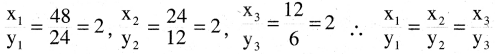Odisha State Board BSE Odisha 10th Class Odia Solutions Chapter 15 କାଳର କପୋଳ ତଳେ Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
BSE Odisha Class 10 Odia Solutions Chapter 15 କାଳର କପୋଳ ତଳେ
ପରୀକ୍ଷା ଉପଯୋଗୀ ଅତିରି
ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦିଷ୍ଟ ଉତ୍ତରମୂଳକ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନୋତ୍ତର
Question ୧।
ଧଉଳି ପାହାଡ଼ ପାଦ ଦେଶରେ କେଉଁ ନଦୀ ବହି ଯାଉଛି ?
Answer:
ଧଉଳି ପାହାଡ଼ ପାଦ ଦେଶରେ ଦୟାନଦୀ ବହି ଯାଉଛି ।
Question ୨।
ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଚଉଧୁରୀ କେଉଁ ବିଷୟର ଛାତ୍ର ?
Answer:
ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଚଉଧୁରୀ ଇତିହାସ ବିଷୟର ଛାତ୍ର ।
Question ୩ ।
ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଚଉଧୁରୀ କେଉଁ ବିଶ୍ଵବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟର ଛାତ୍ର ?
Answer:
ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଚଉଧୁରୀ ନାଳନ୍ଦା ବିଶ୍ଵବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟର ଛାତ୍ର !
![]()
Question ୪।
ଅଙ୍ଗଦ କାହାର ଶିଳାଲେଖ ପଢ଼ିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଅଶୋକଙ୍କ ଶିଳାଲେଖ ପଢ଼ିଛନ୍ତି ।
Question ୫।
କାହା ସ୍ପର୍ଶରେ ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଚମକି ପଡ଼ିଲେ ?
Answer:
ରାଜ ବଂଶର ଲୋକଙ୍କ ସ୍ପର୍ଶରେ ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଚମକି ପଡ଼ିଲେ ।
Question ୬।
“ଆପଣ କ’ଣ କଳିଙ୍ଗର ମହାରାଜା ?”- ଏହା କିଏ କାହାକୁ କହିଛି ?
Answer:
ଏହା ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ରାଜବଂଶର ଲୋକଙ୍କୁ କହିଛି ।
Question ୭।
‘ମୁଁ ତ ଦୁନିଆରେ ସବୁଠାରୁ ଶୀଘ୍ର ଚାଲେ ।? – ଏହା କାହାର ଉକ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ଏହା ରାଜବଂଶର ଲୋକଙ୍କ ଉକ୍ତି ।
Question ୮।
କଳିଙ୍ଗ ମହାରଣାଙ୍କ ନାମ କ’ଣି ଥିଲା ?
Answer:
କଳିଙ୍ଗ ମହାରଣାଙ୍କ ନାମ କୁରୁବାକୀ ଥିଲା ।
Question ୯।
କେଉଁମାନେ ମହାରାଣାଙ୍କୁ ସସଂଭ୍ରମ ଅଭିବାଦନ ଜଣାଇଲେ ?
Answer:
ପାତ୍ର ମନ୍ତ୍ରୀ ପରିଷଦ ବର୍ଗଙ୍କ ସମେତ ସମସ୍ତ ସେନାନାୟକ ମହାରଣାଙ୍କୁ ଅଭିବାଦନ ଜଣାଇଲେ ।
Question ୧୦ ।
କାହା ସହିତ ରାଜଜେମା ଦରବାର କକ୍ଷକୁ ଆସିଲେ ?
Answer:
ପତିଙ୍କ ସହିତ ରାଜଜେମା ଦରବାର କକ୍ଷକୁ ଆସିଲେ ।
Question ୧୧ ।
କଳିଙ୍ଗ କିଏ ଆକ୍ରମଣ କରିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ମଗଧ ସମ୍ରାଟ ଅଶୋକ ଆକ୍ରମଣ କରିଛନ୍ତି ।
Question ୧୨ ।
ଯୁଦ୍ଧ କେଉଁଠି ଆରମ୍ଭ ହୋଇଗଲାଣି ?
Answer:
କଳିଙ୍ଗ ଉପକଣ୍ଠରେ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ ଆରମ୍ଭ ହୋଇଗଲାଣି ।
![]()
Question ୧୩ ।
ଅଚାନକ ଆକ୍ରମଣରେ କଳିଙ୍ଗର କ’ଣ ଧ୍ୱଂସ ହୋଇଛି ?
Answer:
ସୀମାନ୍ତ ବାହିନୀ ଧ୍ୱଂସ ହୋଇଛି ।
Question ୧୪ ।
‘କଳିଙ୍ଗ ଏକ ଅତି ସଙ୍କଟ ମୁହୂର୍ତ୍ତରେ ଆସି ପହଞ୍ଚିଛି?? – ଏହା କାହାର ଉକ୍ତି ?
Answer:
କଳିଙ୍ଗର ମହାମନ୍ତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ଭକ୍ତି ।
Question ୧୫ ।
ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀ କେତେ ଜଣ ଯୋଦ୍ଧାଙ୍କୁ ଚାହୁଁଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ବାରଜଣ ଯୋଦ୍ଧାଙ୍କୁ ରାଜେଶ୍ୱରୀ ଚାହୁଁଥିଲେ ।
Question ୧୬ ।
ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀ କେତେଜଣ ଯୋଦ୍ଧାଙ୍କୁ ବାହାରକୁ ଯିବାକୁ କହିଲେ ?
Answer:
ରାଜେଶ୍ୱରୀ ପାଞ୍ଚଜଣ ଯୋଦ୍ଧାଙ୍କୁ ବାହାରକୁ ଯିବାକୁ କହିଲେ ।
Question ୧୭ ।
ଯୁଦ୍ଧରେ କେତେଜଣ ସେନାପତି ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀ ସ୍ଥିର କଲେ ?
Answer:
ଯୁଦ୍ଧରେ ବାରଜଣ ସେନାପତି ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀ ସ୍ଥିର କଲେ
Question ୧୮ ।
ରକ୍ତର ନଦୀ କିଏ ପାଲଟିଲା ?
Answer:
ରକ୍ତର ନଦୀ ଦୟାନଦୀ ପାଲଟିଲା।
Question ୧୯ ।
କଳିଙ୍ଗ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ କେତେ ମାସ ଲାଗିଥିଲା ?
Answer:
କଳିଙ୍ଗ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ ଚାରିମାସ ଲାଗିଥିଲା
Question ୨୦ ।
କେତେ ଦିନରେ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ ଶେଷ ହେବ ବୋଲି ମହାମନ୍ତ୍ରୀ ମଗଧ ସମ୍ରାଟଙ୍କୁ କହିଥିଲେ ? ମଗଧ ସମ୍ରାଟଙ୍କୁ କହିଥିଲେ ।
Answer:
ଦୁଇଦିନ ଭିତରେ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ ଶେଷ ହେବ ବୋଲି ମହାମନ୍ତ୍ରୀ
Question ୨୧ ।
ମଗଧ ସୈନ୍ୟଙ୍କ ନିକଟରୁ କ’ଣ ସରି ଆସୁଥୁଲା ?
Answer:
ମଗଧ ସୈନ୍ୟଙ୍କ ନିକଟରୁ ରସଦ ସରି ଆସୁଥିଲା ।
Question ୨୨ ।
ଅଶୋକ କେଉଁ ମନ୍ତ୍ରରେ ଦୀକ୍ଷିତ ହେଲେ ?
Answer:
ଅଶୋକ ବୁଦ୍ଧଙ୍କର ଅହିଂସା ମନ୍ତ୍ରରେ ଦୀକ୍ଷିତ ହେଲେ ।
Question ୨୩ ।
ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀ କାହା ସହ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ କରି ମୃତ୍ୟୁବରଣ କଲେ ?
Answer:
ରାଜେଶ୍ୱରୀ ମଗଧ ସେନାପତିଙ୍କ ସହ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ କରି ମୃତ୍ୟୁବରଣ କଲେ ।
Question ୨୪ ।
ରାଜନୀତିର ବ୍ରହ୍ମାସ୍ତ୍ର କ’ଣ ?
Answer:
ଷଡ଼ଯନ୍ତ୍ର ରାଜନୀତିର ବ୍ରହ୍ମାସ୍ତ୍ର ।
Question ୨୫ ।
ଶାନ୍ତିସ୍ତୂପନ କେଉଁଠି ଅବସ୍ଥିତ ?
Answer:
ଧଉଳି ପାଦ ଦେଶ ପାହାଡ଼ରେ ଶାନ୍ତିସ୍ତୂପନ ଅବସ୍ଥିତ ।
![]()
ବିଗତ ବର୍ଷର ହାଇସ୍କୁଲ ପରୀକ୍ଷା (ବାର୍ଷିକ ଓ ସପ୍ଲିମେଣ୍ଟାରୀ)ର ପ୍ରଶ୍ନୋତ୍ତର
Question 1.
‘ଏ ଯୁଦ୍ଧରେ କେହି ଜଣେ ସେନାପତି ନୁହଁନ୍ତି । ଆପଣମାନେ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ଜଣେ ଜଣେ ସେନାପତି ବୋଲି ମନେ ରଖୁବେ ।’’ ଏହା କିଏ କହିଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରା
Question 2.
ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀ ଦରବାର କକ୍ଷକୁ କାହା ସହିତ ଆସିଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ପତିଙ୍କ ସହିତ
Question 3.
ରାଜେଶ୍ୱରୀ ସମ୍ମୁଖ ସମରକୁ ତାଙ୍କ ସହିତ ଯିବାପାଇଁ କେତେ ଜଣକୁ ବାଛିଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ବାର
Question 4.
କଳିଙ୍ଗ ରାଜଜେମା ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀ କିପରି ମୃତ୍ୟୁବରଣ କରିଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ମଗଧ ସେନାପତିଙ୍କ ସହ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ କରି
![]()
Question 5.
‘ମୁଁ ତ ଦୁନିଆରେ ସବୁଠାରୁ ଶୀଘ୍ର ଚାଲେ’’– ଏହା କିଏ କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ବାର୍ଘଦେହା ପୁରୁଷ
Question 6.
ପିତାଙ୍କ ଇଚ୍ଛାକୁ ସ୍ଵୀକାର କରିଥିବାରୁ ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀ କାହାକୁ କୃତଜ୍ଞତା ଜଣାଇଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ସଭାସଦ୍ ମାନଙ୍କୁ
Question 7.
ରାଣୀ କୁରୁବକୀ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ମହାରାଜାଙ୍କର କେଉଁ ବାର୍ତ୍ତା ଧରି ଦରବାର କକ୍ଷରେ ପ୍ରବେଶ କରିଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ରାଜାଙ୍କ ଅନୁପସ୍ଥିତିରେ ରାଜଜେମା ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରା ସମସ୍ତ୍ର କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ପରିଚାଳନା କରିବା
Question 8.
ରାଜନାତିର ବ୍ରହାସ୍ତ କାହାକୁ କୁହାଯାଏ?
Answer:
ଷଡ଼ଯନ୍ତ୍ରକୁ
Question 9.
ରାଜନାତିର ଷଡ଼ଯନ୍ତ୍ରକୁ କ’ଣ ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଇଛି?
Answer:
ବ୍ରହ୍ମାସ୍ତ
Question 10.
‘ଆପଣ କ’ଣ ଇତିହାସ ପୁରୁଷ ?- ଏକଥା କିଏ କହିଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଚୌଧୁରା
ପରୀକ୍ଷା ଉପଯୋଗୀ ଅତିରିକ୍ତ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନୋତ୍ତର
(A) ।ଗୋଟିଏ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ଉତ୍ତର ଦିଅ ।
Question 1.
ଲେଖୁ ନନ୍ଦିନୀ ଶତପଥୀ କେବେ ଜନ୍ମଗ୍ରହଣ କରିଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ଲେଖୁ ନନ୍ଦିନୀ ଶତପଥୀ ୧୯୩୧ ମସିହାରେ ଜନ୍ମଗ୍ରହଣ କରିଥିଲେ ।
Question 2.
ନନ୍ଦିନୀ ଶତପଥୀଙ୍କ ପିତାଙ୍କ ନାମ କ’ଣ ?
Answer:
ନନ୍ଦିନୀ ଶତପଥୀଙ୍କ ପିତାଙ୍କ ନାମ କାଳିନ୍ଦୀଚରଣ ପାଣିଗ୍ରାହୀ ।
Question 3.
ନନ୍ଦିନୀ ଶତପଥୀ ଏକଦା ଓଡ଼ିଶାର କ’ଣ ଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ନନ୍ଦିନୀ ଶତପଥୀ ଏକଦା ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ମୁଖ୍ୟମନ୍ତ୍ରୀ ଥିଲେ ।
Question 4.
ନନ୍ଦିନୀ ଶତପଥୀ କେଉଁ ସମ୍ମାନରେ ସମ୍ମାନିତ ହୋଇଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ନନ୍ଦିନୀ ଶତପଥୀ ‘ସାହିତ୍ୟ ଭାରତୀ’’ରେ ସମ୍ମାନିତ ହୋଇଥିଲେ ।
![]()
Question 5.
