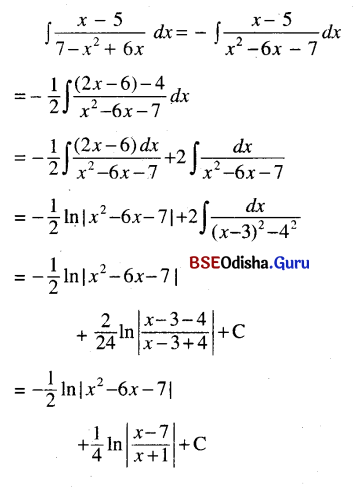
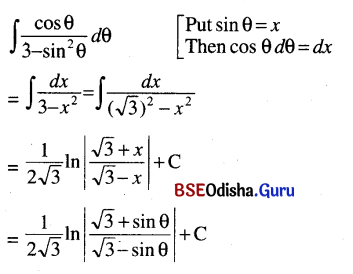
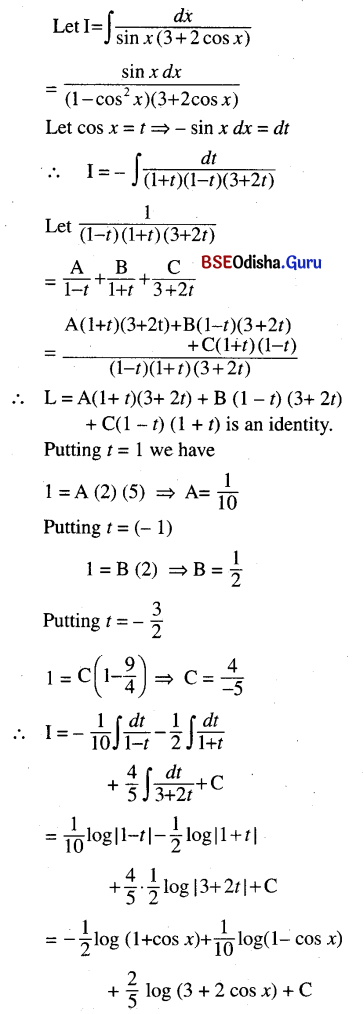Odisha State Board CHSE Odisha Class 11 Invitation to English 1 Solutions Poem 1 Stopping By Woods On A Snowy Evening Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Class 11th Invitation English Poem Chapter 1 Stopping By Woods On A Snowy Evening Question Answers CHSE Odisha
Stopping By Woods On A Snowy Evening Class 11 Questions and Answers
Think it out
Question 1.
How is ‘woods’ different from ‘forest’?
Answer:
‘Woods’ is different from the forest, because the former refers to an area of trees, smaller than a forest.
Question 2.
Where does the rider stop?
Answer:
The rider stops by some woods.
Question 3.
Why does he stop?
Answer:
The beauty of the woods tempts him to stop and enjoy the beauty of snow wood.

Question 4.
“He will not see me stopping here” – what does this expression mean?
Answer:
The expression ‘He will not see me stopping here’ means the owner of the woods living in the village will not see the poet stopping by the woods.
Question 5.
Why does the horse give his harness bells a shake?
Answer:
The poet, riding across the countryside, stops by snow-wrapped woods. The horse is accustomed to stopping at farmhouses, but on the present occasion, he finds it strange that though his master has stopped, there is no farmhouse nearby. Therefore, the horse gives his harness bells a shake as if to ask whether his master has stopped there by mistake
Question 6.
What is ‘the only other sound’ besides that of harness bells?
Answer:
The only other sound besides the harness bells is the sound of easily flowing wind and falling snow.
Question 7.
Why does the poet use the expressions ‘dark’, ‘deep’, and ‘darkest’?
Answer:
The poet uses the expressions ‘dark’, ‘deep’, and ‘deepest’ to express the fact that he is fascinated by the natural beauty of the woods.

