅର୍ଥରେ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତିରେ ‘ଦୁଃଖାତ୍’ ହୋଇଛି । ଅନ୍ୟ ପକ୍ଷରେ ହେତୁ ଅର୍ଥରେ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତିରେ ‘ଦୁଃଖେନ’ ମଧ୍ୟ ହୋଇଛି । କିନ୍ତୁ ଅପତତ୍- (ପତନ କ୍ରିୟା) ର କାରଣ ‘ତୃଷ୍ଣା’ ସ୍ତ୍ରୀଲିଙ୍ଗ ହେତୁ, ହେତୌ ତୃତୀୟା ହୋଇଛି ।
୧୨। (କ) ପୁନଃ ପିତୁଃ ପ୍ରତି । ପୁଅ ବାପାଙ୍କର ପ୍ରତିନିଧି ।
(ଖ) ଧାନ୍ୟଭ୍ୟ ପ୍ରତିଯଚ୍ଛତି ମାଷାନ୍ । ଧାନବଦଳରେ ବିରି ନେଉଛି ।
‘ପ୍ରତିନିଧ୍ଵ ପ୍ରତିଦାନେ ଚ ଯସ୍ମାତ୍ । ପ୍ରତିନିଧ୍ଵ ଓ ପ୍ରତିଦାନ ଅର୍ଥରେ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହେଉଥିବା ‘ପ୍ରତି’ ଯୋଗରେ ‘ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି’ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଏଠାରେ ପୁତ୍ର, ପିତାର ପ୍ରତିନିଧ୍ ଓ ଧାନ ପ୍ରତିଦାନରେ ବିରି ଦେଉଥୁବାରୁ, ପିତୃ ଓ ଧାନ୍ୟ ଶବ୍ଦରେ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ହେଲା ।
୧୩। (କ) ଆ ମୂଳାତ୍ ଶ୍ରୋତୁମ୍ ଇଚ୍ଛାମି । ମୂଳରୁ ଶୁଣିବାକୁ ଇଚ୍ଛା କରୁଛି ।
(ଖ) ଆ କୈଳାସାତ୍ର ଗନ୍ତୁକାମୋଽହମ୍ । କୈଳାସଠାରୁ ଯିବାକୁ ଇଚ୍ଛା କରୁଛି ।
(ଗ) ଅପବିଷୋ ସଂସାରଃ । ବିଷ୍ଣୁଙ୍କଠାରୁ ସଂସାର ଆରମ୍ଭ ।
(ଘ) ପରି ବନାତ୍ର ବର୍ଷତି ମେଘ । ବଣଠାରୁ ମେଘ ବରଷୁଛି ।

‘ପଞ୍ଚମ୍ୟପାରିଭିଂ, ଆଡ୍ ମର୍ଯ୍ୟାଦାବନେ, ଅପପରୀ ବର୍ଜନେ ।’ଅପ, ଆଡ୍ ଏବଂ ପରି ଯୋଗେ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ମର୍ଯ୍ୟାଦା ଓ ଅଭିବିଧ ଅର୍ଥରେ ‘ଆଡ୍’ ତଥା ବଞ୍ଜନ ଅର୍ଥରେ ‘ଅପ’ ଓ ‘ପରି’ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହୋଇଥାଏ । ୧୪ । ନିମ୍ନଲିଖ ପଦମାନଙ୍କ ଯୋଗରେ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ଯଥା –
୧୪ । ନିମ୍ନଲିଖୂତ ପଦମାନଙ୍କ ଯୋଗରେ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ଯଥା –


କୃଚ୍ଛ୍ର (ଅତିକଷ୍ଟରେ) – ଡଃ କୃଚ୍ଛାତ୍ ବିପଦଃ ମୁକ୍ତା । ସେ କଷ୍ଟରେ ବିପଦରୁ ମୁକ୍ତି ପାଇଲ ।
ଅଳ୍ପ (ଅଳ୍ପକରେ) – ଶିଶୁ ଅଳ୍ପାତୁ ଦୁଃଖାତ୍ ରକ୍ଷିତଃ । ପିଲାଟି ଅଦୁଃଖରୁ ରକ୍ଷାପାଇଲା ।
ସ୍ପୋକ (ସାମାନ୍ୟ) – ଅହଂ ସ୍ତୋକାତୁ ବିପଦଃ ମୁକ୍ତା । ମୁଁ ଅଳ୍ପକରେ ବିପଦରୁ ମୁକ୍ତ ହେଲି ।
(କୃଚ୍ଛ୍ର/ ଅଳ୍ପ/ ସ୍ପୋକ ଶବ୍ଦରେ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ଯୁକ୍ତ ହୋଇଛି ।)
ମନେରଖ :
- ଯେଉଁଠାରୁ ବିଚ୍ଛେଦ ହୁଏ, ତାହା ଅପାଦାନ ।
- ଯେଉଁଥୁରୁ କିଛି ପ୍ରାପ୍ତ ହୁଏ ସେଠାରେ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ହୁଏ ।
- ଉତ୍କର୍ଷ ଓ ଅପକର୍ଷ ବୁଝାଇଲେ ନିକୃଷ୍ଟର ଅପାଦାନ ସଂଜ୍ଞା ।
- ଭୟ ଅର୍ଥରେ ଯାହାଠାରୁ ଭୟ ବା ଯିଏ ଭୟର କାରଣ ସେଠାରେ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ହୁଏ ।
- ପୂର୍ବ-ପର ଯୋଗରେ ମଧ୍ୟ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ହୁଏ ।
- ଯେଉଁଠାରୁ ଆରମ୍ଭ ସେଠାରେ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ।
- ଘୃଣା-ବିରାମ-ଅସାବଧାନତା ଯେଉଁ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିଠାରେ ବସ୍ତୁ ବା କାର୍ଯ୍ୟରେ କରାଯାଏ ସେଠାରେ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ।
- ବିନା ଯୋଗେ ଦ୍ୱିତୀୟା, ତୃତୀୟା ଓ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ । ଋତେ ଯୋଗେ ଦ୍ୱିତୀୟ ଓ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ । ଅନ୍ତରେଣ ଯୋଗେ କେବଳ ଦ୍ବିତୀୟା ।
- ଆରାତ୍ (ନିକଟରେ / ଦୂରରେ) ଯୋଗେ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ । କିନ୍ତୁ ନିକଷା/ ସମୟା ଯୋଗେ ଦ୍ଵିତୀୟା ।
ଗୀତ :
ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ଅପାଦାନ ଜାରକରେ
ଭୟାର୍ଥ ରକ୍ଷାର୍ଥ ଧାତୁ ଯୋଗରେ ।
ନିର୍ଲାୟତେ ପ୍ରଜାୟତେ ଯୋଗରେ
ଯୁଗ୍ମପ୍ ବିରାମ ପ୍ରମାଦାର୍ଥରେ ।
ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ପ୍ରଭବ୍ୟତି ବ୍ୟବହାରେ
ଲ୍ୟପ୍, ଲୋପେ, ଅନ୍ୟ, ପ୍ଲାକ୍ ଆରାତ୍
ଋତେ ଆଚ ଆହି ଦିଗ ଦେଶ ସଂଯୁତେ
ଆଚ ଆହି ଦିଗ ଦେଶ ସଂଯୁତେ
ଆରଭ୍ୟ ପ୍ରଭୃତି ବହିଃ ପୃଥକ୍
ସ୍ତୋକାଳ ଉତ୍କର୍ଷ ଅପକର୍ଷକ ।।
ଅଭ୍ୟାସଃ :
ବନ୍ଧନୀମଧ୍ୟାତ୍ ଯଥାର୍ଥପଦେନ ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନଂ ପୂରୟତ ।
ଯଥା –
(କ) ନିର୍ଝରଃ ପର୍ବତେଭ୍ୟ ସ୍ରବନ୍ତି ।
(ଖ) ଭକ୍ତାଃ_______________________ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟାବର୍ତ୍ତନ୍ତେ ।
Answer:
ମନ୍ଦିରାତ୍
(ଗ) ବାରି _______________________ ପତତି ।
Answer:
ଆକାଶାତ୍
(ଘ) ପତ୍ରାଃ ______________________ ପତନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ବୃକ୍ଷାତ୍

(ଙ) ଛାତ୍ରଃ ______________________ ଆଗଚ୍ଛତି ।
Answer:
ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟାତ୍
(ଚ) କୃଷକଃ ______________________ ଆୟାତି ।
Answer:
ଗ୍ରାମାତ୍
(ଛ) ଈଶ୍ଵରଃ ____________________ ରକ୍ଷତି ।
Answer:
ଦୁଃଖାତ୍
(ଦୁଃଖାତ୍, ବୃକ୍ଷାତ୍, ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟାତ୍, ମନ୍ଦିରାତ୍, ଆକାଶାତ୍, ଗ୍ରାମାତ୍)
୨। ବନ୍ଧନୀମଧ୍ଯସ୍ଥଶବ୍ଦାନାଂ ଯଥାର୍ଥରୂପେ ଉପଯୁକ୍ତ କ୍ରିୟାପଦୈଶ୍ଚ ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନଂ ପୂରୟତ ।
ଯଥା – ସର୍ପ ନକୁଳାତ୍ ବିଭେତି । (ନକୁଳ)
(କ) ମୂଷିକ __________________ _________________ । (ମାର୍କାର)
Answer:
ମାର୍ଜାରାତ୍, ବିଭେତି
(ଖ) ଚୌରଃ __________________ _________________ । (ରକ୍ଷିନ୍)
Answer:
ରକ୍ଷିତଃ ବିଭେତି
(ଗ) ମୃଶଃ __________________ _________________ । (ବ୍ଯାଘ୍ର)
Answer:
ବ୍ୟାଘ୍ରାତ୍ ବିଭେତି
(ଘ) ଶୃଗାଳଃ __________________ _________________ । (କୁକ୍କୁର )
Answer:
କୁକ୍କୁରାତ୍ ବିଭେତି
(ଙ) ସାଧଃ __________________ _________________ । (ଦୁର୍ଜନ)
Answer:
ଦୁର୍ଜନାତ୍ ବିଭେତି
(ଚ) ଗୃହସ୍ଥ __________________ _________________ । (ଚୌର )
Answer:
ଚୌରାତ୍ ବିଭେତି
(ଛ) ଧାର୍ମିକଃ __________________ _________________ । (ପାପ)
Answer:
ପାପାତ୍ ବିଭେତି
୩। ଅଧୋଲିଖ ଶ୍ଳୋକଂ ପଠିତ୍ବା ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନଂ ପୂରୟତ ।
ବିଦ୍ୟା ଦଦାତି ବିନୟଂ ବିନୟାତ୍ ଯାତି ପାତ୍ରତାମ୍ ।
ପାତ୍ରତ୍ବାଦ୍ ଧନମାସ୍ମୋତି ଧନାଦ୍ ଧର୍ମ ତତଃ ସୁଖମମ୍ ॥
(କ) କସ୍ମାତ୍ ପାତ୍ରତାଂ ଯାତି ?
(ଖ) ______________________ ପାତ୍ରତାଂଘାତି ।
Answer:
ବିନୟାତ୍
(ଗ) ନରଃ କସ୍ମାତ୍ ଧନମାସ୍ମୋତି ?
(ଘ) ନରଃ _________________________ ଧନମାସ୍ମୋତି ।
Answer:
ଧର୍ମ।ତ୍
(ଙ) ନରଃ କସ୍ମାତ୍ ଧର୍ମକାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରୋତି ?
(ଚ) ନରଃ _____________________ ଧର୍ମକାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରୋତି ?
Answer:
ଧନାତ୍