ଇତିହାସର ଛାତ୍ର କିଏ ଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ଇତିହାସର ଛାତ୍ର ଥିଲେ ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଚୌଧୁରୀ ।
Question 6.
ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଚୌଧୁରୀ କେଉଁଠାରୁ ଗବେଷଣା କାର୍ଯ୍ୟରେ ଆସିଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଚୌଧୁରୀ ନାଳନ୍ଦା ବିଶ୍ବବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟରୁ ଗବେଷଣା କାର୍ଯ୍ୟରେ ଆସିଥିଲେ ।
Question 7.
କିଏ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ବିଜୟ କରିଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ଗଧ ସମ୍ରାଟ ଅଶୋକ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ବିଜୟ କରିଥିଲେ ।
Question 8.
‘ଶିଳାଲେଖ’’ରେ କ’ଣ ଉଲ୍ଲେଖ ଥିଲା ?
Answer:
‘ଶିଳାଲେଖ’ରେ ଅହିଂସା, ଦୟା, କ୍ଷମା ବିଷୟରେ ଉଲ୍ଲେଖ ଥିଲା ।
Question 9.
ସାଧାରଣ ପ୍ରକାର ରନ୍ଧିନଶାଳାରେ ମାଂସ ରନ୍ଧିନ କରାଯାଇପାରିବା
Answer:
ସାଧାରଣ ପ୍ରଜାର ରନ୍ଧନଶାଳାରେ ମୟୂର ମାଂସ ରନ୍ଧନ କରାଯାଇପାରିବ ।
Question 10.
ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟର ଶେଷ କିରଣ କାହାର ଛାତି ଉପରୁ ଅପସରି ଗଲାଣି ?
Answer:
ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟର ଶେଷ କିରଣ ଦୟାନଦୀର ଛାତି ଉପରୁ ଅପସରି ଗଲାଣି ।
Question 11.
କେଉଁଥିପାଇଁ ଧଉଳି ପର୍ବତ କମ୍ପି ଉଠିଲା ?
Answer:
ଘୋଡ଼ାଟାପୁ ଆଉ ବ୍ରେଷାରବ ସହିତ ଅସ୍ତ୍ରର ଝଙ୍କାରରେ ଧଉଳି ପର୍ବତ କମ୍ପି ଉଠିଲା ।
![]()
Question 12.
ଅଙ୍ଗଦ କ’ଣ ଦେଖିଲେ ?
Answer:
ମହାରାଣୀ କୁରୁବକୀ ଧୀରେ ଧୀରେ ଓହ୍ଲାଇ ଆସୁଥିବାର ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଦେଖିଲେ ।
Question 13.
ଅଙ୍ଗଦ କିପରି ବସିଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଦୁଇ ଆଣ୍ଠୁ ଭିତରେ ମୁଣ୍ଡ ଗୁଞ୍ଜି ବସିଥିଲେ ।
Question 14.
ଅଙ୍ଗଦଙ୍କ ସାମନାରେ କିଏ ଠିଆ ହୋଇଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ଅଙ୍ଗଦଙ୍କ ସାମନାରେ ଠିଆ ହୋଇଥିଲେ ଜଣେ ଦୀର୍ଘଦେହୀ ପୁରୁଷ ।
Question 15.
ପୁତ୍ର କାହାକୁ ରାଜ ସିଂହାସନ ପ୍ରଦାନ କରିବାର ପରମ୍ପରା ରହିଛି ?
Answer:
ପୁତ୍ର କନ୍ୟାକୁ ରାଜ ସିଂହାସନ ପ୍ରଦାନ କରିବାର ପରମ୍ପରା ରହିଛି
Question 16.
ବୃଦ୍ଧି ଓ ବୀରତ୍ଵରେ କିଏ ରାଜପୁତ୍ରଠାରୁ ଊଣା ନୁହନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ବୁଦ୍ଧି ଓ ବୀରତ୍ଵରେ ରାଜଜେମା ରାଜପୁତ୍ରଠାରୁ ଊଣା ନୁହନ୍ତି ।
Question 17.
ରାଜଜେମା କେତେ ଜଣ ଯୋଦ୍ଧାଙ୍କୁ ମନୋନୀତ କରିଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ରାଜଜେମା ବାର ଜଣ ଯୋଦ୍ଧାଙ୍କୁ ମନୋନୀତ କରିଥିଲେ ।
Question 18.
ଦୟାନଦୀ କେଉଁ ନଦୀରେ ପରିଣତ ହୋଇଥିଲା ?
Answer:
ଦୟାନଦୀ ରକ୍ତନଦୀରେ ପରିଣତ ହୋଇଥିଲା ।
Question 19.
ଶିବିର ଭିତରେ ସମ୍ରାଟ ଅଶୋକ କେଉଁ ଅବସ୍ଥାରେ ବସିଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ଶିବିର ଭିତରେ ସମ୍ରାଟ ଅଶୋକ ଚିନ୍ତାନ୍ବିତ ଅବସ୍ଥାରେ ବସିଥିଲେ ।
Question 20.
ଆଦେଶକୁ ଅପେକ୍ଷା କରି କିଏ ପାଖରେ ଠିଆ ହୋଇଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ଆଦେଶକୁ ଅପେକ୍ଷା କରି ମହାମନ୍ତ୍ରୀ ପାଖରେ ଠିଆ ହୋଇଥିଲେ ।
![]()
Question 21.
ମଗଧର ସେନାବାହିନୀ କିପରି ଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ମଗଧର ସେନାବାହିନୀ ଅତ୍ୟାଧୁନିକ ଅସ୍ତ୍ରଶସ୍ତ୍ରରେ ସଜ୍ଜିତ ଥିଲେ ।
Question 22.
କଳିଙ୍ଗର ଗାଁ ଗଣ୍ଡାରୁ ଲୋକମାନେ କ’ଣ କ’ଣ ଧରି ଆସୁଥୁଲେ ?
Answer:
କଳିଙ୍ଗର ଗାଁ ଗଣ୍ଡାରୁ ଲୋକମାନେ ଖଣ୍ଡା, ତଲବାର, ତୀର, ବର୍ଚ୍ଛା ଧରି ଆସୁଥିଲେ ।
Question 23.
ରୁଗ୍ଣ ମହାରାଜ କ’ଣ କରିବାକୁ ଅକ୍ଷମ ଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ରୁଗ୍ଣ ମହାରାଜ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ କରିବାକୁ ଅକ୍ଷମ ଥିଲେ |
Question 24.
ପରଦିନ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟୁଷରେ କେଉଁଠାରେ ନାଗରା ବାଜିଲା ?
Answer:
ପରଦିନ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟୁଷରେ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ରାଜ୍ୟରେ ନାଗରା ବାଜିଲା ।
Question 25.
କିଏ ଯୁଦ୍ଧର ବିଭୀଷିକା ଦେଖୁ ଅତ୍ୟନ୍ତ ମର୍ମାହତ ହେଲେ ?
Answer:
ମଗଧରାଜ ଅଶୋକ ଯୁଦ୍ଧର ବିଭୀଷିକା ଦେଖୁ ଅତ୍ୟନ୍ତ ମର୍ମାହତ ହେଲେ ।
Question 26.
କିଏ ନରହତ୍ୟାକୁ ଦେଖ୍ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ ବନ୍ଦ କରିବାକୁ ନିଷ୍ପତ୍ତି କଲେ ?
Answer:
ଅଶୋକ ନରହତ୍ୟାକୁ ଦେଖ୍ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ ବନ୍ଦ କରିବାକୁ ନିଷ୍ପଭି କଲେ ।
Question 27.
ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀ କାହା ସହିତ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ କରି ମୃତ୍ୟୁବରଣ କରିଥିଲା ?
Answer:
ରାଜେଶ୍ୱରୀ ମଗଧ ସେନାପତିଙ୍କ ସହ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ କରି ମୃତ୍ୟୁବରଣ କରିଥିଲା ।
Question 28.
ରାଜନୀତିର ବ୍ରହ୍ମାସ୍ତ୍ର କ’ଣ ?
Answer:
ରାଜନୀତିର ବ୍ରହ୍ମାସ୍ତ୍ର ହେଉଛି ଷଡ଼ଯନ୍ତ୍ର ।
![]()
Question 29.
ଆପଣ କ’ଣ ଇତିହାସ-ପୁରୁଷ – ଏକଥା କିଏ କହିଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ଆପଣ କ’ଣ ଇତିହାସ-ପୁରୁଷ – ଏକଥା ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଚୌଧୁରୀ କହିଥିଲେ ।
Question 30.
କଳିଙ୍ଗର ସାଧାରଣ ପ୍ରଜା କାହିଁକି ଆସୁଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
କଳିଙ୍ଗର ସାଧାରଣ ପ୍ରଜା ଯୁଦ୍ଧ କରିବାକୁ ଆସୁଥିଲେ ।
(B) ଗୋଟିଏ ପଦ ବା ଶବ୍ଦରେ ଉତ୍ତର ଦିଅ ।
Question 1.
ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଧଉଳି ପାହାଡ଼ ପାଦଦେଶରେ କେଉଁଠାରେ ବସିଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ଏକ ବଡ଼ ପଥରମୁଣ୍ଡିଆ ଉପରେ
Question 2.
ଦୀର୍ଘଦେହୀ ପୁରୁଷଙ୍କ ବେଶପୋଷାକରୁ ସେ ରାଜବଂଶର ଲୋକ ବୋଲି କାହାର ମନେ ହୋଇଥିଲା ?
Answer:
ଅଙ୍ଗଦଙ୍କର
Question 3.
ଦୀର୍ଘଦେହୀ ପୁରୁଷଙ୍କ ଆଖ୍ ଦୁଇଟିରେ ଅଙ୍ଗଦ କ’ଣ ଦେଖିବାକୁ ପାଇଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ଅସାମାନ୍ୟ ଦୀପ୍ତି
Question 4.
ଦୀର୍ଘଦେହୀ ପୁରୁଷ ଅଙ୍ଗଦଙ୍କୁ କେଉଁ ସ୍ଥାନକୁ ନେଇଗଲେ ?
Answer:
କଳିଙ୍ଗ ଦରବାର କକ୍ଷ ନିକଟକୁ
Question 5.
ମହାରାଣୀଙ୍କ ପ୍ରବେଶମାତ୍ରେ ଦରବାର କକ୍ଷ ହଠାତ୍ କ’ଣି ହୋଇଗଲା ?
Answer:
ସ୍ତବ୍ଧ
Question 6.
ମହାରାଜା ବିଚାର ନିମନ୍ତେ ବାର୍ତ୍ତା ପଠାଇଥବା କଥା କିଏ କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
Question 7.
‘ସ-ପତି’ – କହିଲେ କ’ଣ ବୁଝାଯାଏ ?
Answer:
ପତି ସହିତ
Question 8.
କାହାର ଅଚାନକ ଆକ୍ରମଣରେ କଳିଙ୍ଗର ସୀମାନ୍ତବାହିନୀ ସମ୍ପୂର୍ଣ ଧ୍ୱଂସ ହୋଇଯାଇଛି ?
Answer:
ଅଶୋକଙ୍କ
Question 9.
କାହାର କଣ୍ଠର ଦୃଢ଼ତା ଅଦ୍ଭୁତ ପ୍ରଭାବ ସୃଷ୍ଟି କରିଥିଲା ?
Answer:
ରାଜେଶ୍ୱରୀଙ୍କ
![]()
Question 10.
ଅଶୋକ ତାଙ୍କ ପାଖରୁ କ’ଣ ଶେଷ ହେଲାଣି ବୋଲି କହିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ରସଦ
Question 11.
କଳିଙ୍ଗର ମହାରାଜା କାହିଁକି ଯୁଦ୍ଧ କରିବାକୁ ଅକ୍ଷମ ଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ରୁଗ୍ଣ ହେତୁ
Question 12.
ସାମ୍ରାଜ୍ୟ ରକ୍ଷା ଅଥବା ବିସ୍ତାର କରିବାପାଇଁ କ’ଣ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିବାକୁ ହୁଏ ?
Answer:
ଷଡ଼ଯନ୍ତ୍ରର ବ୍ରହ୍ମାସ୍ତ୍ର
Question 13.
ଆପଣ କ’ଣ ଇତିହାସ ପୁରୁଷ ? – ଏକଥା କିଏ ପଚାରିଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଚୌଧୁରୀ
Question 14.
କିଏ ଶାନ୍ତସ୍ତୂପ ଉପରେ ଉଜ୍ଜ୍ଵଳ ତାରାଟିଏ ଦେଖିଲେ ?
Answer:
ଅଙ୍ଗଦ
Question 15.
କଳିଙ୍ଗ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ ପରେ ଅଶୋକ ସବୁଦିନ ପାଇଁ କ’ଣ ବନ୍ଦ କରିବାକୁ ନିଷ୍ପତ୍ତି ନେଇଥିଲେ
Answer:
ନରହତତ୍ୟା
Question 16.