Question 8.
How do the speaker, the owner of the woods, and the horse react to the beauties of nature?
Answer:
It may be noted that the fascination of the woods is felt only by the speaker, not by the horse (who is a sub-human) or by the practical man (the owner of the woods).
Question 9.
What picture of natural beauty do you get from the poem?
Answer:
The beauty we get from the poem is natural. It is one of near-silence. The lovely, dark, and deep woods prove this fact.
Question 10.
In the final stanza, the speaker says that he is not yet ready to ‘sleep’. What has he to do before he can take a rest?
Answer:
The poet has his routine duties to do before he can take a rest.
Question 11.
What does the expression, “The darkest evening of the year”, suggest? Does it mean ‘the longest night of the year’ or ‘the most depressing state of his mind’? Give a reasoned answer.
Answer;
The expression ‘the darkest evening of the year’ means the darkest night of the year. Because he has a long way to go. Besides, the poet’s delight in contemplating the woods filling up with snow seems to him to be an abandonment of his responsibilities when he realizes that he has an appointment to keep with his death.

Question 12.
A four-line stanza is called a quatrain. How many quatrains are there in the poem?
Answer:
There are four quatrains in the poem.
Post-Reading Activities.
Question 1.
Arrange the following sentences in their logical order to narrate the theme of the poem.
(a) He passes by the woods which are ‘lovely, dark and deep’.
(b) The poet is riding his horse to a destination.
(c) But he remembers that he has ‘promises to keep’ before he can rest.
(d) It is snowing and the wind blows gently.
(e) The beauty of the woods tempts him to stop and enjoy the sight.
(f) It is an evening in winter.
Answer:
(f) It is an evening in winter.
(d) It is snowing and the wind blows gently.
(b) The poet is riding his horse to a destination.
(a) He passes by the woods which are ‘lovely, dark and deep’.
(e) The beauty of the woods tempts him to stop and enjoy the sight.
(c) But he remembers that he has ‘promises to keep’ before he can rest.

Question 2.
Note the rhyme scheme in the first quatrain. It is AABA (‘know’, ‘though’, ‘here’ ‘snow’). What is the rhyme scheme in other quatrains?
Answer:
The rhyme scheme is BBCB (queer, near, lake, year), CCDE (shake, mistake, sweep, flake), and EEEE (deep, keep, sleep, sleep) in 2nd, the 3rd, and 4th quatrains respectively.
CHSE Odisha Class 11 English Stopping By Woods On A Snowy Evening Important Questions and Answers
A. short Answer Type Questions with Answers
1. Read through the extract and answer the questions that follow.
Whose woods these are I think I know ……
His house is in the village though;
He will not see me stopping here
To watch his woods fill up with snow.
My little horse must think it queer
To stop without a farm house near
Between the woods and frozen lake
The darkest evening of the year.
He gives his harness bells a shake
To ask if there is some mistake
The only other sound’s the sweep
Of easy wind and downy flake.
The woods are lovely, dark and deep
But I have promises to keep
And miles to go before I sleep
And miles to go before I sleep.
Questions :
(i) Where does the owner of the woods live?
(ii) ‘He will not see me stopping here.’ Who is ‘He’ here?
(iii) Describe the woods.
(iv) What is the theme of the poem?
(v) Explain the significance of the repetition of :
‘And miles to go before I sleep,
And miles to go before I sleep.’
Answers :
(i) The owner of the woods lives in a village.
(ii) Here ‘he’ is the owner of the woods.
(iii) Robert Frost gives a beautiful description of the woods. They are lovely, dark, and deep. The sight of the woods being gradually covered with snow is so fascinating that the poet would like to watch it a little longer. The woods are outside the village and their owner does not live here. The poet knows him. Woods that constitute the essence of the poem suggests perilous enchantment.
(iv) The theme of the poem lies in the speaker’s delight in contemplating the woods filling up with snow seems to him to be an abandonment of his responsibilities when he realizes that he has an appointment to keep with death.
(v) The repetition of these lines is quite significant. It brings out the poet’s strong determination. He knows that death is the end of life. Instead of enjoying the fascinating beauty of the woods, he goes on to fulfill the mission of his life. He remembers that he has ‘promises to keep’, duties to perform, and a long journey to complete before he can rest. The repetition of these lines beautifully exemplifies this and indicates the depth of the poet’s feelings.