(ଛ) କୁତଃ ସୁଙ୍ଖ ଲଭ୍ୟତେ ?
(ଜ) ________________________ ସୁଙ୍ଖ ଲଭ୍ୟତେ ।
Answer:
ଧର୍ମାତ୍
୪। କଃ କସ୍ମାତ୍ ପରଃ ? କଃ କସ୍ମାତ୍ ପୂର୍ବ ? ଏତେ ଦ୍ଵାଦଶମାସ ।
୧. ଚୈତ୍ର
୨. ବୈଶାଖ
୩. ଜ୍ୟୈଷ୍ଠା
୪. ଆଷାଢ଼
୫. ଶ୍ରାବଣୀ
୬. ଭାଦ୍ରପଦଃ
୭.ଆଶି୍ନଃ
୮. କାର୍ତ୍ତକଃ
୯. ମାର୍ଗଶୀର୍ଷଃ
୧୦. ପୌଷଃ
୧୧. ମାଘଃ
୧୨. ଫାଲ୍ଗୁନଃ
ଯଥା :
(କ) ଚୈତ୍ର ବୈଶାଖାତ୍ର ପୂର୍ବ । ବୈଶାଖ ଚୈତ୍ରାତ୍ ପରଃ ।
(ଖ) ଜ୍ୟେଷ୍ଠ ଆଷାଢାତ୍ର ପୂର୍ବ । ଆଷାଢ଼ ଜ୍ୟେଷ୍ଠାତ୍ର ପରଃ ।
(ଗ) ଶ୍ରାବଣ ଭାଦ୍ରପଦାତ୍ ପୂର୍ବ । ଭାଦ୍ରପଦଃ ଶ୍ରାବଣାତ୍ ପରଃ ।
(ଘ) ଆଶ୍ୱିନଃ କାର୍ତ୍ତିକାତ୍ମ ପୂର୍ବ । କାର୍ତ୍ତିକଃ ଆଶ୍ୱିନାତ୍ ପରଃ ।
(ଙ) ମାର୍ଗଶୀର୍ଷ ପୌଷାତ୍ର ପୂର୍ବ । ପୌଷ ମାର୍ଗଶୀର୍ଷାତ ପରଃ ।
(ଚ) ମାଘ ଫାଲ୍ଗୁନାତ୍ ପୂର୍ବ । ଫାଲ୍ଗୁନଃ ମାଘାତ୍ର ପରଃ ।
ପୁନଶ୍ଚ ଏତେ ଷଡ଼ରତମଃ । ଯଥା ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନଂ ପୂରୟତ ।
ଯଥା :
(କ) ଆଷାଢ଼ାତ୍ ଆରଭ୍ୟ ଶ୍ରାବଣପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ ବର୍ଷତୁଃ ।
(ଖ) ଭାଦ୍ରପଦାତ୍ ଆରଭ୍ୟ,ଆଶ୍ୱିନପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ ଶରଦ୍ ।
(ଗ) କାର୍ତ୍ତିକାତ୍ର ମାର୍ଗଶୀର୍ଷପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ ହେମନ୍ତଃ ।
(ଘ) ପୌଷାତ୍ର ମାଘପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତଃ ଶିଶିରଃ ।
(ଙ) ଚୈତ୍ର ପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ ଫାଲ୍ଗୁନାତ୍ ବସନ୍ତଃ ।
(ଚ) ବୈଶାଖାତ୍ ଜ୍ୟେଷ୍ଠପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ ଗ୍ରୀଷ୍ମ ।
୫। ଯଥାନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନଂ ପୂରୟତ ।
ଯଥା – ସ୍ବାଧ୍ୟାୟାତ୍ ନ ପ୍ରମଦିତବ୍ୟମ୍ । (ସ୍ୱାଧ୍ୟାୟ)
(କ) ସତ୍ୟାତ୍ ନ ପ୍ରମଦିତବ୍ୟମ୍ । (ସତ୍ୟ)
(ଖ) ଧର୍ମାତ୍ ନ ପ୍ରମଦିତବ୍ୟମ୍ । (ଧର୍ମ)
(ଗ) କୁଶଳାତ୍ ନ ପ୍ରମଦିତବ୍ୟମ୍ । (କୁଶଳ)
(ଘ) ଦେବକାର୍ଯ୍ୟାତ୍ ନ ପ୍ରମଦିତବ୍ୟମ୍ । (ଦେବାକାର୍ଯ୍ୟ)
(ଙ) ପିତୃକାର୍ଯ୍ୟାତ୍ ନ ପ୍ରମଦିତବ୍ୟମ୍ । (ପିତୃକାର୍ଯ୍ୟ)
୬। ବନ୍ଧନୀସ୍ଥିତାନ୍ ଶବ୍ଦାନ୍ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ୍ୟ ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନାନି ପୂରୟତ ।
ଯଥା – ମମ ଭ୍ରାତା କଟକାତ୍ର ଆଗତଃ । (କଟକ)
(କ) ଅହଂ _____________________________ ବହିଃ ଇତସ୍ତତଃ ନ ଭ୍ରମାମି । (ଗ୍ରାମ)
Answer:
ଗ୍ରାମାତ୍
(ଖ) ______________________ ଋତେ ମମ କଃ ସହାୟଃ । (ଈଶ୍ଵର)
Answer:
ଈଶ୍ବରାତ୍
(ଗ) _________________________ ପୂର୍ବମ୍ ଈଶ୍ବରଂ ସ୍ମର । (ଶୟନ)
Answer:
ଶୟନାତ୍
(ଘ) __________________ ପରଂ କ୍ରୀଡ଼ । (ପଠନ)
Answer:
ପଠନାତ୍
(ଙ) ଅର୍ଜୁନଃ ____________________________ ଧନୁର୍ବିଦ୍ୟାମ୍ ଅଶିକ୍ଷତ । (ଦ୍ରୋଣ)
Answer:
ଦ୍ରୋଣାତ୍

(ଚ) ସର୍ବେ ______________________ ଜୁଗୁପ୍ସନ୍ତେ । (କୃପଣ)
Answer:
କୃପଣାତ୍
(ଛ) ପୁତ୍ରଃ ______________________ ବଦତି । (ଶ୍ରୀକ୍ଷେତ୍ର)
Answer:
ଶ୍ରୀକ୍ଷେତ୍ରାତ୍
(ଜ) _______________________ ବୃକ୍ଷୀ ଜାୟତେ । (ବୀଜ)
Answer:
ବୀଜାତ୍
୭। ଅଧସ୍ତନପଦାନାଂ ବାକ୍ୟଷୁ ବ୍ୟବହାରଂ କୁରୁତ ।
ଯଥା : ବିଭେତି : ସର୍ପ ନକୁଳାତ୍ ବିଭେତି ।
ଅନ୍ୟଃ, ନିଲୀୟତେ,ଆରାତ୍, ପ୍ରାକ୍, ପୃଥକ୍, ପ୍ରଭୃତି, କୃଚ୍ଛାତ୍, ବିନା, ବହିଃ, ଅନନ୍ତରମ୍, ନାନା, ଉତ୍ତରା, ଦକ୍ଷିଣାହି, ପ୍ରତି ।
ଅନ୍ୟଃ – ରାମଃ ଶ୍ୟାମାତ୍ର ଅନ୍ୟ ।
ନିଲୀୟତେ – ବଧୂ ଶ୍ୱଶୁରାତ୍ ନିଲୀୟତେ ।
ଆରାତ୍ – ଗ୍ରାମାତ୍ ଆରାତ୍ର ନଦୀ ବହତି ।
ପ୍ରାକ୍ – ଭୋଜନାତୁ ପ୍ରାକ୍ ହସ୍ତଂ କ୍ଷାଳୟ ।
ପୃଥକ୍ – ରାମ ଶ୍ୟାମାତ୍ର ପୃଥକ୍ ।
ପ୍ରଭୃତି – ମାଘାତ ପ୍ରଭୃତି ବସନ୍ତଃ ଭବତି ।
କୃଚ୍ଛାତ୍ – ଅହଂ କୃଚ୍ଛାତ୍ ବିପଦଃ ମୁକ୍ତା ।
ବିନା – ଧର୍ମାତ୍ର ବିନା ମୁକ୍ତା ନାସ୍ତି ।
ବହିଃ – ଗୃହାତ୍ ବହିଃ ଉଦ୍ୟାନଂ ଶୋଭିତେ ।
ଅନନ୍ତରମ୍ – ଶୟନାତ୍ ଅନନ୍ତରଂ ସ୍ବପ୍ନ ପଶ୍ୟାମି ।
ନାନା – ଧନାତ୍ର ନାନା ମୁକ୍ତି ନାସ୍ତି ।
ଉତ୍ତରା – ଗ୍ରାମାତ୍ ଉତ୍ତରା ବନମଣ୍ଡି ।
ଦକ୍ଷିଣାହି – ଗ୍ରାମାତ୍ ଦକ୍ଷିଣାହି ମନ୍ଦିରଂ ଶୋଭତେ ।
ପ୍ରତି – ପୁନଃ ପିତୁଃ ପ୍ରତି ।
୮। ସଂଶୋଧନଂ କୁରୁତ ।
ଯଥା : ଈଶ୍ବରସ୍ୟ ଅନ୍ୟ କଃ ସହାୟ । ଈଶ୍ବରାତ୍ ଅନ୍ୟ କଃ ସହାୟ ।
(କ) ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟସ୍ୟ ବହିଃ ବାଳକା କ୍ରୀଡ଼ନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟାତ୍ ବହିଃ ବାଳକା କ୍ରୀଡ଼ନ୍ତି ।
(ଖ) ବିପଦି ତ୍ରାୟସ୍ୱ ମାମ୍ ।
Answer:
ବିପଦଃ ପ୍ରାୟସ୍ୱ ମାମ୍ ।
(ଗ) ଚୋରଃ ରକ୍ଷିଣଂ ନିଲୀୟତେ ।
Answer:
ଚୋରଃ ରକ୍ଷିତଃ ନିଲୀୟତେ ।
(ଘ) ଅସ୍ୟ ନଗରସ୍ୟ ଉତ୍ତରା ନଦୀ ବର୍ତ୍ତତେ ।
Answer:
ଅସ୍ନାତ୍ ନଗରାତ୍ର ଉତ୍ତରା ନଦୀ ବର୍ଭତେ ।
(ଙ) ଭୋଜନସ୍ୟ ପ୍ରାକ୍ ହସ୍ତଂ ପ୍ରକ୍ଷାଳୟେତ୍ ।
Answer:
ଭୋଜନାତ୍ ପ୍ରାକ୍ ହସ୍ତୀ ପ୍ରକ୍ଷାଳୟେତ୍ ।
(ଚ) ଜ୍ୟେଷ୍ଠ ବୈଶାଖସ୍ୟ ପରଃ ମାନଃ ।
Answer:
ଜ୍ୟେଷ୍ଠ ବୈଶାଖାତ୍ ପରଃ ମାନଃ ।
(ଛ) ବିନୟସ୍ୟ ଯାତି ପାତ୍ରତାମ୍ ।
Answer:
ବିନୟାତ୍ ଯାତି ପାତ୍ରତାମ୍ ।
(ଜି) କଟକଂ ଆରାତ୍ ମହାନଦୀ ।
Answer:
କଟକାତ୍ ଆରାତ୍ ମହାନଦୀ ।
(ଝ) ଜନା ରାଜମାର୍ଗେ ରଥ ପଶ୍ୟନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଜନାଃ ରାଜମାର୍ଗତ୍ ରଥ ପଶ୍ୟନ୍ତି ।