କାହା ସହିତ ତାଳ ପକାଇ ଚାଲିବା ଅଙ୍ଗଦଙ୍କ ପକ୍ଷେ ସହଜ ନଥିଲା ?
Answer:
ଦୀର୍ଘଦେହୀ ପୁରୁଷଙ୍କ ସହ
Question 17.
ରାଜା ନିଜର କ’ଣ ମନୋନୀତ କରିବା ଗଣତନ୍ତ୍ର ପ୍ରଶାସନର ନିୟମ ?
Answer:
ଉତ୍ତରାଧିକାରୀ
Question 18.
ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀ କିଏ ?
Answer:
କଳିଙ୍ଗ ରାଜକୁମାରୀ
Question 19.
ଅଙ୍ଗଦଙ୍କ ଆଖ୍ ଆଗରେ କେଉଁ ନଦୀର ପାଣିର ରଙ୍ଗ ବଦଳି ଯାଇଥିଲା ?
Answer:
ଦୟା
![]()
Question 20.
ରାଜନୀତିର ବ୍ରହ୍ମାସ୍ତ୍ର କିଏ ?
Answer:
ଷଡ଼ଯନ୍ତ୍ର
Question 21.
ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଚୌଧୁରୀ କେଉଁ ଛାତ୍ର ଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ଇତିହାସର
Question 22.
କିଏ କଳଙ୍ଗ ବିଜୟ କରିଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ସମ୍ରାଟ୍ ଅଶୋକ
Question 23.
ଦୀର୍ଘଦେହୀ ଉଜ୍ଜ୍ବଳ ପୁରୁଷଜଣକ କିଏ ଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ଇତିହାସ ପୁରୁଷ
Question 24.
‘‘କଳିଙ୍ଗ ମହାରାଜଙ୍କର ସମସ୍ତ ଆଦେଶ ଶିରୋଧାର୍ଯ୍ୟ’’ – ଏକଥା କିଏ କହିଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ମହାମନ୍ତ୍ରା
Question 25.
ଶାରୀରିକ ଅସୁସ୍ଥତା ହେତୁ ମହାରାଜ ରାଜ୍ୟର ଦାୟିତ୍ଵ କାହାକୁ ଅର୍ପଣ କରିବାକୁ ଚାହିଁଛନ୍ତି ?
Answer:
ରାଜଜେମାଙ୍କୁ
![]()
Question 26.
ରାଜଜେମା ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀ ରାଜ୍ୟ ଦାୟିତ୍ଵ ଗ୍ରହଣ କଲାବେଳେ କିଏ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ଆକ୍ରମଣ କରିଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ସମ୍ରାଟ୍ ଅଶୋକ
Question 27.
ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀ ତାଙ୍କ ସହିତ ସମ୍ମୁଖ ସଂଗ୍ରାମକୁ ଯିବାପାଇଁ କେତେଜଣ ଯୋଦ୍ଧାଙ୍କୁ ଚାହିଁଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
ବାରଜଣ
(C) ଶୂନ୍ୟସ୍ଥାନ ପୂରଣ କର ।
Question 1.
ଶାନ୍ତିସ୍ତୂପ …………………….. ପାହାଡ଼ରେ ଅଛି ।
Answer:
ଧଉଳି
Question 2.
ଅଶୋକ ……………………. ରାଜ୍ୟର ସମ୍ରାଟ ଥ୍ଲେ ।
Answer:
ମଗଧ
Question 3.
ନନ୍ଦିନୀ ଶତପଥୀ ……………………….. ସମ୍ମାନଦ୍ୱାରା ସମ୍ମାନିତା ହୋଇଥ୍ଲେ।
Answer:
ସାହିତ୍ୟ ଭାରତୀ
Question 4.
ନନ୍ଦିନୀ ଶତପଥୀଙ୍କ ପିତାଙ୍କ ନାମ ……………….।
Answer:
କାଳିନ୍ଦୀଚରଣ ପାଣିଗ୍ରାହୀ
Question 5.
ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଚୌଧୁରୀ ………………… ର ଛାତ୍ର ଥିଲେ ।
Answer:
ଇତିହାସ
Question 6.
ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଚୌଧୁରୀ ……………….. ରୁ ଗବେଷଣା କାର୍ଯ୍ୟରେ ଆସିଥିଲେ ।
Answer:
ନାଳନ୍ଦା ବିଶ୍ଵବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟ
Question 7.
………………………. କଳିଙ୍ଗ ବିଜୟ କରିଥିଲେ ।
Answer:
ସମ୍ରାଟ୍ ଅଶୋକ
![]()
Question 8.
ବାର୍ଘଦେହା ଉଦ୍ଦଲ ପୁରୁଷଜଶକ ……………………..ଥିଲା ।
Answer:
ଇତିହାସ ପୁରୁଷ
Question 9.
କଳିଙ୍ଗର ମହାରାଣୀଙ୍କ ନାମ ……………………….. ଥିଲେ ।
Answer:
କୁରୁବକୀ
Question 10.
‘କଳିଙ୍ଗ ମହାରାଜଙ୍କର ସମସ୍ତ ଆଦେଶ ଶିରୋଧାର୍ଯ୍ୟ’’ – ଏକଥା ……………………. କହିଥିଲେ ।
Answer:
ମହାମନ୍ତ୍ରୀ
Question 11.
ମହାରାଣୀଙ୍କ ପ୍ରବେଶମାତ୍ରେ ଦରବାର କକ୍ଷ ହଠାତ୍ …………………..ହୋଇଗଲା
Answer:
ସ୍ତବ୍ଧ
Question 12.
ଯୁଦ୍ଧ ଶେଷରେ …………………………… ପ୍ରାୟ ପୁରୁଷଶୂନ୍ୟ ହୋଇପଡ଼ିଥ୍ ଲା
Answer:
କଳିଙ୍ଗ ରାଜ୍ୟ
Question 13.
କଳିଙ୍ଗ ଯୁଦ୍ଧରେ କେବଳ ସୈନ୍ୟ ନୁହଁନ୍ତି …………………….. ମଧ୍ୟ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ କରିବାକୁ ଆଗେଇ ଆସିଥିଲେ ।
Answer:
ପ୍ରଜାମାନେ
Question 14.
କଳିଙ୍ଗ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ …………………… ମାସ ଧରି ଚାଲିଥିଲା ବୋଲି ଗାଳ୍ପିକ କହିଛନ୍ତି ।
Answer:
ଚାରି
Question 15.
ରାଜେଶ୍ୱରୀ ତାଙ୍କ ସହିତ ସମ୍ମୁଖ ସଂଗ୍ରାମକୁ ଯିବାପାଇଁ ……………………… ଜଣ ଯୋଦ୍ଧାଙ୍କୁ ବାଛିଥିଲେ ।
Answer:
ବାର
Question 16.
କଳିଙ୍ଗ ଯୁଦ୍ଧରେ କଳିଙ୍ଗର ………………………….. ଜଣ ସେନାପତି ଥିଲେ ।
Answer:
ଚାରି
Question 17.
କଳିଙ୍ଗକୁ ଜୟ କରିବାକୁ ………………….. ଦିନ ଲାଗିବ ବୋଲି ମହାମନ୍ତ୍ରୀ ଅଶୋକଙ୍କୁ କହିଥିଲେ ।
Answer:
ଦୁଇ
Question 18.
ସୈନ୍ୟମାନଙ୍କ ବ୍ୟତୀତ ଆଉ ………………………. ମାନେ ହଜାର ହଜାର ସଂଖ୍ୟାରେ ଯୁଦ୍ଧରେ ଯୋଗ ଦେଉଥିଲେ ।
Answer:
ସାଧାରଣ ପ୍ରଜା
![]()
Question 19.
ଯୁଦ୍ଧର ବିଭୀଷିକା ଦୃଶ୍ୟ ………………….. ହୋଇଥିଲେ ।
Answer:
ମର୍ମାହତ
Question 20.
ଇତିହାସରେ …………………. ର ନାମ ନାହିଁ କାହିଁକି ବୋଲି ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଇତିହାସ ପୁରୁଷଙ୍କୁ ପଚାରିଥିଲେ ।
Answer:
ରାଜେଶ୍ୱରୀଙ୍କ
Question 21.
କଳିଙ୍ଗ ଯୁଦ୍ଧର ବିଭୀଷିକା ………………………… ମର୍ମାହତ ହୋଇଥିଲେ ।
Answer:
ସମ୍ରାଟ ଅଶୋକ
Question 22.
ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀ ………………………. ସହ ପ୍ରଚଣ୍ଡ ଯୁଦ୍ଧକରି ମୃତ୍ୟୁବରଣ କରିଥିଲେ ।
Answer:
ମଗଧ ସେନାପତିଙ୍କ
Question 23.
ଅଶୋକ ………………………. ଧର୍ମ ଗ୍ରହଣ କରିଥିଲେ ।
Answer:
ବୌଦ୍ଧ
Question 24.
‘କାଳର କପୋଳ ତଳେ’ ଗଛଟିର ରଚୟିତା …………………..।
Answer:
ନନ୍ଦିନୀ ଶତପଥୀ
Question 25.
ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀ ………………… ଜଣଙ୍କୁ ସଭାଗୃହ ଛାଡ଼ିଯିବାକୁ ନିର୍ଦ୍ଦେଶ ଦେଇଥିଲେ ।
Answer:
ପାଞ୍ଚ
![]()
Question 26.
ଯୁଦ୍ଧ ଶେଷରେ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ରାଜ୍ୟ ପ୍ରାୟ ………………………… ହୋଇପଡ଼ିଥିଲା ।
Answer:
ପୁରୁଷଶୂନ୍ୟ
Question 27.
କଳିଙ୍ଗର ରାଜଜେମାଙ୍କ ନାମ ଥିଲା ………………………..।
Answer:
ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀ
Question 28.
……………………. ନଦା ରକ୍ତର ନଦା ପାଇଟି ଯାଇଥ୍ ଲା
Answer:
ଦୟା
Question 29.
ସମ୍ରାଟ୍ ଅଶୋକ ……………………… ମନ୍ତ୍ରରେ ଦୀକ୍ଷିତ ହୋଇଥିଲେ ।
Answer:
ବୁଦ୍ଧଙ୍କ ଅହିଂସା
(D) ଠିକ୍ ଉକ୍ତି ପାଇଁ ‘T” ଓ ଭୁଲ ଉକ୍ତି ପାଇଁ “F” ଲେଖ ।
1. କଳିଙ୍ଗର ରାଜଜେମାଙ୍କ ନାମ କୁରୁବକୀ ଥିଲା ।
2. ଶାରୀରିକ ଅସୁସ୍ଥତା ହେତୁ କଳିଙ୍ଗର ମହାରାଜ ରାଜ୍ୟର ଦାୟିତ୍ଵ ମହାମନ୍ତ୍ରୀଙ୍କୁ ଅର୍ପଣ କରିବାକୁ ଚାହିଁଛନ୍ତି ।
3. ରାଜଜେମା ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀ ରାଜ୍ୟ ଦାୟିତ୍ଵ ଗ୍ରହଣ କଲାବେଳେ ସମ୍ରାଟ୍ ଅଶୋକ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ଆକ୍ରମଣ କରିଥିଲେ ।
4. ଦୟା ନଦୀ ରକ୍ତର ନଦୀ ପାଲଟିଯାଇଥିଲା ।
5. ସମ୍ରାଟ୍ ଅଶୋକ ବୁଦ୍ଧଙ୍କ ଅହିଂସା ମନ୍ତ୍ରରେ ଦୀକ୍ଷିତ ହୋଇଥିଲେ ।
6. ରାଣୀ କୁରୁବକୀ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ମହାରାଜାଙ୍କର ଅନୁପସ୍ଥିତିରେ ରାଜଜେମା ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀ ସମସ୍ତ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ପରିଚାଳନା କରିବା ବାର୍ତ୍ତା ଧରି ଦରବାର କକ୍ଷରେ ପ୍ରବେଶ କରିଥିଲେ ।
7. ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଧଉଳି ପାହାଡ଼ ପାଦଦେଶରେ ଏକ ବଢ଼ ପଥରମୁଶ୍ରି ଆ ଉପରେ ବସିଥିଲୋ
8. ଦୀର୍ଘଦେହୀ ପୁରୁଷଙ୍କ ବେଶପୋଷାକରୁ ଅଙ୍ଗଦଙ୍କୁ ସେ ରାଜବଂଶର ଲୋକଭଳି ମନେ ହୋଇଥିଲେ ।
9. ଦୀର୍ଘଦେହୀ ପୁରୁଷଙ୍କ ଆଖ୍ ଦୁଇଟିରେ ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଅସାମାନ୍ୟ ଦୀପ୍ତି ଦେଖିବାକୁ ପାଇଥିଲେ ।
10. ଦୀର୍ଘଦେହୀ ପୁରୁଷ ଅଙ୍ଗଦଙ୍କୁ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ଦରବାର କକ୍ଷ ନିକଟକୁ ନେଇଗଲେ ।
11. ରୁଗ୍ଣ ହେତୁ କଳିଙ୍ଗର ମହାରାଜା ଯୁଦ୍ଧ କରିବାକୁ ଅକ୍ଷମ ଥିଲେ ।
12. ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀ ମଗଧ ସେନାପତିଙ୍କ ସହ ପ୍ରଚଣ୍ଡ ଯୁଦ୍ଧକରି ମୃତ୍ୟୁବରଣ କରିଥିଲେ ।
13. ସାମ୍ରାଜ୍ୟ ରକ୍ଷା ଅଥବା ବିସ୍ତାର କରିବାପାଇଁ ଷଡ଼ଯନ୍ତ୍ରର ବ୍ରହ୍ମାସ୍ତ୍ର ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିବାକୁ ହୁଏ ।
14. ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀ ସ୍ଵେଚ୍ଛାରେ ଆଗେଇ ଆସିଥିବା ବାରଜଣ ଯୋଦ୍ଧାଙ୍କୁ ସଙ୍ଗରେ ନେଇ ଯୁଦ୍ଧକୁ ଯିବେ ବୋଲି କହିଥିଲେ ।
15. ମଗଧର ସେନାବାହିନୀ ଆଧୁନିକ ଅସ୍ତ୍ରଶସ୍ତ୍ରରେ ସଜ୍ଜିତ ଥିଲେ ?