2. Read through the extract and answer the questions that follow.
Whose woods these are I think I know …..
His house is in the village though;
He will not see me stopping here
To watch his woods fill up with snow.
My little horse must think it queer
To stop without a farmhouse near
Between the woods and frozen lake
The darkest evening of the year.
He gives his harness bells a shake
To ask if there is some mistake
The only other sound’s the sweep
Of easy wind and downy flake.
The woods are lovely, dark, and deep
But I have promises to keep
And miles to go before I sleep
And miles to go before I sleep.
Questions :
(i) Explain the expression ‘whose woods’.
(ii) What does the line ‘I think I know’ signify?
(iii) What interpretation does this extract admit?
(iv) What moment does the poem capture?
(v) ‘Besides going to sleep, the poet must perform duties.’ What else does the last stanza convey?
Answer:
(i) The implied question is whether the woods belong to the owner or the person who watches or enjoys them. Or is it of God?
(ii) The line ‘I think I know’ signifies characteristically a Frostian hovering between eloquence and silence, understanding and reticence.
(iii) This extract lends itself to a variety of interpretations: Why does the speaker stop by some woods? The reader may ask some pertinent questions: Does the speaker move on rather reluctantly? What is Frost’s attitude toward nature?
(iv) The poem captures a moment of pure delight in mid-winter – a fleeting mood of reflection on the beauty of snow-capped woods before the poet must go on with routine duties.
(v) The last stanza also conveys the poet’s death wish.

Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) with Answers
Choose the correct option.
Warm-up
Do you know…… inspiring it is.
Question 1.
The poem “Stopping by Woods on a Snowy Evening” is written by :
(a) John Keats.
(b) Robert Frost.
(c) Thomas Hardy.
(d) William Wordsworth.
Answer:
(b) Robert Frost.
Question 2.
This poem was a great favorite of :
(a) R. N. Tagore.
(b) Sarojini Naidu.
(c) Jawaharlal Nehru.
(d) Khushwant Singh.
Answer:
(c) Jawaharlal Nehru.
Question 3.
The attraction in this poem is of :
(a) matter.
(b) nature.
(c) a great person.
(d) a great responsibility.
Answer:
(b) nature.
Question 4.
The speaker stops his horse by some_______on a snowy evening.
(a) forest.
(b) river bank.
(c) woods.
(d) sea beach.
Answer:
(c) woods.
Question 5.
The journey through the woods is suggestive of a journey through__________itself.
(a) sea
(b) life
(c) heaven
(d) hill
Answer:
(b) life

The Text
Stanza – I
Whose woods………. with snow.
Question 6.
‘Woods’ here means :
(a) forest.
(b) jungle.
(c) an area of trees, smaller than a forest.
(d) a hillside.
Answer:
(c) an area of trees, smaller than a forest.
Question 7.
From this line ‘Whose woods these are I think I know”, it is clear that these woods belong to :
(a) a person to whom the poet knows.
(b) the animals who live in it.
(c) the forest authority.
(d) none of the above.
Answer:
(a) a person to whom the poet knows.
Question 8.
The owner of the woods lives in a :
(a) town.
(b) hilltop.
(c) village.
(d) Riverside.
Answer:
(c) village.

Question 9.
He will not see me stopping here. In this sentence ‘He’ refers to :
(a) the author of the poem.
(b) the owner of the woods.
(c) the God.
(d) the Nature.
Answer:
(b) the owner of the woods.
Question 10.
The poet watchers that woods are covered with :
(a) snow.
(c) fruits.
(b) hilltop.
(d) Riverside.
Answer:
(a) snow.