(ଞ) ଗୋପାଳ ରାମସ୍ୟ କନୀୟାନ୍ ।
Answer:
ଗୋପାଳ ରାମାତ୍ କନୀୟାନ୍ ।
୯। ସଂସ୍କୃତେନ ଅନୁବାଦଃ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ।
ଯଥା : ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟୋଦୟ ପୂର୍ବରୁ ମୁଁ ଶଯ୍ୟାତ୍ୟାଗ କରେ : ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟୋଦୟାତ୍ ପ୍ରାକ୍ ଅହଂ ଶଯ୍ୟାତ୍ୟାଗଂ କରୋମି ।
(କ) ଭକ୍ତମାନେ ବିଦେଶରୁ ପୁରୀ ଆସନ୍ତି ।
ଅନୁ – ଭକ୍ତା ବିଦେଶାତ୍ ପୁରୀମ୍ ଆଗଛନ୍ତି ।
(ଖ) ଧନ ଅଭାବରୁ ପିଲାଟି ପଡୁନାହିଁ ।
ଅନୁ – ଧନାଭାବାତ୍ ବାଳକ ନ ପଠତି ।
(ଗ) ନଦୀ ଜଳଠାରୁ କୂପଜଳ ଅଧ୍ଵକ ନିର୍ମଳ ।
ଅନୁ – ନଦୀଜଳାତ୍ କୂପଜଳମଧ୍ଵଙ୍କ ନିର୍ମଳମ୍ ।
(ଘ) ତୁମେ ଅଳ୍ପକରେ ବିପଦରୁ ରକ୍ଷା ପାଇଲ ।
ଅନୁ – ତ୍ୱମ୍ ଅର୍ଥାତ୍ ବିପଦଃ ମୁକ୍ତା ।
(ଙ) ଲୋକମାନେ କୋଠା ଉପରୁ ଯାତ୍ରା ଦେଖୁଛନ୍ତି ।
ଅନୁ – ଜନଃ ପ୍ରାସାଦାତ୍ ଯାତ୍ରା ପଶ୍ୟନ୍ତି ।
(ଚ) ଦୂରରୁ ଦର୍ଶନ ଅତୀବ ମନୋହର ।
ଅନୁ – ଦୂରାତ୍ ଦର୍ଶନମତି ମନୋହରମ୍ ।
(ଛ) ମୂର୍ଖମାନେ ପଣ୍ଡିତମାନଙ୍କୁ ଘୃଣା କରନ୍ତି ।
ଅନୁ – ମୂର୍ଖ ପଣ୍ଡିତେଭ୍ୟ ଜୁଗୁପ୍ନ୍ତେ ।
(ଜ) ଲୋଭରୁ ପାପ ପାପରୁ ମୃତ୍ୟୁ ହୁଏ ।
ଅନୁ – ଲୋଭାତ୍ ପାପମ୍, ପାପାତ୍ ମୃତ୍ଯୁ ବ୍ୟ ଜାୟତେ ।
(ଝ) ପୂର୍ବେ ମା’ମାନେ ଝିଅଙ୍କୁ ପଢ଼ିବାରୁ ବାରଣ କରୁଥିଲେ ।
ଅନୁ – ପୁରା ମାତରଃ କନ୍ୟା ପଠନାତ୍ ବାରୟନ୍ତି ସ୍ମ ।
ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧପଦ ଓ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି
୧। (କ) ରାମସ୍ୟ ପୁନଃ କ୍ରୀଡ଼ତି । ରାମର ପୁଅ ଖେଳୁଛି ।’
(ଖ) ରାଜ୍ଞ ପୁରୁଷା ଆଗଛନ୍ତି । ରାଜାଙ୍କ ପୁରୁଷମାନେ ଆସୁଛନ୍ତି ।
(ଗ) ଭକ୍ତ କୃଷ୍ଣସ୍ୟ ପାଦପଙ୍କଜଂ ଭଜତି । ଭକ୍ତ କୃଷ୍ଣଙ୍କ ପଦାରବିନ୍ଦକୁ ଭଜନ କରୁଛି ।
‘ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ’ । ଏଠାରେ ରାମସ୍ୟ, ରାଜ୍ଞ ଓ କୃଷ୍ଣସ୍ୟ ପଦତ୍ରୟ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତନ୍ତ ଅଟନ୍ତି । ଏହି ପଦଗୁଡ଼ିକର କ୍ରିୟାପଦ କ୍ରୀଡ଼ତି, ଆଗଛନ୍ତି ଓ ଭଜତି ସହିତ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ନାହିଁ । ବରଂ ଏମାନଙ୍କର ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ଥିବା ଅନ୍ୟ ବିଶେଷ୍ୟ ପଦଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଯଥା – ପୁତ୍ର ପୁରୁଷ ଓ ପାଦପଙ୍କଜ ସହିତ ରହିଛି । କ୍ରିୟା ସହିତ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ନଥବାରୁ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତନ୍ତ ପଦର ‘କାରକତ୍ଵ’ ସମ୍ଭବ ହୁଏ ନାହିଁ । ତେଣୁ ଏହାକୁ କେବଳ ‘ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧପଦ’ ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ । ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ପଦରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୋଇଥାଏ । ତେଣୁ ରାମସ୍ୟ, ରାଜ୍ଞ ଓ କୃଷ୍ଣସ୍ୟ ଇତ୍ୟାଦି ପଦ ‘ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ-ଷଷ୍ଠୀ’ ସୂତ୍ରରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତାନ୍ତ ହେଲେ । ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧର ପ୍ରକାର ଅସଂଖ୍ୟ । ତେବେ ଉପର୍ୟ୍ୟକ୍ତ ତିନୋଟି ବାକ୍ୟରେ ଯଥାକ୍ରମେ ଜନ୍ୟ-ଜନକ, ସ୍ଵସ୍ଵାମିଭାବ ଓ ଅବୟବାବୟବିଭାବ (ଅଙ୍ଗାଙ୍ଗୀଭାବ) ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ।
ମହର୍ଷି ପାଣିନି ଅଣ୍ଟାଧ୍ୟାୟୀ ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥରେ ଛଅଟି କାରକ ବିଷୟ ଆଲୋଚନା କରି ପରେ କହିଲେ ‘ଆଉ ଯାହା ରହିଲା’ (ଅବଶିଷ୍ଟ/ଶେଷ) ସେହି ସ୍ଥାନରେ ‘ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି’ ହେବ । ଏହାକୁ ‘ଶେଷେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ’ ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ । ଏହାକୁ ‘ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧସାମାନ୍ୟ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ’ ବୋଲି ବୁଝିବାକୁ ହେବ ।
(କ) ବନ୍ଦେ ଗୁରୋ ଚରଣୟୋଃ । ଗୁରୁଙ୍କ ଚରଣକୁ ବନ୍ଦନା କରୁଛି ।
(ଖ) ଭକ୍ତ ଶଙ୍କରସ୍ୟ ପାଦୟୋଃ ଭଜତି । ଭକ୍ତ ଶଙ୍କରଙ୍କ ପାଦକୁ ଭଜୁଛି ।
(ଗ) ତାବତ୍ ଭୟସ୍ୟ ଭେତବ୍ୟମ୍ । ଭୟକୁ ଡ଼ରିବା ଉଚିତ ନୁହେଁ ।
‘କର୍ମାଦୀନାମପିସମ୍ବନ୍ଧମାତ୍ର ବିବକ୍ଷାୟାଂ ଷଷ୍ୟବ’ । ବହୁସ୍ଥଳରେ କାରକ ବିଭକ୍ତିର ସମ୍ଭାବନା ଥିଲେ ମଧ୍ୟ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ବିବକ୍ଷାରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଉପରିଲିଖୁ ବାକ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ‘ଚରଣ’ ପ୍ରଭୃତି କର୍ମାଦି କାରକ ସ୍ଥଳରେ ‘ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ବିବକ୍ଷାରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ’ ହୋଇଛି ।
୩ । (କ) ଧନସ୍ୟ ହେତୋଃ ବିଦେଶଂ ଗଚ୍ଛତି ।(ଧନ ନିମନ୍ତେ ବିଦେଶ ଯାଉଛି)
(ଖ) ଶୀତସ୍ୟ ହେତୋଃ କମ୍ପତେ । (ଶୀତ ନିମନ୍ତେ କଖୁଛି)
(ଗ) ଅଧ୍ୟୟନସ୍ୟ ହେତୋଃ ଅହଂ ଭୁବନେଶ୍ବରେ ତିଷ୍ଠାମି । (ପଢ଼ିବାକୁ ମୁଁ ଭୁବନେଶ୍ବରରେ ରହୁଛି)
‘ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ହେତୁ ପ୍ରୟୋଗେ’ । ବାକ୍ୟରେ ‘ହେତୁ’ ଶବ୍ଦର ସାକ୍ଷାତ୍ ପ୍ରୟୋଗ ହୋଇଥିଲେ ହେତୁ ବାଚକ (ନିମିତ୍ତବୋଧକ) ଶବ୍ଦଠାରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ଏଠାରେ ବିଦେଶଗମନର କାରଣ ‘ଧନ’, ଥରିବାର କାରଣ ‘ଶୀତ’ ଓ ଭୁବନେଶ୍ୱରରେ ରହିବାର କାରଣ ‘ଅଧ୍ୟୟନ’ ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ କାରଣବାଚୀ ଧନ, ଶୀତ ଓ ଅଧ୍ୟୟନ ଶବ୍ଦରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହେଲା । ଏହାକୁ ‘ହେତୁପ୍ରୟୋଗେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ’ ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ ।
୪। (କ) କେନ ହେତୁନା ଅତ୍ର ଆଗଚ୍ଛସି ?
(ଖ) କସ୍ମାତ୍ ହେତୋ ବାଳକ କ୍ରନ୍ଦତି ?
(ଗ) କସ୍ୟ ହେତୋ ଡଃ ପଳାୟିତଃ ?