Answer:
1. କଳିଙ୍ଗର ରାଜଜେମାଙ୍କ ନାମ କୁରୁବକୀ ଥିଲା । (F)
2. ଶାରୀରିକ ଅସୁସ୍ଥତା ହେତୁ କଳିଙ୍ଗର ମହାରାଜ ରାଜ୍ୟର ଦାୟିତ୍ଵ ମହାମନ୍ତ୍ରୀଙ୍କୁ ଅର୍ପଣ କରିବାକୁ ଚାହିଁଛନ୍ତି । (F)
3. ରାଜଜେମା ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀ ରାଜ୍ୟ ଦାୟିତ୍ଵ ଗ୍ରହଣ କଲାବେଳେ ସମ୍ରାଟ୍ ଅଶୋକ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ଆକ୍ରମଣ କରିଥିଲେ । (T)
4. ଦୟା ନଦୀ ରକ୍ତର ନଦୀ ପାଲଟିଯାଇଥିଲା । (T)
5. ସମ୍ରାଟ୍ ଅଶୋକ ବୁଦ୍ଧଙ୍କ ଅହିଂସା ମନ୍ତ୍ରରେ ଦୀକ୍ଷିତ ହୋଇଥିଲେ । (T)
6. ରାଣୀ କୁରୁବକୀ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ମହାରାଜାଙ୍କର ଅନୁପସ୍ଥିତିରେ ରାଜଜେମା ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀ ସମସ୍ତ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ପରିଚାଳନା କରିବା ବାର୍ତ୍ତା ଧରି ଦରବାର କକ୍ଷରେ ପ୍ରବେଶ କରିଥିଲେ । (T)
7. ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଧଉଳି ପାହାଡ଼ ପାଦଦେଶରେ ଏକ ବଢ଼ ପଥରମୁଶ୍ରି ଆ ଉପରେ ବସିଥିଲୋ (T)
8. ଦୀର୍ଘଦେହୀ ପୁରୁଷଙ୍କ ବେଶପୋଷାକରୁ ଅଙ୍ଗଦଙ୍କୁ ସେ ରାଜବଂଶର ଲୋକଭଳି ମନେ ହୋଇଥିଲେ । (T)
9. ଦୀର୍ଘଦେହୀ ପୁରୁଷଙ୍କ ଆଖ୍ ଦୁଇଟିରେ ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଅସାମାନ୍ୟ ଦୀପ୍ତି ଦେଖିବାକୁ ପାଇଥିଲେ । (T)
10. ଦୀର୍ଘଦେହୀ ପୁରୁଷ ଅଙ୍ଗଦଙ୍କୁ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ଦରବାର କକ୍ଷ ନିକଟକୁ ନେଇଗଲେ । (T)
11. ରୁଗ୍ଣ ହେତୁ କଳିଙ୍ଗର ମହାରାଜା ଯୁଦ୍ଧ କରିବାକୁ ଅକ୍ଷମ ଥିଲେ । (T)
12. ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀ ମଗଧ ସେନାପତିଙ୍କ ସହ ପ୍ରଚଣ୍ଡ ଯୁଦ୍ଧକରି ମୃତ୍ୟୁବରଣ କରିଥିଲେ । (T)
13. ସାମ୍ରାଜ୍ୟ ରକ୍ଷା ଅଥବା ବିସ୍ତାର କରିବାପାଇଁ ଷଡ଼ଯନ୍ତ୍ରର ବ୍ରହ୍ମାସ୍ତ୍ର ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିବାକୁ ହୁଏ । (T)
14. ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀ ସ୍ଵେଚ୍ଛାରେ ଆଗେଇ ଆସିଥିବା ବାରଜଣ ଯୋଦ୍ଧାଙ୍କୁ ସଙ୍ଗରେ ନେଇ ଯୁଦ୍ଧକୁ ଯିବେ ବୋଲି କହିଥିଲେ । (T)
15. ମଗଧର ସେନାବାହିନୀ ଆଧୁନିକ ଅସ୍ତ୍ରଶସ୍ତ୍ରରେ ସଜ୍ଜିତ ଥିଲେ ? (T)
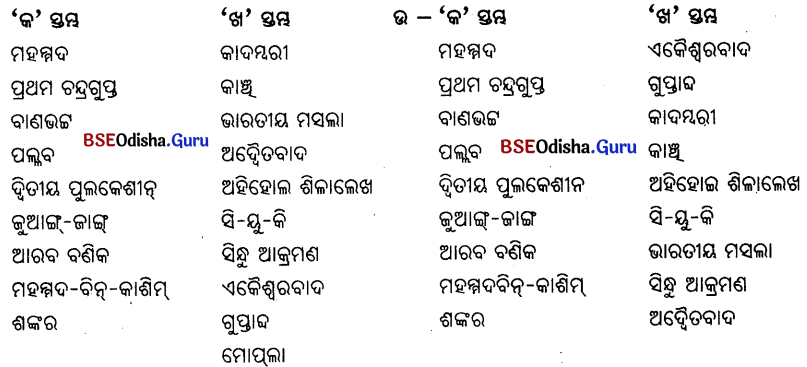
(E) ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ ମିଳନ କର ।
Question 1
‘କ’ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭର ଶବ୍ଦ ସହିତ ‘ଖ’ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭର ସମ୍ପର୍କ ଥିବା ଶବ୍ଦକୁ ଯୋଡ଼ି ଲେଖ ।
| ‘କ’ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ | ‘ଖ’ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ |
| ନନ୍ଦିନା ଶତପଥୀଙ୍କ ମୃତ୍ୟୁ | ଇତିହାସ ଛାତ୍ର |
| ଗାନ୍ଧି କଥାମୃତ | ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରା |
| ମଗଧ ସମ୍ରାଟ | ୨୦୦୬ |
| ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଶ୍ରେପୁରା | କେନ୍ଦ୍ର ସାହିତ୍ୟ ଏକାଡେମୀ |
| ରାଜଜେମା | କଳିଙ୍ଗ ଆକ୍ରମଣ |
Answer:
| ‘କ’ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ | ‘ଖ’ ସ୍ତମ୍ଭ |
| ନନ୍ଦିନା ଶତପଥୀଙ୍କ ମୃତ୍ୟୁ | ୨୦୦୬ |
| ଗାନ୍ଧି କଥାମୃତ | କେନ୍ଦ୍ର ସାହିତ୍ୟ ଏକାଡେମୀ |
| ମଗଧ ସମ୍ରାଟ | କଳିଙ୍ଗ ଆକ୍ରମଣ |
| ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଶ୍ରେପୁରା | ଇତିହାସ ଛାତ୍ର |
| ରାଜଜେମା | ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରା |
ଗାଳ୍ପିକ ପରିଚୟ ।
ନନ୍ଦିନୀ ଶତପଥୀ ଏକ ସୁପ୍ରତିଷ୍ଠିତ ସାହିତ୍ୟିକ ପରିବାରରେ ଜନ୍ମଗ୍ରହଣ କରିଥିଲେ । ତାଙ୍କ ପିତା ଥିଲେ ସବୁଜ ରାଜନୀତିରେ ଅଂଶଗ୍ରହଣ ଏକ ସାମାଜିକ ବିମୁଖତାଭାବେ ଗୃହୀତ ହେଉଥିଲା; ସେତେବେଳେ ବାମପନ୍ଥୀ ଆଦର୍ଶରେ ଅନୁପ୍ରାଣିତ ନନ୍ଦିନୀ ଶତପଥୀ ସକ୍ରିୟ ଅଂଶଗ୍ରହଣ କରିଥିଲେ ଛାତ୍ର ରାଜନୀତିରେ । ପରେ ପରେ ସେ ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ମୁଖ୍ୟମନ୍ତ୍ରୀ ହୋଇଥିଲେ । ଉଚ୍ଚକୋଡ୍ୟୁଲ୍ ଗାଳ୍ପିକ ଭାବେ ତାଙ୍କର ଅଶେଷ ଖ୍ୟାତି ରହିଛି । ତାଙ୍କ ଗଳ୍ପଗୁଡ଼ିକ ବେଶ୍ ବୌଦ୍ଧିକ, ଭାବୋଦ୍ଦୀପକ, ଐତିହାସିକ ତଥା ସାମାଜିକ ଗୁଣବତ୍ତାର ଅଧିକାରୀ । ତାଙ୍କର ସଫଳ ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥଗୁଡିକ ହେଉଛି – ‘କେତୋଟି କଥା’ ଓ ‘ସପ୍ତଦର୍ଶୀ’ ।
ସୃଜନାଭିମୁଖ୍ୟ
ଏକଦା ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ମୁଖ୍ୟମନ୍ତ୍ରୀ ଥିବା ନନ୍ଦିନୀ ଶତପଥୀ ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ରାଜନୀତି ତଥା ଓଡ଼ିଆ ସାହିତ୍ୟ ଜଗତରେ ଥିଲେ ଏକ ସ୍ଵତନ୍ତ୍ର ମର୍ଯ୍ୟାଦାର ଅଧିକାରିଣୀ । ଏକ ସୁପ୍ରତିଷ୍ଠିତ ସାହିତ୍ୟିକ ପରିବାରରେ ଜନ୍ମଗ୍ରହଣ କରିଥିବା ସେହି ଯଶସ୍ବିନୀ ମହାମହିଳା ଛାତ୍ରୀ ଅବସ୍ଥାରୁ ଓଡ଼ିଆ କବିତା ଓ କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ରଗଳ୍ପ ରଚନାରେ ମନୋନିବେଶ କରିଥିଲେ । ରାଜନୀତିକ ଜୀବନର ବ୍ୟସ୍ତତା ମଧ୍ୟରେ ତାଙ୍କ ସାରସ୍ଵତ ସାଧନା ସ୍ଵଚ୍ଛ ହେଲେ ମଧ୍ୟ ଥିଲା ଶକ୍ତିଶାଳୀ । ମାର୍ଜିତ ଭାଷା, ଆକର୍ଷଣୀୟ ଉପସ୍ଥାପନା ଶୈଳୀ ତଥା ବଳିଷ୍ଠ ଭାବାନୁଭୂତିରେ ତାଙ୍କ ସୃଷ୍ଟିସଂପଦ ସତତ ଉଦ୍ଭାସିତ ।
ରାଜନୀତି ଓ ସାହିତ୍ୟ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ସମନ୍ବୟ ସୃଷ୍ଟି କରି ନିଜର ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିପ୍ରତିଭାର ବୈଶିଷ୍ଟ୍ୟ ପ୍ରତିପାଦନ କରିଥିବା କତିପୟ ଉତ୍କଳୀୟମାନଙ୍କ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ନାରୀନେତ୍ରୀ ନନ୍ଦିନୀ ଶତପଥୀଙ୍କ ସ୍ଥାନ ସ୍ଵତନ୍ତ୍ର । କାରଣ ସେ ହିଁ ଏକମାତ୍ର ନାରୀ ଯେକି ସ୍ଵକୀୟ ଶକ୍ତି ଓ ସାଧନା ବଳରେ ଓଡ଼ିଶାର ବରେଣ୍ୟ ମୁଖ୍ୟମନ୍ତ୍ରୀ ଭାବରେ ସାରା ଭାରତବର୍ଷରେ ଚହଳ ସୃଷ୍ଟି କରିଥିଲେ । ଏହି ପ୍ରତିଭାମୟୀ ନାରୀ ଓଡ଼ିଆ ସାହିତ୍ୟର ସବୁଜଯୁଗର ଅନ୍ୟତମ ରଥୀ ଔପନ୍ୟାସିକ କବି କାଳନ୍ଦୀଚରଣ ପାଣିଗ୍ରାହୀଙ୍କର