Stanza – II
My little………. of the year.
Question 11.
My little horse must think it queer. In this sentence, the word ‘little’ means :
(a) small.
(c) nothing.
(b) humble.
(d) short.
Answer:
(b) humble.
Question 12.
What does the word ‘queer’ mean?
(a) Search.
(c) strange.
(b) stop.
(d) sound.
Answer:
(c) strange.
Question 13.
Where do they usually stop?
(a) at a guest house.
(b) at an inn.
(c) at a cottage.
(d) at a farmhouse.
Answer:
(d) at a farmhouse.

Question 14.
What has made the horse feel strange and uncomfortable?
(a) stopping on the way where there is no farmhouse.
(b) stopping in the mid of the forest where life is full of danger.
(c) stopping in a frozen land where life is at risk.
(d) none of the above.
Answer:
(a) stopping on the way where there is no farmhouse.
Question 15.
At what time of the day the poet was passing by the woods?
(a) morning.
(c) evening.
(b) afternoon.
(d) at night.
Answer:
(c) evening.
Stanza – III
He gives ………… downy flake
Question 16.
In the first line of stanza III, there is the word ‘harness bells’ which is tied to the neck of an animal. Which is that animal?
(a) ox.
(b) horse.
(c) bullock.
(d) donkey.
Answer:
(b) horse.

Question 17.
Why does the horse shake the harness bells?
(a) to show some fun
(b) to show some urgency
(c) to show some mistake
(d) to show that he is hungry
Answer:
(c) to show some mistake
Question 18.
Apart from the sounds of harness bells, there are other two natural sounds near the woods. What are they?
(a) sounds of animals and spring.
(b) sounds of stones and rustling of trees.
(c) sounds of easy wind and downy flake.
(d) sounds of spirits and ghosts.
Answer:
(c) sounds of easy wind and downy flake.
Question 19.
What do you mean by the word ‘downy flake’?
(a) down falling water.
(b) down falling stones.
(c) down falling logs.
(d) down falling snow.
Answer:
(d) down falling snow.

Stanza – IV
The woods are ………… before I sleep.
Question 20.
How were the woods according to the poet?
(a) dense, dangerous, and difficult.
(b) natural, attractive, and enjoyable.
(c) lovely, dark, and deep.
(d) none of the above.
Answer:
(c) lovely, dark, and deep.
Question 21.
Why is the poet not willing to stay near the wood?
(a) He has urgent work.
(b) He has promises to keep.
(c) He has no interest to stay.
(d) His horse is unwilling to stay.
Answer:
(b) He has promises to keep.

Question 22.
‘And miles to go before I sleep’. This statement of the poet indicates :
(a) a long journey of life before he leaves for heavenly rest.
(b) a long distance to be traveled by the poet.
(c) a long life of rest and sleep.
(d) none of the above.
Answer:
(a) a long journey of life before he leaves for heavenly rest.

Detailed Summaries and Glossary
Stanza – I (Lines 1-4)
Gist with Glossary
Gist :
The poet, who has to ride long distances in order to fulfill what he has promised, finds himself by the woods late in the evening. It is snowing. So he stops for a while to lose himself in the enjoyment of natural beauty. He thinks he knows the owner of the woods, and also that the owner cannot see him admiring the woods, as he lives in a village away from the woods.
Glossary:
woods: an area of trees, smaller than a forest ( ଛୋଟକାଟିଆ ଜଙ୍ଗଲ )
whose woods: These woods are outside a village and the poet knows the owner of the woods who lives in the village.

Stanza – II (Lines 5-8)
Gist with Glossary
Gist :
The poet’s horse cannot understand why there should be a stop when there is no firm house in sight and also in such an uncomfortable situation as it is snowing. The horse is accustomed to stopping at farmhouses. The master has, as a matter of fact, stopping not for rest but for a brief enjoyment of the beauty of the woods.
Glossary:
Little : humble and ordinary (ସାଧାରଣ ).
Queer : strange (ଆଶ୍ଚର୍ଯ୍ୟ) .
think it queer….. near: The poet says that the horse considers it surprising that the master stops in the midst of the woods and not near any farmhouse.
Frozen Lake : lake turned into ice (ବରଫ ପାଲଟିଥିବା ହ୍ରଦ).