‘ସର୍ବନାମ୍ଳତୀୟା ଚ’ । ହେତୁ ଶବ୍ଦ ସହ ଯଦି ସର୍ବନାମପଦମାନଙ୍କର ପ୍ରୟୋଗ କରାଯାଏ, ତେବେ ଉଭୟ ହେତୁବାଚୀ ଶବ୍ଦ ଓ ସର୍ବନାମବାଚୀ ଶବ୍ଦରୁ ତୃତୀୟା, ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ଓ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତ ହୁଏ । ‘ନିମିତ୍ତ ପର୍ଯ୍ୟାୟପ୍ରୟୋଗେ ସର୍ବାସାଂ ପ୍ରାୟଦର୍ଶନମ୍ ।’ ନିମିତ୍ତ ଓ ତଦର୍ଥବାଚୀ ପର୍ଯ୍ୟାୟଶବ୍ଦ ଯୋଗରେ ସର୍ବନାମ ଏବଂ ନିମିତ୍ତବାଚକ ଶବ୍ଦଠାରେ ପ୍ରାୟଶଃ ପ୍ରଥମାଠାରୁ ସପ୍ତମୀ ପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ ସମସ୍ତ ବିଭକ୍ତି ପ୍ରୟୋଗ ଦେଖାଯାଏ । ଯଥା- (ଘ) କୋ ହେତୁଃ / କଂ ହେତୁମ୍ / କେନ ହେତୁନା । କସ୍ମି ହେତବେ । କସ୍ମାତ୍ ହେତୋ / କସ୍ୟ ହେତୋ/ କସ୍ମିନ୍ ହେତୌ ।
୫। (କ) ପୁନଃ ମାତୁଃ । ମାତରଂ ସ୍ମରତି । ପୁଅ ମାଆଙ୍କୁ ସ୍ମରଣ କରୁଛି ।
(ଖ) ଦରିଦ୍ରସ୍ୟ / ଦରିଦ୍ର୍ୟ ଦୟସ୍ଵ । ଗରିବକୁ ଦୟା କର ।
(ଗ) ଗ୍ରାମସ୍ୟ / ଗ୍ରାମମ୍ ଈଷ୍ଟ । ଗାଁରେ ପ୍ରଭୁତ୍ୱ ବିସ୍ତାର କରୁଛି ।
ସ୍ଵଧାତୁ (ସ୍ମରଣାର୍ଥକ) ଦୟ ଧାତୁ (ଦୟା କରିବା) ଏବଂ ଈଶ୍ ଧାତୁ (ପ୍ରଭୁତ୍ୱ ବିସ୍ତାର କରିବା) ପ୍ରୟୋଗ ହୋଇଥିଲେ କର୍ମକାରକରେ ବିକଳ୍ପରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ ।
୬। (କ) ରାମସ୍ୟ ଗମନମ୍ (ରାମଃ ଗଛତି) ।
(ଖ) ଧନସ୍ୟ ଦାନଂ କୁରୁ (ଧନଂ ଦେହି) ।
(ଗ) ବ୍ୟାକରଣସ୍ୟ ପଠନଂ ଭବତି (ବ୍ୟାକରଣଂ ପଠତି)
‘କର୍ତ୍ତୃକର୍ମଣୋ କୃତି’ । କୃଦନ୍ତପଦର କର୍ତ୍ତା ଓ କର୍ମର ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ପ୍ରଥମ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ଗମ୍ + ଲ୍ୟୁଟ୍ ଗମନମ୍ ଏକ କୃଦନ୍ତପଦ ଅଟେ । ଏହି କୃଦନ୍ତପଦ ଯୋଗରେ କର୍ତ୍ତା ‘ରାମ’ ଠାରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତ ହେଲା । ସେହିପରି ଦାନମ୍ ଓ ପଠନମ୍ କୃଦନ୍ତ ପଦ ପାଇଁ ‘ଧନ’ ଓ ‘ବ୍ୟାକରଣ’ କର୍ମଠାରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତ ହେଲା । ଏହାକୁ ‘କୃଦ୍ଯୋଗେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ’ ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ । ‘ଉଭୟପ୍ରାର୍ତ୍ତୀ କର୍ମଣି’ । କୃଦନ୍ତ ପଦର କର୍ତ୍ତା ଓ କର୍ମ ଉଭୟ ଏକ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ବ୍ୟବହୃତ ହୋଇଥିଲେ ‘କର୍ମ’ର ହିଁ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ଯଥା –
(ଘ) ଶିଶୁଃ ଚନ୍ଦ୍ରସ୍ୟ ଦର୍ଶନଂ କରୋତି (ଶିଶୁ ଚନ୍ଦ୍ର ପଶ୍ୟତି) । (ପିଲାଟି ଚନ୍ଦ୍ର ଦେଖୁଛି)
(ଙ) ପଥଃ ଜଳସ୍ୟ ପାନଂ କରୋତି (ପଥ ଜଳଂ ପିବତି) । (ପଥ୍ୟକ ଜଳ ପିଉଛି)
୭। (କ) ଶିଶୁ କ୍ରୀଡ଼ନକଂ ପଶ୍ୟନ୍ ଅହସତ୍ । ପିଲାଟି ଖେଳଣା ଦେଖୁ ହସିଲା ।
(ଖ) ଦୈତ୍ୟାନ ଘାତୁକଃ ହରି । ଭଗବାନ୍ ରାକ୍ଷସମାନଙ୍କ ହତ୍ୟାକାରୀ ।
(ଗ) ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟଂ ଗନ୍ତୁମ୍ ଇଚ୍ଛାମି । ସ୍କୁଲ ଯିବାକୁ ଇଚ୍ଛା କରୁଛି ।
(ଘ) ଛାତ୍ରୀ ଗୃହଂ ଗତବାନ୍ । ଛାତ୍ରଟି ଘରକୁ ଯାଉଥିଲା ।
(ଙ) ଧନଂ ଦାତା । (ଧନ ଦେବାରେ ଅଭ୍ୟସ୍ତ)
(ଚ) ଇଦଂ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ମୟା ସୁକରମ୍ । ଏହି କାମ ମୋତେ ସହଜ ।
‘ନ ଲୋକାବ୍ୟୟନିଷ୍ଠା ଖଳର୍ଥବୃନାମ୍’ । (ଶତ୍ରୁ, ଶାନଚ୍, କ୍ତ, କ୍ତବତ୍ରୁ, ଉ-ଉକ, କ୍ସା, ଲ୍ୟାପ୍, ତୁମୁନ୍, ଖଳ୍, ତୃନ୍ (ଶୀଳ ବା ସ୍ୱଭାବ ଅର୍ଥକ) ପ୍ରଭୃତି ବୃଦନ୍ତପଦ ଥିଲେ କର୍ମସ୍ଥାନରେ କୃଦ୍ଯୋଗେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ହୁଏ ନାହିଁ ।) ‘ପଶ୍ୟନ୍’ ହୃଦନ୍ତପଦ ପ୍ରୟୋଗ ହୋଇଥିଲେ ମଧ୍ୟ କର୍ମ (କ୍ରୀଡ଼ନକ) ପଦର ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ହେଲା ନାହିଁ । ସେହିପରି ‘ଘାତୁକ’ ଗନ୍ତୁମ୍, ଗତବାନ୍ ଓ ଦାତା ଇତ୍ୟାଦି କୃଦନ୍ତପଦର ପ୍ରୟୋଗ ଥିଲେ ମଧ୍ୟ ଦୈତ୍ୟାନ୍, ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟମ୍, ଗୃହମ୍ ଓ ଧନମ୍ ଠାରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ହୋଇନାହିଁ । କିନ୍ତୁ ‘ତୃବ୍’ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ ହୋଇ କୃଦନ୍ତ ହେଲେ, ସେଠାରେ କୃଦ୍ଯୋଗେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଧାନ ହେବ । ଯଥା – ଜଗତଃ କର୍ତ୍ତା ହରଃ । (କୃ + ତ୍ୱଚ୍ = କର୍ତ୍ତା) ଧନସ୍ୟ ଦାତା (ଦା + ତୃବ୍) ଏହା ଧନ ଦେଉଥିବା ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିକୁ ବୁଝାଉଛି । ତେଣୁ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ । ଧନଂ ଦାତା (ଦା + ତୃନ୍) ଧନ ଦେବାରେ ଅଭ୍ୟସ୍ତ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିକୁ ବୁଝାଏ । ତେଣୁ କର୍ମକାରକରେ ଦ୍ୱିତୀୟା ।
୮। (କ) ଇଦଂ ମମ ମତମ୍ । ଏହା ମୋର ମତ ।
(ଖ) ବିଦ୍ଵାନ୍ ସର୍ବେଷା ପୂଜିତଃ । ବିଦ୍ବାନଙ୍କୁ ସମସ୍ତେ ପୂଜା କରନ୍ତି ।
(ଗ) ଡଃ ମମ ବିଦିତଃ । ତାଙ୍କୁ ମୁଁ ଜାଣେ ।
‘କ୍ତସ୍ୟ ଚ ବର୍ତମାନେ’ । ବର୍ତ୍ତମାନ କାଳ ଅର୍ଥରେ ‘କ୍ତ’ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟାନ୍ତ ପଦ ପ୍ରୟୋଗ ହୋଇଥିଲେ କର୍ଷାଠାରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ‘ନପୁସଂକ ଭାବ ଉପସଂଖ୍ୟାନମ୍’ କିନ୍ତୁ ଭାବବାଚ୍ୟରେ ବିହିତ ‘କ୍ତ’ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟାନ୍ତ ପଦର କର୍ତ୍ତାଠାରେ ବିକଳ୍ପରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ହୁଏ ।
ଯଥା – ମମ ହସିତମ୍, ତବ ଜୀବିତମ୍ ।
ଏଠାରେ ମୟା ହସିତମ୍ ଓ ୟା ଜୀବିତମ୍ ମଧ୍ୟ ହେବ । ମୁଁ ହସିଲି । ତୁମେ ବଞ୍ଚୁଲ ।
୯। (କ) ବାଳକସ୍ୟ/ବାଳକେନ ଚନ୍ଦ୍ର ଦର୍ଶନୀୟ । ପିଲାଟି ଜହ୍ନ ଦେଖିପାରେ ।
(ଖ) ଛାତ୍ରସ୍ୟ। ଛାତ୍ରେଣ ପୁସ୍ତକଂ ପଠିତବ୍ୟମ୍ । ଛାତ୍ରଟି ବହି ପଢ଼ିବା ଉଚିତ ।
(ଗ) ଭକ୍ତସ୍ୟ/ ଭକ୍ତନ ସେବ୍ୟ ହରି । ଭକ୍ତ ହରିଙ୍କୁ ସେବା କର ।
‘କୃତ୍ୟାନାଂ କଉଁରିବା’ କୃତ୍ୟ (ତବ୍ୟ, ଅନୀୟ, ଯତ୍ନ, ଶ୍ୟତ୍, କ୍ୟପ୍) ପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟାନ୍ତ ପଦଯୋଗରେ କର୍ତ୍ତାର ବିକଳ୍ପରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ଓ ପକ୍ଷେ ‘ଅନୁକ୍ତ କର୍ଭରି ତୃତୀୟା’ ସୂତ୍ରରେ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
ଉପରିଲିଖୁତ ଉଦାହରଣ ଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ଦର୍ଶନୀୟ-ଦୃଶ୍ + ଅନୀୟ, ପଠିତବ୍ୟ-ପଦ୍ + ତଥ୍ୟ ଓ ସେବ୍ୟ – ସେବ୍ + ଯତ୍ ହୋଇ ବ୍ୟବହାର ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ କର୍ତ୍ତା ବାଳକ, ଛାତ୍ର ଓ ଭକ୍ତଠାରେ ବିକଳ୍ପେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ଓ ପକ୍ଷେ ତୃତୀୟା ହୋଇଛି ।
୧୦। (କ) ରାମେଣ / ରାମସ୍ୟ ତୁଲ୍ୟ ରାଜା ନାସ୍ତି । ରାମଙ୍କ ପରି ରାଜା ନାହାଁନ୍ତି ।
(ଖ) ତବ ତୁଳା/ ଉପମା ନାସ୍ତି । ତୁମର ତୁଳନା ନାହିଁ ।
‘ତୁଲ୍ୟାର୍ଥେଋତୁଳୋପମାଭ୍ୟ ତୃତୀୟାନ୍ୟତରସ୍ୟାମ୍’ ତୁଲ୍ୟାର୍ଥକ ତୁଲ୍ୟ, ସଦୃଶ, ସମାନ, ସମ ପ୍ରଭୃତି ଶବ୍ଦଯୋଗରେ ଯାହା ସହିତ ତୁଲ୍ୟ, ତା’ଠାରେ ବିକଳ୍ପରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ପକ୍ଷେ ତୃତୀୟା ବିଭକ୍ତି ମଧ୍ୟ ହୁଏ । କିନ୍ତୁ ତୁଲ୍ୟାର୍ଥକ ତୁଳା ଓ ଉପମା ଶବ୍ଦଯୋଗରେ କେବଳ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ ।( ଅତୁଳୋପମାଭ୍ଯାମ୍)
୧୧। (କ) ନଦୀନାଂ / ନଦୀଷୁ ଗଙ୍ଗା ପବିତ୍ରତମ । ନଈମାନଙ୍କ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଗଙ୍ଗା ପବିତ୍ରତମ ।
(ଖ) ପ୍ରାଣିନାଂ / ପ୍ରାଣିଷୁ ନରଃ ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ । ପ୍ରାଣୀମାନଙ୍କ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ମଣିଷ ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ ।
(ଗ) ଗଚ୍ଛତାଂ/ ଗଚ୍ଛସୁ ଧାବନ୍ ଦ୍ରୁତତମଃ । ଯାଉଥିବା ଲୋକଙ୍କ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଧାଉଁ ଥିବା ଲୋକ ଶୀଘ୍ରଯାଏ ।
‘ଯତଶ୍ଚ ନିର୍ଦ୍ଧାରଣମ୍’ ଯେଉଁ ସମୁଦାୟ ବା ସମଷ୍ଟିରୁ ଜାତି, ଗୁଣ, କ୍ରିୟା ବା ସଂଜ୍ଞାବାଚକ ଶବ୍ଦଦ୍ୱାରା ଗୋଟିକୁ ପୃଥକ୍ କରାଯାଏ, ସେହି ସମୁଦାୟବୋଧକ ଶବ୍ଦର ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ଓ ସପ୍ତମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ଏହାକୁ ନିର୍ଦ୍ଧାରଣେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ । ଓ ସପ୍ତମୀ କୁହାଯାଏ । ନଦୀମାନଙ୍କ ମଧ୍ୟରୁ ‘ଗଙ୍ଗା’, ପ୍ରାଣୀମାନଙ୍କ ମଧ୍ୟରୁ ‘ନର’ ଓ ଚାଲୁଥିବା ଲୋକମାନଙ୍କ ମଧ୍ୟରୁ ଦୌଡ଼ୁଥିବା ଲୋକକୁ ପୃଥକ୍ କରାଯାଇଥିବାରୁ ନଦୀ, ପ୍ରାଣୀ ଓ ଗଚ୍ଛତ୍ ଶବ୍ଦରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ଓ ସପ୍ତମୀ ହେଲା ।

୧୨। (କ) ଗ୍ରାମସ୍ୟ / ଗ୍ରାମାତ୍ ଦୂରେ ନଦୀ ବହତି । ଗାଁର ଦୂରରେ ନଈ ବହୁଛି ।
(ଖ) ଗୃହସ୍ୟ / ଗୃହାତ୍ ଅନ୍ତିକେ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରମ୍ ଅସ୍ଥି । ଘର ପାଖରେ ଜମି ଅଛି ।
‘ଦୂରାନ୍ତକା ଷଷ୍ୟନ୍ୟତରସ୍ୟାମ୍’ ଦୂର ଓ ସମୀପାର୍ଥକ ଶବ୍ଦଯୋଗରେ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ଓ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । (ଦୂର ଅନ୍ତଃକ ଶବ୍ଦ ଯୋଗେ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ ବେଗେ ।)
୧୩। (କ) ଅଗ୍ଃନି କାଷ୍ଠାନାଂ । କାଷ୍ଠିଃ ନ ତୃପ୍ୟତି । ଅଗ୍ନି କାଠରେ ତୃପ୍ତ ହୁଏ ନାହିଁ ।
(ଖ) ପଥକଃ ଶୀତଳଜଳାନାଂ । ଶୀତଳଜଳେ ତୃପ୍ୟତି । ବାଟୋଇ ଥଣ୍ଡାପାଣିରେ ତୃପ୍ତ ହୁଏ ।
‘ତୃପ୍ରାର୍ଥନାଂ ବିଭାଷାକରଣେ ’ ତୃପ୍ତିର୍ଥକ ପଦଯୋଗରେ କରଣ କାରକଠାରେ ବିକଳ୍ପରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ ।
୧୪। (କ) ବାଳିକା ଜଳସ୍ୟ କୃତେ ଗଛତି । ଝିଅଟି ପାଣିପାଇଁ ଯାଉଛି ।
(ଖ) ତବ କୃତେ କିଂ କରିଷ୍ୟାମି ? ତୁମପାଇଁ କ’ଣ କରିବି ।
‘କୃତେ ପ୍ରୟୋଗେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ’ ନିମିତ୍ତ ଅର୍ଥରେ ‘କୃତେ’ ଶବ୍ଦର ପ୍ରୟୋଗ ହୋଇଥିଲେ, ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ ।
୧୫। (କ) ପିତୁଃ ରୁଦତଃ । ପିତରି ରୁଦ୍ଧତି ପୁନଃ ଅଗଚ୍ଛତ୍ । ବାପା କାନ୍ଦୁଥିବାବେଳେ ପୁଅ ଚାଲିଗଲା
(ଖ) ମମ ପଶ୍ୟତଃ । ମନ୍ଦି ପଶ୍ୟତି କାକଃ ପିଷ୍ଟକମ୍ ଅନୟତ୍ । ମୁଁ ଦେଖୁ ଦେଖୁ କାଉ ପିଠା ନେଇଗଲା ।
‘ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ଚାନାଦରେ ’ଯାହାକୁ ଅବଜ୍ଞା ବା ଅନାଦର କରି କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ କରାଯାଏ, ତାହାଠାରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ କିମ୍ବା ସପ୍ତମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ଏହାକୁ ‘ଅନାଦରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ’ । ସପ୍ତମୀ ବୋଲି କୁହନ୍ତି ।
୧୬। ନିମ୍ନଲିଖୂତ ପଦମାନଙ୍କ ଯୋଗରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ ।
ପୂର୍ବତଃ (ପୂର୍ବରେ )- ଭାରତସ୍ୟ ପୂର୍ବତଃ ଗଙ୍ଗାସାଗରଃ । ଭାରତର ପୂର୍ବରେ ଗଙ୍ଗାସାଗର
ପଶ୍ଚିମତଃ (ପଶ୍ଚିମରେ ) – ଉତ୍କଳସ୍ୟ ପଶ୍ଚିମତଃ ଛତିଶଗଡ଼ । ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ପଶ୍ଚିମରେ ଛତିଶଗଡ଼