ସୁପୁତ୍ରୀ ଥିଲେ । ତାଙ୍କ ପିତୃବ୍ୟ ଭଗବତୀଚରଣ ପାଣିଗ୍ରାହୀ ମଧ୍ୟ ପ୍ରଗତିବାଦୀ ଓଡ଼ିଆ ସାହିତ୍ୟ ଆନ୍ଦୋଳନର ଜଣେ ମୁଖ୍ୟ ପୁରୋଧା ଭାବରେ ପରିଚିତ ଥିଲେ । ବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟ ଜୀବନରୁ କବି ନନ୍ଦିନୀଙ୍କର ଓଡ଼ିଆ କବିତା ଓ କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ର ଗଳ୍ପ ରଚନାରେ ପାରଦର୍ଶିତା ରହିଥିଲା । ପରବର୍ତ୍ତୀ ଜୀବନର ରାଜନୈତିକ ବ୍ୟସ୍ତ-ବହୁଳତା ଭିତରେ ଏ ପ୍ରତିଭାରେ ସାମାନ୍ୟ ଶିଥୁଳତା ଆସିଥିଲେ ମଧ୍ୟ ତାଙ୍କର ସ୍ଵଳ୍ପ କେତୋଟି ସାରସ୍ଵତ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଶକ୍ତିଶାଳୀ ସାହିତ୍ୟିକ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଭଙ୍ଗୀର ଉଜ୍ଜ୍ବଳ ନିଦର୍ଶନ ରହିଥିଲା । ସାହିତ୍ୟର ସୃଜନୀଶକ୍ତି କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ତାଙ୍କର ଲେଖନୀ ଯେପରି ବଳିଷ୍ଠ ଓ ଶକ୍ତିଶାଳୀ ଥିଲା ରାଜନୈତିକ ପୃଷ୍ଠଭୂମିରେ ତାଙ୍କର ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଭଙ୍ଗୀ ଏବଂ ପଦକ୍ଷେପ ସେତିକି ଶକ୍ତିଶାଳୀ ଥିଲା । ତାଙ୍କ ମୁଖ୍ୟମନ୍ତ୍ରୀତ୍ୱ ସମୟରେ ରାଜ୍ୟର ଦୁଃସ୍ଥ ଶିକ୍ଷକ ସମାଜ ପାଇଁ ଏକ ନୂତନ ପଦକ୍ଷେପ ଶିକ୍ଷାକ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ବୈପ୍ଳବିକ ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନ ସୃଷ୍ଠି କରିପାରିଥ୍ ଲା।
ତାଙ୍କର ସାରସ୍ବତ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ସମୂହ ମଧ୍ଯରେ ତାଙ୍କ କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ରଗଳ୍ପ ସମାହାର ସମ୍ବଳିତ ‘କେତୋଟି କଥା’ ଓ ‘ସପ୍ତଦଶୀ’ ନାମକ ଦୁଇଟି ପୁସ୍ତକର ନାମ ଉଲ୍ଲେଖଯୋଗ୍ୟ । ତାଙ୍କ ରାଜନୈତିକ ଓ ସାରସ୍ଵତ ଜୀବନର ସମସ୍ତ ଅଭିଜ୍ଞତା ଓ ଅନୁଭୂତି ଉକ୍ତ କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ରଗଳ୍ପଗୁଡ଼ିକରେ ପ୍ରତିଫଳିତ ହୋଇଛି । ଅନୁବାଦ ସାହିତ୍ୟରେ ତାଙ୍କର କୃତିତ୍ଵ ମଧ୍ଯ ଅନସ୍ବୀକାର୍ଯ୍ୟ । ‘ଗାନ୍ଧି କଥାମୃତ’ ପାଇଁ ସେ କେନ୍ଦ୍ର ସାହିତ୍ୟ ଏକାଡ଼େମାଦ୍ୱାରା ପୁରସ୍କୃତ ହୋଇଥିଲା ୧୯୯୮ରେ ସେ ସମ୍ମାନଜନକ ‘ସାହିତ୍ୟଭାରତା’ ଉପାଧ୍ଧରେ ଭୂଷିତ ହୋଇଥିଲେ । ବାସ୍ତବରେ ସେ ଥିଲେ ‘ମାଟିର ମଣିଷ’ ସୃଷ୍ଟିକର୍ତ୍ତାଙ୍କର ସୁନାର କନ୍ୟା ।
ଗଦିର ପ୍ଠଷ୍ଠଭୂମି
ମହାମହିମ ମଗଧ ସମ୍ରାଟ ଅଶୋକଙ୍କର ଭାରତ ବିଜୟ ଅଭିଯାନ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ଦୁଷ୍କର୍ଷ ଓଡ଼ିଆ ପାଇକ ସୈନ୍ୟଙ୍କଦ୍ୱାରା ସୁରକ୍ଷିତ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ସାମ୍ରାଜ୍ୟ ସେଥିରେ ପ୍ରତିବନ୍ଧକ ସୃଷ୍ଟି କରିଥିଲା । ସେତେବେଳେ କଳିଙ୍ଗର ମହାରାଜା ଏବଂ ତାଙ୍କର ସୈନ୍ୟସାମନ୍ତ ଅତ୍ୟନ୍ତ ପରାକ୍ରମଶାଳୀ ଥିଲେ । ଏହା ସତ୍ତ୍ଵେ ସମ୍ରାଟ ଅଶୋକଙ୍କର ସାମ୍ରାଜ୍ୟବାଦ ଲିପ୍ସାର ଅଭିଳାଷ କରିଥିଲେ । ସେତେବେଳେ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ସାମ୍ରାଜ୍ୟ ଗଙ୍ଗାନଦୀର ମୁହାଣଠାରୁ ଗୋଦାବରୀ ମୁହାଣ ପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ ପରିବ୍ୟାପ୍ତ ଥିଲା ଏବଂ ଏହାର ବିଭିନ୍ନ ଅଞ୍ଚଳ କଳିଙ୍ଗ, ତୋଷାଳୀ, ଉଡୁ ଓ ଉତ୍କଳ ନାମରେ ଅଭିହିତ ଥିଲା ।
ଇତିହାସ କହିବା ଅନୁଯାୟୀ ଧଉଳି ପାହାଡ଼ର ପାଦଦେଶରେ ବହିଯାଉଥବା ଦୟାନଦୀ କୂଳରେ ସମ୍ରାଟ ଅଶୋକ ଏବଂ କଳିଙ୍ଗାଧୂପତିଙ୍କ ସାମରିକ ଫୌଜ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ପ୍ରଳୟଙ୍କରୀ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ ସଂଘଟିତ ହୋଇଥିଲା । ଯୁଦ୍ଧରେ ଅସଂଖ୍ୟ ସୈନ୍ୟଙ୍କ ଲାଲରକ୍ତରେ ଜୟାନଦା ରକ୍ତରଞ୍ଜ ହୋଇଉଠିଥ୍ ଲା ଉଭୟପକ୍ଷର ବିପୁଳ କ୍ଷୟ୍ କ୍ଷତି ହୋଇଉଠିଥ୍ ଲା । ଉଭୟ ପକ୍ଷୟ ପକ୍ଷଙ୍କ ହୃଦୟରେ ପ୍ରତିହିଂସା ବହ୍ନି ନିର୍ବାପିତ ହୋଇପାରି ନଥିଲା । ସ୍ୱାଭିମାନୀ କଳିଙ୍ଗବାସୀ ଅସ୍ଥିର ହୋଇଉଠିଥିଲେ । ବିପୁଳ ମଗଧ ସୈନ୍ୟମାନଙ୍କ ଆକ୍ରମଣରେ କଳିଙ୍ଗର ମହାରାଜା ପରାହତ ହୋଇ ବନ୍ଦୀ ହେଲେ । ରାଣୀ କୁରୁବକୀଙ୍କୁ ନାନାପ୍ରକାର ମାନସିକ ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣା ଦିଆଗଲା ।
ଘମାଘୋଟ ଯୁଦ୍ଧରେ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ପ୍ରଜାଶୂନ୍ୟ ହେବାରେ ଲାଗିଲା । ଚତୁର୍ଦ୍ଦିଗରେ ମୃତ, ପରାହତ ସୈନ୍ୟମାନଙ୍କ ଆର୍ଭଚିତ୍କାର ସମଗ୍ର କଳିଙ୍ଗକୁ ପ୍ରକମ୍ପିତ କରିଦେଲା । ଶେଷରେ କଳିଙ୍ଗଯୁଦ୍ଧର ବିଭୀଷିକା ଅଶୋକଙ୍କ ମନରେ ଦାରୁଣ ଆଘାତ ଦେଇଥିଲା ଏବଂ ଏହାଫଳରେ ତାଙ୍କ ହୃଦୟରେ ଅପୂର୍ବ ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନ ଦେଖାଦେଇଥିଲା। କଳିଙ୍ଗର ଏକ ସାଧାରଣ ବୃଦ୍ଧାଙ୍କର ନିଜ ପୁତ୍ରର ଜୀବନ ଭିକ୍ଷା ଏବଂ ବୌଦ୍ଧଭିକ୍ଷୁ ଉପଗୁପ୍ତଙ୍କର ଶାନ୍ତିର ଆବାହନୀ ତାଙ୍କୁ ଚଣ୍ଡାଶୋକରୁ ଧର୍ମାଶୋକରେ ପରିଣତ କରିଥିଲା । ଏହାପରେ କଳିଙ୍ଗର ପ୍ରଜାମାନଙ୍କ ପ୍ରତି ତାଙ୍କର ଏକ ସ୍ୱତନ୍ତ୍ର ଅନୁରାଗ ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହୋଇଥିଲା । କଳିଙ୍ଗ ବିଜୟ ପରେ ଅଶୋକ କଳିଙ୍ଗକୁ ପ୍ରାଚ୍ୟ-
ପ୍ରଦେଶରେ ସମ୍ମିଳିତ କରି ଏହାକୁ ନିଜର ପ୍ରତ୍ୟକ୍ଷ ଶାସନାଧୀନରେ ରଖିଲେ । କଳିଙ୍ଗ ହିଁ ଅଶୋକଙ୍କ ଯୁଦ୍ଧଭେରୀକୁ ନିସ୍ତବ୍ଧ କରି ତାଙ୍କୁ ଧର୍ମଭେରୀର ନିନାଦ ପାଇଁ ଆହ୍ୱାନ ଦେଇଥିଲା । ସୁତରାଂ ଏହାପରେ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ଅଶୋକଙ୍କ ପାଇଁ ବିଶେଷ ଆକର୍ଷଣ ତଥା ଏକ ଦୁର୍ବଳତା ରୂପେ ପ୍ରକାଶ ପାଇଥିଲା । ଏହାପରେ ଏହି ବିରାଟ ରାଜ୍ୟକୁ ମଗଧ ସାମ୍ରାଜ୍ୟରେ ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକ୍ତ କରି ଏଠାରେ ଏକ ପ୍ରାଦେଶିକ ଶାସନ ପ୍ରଚଳନ କଲେ । କଳିଙ୍ଗ ଯୁଦ୍ଧରେ କଳିଙ୍ଗବାସୀ ବିଶେଷ ଭାବରେ କ୍ଷତିଗ୍ରସ୍ତ ହୋଇଥିବାରୁ ସେମାନଙ୍କ ମନରୁ ପ୍ରତିହିଂସାର ବହ୍ନି ଲିଭିପାରିନଥିଲା । ତେଣୁ ଅଶୋକ କଳିଙ୍ଗର ପ୍ରଶାସନରେ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିଗତ ହସ୍ତକ୍ଷେପ କରି କର୍ମଚାରୀମାନଙ୍କୁ ନିୟନ୍ତ୍ରଣ କଲେ ଏବଂ ସେମାନଙ୍କୁ କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟନିଷ୍ଠା ଓ ମାନବପ୍ରେମରେ ଉଦ୍ବୁଦ୍ଧ କଲେ । କଳିଙ୍ଗରେ ଏକ ଜନମଙ୍ଗଳ ପ୍ରଶାସନର