Stanza – III (Lines 9-12)
Gist with Glossary
Gist :
The poet’s horse is not impressed by the woods. It does not understand why they have stopped in such a lonely place, especially as there is no sign of any farmhouse nearby. The horse shakes his harness bells as if to ask whether his master has stopped there by mistake. But the only sound that is there is the swift movement of the wind and the fall of the flakes of snow.
Glossary:
Harness Bells: small bells attached to a strap/band around the neck of a horse. (ଘୋଡ଼ା ବେକର ଘଣ୍ଟି )
Easy Wind: easily flowing wind. (ମୃଦୁ ପବନ)
Flakes: pieces of snow that are soft, light, and white. (ନ ର ମ ହାଲୁକା ଧଳା )
Downy Flakes: downfalling snow. (ତଳକୁ ଖସୁଥିବା ବରଫ)

Stanza – IV (Lines 13-16)
Gist with Glossary
Gist:
The beauty of the woods tempts the poet powerfully to stop the journey and to lose himself in the enjoyment of natural beauty. But he remembers that he has ‘promises to keep’, duties to perform, and a long journey to complete before he can rest. The intensity of the poet’s feeling finds a beautiful expression in this stanza.
Glossary:
Promises : assurance to perform certain duties and miles….. (କଉଁ ବ୍ଯ ପାଳନର ପ୍ରତିଜ୍ଞା)
before I sleep: the poet brings out the idea that he has to perform a long, long journey, and before it is completed, he can have no rest. The repetition is indicative of the depth of the poet’s feelings. ‘
Mile : a distane of 1.6 kilometres (1.6 କି.ମି. ଦୂରତ୍ବ)

Introducing The Poet
Robert Lee Frost, perhaps the best-loved of American poets, was born in San Francisco, California, on 26 March 1874. On the death of his father when he was only ten, he was taken to Lawrence, Massachusetts. Frost attended Lawrence High School and Dartmouth College, which he left after a few months. He taught in school, tried his hand at farming, and also worked as a newspaperman. In 1885 he married Elinor White, his former sweetheart at the high school. Though he enrolled at Harvard University as a special student in 1897 he left it after only two years.
In 1912 the Frosts moved to England. A Boy’s Will, Frost’s first book of poems, was published in England in 1913. North of Boston in 1914, contains some of the finest of Frost’s lyrics. In 1915 the Frosts returned to America and settled on a farm in New Hampshire. Other significant collections of his poems are Mountain Interval (1916), New Hampshire (1923), West-Running Brook (1928), A Further Range (1936), A Witness Tree (1942), and Steeple Bush (1947).
The complete poem of Robert Frost appeared in 1949. He gave public readings of his poems at several American Universities. In his later years, he achieved the status of a folk hero. He died in Boston in 1963. He was awarded the Pulitzer Prize for poetry four times in 1924, 1931, 1937, and 1943. Surprisingly however his first book of poetry was published in England in 1913. No American publisher had accepted it.
It is not difficult to understand why Frost is Americans’ favorite poet. He writes very simply about familiar, ordinary things. However, the simplicity is only on the surface, Frost’s poems actually talk about ideas and thoughts that are deep, not ordinary. The poems talk about truth, they teach you wisdom. Frost is a poet whose style is as fine as a goldsmith’s skill. His poems are delightful to read. Frost himself has said, that for him, a poem begins in delight and ends in wisdom.