ଡାଃ (ଦୁଇଥର) – ଅହଂ ମାସସ୍ୟ ହିଂ ଗ୍ରାମଂ ଗଚ୍ଛାମି । ମୁଁ ମାସକୁ ଦୁଇଥର ଗାଁକୁ ଯାଏ ।
ତ୍ରି (ତିନିଥର) – ମୁନୟ ଦିବସସ୍ୟ ତ୍ରିଂ ସ୍ନାନ୍ତି । ମୁନିମାନେ ଦିନକୁ ତିନିଥର ସ୍ନାନ କରନ୍ତି ।
ଚତୁଃ (ଚାରିଥର ) – ବର୍ଷସ୍ୟ ଚତୁଃ ପୁରୀଂ ଗଚ୍ଛେତ୍ । ବର୍ଷକୁ ଚାରିଥର ପୁରୀ ଯିବା ଦରକାର ।
ପଞ୍ଚକୃତ୍ୱ (ପାଞ୍ଚଥର) – ଶିଶୁ ଦିବସସ୍ୟ ପଞ୍ଚକୃତଃ ଖାଦତି । ପିଲାଟି ଦିନକୁ ୫ଥର ଖାଏ ।
(ଛଅଥର) (ସାତଥର)
(ଏହିପରି ଷଟ୍କୃତ୍ୱ, ସପ୍ତକୃତ୍ୱ ପ୍ରଭୃତି ଯୋଗରେ କାଳାଧ୍ଵରଣରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହେବ ।)
ମନେରଖ :
- ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧବାଚକ ପଦର ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ ।
- ପଠନମ୍, ଗମନମ୍ ପ୍ରଭୃତି ଭାବବାଚକ ପଦ ଯୋଗେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ।
- ପୁରଃ, ପୁରତଃ, ଅଗ୍ରତଃ ଇତ୍ୟାଦି ଯୋଗେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ।
- ଯେଉଁମାନଙ୍କ ମଧ୍ୟରୁ ନିର୍ଦ୍ଧାରଣ – ସମୁଦାୟଠାରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ।
- ଅନାଦରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ।
- ତୁଲ୍ୟ, ସମାନ, ସମ, ସଦୃଶ, ତୁଳା, ଉପମା’ପ୍ରଭୃତି ଯୋଗରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ।
- ହୃଦନ୍ତପଦ ଯୋଗେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ
ଗୀତ :
ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ଅର୍ଥରେ ହୁଅଇ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ସଦା
ସ୍ମର୍ ଦୟ ଲଶ ଧାତୁରେ ହୁଏ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ସର୍ବଦା ।୧।
ହୃଦନ୍ତ ପଦର କର୍ତ୍ତା ଓ କର୍ମେ ହୁଅଇ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ
ବର୍ତ୍ତମାନକାଳ କ୍ତ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟାନ୍ତ କର୍ତ୍ତାରେ ନୀତି । ୨ ।
କୃତ୍ୟ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟାୟନ୍ତ ଯୋଗରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିକଳ୍ପ ହୁଏ
ତୁଲ୍ୟ ସଦୃଶ ସମାନ ଓ ସମେ ସେପରି ଯାଏ । ୩ ।
ତୁଳା ଓ ଉପମା ଯୋଗରେ ହୁଏ କେବଳ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ
କୁଶଳ, ସୁଖ, ଅର୍ଥହିତ ଯୋଗେ ସେହି ବିଭକ୍ତ । ୪।
ଦୂରାର୍ଥକ ସମୀପାର୍ଥକ ଶବ୍ଦ ପଞ୍ଚମୀ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ
ଏନପ୍ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟାନ୍ତ ଯୋଗରେ ତଥ୍ୟର୍ଥରେ ସେ ନୀତି । ୫ ।
କୃତ୍ର, ସୁବ୍, ସୁତ୍, ପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟ ଏବଂ ଅତସ୍ ଆଦି
ଅସି, ଅସ୍ତାତି ପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟାନ୍ତ ପଦେ ହୁଅଇ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ । ୬।

ଅଭ୍ୟାସଃ :
୧। ଉଦାହରଣମ୍ ଅନୁସୃତ୍ୟ ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନାନି ପୂରୟତ ।
ଯଥା – ପୁରାଣସ୍ୟ ଶ୍ରବଣେନ ବୃଦ୍ଧା ଆନନ୍ଦିତ ଭବନ୍ତି । (ପୁରାଣମ୍)
(କ) ____________________ ପଠନେନ ଜ୍ଞାନଂ ବର୍ଷତେ । (ପୁସ୍ତକାନି)
Answer:
ପୁସ୍ତକାନାଂ
(ଖ) ________________________ ଭକ୍ଷଣେନ ସ୍ଵାସ୍ଥ୍ୟ ଭବତି । (ଫଳାନି)
Answer:
ଫଳାନାଂ
(ଗ) _______________________ ଧାରଣେନ ଶୋଭା ବର୍ଷ । (ସ୍ୱଚ୍ଛବସ୍ତ୍ରମ୍ )
Answer:
ସ୍ଵଚ୍ଛବସ୍ତ୍ରସ୍ୟ
(ଘ) _______________________ ରକ୍ଷଣେନ ସମ୍ମାନଃ ଲଭ୍ୟତେ । (ଦେଶଃ)
Answer:
ଦେଶ୍ୟ
(ଙ) _______________________ ପାଳନେନ ତେଷା ସଂରକ୍ଷଣଂ ଭବତି । (ଜୀବା )
Answer:
ଜୀବାନାଂ
(ଚ) _______________________ ଦାନେନ ତସ୍ୟା ବୃଦ୍ଧି ଜାୟତେ । (ବିଦ୍ୟା)
Answer:
ବିଦ୍ୟାୟା
(ଛ) _______________________ ପ୍ରଦାନେନ ପୁଣ୍ୟ ଲଭ୍ୟତେ । (ଧନ)
Answer:
ଧନସ୍ଯ
୨। ଅଧୋଲିଖ୍ୟାତାନାଂ ପଦାନାଂ ସହାୟତୟା ତେଷା ଯୋଗେ ବନ୍ଧନୀସ୍ଥିତଶବ୍ଦାନାଂ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ବିଭକ୍ତିଗତ ରୂପଂ କୃତ୍ୱା ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନାନି ପୂରୟତ ।
(ପୁରତଃ (ଆଗରେ), ଅଧଃ (ତଳେ), ଉତ୍ତରତଃ (ଉତ୍ତରରେ), ଦକ୍ଷିଣତଃ (ଦକ୍ଷିଣରେ), ଅଗ୍ରତଃ (ଆଗରେ), ପୂର୍ବତଃ (ପୂର୍ବଦିଗରେ), ପାଶ୍ଚିମତଃ (ପଶ୍ଚିମରେ))
(କ) ___________________________ _______________________ ଜଗନ୍ନାଥପୁରୀ ଅସ୍ତି । (ମହୋଦଧୂ)
Answer:
ମହୋଦଧଃ ପୂର୍ବତଃ
(ଖ) ___________________________ _______________________ ହିମାଳୟ ବିରାଜତେ । (ଭାରତ)
Answer:
ଭାରତସ୍ୟ ଉତ୍ତରତଃ
(ଗ) ___________________________ _______________________ ଆନ୍ଧ୍ରପ୍ରଦେଶଃ ଅବସ୍ଥିତଃ । (ଉତ୍କଳ)
Answer:
ଉତ୍କଳସ୍ୟ ଦକ୍ଷିଣତଃ
(ଘ) ___________________________ _______________________ ରତ୍ନାନି ସନ୍ତି । (ଭୂମି)
Answer:
ଭୂମେ ଅଧଃ
(ଙ) ___________________________ _______________________ ସେନାପତିଃ ଅସ୍ତ । (ସୈନିକ)
Answer:
ସୈନିକାନାଂ ପୁରତଃ
(ଚ) ___________________________ _______________________ ଦ୍ଵାରକାପୁରୀ ବର୍ତତେ । (ଭାରତବର୍ଷ)
Answer:
ଭାରତବର୍ଷସ୍ୟ ପଶ୍ଚିମତଃ
(ଛ) ___________________________ _______________________ ଶିଶୁ କ୍ରୀଡ଼ତି । (ମାତୃ)
Answer:
ମାତୁଃ ଅଗ୍ରତଃ

୩। ଉଦାହରଣମ୍ ଅନୁସୃତ୍ୟ ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନାନି ପୂରୟତ ।
ଯଥା – ବାଳକାନାଂ ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ ରବି । (ବାଳକ) ବାଳକାନାଂ / ବାଳକେଷୁ
(କ) __________________________ ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ ରାମଃ । (ନୃପତି)
Answer:
ନୃପତୀନାଂ / ନୃପତିଶ୍ରୁ
(ଖ) __________________________ ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ ହନୁମାନ୍ । (ଭକ୍ତି)
Answer:
ଭକ୍ତାନାଂ / ଭକ୍ତେଷୁ
(ଗ) __________________________ ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠା ଦିଲ୍ଲୀ । (ନଗରୀ)
Answer:
ନଗରୀଣାଂ / ପୁଷ୍ପେଷୁ
(ଘ) __________________________ ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ କମଳମ୍ । (ପୁଷ୍ପ)
Answer:
ପୁଷ୍ପାମାଂ / ପୁଖେଷୁ
(ଙ) __________________________ ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ ମୟୂରଃ । (ପକ୍ଷିନ୍)
Answer:
ପକ୍ଷିଣାଂ / ପକ୍ଷିଷୁ
(ଚ) __________________________ ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ ମାଘ । (କାବ୍ୟ)
Answer:
କାବ୍ୟାନାଂ/ କାବ୍ଯଷୁ
(ଛ) __________________________ ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ କାଳିଦାନଃ । (କବି)
Answer:
କବୀନାଂ/କବିଷୁ
୪। ରେଖାଙ୍କିତପଦାନାଂ ସକାରଣଂ ବିଭଣ୍ଡିଂ ନିରୂପୟତ ।
ଯଥା – ବିପଦି ମାତୁଃ ସ୍ମରଣମ୍ ଆପଦ୍ ହରତି । (କୃଦ୍ଯୋଗେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ)
(କ) ହେ ରାମ । ଦରିଦ୍ରାମିଂ ଦୟସ୍ଵ । ( )
Answer:
(ଦୟଧାତୁ ଯୋଗେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ)
(ଖ) ବାଜଃ ମାତୁଃ ସ୍ମରତି । ( )
Answer:
(ସୁ ଧାତୁ ଯୋଗେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ)
(ଗ) କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ରାଣଂ ପ୍ରାଣିନାଂ କୃତେ ଅସତ୍ୟ ମା ବଦ । ( )
Answer:
(କୃତେ ଯୋଗେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ)
(ଘ) ଗ୍ରାମସ୍ୟ ଅନ୍ତଃକମ୍ ଉପବନମ୍ ଅସ୍ଥି। ( )
Answer:
(ଅନ୍ତଃକମ୍ ଯୋଗେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ)
(ଙ) ପରିଶ୍ରମେ ଡଃ ମାତୁଃ ତୁଲ୍ୟ । ( )
Answer:
(ତୁଲ୍ୟ ଯୋଗେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ)
(ଚ) ଅଳ୍ପସ୍ୟ ହେତୋ ମହତଃ ତ୍ୟାଗ ନ କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟଃ । ( )
Answer:
(ହେତୁପ୍ରୟୋଗେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ)
(ଛ) ଶିଶୋ ସ୍ମିତହାସ୍ୟ ପିତ୍ରୋ ଆନନ୍ଦକରମ୍ । ( )
Answer:
(ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ / ଶେଷ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ)
୫। ସଂଶୋଧନଂ କୁରୁତ ।
ଯଥା – ବ୍ୟଜନମ୍ ଅଧଃ ବାଲ୍ୟ ଶେତେ । ଶୁଦ୍ଧ – ବ୍ୟଜନସ୍ୟ । (ବ୍ୟଜନ-ପଙ୍ଖା )
(କ) ମୂଷିକ ମାର୍ଜାରଂ ବିଭେତି ।
Answer:
ମୂଷିକ ମାର୍ଜାରାତ୍ ବିଭେତି ।
(ଖ) ପୁରାଣଂ ଶ୍ରବଣେନ ପୁଣ୍ୟ ଭବତି ।
Answer:
ପୁରାଣସ୍ୟ ଶ୍ରବଣେନ ପୁଣ୍ୟ ।
(ଗ) ବ୍ୟାକରଣଂ ପଠନଂ ଅତୀବ ସହଜମ୍ ।
Answer:
ବ୍ୟାକରଣସ୍ୟ ପଠନମ୍ ଅତୀବ ସହଜମ୍ ।
(ଘ) ପୁତ୍ରେଣ ତୁଳା କଃ ପ୍ରିୟ ?
Answer:
ପୁତ୍ରସ୍ୟ ତୁଳା କଃ ପ୍ରିୟ ?
(ଙ) କାର୍ଯ୍ୟମିଦଂ ତବ ସୁକରମ୍ ।
Answer:
କାର୍ଯ୍ୟମିଦଂ ତ୍ୱୟା ସୁକରମ୍ ।
(ଚ) ସଃ ମାସେ ନିଃ ଚଳଚ୍ଚିତ୍ର ପଶ୍ୟତି ।
Answer:
ଡଃ ମାସସ୍ୟ ତ୍ରିଂ ଚଳଚ୍ଚିତ୍ର ପଶ୍ୟତି ।