ପ୍ରବର୍ତ୍ତନ ହେଲା । ପ୍ରଶାସନ ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ ଜନସାଧାରଣଙ୍କୁ ଧର୍ମ ଓ ନୈତିକ ମୂଲ୍ୟବୋଧ ପ୍ରତି ଆକୃଷ୍ଟ କରାଗଲା । ଏହି ସୁଶାସନ ପ୍ରଚଳନ କରି ସମ୍ରାଟ ଅଶୋକ ଜଣେ ପ୍ରଜାପ୍ରିୟ ସୁଶାସକ ହେଲେ ଏବଂ ତାଙ୍କର ଶାସନ ପ୍ରକ୍ରିୟା ସମଗ୍ର ଭାରତର ଶାସନ ପାଇଁ ଏକ ଆଦର୍ଶ ଶାସନ ରୂପେ ସ୍ବୀକୃତ ହୋଇ ତାହା ସମଗ୍ର ଭାରତୀୟଙ୍କ ପ୍ରଶାସନ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ଅନୁସୃତ ହେଲା । ଏ ହେଲା ଇତିହାସର କଥାବସ୍ତୁ ।
କିନ୍ତୁ ଏହି ଐତିହାସିକ ତଥ୍ୟ ପଛରେ କିଛି ଅନାଲୋଚିତ ତଥା ଅଲିଖ୍ ତଥ୍ୟ ଆତ୍ମଗୋପନ କରି ରହିଛି, ଯାହା ଇତିହାସ ତାହାର ପୃଷ୍ଠାରେ ସ୍ଥାନିତ କରିବାକୁ ସମର୍ଥ ହୋଇପାରିନାହିଁ । ସେହି ଅନାଲୋଚିତ ତଥା ଅଲିଖ୍ତ ତଥ୍ୟକୁ ସମ୍ବଳ କରି ପଠିତ ଗଳ୍ପଟିକୁ ଗାଳ୍ପିକା ଲୋକଲୋଚନକୁ ଆଣିବା ସଙ୍ଗେ ସଙ୍ଗେ ଉତ୍କଳର ଏକ ଉଜ୍ଜଳ ଇତିହାସକୁ ଉତ୍କଳୀୟମାନଙ୍କ ନିକଟରେ ପହଞ୍ଚାଇବାକୁ ଅଭିଳାଷ ପୋଷଣ କରିଛନ୍ତି । ଏ ପ୍ରକାର ତଥ୍ୟ ପ୍ରଚଳିତ ଐତିହାସିକ ତଥ୍ୟଠାରୁ ସାମାନ୍ୟ ଭିନ୍ନ । ଏହି ତଥ୍ୟ ଅନୁଯାୟୀ ମହାମହିମ ସମ୍ରାଟ ଅଶୋକ ନିଜର ଅପରାଜେୟ ସୈନ୍ୟସାମନ୍ତଙ୍କ ପରାକ୍ରମରେ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ଯୁଦ୍ଧରୁ ବିରତ ହୋଇନଥିଲେ । କିଛି ପରିସ୍ଥିତି ତାଙ୍କୁ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ଯୁଦ୍ଧରୁ ବିରତ ହେବାକୁ ବାଧ୍ୟ କରିଥିଲା । ବାସ୍ତବରେ ଇତିହାସ ବାରମ୍ବାର ପ୍ରମାଣ କରିଆସିଛି, ରାଜନୀତିର ବ୍ରହ୍ମାସ୍ତ୍ର ହେଉଛି ଷଡ଼ଯନ୍ତ୍ର । ଜଣେ ସ୍ବକୀୟ ପରାକ୍ରମରେ ବୀର ହୋଇପାରେ, କିନ୍ତୁ ସାମ୍ରାଜ୍ୟ ବିସ୍ତାର କରିନପାରିଲେ, ଇତିହାସ ତାଙ୍କୁ ସମ୍ରାଟ ବା ବୀର ବୋଲି ଆଖ୍ୟା ଦେଇପାରେ ନାହିଁ। ପଠିତ ଗଳ୍ପରେ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ରାଜଜେମାଙ୍କର ଅପୂର୍ବ ବୀରତ୍ଵ ଓ ଚତୁର ଯୁଦ୍ଧ ପରିଚାଳନାରେ ହତୋତ୍ସାହ ହୋଇ ସମ୍ରାଟ ଅଶୋକ ଯୁଦ୍ଧରୁ ବିରତ ରହି ଧର୍ମର ପଥ ଅନ୍ଵେଷଣ କରିବାର ସିଦ୍ଧାନ୍ତ ଗ୍ରହଣ କରିଥିଲେ ।
ବାସ୍ତବରେ ଅଶୋକ ବହୁକାଳ ଧରି ଅଶାନ୍ତ କଳିଙ୍ଗବାସୀଙ୍କ ପ୍ରତି କଠୋର ଆଚରଣ କରିଚାଲିଥିଲେ । ଇତିହାସର ଶିଳାଲେଖମାନଙ୍କରୁ ଏହାର ଦୃଷ୍ଟାନ୍ତ ମିଳିଥାଏ । ଅଥଚ ସମ୍ରାଟଙ୍କର ଏହି ଛଳନାତ୍ମକ ରାଜନୀତିକୁ ଇତିହାସ ସମ୍ମାନ ଦେଇଥିଲେ ମଧ୍ୟ ରାଜଜେମା ରାଜେଶ୍ୱରୀଙ୍କ ଅପୂର୍ବ ସାହସ, ନିଷ୍ଠା ଓ ଚତୁରତା ଯୁଦ୍ଧ ପରିଚାଳନାର ଦକ୍ଷତାକୁ ସମ୍ମାନ ଦେବାରେ ନୀରବତା ଅବଲମ୍ବନ କରିଛି । ଇତିହାସର ଏହି ଅନାଲୋଚିତ ସତ୍ୟକୁ ଗାଳ୍ପିକା ନନ୍ଦିନୀ ଶତପଥୀ ଦୁଇଟି ବିଶେଷ ଚରିତ୍ର ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ ପରିପ୍ରକାଶ କରିବାକୁ ଚେଷ୍ଟା କରିଛନ୍ତି । ଏହି ଦୁଇଟି ଚରିତ୍ର ମଧ୍ୟରୁ ଗୋଟିଏ ଚରିତ୍ର ହେଲେ ନାଳନ୍ଦା ବିଶ୍ବବିଦ୍ୟାଳୟରୁ ଗବେଷଣା କାର୍ଯ୍ୟରେ ଓଡ଼ିଶାକୁ ଆସିଥିବା ଇତିହାସର ଛାତ୍ର ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଚୌଧୁରୀ ଏବଂ ଅନ୍ୟ ଚରିତ୍ରଟି ସମୟ ବା ଇତିହାସ ପୁରୁଷ ।
![]()
ସାରକଥା
ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଚୌଧୁରୀ ଧଉଳି ପାହାଡ଼ର ପାଦଦେଶରେ ଥିବା ଏକ ବଡ଼ ପଥର ମୁଣ୍ଡିଆ ଉପରେ ବସିରହି ଖ୍ରୀ.ପୂ. ତୃତୀୟ ଶତାବ୍ଦୀରେ ମଗଧ ସମ୍ରାଟ ଅଶୋକ ଓ ପରାକ୍ରମଶାଳୀ କଳିଙ୍ଗସେନା ମଧ୍ୟରେ ସଂଘଟିତ ପ୍ରଳୟଙ୍କରୀ କଳିଙ୍ଗଯୁଦ୍ଧର ସ୍ମୃତିକୁ ରୋମନ୍ଥନ କରିଚାଲିଛନ୍ତି । ରୋମନ୍ଥନ ଭିତରେ ସେ ଇତିହାସର କିଛି ରହସ୍ୟମୟ ଘଟଣା ସମ୍ପର୍କରେ ଦ୍ବନ୍ଦ୍ବରେ ପଡ଼ିଯିବା ସମୟରେ ଇତିହାସ ତାକୁ ପ୍ରକୃତ ସତ୍ୟ ସମ୍ପର୍କରେ ଅବତାରଣା କରିଛି । ବହୁବର୍ଷତଳେ ମଗଧ ସମ୍ରାଟ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ବିଜୟ କରି ଏହାକୁ ତାଙ୍କର ସାମ୍ରାଜ୍ୟରେ ଅନ୍ତର୍ଭୁକ୍ତ କରିଥିଲେ । କଳିଙ୍ଗ ବିଜୟ ସମୟରେ ସମ୍ରାଟ ଅଶୋକ ବହୁ ପ୍ରତିବନ୍ଧକର ସମ୍ମୁଖୀନ ହୋଇଥଲେ ଦୁର୍ବର୍ଷ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ସେନାନୀଙ୍କୁ ପ୍ରତିହତ କରି ସହଜରେ କଳିଙ୍ଗକୁ ବିଜୟ କରିବା ସମ୍ଭବପର ନଥିଲା । ବିରାଟ ମଗଧ ବାହିନୀକୁ କ୍ଷୁଦ୍ର କଳିଙ୍ଗର ଦୁର୍ଦ୍ଧର୍ଷ ସେନାବାହିନୀ ସହଜରେ ନିଜ ରାଜ୍ୟକୁ ସମର୍ପଣ କରିଦେବାକୁ ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ ନଥିଲେ । ପରାକ୍ରମୀ କଳିଙ୍ଗସେନା ନିଜର ଶେଷ ରକ୍ତବିନ୍ଦୁ ଥିବା ପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ ମଗଧବାହିନୀକୁ ପ୍ରତିରୋଧ କରିବାକୁ ଦୃଢ଼ ଶପଥ ନେଇଥିଲେ ।
ଅନ୍ୟ ଉପାୟ ନପାଇ ମଗଧ ସମ୍ରାଟ ଷଡ଼ଯନ୍ତ୍ର କରି ନିଷ୍ଠୁର ଭାବରେ ମୁଷ୍ଟିମେୟ କଳିଙ୍ଗସେନାକୁ ଦମନ କରି କଳିଙ୍ଗକୁ ଅକ୍ତିଆର କରିଥିଲେ । କଳିଙ୍ଗ ସେନାବାହିନୀଙ୍କ ପାଇଁ ତାଙ୍କର ମହାରାଜାଙ୍କର ସ୍ୱାଭିମାନ ରକ୍ଷାଥିଲା ପ୍ରଥମ କର୍ଭବ୍ୟ । ଏଣୁ ଏହି ଗୁରୁତ୍ୱପୂର୍ଣ ଯୁଦ୍ଧରେ ଅଶୋକ ଏବଂ ତାଙ୍କ ସେନାପତିମାନଙ୍କୁ ଇତିହାସ ତା ପୃଷ୍ଠାରେ ସ୍ମୃତିର ଶଙ୍ଖାଳି କରି ସାଇତି ରଖୁଥିବାବେଳେ କଳିଙ୍ଗର ସ୍ଵାଭିମାନୀ ଏବଂ ପରାକ୍ରମଶାଳୀ ରାଜାଙ୍କର ସ୍ମୃତି ପାଇଁ ନୀରବ କାହିଁକି ? ସେତେବେଳେ କଳିଙ୍ଗର ରାଜା କିଏ ଥିଲେ ଏବଂ କାହାକୁ ପରାଜିତ କରି ଅଶୋକ ବିଜୟର ଧ୍ଵଜା ଉଡ଼ାଇଥିଲେ- ଏ ସମ୍ପର୍କରେ ଇତିହାସର ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ଅଭିମତ କିଛି ନଥିବା ସମ୍ପର୍କରେ ଇତିହାସ ଛାତ୍ର ଅଙ୍ଗଦଙ୍କ ମନରେ ବିଭିନ୍ନ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନବାଚୀ ଉଙ୍କିମାରିଛି । ଅଶୋକଙ୍କ ଶିଳାଲେଖ ପଢ଼ିଛନ୍ତି ଅଙ୍ଗଦ । ସେଥୁରେ ଅହିଂସା, ଦୟା, କ୍ଷମା ଇତ୍ୟାଦି ବିଷୟରେ ବହୁ ଆଲୋଚନାତ୍ମକ ତଥ୍ୟ ପ୍ରଦର୍ଶନ କରାଯାଇଛି । ରାଜାଙ୍କର ରନ୍ଧନଶାଳାରେ କେତୋଟି