About The Poem
Stopping by Woods on a Snowy Evening presents the thoughts that pass through the poet’s mind as he stops his horse in wood on an evening when the snow has begun to fall. The poet conveys the idea that the beauties of nature can be very attractive but man has to perform his duties and keep his promises. He has to continue the journey of life and cannot afford to spend his time only watching the scenic beauties of nature. The poet brings out this message through a presentation of the conflict between the lovely woods and the promises that he has to keep.
Summary
The poem starts with a concrete situation arising from the ordinary life of a man but moves on to philosophic speculation about the relationship between man and nature. It is a dark and quiet evening of winter, and it is snowing. The poet, riding a horse to a destination, passes by woods that are lovely, dark, and deep. These woods are outside a village. The poet knows the owner of the woods who lives in the village.
The beauty of the woods tempts him powerfully to stop the journey and to lose himself in the enjoyment of natural beauty. He says that the horse considers it surprising that the master stops in the midst of the woods and is not near any farmhouse. The horse is accustomed to stopping at farmhouses, but on the present occasion, his reaction is natural.
He knows if his master, in the course of riding across the countryside stops at all, he stops at some farmhouse where both can find food and rest. The master has, as a matter of fact, stopped in such a lonely place not for the rest but for a brief enjoyment of the scenic beauty of the woods. The horse shakes his harness bells as if to ask whether his master has stopped there by mistake.
There are no other sounds except the swift movement of the wind and the fall of snowflakes which are soft, light, and white as feathers. The poem ends on a note of wisdom. In spite of wishing to enjoy the natural beauty, the poet cannot linger there. He moves on as he has to cover long distances in order to keep his promises. He cannot stay back the mission in his life still awaits completion. He remembers that he has ‘promises to keep’, duties to perform a long journey to complete before he can rest