୬। ବାକ୍ୟଷୁ ବ୍ୟବହରତ ।
କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟମ୍ , ମତମ୍, ସପ୍ତକୃତ୍ୱ, ନିଃ, ଦକ୍ଷିଣତଃ, ସ୍ମରନ୍ତି, ଅନ୍ତଃକମ୍, ସୁଖମ୍, ଅଧସ୍ତାତ୍, ପୁରଃ.
ଯଥା – ତୁଲ୍ୟ – ରାମେଣ ତୁଲ୍ୟ ରାଜା ନାସ୍ତି । (ରାମ ପରି ରାଜା ନାହାଁନ୍ତି)
କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟମ୍ – ମମ ଇଦଂ କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟମ୍ ।
ମତମ୍ – ଇଦଂ ତବ ମତମ୍ ।
ସପ୍ତକୃତଃ – ଦିବସସ୍ୟ ସପ୍ତକୃତଃ ଶିଶୁ ଖାଦତି ।
ତ୍ରିଃ – ଅହଂ ଦିନସ୍ୟ ତ୍ରିଃ ଖାଦାମି ।
ଦକ୍ଷିଣତଃ – ଗ୍ରାମସ୍ୟ ଦକ୍ଷିଣତଃ ମନ୍ଦିରଂ ଶୋଭତେ ।
ସ୍ମରନ୍ତି – ପୁତ୍ରା ମାତରଂ ସ୍ମରନ୍ତି ।
ଅନ୍ତଃକମ୍ – ମମ ଅନ୍ତଃକମ୍ ଆଗଚ୍ଛ ।
ସୁଖମ୍ – ତବ/ତୁଭ୍ୟ ସୁଙ୍ଖ ଭବତୁ ।
ଅଧସ୍ତୋତ୍ – ଭୁମେ ଅଧସ୍ତୋତ୍ ଜଳମସ୍ତ ।
ପୁନଃ – ଶିକ୍ଷକସ୍ୟ ପୁନଃ ଛାତ୍ରା ପଠନ୍ତି ।
୭। ସଂସ୍କୃତେନ ଅନୁବାଦଃ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ
ଯଥା – ବିପଦରେ ହରିଙ୍କୁ ସ୍ମରଣ କର ।
(କ) ଶିଶୁଟି ଦିନରେ ଛଅଥର ଦୁଧ ପିଏ ।
ଅନୁ – ବିପଦି ହରଃ ସ୍ମର ।
(ଖ) ବନ୍ଧୁଙ୍କର ଉପଦେଶ ତୁମର ଶୁଣିବା ଉଚିତ ।
ଅନୁ – ମିତ୍ରସ୍ୟ ଉପଦେଶଃ ତବ ଶ୍ରୋତବ୍ୟ ।
(ଗ) କ୍ଷମା ସମାନ ଗୁଣ ନାହିଁ ।
ଅନୁ – କ୍ଷମାୟା ସମଃ ଗୁଣୋ ନାସ୍ତି ।
(ଘ) ତୃଷାର୍ଥ ଥଣ୍ଡାପାଣିରେ ତୃପ୍ତ ହୁଏ ।
ଅନୁ – ତୃଷାର୍ଥୀ ଶୀତଳଜଳେନ ତୃପ୍ୟତି/ତୃସ୍ତୋ ଭବତି
(ଙ) ଧନ ହେତୁ ଗର୍ବ କରିବା ଉଚିତ ନୁହେଁ ।
ଅନୁ – ଧନସ୍ୟ ହେତୋ ଗର୍ବ ନ କରଣୀୟମ୍ ।
(ଚ) ବାରବାଟୀ ଦୁର୍ଗ ଆଗରେ ବିଶାଳ ଖେଳପଡ଼ିଆ ଅଛି ।
ଅନୁ – ବାରବାଟୀଦୁର୍ଗସ୍ୟ ପୁରସ୍ତାତ୍ୱ ବିଶାଳଂ କ୍ରୀଡାପ୍ରାନ୍ତରଂ ବର୍ଷତେ ।
(ଛ) ତୁମର ସେଠାକୁ ଯିବା ଉଚିତ ନୁହେଁ ।
ଅନୁ – ତବ ତତ୍ର ନ ଗନ୍ତବ୍ୟମ / ଗମନୀୟମ୍ ।
(ଜ) ବ୍ରାହ୍ମଣ ଦେବତାଙ୍କୁ ପୂଜା କରନ୍ତି ।
ଅନୁ – ବ୍ରାହ୍ମଣୀ ଦେବାନାଂ ପୂଜା କୁର୍ବନ୍ତି ।
(ଝ) ମନ୍ଦିର ଆଗରେ କଦମ୍ବଗଛ ଅଛି ।
ଅନୁ – ମନ୍ଦିରସ୍ୟ ପୁରତଃ କଦମ୍ବ ରାଜତେ ।
ଅଧୂରଣ କାରକ ଓ ସପ୍ତମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି
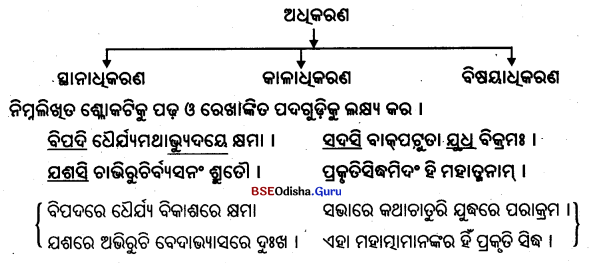
ଉପରିଲିଖ୍ତ ଶ୍ଳୋକଟିର ରେଖାଙ୍କିତ ପଦଗୁଡ଼ିକ ସପ୍ତମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତିରେ ରହିଛି ।
୧। ବର୍ତ୍ତମାନ ନିମ୍ନଲିଖ୍ତ ବାକ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକୁ ପଢ଼ ।
(କ) କୃଷକାଃ ଗ୍ରାମେ ବସନ୍ତି । ( ଚାଷି ଗାଁରେ ବାସକରନ୍ତି)
(ଖ) ବସନ୍ତେ ସକଳଂ ରମ୍ୟଂ ଭବତି । ( ବସନ୍ତରତୁରେ ସବୁ ସୁନ୍ଦର)
(ଗ) ରାଧାନାଥଃ ସଂସ୍ବତେ ନିପୁଣଃ ଆସୀତ୍ । ( ରାଧାନାଥ ସଂସ୍କୃତରେ ନିପୁଣ ଥ୍ଲେ)