ମୟୂରମାଂସ ରନ୍ଧାଯାଇ ପାରିବ ଏବଂ କେଉଁ କେଉଁ ପ୍ରାଣୀଙ୍କୁ ବଧ କରାଯିବ ନାହିଁ, ସେସବୁ ଉଲ୍ଲେଖ ରହିଛି, ଅଥଚ କଳିଙ୍ଗରାଜାଙ୍କ ବିଷୟରେ କେଉଁଠି କିଛି ଆଲୋଚନା କରାଯାଇନାହିଁ । ଏଇସବୁ ପୁଞ୍ଜୀଭୂତ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନର ଉତ୍ତର ଖୋଜୁଖୋଜୁ ସୂର୍ଯ୍ୟ ପଶ୍ଚିମ ଦିଗରେ ରକ୍ତମଧ୍ଵଜାର ସଙ୍କେତ ଦେଇ ବିଦାୟ ନେବାକୁ ବସିଲେଣି। ମନ ଭିତରେ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ଯୁଦ୍ଧର ଭୟଙ୍କରତା ଉଙ୍କିମାରି ଉଠିବାରୁ ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଚମକି ଉଠିଲେ । ଯେଉଁଠି ମଗଧସେନା ଏବଂ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ସେନାଙ୍କ ଭିତରେ ଘମାଘୋଟ ଲଢ଼େଇ ଚାଲିଥିଲା, ସେ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ଘଞ୍ଚ ଜଙ୍ଗଲର ପ୍ରାବଲ୍ୟ । ତାରି ସ୍ମ ତିପଟରୁ ତାଙ୍କୁ ଶୁଣାଯାଉଥିଲା ଅସଂଖ୍ୟ ଘୋଡ଼ାଟାପୁର ଶବ୍ଦ । ଘୋଡ଼ାଟାପୁ ଆଉ ସେମାନଙ୍କର ଭୟଙ୍କର ଚିତ୍କାର ସହିତ ଢାଲ, ତରବାରି ଅସ୍ତ୍ରସମୂହର ଝଣତ୍କାର ଶବ୍ଦ । ଦୟାନଦୀରେ ରକ୍ତର ସୁଅ, ଅସଂଖ୍ୟ ସେନାନୀଙ୍କ ମୃତ୍ୟୁକଳୀନ ବିକଟ ଚିତ୍କାର । ଦୁଇଆଣ୍ଠୁ ଭିତରେ ମୁହଁକୁ ଗୁଞ୍ଜି ବସିରହିଲେ ଅଙ୍ଗଦ । ଭୟରେ ସମଗ୍ର ଶରୀର ତାଙ୍କର କମ୍ପି ଉଠୁଥିଲା ।
ହଠାତ୍ ତାଙ୍କ କାନ୍ଧ ଉପରେ ଜଣେ ଦୀର୍ଘଦେହୀ ପୁରୁଷଙ୍କର କୋମଳସ୍ପର୍ଶରେ ତାଙ୍କ ସ୍ବପ୍ନ ଭଙ୍ଗ ହୋଇଥିଲା । ତାଙ୍କର ବେଶପୋଷାକରୁ ସେ ଜଣେ ରାଜପୁରୁଷ ଭାବି ଅଙ୍ଗଦଙ୍କ ମନରେ ସନ୍ଦେହ ଆସିବାରୁ ସେ ତାଙ୍କୁ କଳିଙ୍ଗର ରାଜା ମନେକରି ପ୍ରଶ୍ନ କରିଥିଲେ । ଅଙ୍ଗଦଙ୍କ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନର ଉତ୍ତରକୁ ଏଡ଼ିଦେଇ ସେ ଦୀର୍ଘକାୟ ପୁରୁଷ ସ୍ମୃତିର କଳିଙ୍ଗର ମହାରାଜାଙ୍କ ନିକଟରେ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନ କରିଥିଲେ । ଅଙ୍ଗଦଙ୍କ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନର ଉତ୍ତରକୁ ଏଡ଼ିଦେଇ ସେ ଦୀର୍ଘକାୟ ପୁରୁଷ ସ୍ମୃତିର କଳିଙ୍ଗର ମହାରାଜାଙ୍କ ନିକଟରେ ତାଙ୍କୁ ପହଞ୍ଚାଇ ଦେଇଥିଲେ ।
କଳିଙ୍ଗର ରାଜଦରବାରରେ ସେତେବେଳକୁ ବିମର୍ଷର ବାତାବରଣ ଭରିଯାଇଥାଏ । ଆହତ କଳିଙ୍ଗାଧୂପତି ଶଯ୍ୟାଶାୟୀ । ଏହି ସମୟରେ ରାଣୀଅନ୍ତଃପୁରରୁ ଧୀରେ ଧୀରେ ପାହାଚ ପରେ ପାହାଚ ଅତିକ୍ରମ କରି ଓହ୍ଲାଇ ଆସୁଥିଲେ ନୂତନ ଏକ ମନ୍ତ୍ରଣା ସହିତ କଳିଙ୍ଗକୁ ଆସନ୍ନ ବିପଦରୁ ରକ୍ଷା କରିବାପାଇଁ । ମହାରାଣୀଙ୍କ ପ୍ରବେଶମାତ୍ରେ ଦରବାର କକ୍ଷର ସମସ୍ତ ଗୁଞ୍ଜରଣ ହଠାତ୍ ସ୍ତବ୍ଧ ହୋଇଗଲା । ପାତ୍ରମନ୍ତ୍ରୀ ପାରିଷଦବର୍ଗଙ୍କ ସମେତ ସମସ୍ତ ସେନାନାୟକମାନେ ତାଙ୍କୁ ସସପ୍ତମ ଅଭିବାଦନ ଜ୍ଞାପନ କଲେ । ଦରବାର କକ୍ଷରେ ସମସ୍ତଙ୍କ ମୁହଁରେ ଗଭୀର ଉତ୍କଣ୍ଠା ଭରିରହିଥିଲା । ସମସ୍ତ ଉତ୍କଣ୍ଠାର ଅବସାନ ଘଟାଇ ମହାରାଣୀ ପାରିଷଦ ବର୍ଗଙ୍କ ପାଇଁ ଆଣିଥିବା ମହାରାଜାଙ୍କର ଏକ ନୂତନ ବାର୍ତ୍ତା ସମ୍ପର୍କରେ ସୂଚନା ଦେଇଥିଲେ ।
ସେହି ନୂତନ ବାର୍ତ୍ତାଟି ହେଲା, କରିଛନ୍ତି । ତାଙ୍କର ନିଷ୍ପତ୍ତି ଏବଂ ବିଚାର ବର୍ତ୍ତମାନର ସଙ୍କଟମୟ ମୁହୂର୍ତ୍ତ ପାଇଁ ଶେଷସମ୍ବଳ । ଏ ସମ୍ପର୍କରେ ମହାରାଣୀ କୁରୁବକୀ ପାରିଷଦ ବର୍ଗଙ୍କର ମତାମତ ଲୋଡ଼ିଥିଲେ । କଳିଙ୍ଗର ମହାରାଜାଙ୍କ ସିଦ୍ଧାନ୍ତ ହିଁ ସର୍ବଶେଷ ସିଦ୍ଧାନ୍ତ ବୋଲି ପାରିଷଦବର୍ଗ ଏକ କଣ୍ଠରେ ସ୍ଵୀକାର କରିବାପରେ ରାଜଜେମା ରାଜେଶ୍ୱରୀଙ୍କୁ ଯୁଦ୍ଧପରିଚାଳନାର ଦାୟିତ୍ବ ପ୍ରଦାନ କରାଯାଇଥିଲା ।
ତା’ପରେ ଆରମ୍ଭହେଲା ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀଙ୍କର ଯୁଦ୍ଧ ମନ୍ତ୍ରଣା । ଦରବାର କକ୍ଷରେ ସପତି ପ୍ରବେଶ କରିବାପରେ ସର୍ବପ୍ରଥମେ ସପ୍ତମତାର ସହ ରାଜକୁମାରୀ ସଭାସଦ୍ମାନେ ତାଙ୍କର ପିତାଙ୍କର ଇଚ୍ଛାକୁ ସମ୍ମାନ ଦେଇଥିବାରୁ ସେମାନଙ୍କୁ ତାଙ୍କର କୃତଜ୍ଞତା ସମ୍ପର୍କରେ ସଚେତନ କରାଇବା ପରେ ତାଙ୍କ ପ୍ରତି ରାଜ୍ୟବାସୀଙ୍କର ଆସ୍ଥା ରହିଛି କି ନାହିଁ ତାହା ଜାଣିବାକୁ ଚାହିଁଥିଲେ । ରାଜକୁମାରୀଙ୍କର ବିନୟ ସପ୍ତମ ବାକ୍ୟରେ ସଭାସଦ୍ମାନେ ନିର୍ଭିକ ଓ ମୁକ୍ତକଣ୍ଠରେ ରାଜକୁମାରୀଙ୍କୁ ଉପସ୍ଥିତ ପରିସ୍ଥିତିର ସଙ୍କଟ ସମ୍ପର୍କରେ ଅବଗତ କରାଇଥିଲେ । ମହାମନ୍ତ୍ରୀଙ୍କ ସମେତ ରାଜପରିଷଦର ଅନ୍ୟାନ୍ୟ ସଭ୍ୟବୃନ୍ଦଙ୍କର ସମସ୍ତ ବ୍ୟଗ୍ରତା
ସଙ୍କଟ ସମ୍ପର୍କରେ ଅବଗତ କରାଇଥ୍ ଲୋ ମହାମନ୍ତ୍ରାଙ୍କ ସମେତ ରାଜପରିଷଦର ଅନ୍ୟାନ୍ୟ ସଭ୍ୟବୃନ୍ଦଙ୍କର ସମସ୍ତ ବ୍ୟଗ୍ରତା ଶୁଣିବାପରେ କଳିଙ୍ଗର ଏହି ଉପସ୍ଥିତ ସଙ୍କଟ ସର୍ମର୍କରେ ସେ ପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ ଅବଗତ ଅଛନ୍ତି ବୋଲି ରାଜ୍ୟବାସୀଙ୍କୁ ଆଶ୍ୱାସନା ଦେଇଥିଲେ ଏବଂ ଏଭଳି ପରିସ୍ଥିତିରେ ସେ ରାଜପରିଷଦର ସମସ୍ତ ପ୍ରତିନିଧ୍ଵଙ୍କର ପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ ସହଯୋଗ ଆଶା କରନ୍ତି ବୋଲି ବ୍ୟକ୍ତ କରିଥିଲେ । ରାଜେଶ୍ୱରୀଙ୍କ କଣ୍ଠର ଦୃଢ଼ତା ରାଜପ୍ରତିନିଧ୍ଵଙ୍କ ନିକଟରେ ଅଦ୍ଭୁତ ପ୍ରଭାବ ସୃଷ୍ଟି କରିଥିଲା । ସମସ୍ତେ ଏକ ସ୍ବରରେ ରାଜକୁମାରୀଙ୍କୁ ସମର୍ଥନ କରିବାକୁ ପ୍ରତିଶ୍ରୁତି ଦେଇଥିଲେ ।
ଏହାପରେ ରାଜକୁମାରା ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରା ତୁରନ୍ତ ସେମାନଙ୍କ ମଧ୍ୟରୁ ବାରଜଣ ଯୋଦ୍ଧାଙ୍କର ଆଚ୍ଶ୍ୟକତା ସମ୍ପର୍କରେ ଜଣାଇଥିଲେ । ସମ୍ରାଟ ଅଶୋକଙ୍କ ବିରାଟ ମଗଧବାହିନୀର ମୁକାବିଲା କରି ହତୋତ୍ସାହ ହୋଇପଡ଼ିଥିବା କଳିଙ୍ଗ ଯୋଦ୍ଧାମାନେ ଏତେଶୀଘ୍ର ଏକ ଗୁରୁତ୍ଵପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ ନିଷ୍ପତ୍ତି ଆଶାକରି ନଥିଲେ ମଧ୍ୟ ରାଜକୁମାରୀଙ୍କ ଦୃଢ଼ ନେତୃତ୍ୱ ପ୍ରତି ଆସ୍ଥା ସ୍ଥାପନ କରି ତାଙ୍କସହ ସମ୍ମତ ହୋଇଥିଲେ ଏବଂ ତାଙ୍କର ପତିଙ୍କ ସହ ବାରଜଣରୁ ବହୁ ଅଧ୍ଵ ଯୁଦ୍ଧରେ ଅବତୀର୍ଣ୍ଣ ହେବାକୁ ସ୍ଵେଚ୍ଛାକୃତ ଭାବରେ