ସାରାଂଶ:
ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଯେଉଁ ସମ୍ପର୍କ ବିଦ୍ୟମାନ, କବି ତାକୁ ଏକ ଦାର୍ଶନିକ ଦୃଷ୍ଟିଭଙ୍ଗୀରୁ ଦେଖୁଛନ୍ତି । ଶୀତକାଳର ଗୋଟିଏ ନୀରବ ସନ୍ଧ୍ୟା । ଅନ୍ଧକାର ପୃଥିବୀକୁ ଆଚ୍ଛାଦିତ କରିଛି । ଆକାଶରୁ ଝରିପଡ଼ୁଛି ବରଫରାଶି । କବି ଅଶ୍ୱାରୋହଣ କରି ତାଙ୍କର ସୁଦୂର ଲକ୍ଷ୍ୟସ୍ଥଳ ଅଭିମୁଖେ ଯାତ୍ରା କରୁଛନ୍ତି । ଚାରିପଟରେ ଘନ ଜଙ୍ଗଲ । କବିଙ୍କ ଭାଷାରେ, ‘ସୁନ୍ଦର, ଅନ୍ଧକାରାଚ୍ଛନ୍ନ ଓ ଘଞ୍ଚ’’ ଗ୍ରାମାଞ୍ଚଳର ଉପକଣ୍ଠରେ ବିସ୍ତୃତ ହୋଇ ରହିଛି ସେହି ଅରଣ୍ୟ । ଏହି ଜଙ୍ଗଲର ମାଲିକଙ୍କୁ କବି ଜାଣନ୍ତି । ସେ ନିକଟସ୍ଥ ଗ୍ରାମର ଅସ୍ଵାସୀ । ଜଙ୍ଗଲର ସୌନ୍ଦର୍ଯ୍ୟ କବିଙ୍କୁ ପ୍ରଲୁବ୍ଧ କରୁଛି । ଶକ୍ତିଶାଳୀ ତା’ର ଆକର୍ଷଣ । ଯାତ୍ରାକୁ ସ୍ଥଗିତ ରଖି ପ୍ରାକୃତିକ ସୁଷମା ଭିତରେ ନିଜକୁ ହଜାଇ ଦେବାପାଇଁ ସେହି ଅରଣ୍ୟ ତାଙ୍କୁ ଯେପରି ଆମନ୍ତ୍ରଣ କରୁଛି । ଯାତ୍ରା ବନ୍ଦକରି ବନାନୀର ଶୋଭା ଦର୍ଶନ କରୁଥିବା ମାଲିକଙ୍କୁ ଦେଖ୍ ତାଙ୍କର ଘୋଡ଼ା ବିସ୍ମିତ ହୋଇଛି । କାରଣ ରହିଯାଇଥିବାରୁ ଅଶ୍ଵଟି ବିସ୍ମିତ ହୋଇଛି । ଅଶ୍ଵଟିର ଏହି ପ୍ରତିକ୍ରିୟା ଅତ୍ୟନ୍ତ ସ୍ଵାଭାବିକ । କାରଣ ଖମାରଗୃହ ପାଖରେ ଥିଲେ ଉଭୟ ମାଲିକ ଓ ସେ ଖାଦ୍ୟ ଓ ବିଶ୍ରାମ ପାଇ ପାରିଥା’ନ୍ତେ । ମାତ୍ର କବିଙ୍କର ଉଦ୍ଦେଶ୍ୟ ଭିନ୍ନ । ସେ ବିଶ୍ରାମ ଉଦ୍ଦେଶ୍ୟରେ ଏଠାରେ ଅଟକି ଯାଇନାହାନ୍ତି ।
ଅରଣ୍ୟର ନୈସର୍ଗିକ ସୌନ୍ଦର୍ଯ୍ୟକୁ ମନଭରି ଉପଭୋଗ କରିବାପାଇଁ ସେ ସେଠାରେ ଅଟକି ଯାଇଛନ୍ତି । ମାତ୍ର ଅବୋଧ ପଶୁ ସେ କଥା ବୁଝିବ କିପରି ? ଭାବୁଛି, ତା’ର ମାଲିକ ହୁଏତ ଭ୍ରମବଶତଃ ସେଠାରେ ଅଟକି ଯାଇଛନ୍ତି । ତାଙ୍କୁ ସେ କଥା ମନେପକାଇ ଦେବାପାଇଁ ଘୋଡ଼ାଟି ତା’ର ସାମ୍ପୁରେ ଲାଗିଥିବା ଘଣ୍ଟିକୁ ବଜାଇ ଦେଉଛି । ନିର୍ଜନ ଅରଣ୍ୟର ନୀରବତାର ରାଜତ୍ଵ । କେବଳ ବାୟୁର ମୁଦ୍ରା ପ୍ରବାହ ସେହି ନୀରବତାକୁ ଭଙ୍ଗ କରୁଛି । ନରମ, ହାଲୁକା ଓ ପକ୍ଷୀପର ଭଳି ମୁଲାୟମ ତୁଷାର କେବଳ ଝରିପଡ଼ୁଛି । କବିଙ୍କର ମୁଗ୍ଧସଭା ସେହି ଜଙ୍ଗଲର ଆକର୍ଷଣକୁ ଛାଡ଼ି ଆଗ୍ରସର ହେବାପାଇଁ ପ୍ରତିଜ୍ଞାବଦ୍ଧ । ଇଚ୍ଛା ଥିଲେ ବି ସେ ନିରୁପାୟ । କାରଣ ଲକ୍ଷ୍ୟସ୍ଥଳରେ ପହଞ୍ଚିବା ପାଇଁ ତାଙ୍କୁ ସୁଦୂର ପଥ ଯାତ୍ରା କରିବାକୁ ହେବ । କାରଣ ତାଙ୍କୁ ତାଙ୍କର ପ୍ରତିଜ୍ଞା ପୂରଣ କରିବାକୁ ହେବ । ଯେପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ ସେହି ଲକ୍ଷ୍ୟ ହାସଲ ହୋଇନାହିଁ, ସେପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ ତାଙ୍କର ବିଶ୍ରାମ ନାହିଁ । ତାଙ୍କର ଠିକ୍ ମନେଅଛି, ତାଙ୍କୁ ଗୋଟାଏ ଦୀର୍ଘ ପଥ ଅତିକ୍ରମ କରିବାକୁ ହେବ, ତାଙ୍କର କର୍ତ୍ତବ୍ୟ ସାଧନ କରିବାକୁ ହେବ । ତା’ ପୂର୍ବରୁ ସେ ବିଶ୍ରାମ ନେଇପାରିବେ ନାହିଁ ।
CHSE Odisha 11th Class English Poetry:


![]()
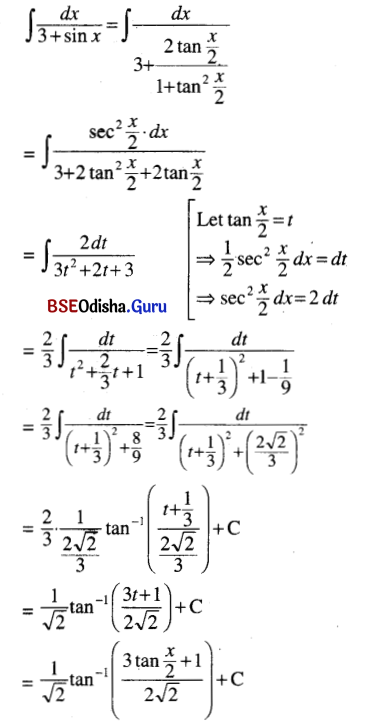


![]()


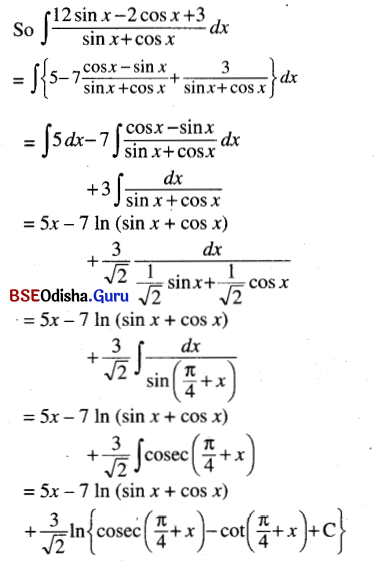
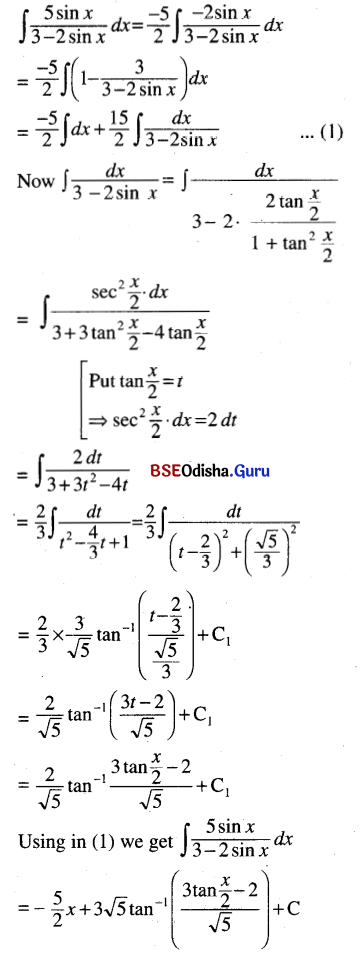
![]()

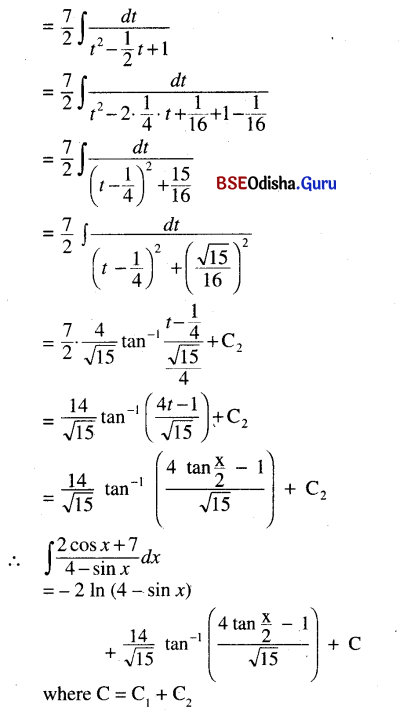

![]()


![]()