ଆଧାରୋଽଧ୍କଜଳଣ/ନନ ‘ ଉପରିଲିଖ୍ତ ଉଦାହରଣ ବାକ୍ୟଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ‘ବସନ୍ତିଂ, “ଭବତି” ଓ ‘ ଆସୀତୃ’ କ୍ରିୟାପଦ ଅଟନ୍ତି । ଏଠାରେ କ୍ରିୟାପଦଗୁଡ଼ିକର “ଅଧାର” ଭାବେ ଯଥାକ୍ରମେ ‘ଗ୍ରାମ’, “ବସନ୍ତେଂ ଓ “ସଂସ୍ତତ’ ଏମାନେ କ୍ରିୟାର ଆଧାର ଏବଂ ଅଧ୍କରଣ କାରକ କୁହାଯାଏ । “ ସପ୍ତମ୍ୟେଧ୍କରଣେ” ତେଣୁ ‘ଗ୍ରାମ’, “ବସନ୍ତ’ ଓ ‘ସଂସ୍ତତ’ ଏମାନେ କ୍ରିୟାର ଆଧାର ଏବଂ ଅଧ୍କରଣ କାରକ ଅଟନ୍ତି । ଅଧ୍କରଣ କାରକରେ ସପ୍ତମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ଏହାକୁ ଅଧ୍କରଣେ ସପ୍ତମୀ ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ । ପୁନଶ୍ଚ “ଆଧାର” ସାଧାରଣତଃ ତିନିପ୍ରକାର । ତେଣୁ ଅଧ୍କରଣ ତିନିପ୍ରକାର ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଯଥା-ସ୍ଥାନାଧ୍କରଣ, କାଳାଧ୍କରଣ ଓ ବିଷୟାଧ୍କରଣ । ଉପର୍ଯୁକ୍ତ ଉଦାହରଣରେ ‘ ଗ୍ରାମ” ସ୍ଥାନକୁ ବସନ୍ତ ସମୟକୁ ଏବଂ ସଂସ୍କୃତ ବିଷୟକୁ ବୁଝାଉଥ୍ବାରୁ ଏମାନେ ଯଥାକ୍ରମେ ସ୍ଥାନାଧ୍କରଣ, କାଳାଧ୍କରଣ ଓ ବିଷୟାଧ୍କରଣ ହୋଇଥାନ୍ତି ।
୨ । (କ) ଶିକ୍ଷକେ ଆଗତେ ଛାତ୍ରାଃ ଉରିଷ୍ପନ୍ତି । ( ଶିକ୍ଷକ ଆସନ୍ତେ ଛାତ୍ରମାନେ ଠିଆ ହୁଅନ୍ତି ।)
((ଖ) ରାମେ ଗତେ ଦଶରଥଃ ମୃତଃ | ( ରାମ ଚାଲିଯିବାରୁ ଦଶରଥ ପ୍ରାଣତ୍ୟାଗ କଲେ ।)
(ଗ) ଅସୁରେଷୁ ପରାସ୍ତେଷ୍ଣୁ ସୁରାଃ ଆନହିତାଃ ଅଭବନ୍ନ । ( ଅସୁରମାନେ ପରାସ୍ତ ହେବାରୁ ଦେବତାମାନେ ଖୁସି ହେଲେ)
ଏସସ୍ଯ ଚ ଭାବେନ ଭାବଲକ୍ଷଣମ୍ ଯେଉଁ ଭାବ ବା କ୍ରିୟାଦ୍ଵାରା ପରବର୍ଭୀ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟର ସୂଚନା ମିଳେ, ସେହି ପୂର୍ବୋକ୍ତ ଭାବବାଚୀ ଶବ୍ଦରେ ସପ୍ତମୀ ବିଭଲ୍ଛି ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଏଠାରେ ଶିକ୍ଷକଙ୍କ ଆସିବା କ୍ରିୟାଦ୍ବାରା ଛାତ୍ରମାନଙ୍କର ଉଠିବା କ୍ରିୟା, ରାମଙ୍କ ଗମନ କ୍ରିୟାଦ୍ଵାରା ଦଶରଥଙ୍କ ମରଣ କ୍ରିୟା ଏବଂ ଅସୁରମାନଙ୍କର ପରାସ୍ତ ହେବା କ୍ରିୟାଦ୍ଵାରା ଦେବତାଙ୍କ ଆନନ୍ଦ ହେବା କ୍ରିୟା ଲକ୍ଷ୍ୟ କରାଯାଉଛି ।
ତେଣୁ ସମାପିକା କ୍ରିୟାଗୁଡ଼ିକର କାଳ ଯେଉଁ ଯେଉଁ କ୍ରିୟାଦ୍ଵାରା ସୂଚିତ ହେଲା ତାଂଠାରେ ସପ୍ତମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି । ଏହାକୁ “ ଭାବେ ସପ୍ତମୀ? କୁହାଯାଏ । “ଭାବ” ଅର୍ଥ କ୍ରିୟା । ଭାବେ ସପ୍ତମୀରେ ଗୋଟିଏ ପଦ “ବିଶେଷ୍ଯ” କିମ୍ବା “ ସର୍ବନାମ” ଅନ୍ୟ କୃଦନ୍ତ ପଦଟି ‹ ବିଶେଷଣ” ହୁଏ । ଏଣୁ ସପ୍ତମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ଉଭୟତ୍ର ଦେଖାଯାଏ । ତେଣୁ ‘ ଶିକ୍ଷକେ ଆଗେତ, “ରାମେ ଗତେ” ଓ ‘ଅସୁରେଷୁ ପରାସ୍େେଷୁ! ପ୍ରଭୃତି କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ସପ୍ତମୀ ବିଭଚି ହେଲା ।
୩। (କ) ଚର୍ମଣି ଦ୍ବିପିନଂ ହନି । ( ଚମଡ଼ାପାଇଁ ବାଘକୁ ମାରନ୍ତି)
( ଖ) ଦନ୍ତୟୋଃ ହନି କୁଞ୍ଜରମ୍ । ( ଦାନ୍ତନିମନ୍ତେ ହାତୀକୁ ମାରନ୍ତି)
(ଗ) ରାଜା ଯଶସେ ବ୍ଯାଘୁଂ ହନ୍ତି । ( ରାଜାଯଶପାଇଁ ବାଘକୁ ମାରନ୍ତି)
ଲିନ୍ହ/ଚ କର୍ନେୋଶରୋଂ ନିମିର ବା ଫଳର ଯଦି ଅବୟବାବୟବ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧରେ ( ଅଙ୍ଗାଙ୍ଗୀ) ଯୋଗ ହୋଇଥାଏ, ସେହି ନିମିତ୍ତ ବା ଫଳକୁ ବୁଝାଉଥ୍ବା ଶବ୍ଦର ସପ୍ତମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ଉପର୍ଯ୍ୟୁକ୍ତ “କ” ଓ “ଖ” ବାକ୍ୟରେ “ଚର୍ମ” ଓ ‘ଦନ୍ତ’, ନିମିଭ୍ବୋଧକ ଓ ଅବୟବ ( ଅଙ୍ଗ) ବାଚକ । ତେଣୁ ସେଠାରେ ସପ୍ତମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହେଲା । ଏହାକୁ ‘ ନିମିରାତ୍ବ କର୍ମଯୋଗେ ସପ୍ତମୀ” ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଏ । କିନ୍ତୁ ଯେଉଁଠାରେ ନିମିତ୍ତ ବା ଫଳର କର୍ମ ସହିତ ସଂଯୋଗ ସମ୍ବନ୍ଧ ନ ଥାଏ, ସେଠାରେ ସପ୍ତମୀ ହୁଏ ନାହିଁ । “ଗ” ବାକ୍ୟରେ “ଯଶଃ ଲବ୍ଧୁମ୍’, ଏହି ଅର୍ଥରେ କ୍ରିୟାର୍ଥୋପପଦ ଇତ୍ୟାଦି ସୂତ୍ରରେ “ ତୁମୁନ’ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟୟାନ୍ତ ପଦ ଲୋପ ହୋଇ ତାହାର କର୍ମରେ ଚତୁର୍ଥୀ ବିଭସ୍ତି ହୋଇଛି । “
୪। (କ) ଅନ୍ଧଂ କରେ ଧୃତ୍ବା ନୟ । ଅନ୍ଧଟିକୁ ହାତ ଧରି ନିଅ ।
(ଖ) କମପି ମସ୍ତକେ ମା ତାଡ଼ୟ । କାହାରି ମୁଣ୍ଡରେ ମାଡ଼ଦିଅ ନାହିଁ ।
( ଗ) ଛାତ୍ରଂ କର୍ଣ୍ଣେ ଧୃତ୍କା ଆନୟ । ଛାତ୍ରଟିକୁ କାନ ଧରି ଆଣ ।
ଏନ ଥବଣମଣଦ । ଶରୀରର କୌଣସି ଅଂଶକୁ ପୃଥକ୍ ଭାବରେ ଗ୍ରହଣ କରିବା ବୁଝାଇଲେ, ସେହି ଅଂଶବାଚକ ଶବ୍ଦର ଦ୍ବିତୀୟା ନ ହୋଇ ସପ୍ତମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ଏହାକୁ ଅବଚ୍ଛେଦେ ସପ୍ତମୀ କୁହାଯାଏ । ଅବଚ୍ଛେଦ ଶରୀରର ଅଂଶବିଶେଷ । ଉପର ଉଦାହରଣଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ କର, ମସ୍ତକ ଓ କର୍ଣ୍ଣ ପ୍ରଭୂତି ଶରୀରର ଗୋଟିଏ ଗୋଟିଏ ଅଂଶ ହୋଇଥ୍ବାରୁ ସେଗୁଡ଼ିକର ସପ୍ତମୀ ବିଭଲ୍ତି ହେଲା ।
୫। (କ) (ଏକ) ଗବାଂ / ଗୋଷୁ ସ୍ଵାମୀ । ( ଗୋରୁମାନଙ୍କ ସ୍ଵାମୀ / ପୃଥ୍ବୀର ସ୍ବାମୀ)
(ଖ) ନରାଣାଂ / ନରେଷୁ ଭଶ୍ଵରଃ/ ଅଧ୍ପତିଃ | ( ଲୋକମାନଙ୍କ ମଧରେ ଅଧ୍ପତି)
(ଗ) ବିବାଦସ୍ଯ / ବିବାଦେ ସାକ୍ଷୀ । ( ଝଗଡ଼ାରେ ସାକ୍ଷୀ)
(ଘ) ବ୍ୟବହାରସ୍ୟ / ବ୍ଯବହାରେ ପ୍ରତିଭୂଃ । ( ବିଚାର ବ୍ୟବସ୍ଥାରେ ମଧ୍ପସ୍ଥି/ ଜାମିନ)
(ଝ) କୁଳସ୍ଯ / କୁଳେ ଦାୟାଦଃ । ( ବଂଶର / ବଂଶରେ ଭଭରାଧ୍କାରୀ)
ସ୍ୱାମୀଶ୍ୱରାଧ୍ପତିଦାୟାଦସାକ୍ଷିପ୍ରତିଭପ୍ରସୂତୈଶ୍ମ ସାମୀ, ଭଶ୍ବର, ଅଧ୍ପତି, ସାୟ୍ଷିନ, ପ୍ରତିଭୁଃ ( ଜାମିନ / ମଧସି): ଦାୟାଦ ପ୍ରଭୃତି ଶବ୍ଦ ଯୋଗରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ଓ ସପ୍ତମୀ ବିଭଚ୍ତି ହୁଏ । ସ୍ଵାମୀ, ଭଶ୍ନର ଓ ଅଧ୍ପତି ଶଦ୍ଦ ବ୍ୟତୀତ ସ୍ଵାମୀଅର୍ଥକ ଅନ୍ୟ ଶବ୍ଦଯୋଗରେ ସପ୍ତମୀ ହେବ ନାହିଁ । ଯଥା –
(ଚ) ନରାଣାମ୍ ଭଶଃ / ପ୍ରଭୁଃ । ( ଲୋକମାନଙ୍କ ମଧ୍ଯରେ ଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ)
(ଏଠାରେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ହେଲା, ନରେଷୁ ହେବ ନାହିଁ)
୬। (କ) (ଏକ) ଶ୍ରୀକୃଷ୍ଣଃ ବଂଶୀବାଦନେ କୁଶଳଃ / ଦକ୍ଷଃ । ( ଶ୍ରୀ କୃଷ୍ଣ ଦଂଶୀବଜାଇବାରେ କୁଶଳୀ)
(ଖ) ମାତା ପାଚନେ ନିପୁଣା / ପ୍ରବୀଣା । ( ମାଆ ରୋଷେଇରେ ନିପୁଣ)
(ଗ) ଶ୍ରମିକଃ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟେ ବ୍ୟାପୃତଃ / ଲଗ୍ନଃ / ତତ୍ପରଃ । ( ଶ୍ରମିକଟି କାମରେ ଲାଗିଛି)
(ଘ) ଅନୁରାଧା ଧାବନେ ପଟୁଃ ।( ଅନୁରାଧା ଧାଇଁବାର ଧୂରନ୍ଧର)
ନିଯୁଣ/ଜ//ମରାୟ/* ସ9ନ୍#୭/ ^ ବ୍ୟାପୃତ, ଲଗ୍ନ, ତତୃପର, କୁଶଳ, ନିପୁଣ, ଦକ୍ଷ, ପଟୁ, ପ୍ରବୀଣ
ପ୍ରଭୂତି ଶବ୍ଦଯୋଗରେ ସପ୍ତମୀ ବିଭଳ୍ତି ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
୭। (କ) ମନୁଷ୍ୟଃ ମନୁଷ୍ୟେ ବିଶ୍ଵସେତ୍ବ । ( ମଣିଷ ମଣିଷକୁ ବିଶ୍ଵାସ କରିବା ଉଚିତ)
(ଖ) ମାତା ପୁତ୍ରେ ସ୍ଵିହ୍ଯତି । ( ମାଆ ପୁଅକୁ ଭଲପାଏ)
(ଗ) ଗୂରୌ ଶିଷ୍ୟାଃ ଅନୁରକ୍ତାଃ । ( ଶିଷ୍ୟମାନେ ଗୁରୁଙ୍କ ଉପରେ ବିରକ୍ତ)
(ଘ) ପିତା ମୟି ବିରକଃ ଜାତଃ । ( ବାପା ମୋ ଭପରେ ବିରକ୍ତ ହେଲେ)
(ଙ) ଅହଂ ଶିକ୍ଷକେ ଭକ୍ଂ କରୋମି । ( ମୁଁ ଶିକ୍ଷକକୁ ଭଲି କରେ)
(ଚ) ବାୟୁଯାନସ୍ଯ- ଆରୋହଣେ ତସ୍ୟ ଅଭିଳାଷଃ | ( ଉଡ଼ାଜାହାଜ ଚଢ଼ିବାରେ ତା’ର ଇଛା)
ବିଶ୍ଵାସ, ସ୍ନେହ, ଅନୁରକ୍, ବିରଚି, ଭଚି, ଅଭିଳାଷ ପ୍ରଭୃତି ଅର୍ଥ ବିଶିଷି ପଦଯୋଗରେ ଯାହାଠାରେ ବିଶ୍ବାସ ପ୍ରଭୃତି କରାଯାଏ, ତା’ଠାରେ ସପ୍ରମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ ।
୮। (କ) ଏତତ୍ କଥଂ ମୟି ସମ୍ଭାବ୍ୟତେ ? ( ଏହା କିପରି ମୋ ପାଖରେ ସମ୍ଭବ)
(ଖ) ଅଯୋଧ୍ଯାୟାଃ ନୃପତ୍ସଂ ରାମେ ଯୁଜ୍ୟତେ । ( ଅଯୋଧ୍ୟାର ରାଜା ହେବାକୁ ରାମ ସମର୍ଥ)
(ଗ) ଏତତ୍ ତ୍ଵୟି ନ ଉପପଦ୍ୟତେ । ( ଏହା ତୁମଠାରେ ସମ୍ଭାବନା ନାହିଁ)
ସମ୍ଭାବ୍ୟତେ, ଯୁଜ୍ୟତେ ଉପପଦ୍ୟତେ ଯୋଗରେ ଯାହାଠାରେ ଯୋଗ୍ୟତା, ସମ୍ଭାବନା ଇତ୍ୟାଦି ବୁଝାଇଥାଏ ତାଠାରେ ସପ୍ତମୀ ବିଭକ୍ତି ହୁଏ ।

ମନେରଖ:
- କ୍ରିୟାର ଆଧାର ଅଧ୍କରଣ ।
- ସ୍ଥାନାଧ୍କରଣ, କାଳାଧ୍କରଣ, ବିଷୟାଧ୍କରଣ ।
- ନିମିତ୍ତ କର୍ମସଂଯୋଗ ହେଲେ ସପ୍ତମୀ ହୁଏ ।
- ସପ୍ତମୀ ଅବଚ୍ଛେଦେ ।
- ସ୍ଵାମୀ, ଭଶ୍ବର, ଅଧ୍ପତି, ସାକ୍ଷିନ୍ ପ୍ଭୂତି ଶନ୍ଦଯୋଗେ ଷଷ୍ଠୀ ଓ ସପ୍ମୀ ।
- କୌଣସି ଏକ କ୍ରିୟାର ସମାଷ୍ତିରେ, ଅନ୍ୟ କ୍ରିୟାର ଆରମ୍ଭ ହେଲେ, ସମାପ୍ତ କ୍ରିୟା ଓ କର୍ତାରେ ସପ୍ତମୀ ।
- କୁଶଳ, ନିପୁଣ, ଦକ୍ଷ, ପଟୁ ପ୍ରଭୃତି ଶବ୍ଦ ବା କ୍ରିୟା ଯୋଗେ ସପ୍ତମୀ ।
- ବିଶ୍ଵାସ, ସ୍ନେହ, ଅନୁରଳି, ବିରକି ପ୍ରଭୁତି ଶବ୍ଦ ବା କ୍ରିୟା ଯୋଗେ ସପମୀ ।
- ସମ୍ଭାବ୍ୟତେ, ଯୁଜ୍ଯତେ ଓ ଉପପଦ୍ୟତେ କ୍ରିୟାଯୋଗେ ସପ୍ତମୀ ।
ଗୀତ :
ସପ୍ତମୀ ଅଧୂରଣରେ
ଭାବେ ସପ୍ତମୀ ଅନାଦରେ । ୧ ।
ସ୍ବାମୀ ଈଶ୍ୱର ଯୋଗେ ଯାହା
ନିର୍ଦ୍ଧାରଣରେ ହୁଏ ତାହା । ୨ ।
ଅଙ୍ଗାଙ୍ଗୀଭାବେ ଯଦି ଥିବ
ନିମିତ୍ତର ସପ୍ତମୀ ହେବ । ୩।
ସାଧୁ ଓ ଅସାଧୁ ଯୋଗରେ
ସପ୍ତମୀ ହୁଏ ନିଶ୍ଚିତରେ । ୪ ।
ବିଶ୍ବାସ ସ୍ନେହ ଅନରାଗ
ଭକ୍ତି ଯୋଗେ ସପ୍ତମୀ ଆଗ । ୫ ।
ଯୁଜ୍ୟତେ ସମ୍ଭାବ୍ୟତେ ଥିଲେ
ସପ୍ତମୀ ହୁଏ କାଳେ କାଳେ । ୬ ।
ବିଭକ୍ତିର ନିୟମମାନ
ମନେରଖ ହେ ଛାତ୍ରଛାତ୍ରୀଗଣ । ୭।
ଅଭ୍ୟାସଃ :
୧। ନିମ୍ନଲିଖ୍ତଶ୍ଳୋକେଷୁ ସପ୍ତମ୍ୟନ୍ତପଦାନି ରେଖାଙ୍କିତାନି କୁରୁତ ।
(କ) ଶୈଳେ ଶୈଳେ ନ ମାଣିକ୍ୟଂ ମୌକ୍ତିକଂ ନ ଗଜେ ଗଜେ ।
ଉତ୍ତର ସାଧବୋ ନ ହି ସର୍ବତ୍ର ଚନ୍ଦନଂ ନ ବ୍ରନେ ବନେ ॥
Answer:
(କ) ଶୈଳେ ଶୈଳେ,ଗଜେ ଗଜେ,ବନେ ବନେ
(ଖ) ମନ୍ତ୍ର ତୀର୍ଥେ ଦ୍ଦିଜେ ଦେବେ ଦୈବଞ୍ଚେ ଭେଷଜ୍ରେ ଗୁରୌ ॥
ଯାଦୃଶୀ ଭାବନା ଯସ୍ୟ ସିଦ୍ଧିଃ ଭବତି ତାଦୃଶୀ ॥
Answer:
( ଖ) ମନ୍ତ୍ରେ ତୀର୍ଥେ ଦ୍ବିଜେ ଦେବେ ଦୈବଜ୍ଞେ ଭେଷଜେ ଗୁରୌ ।
(ଗ) ବ୍ରୁହୂଘ୍ରେ ଚ ସୁରାପେ ଚ ଚୌର୍ରେ ଭଗୁବ୍ରତେ ଶଠେ ।
ନିଷ୍କୃତିଃ ବିହିତା ସଭିଃ କୂତଘ୍ରେ ନାସ୍ତି ନିଷ୍କୃତିଃ ॥
Answer:
(ଗ) ବ୍ରହ୍ମଘ୍ନେ ସୁରାପେ ଚୌରେ ଉଗ୍ନବ୍ରତେ ଶ କୃତଘ୍ନେ ।
(ଘ) ମାତୃବତ୍ଵ ପରଦାରେଷ୍ଟ୍ ପରଦ୍ରବ୍ୟେଷୁ ଲୋଷ୍ଟବତ୍ର ।
ଆତ୍ମବତଵ ସର୍ବଭୂତେଷୁ ଯଃ ପଶ୍ୟତି ସ ପଣ୍ଡିତଃ ॥
Answer:
(ଘ) ପରଦାରେଷୁ ପରଦବ୍ୟେଷୁ ସର୍ବଭୂତେଷୁ
୨। ଉଦାହରଣମନୁସୃତ୍ୟ ବାକ୍ୟାନି ପୂରୟତ ।
ଯଥା – ପିତା ସ୍ନିହ୍ୟତି । ( ପୁତ୍ର ଉତ୍ତର – ପିତା ପୁତ୍ରେ ସ୍ନିହ୍ଯତି ।
(କ) ଦଶରଥଃ ____________________ ଅଧ୍କଂ ସ୍ନିହ୍ଯତି ସ୍ମ । (କୈକେୟୀ )
Answer:
କୈକେୟ୍ୟାମ୍
(ଖ) କୋଏପି ____________________ ନ ବିଶ୍ଵସେତ୍ । ( ଅବିଶ୍ବସ୍ତ)
Answer:
ଅବିଶ୍ବସ୍ତ
(ଗ) ଶିକ୍ଷକଃ ____________________ ବିରକ୍ତଃ ଜାତଃ । ( ଛାତ୍ର)
Answer:
ଛାତ୍ରେ
(ଘ) ଅହଂ ____________________ ନିତରାମ୍ ଅନୁରକ୍ତଃ । ( ଯୁଷ୍ଦ୍ )
Answer:
କ୍ଷୁଷ୍ମାସୁ
(ଙ) ଛାତ୍ରାଃ ____________________ ଭକ୍ତିଂ କୁର୍ବନ୍ତି । ( ସରସ୍ବତୀ)
Answer:
ସରସ୍ଵତ୍ୟାଂ
୩। ଉଦାହରଣାନୁସାରଂ ବାକ୍ୟାନି ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନେ ଲିଖତ ।
ଯଥା – ଭୀମଃ ରାକ୍ଷସଂ ଶିରସି ଅତାଡ଼ୟତ୍ । ( ଶିରସ୍ )
(କ) ଆରକ୍ଷୀ ଚୌରଂ ____________________ ଗୃହୀତବାନ୍ । ( ହସ)
Answer:
ହସ୍ତେ
(ଖ) କମପି ____________________ ନ ତାଡ଼ୟିତବ୍ୟମ୍ । ( ଉଦର )
Answer:
ଉଦରେ