ଆଗେଇ ଆସିଲେ । କାରଣ ରାଜକୁମାରୀଙ୍କର ସର୍ଭ ଥିଲା ଯେ ସେ ନିଜେ ବାରଜଣଙ୍କୁ ନିର୍ବାଚନ କରିବେ ନାହିଁ । ଯୋଦ୍ଧାମାନେ ନିଜ ଇଚ୍ଛାରେ ତାଙ୍କ ସହିତ ସାମିଲ ହେବେ । ଏଣୁ ବହୁ ଦେଶପ୍ରେମୀ ଯୋଦ୍ଧା ରାଜକୁମାରୀଙ୍କ ରଣକୌଶଳ ଯୋଜନାରେ ସାମିଲ ହୋଇଥିଲେ । ହେଲେ ରାଜକୁମାରୀ ମାତ୍ର ବାରଜଣ ଯୋଦ୍ଧାଙ୍କର ଆବଶ୍ୟକତା ଚାହିଁଥିଲେ । ଏଥିପାଇଁ ପୂର୍ବରୁ ତାଙ୍କ ପ୍ରତି ଆସ୍ଥା ସ୍ଥାପନ କରିନଥିବା ବଳକା ପାଞ୍ଚଜଣ ଯୋଦ୍ଧାଙ୍କୁ ସେ ତାଙ୍କ ମନ୍ତ୍ରଣାକକ୍ଷରୁ ଦୂରେଇ ରଖୁଥିଲେ ଏବଂ ଆବଶ୍ୟକ ହେଲେ ତାଙ୍କର ସାହାଯ୍ୟ ପରବର୍ତ୍ତୀ ସମୟରେ ନିଆଯିବ ବୋଲି କହିଥିଲେ । ଏ ସଂଗ୍ରାମ ଦୀର୍ଘଦିନ ଧରି ଲାଗିରହିପାରେ ବୋଲି ମଧ୍ୟ ସୂଚନା ଦେଇଥିଲେ ।
ଏହାପରେ ସେହି ବାରଜଣ ଯୋଦ୍ଧାଙ୍କୁ ନିଜର ମନ୍ତ୍ରଣାକକ୍ଷକୁ ଡାକି ତାଙ୍କର ରଣକୌଶଳ ସମ୍ପର୍କରେ ଗୁପ୍ତନିର୍ଦେଶ ପ୍ରଦାନ କରିଥିଲେ ଏବଂ ତାଙ୍କର ସେଇ ଗୁପ୍ତମନ୍ତ୍ରଣା ସେମାନଙ୍କ ବ୍ୟତୀତ କୌଣସି ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିଙ୍କ ନିକଟରେ ନ ପହଞ୍ଚିବାପାଇଁ ସତର୍କ କରାଇଦେଲେ । ବାରଜଣ ଯୋଦ୍ଧାଙ୍କୁ ବାରଟି ସେନାପତିର ଅଧିକାର ପ୍ରଦାନ କରାଗଲା ।
ଏହାପରେ ଧଉଳିର ପାଦଦେଶ ରଣହୁଙ୍କାରରେ ପ୍ରକମ୍ପିତ ହେଲା ଘୋଡ଼ାଟାପୁର ଶବ୍ଦରେ । ଅସ୍ତ୍ରର ଝଣତ୍କାର ଶବ୍ଦ ଏବଂ ସୈନିକମାନଙ୍କର ଆହତ ଚିତ୍କାରରେ ଧଉଳି ପ୍ରତିଧ୍ଵନିତ ହୋଇଉଠିଥିଲା । ଦୟାନଦୀର ସୁଅରେ ରକ୍ତର ଛଟା ଖେଳିଗଲା । କଳିଙ୍ଗ ସେନାପତିଙ୍କର ଆଦେଶ ଏବଂ ଯୁଦ୍ଧର ଭୟଙ୍କରତା ଧଉଳି ଅଞ୍ଚଳକୁ ବିଭୀଷିକାମୟ କରିଉଠିଥିଲା । କଳିଙ୍ଗର ଗାଁ ଗଣ୍ଡାରୁ ହାତରେ, ଖଣ୍ଡା, ତଲବାର, ତୀର, ବର୍ଚ୍ଛା ଧରି ଲଢ଼େଇ କ୍ଷେତ୍ରକୁ ଛୁଟି ଆସିଥିଲେ ଅଗଣିତ ଦେଶପ୍ରେମୀ । ଅସଂଖ୍ୟ ଯୋଦ୍ଧାରେ ରଣକ୍ଷେତ୍ର ପୂଣ୍ଡିହେବାଯୋଗୁଁ କେଉଁ ପକ୍ଷର କେତେ ସୈନ୍ୟ ମୃତାହତ ହେଉଥିଲେ, ତାହା କଳନା କରି ହେଉନଥିଲା ।
ମାସ ପରେ ମାସ ଅତିକ୍ରମ କରି ଚାଲିଲା । ହେଲେ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ସେନାବାହିନୀ ପରାଜିତ ହେବାର କୌଣସି ସୂଚନା ମିଳୁନଥିଲା । ଏଣୁ ଚିନ୍ତାନ୍ବିତ ସମ୍ରାଟ ଅଶୋକ ମହାମନ୍ତ୍ରୀଙ୍କଠାରୁ ଏହାର ପ୍ରକୃତ କାରଣ ଜାଣିବାକୁ ଚାହିଁଥିଲେ । କଳିଙ୍ଗ ରାଜକୁମାରୀଙ୍କର ଚତୁର ଯୁଦ୍ଧପରିଚାଳନା, କଳିଙ୍ଗ ଯୋଦ୍ଧା ମନରେ ଅସୀମ ଦୃଢ଼ତା ଓ ପ୍ରଜାମାନଙ୍କର ସ୍ବାଧୀନତା ରକ୍ଷା ପାଇଁ ଅକ୍ଳାନ୍ତ ଉଦ୍ୟମହିଁ ଏହାର ପ୍ରକୃତ କାରଣ ବୋଲି ଜାଣିବାକୁ ପାଇଥିଲେ ମଗଧ ସମ୍ରାଟ । ଚାରିମାସ ଧରି ଯୁଦ୍ଧ ଚାଲିଛି । ହଜାର ହଜାର ସୈନ୍ୟ ମୃତାହତ ହେଲେଣି । ମଗଧ ସୈନ୍ୟବାହିନୀଙ୍କ ପାଇଁ ସଞ୍ଚତ ଖାଦ୍ୟ ଏବଂ ଆବଶ୍ୟକ ଦ୍ରବ୍ୟ ମଧ୍ୟ ଶେଷହେବାକୁ ବସିଲାଣି । ଭ୍ରମ ବୁଝିପାରିଥିଲେ । ଏଣୁ ତୁରନ୍ତ ସମ୍ମାନର ସହ ଏ ଯୁଦ୍ଧର ଅବସାନ ଘଟାଇବାପାଇଁ ସମ୍ରାଟ ଅଶୋକ ରାଜନୀତିର ବ୍ରହ୍ମାସ୍ତ୍ର ଭ୍ରମ ବୁଝିପାରିଥିଲେ । ଏଣୁ ତୁରନ୍ତ ସମ୍ମାନର ସହ ଏ ଯୁଦ୍ଧର ଅବସାନ ଘଟାଇବାପାଇଁ ସମ୍ରାଟ ଅଶୋକ ରାଜନୀତିର ବ୍ରହ୍ମାସ୍ତ୍ର ବୋଲି କୁହାଯାଉଥିବା କୂଟନୀତିର ପ୍ରୟୋଗ କରିଥିଲେ ।
ପରଦିନ ପ୍ରତ୍ୟୁଷରେ ସମଗ୍ର କଳିଙ୍ଗ ରାଜ୍ୟରେ ଉଦ୍ଘୋଷଣା କରାଗଲା ଯେ, ମଗଧ ସମ୍ରାଟ ଅଶୋକ ଯୁଦ୍ଧର ଏ ବିଭୀଷିକା ଦେଖ୍ ମର୍ମାହତ । ଏହି ନରହତ୍ୟାକୁ ସେ ଆଜିଠାରୁ ବନ୍ଦ କରିବାକୁ ନିଷ୍ପତ୍ତି ଗ୍ରହଣ କରିଛନ୍ତି । କେବଳ ଆଜି ନୁହେଁ, ଭବିଷ୍ୟତରେ ମଧ୍ୟ ସମ୍ରାଟ ଅଶୋକ ଆଉ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ କରିବେ ନାହିଁ । ସେ ବୁଦ୍ଧଙ୍କର ଅହିଂସା ମନ୍ତ୍ରରେ ଦୀକ୍ଷିତ । ଯୁଦ୍ଧର ଏହି ରହସ୍ୟମୟ ବିରତି ବେଳକୁ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ପୁରୁଷ-ଶୂନ୍ୟ ପ୍ରାୟ ହୋଇଥିଲା । ଅମିତ ବିକ୍ରମ ସହ ଲଢ଼େଇ କରିଥିବା କଳିଙ୍ଗ ରାଜଜେମା ରାଜେଶ୍ଵରୀ ଦେଶ ପାଇଁ ଯୁଦ୍ଧକ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ଜୀବନ ବିସର୍ଜନ କରିସାରିଥିଲେ । ସମ୍ରାଟ ଅଶୋକଙ୍କର ଏ ଯୁଦ୍ଧବିରତି ପାଇଁ ଆଉ କାହାର ପ୍ରତିରୋଧ କରିବାର ନଥିଲା ।
ହେଲେ ଯାହାର ତ୍ୟାଗ, ବୀରତ୍ଵ ଆଉ ଦେଶପ୍ରେମ ପାଇଁ ଏ ଭୟଙ୍କର ଯୁଦ୍ଧର ଅବସାନ ଘଟିଲା, ତାଙ୍କୁ କିମ୍ବା ତାଙ୍କର ଦେଶପ୍ରେମୀ ସ୍ଵାଭିମାନୀ ପିତା କଳିଙ୍ଗର ମହାରାଜଙ୍କୁ ଇତିହାସ ପରିଚୟ ଦେବାରେ ଏପରି ପକ୍ଷପାତୀତା କାହିଁକି କରିଛି ? ଇତିହାସ ଛାତ୍ର ଅଙ୍ଗଦ ଚୌଧୁରୀଙ୍କର ଏହି ଭାବପ୍ରବଣ ପ୍ରଶ୍ନର ଉତ୍ତର ଦେବାପାଇଁ ସେଇ ଇତିହାସ ପୁରୁଷ ପୁନର୍ବାର ଆବିର୍ଭୂତ ହୋଇଛନ୍ତି ତାଙ୍କ ସମ୍ମୁଖରେ । ସେ ତାଙ୍କର ପକ୍ଷପାତିତାକୁ ବିନମ୍ର କଣ୍ଠରେ ସ୍ବୀକାର କରିଛନ୍ତି ହେଲେ ସେ ଏଥିପାଇଁ ଅସହାୟ ବୋଲି ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନା କରିଛନ୍ତି । କାରଣ ଯେ ଯେତେବଡ଼ ବୀର ହେଲେ ବି ରାଜ୍ୟ ଜୟକରି ଯେ ସିଂହାସନକୁ ଅସ୍ଵୀକାର କରିପାରି ନାହିଁ, ତାଙ୍କୁ ଦିଗ୍ବିଜୟୀ ରାଜାର ସମ୍ମାନ ଦେବାକୁ ଇତିହାସ ପାଇଁ ପ୍ରତିବନ୍ଧକ ରହିଛି ।
କାଠିନ ଶବ୍ଦାର୍ଥ ଓ ଟିପ୍ପଶା
- କ୍ଷାଶ – ଦୁର୍ବଳ
- ଚେତନ – ପତକା
- ଅପସରି – ଓହରି ବା ହରେଇଯାଇ
- କ୍ଷେତରାତି – ଜମିଜମା
- ଘଞ୍ଚ – ଗହଳ
- ହ୍ରେଷାରବ – ଘେ।ତ଼ାଙ୍କର ଶବ୍ଦ
- ଝଣତ୍କାର – ଝଣଝଣ ଶବ୍ଦ
- ଖ୍ଆଲ – କନା, ମନେରଖିବା
- ଅସାମାନ୍ୟ – ଅସାଧାରଣ
- ପଣ୍ଡିଚାଳିତବତ୍ – ମନ୍ତ୍ରଦ୍ଵାରା ଚାଳିବା ପରି
- ଅନୁସରଣ – ପଛେ ପଛେ ଯିବା
- ଶ୍ରିମଳ – ଧାର ବା ମନ୍ତ୍ରର
- ଗୁଞ୍ଜନ – ଗୁଣୁଗୁଣୁ ଶବ୍ଦ
- ସ୍ତଵ – ନୀରବ / ନିଷ୍ଠଳ
- ପରିଷଦ – ପରିଷଦ ବା ସଭାର ବ୍ୟବନ୍ଦ
- ଅଭିବାଦନ – ସମ୍ମାନ
- ଆସାନ – ବସିଥିବା
- ଉତ୍କଣ୍ଠା – ଆଗ୍ରହ ଚା ବ୍ୟଗ୍ରତା
- ହୃତ୍ ସ୍ପନ୍ଦନ -ହୃଦୟର ଗତି
- ଅବ୍ଜାନ – ଶେଷ
- ବାର୍ତ୍ତା – ସନ୍ଦେଶ ବା ଖବର
- ବିରୋଧୀର୍ଯ୍ୟ – ମସ୍ତକରେ ବହନଯୋଗ୍ୟ
- କାର୍ଯ୍ୟଦ – ଉତ୍ତରାଧ୍ କାରା
- ଉତ୍ତରାଧ୍ କାରା – ଉତ୍ତର ପୁରୁଷ
- ସମ୍ମତି – ସ୍ଵାକୃତି / ହଁ କରିବା
- ପପତି – ପତିଙ୍କ ସହ
- ଅଭିଜ୍ଞତା – ଅନୁଭୂତି ବା ଜ୍ଞାନ
- ବିପୁଳ – ବହୁତ, ପ୍ରଚୁର
- ଅଚାନଳ – ହଠାତ୍
- ମନ୍ତ୍ରଣା – ପରମର୍ଶ
- ପ୍ରଜାର – ସଚେତନ
- ଘନ – ଗହଳ
- ଶ୍ରିଶିର – ଅସ୍ଥାୟୀ ବାସସ୍ଥାନ
- ଚିନ୍ତାନିତ – ଚିନ୍ତିତ ଅବସ୍ଥା
- ରସହ – ଖାଦ୍ୟ
- କ୍ଷୁବ୍ଧ – ବିଚଳିତ
- ତୁରନ୍ତ – ସଙ୍ଗେ ସଙ୍ଗେ,ଶାଘ୍ର
- ବିଭାଷିକା – ଭଣ୍ଟଙ୍କରତା
- ମର୍ମାହତ – ଦୁଃଖିତ
- ଦାକ୍ଷିତ – ଦାକ୍ଷା ପ୍ରଦଶ କରିଥିବା ବା ନିୟମାବଦ୍ଧ
- ବ୍ରହ୍ମାସ୍ତ – ସବୁଠାରୁ ଶକ୍ତିଶାଳା ଅସ୍ତ
- ହୁତ – ଶାଘ୍ର