(ଗ) ରାବଣଃ ଜଟାୟୁଂ ____________________ ପ୍ରହୃତବାନ୍ । ( ପକ୍ଷ)
Answer:
ପକ୍ଷେ
(ଘ) ବାଳକଃ ବାଳକଂ ____________________ ଗୃହୀତ୍ବାନ୍ | ( କେଶ)
Answer:
କେଶେଷୁ
(ଡ) ଅନ୍ଧଂ ____________________ ଧୃତ୍ଵା ଆନୟ । ( ହସ୍ତ)
Answer:
ହସ୍ତେ
୪। ନିମ୍ନଲିଖ୍ତପଦାନି ବ୍ୟବହୃତ୍ୟ ସ୍ଵଦିନଚର୍ଯ୍ୟାଂ ଲିଖତ ।
ପ୍ରାତଃକାଳେ, ସାର୍ଦସପ୍ତବାଦନେ, ଦଶବାଦନେ, ଏକବାଦନେ, ସାୟଂକାଳେ, ସାୟଂସପବାଦନେ, ରାତ୍ରୈ
ଦଶବାଦନେ
ଯଥା – ପ୍ରାତଃକାଳେ – ପ୍ରାତଃକାଳେ ଅହଂ ଷଡ଼୍ବାଦନେ ଶଯ୍ୟାତ୍ୟାଗଂ କରୋମି ।
ସାର୍ଦ୍ବସପ୍ତବାଦନେ ସାର୍ଵସପ୍ତବାଦନେ ଅଳ୍ପାହାରଂ ସ୍ଵୀକରୋମି ।
ଦଶବାଦନେ – ଦଶବାଦନେ ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟଂ ଗଚ୍ଛାମି ।
ଏକବାଦନେ – ଏକବାଦନେ ଭୋଜନଂ କରୋମି ।
ସାୟଂକାଳେ – ସାୟଂକାଳେ ପ୍ରାର୍ଥନାଂ କରୋମି ।
ସାୟଂସପ୍ତବାଦନେ – ସାୟଂ ସପ୍ତବାଦନେ ପାଠଂ କରୋମି ।
ରାତ୍ରୈ ଦଶବାଦନେ – ରାତ୍ରୌ ଦଶବାଦନେ ଶୟନଂ କରୋମି
୫। କୋଷ୍ଠକସ୍ଥିତଶବ୍ଦାନାମ୍ ଉପଯୁକ୍ତରୂପୈଃ ଶୂନ୍ଯସ୍ଥାନଂ ପୂରୟତ ।
(କ) ମମ ବନ୍ଧୁଃ ______________________ ନିପୁଣଃ। ( କୀଡ଼ା)
Answer:
କ୍ରୀଡ଼ାୟାଂ
(ଖ) ଶ୍ରୀକୃଷ୍ଣଃ ______________________ ଦକ୍ଷଃ । ( ବଂଶୀବାଦନ )
Answer:
ବଂଶୀବାଦନେ
(ଗ) ଅସ୍ମାକଂ ଶିକ୍ଷକଃ ______________________ ପଟୁଃ । (ଗଣିତ)
Answer:
ଗଣିତେ
(ଘ) ଅନୁରାଧା ______________________ ପ୍ରବୀଣା । ( ଶ୍ଳୋକପଠନ )
Answer:
ଶ୍ଳୋକପଠନେ
(ଙ) ମମ ଅନୁଜଃ ______________________ ଲଗ୍ନଃ । (ରାଜନୀତି )
Answer:
ରାଜନୀତୌ
୬। ରେଖାକ୍କିତପଦାନାଂ ସକାରଣବିଭକ୍ତିଂ ନିରୂପୟତ ।
(କ) ଛାତ୍ରାଃ ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟେ ପଠ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଅଧ୍କରଣେ ସପ୍ତମୀ
(ଖ) ଚୌର୍ଯ୍ୟଂ ମୟି ନ ସମ୍ଭାବ୍ୟତେ ।
Answer:
ସମ୍ଭାବ୍ୟତେ ପଦଯୋଗେ ସପ୍ତମୀ
(ଗ) ମହାତ୍ମା ରାଜନୀତୌ ନିପୁଣଃ ଆସୀତ୍ ।
Answer:
ନିପୁଣ ଶବ୍ଦଯୋଗେ ସପ୍ତମୀ
(ଘ) କେଶେଷ ଚମରୀଂ ହନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ନିମିତ୍ତାତ୍ କର୍ମଯୋଗେ ସପ୍ତମୀ
(ଙ) ଧେନବଃ ବସ୍ପାସୁ ସ୍ନିହ୍ୟନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ସ୍ନିହ୍ୟନ୍ତି କ୍ରିୟା ପଦ ଯୋଗେ ସପ୍ତମୀ

(ଚ) ବାଳକେ ନିଦ୍ରିତେ ମାତା ଗମିଷ୍ୟତି ।
Answer:
ଭାବେ ସପ୍ତମୀ
(ଛ) ପିତରି ମାତରି ଚ ଭୂଚିଂ କୁରୁ ।
Answer:
ଭକ୍ତି ପଦଯୋଗେ ସପ୍ତମୀ
(ଜ) କୃଷଃ ମାତରି ସାଧୁଃ, ମାତୁଳେ ଅସାଧୁଃ ।
Answer:
ସାଧୁଃ ଆସାଧୁଃ ଶବ୍ଦଯୋଗେ ସପ୍ତମୀ
୭। ଭ୍ରମସଂଶୋଧନଂ କୁରୁତ ।
ଯଥା – ନଦୀଭ୍ୟଃ ଗଙ୍ଗା ପବିତ୍ରତମା।
ଭ – ନଦୀଷୁ/ ନଦୀନାଂ
(କ) କଥଂ ମାଂ ନ ବିଶ୍ବସିଷି ?
Answer:
କଥଂ ମୟି ନ ବିଶ୍ବସିଷି ?
(ଖ) ଜନନୀ ପୁତ୍ାୟ ସ୍ନିହ୍ଯତି ।
Answer:
ଜନନୀ ପୁତ୍ରେ ସ୍ନିହ୍ୟତି ।
(ଗ) ହସ୍ତଂ ଧୃତ୍ଵା କ୍ଷମାଂ ଯାଚିତବାନ୍ ।
Answer:
ହସ୍ତେ ଧୃତ୍ଵା କ୍ଷମାଂ ଯାଚିତବାନ୍ ।
(ଘ) ପ୍ରଭୁଃ ସେବକାୟ ଅନୁରକ୍ତଃ ଭବତି ।
Answer:
ପ୍ରଭୁଃ ସେବକେ ଅନୁରକ୍ତଃ ଭବତି ।
(ଡ) ଶ୍ରବଣକୁମାରଃ ମାତରଂ ସାଧୁଃ ଆସୀତ୍ ।
Answer:
ଶ୍ରବଣକୁମାରଃ ମାତରି ସାଧୁଃ ଆସୀତ୍ ॥
(ଚ) ସର୍ବେଷାଂ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟାଣାଂ ସଃ ତତୃପରଃ ।
Answer:
ସର୍ବେଷୁ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟେଷୁ ସଃ ତତ୍ନପରଃ ।
(ଛ) ଏବ ତବ ଅଧ୍କାରଃ ।
Answer:
କର୍ମଣି ଏବ ତବ ଅଧ୍କାରଃ।
୮। ସଂସ୍କୃତେନ ଅନୁବାଦଃ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟଃ ।
(କ) ନଭରେ ମାଛଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଆନନ୍ଦରେ ପହଁରୁଛନ୍ତି ।
ଅନୁ – ନଦ୍ୟାଂ ମତ୍ସ୍ୟାଃ ଆନନ୍ଦେନ ସନ୍ତରନ୍ତି ।
(ଖ) ବର୍ଷାକାଳରେ ମୟୂରଗୁଡ଼ିକ ନୁତ୍ୟ କରନ୍ତି ।
ଅନୁ – ବର୍ଷାସୁ ମୟୂରାଃ ନୃତ୍ୟନ୍ତି ।
(ଗ) ବୃଦ୍ଧଲୋକଟିକୁ ହାତ ଧରି ନିଅ ।
ଅନୁ – ବୃ୍ଧଂ କରେ ଧୃତ୍ବା ନୟ ।
(ଘ) ମୋର ମନ ଗଣିତରେ ରହୁ ନାହିଁ ।
ଅନୁ – ମମ ମନଃ ଗଣିତମ୍ ନାଭିନିବିଶତେ ।
(ଙ) ଗୋବିନ୍ଦ ରାମକୁ ଭାଇ ଭଳି ସ୍ନେହ କରେ ।
ଅନୁ – ଗୋବିନ୍ଦଃ ରାମେ ଭ୍ରାତା ଇବ ସ୍ନିହ୍ୟତି ।
(ଚ) ଏ ସିଂହାସନ ତୁମ ପାଇଁ ଯୋଗ୍ୟ।
ଅନୁ – ସିଂହାସନମ୍ ଇଦଂ ତ୍ଵୟି ଯୁଜ୍ୟତେ ।
(୫) ସାଙ୍ଗମାନେ ଆସିଲେ, ମୁଁ ଯିବି ।
ଅନୁ – ଆଗଳ୍ଛସୁ ମିତ୍ରେଷୁ ଅହଂ ଗମିଷ୍ୟାମି ।

(ଜ) ସଙ୍କଟବେଳେ ବନ୍ଧୁଙ୍କୁ ଜାଣିବ ।
ଅନୁ – ବିପଦି ବନ୍ଧୁଂ ଜାନୀୟାତବ ।
(ଝ) ଉଡ଼ାଜାହାଜରେ ଭ୍ରମଣପାଇଁ ମୋର ପ୍ରବଳ ଇଚ୍ଛା ।
ଅନୁ – ବାୟୁଯାନେନ ଭ୍ରମଣାୟ ମମ ମହତୀ ଇଚ୍ଛା ।
(୫) ମୁଁ ଚାହୁଁ ଚାହୁଁ ସେ ମୋ କଲମଟି ନେଇଗଲା ।
ଅନୁ – ମମ ପଶ୍ୟତଃ ସ ମମ ଲେଖନୀମ୍ ଅନୟତ୍ ।